Study on Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells under Seepage-Stress Coupling Condition Based on Finite Element Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Seepage Model
2.2. Effective Stress Model
2.3. Equilibrium Equation
2.4. Continuity Equation
2.5. Yield Criterion
2.6. Boundary Conditions
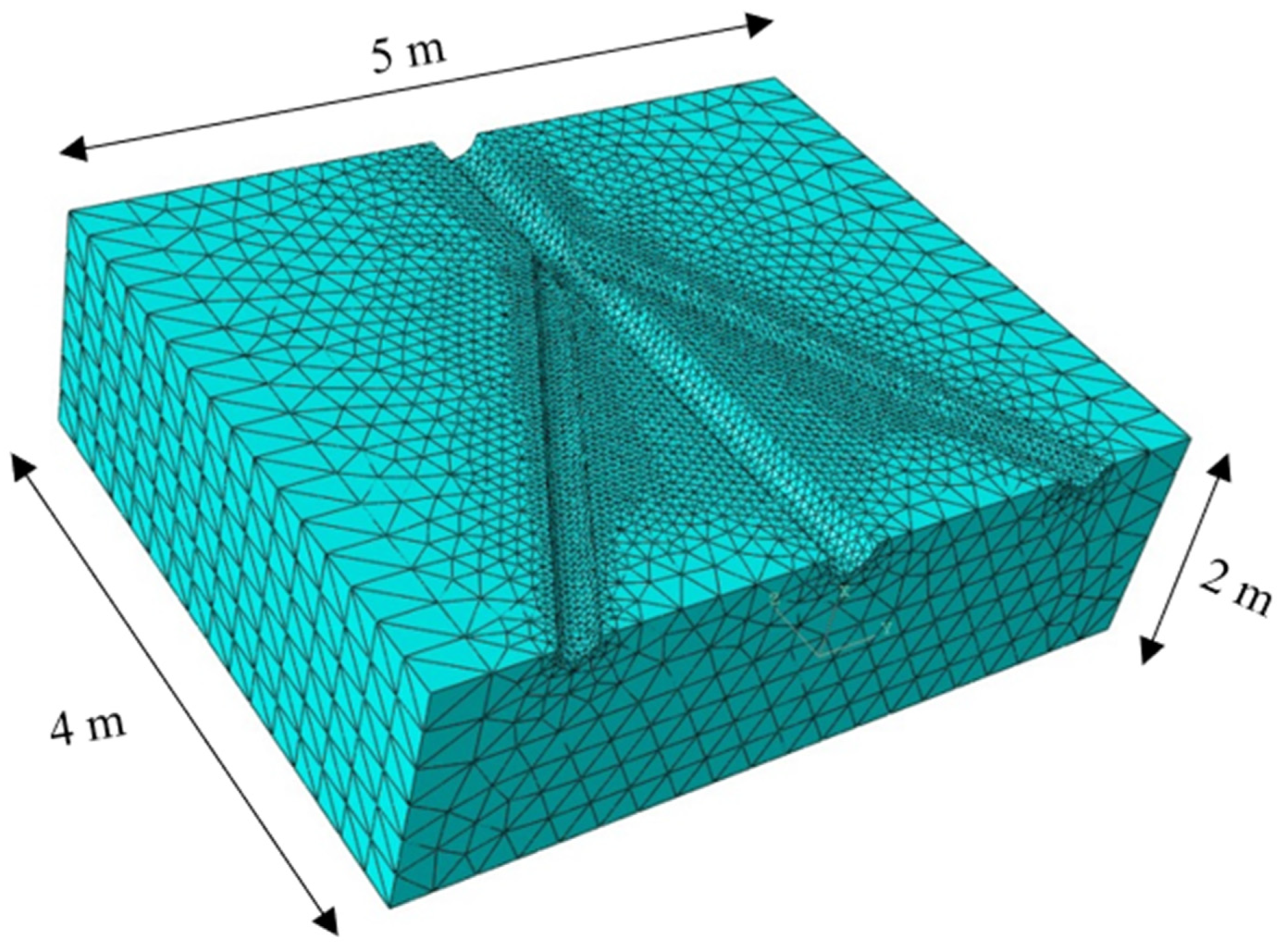
3. Numerical Model
4. Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells
5. Influencing Factors of Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells
5.1. Influences of Wellbore Diameters of Multilateral Wells
5.2. Influences of the Angle between Main Wellbore and Branches
5.3. Influences of Azimuth of Multilateral Wells
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Stress concentration is most serious at multilateral junctions of multilateral wells, where wellbore instability is most likely to occur.
- (2)
- The maximum plastic strain at multilateral junctions increases slightly with the enlargement of wellbore diameter of multilateral wells, and the wellbore diameter exerts slight influences of the wellbore stability.
- (3)
- The larger the angle between main wellbore and branches, the more stable the multilateral wells. When the azimuth of multilateral wells is parallel to the direction of the minimum horizontal principal stress, the equivalent plastic strain is lowest and wellbores are most stable.
- (4)
- Appropriately increasing the drilling fluid density can effectively reduce the risk of wellbore instability at multilateral junctions.
- (5)
- When the angle between main wellbore and branches is larger than or equal to 45°, the regions at the risk of wellbore instability transfer from multilateral junctions to the inner areas of multilateral wellbores.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeynali, M.E. Mechanical and physico-chemical aspects of wellbore stability during drilling operations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 82, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Jiatian, J.; Jiansong, Y.; Xi, J. The destruction characteristic analysis of the multilateral junctions borehole. Drill. Prod. Technol. 2005, 3, 18–20+115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.-L.; Dong, L.-F.; Zhao, K.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Li, X.-R.; Deng, J.-G.; Li, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y. Time-dependent borehole stability in hard-brittle shale. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanfar, M.F.; Chen, Z.; Rahman, S.S. Effect of material anisotropy on time-dependent wellbore stability. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 78, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Deng, J.; Yu, B.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, Y. Borehole stability in high-temperature formations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Miska, S.; Yu, M.; Zamanipour, Z. Transient coupling of swab/surge pressure and in-situ stress for wellbore-stability evaluation during tripping. SPE J. 2018, 23, 1019–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Zamanipour, Z.; Miska, S.; Yu, M.; Ozbayoglu, E.M. Dynamic Wellbore Stability Analysis Under Tripping Operations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 3063–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Zou, L.; Lu, W. Applied research of collapse cycle of shale in wellbore using a coupled physico-chemical model. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 27, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi, A.; Tao, Q.; Diek, A. Influence of coupled chemo-poro-thermoelastic processes on pore pressure and stress distributions around a wellbore in swelling shale. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 67, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y. A fluid-solid-chemistry coupling model for shale wellbore stability. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, W.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z. Calculation of safe drilling mud density window for shale formation by considering chemo-poro-mechanical coupling effect. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chen, P. A wellbore stability analysis model with chemical-mechanical coupling for shale gas reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 72–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Deng, J.; Lan, K.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Porothermoelastic effect on wellbore stability in transversely isotropic medium subjected to local thermal non-equilibrium. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 96, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, H. Well stability of juncture of multilateral drilling well. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2012, 12, 4616–4619. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Analysis of stability of wellface of fish-bone multiple lateral horizontal wells. China Coalbed Methane 2012, 9, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Fan, J. Study of wellbore stability. J. Chongqing Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 2, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C. Mechanical analysis of directional well wall stability in Chunxiao Gas field. West-China Explor. Eng. 2009, 21, 109–111+114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Goshtasbi, K.; Elyasi, A.; Naeimipour, A. 3D numerical stability analysis of multi-lateral well junctions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasbi, K.; Elyasi, A.; Naeimipour, A. Stability assessment of a dual-opposing well junction. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad-Hussein, A.; Heiland, J. 3D finite element modelling of multilateral junction wellbore stability. Pet. Sci. 2018, 15, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, S.K.; Abousleiman, Y.N.; Ashraf, A.T. Multilaterals Drilling and Sustainable Openhole Production from Theory to Field-Case Studies. SPE J. 2010, 15, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Deng, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, Y. Mechanical properties of gas shale during drilling operations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; He, S.; Tang, M.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, P. Analysis of wellbore stability considering the effects of bedding planes and anisotropic seepage during drilling horizontal wells in the laminated formation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 170, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Yao, B.; Lv, D. Wellbore stability and failure regions analysis of shale formation accounting for weak bedding planes in ordos basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 77, 103258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, J.; Tian, W.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Multifield coupling mechanism in formations around a wellbore during the exploitation of methane hydrate with CO2 replacement. Energy 2022, 245, 123283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokhani, V.; Yu, M.; Bloys, B. A wellbore stability model for shale formations: Accounting for strength anisotropy and fluid induced instability. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Dong, L.; Ren, X.; Cheng, Y. Stability of submarine slopes during replacement of methane in natural gas hydrates with carbon dioxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjaer, E.; Holt, R.M.; Horsrud, P.; Raaen, A. Petroleum Related Rock Mechanics, 2nd ed.; Developments in Petroleum Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]

















| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rock density | 2300 kg/m3 | Well depth | 1300 m |
| Elastic modulus | 6000 MPa | Overburden pressure | 30 Mpa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25 | Maximum horizontal principal stress | 27 Mpa |
| Internal frictional force | 32° | Minimum horizontal principal stress | 23 Mpa |
| Cohesion | 5 Mpa | Formation pressure | 12.6 Mpa |
| Drilling fluid density | 1.1 g/cm3 | Porosity ratio | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Cao, J.; Dong, L.; Yan, C. Study on Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells under Seepage-Stress Coupling Condition Based on Finite Element Simulation. Processes 2023, 11, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061651
Xu H, Cao J, Dong L, Yan C. Study on Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells under Seepage-Stress Coupling Condition Based on Finite Element Simulation. Processes. 2023; 11(6):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061651
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hao, Jifei Cao, Leifeng Dong, and Chuanliang Yan. 2023. "Study on Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells under Seepage-Stress Coupling Condition Based on Finite Element Simulation" Processes 11, no. 6: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061651
APA StyleXu, H., Cao, J., Dong, L., & Yan, C. (2023). Study on Wellbore Stability of Multilateral Wells under Seepage-Stress Coupling Condition Based on Finite Element Simulation. Processes, 11(6), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061651






