Abstract
To solve the problem of deposits formation in the exhaust pipe of a diesel engine SCR (selective catalytic reduction) system, the CFD (computational fluid dynamics) model of the exhaust pipe was established to research the influence of structural parameters on the wall film from the perspective of optimizing the flow field. The solid structure was simplified in the modeling without considering the flow fields inside the catalytic converter. The simulation conditions were obtained through bench tests and vehicle real road tests. The spray and temperature simulation results were verified via high-speed photographic and bench tests under three typical operating conditions. The conclusions are as follows: compared to the case with a step surface, wall film mass was reduced by 48.27~55.4% when the exhaust pipe had no step surface; compared to the case where the nozzle orifices were located 10 mm off center axis, wall film mass reduced by 2.83~6.38% when the nozzle orifices located in the center axis of exhaust pipe; compared to the case of 110 mm, wall film mass reduced by 21.3~24.72% when the exhaust pipe diameter was 100 mm. To eliminate the potential problem of deposit formation inside the catalytic converter, the nozzle should be arranged close to the engine turbine, and there should be no abrupt cross-section downstream of the exhaust pipe.
1. Introduction
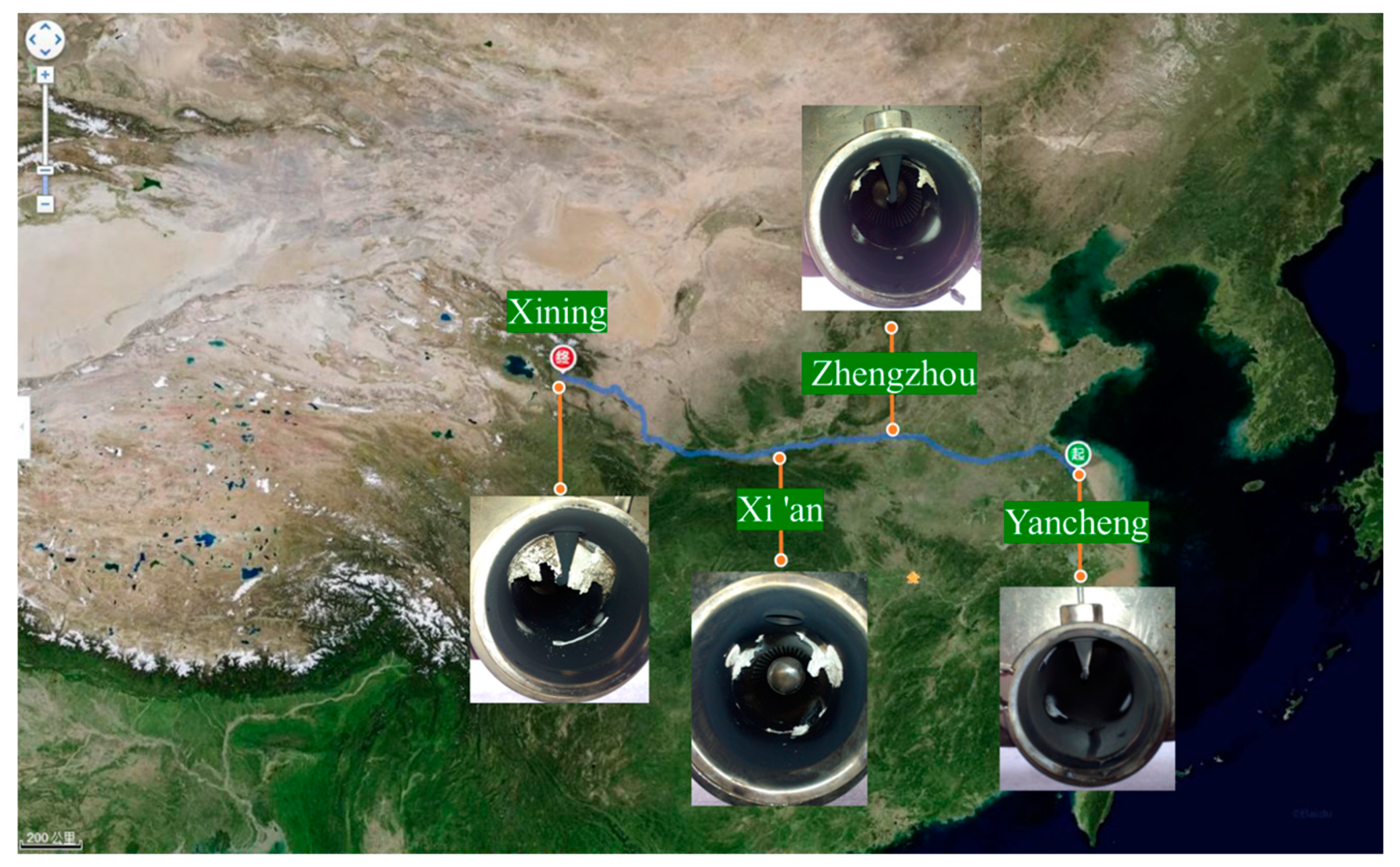
To bring down the nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission of diesel engines and meet the increasingly strict emission regulation, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology is widely regarded as one of the most promising technologies [1,2,3]. However, the urea deposits in the exhaust after-treatment system (ATS) have always been a challenging problem. Severe deposits can lead to ammonia leakage and exhaust pipe blockage, and they will add back pressure, reducing nitrogen oxide conversion efficiency [4,5]. Therefore, the actual operation process of a commercial vehicle equipped with an SCR system (hereinafter referred to as “vehicle real road test”) was tracked and monitored, and it was found that there was a large amount of deposits formation on the wall surface of the exhaust pipe. As shown in Figure 1, the commercial vehicle started from Yancheng, Jiangsu Province, passed through Zhengzhou, Xi’an, Lanzhou, et al., and finally reached Xining, Qinghai Province, covering a total distance of about 2000 km. There was no deposit in the exhaust pipe before departure from Yancheng. However, upon arrival in Zhengzhou, it was found that there was deposits formation on the upper left and upper right of the exhaust pipe. Upon arrival in Xi’an, there were large amounts of deposits formation. After arriving at Xining for inspection, all the deposits were cleaned and collected, weighing 105.5 g.
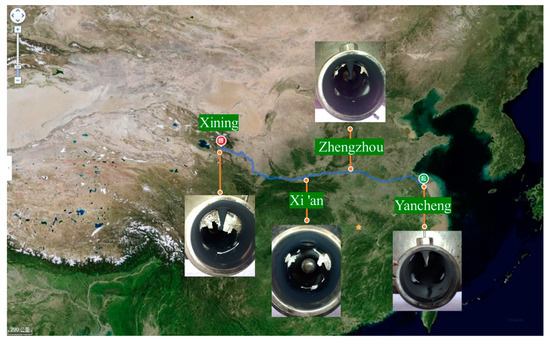
Figure 1.
Deposits formation in the exhaust pipe during the vehicle’s operation equipped with SCR system. (Cities: Yancheng in Jiangsu Province, Zhengzhou in Henan Province, Xi’an in Shaanxi Province, and Xining in Qinghai Province).
Automobile NOx emissions account for 95% of global NOx emissions, highlighting the importance of reducing NOx emissions from diesel engines [6]. As the mainstream technology to control NOx emission of heavy commercial vehicles, many problems still need to be explored and solved in the SCR system, among which the problem of deposit formation is particularly prominent. The urea aqueous solution sprayed into the exhaust pipe is gradually heated by the high-temperature exhaust, and the liquid evaporates after reaching a certain temperature. As the boiling point of water is lower than that of urea, the evaporated gas is mainly water steam. If the water evaporates too fast, it is easy to precipitate urea solids and form deposits. These deposits are called “soft crystals”, which are crystals of the urea itself. Soft crystals dissolve easily in water and decompose easily by heating, with less influence on the SCR system and engine. The other type of deposit is urea-related by-products formed through a series of chemical reactions called “hard crystals”. Hard crystals hardly dissolve in water, are not easy to pyrolyze, and have strong mechanical stability. However, once formed, it is difficult to remove, significantly influencing the SCR system and engine [7,8].
World harmonized transient cycle (WHTC) urea deposits are urea, cyanuric acid (CYA) and ammelide, implying that accelerating the decomposition of these species could prevent the accumulation of urea deposits [9]. To explore the influence factors of deposit formation, scholars have conducted lots of relevant studies. Xu et al. [10] from Ford Research and Innovation Center found that solid deposits were generated on the exhaust pipe wall surface downstream of the urea nozzle and mixer in the diesel exhaust post-treatment system. Two different SCR catalysts (iron zeolite and cupric zeolite, both of which use cordierite as a base) were studied the results showed that iron zeolite was more likely to form deposits than cupric zeolite. Zhao [11] researched the effects of exhaust temperature, exhaust velocity, the injection rate of urea aqueous solution, nozzle installation position and injection system type on deposit formation through bench tests. The results showed that the airless-assisted injection system produced more deposits than the air-assisted injection system under the same conditions. The airless assisted injection system with a nozzle positioned diagonally forward in the straight section of the exhaust pipe produced more deposits than the nozzle positioned at the elbow of the exhaust pipe. Exhaust temperature, exhaust velocity, and injection rate of urea aqueous solution all significantly influence deposit formation. To reduce urea deposits in the SCR system, Chen et al. [12] studied the relationship between liquid film temperature and reactants and designed mixers with different structures. CFD method was used to simulate the evaporation and pyrolysis process of urea aqueous solution. It was found that in a mixer with low turbulence intensity, the mass and distribution area of liquid film and deposit decreased significantly with the decrease of injection angle and pressure; however, when the turbulence intensity was high in the mixer, urea droplets were enjoined by strong turbulence, and the decrease of injection angle and pressure did not significantly reduce the liquid film and deposit. The structure of the SCR system was optimized to improve the effect of urea mixing by Jungmin [13] from Hyundai-Kia R&D Center as a result of reducing the deposit yield from 14.3 g to 5 g under the same conditions. Way et al. [14] from Donaldson Company used CFD simulation to optimize the installation geometry of the injection unit and solved the deposit problem in the reflux area near the nozzle. Munnannur et al. [15] from Cummins CES Department studied the influence factors of wall film formation in exhaust pipes by CFD simulation. It was beneficial to reduce deposits to increase the shear force between the exhaust flow and the wall surface. The larger the shear force, the easier the wall film is peeled off and the easier the droplets are entrained and rolled into the airflow. Zheng et al. [16] from Tenneco Company established a three-dimensional simulation model of the SCR system by combining the spray, droplet breakage, evaporation process of urea aqueous solution and the interaction with the exhaust flow field. They qualitatively researched the effect of diesel exhaust pipe diameter on the amount of urea droplets striking the pipe wall. The results showed that increasing the diameter of the exhaust pipe in the inlet section of the catalytic converter can reduce the amount of wall film and decrease the risk of deposit formation. Canyurt et al. [17] investigate the spray-wall interaction, the liquid film formation at different severities, the liquid film evaporation by injecting urea water solution into an impingement plate in a non-uniform flow medium under different operating conditions, experimentally and numerically, and they found that the liquid film layer formed in the stagnant flow regions has greater risks in terms of deposit formation than the other regions. The urea water solution is often used as a source of the reduction agent ammonia for the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxides in combustion after-treatment systems. In applications, however, some technical problems appear, for example, the formation of solid residuals or incomplete decomposition of urea [18]. It should be pointed out that because urea water solution has higher evaporation and atomization, it is not easy to form a deposit at a higher gas flow temperature and mass flow rate [19]. In addition, deposit growth can also be observed at the peripheral boundary because urea water solution is transported through capillary structures on the surface or within the deposit [20].
To guarantee the normal operation of the SCR system and engine, it is necessary to solve the problem of deposit formation in the exhaust pipe. In this paper, the CFD model of diesel engine exhaust pipe is proposed to explore the influence rules of exhaust pipe structural parameters on deposit formation from the perspective of flow field optimization. Through its research, this article hopes to provide a reference for avoiding deposit formation in the exhaust pipe.
2. Materials and Methods
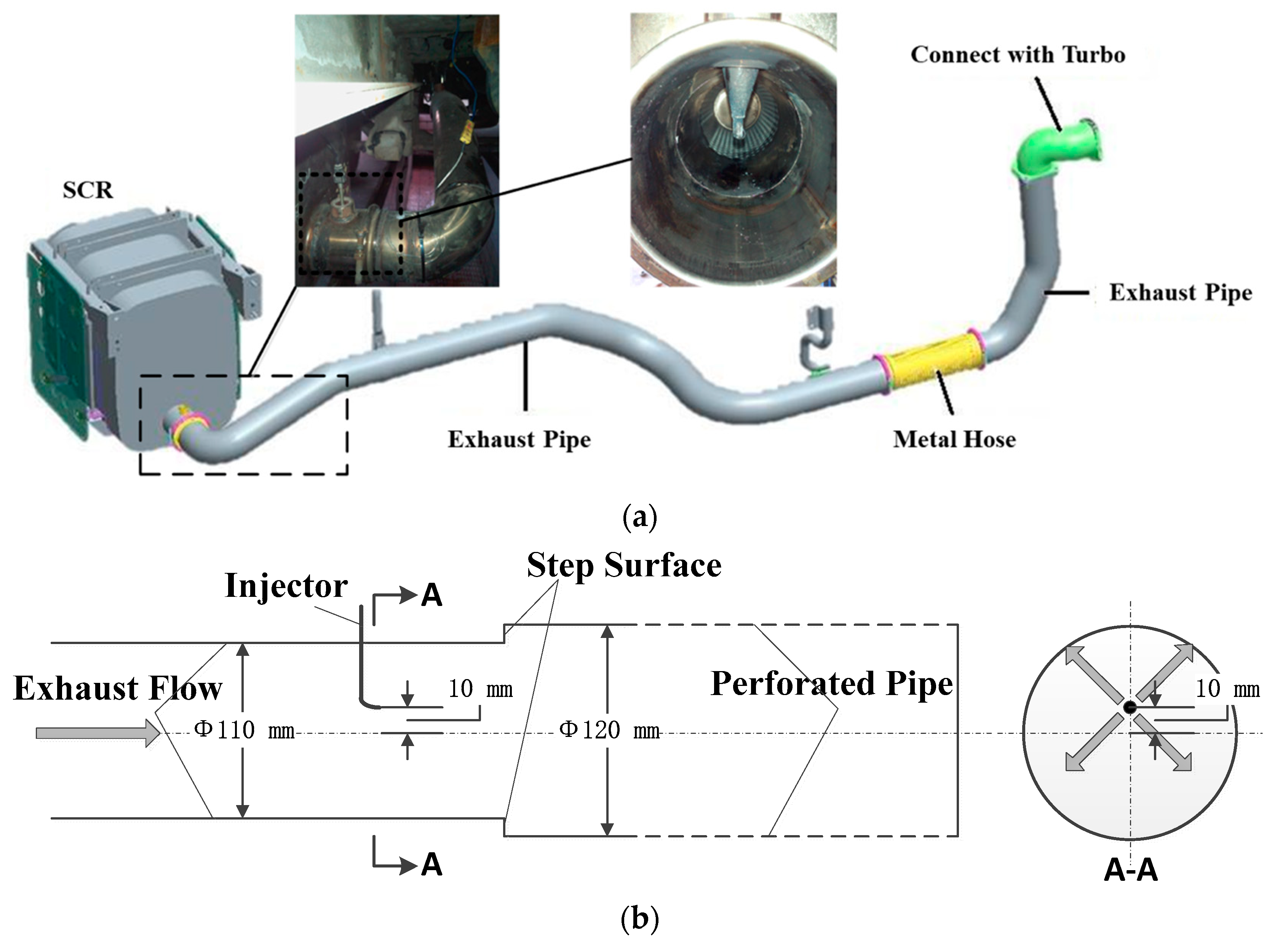
Through the vehicle real road test, the deposits formation in the exhaust pipe of a diesel engine was understood preliminarily, and the deposits were mainly formed on the upward side of the exhaust pipe. However, further study revealed that the exhaust pipe where the deposits accumulated had an abrupt cross-section (hereinafter referred to as “step surface”), and the nozzle hole was 10 mm off the center of the exhaust pipe shown in Figure 2.
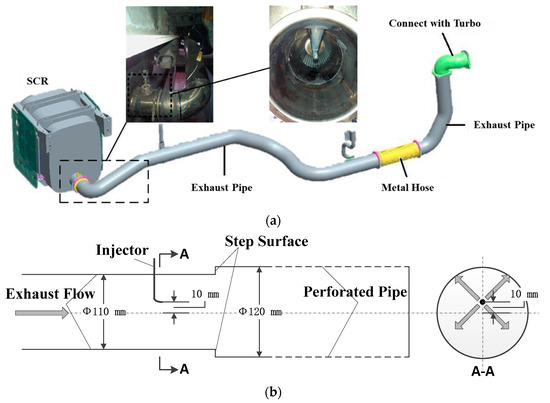
Figure 2.
Diesel engine exhaust after-treatment system layout. (a) Arrangement and assembly of SCR system, (b) Sketch map of nozzle position and step surface.
2.1. Geometric Modeling
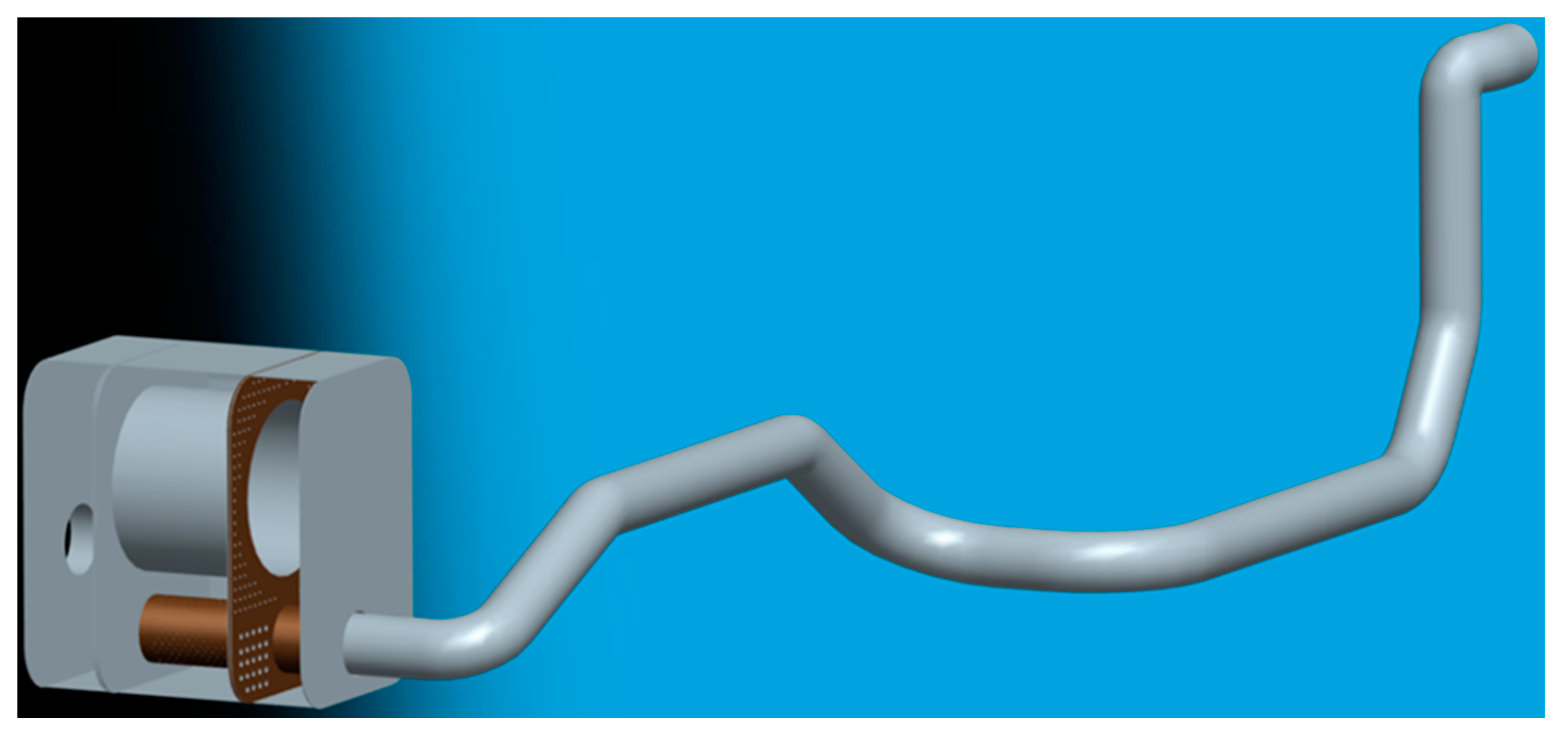
To ensure the simulation accuracy of the diesel engine after-treatment system, it is necessary to describe the geometric model accurately. A full after-treatment system should include an exhaust pipe, injection unit, and catalytic converter. The corresponding geometric model should consist of geometries from the turbo to the catalyst. The full-scale geometric model of an SCR system with an engine displacement of 11.12 L was established, as shown in Figure 3. The diameter of the exhaust pipe was 110 mm, and the wall material of the pipe was stainless steel. In addition, a perforated tube and a perforated plate were integrated inside the catalytic converter. This design was conducive to the evaporation and pyrolysis of urea aqueous solution and improving the concentration and uniformity of NH3 at the catalyst entrance.
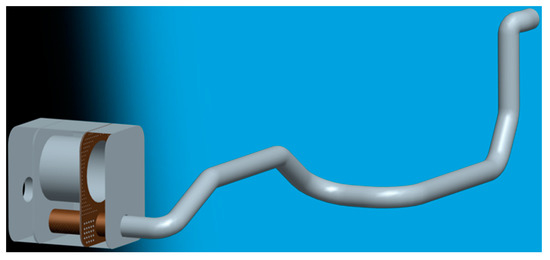
Figure 3.
The full-scale geometric model of the SCR system.
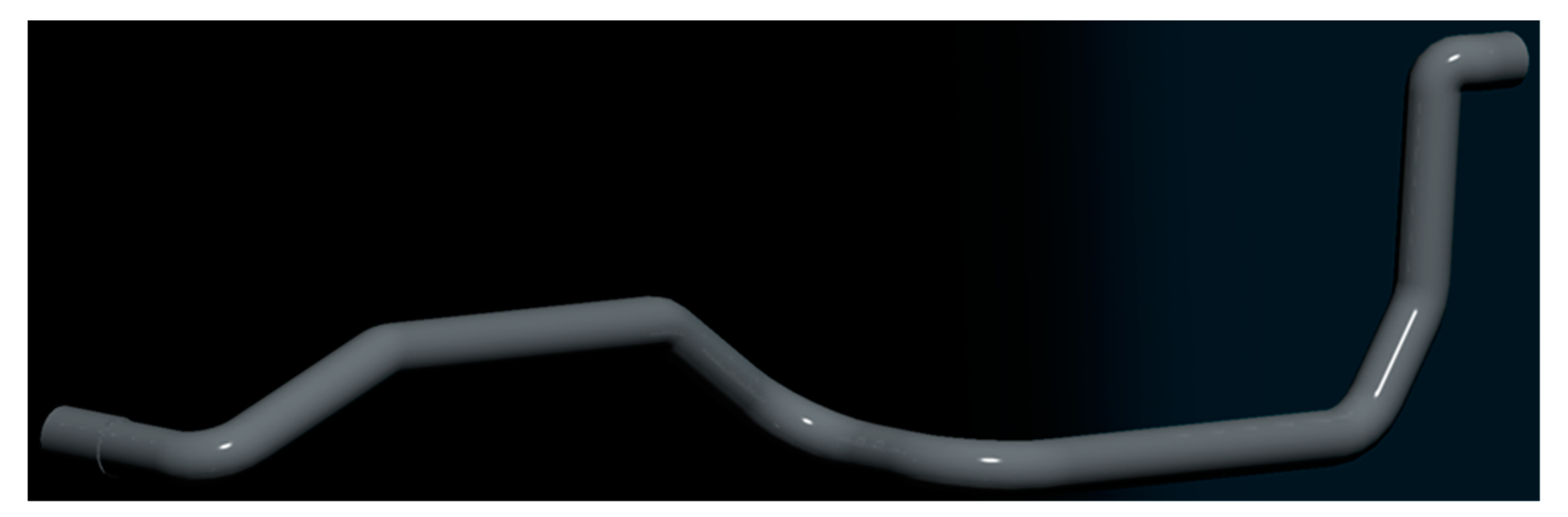
Due to the small diameter and large number of holes, it would generate a huge amount of calculation grids for the full model, which affected the calculation efficiency. In addition, this research focused on the formation of deposits inside the diesel engine exhaust pipe. Therefore, the solid structure was simplified in the modeling without considering the flow fields inside the catalytic converter. The geometric model of the diesel engine exhaust pipe is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Geometric model of diesel engine exhaust pipe.
2.2. Initial Parameters and Boundary Conditions
In a sense, CFD technology is the process of extrapolating and extending the data of initial parameters and boundary conditions. Therefore, the initial parameters and boundary conditions should conform to the actual situation, which is the premise to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the simulation results. This study used AVL Fire to carry out the simulation work. Table 1 shows the basic parameters of the diesel engine and SCR system.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of the diesel engine and SCR system.
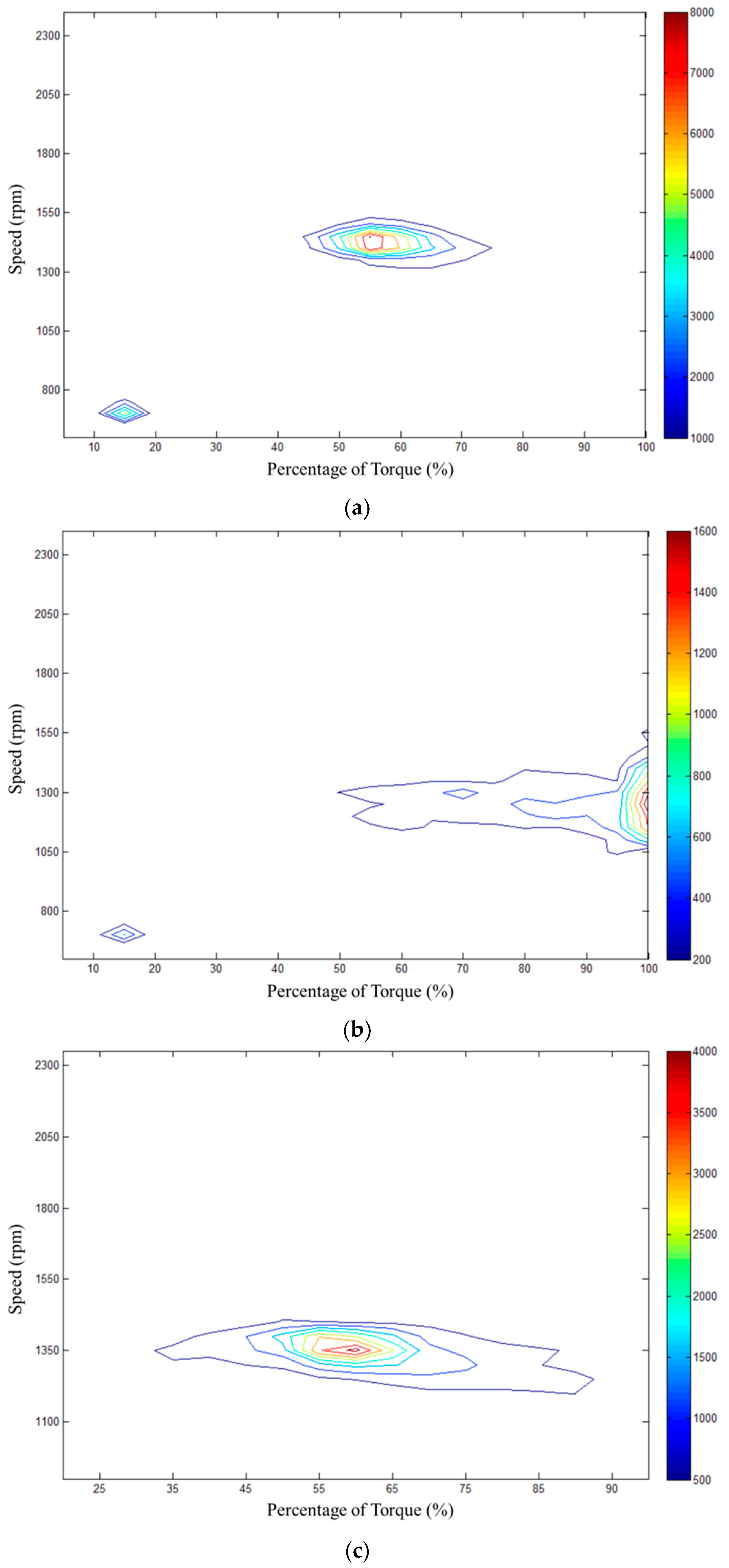
According to the vehicle real road test, the data of three groups were collected and used to indicate the operating conditions distribution of the employed commercial vehicle, as shown in Figure 5. A representative operating condition with the highest probability of occurrence was selected for the following simulation work.
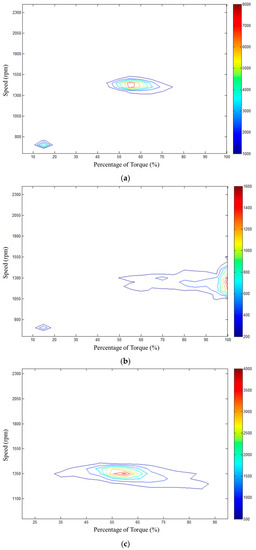
Figure 5.
Distribution of the operating conditions from vehicle real road test. (a) Case 1: Distribution of the operating conditions from Yancheng to Zhengzhou; (b) Case 2: Distribution of the operating conditions from Zhengzhou to Xi’an; (c) Case 3: Distribution of the operating conditions from Xi’an to Xining.
The diesel engine and SCR system parameters under typical operating conditions were obtained through bench tests, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Test data under each typical operating condition.
The exhaust gas of the diesel engine was a compressible fluid with similar properties to air, so the fluid’s inlet boundary was defined by giving the exhaust gas mass flow rate and temperature. Next, the static pressure was used to define the outlet boundary. Next, the convective heat transfer with the atmosphere at the wall boundary was proposed. Finally, the fluid velocity component in the normal direction of the wall was defined as 0.
2.3. Model Validation
2.3.1. Verification of Spray
Urea aqueous solution was sprayed into the exhaust pipe in mist. The unevaporated urea droplet, which hit the inner surface of the exhaust pipe wall, would convert into wall film under certain conditions. In this paper, the droplet size, initial velocity, and atomization cone angle of different urea injection rates were measured to accurately describe the movement of urea droplets.
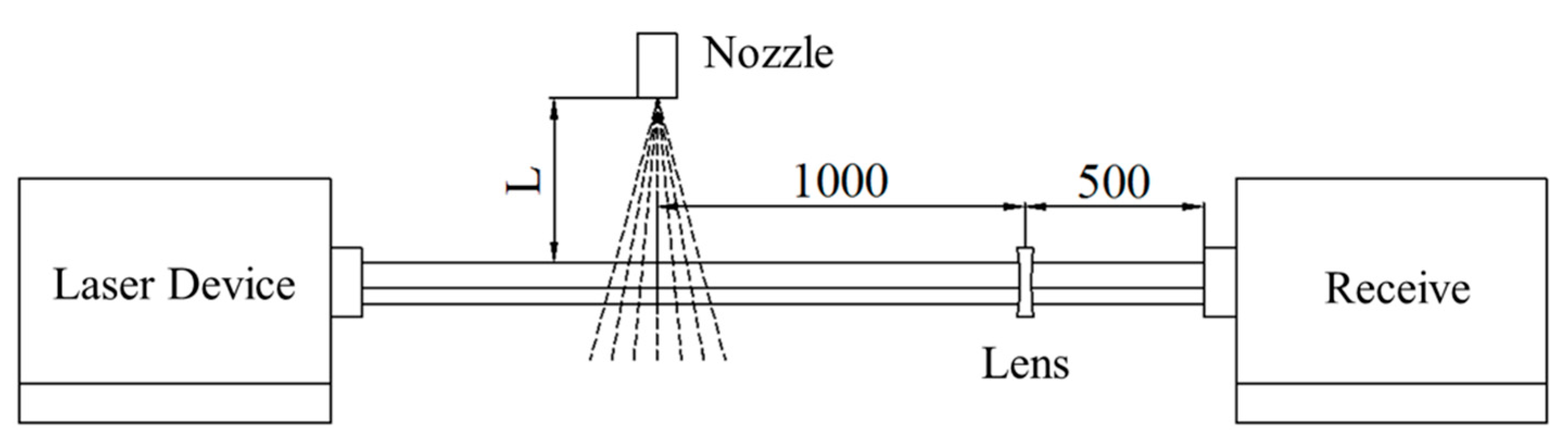
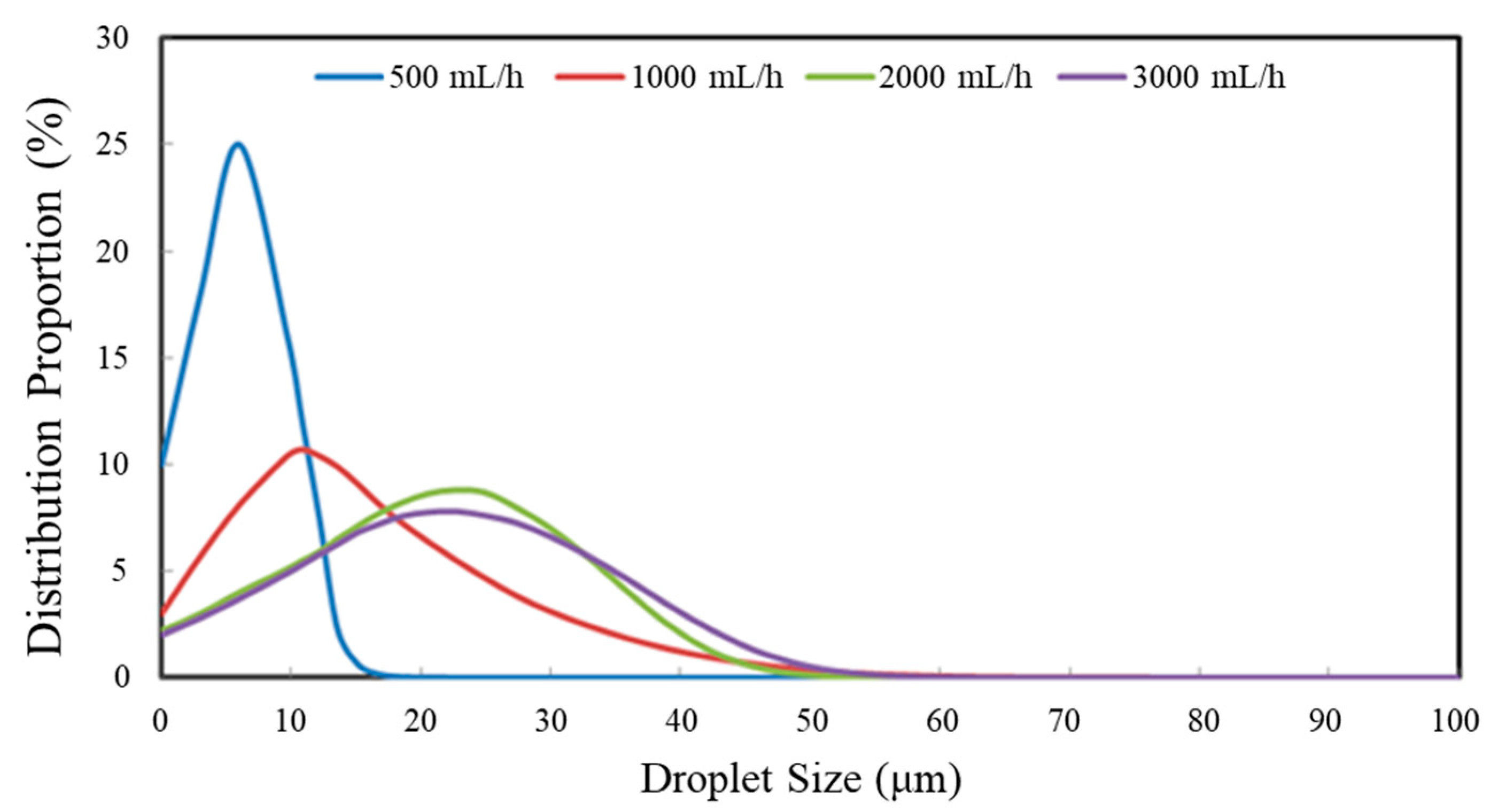
As shown in Figure 6, the LSA-III laser particle size tester was used to measure the droplet size of the urea nozzle. Due to the symmetrical distribution of the four holes of the urea nozzle, only one of the holes was measured. The droplet size distribution of different urea injection rates is shown in Figure 7.
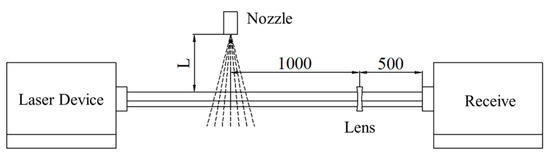
Figure 6.
LSA-III Laser particle size tester configurations.
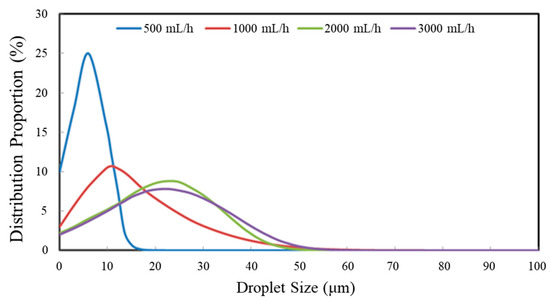
Figure 7.
The droplet size distribution of different urea injection rates.
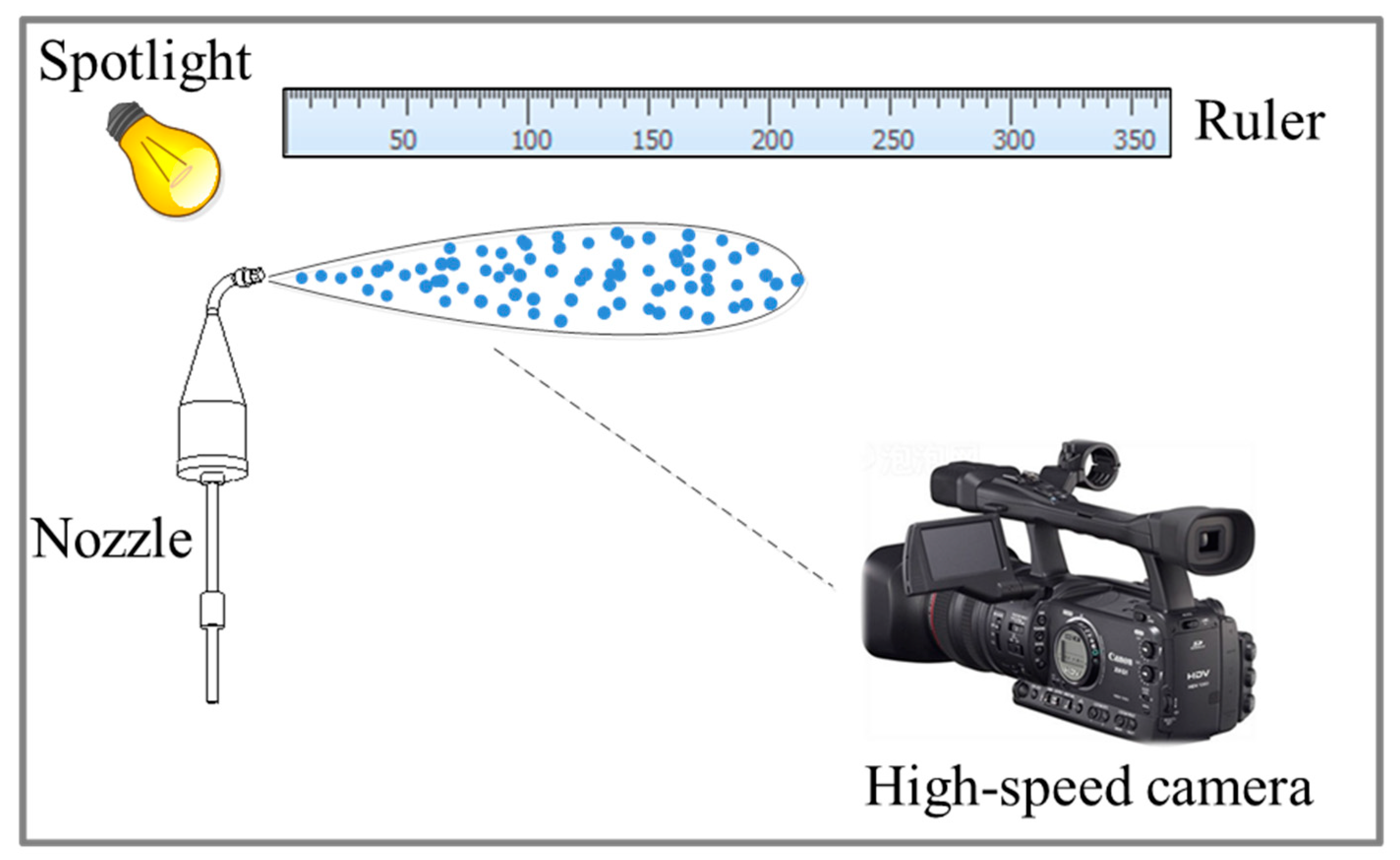
As shown in Figure 8, the high-speed photographic test measured the urea nozzle’s droplet initial velocity and atomization cone angle. It can take 1000 pictures per second by setting the frequency of the high-speed camera to 1000 frames. Based on the beginning of the spray, the droplet’s initial velocity was obtained by measuring the spray penetration distance in 1 ms. The atomization cone angle was measured directly from the spray geometrical morphology. Table 3 shows different urea injection rates’ droplet initial velocity and atomization cone angle.
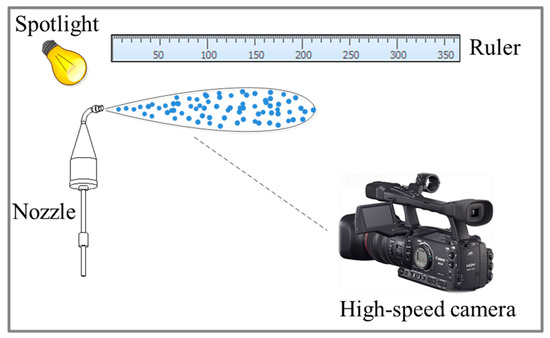
Figure 8.
Diagram of high-speed photography test.

Table 3.
The droplet initial velocity and atomization cone angle of different urea injection rates.
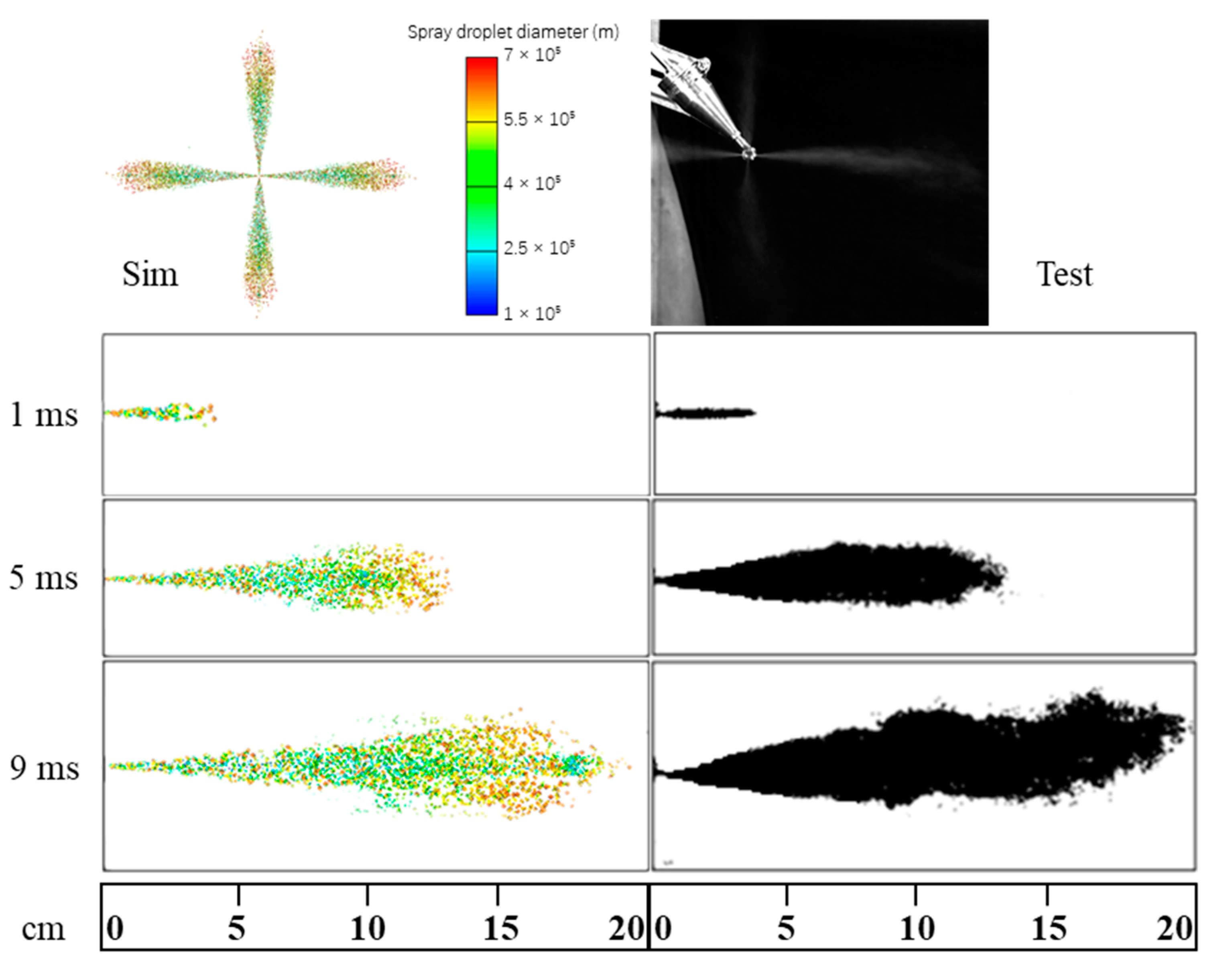
Figure 9 shows the comparison results between the simulation and test of spray morphology. The results indicate that the spray penetration distance and cone angle are consistent between the simulation and test at the same moment.
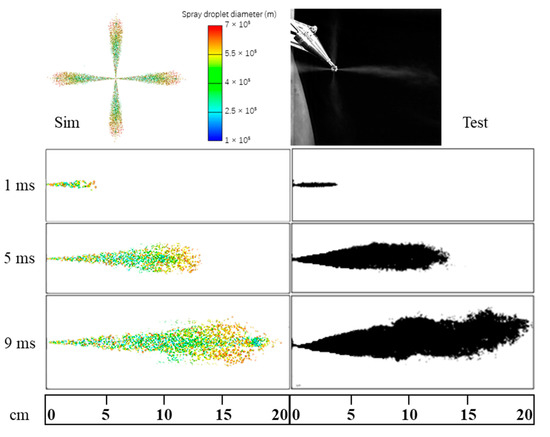
Figure 9.
Comparison between simulation result and experimental result of spray morphology.
2.3.2. Verification of Temperature
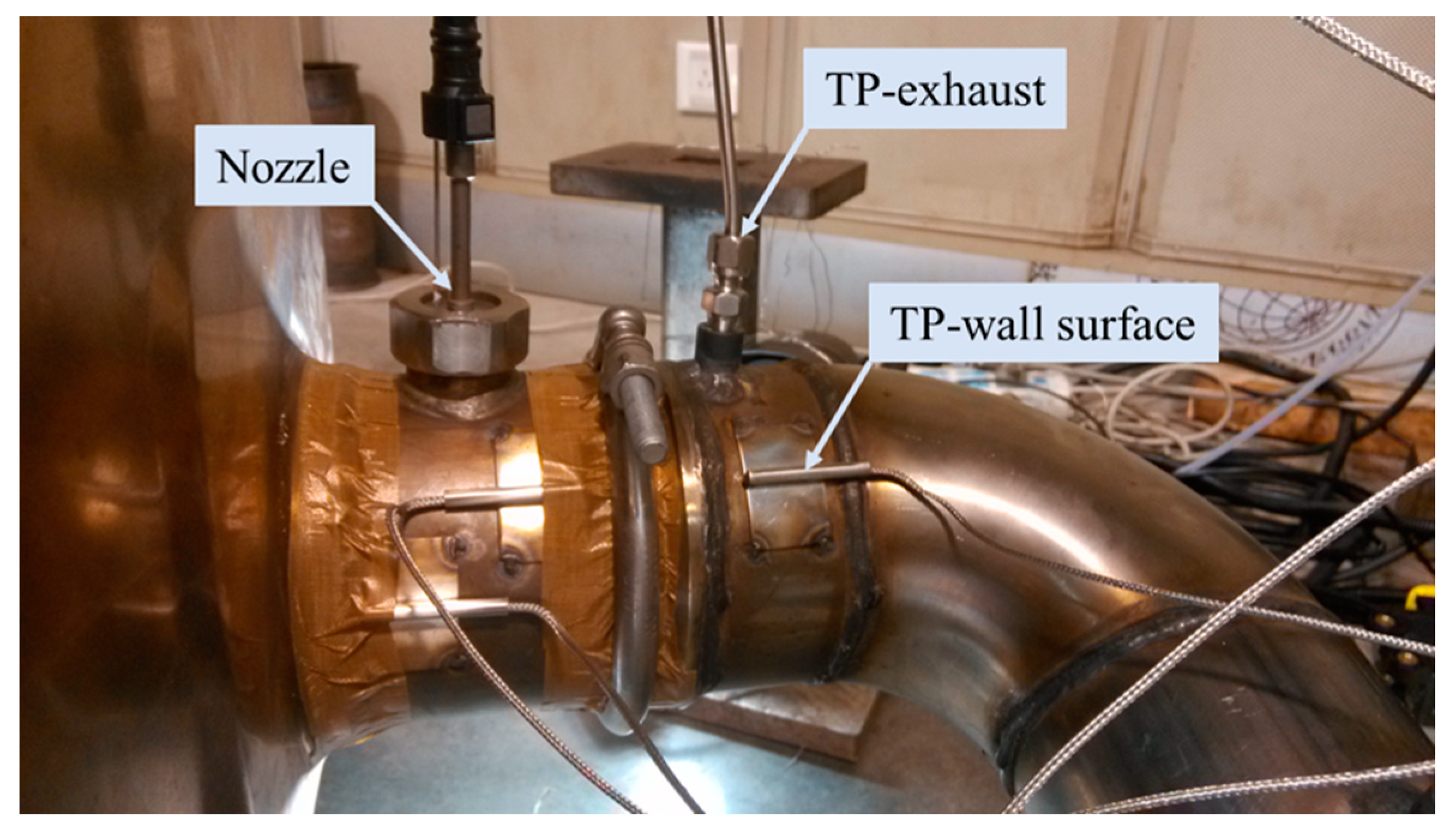
The temperature field in the exhaust pipe affects not only the evaporation rate of urea droplets, but also the formation and evaporation rate of wall film. Therefore, it is necessary to verify the exhaust temperature and pipe wall temperature. The exhaust temperature and pipe wall temperature before the nozzle for each typical operating condition in Table 2 were measured by bench test. As shown in Figure 10, an exhaust temperature sensor and a wall surface temperature sensor were arranged 100 mm upstream of the nozzle, respectively.
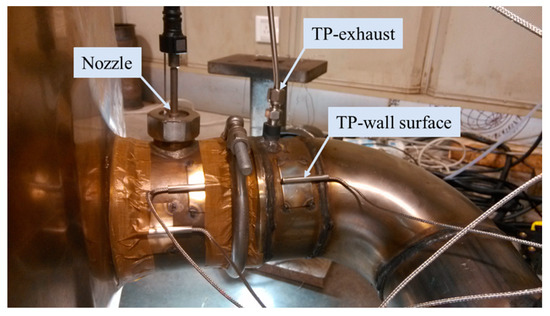
Figure 10.
Layout diagram of the temperature sensors.
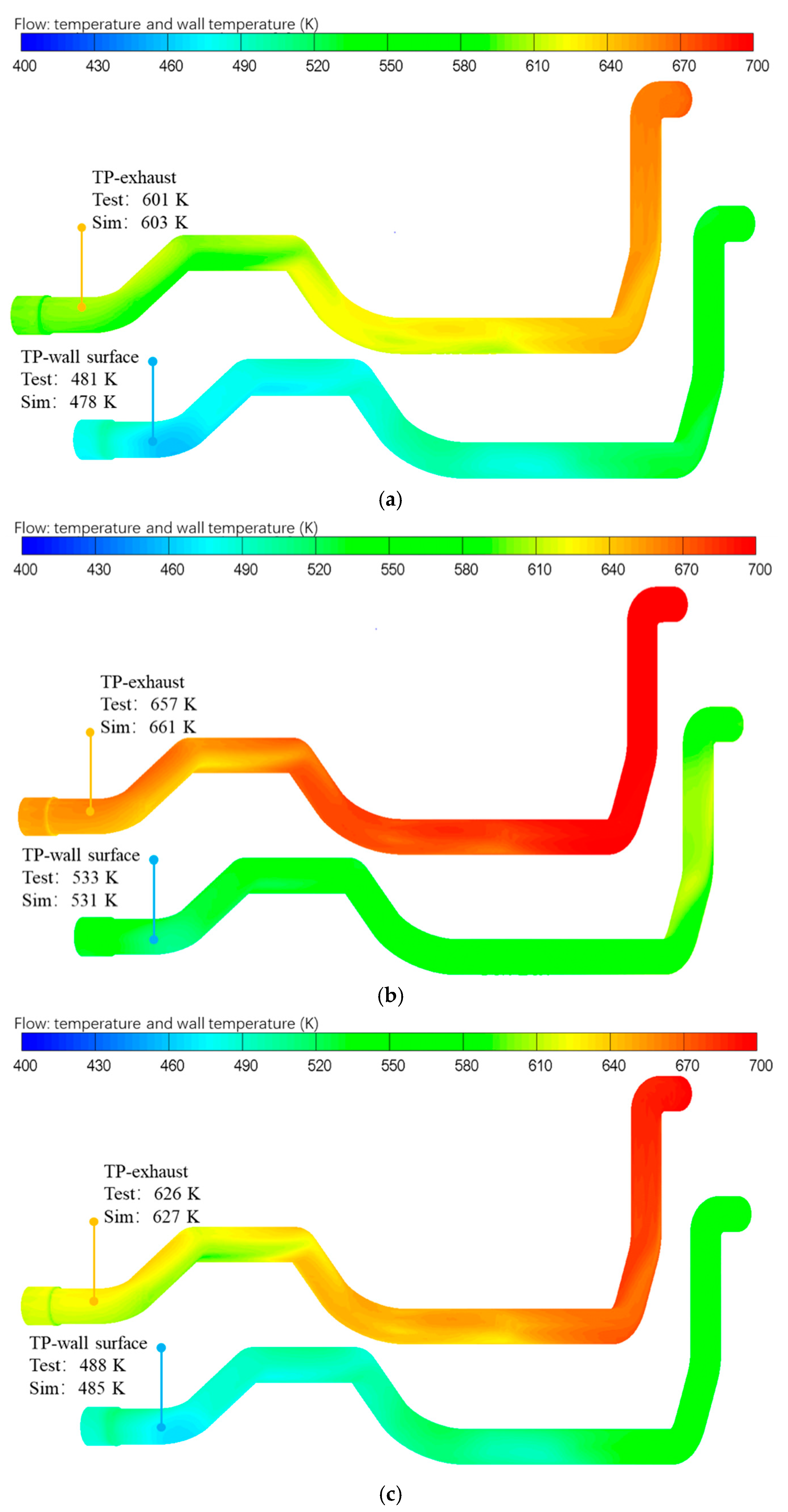
Figure 11 shows the comparison results between the simulation and test of exhaust temperature and pipe wall temperature under the three typical operating conditions. The results indicate that the difference between the simulation and test values was within 5 °C under each typical operating condition.
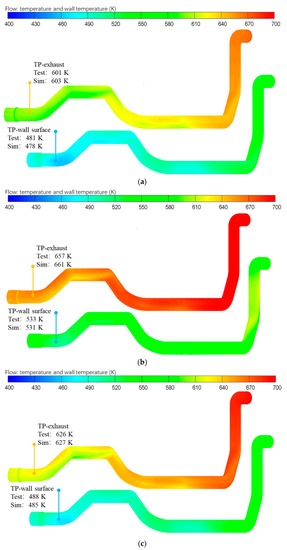
Figure 11.
Simulation and experimental results of exhaust temperature and pipe wall temperature under typical operating conditions. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
3. Results
The formation of deposits can be divided into three processes: the urea aqueous solution hits the wall to form wall film in the exhaust pipe; when the urea concentration in the wall film is higher than a certain threshold value, it will convert into “soft crystals”; the urea in the soft crystals develops into “hard crystals” through complex physical and chemical reactions at different temperatures. Therefore, wall film is the precursor of deposits formation on the exhaust pipe wall, and the residual mass of wall film reflects the yield of deposits from a sideways perspective. To assess the risk of deposits formation under different conditions, the evaluation indexes, including wall film area, wall film thickness and wall film mass, were proposed.
3.1. Influence of Step Surface on Wall Film
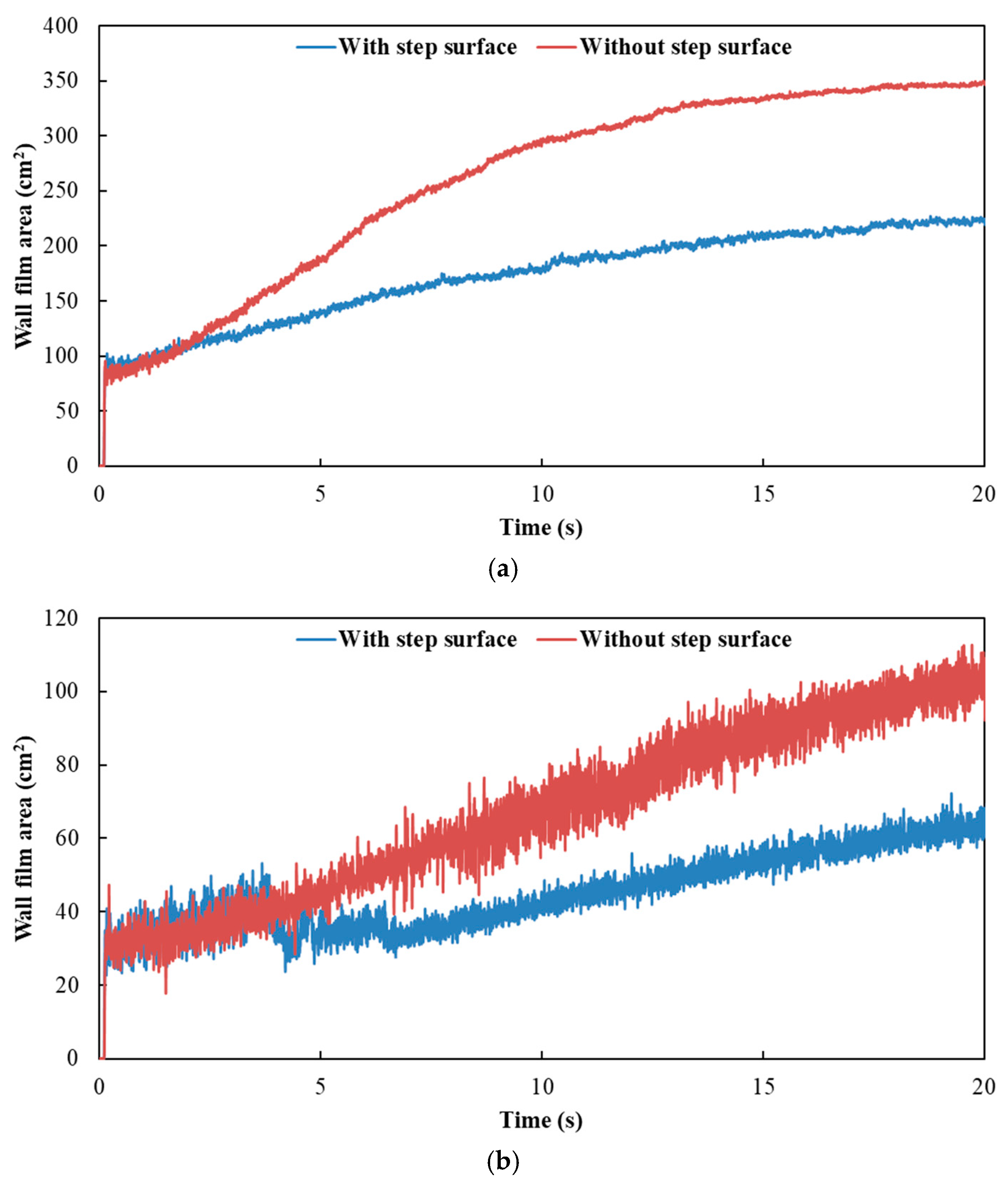
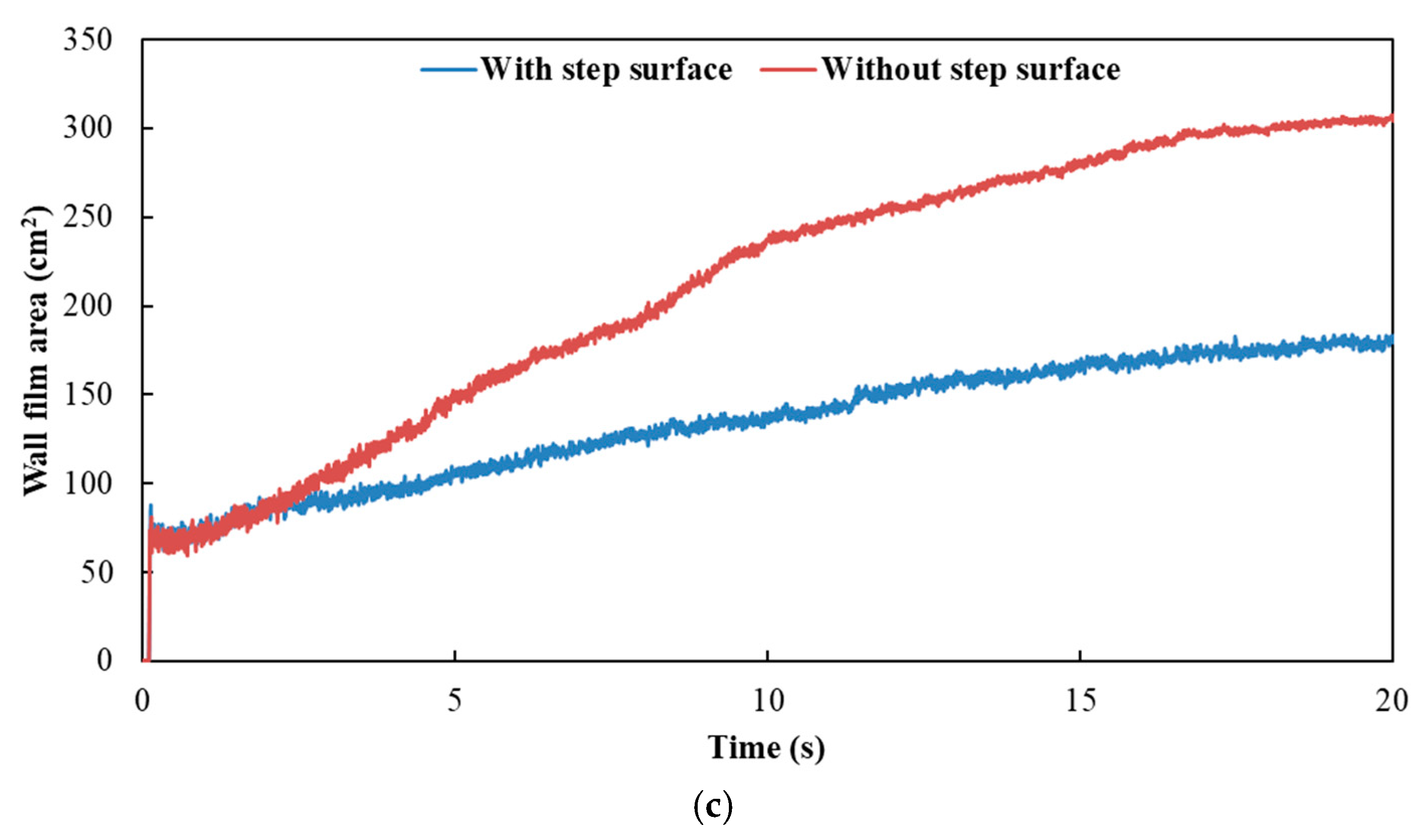
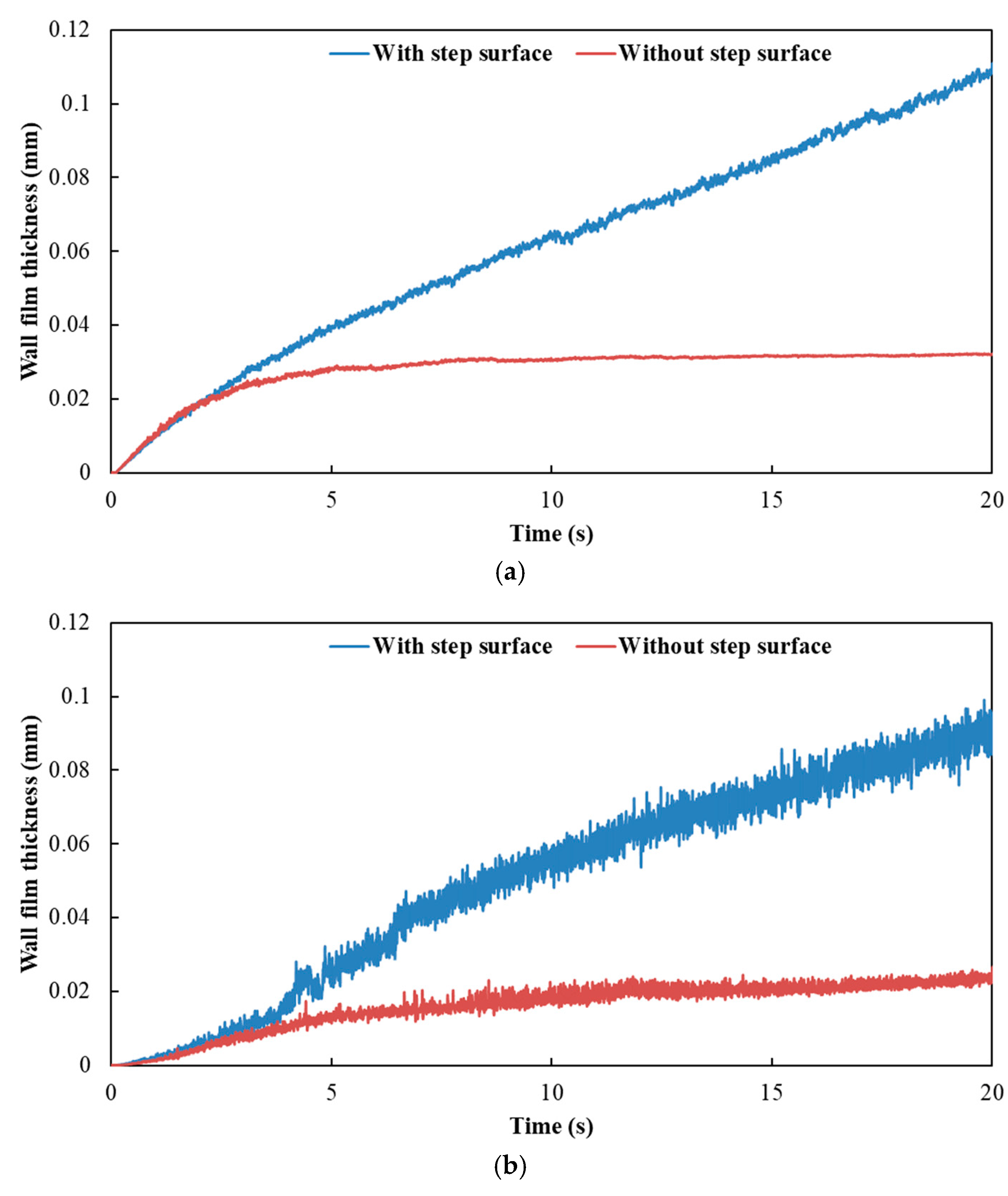
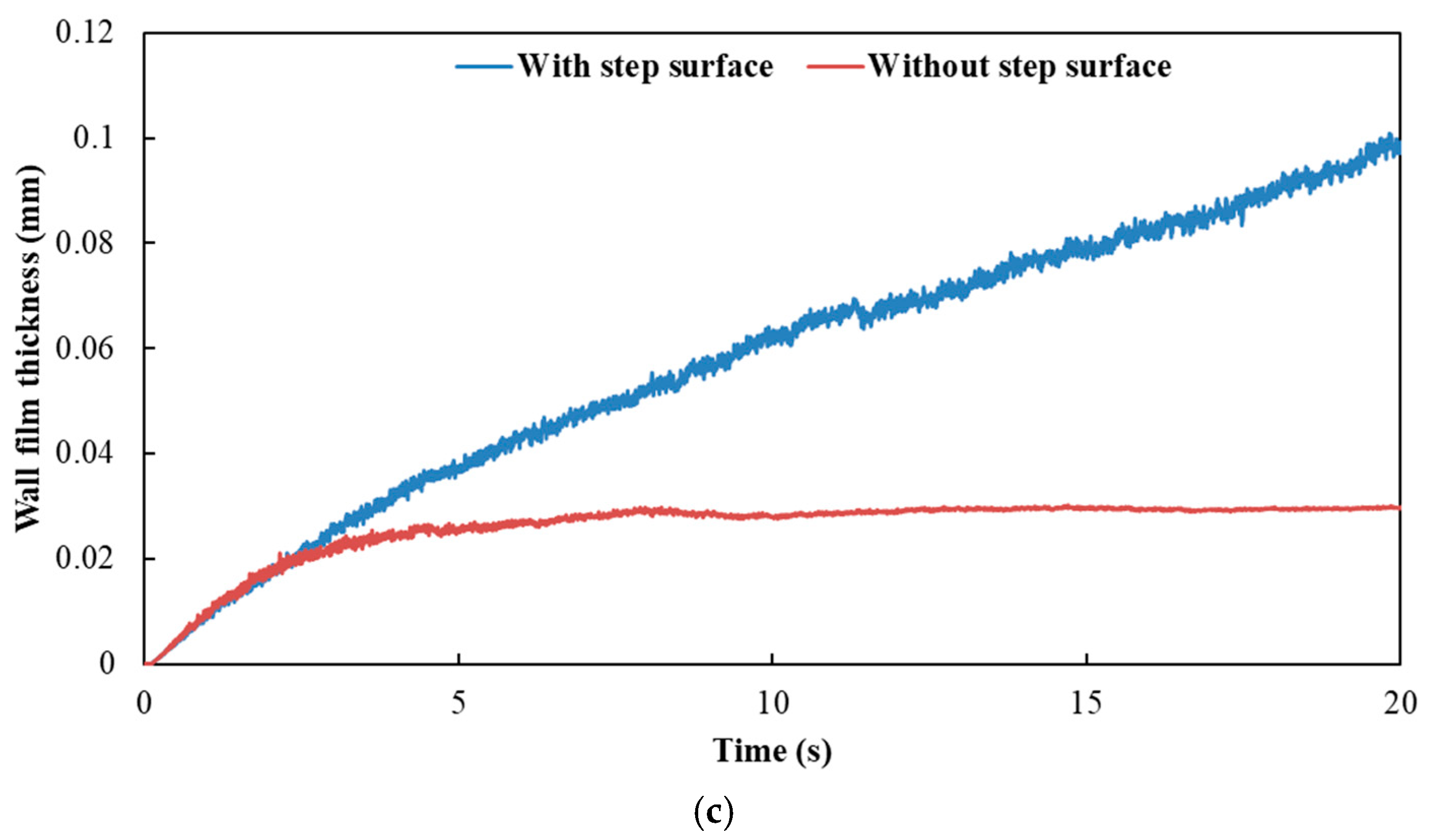
Figure 12 and Figure 13 show the influence of exhaust pipe with or without step surface on wall film area and thickness, respectively. The results indicated that the variation trends of wall film area and wall film thickness were the same for the three typical operating conditions. When there was no step surface in the exhaust pipe, the wall film area was larger, and the wall film thickness was thinner, which was beneficial to the evaporation and pyrolysis of the wall film.
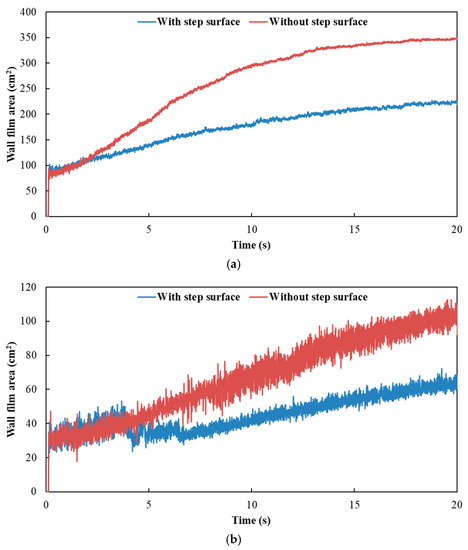
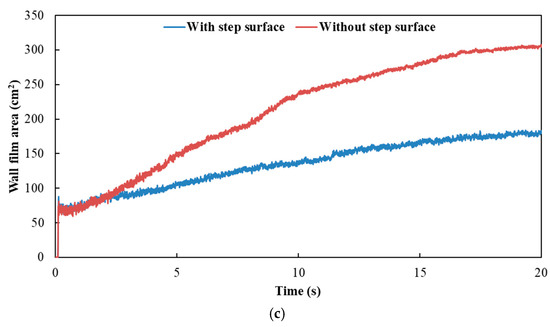
Figure 12.
Influence of exhaust pipe with or without step surface on wall film area. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
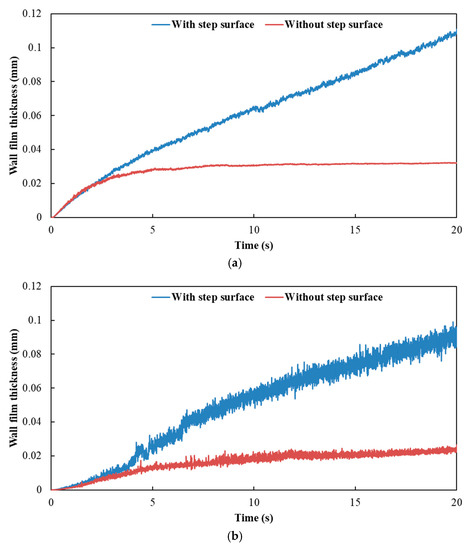
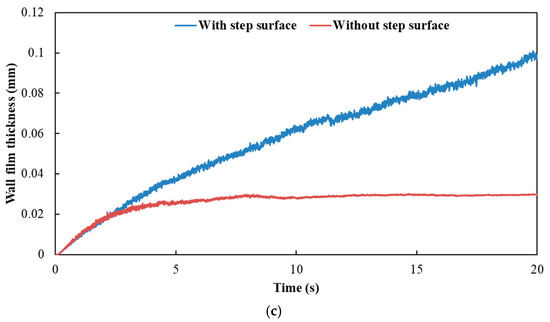
Figure 13.
Influence of exhaust pipe with or without step surface on wall film thickness. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
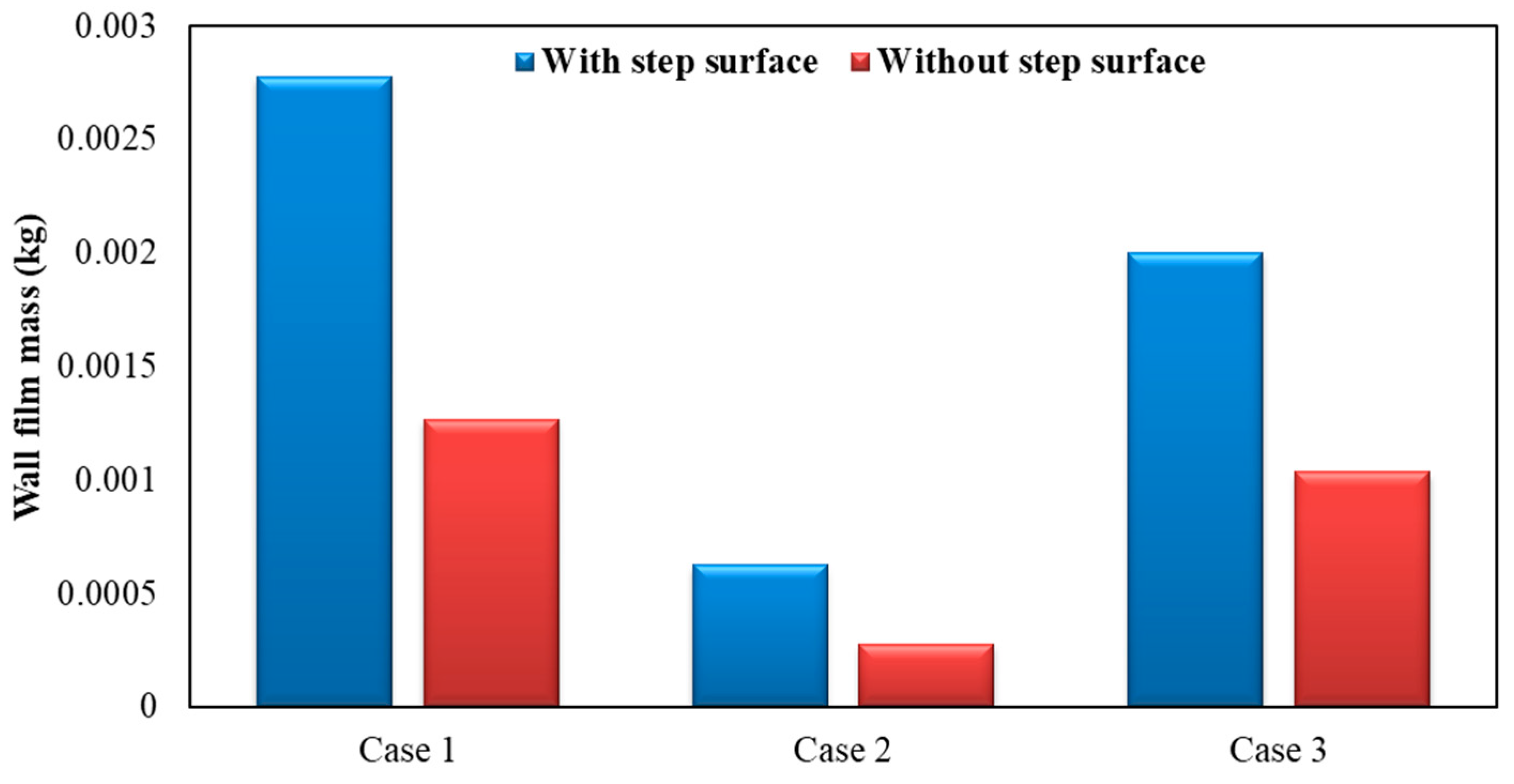
Figure 14 shows the influence of exhaust pipe with or without step surface on wall film mass. As can be seen, by the figure below, the wall film mass was lighter when the exhaust pipe had no step surface. Compared to the case with a step surface, wall film mass was reduced by about 54.44%, 55.40% and 48.27% for each operating condition, respectively, in the exhaust pipe without a step surface.
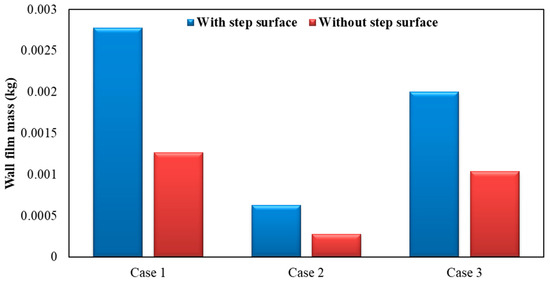
Figure 14.
Influence of exhaust pipe with or without step surface on wall film mass.
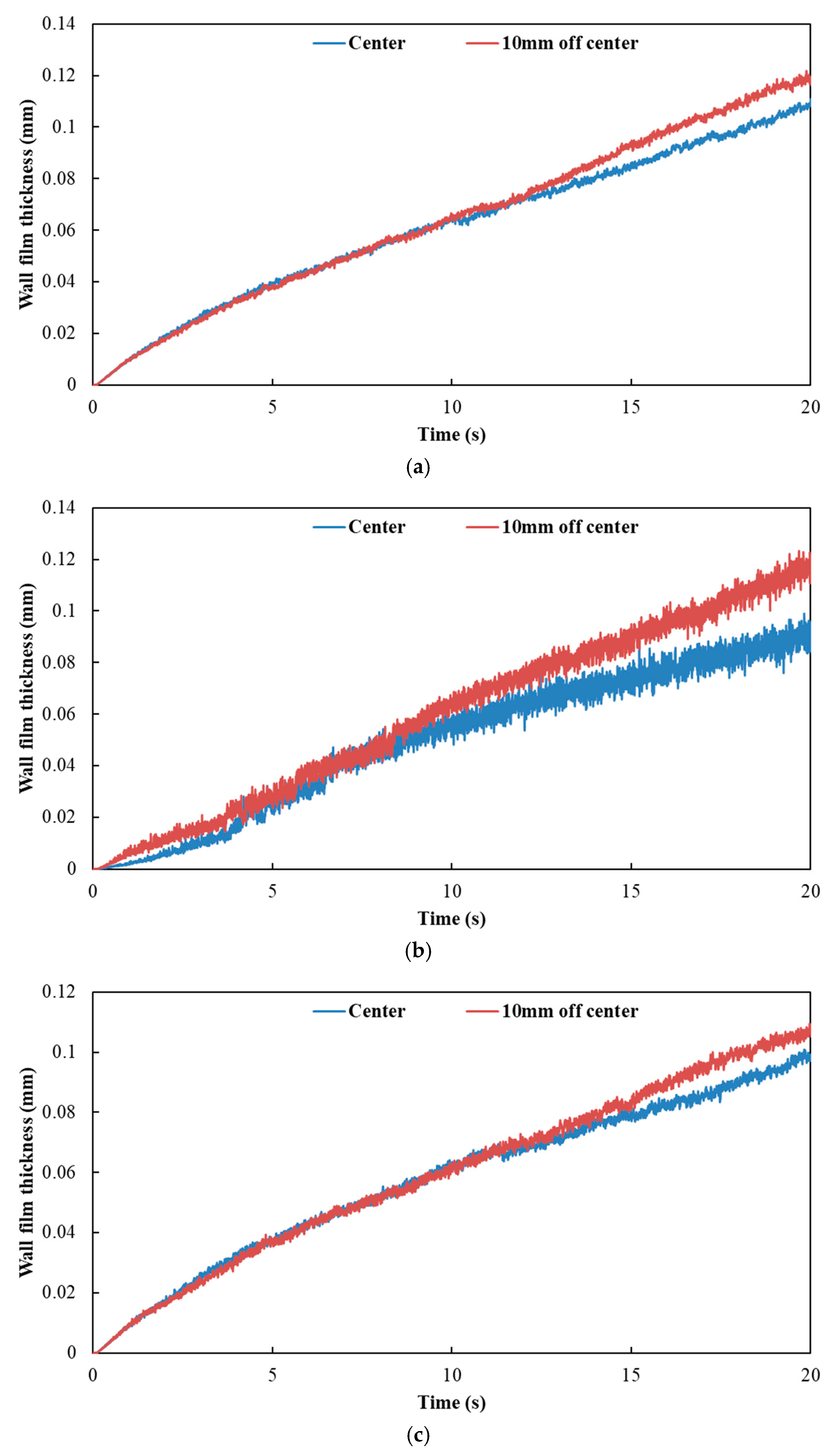
3.2. Influence of Nozzle Position on Wall Film
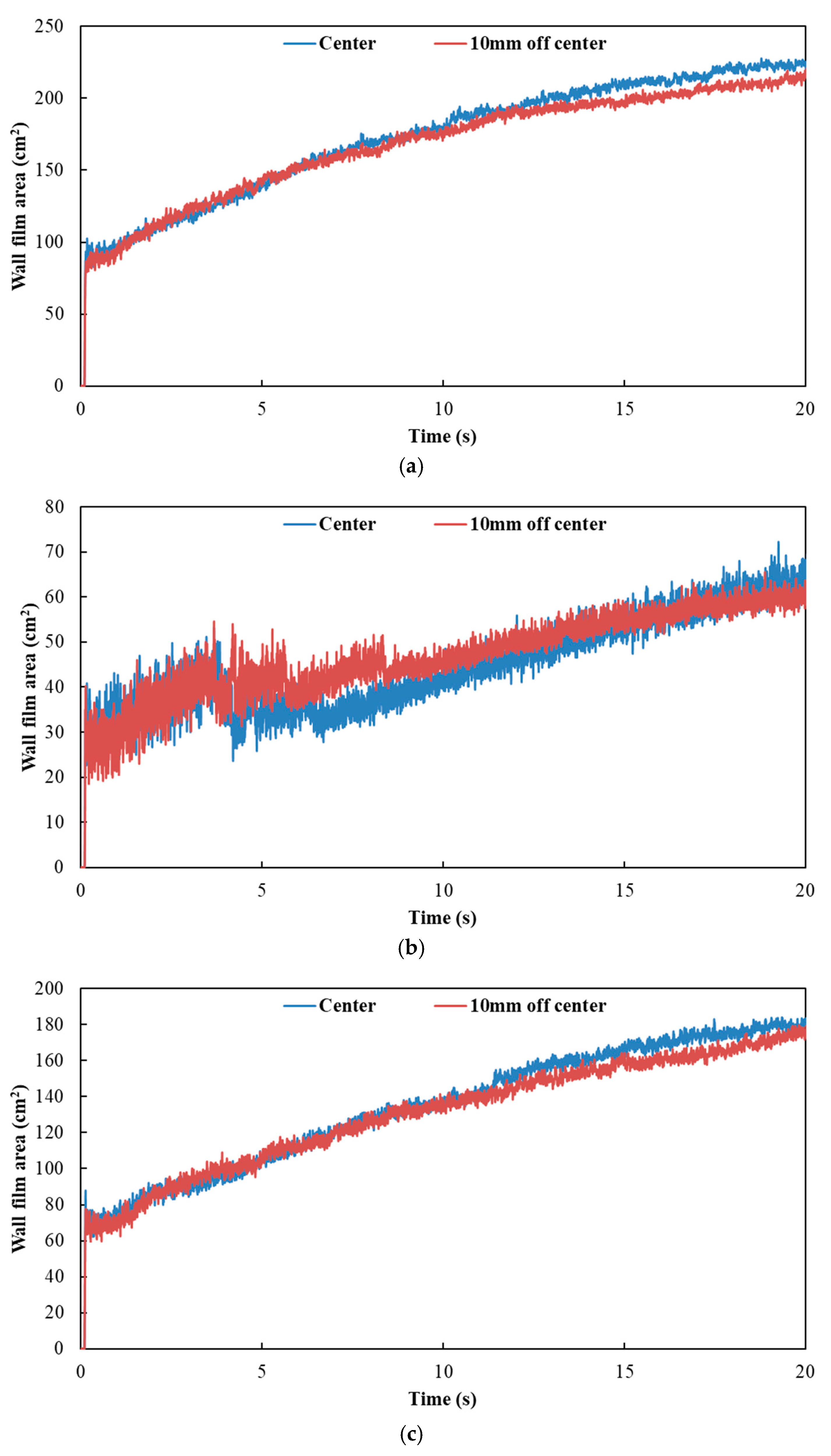
Figure 15 and Figure 16 show the influence of different nozzle positions on wall film area and wall film thickness, respectively. The results indicated that the variation trends of wall film area and wall film thickness were the same for the three typical operating conditions. When the nozzle orifices were located in the center axis of the exhaust pipe, the wall film area was larger. The wall film thickness was thinner, which was beneficial to the evaporation and pyrolysis of the wall film.
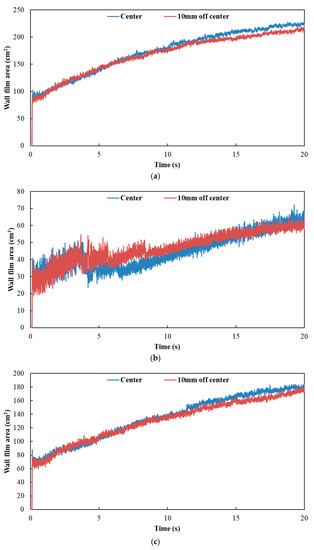
Figure 15.
Influence of different nozzle positions on wall film area. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
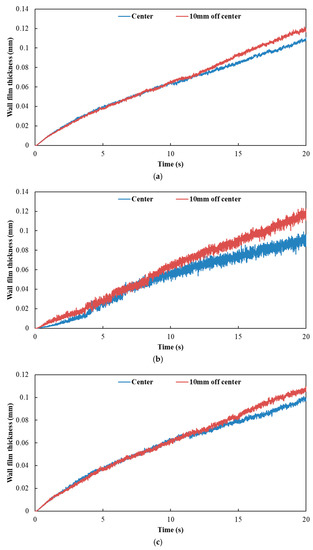
Figure 16.
Influence of different nozzle positions on wall film thickness. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
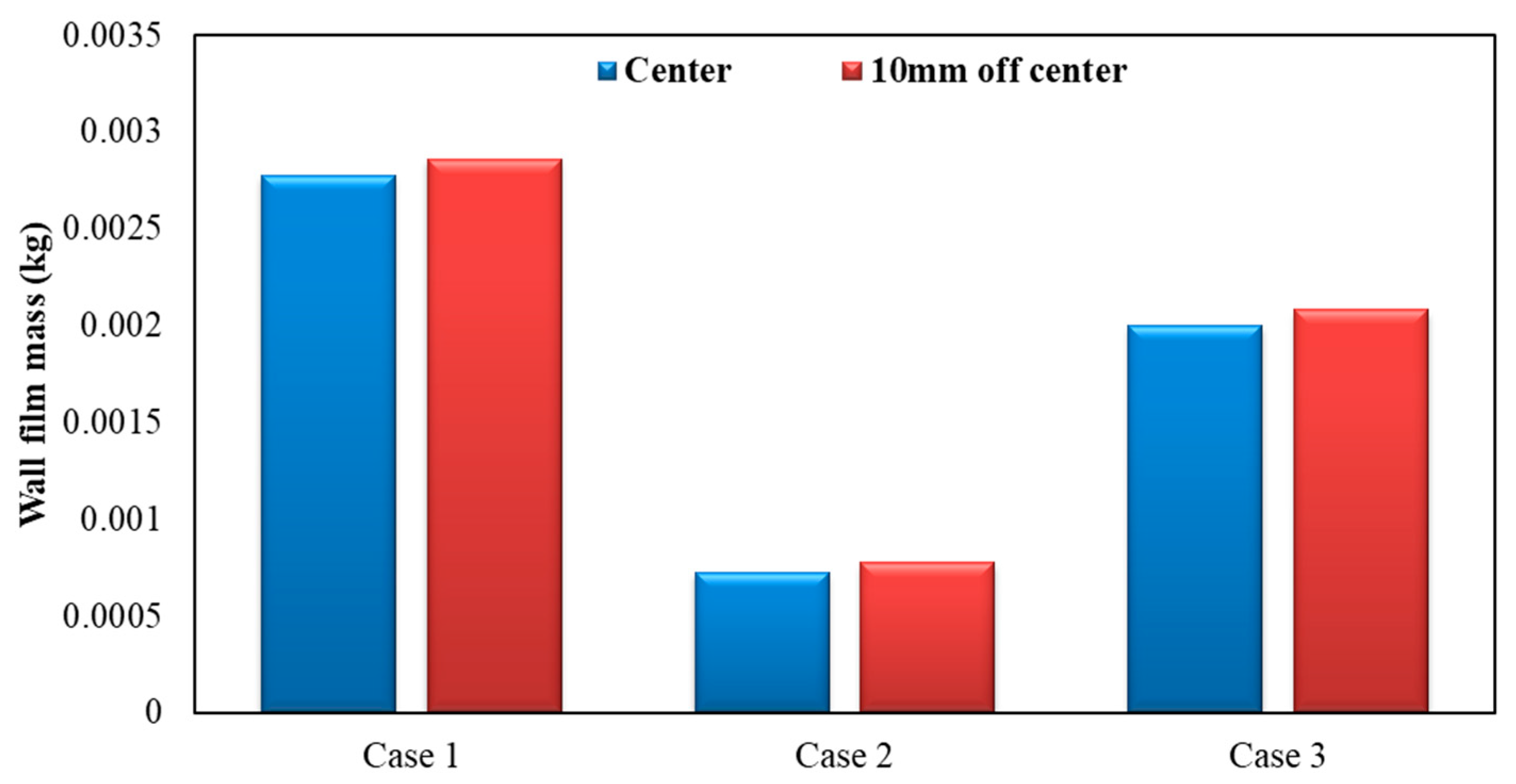
Figure 17 shows the influence of different nozzle positions on wall film mass. As can be seen, by the figure below, the wall film mass was lighter when the nozzle orifices were located in the center axis of the exhaust pipe. Compared to the case where the nozzle orifices are located 10 mm off the center axis, wall film mass was reduced by about 2.83%, 6.38% and 3.87% for each operating condition, respectively, when the nozzle orifices located in the center axis of the exhaust pipe.
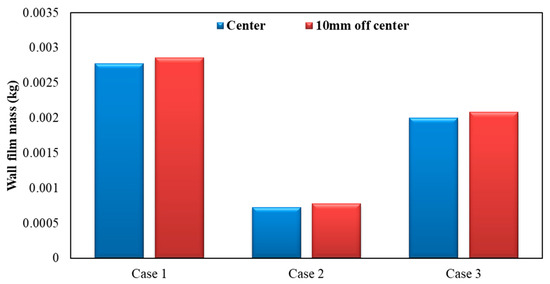
Figure 17.
Influence of different nozzle positions on wall film mass.
3.3. Influence of Pipe Diameter on Wall Film
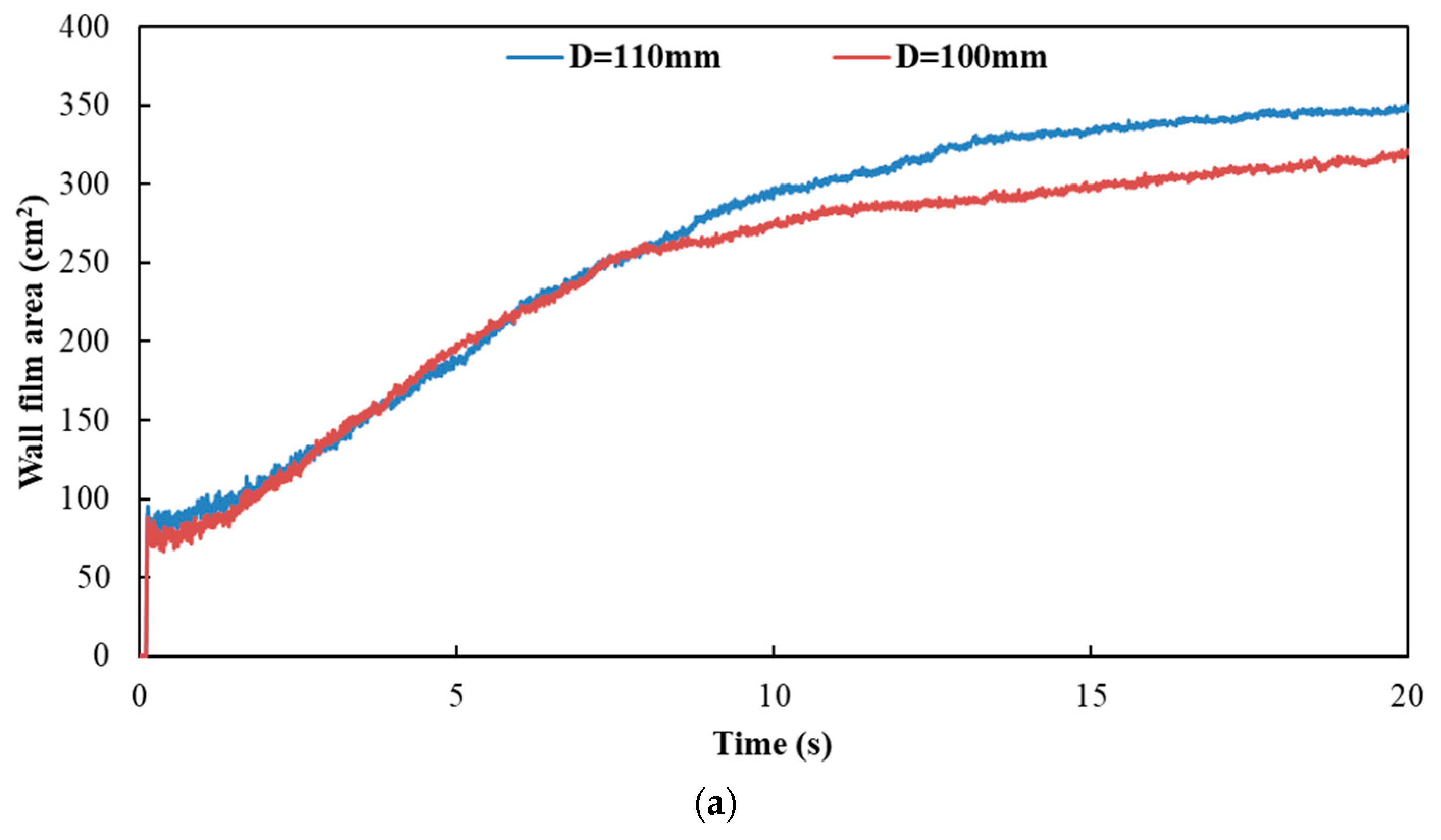
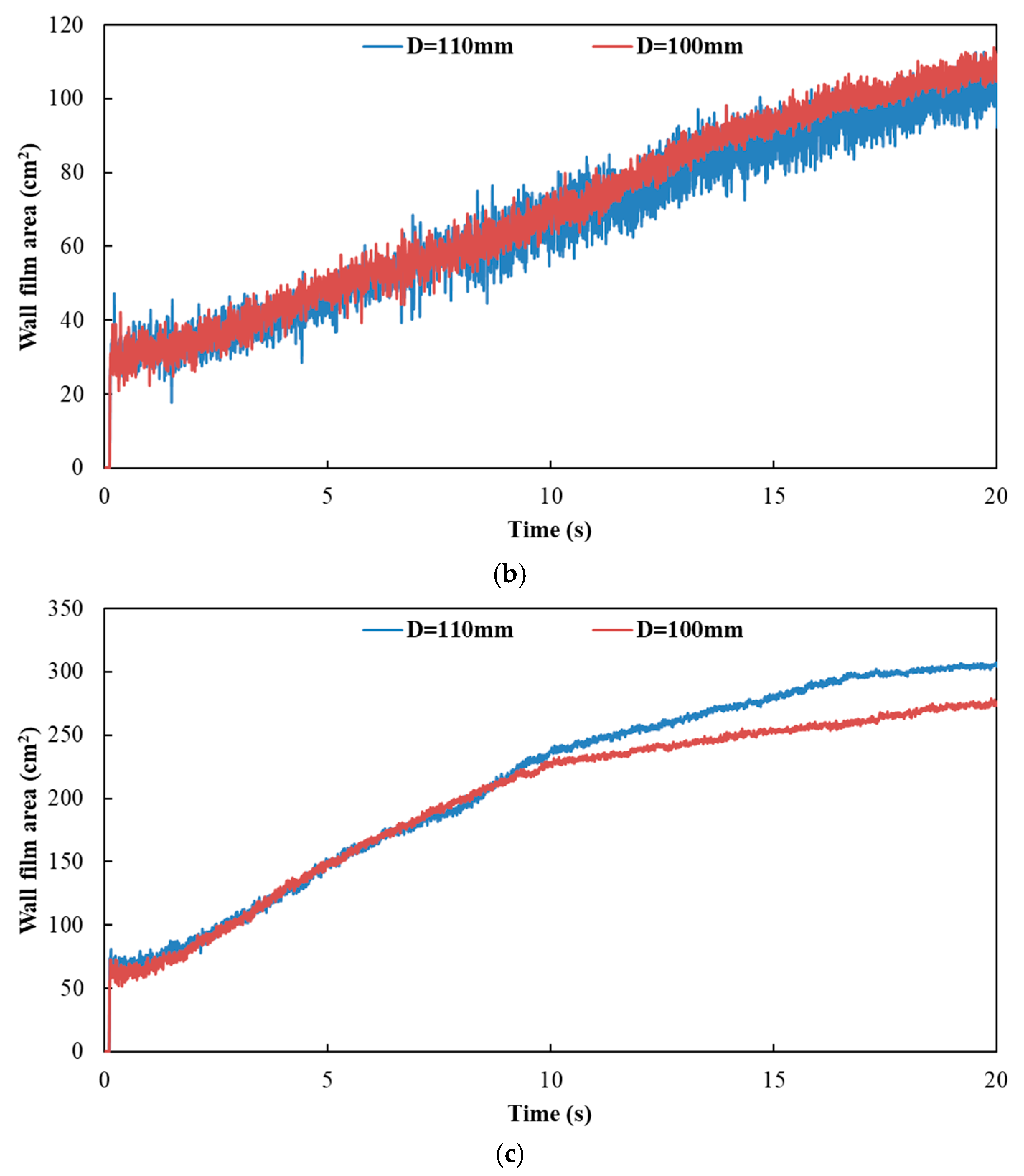
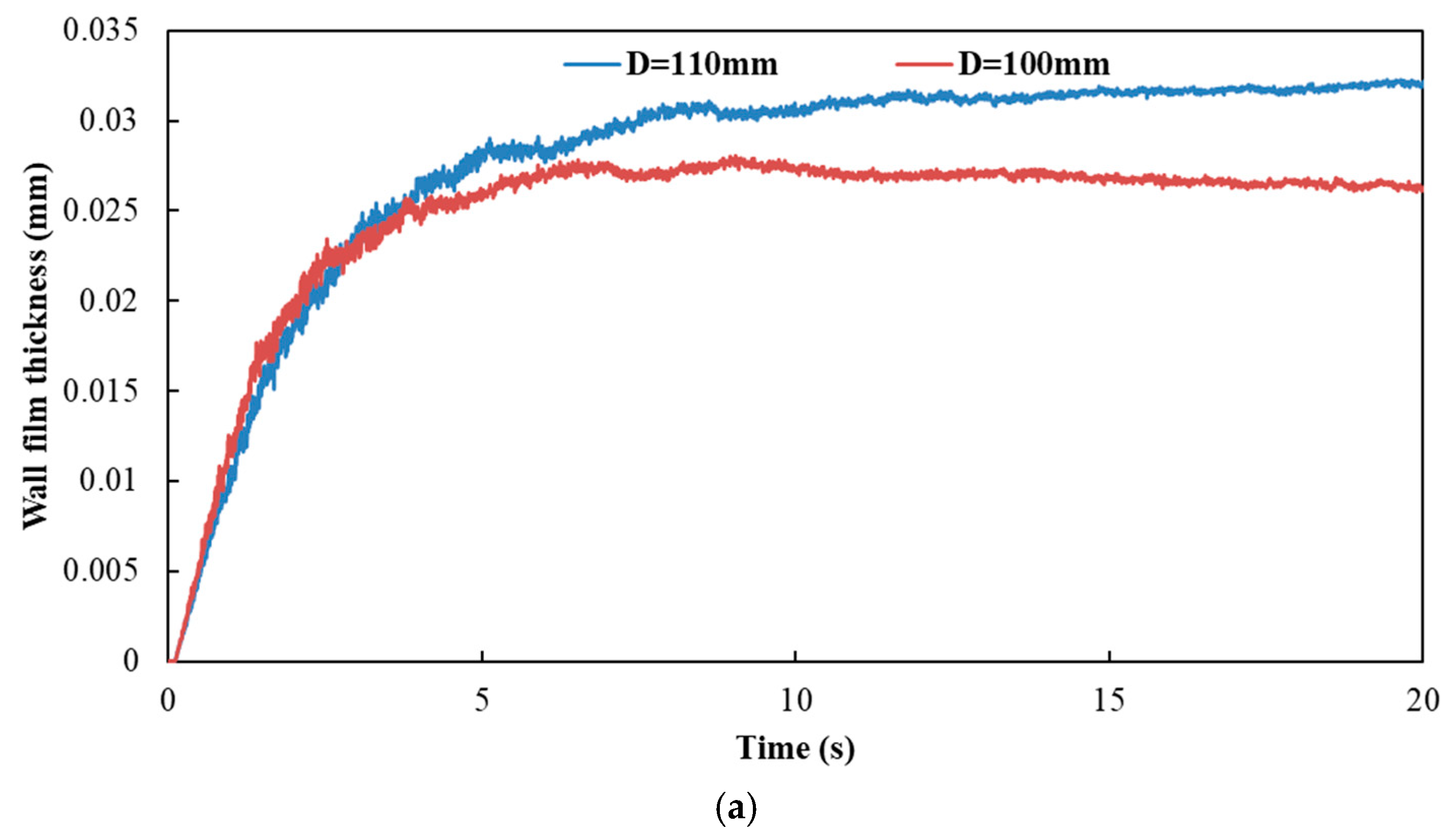
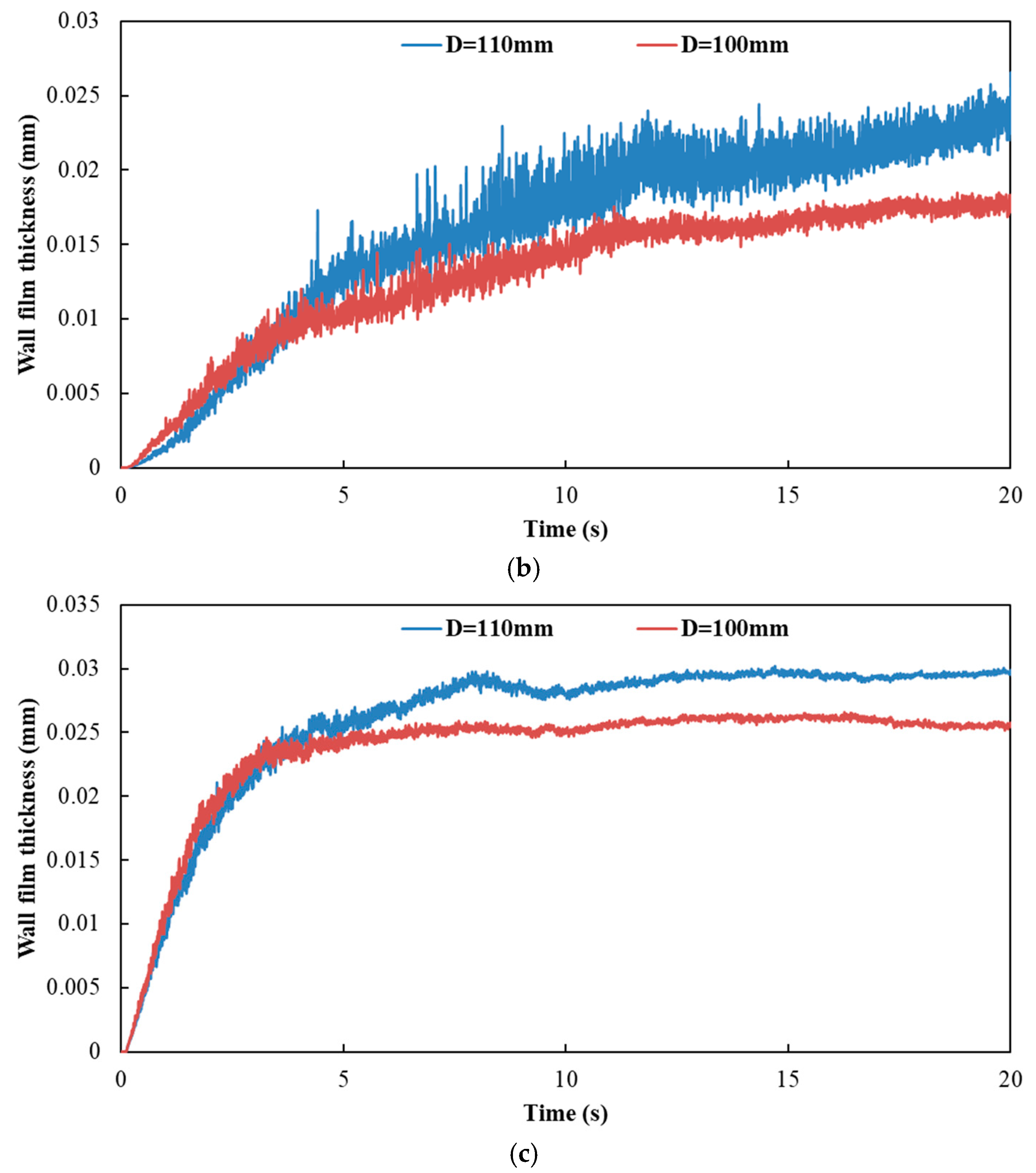
Figure 18 and Figure 19 show the influence of different exhaust pipe diameters on wall film area and wall film thickness, respectively. The results indicated that the variation trends of wall film area and wall film thickness were the same for the three typical operating conditions. When the exhaust pipe diameter dropped from 110 mm to 100 mm, the wall film area was smaller, which was averse to the evaporation and pyrolysis of the wall film. On the other hand, the smaller diameter contributed to the faster flow velocity and the higher shear stress to obtain a thinner wall film thickness, which was beneficial to the evaporation and pyrolysis of wall film.
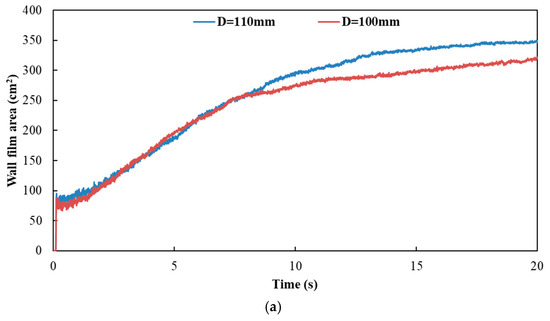
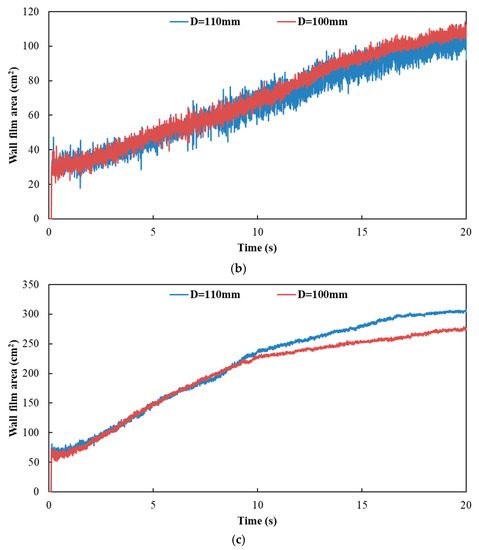
Figure 18.
Influence of different exhaust pipe diameters on wall film area. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
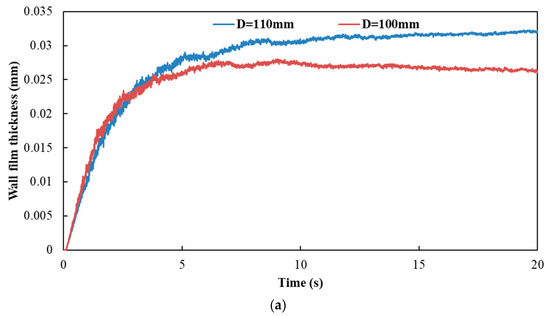
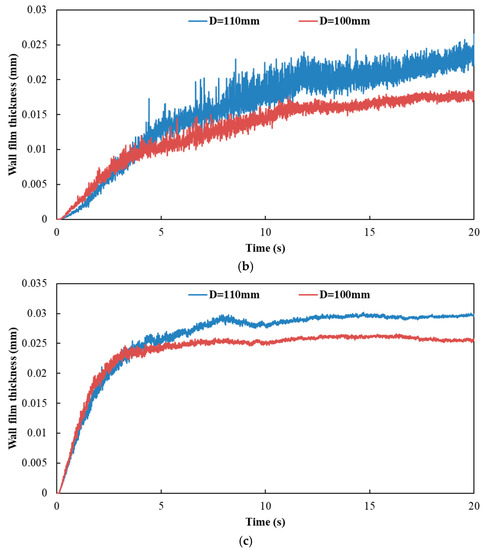
Figure 19.
Influence of different exhaust pipe diameters on wall film thickness. (a) Case 1; (b) Case 2; (c) Case 3.
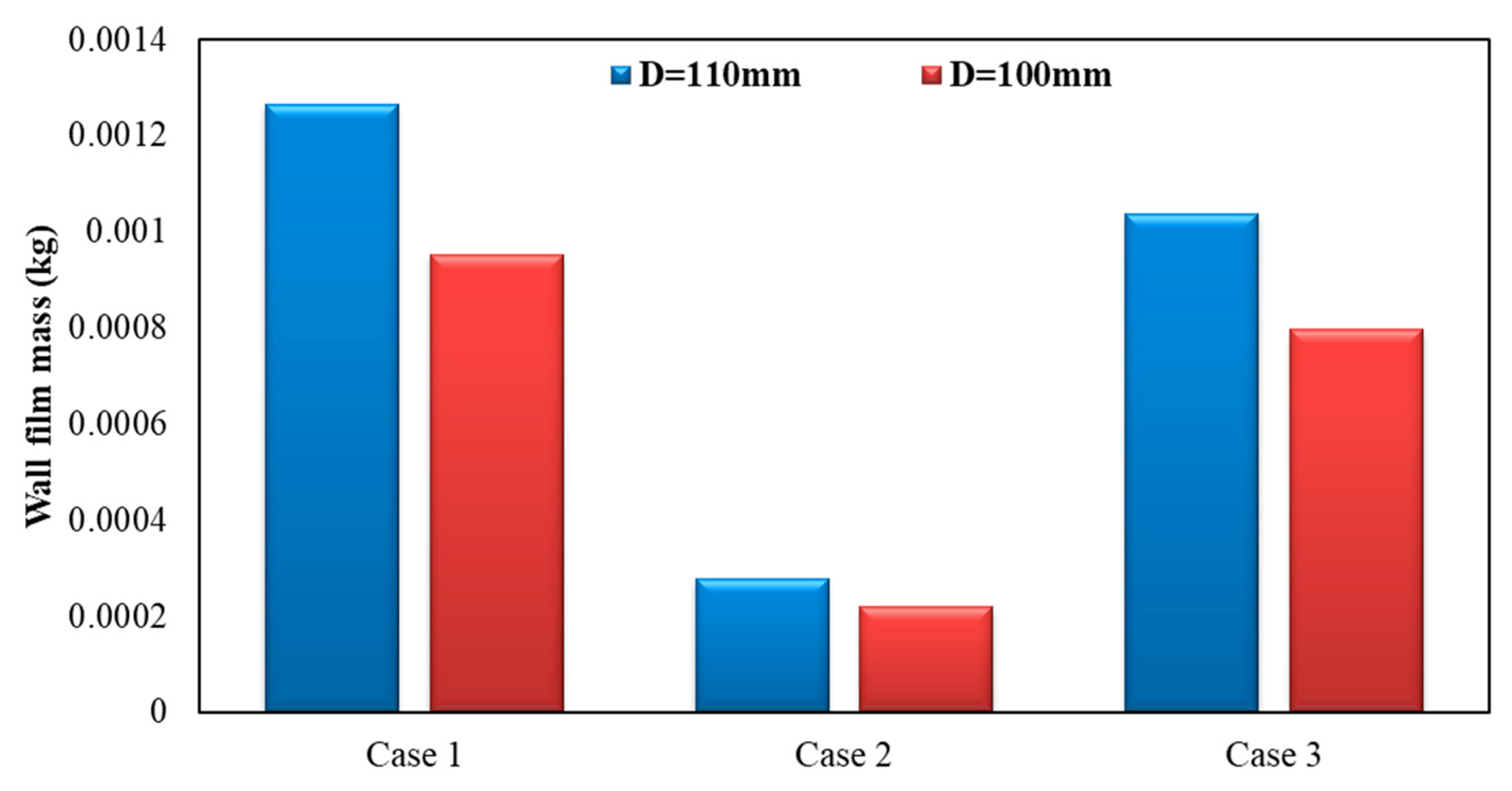
Figure 20 shows the influence of different exhaust pipe diameters on wall film mass. As can be seen, by the figure below, the wall film mass was lighter when the exhaust pipe diameter was 100 mm. Compared to the case of 110 mm, wall film mass was reduced by about 24.72%, 21.30% and 23.14% for each operating condition, respectively, when the exhaust pipe diameter was 100 mm.
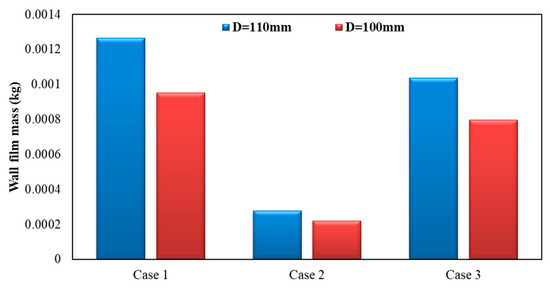
Figure 20.
Influence of different exhaust pipe diameters on wall film mass.
4. Discussion
According to the results of the above simulation analysis, it is found that it can effectively reduce the residual wall film mass after optimization of the structural configuration. However, it is worth noting that the diameter reduction of the exhaust pipe inevitably allows the exhaust back pressure to build up, which should influence the normal operation of the engine. Therefore, the acceptable measures to optimize the exhaust flow field were to remove the abrupt cross section in the exhaust pipe downstream of the nozzle and arrange the nozzle orifices in the center axis of the exhaust pipe.
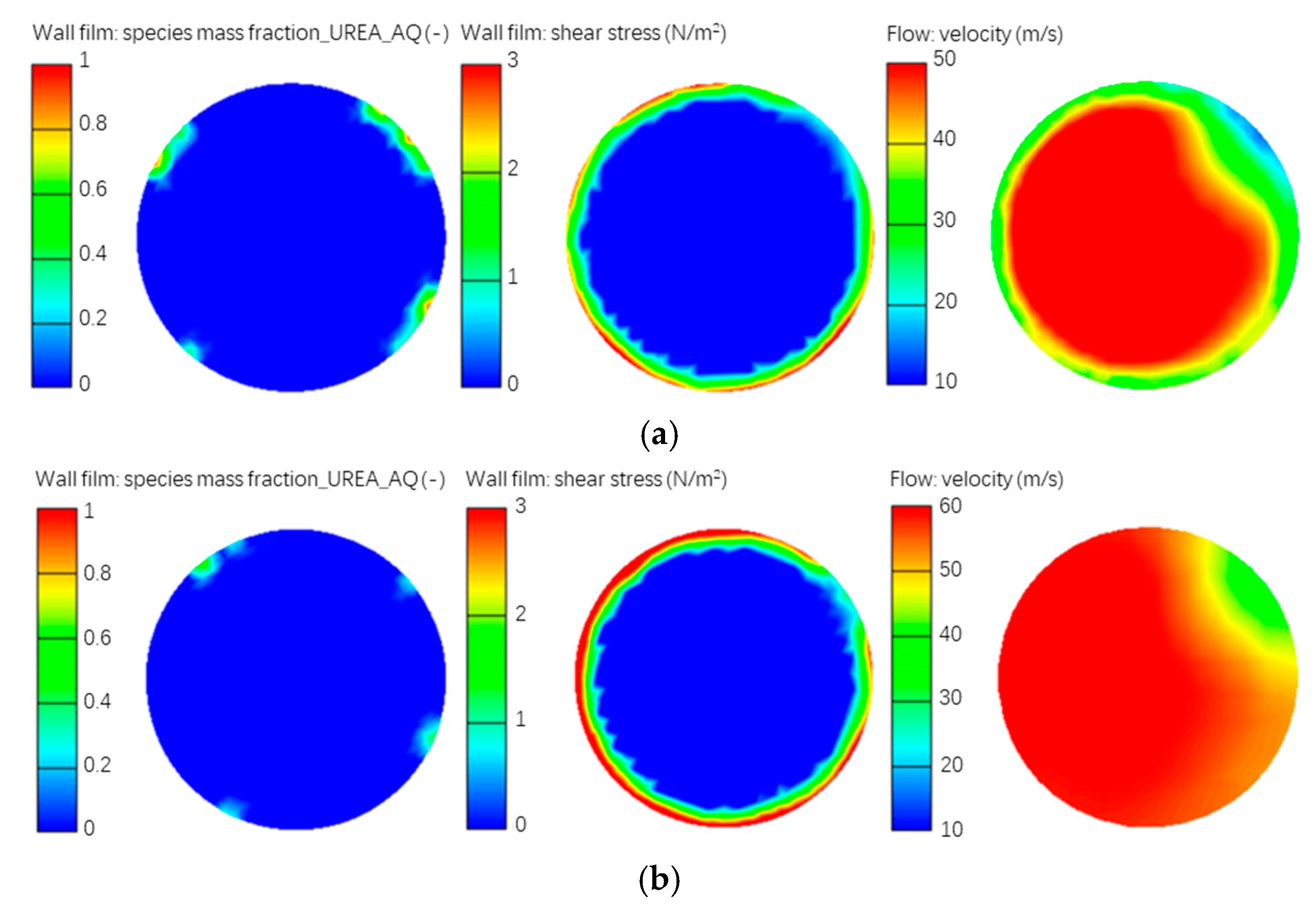
Figure 21 shows the distribution of wall film, shear stress and flow field velocity at the section of step surface in the exhaust pipe. After optimization, the region of wall film formed on the exhaust pipe wall became smaller, the shear stress on the wall film was significantly increased, and the flow field velocity nearby the wall surface increased by 20 m/s on average, which helped promote spalling, flow, and evaporation of wall film.
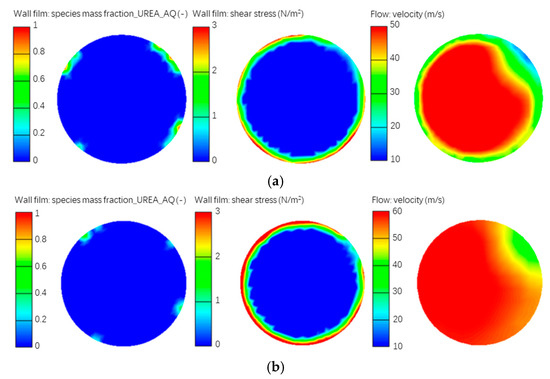
Figure 21.
Comparison results of flow field simulation before and after optimization. (a) Before optimization; (b) After optimization.
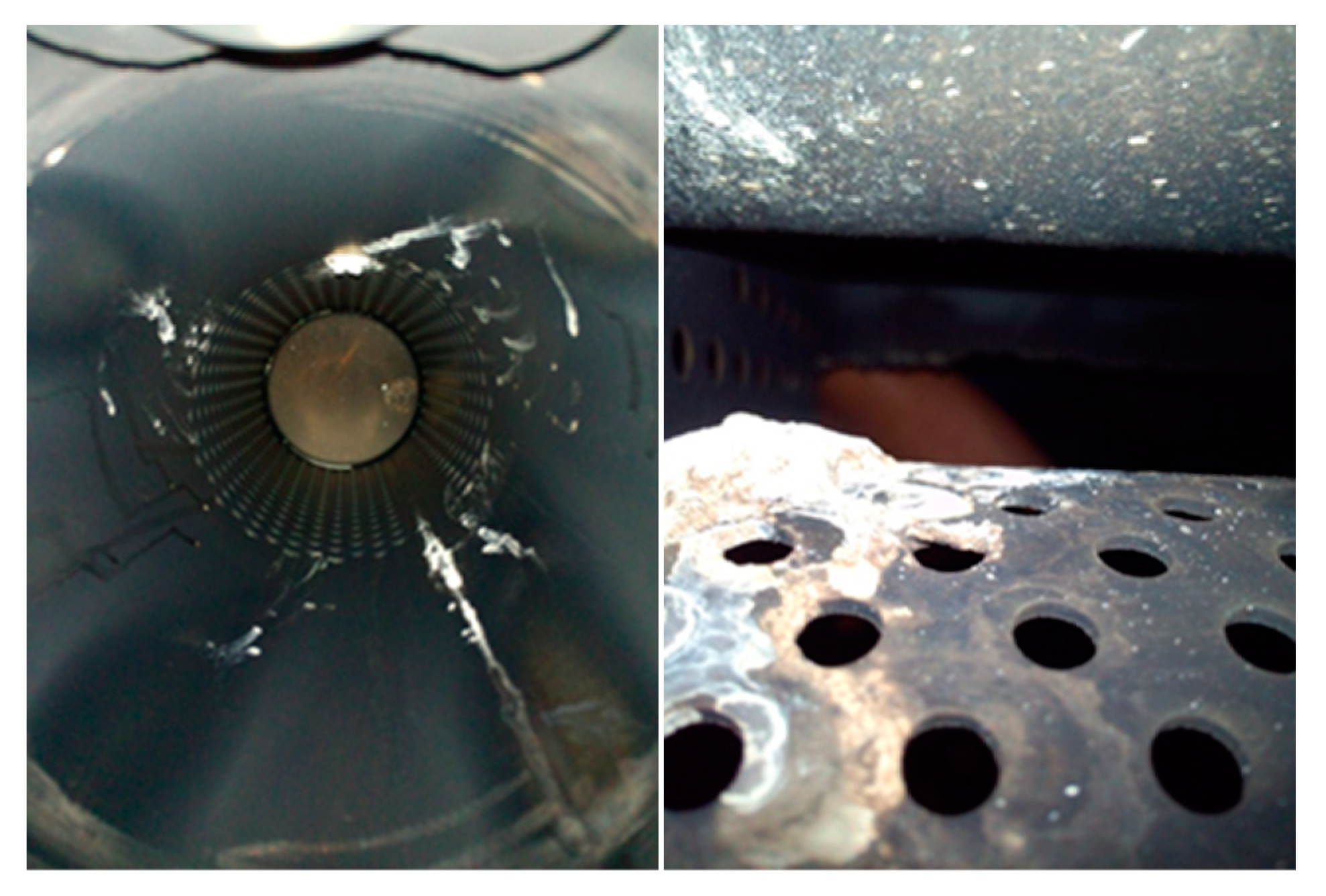
Another supplementary vehicle real road test was conducted to verify the effectiveness of the optimization scheme. It was found that a small number of deposits formed on the perforated pipe at the entrance of the catalytic converter, as shown in Figure 22.

Figure 22.
Both sides of the perforated pipe are at the entrance of the catalytic converter.
After spraying into the exhaust pipe, urea droplet usually takes time for evaporation and pyrolysis. Currently, the nozzle is arranged at the entrance of the catalytic converter, which is only 150 mm away from the perforated pipe. However, a urea droplet was attached to the perforated pipe, which might cause hidden trouble in deposit formation. Therefore, to explore the suitable nozzle location, further simulation research was conducted. The distances from the perforated pipe to each nozzle location are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Nozzle location.
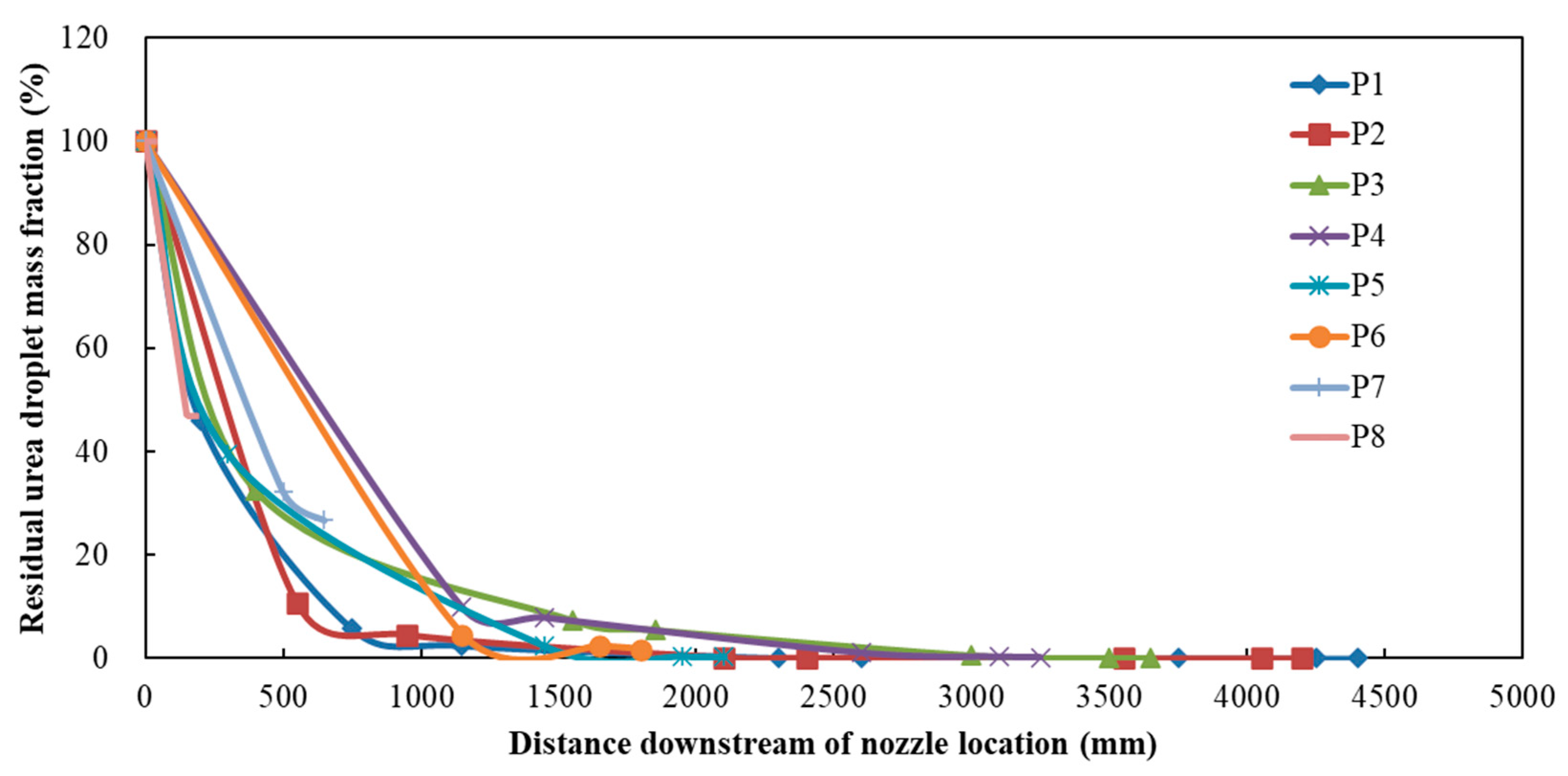
Part of the urea droplets sprayed into the exhaust pipe is heated to evaporation and become gas, and another part attaches to the exhaust pipe wall to form wall films. The rest part of the unevaporated urea droplets keeps moving with the exhaust flow. Figure 23 shows the change in residual urea droplet mass fraction with the distance downstream of the nozzle location. The results indicated that there was almost no residue of urea droplet at the distance 10D downstream of the nozzle location (D was the exhaust pipe diameter of 110 mm). Therefore, the nozzle location should be arranged at least 10D upstream of the perforated pipe to eliminate the hidden trouble of deposit formation inside the catalytic converter.
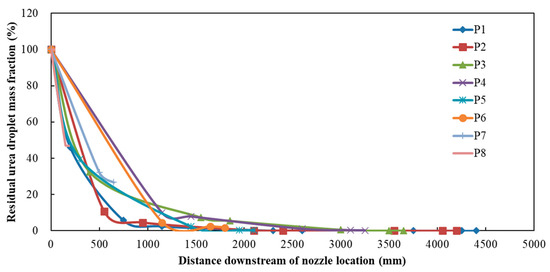
Figure 23.
Residual urea droplet mass fraction at different positions.
The primary purpose of arranging the nozzle location at least 10D upstream of the perforated pipe is to increase temperature. However, reducing the injection rate is another way of avoiding deposit formation. Our previous studies show a critical injection rate of Q. When the actual injection rate R is lower than Q. No deposits generate in the exhaust pipe. Conversely, when R is higher than Q, there are deposits. The injection rate is also closely related to NOx emission. Therefore, the appropriate control strategy for urea injection needs to balance the formation of deposits and NOx emission.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the CFD model of diesel engine exhaust pipe was established and showed a good performance verified by the experimental results of spray and temperature. A commercial vehicle was employed to conduct a real road test, and the statistical result showed three typical operating conditions for the employed vehicle. The research indicated that the variation trends of wall film area and wall film thickness were the same for the three typical operating conditions. When the exhaust pipe had no step surface or nozzle orifices located in the center axis of the exhaust pipe, or the exhaust pipe diameter dropped from 110 mm to 100 mm, wall film mass reduced by about 48.27~55.4%, 2.83~6.38% and 21.3~24.72% respectively. However, in another supplementary vehicle real-road test, deposits formed on the perforated pipe at the entrance of the catalytic converter, which indicated that only optimizing the exhaust flow field could not solve the problem of deposit formation completely. According to further simulation research, it can be inferred that the hidden trouble of deposits formation inside the catalytic converter would disappear when the nozzle location was arranged at least 10D upstream of the perforated pipe.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Z.; investigation, F.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, grant number 2022CFB730.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support of the School of Automotive and Transportation Engineering (Wuhan University of Science and Technology) and the Wuhan University of Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, T.V. Diesel Emissions in Review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wang, L. Model-based optimization of parameters for a diesel engine SCR system. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2013, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N. Investigation on the Formation Mechanism of Deposit in the Exhaust Pipe of SCR System for Diesel Engine. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Bai, S.; Zang, Z.; Li, G. Study on urea deposits risk of after-treatment system based on deposits boundary method. Energy 2023, 267, 126624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, J.; Börnhorst, M.; Ates, C.; Samkhaniani, N.; Pfeil, J.; Wörner, M.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.-J.; Deutschmann, O.; Frohnapfel, B.; et al. A Holistic View on Urea Injection for NOx Emission Control: Impingement, Re-atomization, and Deposit Formation. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2020, 6, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Pyo, Y.D.; Jang, J.; Kim, G.C.; Cho, C.P.; Yang, C. NO, NO2 and N2O emissions over a SCR using DOC and DPF systems with Pt reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryddner, D.T.; Trujillo, M.F. Modeling Urea-Water Solution Droplet Evaporation. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, W.; Heine, B.; Birkhold, F.; Kruse, M.; Deutschmann, O. Formation of Urea-Based Deposits in an Exhaust System: Numerical Predictions and Experimental Observations on a Hot Gas Test Bench. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Investigation on the urea deposit formation and thermal decomposition characteristics in the SCR aftertreatment system of a diesel engine. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 103, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Watkins, W.; Snow, R.; Graham, G.; McCabe, R.; Lambert, C.; Carter, R.O. Laboratory and Engine Study of Urea-Related Deposits in Diesel Urea-SCR After-Treatment Systems; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Experimental Study of Urea Solution Spray and Decomposition and Ammonia Storage in Selective Catalytic Reduction System for Diesel Engines. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Hao, B.; Chen, Y.; Huang, G.; Guo, X. Study of reducing deposits formation in the urea-SCR system: Mechanism of urea decompo-sition and assessment of influential parameters. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 164, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungmin, S. Aftertreatment Package Design for SCR Performance Optimization; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Way, P.; Viswanathan, K.; Preethi, P.; Gilb, A.; Zambon, N.; Blaisdell, J. SCR Performance Optimization through Advancements in Aftertreatment Packaging; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Munnannur, A.; Chiruta, M.; Liu, Z.G. Thermal and Fluid Dynamic Considerations in Aftertreatment System Design for SCR Solid Deposit Mitigation; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Fila, A.; Kotrba, A.; Floyd, R. Investigation of Urea Deposits in Urea SCR Systems for Medium and Heavy Duty Trucks; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyurt, T.G.; Ergin, S.; Zeren, H.B.; Savcı, I.H. Experimental and numerical investigation on the urea-deposit formation at different severities in selective catalytic reduction systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 214, 118884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berszány, E.; Stein, M.; Bykov, V.; Maas, U. An improved reduced model for the evaporation and decomposition of urea-water solution (UWS) droplets. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.S.; Nayak, N.S.; Kapilan, N.; Hindasageri, V. An experimental and numerical study on effects of exhaust gas temperature and flow rate on deposit formation in Urea-Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system of modern automobiles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 1211–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, C.; Börnhorst, M.; Koch, R.; Eck, M.; Deutschmann, O.; Bauer, H.-J. Morphological characterization of urea derived deposits in SCR systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).