Physicochemical Analysis and Wound Healing Activity of Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) Fruits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Their Preparation
2.2. Extractions
2.2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
2.2.2. Animals
2.2.3. Herbal-Extraction Methods
2.2.4. Preparation of the Free-Fatty-Acid Fraction
2.2.5. Preparation of the Non-Saponifiable Fraction
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Physicochemical Analyses
- Water content:
- Dosage of ash rate:
- Total protein content:
- Determination of relative density:
- Determination of the refractive index:
- Determination of acid index:
- Determination of saponification index:
- Iodine value:
2.3.2. Analyses of Fatty Acids by GC-MS
2.3.3. Analyses of Phytosterols by GC-MS
2.3.4. α-Tocopherol Analysis by HPLC
2.3.5. Biological Analyses
Skin-Safety Assessment
Eye-Irritation Test
Primary Skin-Irritation Test
- -
- Erythema and pressure ulcer formation;
- -
- Edema formation.
Acute-Toxicity Test
Assessment of Healing Activity
- -
- Cont (−): untreated operated animals;
- -
- CONT (+): operated animals receiving MADECASOL®;
- -
- HEAI: operated animals receiving the oily preparation.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Organoleptic Characterization of the Herbal Drug
3.2. Determination of Protein, Ash, and Water Levels in DV
3.3. Physicochemical Characterizations of Oily Preparations
3.3.1. Hexane-Extraction Yield
3.3.2. Organoleptic and Physicochemical Analyses of HEAI
3.4. Characterizations by GC-MS of Fatty Acids and Phytosterols in the Oily Preparation
3.4.1. Chromatographic Characterization of Fatty Acids by GC-MS
3.4.2. Chromatographic Characterization of Phytosterols by GC-MS
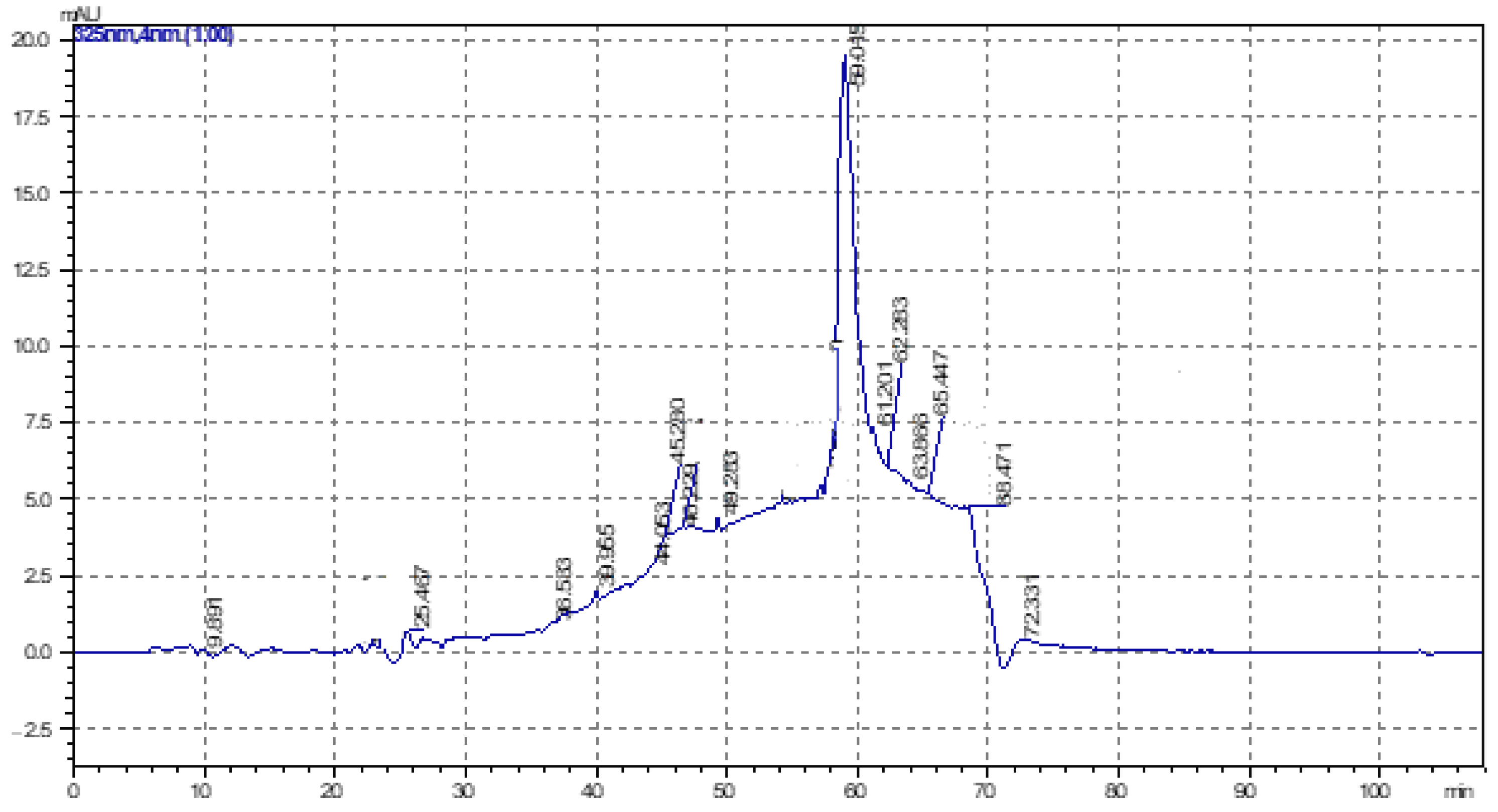
3.5. Determination of α-Tocopherols by HPLC in Oily Preparations
3.6. Biological Analyses
3.6.1. Toxicological Studies
3.6.2. Safety Studies
Eye Irritation
Skin Irritation
3.6.3. Assessment of Healing Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Expósito, I.; Castillo, A.; Yang, N.; Liang, B.; Li, X.M. Chinese herbal extracts of Rubia cordifolia and Dianthus superbus suppress IgE production and prevent peanut-induced anaphylaxis. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L. Natural products in drug discovery. Drug Disco. Tod. 2008, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruneton, J. Pharmacognosie, Phytochimie, Plantes Médicinales, 3rd ed.; Editions TEC & DOC: Paris, France, 1999; pp. 319, 384, 680, 791–793. [Google Scholar]
- Baba Aïssa, F. Encyclopédie des Plantes Utiles, Flore Méditerranéenne (Maghreb et Europe Méridionale), Substances Végétales d’Afrique, d’Orient et d’Occident; Ed.El Maarifa: Algiers, Algeria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sandanasamy, J.D.; Nour, A.H.; Tajuddin, S.N.B.; Hamid Nour, A. Fatty acid composition and antibacterial activity of neem (Azadirachta indica) seed oil. Open Conf. Proc. J. 2013, 4, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, U.M.; Desai, B.S.; Chavda, J.R.; Tandel, M.B.; Jha, S.K. A. Juss. (Neem). J. Non-Timber Forest Prod. 2016, 23, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brototi, B.; Kaplay, R.D. Azadirachta indica (Neem): It’s economic utility and chances for commercial planned plantation in Nanded District. Int. J. Pharma. 2011, 1, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, K.; Chattopadhyay, I.; Banerjee, R.K.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Biological activities and medicinal properties of neem (Azadirachta indica). Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmat, I.; Azad, H.; Ahmed, A. Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss)—A nature’s drugstore: An overview. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 1, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Islas, J.F.; Acosta, E.; Zuca, G.; Delgado-Gallegos, J.L.; Moreno-Treviño, M.G.; Escalante, B.; Moreno-Cuevas, J.E. An overview of Neem (Azadirachta indica) and its potential impact on health. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, J.; Medvigy, D.; Fueglistaler, S.; Walko, R. Regional dry-season climate changes due to three decades of Amazonian deforestation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, V. Vitamins in Medicine. JAMA 1983, 249, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.O.; Coutinho, D.J.G.; Santos, J.; Cordeiro, R.P.; Muniz, L.R.; Alves, R.C.; Bessa, C.M.A.S.; da Silva, M.V.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; de Oliveira, A.F.M. Composition of fatty acids, tocopherols, tocotrienols and β-carotene content in oils of seeds of Brazilian Sapindaceae and Meliaceae species. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3164–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N. Determination of azadirachtin and fatty acid methyl esters of Azadirachta indica seeds by HPLC and GLC. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 374, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finglas, P.M.; Wigertz, K.; Vahteristo, L.; Witthöft, C.; Southon, S.; de Froidmont-Görtz, I. Standardisation of HPLC techniques for the determination of naturally-occurring folates in food. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFNOR (Association française de normalization). Recueil des Normes Française, Graine oléagineuses–Détermination de la Teneur en Acides Gras par Chromatographie en Phase Gazeuse; T60-233 et T60-234; AFNOR: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarda, M.J.; García-Llatas, G.; Farré, R. Analysis of phytosterols in foods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosulski, F.W.; Imafidon, G.I. Amino acid composition and nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for animal and plant foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidibé-Anago, A.G.; Ouédraogo, G.A.; Ledin, I. Effect of partly replacing cottonseed cake with Mucuna spp. (var. Ghana) hay on feed intake and digestibility, milk yield and milk composition of zebu cows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2006, 38, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukeloua, A.; Belkhiri, A. Caractérisation Botanique et Chimique et Evaluation Pharmaco-Toxicologique D’une Préparation Topique à Base D’huile de Pistacia lentiscus L. (Anacardiaceae). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Frères Mentouri-Constantine 1, Constantine, Algeria, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boukeloua, A.; Belkhiri, A.; Djerrou, Z.; Bahri, L.; Boulebda, N.; Pacha, Y.H. Acute toxicity of Opuntia ficus indica and Pistacia lentiscus seed oils in mice. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoq, R. Manuel D’analyses Alimentaires et D’expertises Usuelles. 1965. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201300598471 (accessed on 16 May 2016).
- AOAC Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 16th ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, H.; Cherif, O.A.; Sakouhi, F.; Villeneuve, P.; Renaud, J.; Barouh, N.; Sadok, B.; Mayer, P. Total lipid content, fatty acids and 4-desmethylsterols accumulation in developing fruit of Pistacia lentiscus L. growing wild in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piironen, V.; Toivo, J.; Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Lampi, A.M. Plant sterols in vegetables, fruits and berries. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.Z.; Islam, T.; Mostofa, F.; Uddin, M.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Satter, M.A. Comparative assessment of the physicochemical and biochemical properties of native and hybrid varieties of pumpkin seed and seed oil (Cucurbita maxima Linn.). Heliyon 2019, 5, e02994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi Pacha, Y. Effect Biologique d’un Nectar de Fleur. JAM 1993, 3, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zaoui, A.; Cherrah, Y.; Mahassini, N.; Alaoui, K.; Amarouch, H.; Hassar, M. Acute and chronic toxicity of Nigella sativa fixed oil. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjoungoua, A.L.; Koffi, A.; Traore, F.; Diafouka, F. Etude Phytochimique et Toxicologique de Ziziphus mauritiana, (Rhamnaceae), Une Plante Anti-hypertensive. Med. Pharm. Afr. 2008, 21, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Boulebda, N.; Belkhiri, A.; Belfadel, F.; Bensegueni, A.; Bahri, L. Dermal wound healing effect of Pistacia lentiscus fruit’s fatty oil. Pharmacog. Res. 2009, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.; Durgaprasad, S. Burn wound healing property of Cocos nucifera: An appraisal. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2008, 40, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Hichey, M.; King, C. 100 Families of Flowering Plants, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University (Botanic Garden): London, UK, 1988; 291p. [Google Scholar]
- Baba Aissa, F. Encyclopédie des Plantes Utiles, Flore d’Algérie et du Maghreb; Librairie Moderne: Rouiba, Algérie, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Iserin, P.; Masson, M.; Restellini, J.; Ybert, E.; De Laage de Meux, A.; Moulard, F.; Vican, P. Larousse des Plantes Médicinales: Identification. Préparation, Soins, 2nd ed.; VUEF: Hong Kong, China, 2001; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- El Monfalouti, H.; Guillaume, D.; Denhez, C.; Charrouf, Z. Therapeutic potential of argan oil: A review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karleskind, A. (Ed.) Manuel des Corps Gras; Technique et Documentation-Lavoisier: Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Farines, M.; Soulier, J.; Charrouf, M.; Soulier, R. Etude de l’huile de graines d’«Argania spinosa» (L.), Sapotaceae. 1. La fraction glycéridique. Rev. Fran. Corps. Gras. 1984, 31, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Maurin, R. Argan oil, Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels (Sapotaceae). Rev. Fr. Corps Gras 1992, 39, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Boudjira, M. Contribution à l’Etude Biochimique de l’Huile d’Arganier (Argania spinosa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, National Agronomic Institute (INA), Algiers, Algeria, 2002; 69p. [Google Scholar]
- Djerrou, Z. Anti-hypercholesterolemic effect of Pistacia lentiscus fatty oil in egg yolk-fed rabbits: A comparative study with simvastatin. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribarova, F.; Zanev, R.; Shishkov, S.; Rizov, N. α-Tocopherol, fatty acids and their correlations in Bulgarian foodstuffs. J. Food Compo. Anal. 2003, 16, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.H.; Jones, P.J.H. Dietary phytosterols: A review of metabolism, benefits and side effects. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeidnia, S.; Manayi, A.; Gohari, A.R.; Abdollahi, M. The story of beta-sitosterol—A review. Eur. J. Med. Plant. 2014, 4, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menvielle-Bourg, F.J.; Joanny, F. L’extrait huileux au CO2 supercritique de baies et de graines d’argousier (Hippophaer hamnoides L.) et ses effets sur la peau et les muqueuses. Phytothérapie 2009, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Presumed Acid Value | Mass of Test Portion (g) | Accuracy of Test Portion (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Below 1 | 20 | 0.05 |
| 1 to 4 | 10 | 0.02 |
| 4 to 15 | 2.5 | 0.01 |
| 15 to 75 | 0.5 | 0.001 |
| Up to 75 | 0.1 | 0.0002 |
| RT min | Common Name | Systematic Name |
|---|---|---|
| 0.77 | Cholesterol | Cholest-5-en-3β-ol |
| 0.89 | Campesterol | Campest-5-en-3β-ol |
| 0.95 | Stigmasterol | (22 E)-stigmasta-5,22-dien-3β-ol |
| 1.04 | β-Sitosterol | Stigmast-5-en-3β-ol |
| Time (min) | Mobile Phase B (%) | Mobile Phase A (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0 | 100 |
| 9.01 | 4 | 96 |
| 30.01 | 8 | 92 |
| 45.01 | 22 | 78 |
| 50.01 | 28 | 72 |
| 65.01 | 45 | 55 |
| 66.01 | 0 | 100 |
| 108.00 | 0 | 100 |
| Parameters | Sample |
|---|---|
| AI (Seed) (n = 100) | |
| Dimension (diam./long, mm) | 2.16 ± 0.5/1.25 ± 0.3 |
| Mass (g) | 4.95 ± 0.86 |
| Color | Yellowish or light brown |
| Form | Oval in shape, elongated to a rounded shape |
| Rate (%) of Physicochemical Properties | HEAI (Hexane Extract of A. indica) |
|---|---|
| Water | 8.02 ± 0.35 |
| Total proteins | 27.45 ± 0.84 |
| Ash | 5.89 ± 0.13 |
| Parameters | Hexane Extract of A. indica |
|---|---|
| Color | Green |
| Liquide state | Viscous |
| Flavor | Aromatic |
| Smell | Odorless |
| Density 20 °C (g/mL) * | 0.924 ± 0.1 |
| Refraction index (20 °C) * | 1.471 ± 0.4 |
| Acid index (mg KOH/g) * | 1.01 ± 0.13 |
| Saponification index (mg KOH/g) * | 195.06 ± 0.1 |
| Iodine value (I2 g/100 g) * | 90.78 ± 0.2 |
| Peack | RT | Peack Report Area | Hight | Fatty Acid | Hexane Extract of A. indica (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.65 | 85,920 | 23,912 | Myristic Acid (C14:0) | 0.77 |
| 2 | 19.82 | 13,734 | 6257 | Pentadecanoic A. (C15:0) | 0.32 |
| 3 | 21.95 | 8,442,934 | 2,009,236 | Palmitic A. (C16:0) | 23.94 |
| 4 | 22.56 | 53,682 | 17,029 | Palmitoleic A. (C16:1) | 1.28 |
| 5 | 23.85 | 39,313 | 13,628 | Stearic A. (C18:0) | 7.87 |
| 6 | 25.86 | 4,601,634 | 957,939 | Elaidic A. (C18:1n9t) | 5.11 |
| 7 | 26.36 | 33,537,271 | 4,729,576 | Oleic A. (C18:1n9c) | 46.05 |
| 8 | 28.48 | 27,710,269 | 4,631,303 | γ-linolenic A. (C18:3n6) | 2.27 |
| 9 | 27.35 | 84,416 | 27,068 | Linoleic A. (C18:2n6c) | 11.39 |
| 10 | 28.48 | 316,874 | 101,678 | Linolenic A. (C18:3n6) | 0.30 |
| 11 | 29.23 | 301,162 | 96,745 | Arachidic A. (C20:0) | 0.51 |
| 12 | 29.68 | 90,046 | 27,936 | Cis-11-eicosenoic A. (C20:1) | 0.11 |
| 13 | 34.10 | 179,371 | 49,466 | Cis-13,16-docosadienoic (C22:2) | 0.06 |
| 14 | 35.46 | 26,698 | 10,159 | Lignoceric A. (C24:0) | 0.02 |
| 75,527,146 | 12,716,469 |
| Peak | Sterols | RT (min) | Hexane Extract of A. indica (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cholesterol | 0.78 | 0.31 ± 0.02 |
| 2 | Campesterol | 0.85 | 18.94 ± 0.63 |
| 3 | Stigmasterol | 0.92 | 12.05 ± 0. 98 |
| 4 | β-sitosterol | 1.03 | 97.26 ± 0.77 |
| Total | 128.56 ± 2.40 |
| Wound Contraction (%) * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Day 4 | Day 8 | Day 12 | Day 16 | Day 20 | |
| Cont (−) | 16.08 ± 1.71 | 29.87 ± 2.36 | 36.24 ± 1.75 | 69.17 ± 4.05 | 91.66 ± 1.87 | Analysis of Variance |
| Cont (−) |  |  |  |  |  | df = 10 F(4,10) = 457.6 p < 0.0001 |
| Tukey’s HSD test (time slots) | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| HEAI | 23.93 ± 2.50 | 41.69 ± 1.25 | 49.08 ± 2.53 | 75.84 ± 3.00 | 96.78 ± 1.75 | Analysis of Variance |
| HEAI |  |  |  |  |  | df = 10 F(4,10) = 474.8 p < 0.0001 |
| Tukey’s HSD test (time slots) | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| CONT (+) | 31.16 ± 1.36 | 47.92 ± 2.69 | 64.82 ± 2.09 | 81.12 ± 1.14 | 98.03 ± 0.77 | Analysis of Variance |
| CONT (+) |  |  |  |  |  | df = 10 F(4,10) = 289.5 p < 0.0001 |
| Tukey’s HSD test (time slots) | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Analysis of Variance | df = 6 F(2,6) = 61.65 p = 0.0209 | df = 6 F(2,6) = 46.5 p = 0.0016 | df = 6 F(2,6) = 202.4 p = 0.0010 | df = 6 F(2,6) = 103.7 p = 0.0285 | df = 6 F(2,6) = 73.8 p = 0.0461 | |
| Tukey’s HSD test [CONT (−) vs. HEAI] | p = 0.0127 | p = 0.00425 | p = 0.0022 | p = 0.0409 | p = 0.0326 | |
| Tukey’s HSD test [CONT (+) vs. HEAI] | p = 0.4819 | p = 0.4113 | p = 0.0727 | p = 0.3456 | p = 0.7501 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boukeloua, A.; Kouadria, M.; Bendif, H.; Plavan, G.; Alsalamah, S.A.; Alghonaim, M.I.; Boufahja, F.; Abd-Elkader, O.H. Physicochemical Analysis and Wound Healing Activity of Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) Fruits. Processes 2023, 11, 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061692
Boukeloua A, Kouadria M, Bendif H, Plavan G, Alsalamah SA, Alghonaim MI, Boufahja F, Abd-Elkader OH. Physicochemical Analysis and Wound Healing Activity of Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) Fruits. Processes. 2023; 11(6):1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061692
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoukeloua, Ahmed, Mostefa Kouadria, Hamdi Bendif, Gabriel Plavan, Sulaiman A. Alsalamah, Mohammed I. Alghonaim, Fehmi Boufahja, and Omar H. Abd-Elkader. 2023. "Physicochemical Analysis and Wound Healing Activity of Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) Fruits" Processes 11, no. 6: 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061692
APA StyleBoukeloua, A., Kouadria, M., Bendif, H., Plavan, G., Alsalamah, S. A., Alghonaim, M. I., Boufahja, F., & Abd-Elkader, O. H. (2023). Physicochemical Analysis and Wound Healing Activity of Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) Fruits. Processes, 11(6), 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061692










