Anisotropic Analysis of Etch Rates for Sapphire Based on a Layer-by-Layer Removal Model of Surface Atoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
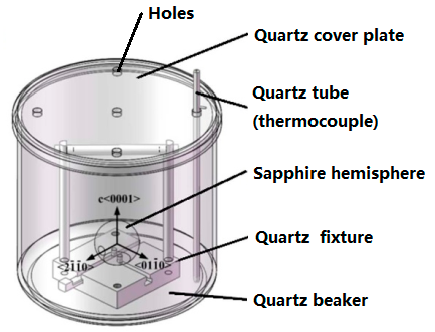
2. Experimental Methods
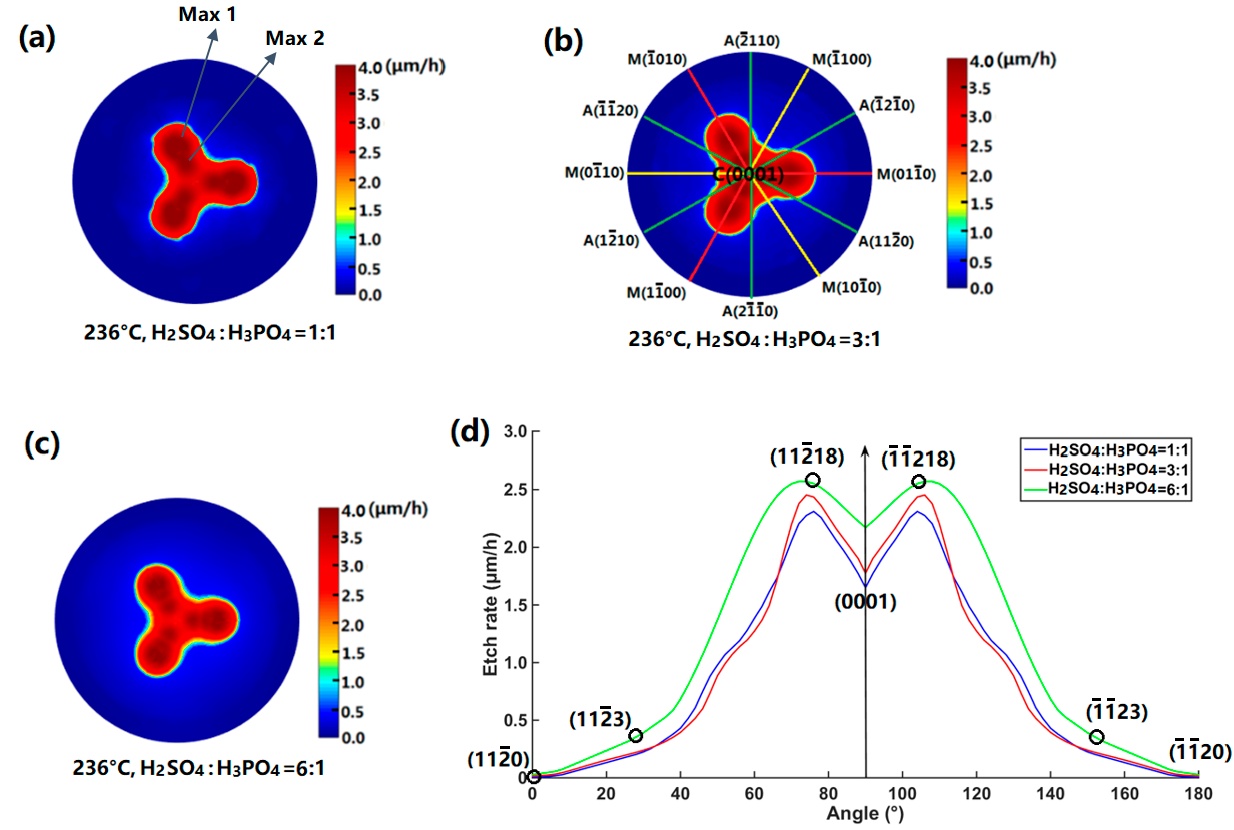
3. Results and Discussion
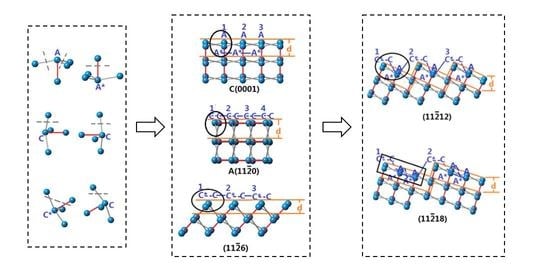
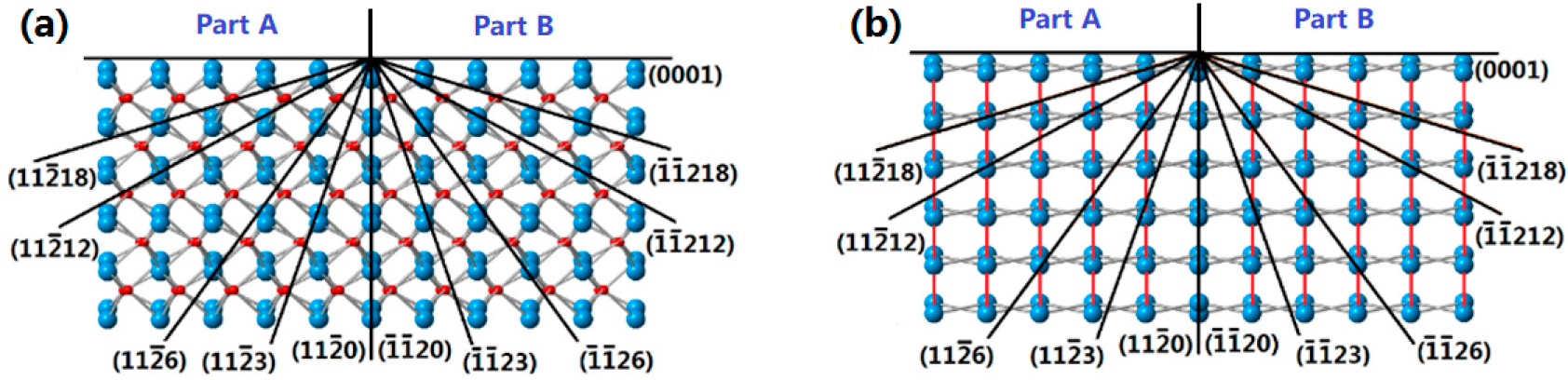
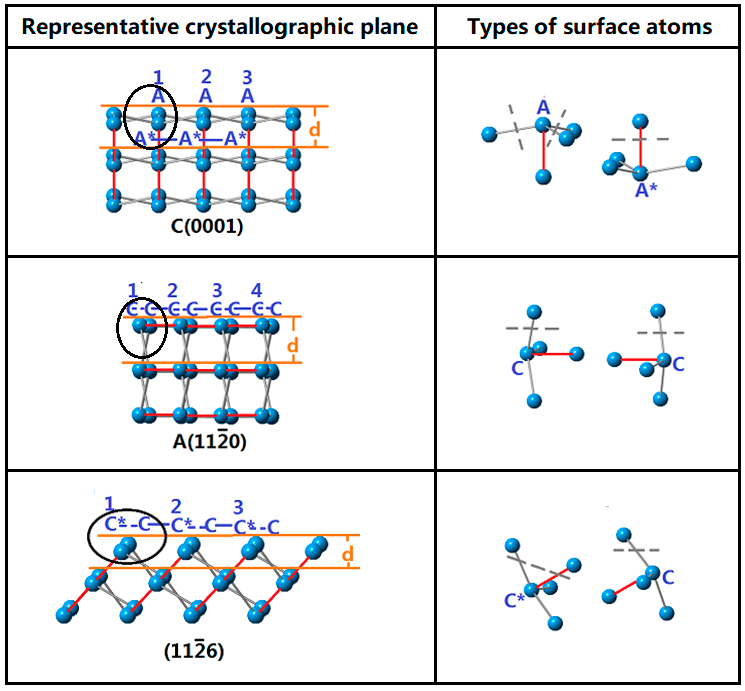
3.1. Simplification of Sapphire’s Atomic Structure
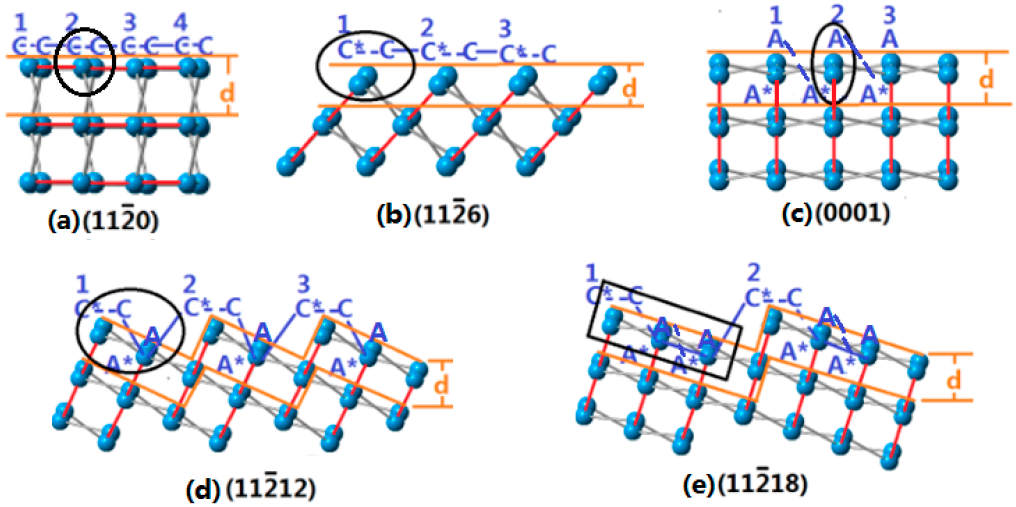
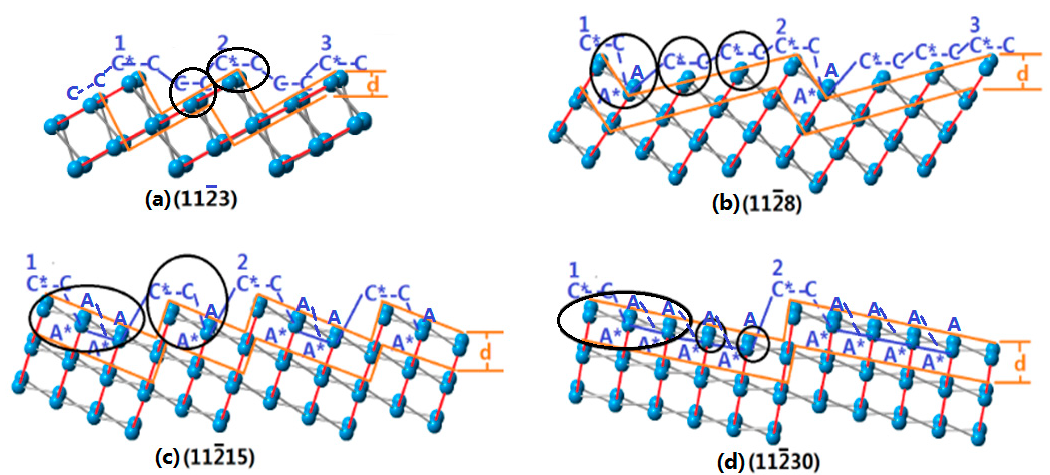
3.2. Arrangements of Surface Atoms of Crystal Planes of Sapphire
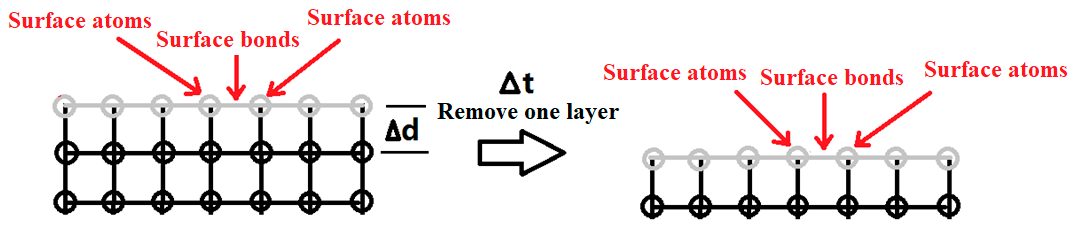
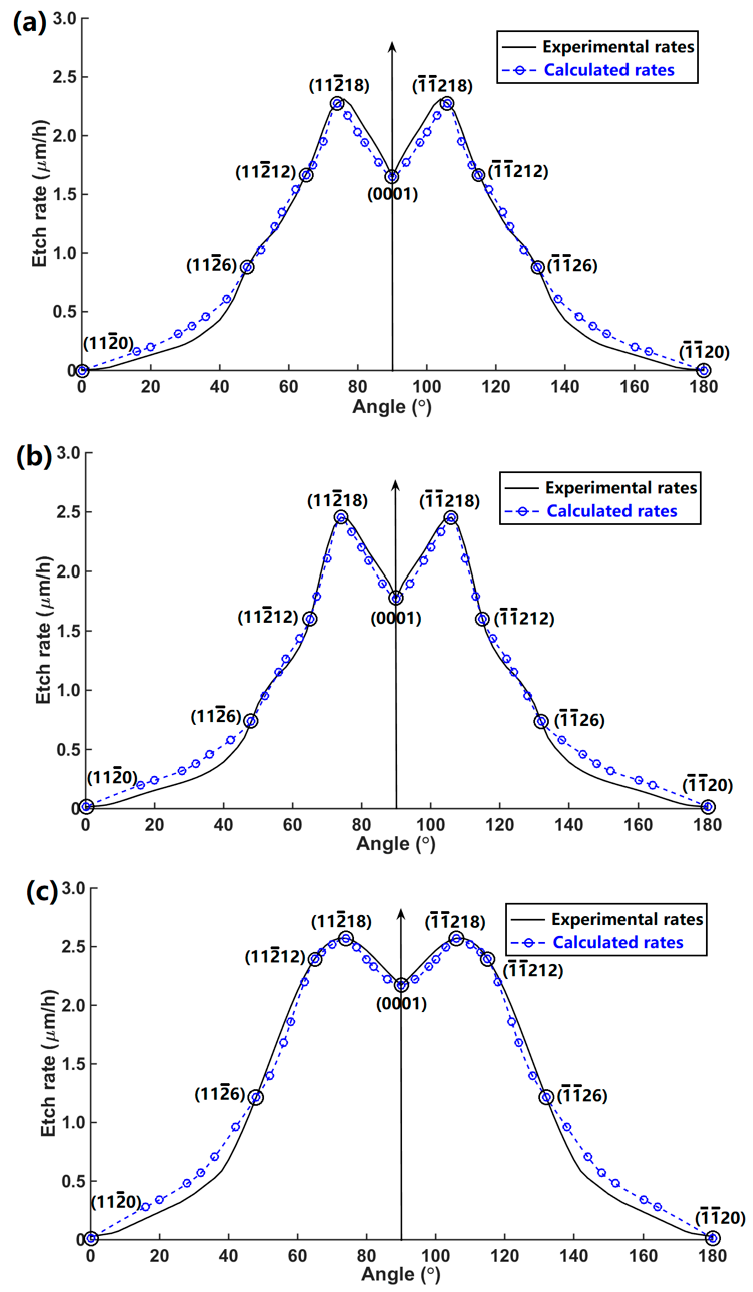
3.3. Calculation of Etch Rates of Crystal Planes of Sapphire
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Rao, S.; Singh, D.; Singh, R.K. Low temperature wet etching to reveal sub-surface damage in sapphire substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.K.; Feng, K.Y.; Lin, Q.L.; Huang, H. Low-temperature wetting of sapphire using Sn–Ti active solder alloys. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22175–22182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chin, J.K.; Cheah, K.H.; Tang, H.B. Fabrication and preliminary testing of hydroxylammonium nitrate (HAN)-based ceramic microthruster for potential application of nanosatellites in constellation formation flying. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.Q.; Qi, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Study on sapphire microstructure processing technology based on wet etching. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 1741004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.X.; Chu, C.S.; Tian, K.K.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Bi, W.G. The morphology evolution of selective area wet etched commercial patterned sapphire substrates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 035012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.W.; Lu, Y.M.; Fan, H.; Xia, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.L. Wet-etching-assisted femtosecond laser holographic processing of a sapphire concave microlens array. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9604–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N. Low temperature dealloying preparation of extremely fine double-levels nano-SnO2 particles with excellent photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N. Fabrication of unique Ti0.8Sn0.2O2 double-levels nanoparticles with extremely fine structure and promising photocatalytic activity by dealloying novel Cu-Ti-Sn-Y metallic glasses. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2022, 141, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.T.; Hsu, L.H.; Huang, B.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Lin, C.C.; Cheng, Y.J. Influence of the microstructure geometry of patterned sapphire substrates on the light extraction efficiency of GaN LEDs. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 7387–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capano, L.; Tiggelaar, R.M.; Berenschot, J.W.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Romer, G.R.B.E. Fabrication of millimeter-long structures in sapphire using femtosecond infrared laser pulses and selective etching. Opt. Laser. Eng. 2020, 133, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Lin, Z.Q.; Zhao, D.D.; Han, J.C. Enhanced Transmission and Self-Cleaning of Patterned Sapphire Substrates Prepared by Wet Chemical Etching Using Silica Masks. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8898–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Wuu, D.S.; Shen, C.C.; Ou, S.L. Surface Modification on Wet-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrates Using Plasma Treatments for Improved GaN Crystal Quality and LED Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, H988–H993. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin, B.W.; Hsu, W.C.; Wu, Y.S. Morphologies and plane indices of pyramid patterns on wet-etched patterned sapphire substrate. Mater. Lett. 2014, 118, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Hsiao, F.C.; Lin, B.W.; Hsu, W.C.; Wu, Y.S. Evolution of Bottom c-Plane on Wet-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrate. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2013, 2, R169–R171. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N. FeCoNiMnCuTi high entropy amorphous alloys and M50Ti50 (M = Fe, Cu, FeCoNiMnCu) amorphous alloys: Novel and efficient catalysts for heterogeneous photo-Fenton decomposition of Rhodamine B. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 33, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasu, T.; Aiba, T.; Yamashita, S.; Hattori, S.; Kizu, T.; Sun, W.C.; Taguri, K.; Kazami, F.; Kobayashi, M. Growth of ZnTe epilayers on r- and n-plane sapphire substrates. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 075501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, A.V.; Lundin, W.V.; Zavarin, E.E.; Sinitsyn, M.A.; Nikolaev, A.E.; Lundina, E.Y.; Tsatsulnikov, A.F. Formation of textured sapphire substrates by self-arrangement process and wet etching for InGaAlN LEDs. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 5151–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y. AFM and SEM Study on Crystal Topographical Evolution of Wet-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrates (PSS): I. Cone-Shaped PSS Etched in Sulfuric Acid and Phosphoric Acid Mixture (3:1) at 230 °C. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2017, 6, R24–R34. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y. AFM and SEM Study on Crystal Topographical Evolutions of Wet-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrate (PSS): Part III. Cone-Shaped PSS Etched in H2SO4 and H3PO4 Mixture at Various Temperatures. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2017, 6, R163–R169. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y. AFM and SEM Study on Crystal Topographical Evolutions of Wet-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrate (PSS): Part II. Cone-Shaped PSS Etched in H2SO4 and H3PO4 Mixture with Varying Volume Ratio at 230 °C. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2017, 6, R122–R130. [Google Scholar]
- Aota, N.; Aida, H.; Kimura, Y.; Kawamata, Y.; Uneda, M. Fabrication Mechanism for Patterned Sapphire Substrates by Wet Etching. ECS J. Solid State Sci. 2014, 3, N69–N74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.R.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.F. Application of the evolutionary kinetic Monte Carlo method for the simulation of anisotropic wet etching of sapphire. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.F.; Huang, Q.A.; Li, W.H. Modeling and Simulations of Anisotropic Etching of Silicon in Alkaline Solutions with Experimental Verification. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, F29–F37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Sato, K.; Gosalvez, M.A.; Kimura, Y.; Ishibashi, K.I.; Niwano, M.; Hida, H.; Tang, B.; Itoh, S. Surfactant Adsorption on Single-Crystal Silicon Surfaces in TMAH Solution: Orientation-Dependent Adsorption Detected by In Situ Infrared Spectroscopy. J. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2009, 18, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubel, I. The influence of atomic configuration of (h k l) planes on adsorption processes associated with anisotropic etching of silicon. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2001, 94, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Kal, S. Etch characteristics of KOH, TMAH and dual doped TMAH for bulk micromachining of silicon. Microelectron. J. 2006, 37, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramkowska, M.; Zubel, I. Silicon anisotropic etching in KOH and TMAH with modified surface tension. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola, K.P.; Zubel, I. Effect of molecular structure of alcohols on wet anisotropic etching of silicon. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2016, 242, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubel, I. The Model of Etching of (hkl) Planes in Monocrystalline Silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, C391–C400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.Y.; Kwon, S.K.; Chang, Y.I.; Cho, M.J.; Park, K.H. Reducing dislocation density in GaN films using a cone-shaped patterned sapphire substrate. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4167–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.M.; Lu, Y.C.; Yu, S.F.; Wu, Y.S.; Chiang, C.H.; Hsu, W.C.; Chang, S.J. Enhanced Extraction and Efficiency of Blue Light-Emitting Diodes Prepared Using Two-Step-Etched Patterned Sapphire Substrates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, H874–H876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, T.V.; Cheong, H.S.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Hong, C.H.; Suh, E.K.; Cho, H.K.; Kong, B.H. Enhanced light output from aligned micropit InGaN-based light emitting diodes using wet-etch sapphire patterning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 131107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, L.W.; Jia, H.Q.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Z.G.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.M. Fabrication of Patterned Sapphire Substrate by Wet Chemical Etching for Maskless Lateral Overgrowth of GaN. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, C182–C185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Shikida, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Yamashiro, T.; Asaumi, K.; Iriye, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Characterization of orientation-dependent etching properties of single-crystal silicon: Effects of KOH concentration. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 1998, 64, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Shikida, M.; Yamashiro, T.; Tsunekawa, M.; Ito, S. Roughening of single-crystal silicon surface etched by KOH water solution. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 1999, 73, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toifl, A.; Quell, M.; Klemenschits, X.; Manstetten, P.; Hossinger, A.; Selberherr, S.; Weinbub, J. Continuum level-set model for anisotropic wet etching of patterned sapphire substrates. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, N.; Gosalvez, M.A.; Colom, R.J. Evolutionary continuous cellular automaton for the simulation of wet etching of quartz. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 025021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Crystal Planes | (2 2 1) | (3 3 1) | (2 1 0) | (3 1 0) | (3 2 0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental rates (μm/min) | 0.59 | 0.85 | 1.24 | 1.08 | 1.28 |
| Calculated rates (μm/min) | 0.61 | 0.83 | 1.22 | 1.15 | 1.26 |
| Group | Concentration | Temperature (°C) | Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2SO4:H3PO4 = 1:1 | 236 | 24 |
| 2 | H2SO4:H3PO4 = 3:1 | 236 | 24 |
| 3 | H2SO4:H3PO4 = 6:1 | 236 | 24 |
| Concentration | (0 0 0 1) (μm/h) | Max 1 (μm/h) | Max 2 (μm/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2SO4:H3PO4 = 1:1 | 1.65 | 3.40 (1 −1 0 10) | 3.96 (1 −1 0 4) |
| H2SO4:H3PO4 = 3:1 | 1.77 | 3.11 (1 −1 0 11) | 2.97 (1 −1 0 4) |
| H2SO4:H3PO4 = 6:1 | 2.17 | 3.28 (1 −1 0 11) | 2.54 (1 −1 0 4) |
| Basic Unit of Surface Atoms | C*--C | A*--A | C*--C--A*--A | C*--C--A*--A--A*--A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corresponding basic crystal planes | (1 1 −2 6) | (0 0 0 1) | (1 1 −2 12) | (1 1 −2 18) |
| Vertical distances between two adjacent layers of surface atoms (Å) | 1.61 | 2.17 | 1.98 | 2.08 |
| Etch rates (μm/h) | 0.74 | 1.77 | 1.71 | 2.42 |
| Removal times (10−4 h) | 2.18 | 1.23 | 1.16 | 0.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wu, G. Anisotropic Analysis of Etch Rates for Sapphire Based on a Layer-by-Layer Removal Model of Surface Atoms. Processes 2023, 11, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041290
Li Y, Wu G. Anisotropic Analysis of Etch Rates for Sapphire Based on a Layer-by-Layer Removal Model of Surface Atoms. Processes. 2023; 11(4):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, and Guorong Wu. 2023. "Anisotropic Analysis of Etch Rates for Sapphire Based on a Layer-by-Layer Removal Model of Surface Atoms" Processes 11, no. 4: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041290
APA StyleLi, Y., & Wu, G. (2023). Anisotropic Analysis of Etch Rates for Sapphire Based on a Layer-by-Layer Removal Model of Surface Atoms. Processes, 11(4), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041290