Abstract
Energy generation using microbial fuel cells (MFC) and removing toxic metal ions is a potentially exciting new field of study as it has recently attracted a lot of interest in the scientific community. However, MFC technology is facing several challenges, including electron production and transportation. Therefore, the present work focuses on enhancing electron generation by extracting sugarcane waste. MFC was successfully operated in a batch mode for 79 days in the presence of 250 mg/L Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions. Sugarcane extract was regularly fed to it without interruption. On day 38, the maximum current density and power density were recorded, which were 86.84 mA/m2 and 3.89 mW/m2, respectively. The electrochemical data show that a sufficient voltage generation and biofilm formation produce gradually. The specific capacitance was found to be 11 × 10−4 F/g on day 79, indicating the steady growth of biofilm. On the other hand, Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal efficiencies were found to be 82% and 74.85%, respectively. Biological investigations such as biofilm analysis and a recent literature survey suggest that conductive-type pili species can be responsible for energy production and metal removal. The current research also explored the oxidation method of sugarcane extract by bacterial communities, as well as the metal removal mechanism. According to the parameter optimization findings, a neutral pH and waste produced extract can be an optimal condition for MFC operation.
1. Introduction
Microbial fuel cells (MFC) are a potential bio-electrochemical technique that can generate electricity from chemical energy via the catalytic activities of microorganisms [1,2,3]. They can degrade pollutants while generating electricity and are preferred to other removal methods due to their sustainability, safety, and efficiency. They do not require any external power supply and let out 50–90% less sludge than other bioremediations, thus cutting the cost of sludge removal [4]. They also have a relatively simple configuration which is easy to operate, and have negligible impact on the environment, thus making them an efficient and eco-friendly method to remove toluene from wastewater [5]. This study utilizes a simple MFC setup in a single chamber. Exoelectrogens are bacteria that produce protons (H+) and electrons (e-) at the anodes in simple MFCs. The electrons may also flow to the cathode via an external circuit, where oxygen is reduced before interacting with hydrogen ions and changing into water through a membrane. The biofilm forms on the electrode surface over time due to the microbe’s activity. The biofilm also assists in the passage of electrons from the microorganism to the anode, boosting the pace at which organic contaminants degrade [6,7,8]. The MFC technique has been utilized in many studies to remove both heavy metals and organic pollutants [9,10,11]. Since life is unimaginable without water, it is an essential resource on the planet, and it being accessible in its purest state is crucial for both humans and other living things. Due to its versatile characteristics, such as solubility, strength, etc., water has been referred to as the universal solvent [12,13]. The pollution of water, which is now the most imperative issue facing the entire world, might be due to poor sewage treatment, industrial wastes, marine dumping issues, radioactive waste, agricultural perspectives, etc. The pollution of water has a harmful influence on the surrounding atmosphere, and it may also be accountable for the pollution of the air, which has highly negative consequences for human health. The economic progress and social outlook of the societies or nations that are polluted also suffer because of water pollution’s negative effects. Recently, a study that was issued by the United Nations claimed that the availability of clean water is a problem that affects the whole globe and has become a challenge in the 21st century for the entire planet [14].
Water is polluted when undesirable substances have found their way into bodies of water reservoirs, rendering the water unfit for consumption and other uses. Although, there are a variety of chemical, physical, and mechanical solutions that may be used to address this developing issue. In addition, researchers are still hard at work investigating various new technologies to develop more efficient and cost-effective techniques for water filtration. However, newly developing areas of green technology, such as MFCs, present an opportunity to filter water at a cheap cost, with a high operating efficiency in the removal of impurities and with the capacity to reuse the purified water [15]. Furthermore, the heavy metal contamination of water has become a major environmental problem, such as mercury, lead, cadmium, etc. For example, lead (Pb2+) and mercury (Hg2+) impact our health negatively. Due to their use in petroleum, the mining sector, recycling, and commercial activities, Pb2+ and Hg2+ accumulate in the environment (water resources) [16]. There are some articles in the literature on different techniques of extracting metals during the mining process [17,18]. Children are the most at-risk category when it comes to Pb2+ and Hg2+ exposure [19]. Exposure to Pb2+ and Hg2+ in children can damage the central and peripheral nervous systems, cause impaired hearing, stunted growth, learning disabilities, and the disfunction of blood cells [20,21]. The most recent research found that MFCs are one of the most effective ways to remove heavy metals from water sources, and the selection of focusing on Pb2+ and Hg2+ in the present study was made in accordance with earlier recommendations [22,23,24]. Despite several advancements in MFC, there are still a few challenges that electrochemically limit its efficiency [25,26,27]. Metals are removed by MFCs using an electrochemical principle. However, the generation of electrons by bacterial species seems to be quite minimal, which does not improve the 100% removal of metal ions. In fact, the MFC converts hazardous metal ions to less poisonous metal ions. The generation of electrons depends on the stability of the organic substrate [28]. The type of substrate chosen is a key factor in determining the success of energy generation and the degradation of pollutants due to its impact on bacterial growth in MFC. The production of power is also inhibited when the concentration of substrates exceeds a certain value [29,30].
Several earlier investigations have shown that the highly carbohydrate-rich organic substrate is beneficial to bacterial species such as sugarcane extract [31,32]. The current work focuses on sugarcane waste as an organic substrate for heavy metal removal. The sugarcane culms are ground to produce sugarcane extract. It is mostly made up of 13–15% sucrose, 70–75% water, and 10–15% fiber [33]. Previous research has shown that it is best suited for use as an organic substrate. The present investigation is limited to Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal in high concentrations in wastewater. Many studies used 50 mg/L or 100 mg/L, which is impractical given that many companies release Pb2+ and Hg2+ in substantial quantities. As a result, the current work focuses on high concentrations to evaluate MFC performance.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Material and Chemical Regaents
Sugarcane waste material, bought from a local market in Penang 11800, Malaysia; pond water (collected from a pond in Bandar Putra Bertam, Penang, 11800, Malaysia); lead nitrate; mercury (II) nitrate monohydrate; phosphate buffer; all of these chemicals were received from Sigma-Aldrich) graphite electrodes (GR series, FUDA 2B Lead, NY, USA); and copper wires.
2.2. Preparation of Sugarcane Extract
The sugarcane waste material was obtained from the local market. To begin, 1 kg of sugarcane waste material was employed in an extraction machine to obtain sugarcane extract. Following the collection of sugarcane extract, filtration was carried out to eliminate impurities, i.e., to obtain pure sugarcane extract. This extract was used as an organic substrate in MFC.
2.3. Supplementation of Metal in Pond Water
The present investigation did not use naturally polluted Pb2+ and Hg2+ wastewater. To produce Pb2+- and Hg2+-polluted wastewater, commercial Pb2+ and Hg2+ (250 mg/L) was mixed with local pond water. The current study refers to metal-supplemented wastewater (MSW-water) after Pb2+ and Hg2+ supplementation. Table 1 shows the physicochemical characteristics of MSW-water compared with pond water.

Table 1.
Pond and MSW-water recorded physicochemical properties.
2.4. MFC Assembly and Operational Process
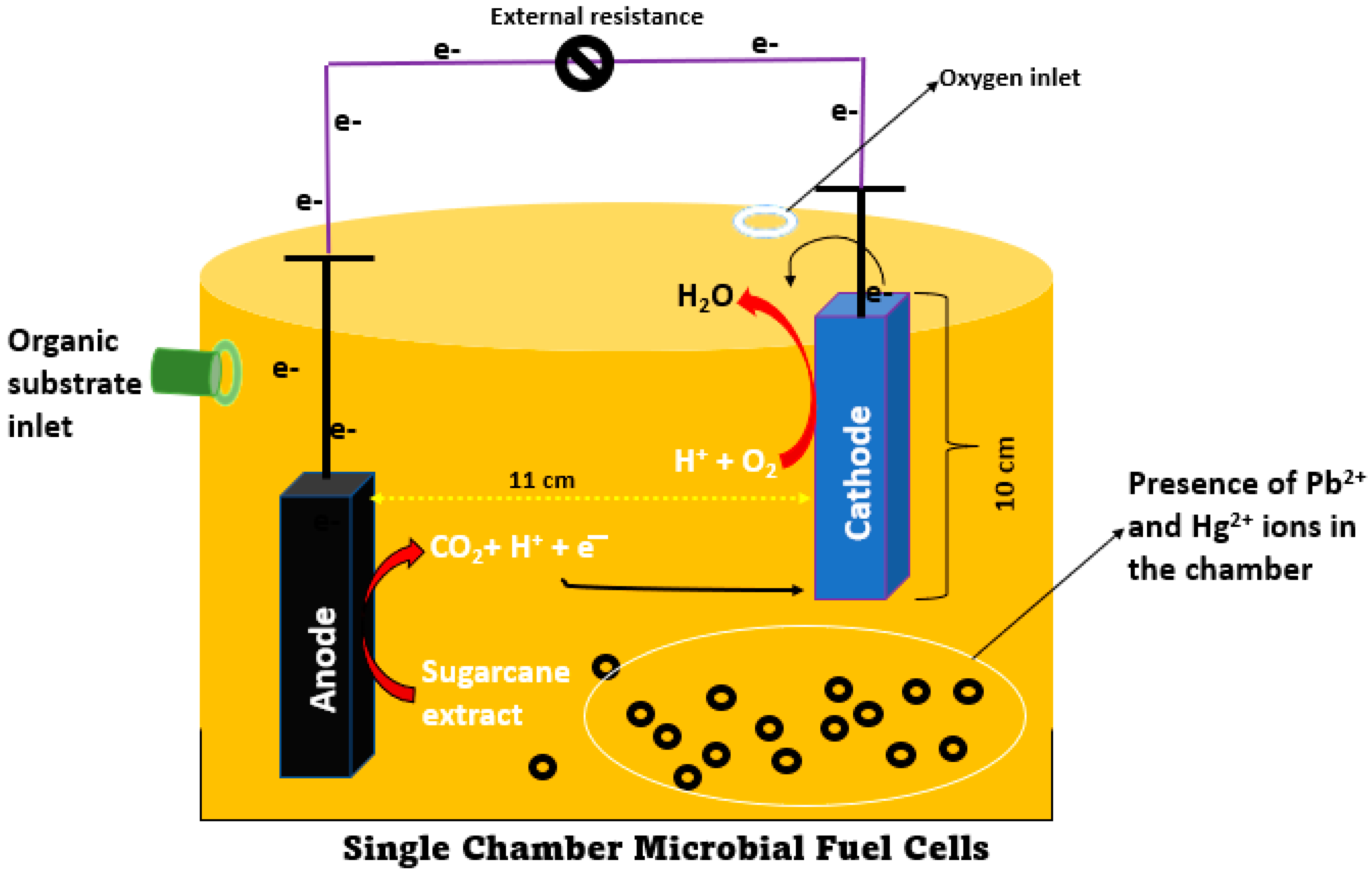
In the research, a single-chambered MFC was developed, as systematically drawn in Figure 1. The overall capacity was 2000 mL, with a working volume of 1500 mL. The working volume was full of MSW-water (1000 mL) and 500 mL of phosphate buffer solution (pH 7). In this investigation, the cathode was represented by a single electrode that measured 10 cm in height and 1 cm in radius. Multiple anodes were provided by two electrodes, each of which had dimensions of 10 cm high by 1 cm wide (h × r). The electrode had a surface area of 69.13 cm2, according to the calculations. There was a space of 11 cm that separated the anode electrode from the cathode electrode. Copper wire linked the electrodes to permit electrons to flow between them. The anode was fully submerged in the water, while the cathode was partially submerged. Following the passage of two days of open-circuit voltage, a resistance of 1000 Ω was introduced into the system. The voltage value dropped noticeably after adding the external resistance; nevertheless, it gradually recovered after some time had elapsed. When there is no voltage recovery, a higher resistance should be utilized. On the other hand, when there is no substantial change in the voltage’s value, lower values of external resistance should be selected [34]. As the substrate, around 10 mL of sugarcane extract was given to the anode on a daily basis. The sugarcane extract MFC experiment was conducted for 79 days at normal temperatures.
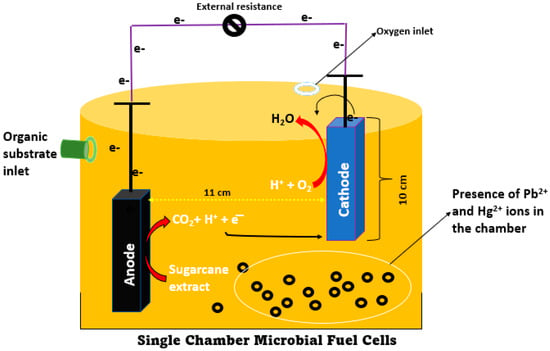
Figure 1.
Systematic presentation of single chamber MFC, used in the present work.
2.5. Analytical and Electrochemical Measurements
Using a multimeter, we acquired a reading once every 24 h to determine the voltage. To convert the voltage data into current (Ampere), Ohm’s law was used. Power density (PD), internal resistance (r), and current density (CD) were calculated by using the equations as described in the literature [35,36]. A polarization curve was produced by using various resistance values from 5000 Ω to 100 Ω, and the slope of the curve was used in order to determine the internal resistance of the MFC.
To study the redox reaction during the whole reaction, a cyclic voltammetry model (CV, -USA) was applied. The surface was computed at a scanning rate of 5 mV/s−1, between +0.8 V to −0.8 V potential range at the 1st, 10th, 30th, 50th, and the 79th day of the MFC reaction. The electrodes used were copper wire (counter), anode (operational), and Ag/AgCl (reference), respectively. The potential difference between the working electrode and the reference electrode was then recorded. The specific capacitance, Cp (F/g), is calculated by adding together all the data for cathode and anode per unit area. Information from the CV calculation was used to obtain this Cp value using Equation (1). However, the area of CV = A, loaded sample quantity in CV instrument = m, potential range of CV = (V2 − V1), and the scan rate of CV (mV s−1) = k.
Apart from CV, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was also performed at multiple time intervals to measure the resistance effect of the anode towards voltage. EIS analysis was performed on the 31st day in the operative mode of the MFC, from a frequency range of 10,000 Hz to 0.1 Hz. The amplitude of alternating current (AC) was evaluated at 1 mV to minimize the disruption of the steady-state system and to refrain from the attachment of biofilm.
2.6. Pb2+ and Hg2+ Removal Efficiency
The contents of the Hg2+ was analyzed via inductively coupled plasma—optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES; PerkinElmer Optima 8000 spectrometer) to study the removal performance. Meanwhile, to study the removal performance of Pb2+, the present study used the atomic adsorption spectrometer (AAS-PerkinElmer AAnalyst 400). A 1.0 mL solution was taken from the anode chamber for Pb analysis based on the sample interval plan. In the case of ICP, we collected 1 mL and diluted it to 5 ppb (part per billion) before passing it to the lab technician for further examination. The ICP and AAS only indicated the concentration that had been converted into insoluble form. This is referred to as removal efficiency in the present study. The samples were collected on the 10th, 30th, 50th, 70th, and the 79th day and the metal contents were analyzed. The percentage of removal efficiency (% RE) was calculated via Equation (2).
where M(initial) = the initial concentration of metal ions; M(final) = the concentration of metal ions after MFC operation.
2.7. Biofilm Analysis of Anode
Scanning electron microscopy, often known as SEM, was used to evaluate the biofilm’s formation and its stability, development, and surface shape. The SEM photos are critical in establishing the presence of bacterial growth at the anode surface, which is the location of the process that removes Pb2+ and Hg2+ from MSW water.
2.8. Multiple Parameter Optimization
In the studies on optimization, several parameters were simultaneously studied. In this investigation, consideration was given to both the pH and the organic substrate. As a first step, we identified an optimal pH range between 4 and 10 in terms of energy production and metal removal. To achieve the desired pH level, NaOH and H2SO4 were used. Using MSW-water in MFCs, a series of studies with 1000 Ω were performed at room temperature. In these studies, sugarcane extract was used as an organic substrate. After a period of 10 days, the voltage deterioration efficiency across each pH range was determined. In a similar manner, commercial raw sugar was used to compare the effectiveness of sugarcane extract with that of other substrates, such as raw sugar and commercial glucose. Following a period of 10 days, each substrate reading was analyzed. The MSW water utilized had a pH of 7, and the same 1000 Ω of external resistance that were used in the above experiment were employed.
3. Results and Scientific Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Investigation of MFCs with Sugarcane Extract
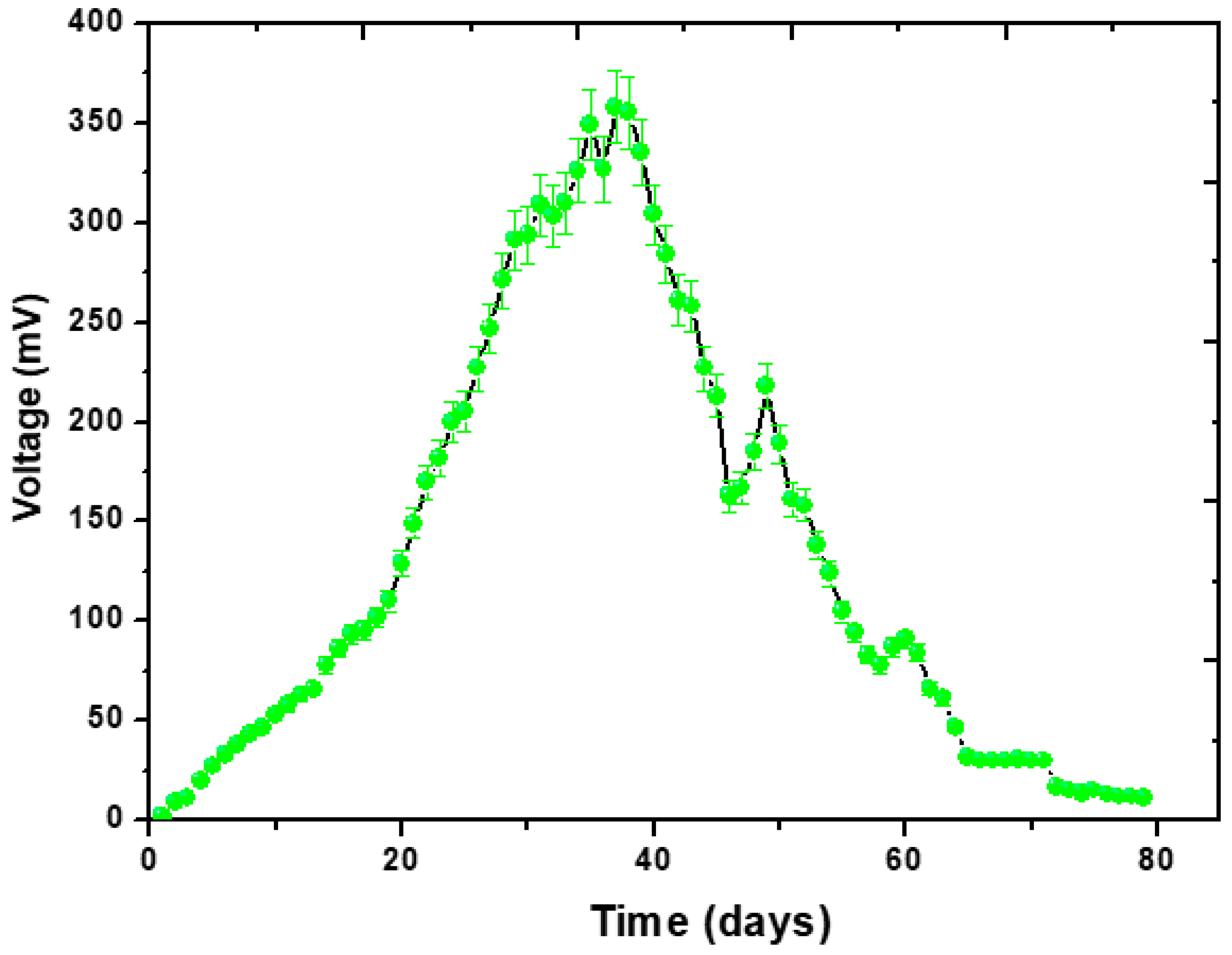
The experiment was operated successfully for 79 days with sugarcane extract as the inoculation source for the MFC operation. The operation of the MFCs was run in batch mode, according to Figure 2, to achieve maximum voltage generation. The voltage was at its maximum on the 38th day of the reaction, at 355 mV. We noted a significant peak and, subsequently, a decline in the voltage generation pattern. According to previous literature, the reasons to achieve a maximum voltage are (a) the presence of the fresh inoculation source, which has several active bacterial species and (b) the supply of organic substrate to all types of bacterial species enhances their exoelectrogenic activities [31,32]. According to Fadzli et al. [31,32], fresh wastewater contains a variety of bacterial species, some of which have short life cycles. These became active for a short period following the supply of an organic substrate and generate considerable electrons. They also stated that one of the primary challenges of MFCs is to sustain the life cycle of the bacterial species on a highly carbohydrate-rich organic substrate. After a peak (on day 38), the voltage values dropped to 185 mV. It is speculated that this was experienced because the bacterial species had reached the end of their life cycle [37]. It increased again after a few days until it reached 218 mV on day 49. However, this value did not exceed the first maximum value recorded. Again, after the continued supply of organic substrate, the value rose to 91 mV but still did not exceed the previous maximum value recorded on day 38. After day 60, the voltage decreased constantly until the 79th day, with no signs of increment, indicating that the operation had completed. According to several articles, if the voltage following the continuous supply of organic substrate becomes constant or reaches zero, it signifies that most bacterial species have lost the ability to generate electrons. They can start producing electrons again after a long period of time, but evidence showed that they could not provide the maximum that they did in the beginning. This represents the completion of the MFC operation [9,10,11]. Similar trends were observed by Daud et al. [7] where a maximum of 510 mV was noted in a 30-day operation. They stated that the study used rotten rice as the inoculation source. According to the study, a higher voltage trend was linked to the stability of the inoculation source. In this study, however, the voltage trend was not very high compared with Daud et al. [7]. There are two possible reasons: (i) the lower stability of sugarcane extract or (ii) the presence of a high concentration of Hg2+ and Pb2+. The steady increase in voltage also served as a marker for the effectiveness of the pollutant’s removal. The first maximum voltage (on day 38) indicated the reduction of Pb2+ into Pb(s) and Hg2+ into Hg(s) according to a previous study [38]. Lastly, to obtain mathematical models, we studied the regression analysis of the voltage trend. According to Figure S1, the voltage trend showed coefficient (R2) = 0.02, which means that the regression model accounted for 20% of the observed variability in the target variable. It seems that there is a non-linear variability and a relationship between voltage and time. Figure 2 also proves that, in the beginning, the voltage increased with the passage of time, while it decreased after some time.

Figure 2.
Trend of energy generation with closed-circuit condition.
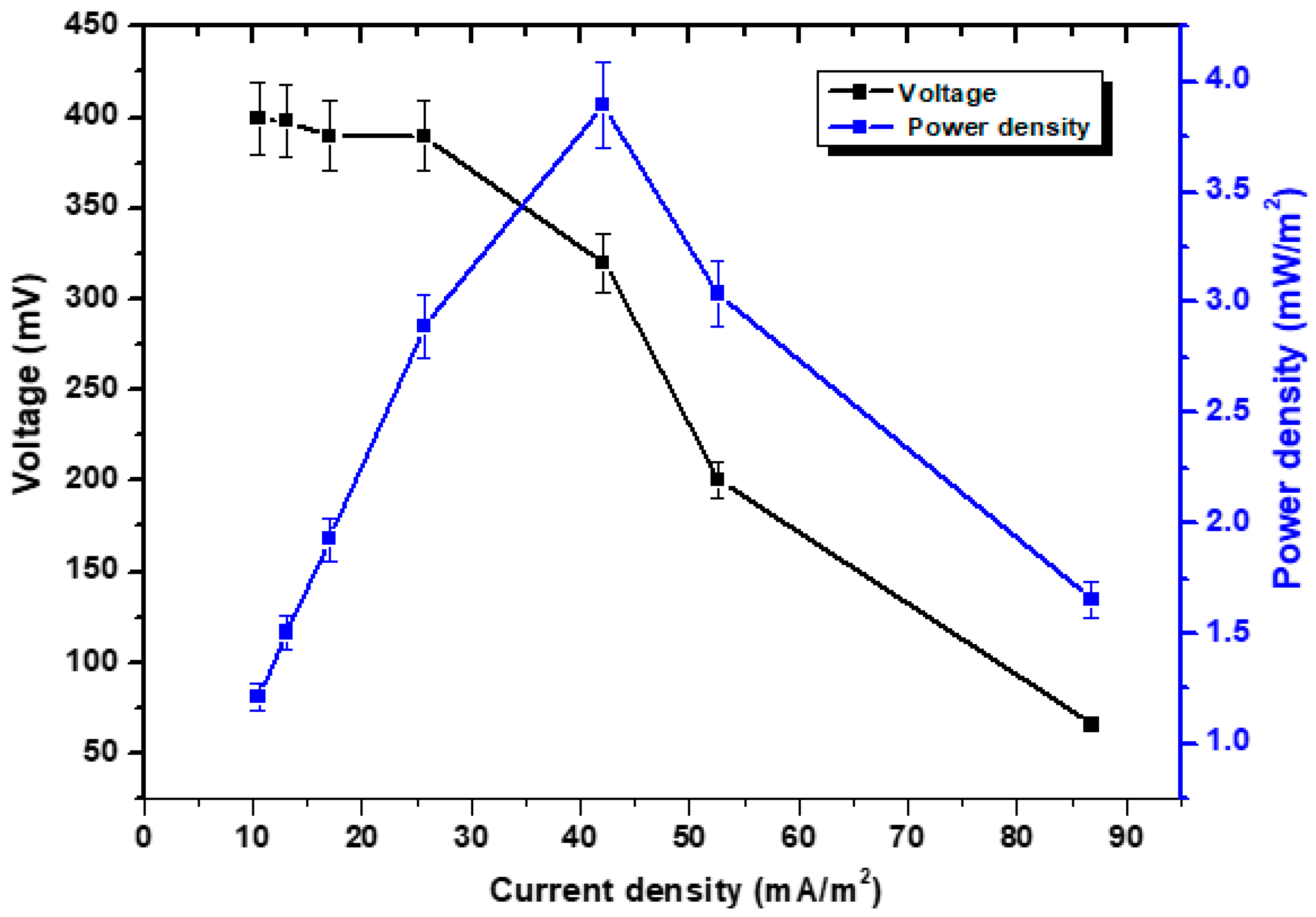
Apart from the voltage trend, polarisation studies were carried out to study CD, PD, and voltage relationships, as shown in Figure 3. This was achieved by varying the external resistance. During the functioning of the MFC, individual connections were made between resistance values ranging from 5000 Ω to 100 Ω. The correlation between voltage and CD has been shown to be inverse. The maximum CD value recorded was 86.84 mA/m2, while the maximum PD value achieved was 3.89 mW/m2 at 1000 Ω. A high external resistance value, for instance, 5000 Ω, gave out 1.20 mW/m2. Due to the rapid passage of electrons, low levels of external resistance indicate lower levels of electrical movement stability. The introduction of oxygen from the outside world helped to stimulate the cathodic reaction rate, which, in turn, led to voltage stabilization while increasing the value of resistance. The cell design point was found at 1000 Ω resistance. Several investigations produced consistent results while attempting to characterize the electrochemical analysis of MFC [39,40,41]. Additionally, we considered the regression analysis to provide information for researchers to predict mathematical models. In the case of polarization curves, we found that the voltage R2 was 0.95, while in the case of PD, the R2 was 0.04. R2 is a metric that reveals details about a model’s goodness of fit as shown in Figure S2. It is a statistical indicator of how closely the regression line resembles the real data in the context of regression. It can help to predict the effects of the independent variable on the dependent one through the use of a regression analysis. Depending on how accurate you need to be, an R2 number has to be as high as possible. For example, in scientific investigations, a regression model’s R2 may need to be above 0.95 to be regarded as reliable. If the dataset exhibits severe variability, an R2 of merely 0.3 may be acceptable in other areas [42]. In the present case, the voltage trend of polarization study is seeming a very reliable inverse relationship with CD while the PD also exhibit a linear relationship until a certain point. A high R2 does not, however, automatically indicate a successful regression model. The type of the variables included in the model, how the variables are measured, and how the data is transformed are just a few of the variables that affect how accurate a statistical measure becomes. Therefore, a high R2 might sometimes point to regression model issues. Predictive models should typically avoid having low R2 values. A good model, however, could sometimes display a little value [43].
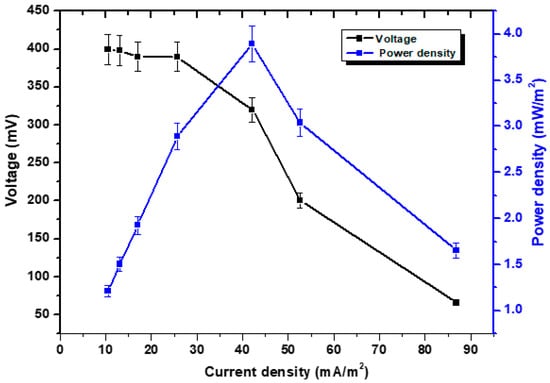
Figure 3.
Polarization curves with the usage of variable resistances from 5000 Ω to 100 Ω.
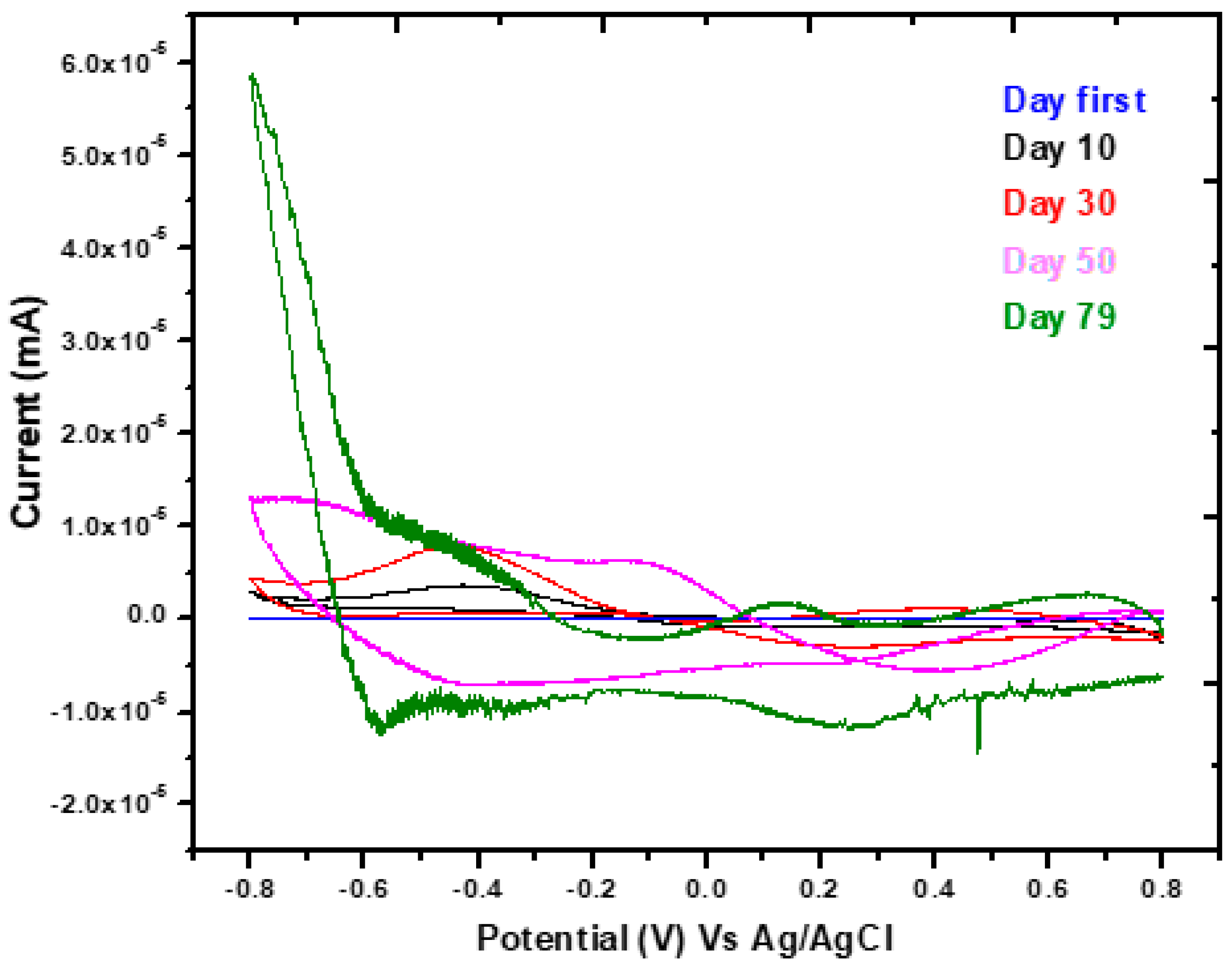
The electron mobility during MFC operation was investigated by recording CV curves at the various times shown in Figure 4. Forward scan (FS) and reverse scan (RS) current were shown on the CV curve performed on different days. On the 10th day, the FS was 0.4 × 10−5 mA, and the RS current was −0.1 × 10−5 mA. Moreover, the 30th day FS and RS currents were 0.8 × 10−5 mA and −0.3 × 10−5 mA respectively, while the 50th day FS and RS currents were 1.3 × 10−5 mA and −0.7 × 10−5 mA respectively. The highest FS and RS currents were recorded on 79th day, which were found at 5.8 × 10−5 mA and −1.5 × 10−5 mA respectively. This indicates that the oxidation and the reduction rate of the substrate gradually increased and eventually reached the highest peak on the 79th day. The CV graphs show a clear difference from day first to day 79. This current study displayed a maximum oxidation of 0.8 mA, and the reduction rate was found to be −0.8 mA. The CV curves exhibit maximum oxidation and reduction rates throughout the reaction. However, sugarcane extract does not produce a fast reaction in comparison with previous studies. Several researchers follow the same pattern to explain the CV results [9,10,23]. The redox processes that took place throughout the process were reflected in the CV analysis, which showed the catalyzing activity of the bacterial biomass connected to the electrodes at various time intervals. To study the oxidation and reduction processes via various peaks acquired in the CV, MFC was investigated at various time intervals. Considering that the standard reduction potentials (at 25 °C) for Hg2+ and Pb2+ are 0.79 V and −0.13 V, respectively, these values may be used as a guide to extrapolate from the CV curves. If a metal reduction has taken place, the CV will peak at a low value. In the case of the present investigation, the maximum reduction current was used to detect reduction maximums at −0.6 V to +0.8 V on the 79th day. It can indicate the presence of additional species that resulted from the fermentation of organic materials, giving the system a high reduction potential, and raising the possibility that the metals precipitated prior to the measurements. As an example, on the 10th day, 27% of the metals were removed, and on the 79th day, more than 70% of the metals were removed.

Figure 4.
CV curves at a variety of different time points.
The CV results are an essential part of the investigation into the Cp values. The Cp values serve as a measure of the stability of the biofilm as well as the pace at which it forms during MFC operation. The CV curves demonstrate the development of biofilm and stability with time. The sugarcane extract served as the substrate for this study. Cp values that are low prove that biofilm is still growing. Furthermore, increasing Cp values showed that biofilm has high stability on the anode. The Cp values of this study are tabulated in Table 2. It showed that biofilm has high performance. Previous literature reviews also utilized similar theories to explain the formation rate of biofilm and its stability through the interpretation of CV curves [44,45].

Table 2.
The value of Cp for the rate at which biofilm is produced.
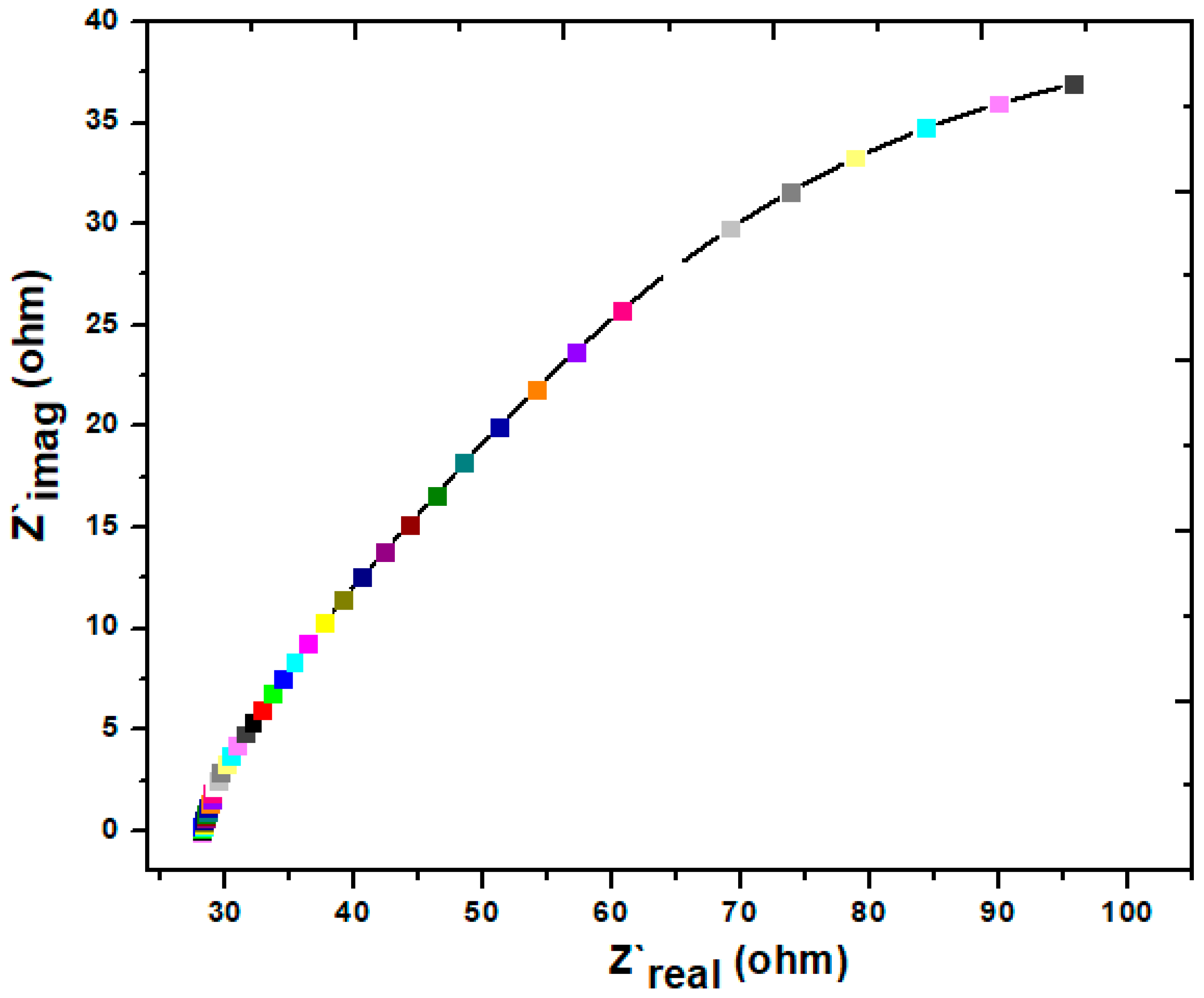
Additionally, by plotting the EIS–Nyquist curve, it has been possible to investigate the charge transfer resistance via the MFCs used in this work. The results are shown in Figure 5 below, which was generated once the experiment had been completed. It displays a semi-straight line with a high Z’image (Ohm), which indicates the average rate of the electrons’ transportation. This pattern was observed throughout the whole operation. According to the findings of this study, a straight line with a high Z’image (Ohm) is indicative of a poor electron transportation rate, but a semicircle or semibent line demonstrates a high rate in spite of having a lower Z’image (Ohm) [46]. According to the most recent findings, the semi-bent lines at the beginning of the Z’real (Ohm) signal indicate the electronic activity; however, after that, the straight line suggests that there is not a high level of electronic movement. In general, a low internal resistance and a semicircular shape may be used to figure a high electron mobility. An increase in electronic mobility may result from a decrease in internal resistance relative to external resistance. The present study’s internal resistance was 250 Ω. Overall, the present study presents a moderate electronic mobility. In the EIS study, the R2 value was 0.95, which means the regression model’s R2 is regarded as reliable. Figure S3 shows that the regression model accounts for 95% of the observed variability in the target variable. In general, high R2 means that the model is able to explain more variability. It can be concluded that electron transportation increases with the passage of time, but at certain limits, it shows a decreasing trend.
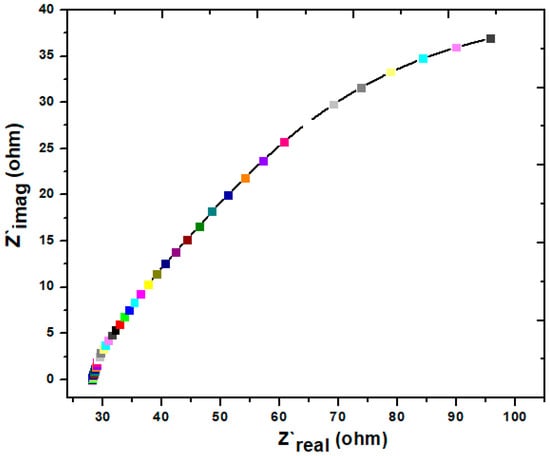
Figure 5.
EIS curve on day 38th of the MFC operation.
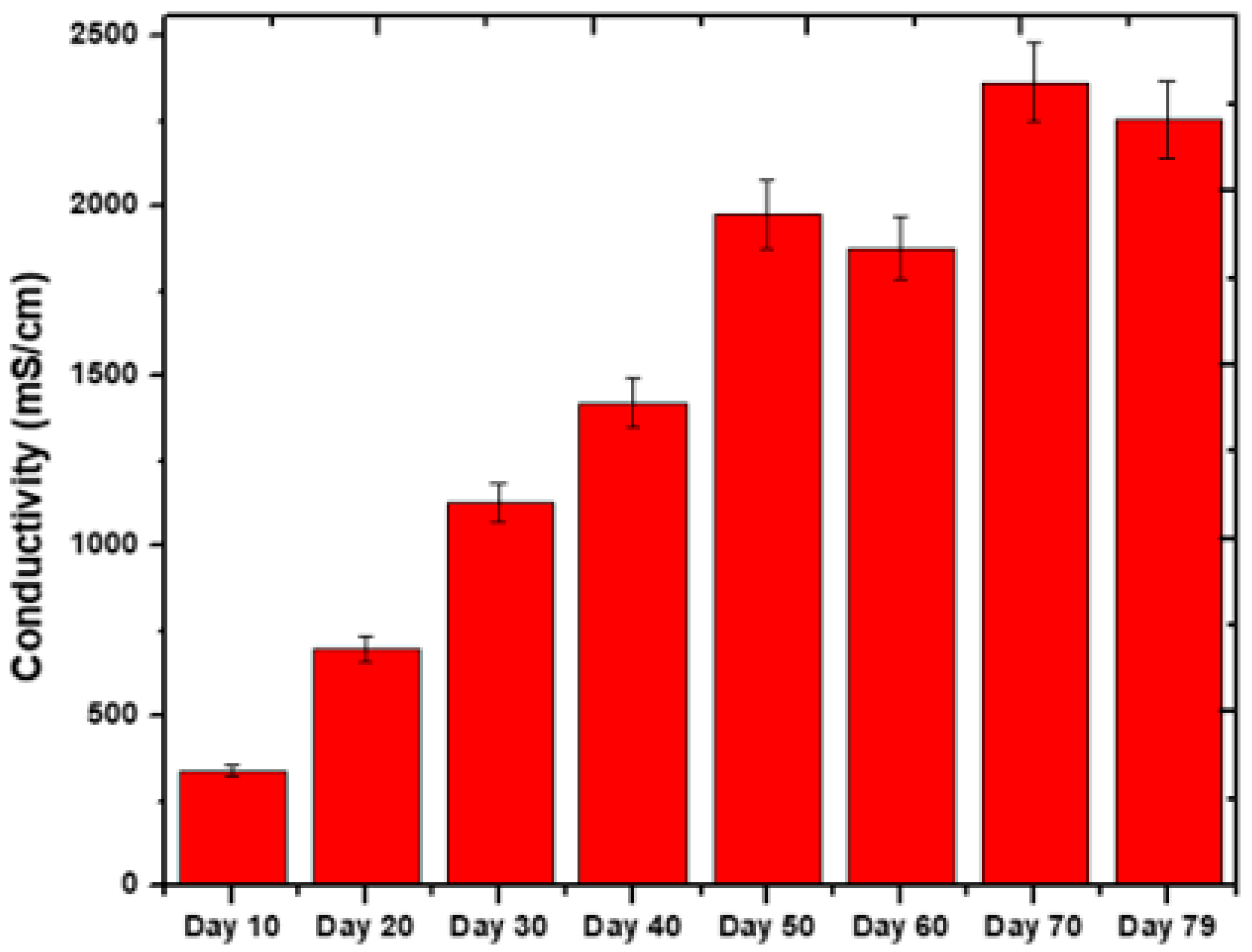
Conductivity data was also tracked throughout the 79-day MFC operation. The conductivity pattern of the cell in the present investigation is shown in Figure 6. The conductivity of the cell showed an increment from the start (341 mS/cm) until day 50 (1978 mS/cm) but this decreased after day 50 (1878 mS/cm). The values kept oscillating beyond day 60 (day 70: 2368 mS/cm, day 79: 2250 mS/cm). This indicates that the performance of the cell declined due to various factors such as the instability of the bacteria, changes in pH, and insufficient organic substrates. A recent study by Rojas-Flores et al. [47] also displayed the same trend. Figure S4 shows that the R2 was 0.94, indicating a 94% variability in the target variable. It means that there is a general linear relationship between conductivity and time. However, as seen in Figure 6, multiple additional factors are also involved, resulting in some bit reduction in conductivity with the passage of time.

Figure 6.
Conductivity of operation at different time intervals.
3.2. Biological Characterizations of MFC
Table 3 displays the results of the removal of Pb2+ and Hg2+ in the current study. This study illustrates the interesting results of remediating pond water treated with Pb2+ and Hg2+. The removal efficiency of Pb2+ and Hg2+ increased throughout the MFC operation, reaching a maximum of 82.00 and 74.85% removal efficiency, respectively. These results were found to be comparable with previous studies, giving rise to cautious optimism. As an example, Yaqoob et al. [48] demonstrated that MFCs (using sweet potato as a substrate) were successful in removing around 65.51% of Cd and roughly 60% of Pb. A comparative profile is tabulated in Table 4 to compare the removal efficiency of the present study with earlier studies. According to the most recent data and our literature review, most works reported concentrations of 100 or 200 mg/L, with just a few papers reporting concentrations of more than 200 mg/L. In comparison with prior studies, performance remains significantly better in this study.

Table 3.
Removal of the Pb2+ and Hg2+ from MSW-water via MFC.

Table 4.
List of most recent work on Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal from literature compared with present work.
The SEM-EDX technique was used to investigate the biofilm formation on the surface of an anode. Biofilms may be considered as “colonies of bacterial species” that have accumulated in a single location. Due to the biofilm’s oxidation of the organic substrate, electrons are transferred from the biofilm to the anode electrode. The majority of a biofilm is composed of 2.5 to 5% bacterial cells, 97% water, and 3.5% to 6% extracellular polymeric substances (EPS’) [54]. Electrons and protons are produced as a by-product of the oxidation process, and EPSs, which are the most important components. The EPSs are made up of 1% to 60% protein, 40% to 95% polysaccharides, 10% nucleic acids, and 40% lipids. EPSs are often used because of their ability to retard the ageing process of biofilms [55,56]. When the organic substrate supply runs out, there is a reduction in the number of EPSs, which leads to a drop in the generation of electrons. Further, biofilm plays a vital role in generating energy and degrading metal. It is a bacterial species that accumulates on the surface of the anode. In accordance with the CV data, the biofilm formed at the anode was found to be stable. Figure 7 illustrates the SEM images of an untreated graphite rod, a treated graphite anode, and a treated graphite cathode. The SEM images of treated anodes show distinct rod-shaped features on the anodes’ surfaces. Several studies claim that the appearance of such structures on SEM indicates the presence of bacterial species. Although we observed other articles that followed the same pattern, this is just a hypothesis [57,58,59]. The anode biofilm was observed to possess the rod filament appendage’s structure. This indicates the presence of bacterial species that are conductive pili types. It has been reported in several studies that examples of bacterial species that possess this feature are Lysinibacillus species, Shewanella species, and Geobacter species [8,34,60]. Apart from that, it was observed that an insoluble sludge was formed at the end of the MFC operation. This specifies that the Pb2+ and Hg2+ were successfully reduced into an insoluble state, rather than adsorbing themselves at the anode’s surface.

Figure 7.
SEM images of untreated graphite rod, treated graphite anode electrode, and treated graphite cathode electrode.
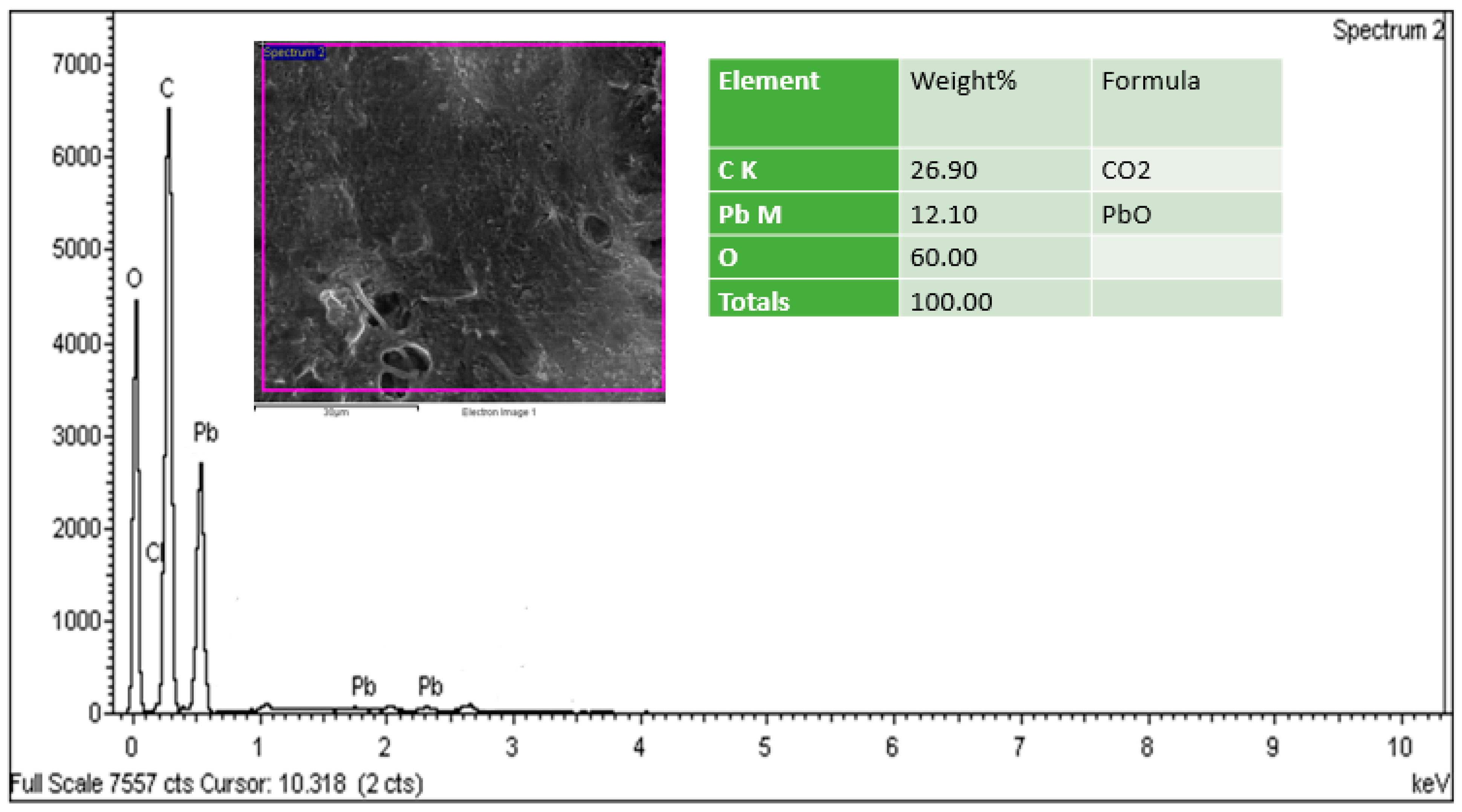
The elemental investigation of the anode’s surface was carried out using an EDX analysis of the biofilm, as shown in Figure 8. According to the results of the EDX analysis of the biofilm, there were some traces of Pb present on the surface of the anode, but no traces of Hg were found. The fact that the biofilm included just a trace amount of Pb suggested an adverse impact on biofilm, which lowered the efficiency. Based on the results of this study, it was observed that MFCs with high levels of metal ions should be treated with very stable organic substates by using a large scale MFC setup throughout the long term. Although previous studies have shown that Pb2+ and Hg2+ levels of 50 to 200 mg/L are safe to treat, levels of more than 250 mg/L are a challenge for MFCs’ systems [61]. We followed the same approach as other researchers and used EDX to analyze the biofilm [59,62]. It is obvious that EDX cannot provide information regarding metal ions.

Figure 8.
EDX spectra of anode electrode with biofilm (scale bar: 30 μm).
3.3. Oxidation of Sugarcane Extract and MFCs’ Working Mechanism of the Present Work
In MFCs, the removal of metal ions and the generation of energy in the form of electrical current depend on the bacterial metabolism. This study utilized sugarcane extract as the organic substrate for bacterial species. The sugarcane extract contained sucrose that was oxidized further by bacterial species to generate electrons and protons. The redox reactions involved in this study are as follows:
Oxidation reaction: sugarcane extract  C12H22O11 + 13H2O
C12H22O11 + 13H2O  12CO2 + 48H+ + 48e−
12CO2 + 48H+ + 48e−
 C12H22O11 + 13H2O
C12H22O11 + 13H2O  12CO2 + 48H+ + 48e−
12CO2 + 48H+ + 48e−
Reduction reaction: 4H+ + 4e− + O2  2H2O
2H2O
 2H2O
2H2O
Overall reaction: C12H22O11 + 12O2  12CO2 + 11H2O + Electricity
12CO2 + 11H2O + Electricity
 12CO2 + 11H2O + Electricity
12CO2 + 11H2O + Electricity
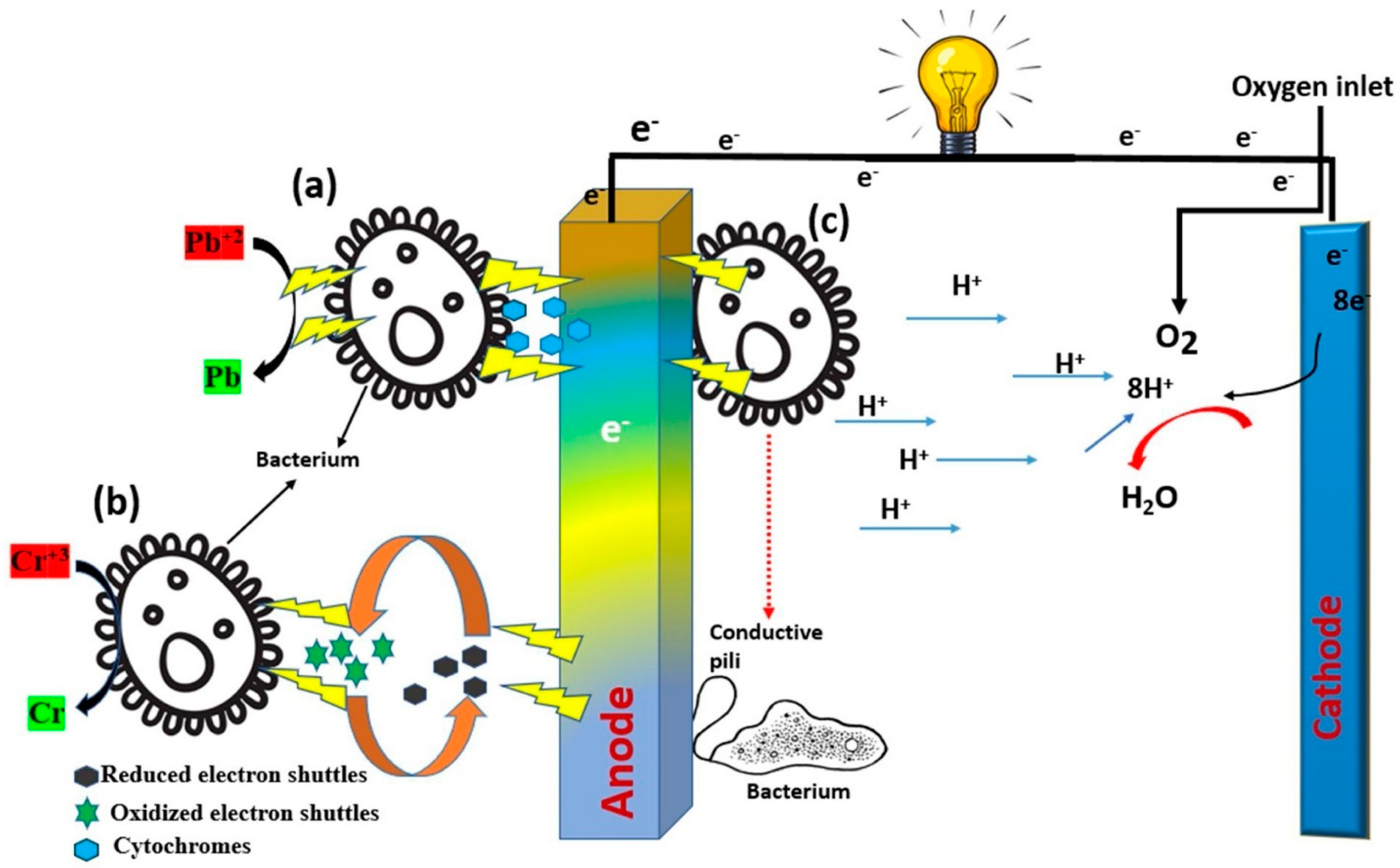
The electrons and protons that are generated during the oxidation were then transferred to the cathode from the anode. The protons moved directly to the cathode without any obstacles since the setup of the MFC is single-chambered. Electrons moved via the outer circuit of the cell. The electrons from the bacterial species, however, have several mechanisms (such as Figure 9a–c) for reaching the anode before they move towards the cathode, as shown in Figure 9 and well explained in the literature [61,63].

Figure 9.
Mechanism of electron transfer in single-chambered microbial fuel cells (Adapted from reference [52] with Elsevier permission).
Bacteria such as the Geobacter families use redox-active proteins to transfer the electrons from bacteria cells to the anode. Such proteins are OmcS, OmcZ, OmcT, OmcE, and OmcB. Moreover, some bacteria such as Geobacteraceae and Desulfuromonadaceae produce self-electron shuttles such as MtrE, OmcA, MtrF, and MtrC components in order to transport electrons via short-range electron transfer.
Few bacteria utilize conductive pili, which are parts of the bacteria’s body and are conductive like metal, to transfer electrons directly from the bacteria’s cells to the anodes. Such a method is called long-range electron transfer. The Shewanella species is one of the many famous conductive-pili-typed bacterial species [63].
The biological analysis of the electrodes proved that the current study utilized long-range electron transfer. SEM images of the anode biofilm confirm the presence of a rod-shaped structure which is the conductive pili of the bacterial species and is found to be responsible for the removal of the soluble Pb2+ and Hg2+ in this study. The soluble Pb2+ and Hg2+ had been reduced successfully into an insoluble form of sludge that stayed at the end of the operation, instead of absorbing itself onto the anode. The biochemical reaction of the Pb2+ and Hg2+ conversion to an insoluble form is as follows [10]:
- -
- Reduction of Pb2+ into Pb(s)
Pb2+ + 2e−  Pb(s)
Pb(s)
 Pb(s)
Pb(s)
2Pb2+ + 2H2O  2PbO + 4H+
2PbO + 4H+
 2PbO + 4H+
2PbO + 4H+
PbO + 2e− + 2H+  Pb(s) + H2O
Pb(s) + H2O
 Pb(s) + H2O
Pb(s) + H2O
- -
- Reduction of Hg2+ into Hg(s)
Hg2+ + 2e−  Hg(s)
Hg(s)
 Hg(s)
Hg(s)
2Hg2+ + 2H2O  2HgO + 4H+
2HgO + 4H+
 2HgO + 4H+
2HgO + 4H+
HgO + 2e− + 2H+  Hg(s) + H2O
Hg(s) + H2O
 Hg(s) + H2O
Hg(s) + H2O
3.4. Multiple Parameter Optimization Studies
3.4.1. pH
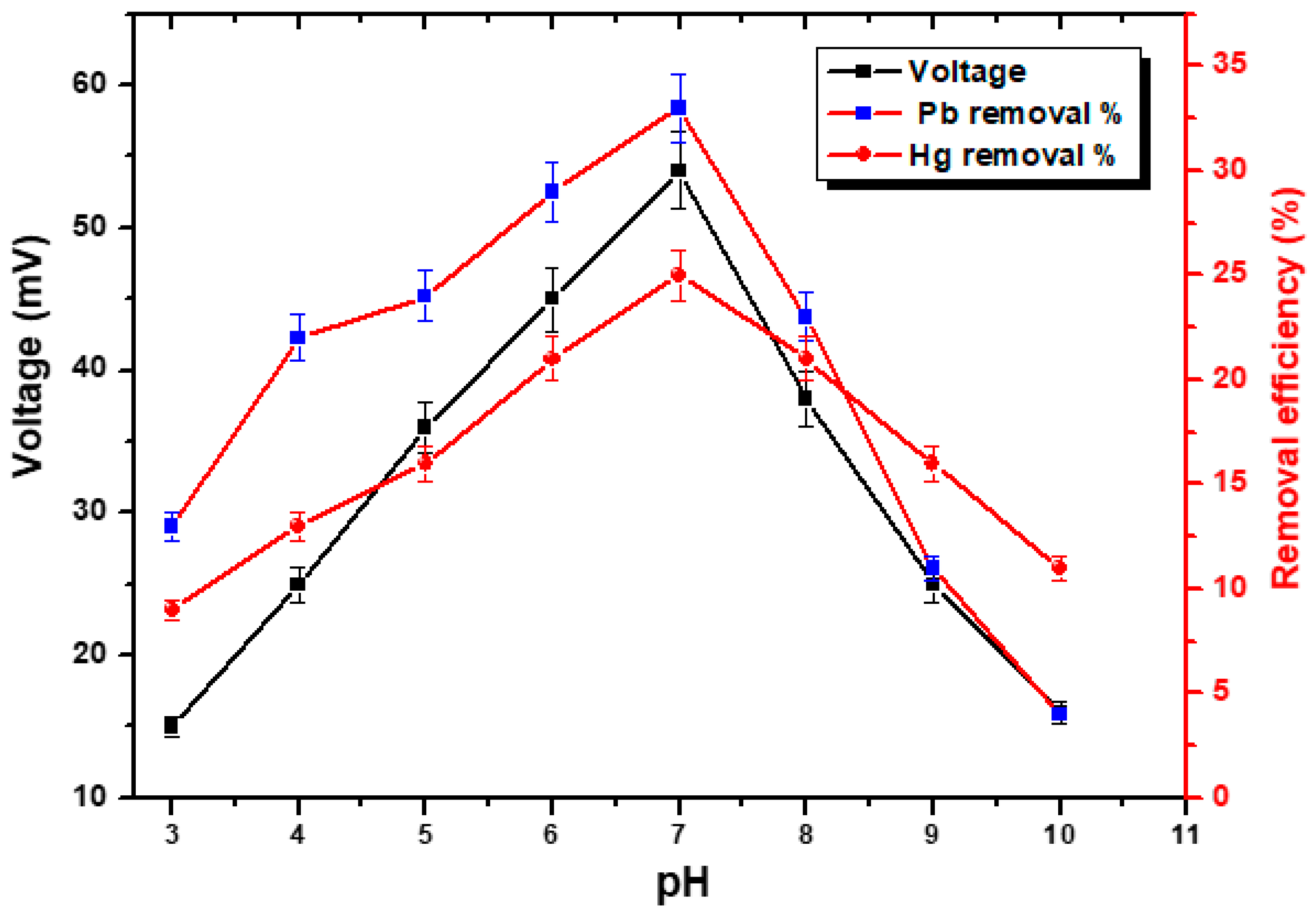
The effect of pH on the voltage generation trend as well as the efficiency of Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal is shown in Figure 10. According to the current observation, the voltage increases steadily from pH 3 to 7, but after pH 7, a decrease in the voltage production is observed. This indicates that circumstances that are either very alkaline or extremely acidic are not optimal to operate this process. The continuous running of MFCs resulted in a maximum voltage of 54 mV being reached at a pH of 7. When compared, pH 3 displayed 15 mV, but pH 10 showed 16 mV. The disruption in the development of bacteria, which has a direct impact on the production of biofilm, is the root cause of the low voltage generation that occurs in situations that are alkaline and acidic, respectively. A biofilm that is fragile and prone to instability does not result in improved performance. Since pH optimization is one of the key components of the operation, Huang et al. [64] previously researched the optimization parameter and went into great depth about pH optimization. According to the research, a pH of 5.2 produced the acidic sludge that severely disturbed the voltage output, while a neutral pH recorded the greatest possible voltage output. In a similar manner, the influence of pH was seen on the decomposition of Pb2+ and Hg2+. In accordance with the findings shown in Figure 10, the optimal pH for maximal Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal % were determined to be 7. Despite this, the acidic state provides a maximum Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal efficiency compared with the alkaline condition. The results obtained at pH 6 were essentially identical to those obtained at pH 7, but beginning at pH 8 and above, there was a discernible slowdown in the rate of Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal efficiency. At a pH of 10, the removal efficiency rate was measured to be at its lowest. The reason for this is that when alkaline conditions are present, there is a greater likelihood of the formation of metal oxides directly from metal salts. One other explanation is that the bacterial population needed certain conditions to exist under alkaline circumstances as opposed to acidic medium requirements. It has been found that a pH that is close to neutral is the most optimal environment.

Figure 10.
pH optimization by using sugarcane extract as a substrate.
3.4.2. Organic Substrate
The organic substrate is one of the most crucial considerations to make when seeking to maximize MFC performance. Several studies have used a range of natural organic substrates and yielded unique results. Any form of carbohydrate that serves as an organic substrate during the operation of MFCs may provide bacteria with the energy required to carry out their oxidation and respiratory activities. However, in the previous research, there have only been a couple of attempts to use natural organic substrates in MFCs. These substrates include rice, fruits, chocolate, and vegetables. Salvin and colleagues [65] used mangroves as an organic substrate in MFCs to improve the energy performance of the devices. In contrast, we use sugarcane extract in our experiment as an organic substrate. Even though its carbohydrate-based organic substrates have a higher concentration of bacterial nutrients than glucose, this was undertaken to analyze the relative performance in comparison with the other commercial substrates. Table 5 provides a summary of how well each of the organic substrates performed, and it shows that sugarcane extract was able to obtain the most significant results of all the organic substrates. This results in sugarcane being readily and quickly oxidized, which not only lessens the operation’s longevity but also slows down the pace at which it can be transported.

Table 5.
Organic substrate optimization study outcomes.
4. Challenges and Future Research Directions
MFCs have provided a new research direction and a controlled, eco-friendly, and reliable means of power production and wastewater treatment. There is a growing appreciation for MFCs because of their potential use in fields as diverse as chemical oxygen demand, wastewater treatment, and sensing. MFCs open a broad range of options for improving marine-based gadgets, tracking and monitoring systems, and related software. Manufacturing highly conductive electrodes and modifying them with various metals or conducting polymers has led to the widespread and critical use of MFCs in the electronic industry. In addition to providing people with energy that is clean, safe, and sustainable, MFCs are a promising technology that contribute to the preservation of Earth’s pristine ecology [66]. In addition, making MFCs acceptable for use in commercial environments would require considerable time and effort since it is a relatively new field of study in the scientific community. MFCs’ organic substrate and electrode material are becoming more unstable, which is causing a number of new issues [67]. Even if the present investigation has shown encouraging results, it will not be possible to continue with it for more than 38 days. An organic substrate that is stable over the long term is required for the MFC activity to be carried out on a commercial scale. In several recent studies, a substrate made from waste sugarcane extract was used, and the findings showed that the extract remained stable for a moderate time period. It is vital to have a basic organic substrate that is both highly stable and rich in carbohydrates if one wishes to tackle this issue and promote MFC production up to pilot scale. Several other waste materials can be used as organic substrates, such as rotten rice, food waste, bakery waste, etc. Another common issue that might arise with MFC is related to the material that is used for the electrodes. The production of energy from the MFC was still below expectations because of the material that was employed for the electrodes. The material that is utilized for the electrodes, in particular the anode, should have the capability of transporting electrons more effectively while simultaneously creating a biocompatible environment in which bacteria may form biofilm around the anode surface [68]. Recently, the electrode material that is made from biomass has been the topic of the most promising conversations due to its efficiency, cost, and performance. This is because it has been the subject of the most encouraging recent debate [69,70]. There has been a significant amount of research conducted in the past on the process of converting biomass into electrodes, such as biomass-derived anode electrodes. At the moment, it is essential that we focus our whole attention on this aspect of the assignment.
The electron transportation to the cathode is one of the emerging challenges. This problem stemmed from the choice of electrode; the electrodes utilized in this study were commercial graphite electrodes. It was not conductive enough for electron transfer. In future studies, better electrodes should be chosen, such as composite electrodes and graphene-derived electrodes. They are better in terms of conductivity and, thus, can deliver the desired results in electron transfer. Other factors should also be taken into consideration, such as the fact that the electrodes must be biocompatible, and not prone to microbial fouling.
5. Conclusions
The use of sugarcane extract as the organic substrate in single-chambered MFC to remove the Pb2+ and Hg2+ from MSW-water and energy production was highlighted in this article. The maximum voltage was found to be 355 mV for this study. On day 38, the maximum current density and power density were found to be 86.84 mA/m2 and 3.89 mW/m2, respectively. The specific capacitance was found to be 11 × 10−4 F/g on day 79, indicating the steady growth of biofilm. On the other hand, Pb2+ and Hg2+ removal efficiencies were found to be 82% and 74.85%, respectively. Biological analysis confirmed that bacterial species are present on the anode surface which utilize long-range electron transfer and are responsible for treating metal. When the organic substrate is completely oxidized, excellent bacterial metabolism leads to a high proportion of metal removal. It also must be stable in terms of chemical and thermal factors for long-term performance. The parameter optimization also revealed that pH 7 is ideal for high MFC performance with sugarcane extract, while the high quantity of Pb2+ and Hg2+ at the lab scale is difficult to remove.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr11082434/s1, Figure S1: Regression analysis of voltage trend. Figure S2: Regression analysis of polarization curves. Figure S3: Regression analysis of EIS curves. Figure S4: Regression analysis of conductivity trend.
Author Contributions
G.M.A., A.S.A. and A.R.D.A.: Conceptualization, Visualization, and Investigation. M.N.M.I. and K.U.: Supervision, Methodology, and Experiments. G.M.A., A.S.A. and A.R.D.A.: writing—original draft preparation, S.-E.O.: Writing, Reviewing, and Editing. K.U., F.H., A.A. and M.N.M.I.: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No specific funding is available for this work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data have been included in the text.
Acknowledgments
The author (Khalid Umar) expresses his gratitude to the collaborators for their assistance in completing this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have stated that there are no competing interests that might influence their work.
References
- Logan, B.E. Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Regan, J.M. Microbial fuel cells—Challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5172–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: When i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, A.; Mohd Setapar, S.H.; Umar, K.; Parveen, T.; Ahmad, A.; Rafatullah, M. Outlook on the role of microbial fuel cells in remediation of environmental pollutants with electricity generation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 819. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.O.; Kim, H.-C. Exploring the effectiveness of microbial fuel cell for the degradation of organic pollutants coupled with bio-energy generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Application of rotten rice as a substrate for bacterial species to generate energy and the removal of toxic metals from wastewater through microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62816–62827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Yaqoob, A.A.; Setapar, S.H.M. Microbial Fuel Cells for Environmental Remediation; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, M.F.; Rafatullah, M.; Abbas, S.Z.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ismail, N. Bioelectricity production and xylene biodegradation through double chamber benthic microbial fuel cells fed with sugarcane waste as a substrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakop, A.S.; Ahmad, A. Application of microbial fuel cells energized by oil palm trunk sap (OPTS) to remove the toxic metal from synthetic wastewater with generation of electricity. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Enguita, F.J.; Leitão, A.L. Hydroquinone: Environmental pollution, toxicity, and microbial answers. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 542168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, T.; Umar, K.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N. Role of nanomaterials in the treatment of wastewater: A review. Water 2020, 12, 495. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Akil, A.; Umar, K.; Rashid, M. Chapter 13— Extraction of lignin from agro-industrial waste. In Extraction of Natural Products from Agro-Industrial Wastes; Bhawani, S., Khan, A., Ahmad, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, B.C.; Cates, E.L.; Kim, J.-H. Challenges and prospects of advanced oxidation water treatment processes using catalytic nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, C.; Arbizzani, C.; Erable, B.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legret, M.; Colandini, V. Effects of a porous pavement with reservoir structure on runoff water: Water quality and fate of heavy metals. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golik, V.I.; Klyuev, R.V.; Martyushev, N.V.; Brigida, V.; Efremenkov, E.A.; Sorokova, S.N.; Mengxu, Q. Tailings utilization and zinc extraction based on mechanochemical activation. Materials 2023, 16, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golik, V.; Stas, G.; Liskova, M.; Kongar-Syuryun, C. Improvement of the occupational safety by radical isolation of pollution sources during underground ore mining. Bezop. Tr. V Promyshlennosti 2021, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, H.; Parveen, T.; Ahmad, A.; Oves, M.; Ismail, I.M.; Qari, H.A. Recent advances in metal decorated nanomaterials and their various biological applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Laxen, D.; Harrison, R. The highway as a source of water pollution: An appraisal with the heavy metal lead. Water Res. 1977, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Malyan, S.K.; Sharma, J.; Mathimani, T.; Maskarenj, M.S.; Ghosh, P.C.; Pugazhendhi, A. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for bioelectrochemical treatment of different wastewater streams. Fuel 2019, 254, 115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M.; Ismail, N.; Nastro, R.A. Enhanced bioremediation of toxic metals and harvesting electricity through sediment microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaqri, N.; Yaakop, A.S.; Umar, K. Potato waste as an effective source of electron generation and bioremediation of pollutant through benthic microbial fuel cell. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102560. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero–Barajas, C.; Umar, K.; Yaakop, A.S. Local fruit wastes driven benthic microbial fuel cell: A sustainable approach to toxic metal removal and bioelectricity generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32913–32928. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.O.; Guerrero–Barajas, C.; Kim, H.-C. Scalability of biomass-derived graphene derivative materials as viable anode electrode for a commercialized microbial fuel cell: A systematic review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 55, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Barajas, C. Modern trend of anodes in microbial fuel cells (MFCs): An overview. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101579. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzli, F.; Yaakop, A. Benthic microbial fuel cells: A sustainable approach for metal remediation and electricity generation from sapodilla waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 3927–3940. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaey, K.; Verstraete, W. Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Chae, J. Miniaturizing microbial fuel cells for potential portable power sources: Promises and challenges. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Adam Mohammad, R.E. Microbial fuel cell: Recent developments in organic substrate use and bacterial electrode interaction. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4570388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleid, G.M.; Alshammari, A.S.; Alomari, A.D.; Almukhlifi, H.A.; Ahmad, A. Dual role of sugarcane waste in benthic microbial fuel to produce energy with degradation of metals and chemical oxygen demand. Processes 2023, 11, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Lal, U.R.; Mukhtar, H.M.; Singh, P.S.; Shah, G.; Dhawan, R.K. Phytochemical profile of sugarcane and its potential health aspects. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Bhawani, S.A.; Khan, A.; Alorfi, H.S.; Asiri, A.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Khan, I.; Umar, K. Utilizing biomass-based graphene oxide–polyaniline–ag electrodes in microbial fuel cells to boost energy generation and heavy metal removal. Polymers 2022, 14, 845. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Ahmad, A. Preparation, characterization, and application of modified carbonized lignin as an anode for sustainable microbial fuel cell. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yaakop, A.S.; Rafatullah, M. Utilization of biomass-derived electrodes: A journey toward the high performance of microbial fuel cells. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zaqri, N. A Pilot Trial in the Remediation of Pollutants Simultaneously with Bioenergy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cell. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110643–110660. [Google Scholar]
- Stortini, A.M.; Baldo, M.A.; Moro, G.; Polo, F.; Moretto, L.M. Bio-and biomimetic receptors for electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions. Sensors 2020, 20, 6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, M.O.; Noh, N.A.M. Sustainable microbial fuel cell functionalized with a bio-waste: A feasible route to formaldehyde bioremediation along with bioelectricity generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.A.B.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Yaakop, A.S. Oxidation of food waste as an organic substrate in a single chamber microbial fuel cell to remove the pollutant with energy generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102282. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, K. Biomass-derived composite anode electrode: Synthesis, characterizations, and application in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106111. [Google Scholar]
- Adekunle, A.; Raghavan, V.; Tartakovsky, B. A comparison of microbial fuel cell and microbial electrolysis cell biosensors for real-time environmental monitoring. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 126, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, N.E.; Hamelers, H.M.; van Straten, G.; Keesman, K.J. On-line detection of toxic components using a microbial fuel cell-based biosensor. J. Process Control 2012, 22, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Ma, J. Capacitance-enhanced 3D graphene anode for microbial fuel cell with long-time electricity generation stability. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soavi, F.; Santoro, C. Supercapacitive operational mode in microbial fuel cell. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.-H.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y. Renewable coffee waste-derived porous carbons as anode materials for high-performance sustainable microbial fuel cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16991–16999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Flores, S.; Benites, S.M.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Cabanillas-Chirinos, L.; Valdiviezo-Dominguez, F.; Quezada Álvarez, M.A.; Vega-Ybañez, V.; Angelats-Silva, L. Bioelectricity production from blueberry waste. Processes 2021, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Bhawani, S.A.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, M.R.; Azam, M.; AlAmmari, A.M. Cellulose Derived Graphene/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Anode for Energy Generation and Bioremediation of Toxic Metals via Benthic Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibul, N.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, G.-P. Microbial fuel cell driving electrokinetic remediation of toxic metal contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, C.; Jiao, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, L. Behavior of copper, nickel, cadmium and mercury ions in anode chamber of microbial fuel cells. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 3050–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakop, A.S.; Ahmad, A. Modified Graphene Oxide Anode: A Bioinspired Waste Material for Bioremediation of Pb2+ with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 417, 128052. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Rashid, M. Electricity generation and heavy metal remediation by utilizing yam (Dioscorea alata) waste in benthic microbial fuel cells (BMFCs). Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 172, 108067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundas, B.; Bhawani, S.A.; Ismail Abdulrahman, R.M. Utilization of mangifera Indica as substrate to bioremediate the toxic metals and generate the bioenergy through a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Songera, D.S. A review on microbial fuel cell using organic waste as feed. CIBTech J. Biotechnol. 2012, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Di Martino, P. Extracellular polymeric substances, a key element in understanding biofilm phenotype. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.A.; Anandapandian, K.T.K.; Parthiban, K. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides (EPS) from biofilm forming marine bacterium. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M.; Ismail, N.; Shakoori, F.R. Electrochemistry and microbiology of microbial fuel cells treating marine sediments polluted with heavy metals. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18800–18813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaakop, A.S.; Ahmad, A.; Hussain, F.; Oh, S.-E.; Alshammari, M.B.; Chauhan, R. Domestic Organic Waste: A Potential Source to Produce the Energy via a Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 2023, 2425735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torlaema, T.A.M.; Ahmad, A.; Guerrero-Barajas, C.; Alshammari, M.B.; Oh, S.-E.; Hussain, F. Degradation of Hydroquinone Coupled with Energy Generation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Organic Waste. Processes 2022, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Yaakop, A.S. Self-assembled oil palm biomass-derived modified graphene oxide anode: An efficient medium for energy transportation and bioremediating Cd (II) via microbial fuel cells. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103121. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B. Basic principles and working mechanisms of microbial fuel cells. In Microbial Fuel Cells: Emerging Trends in Electrochemical Applications; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sevda, S.; Dominguez-Benetton, X.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; De Wever, H.; Sreekrishnan, T.; Pant, D. High strength wastewater treatment accompanied by power generation using air cathode microbial fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M.; Ismail, N.; Syakir, M.I. A review on sediment microbial fuel cells as a new source of sustainable energy and heavy metal remediation: Mechanisms and future prospective. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 1242–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chai, X.; Quan, X.; Logan, B.E.; Chen, G. Reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol in biocathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvin, P.; Ondel, O.; Roos, C.; Robert, F. Energy harvest with mangrove benthic microbial fuel cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaqri, N.; Alamzeb, M.; Hussain, F.; Oh, S.-E. Bioenergy Generation and Phenol Degradation through Microbial Fuel Cells Energized by Domestic Organic Waste. Molecules 2023, 28, 4349–4360. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Couto, S. Development and modification of materials to build cost-effective anodes for microbial fuel cells (MFCs): An overview. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 164, 107779. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B. Impact of Self-Fabricated Graphene–Metal Oxide Composite Anodes on Metal Degradation and Energy Generation via a Microbial Fuel Cell. Processes 2023, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Kishore, S.; Dhasmana, A.; Kumari, P.; Mitra, T.; Chaudhary, V.; Kumari, R.; Bora, J.; Ranjan, A.; Minkina, T. A Perspective Review on Microbial Fuel Cells in Treatment and Product Recovery from Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Rafatullah, M.; Chua, Y.S.; Ahmad, A.; Umar, K. Recent advances in anodes for microbial fuel cells: An overview. Materials 2020, 13, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).