Distribution, Origin, and Impact on Diagenesis of Organic Acids in Representative Continental Shale Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
Geological Overview of Sample Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis Methods of Oil Shale
2.2. Extraction of Organic Acids
2.3. Analysis Methods for Organic Acids
3. Results and Discussion
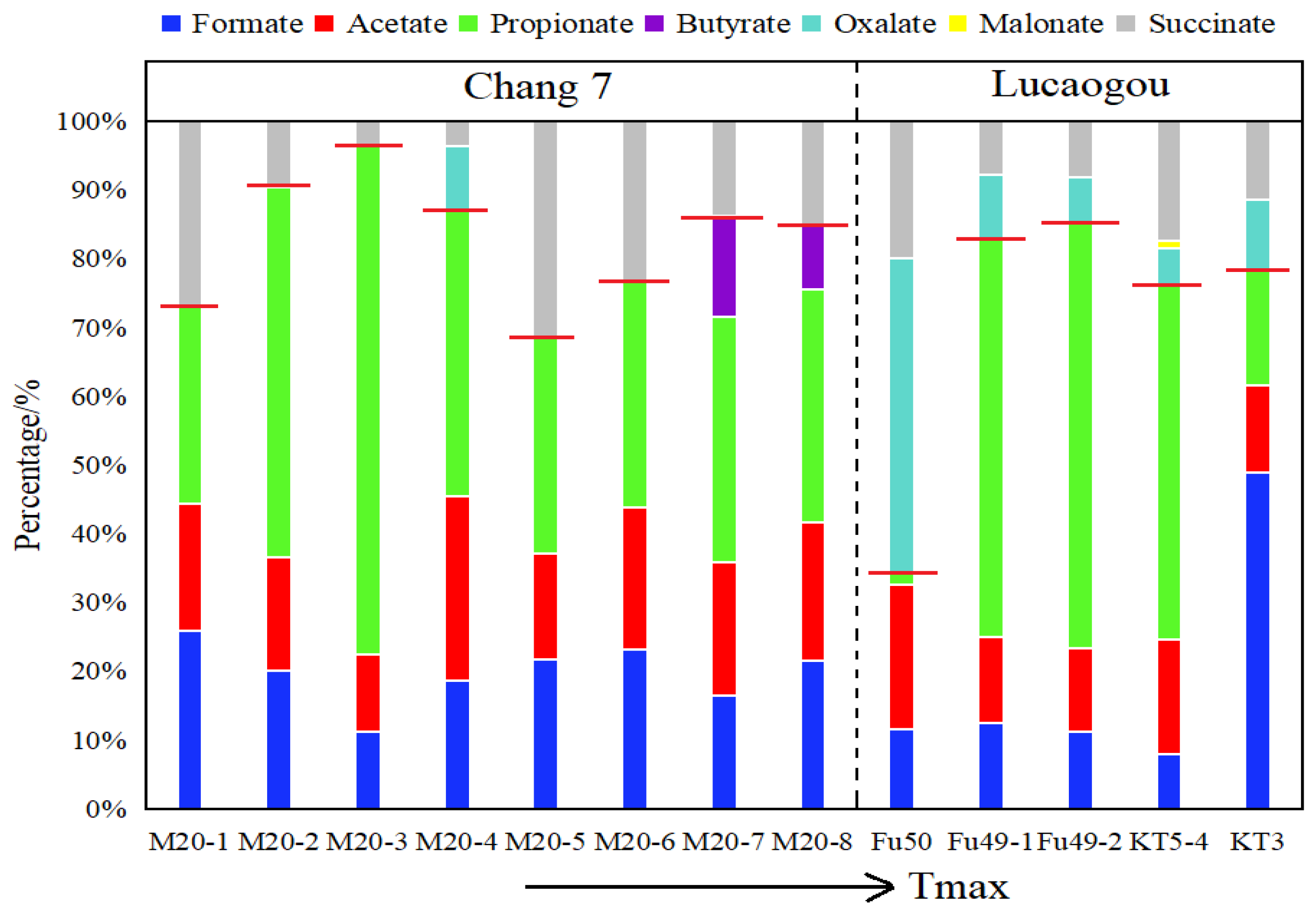
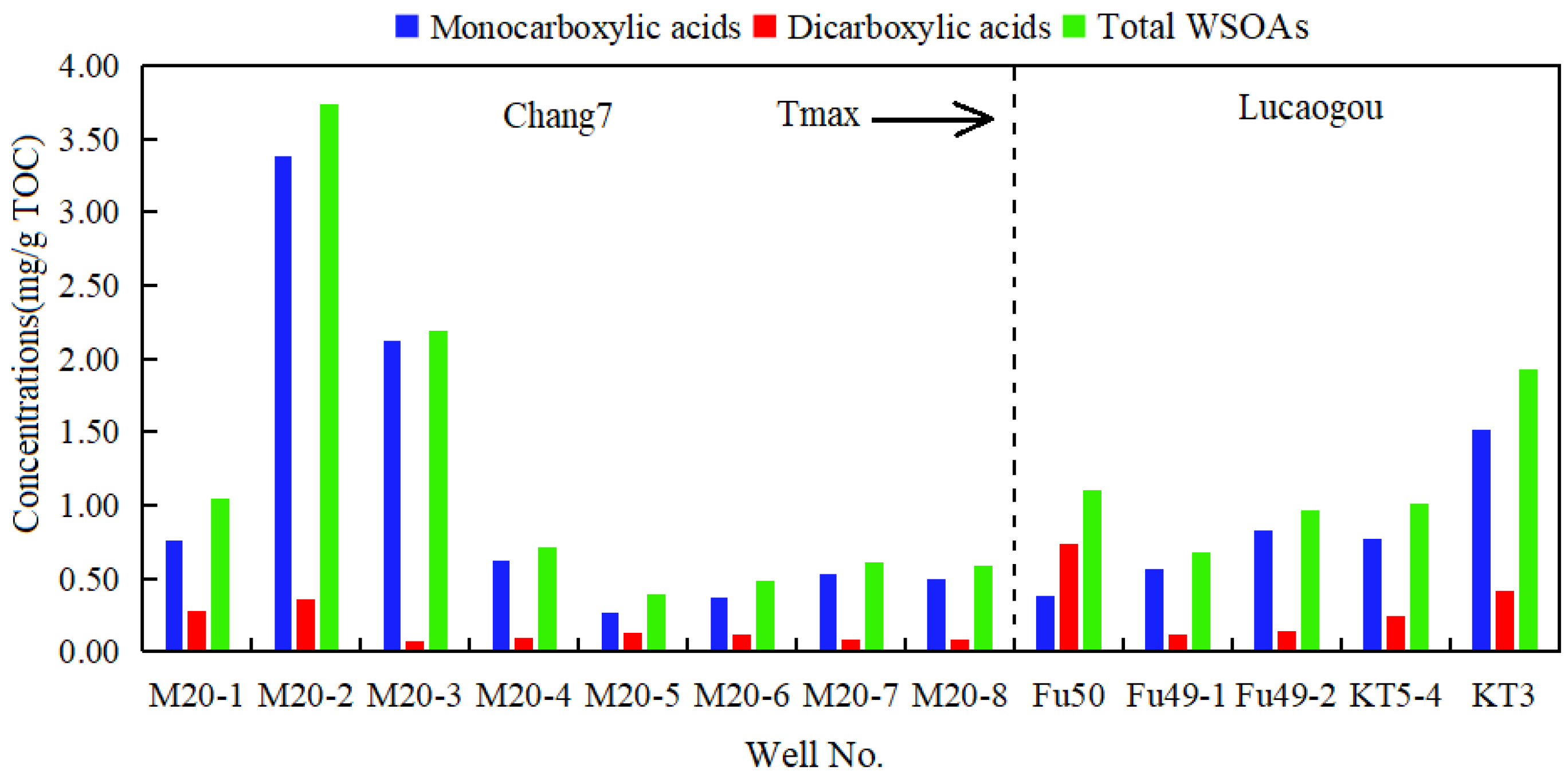
3.1. Organic Acid Distribution Characteristics in the Yanchang Formation Chang 7 Member of the Yijun Area, Ordos Basin, and the Lucaogou Formation of the Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
3.2. Origin Analysis of Organic Acid in the Yanchang Formation Chang 7 Member of the Ordos Basin, and the Lucaogou Formation of the Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
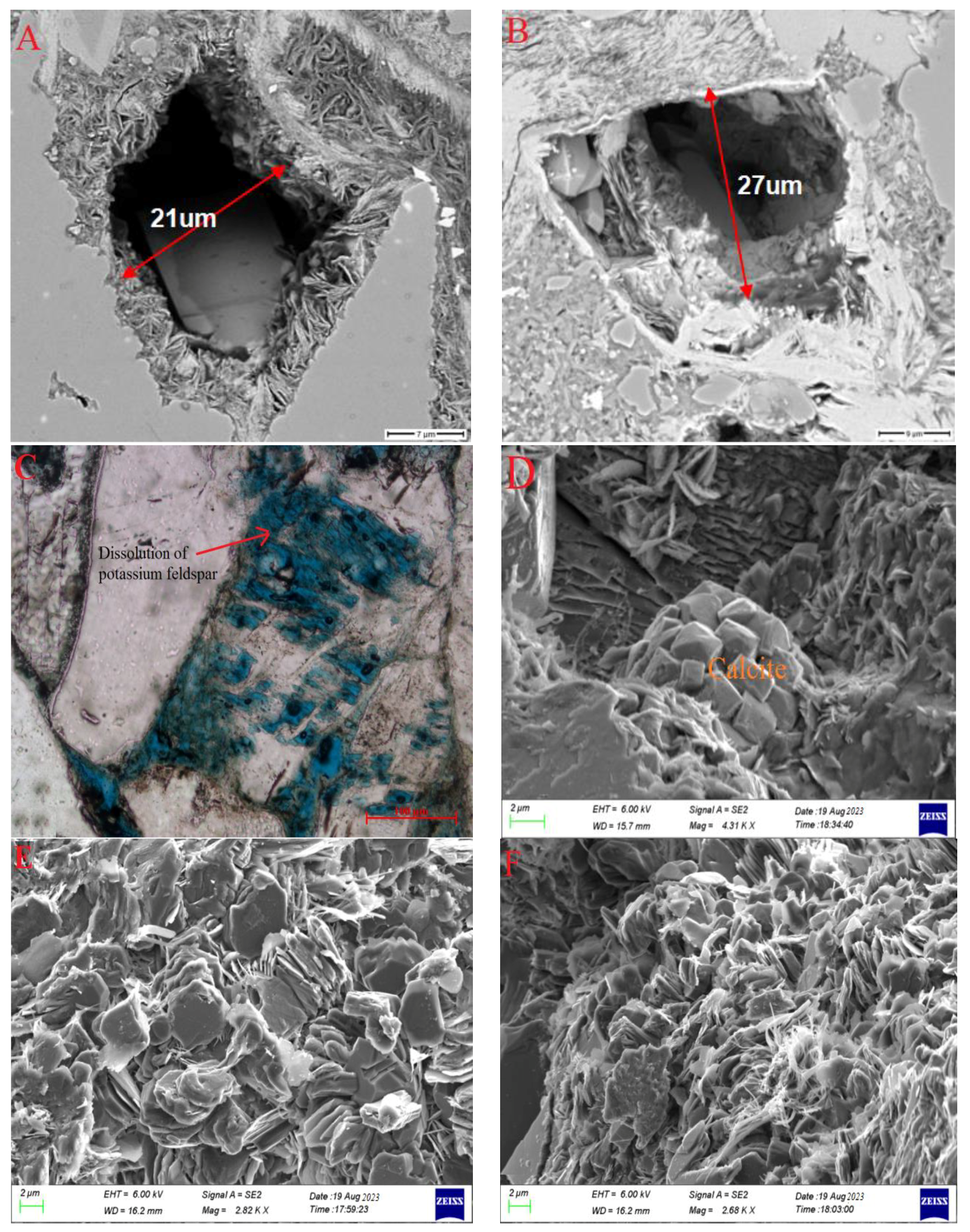
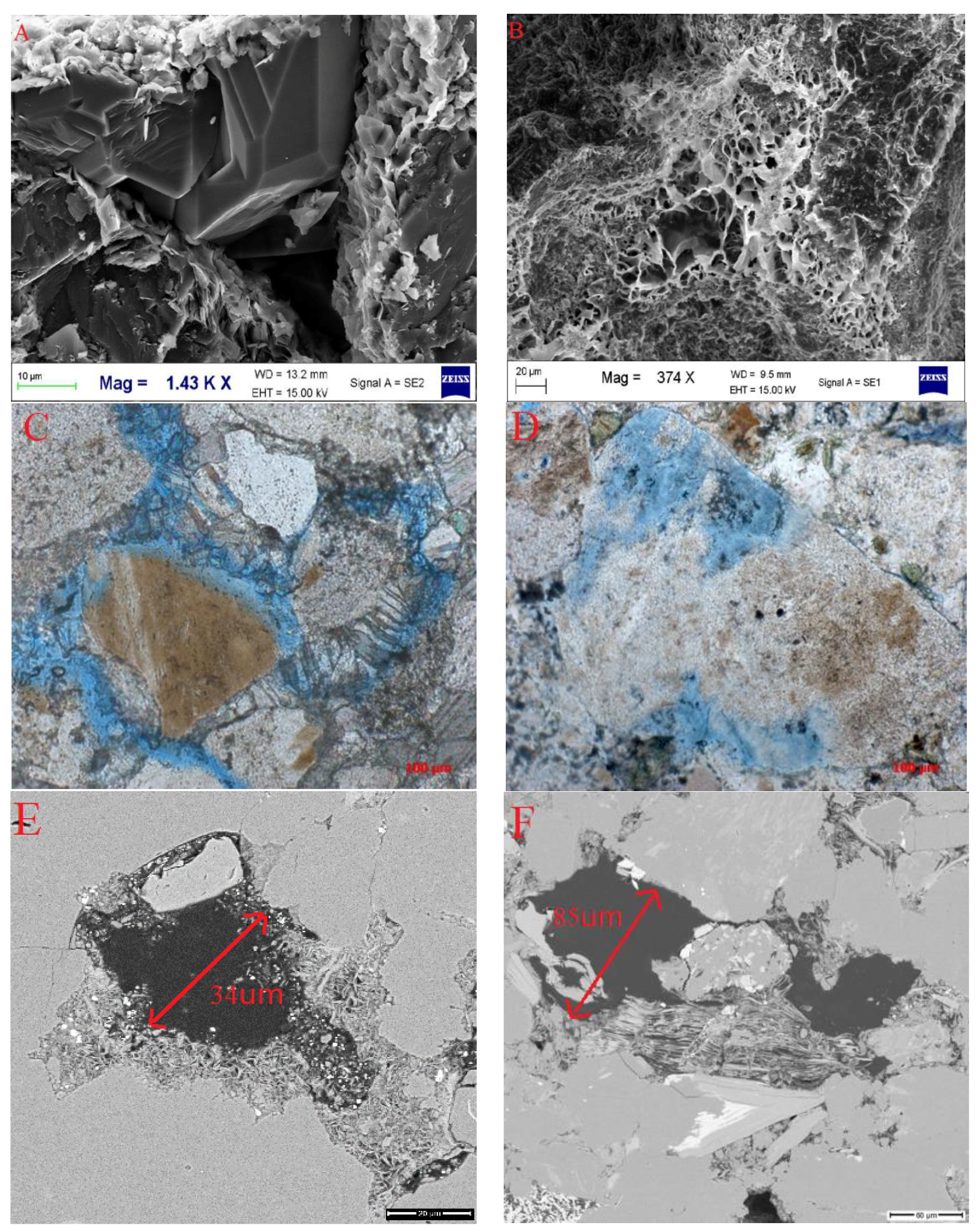
3.3. The Influence of Organic Acids on Reservoir Space Development during the Hydrocarbon Generation Process in the Chang 7 Member of the Yijun Area, Ordos Basin and the Lucaogou Formation in the Fukang Sag in the Junggar Basin
- Immature stage
- 2.
- Low maturity—mature stage
- 3.
- High maturity–overmature stage
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the increase in thermal maturity, the total concentration of organic acids in the Chang 7 member shows a pattern of “sharply rising first and then rapidly declining”, while the Lucaogou Formation shows a gradually increasing trend. In both shale formations, the concentration of monocarboxylic acids predominates, and the concentration of monocarboxylic acids is significantly greater than that of dicarboxylic acids. In the Chang 7 member of the Yanchang Formation, propionate is the main component, supplemented by formate and acetate, and the dicarboxylic acid is mainly succinate. In the Lucaogou Formation, formate, acetate, and propionate are the main monocarboxylic acids, and the dicarboxylic acids are mainly oxalate and succinate.
- (2)
- The origin of organic acids in the oil shale of the Chang 7 member of the Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin differs from that in the Lucaogou Formation within the Fukang Sag, and is associated with the sedimentary environment during their formation. During the Triassic period, a significant proliferation of aquatic algae occurred in freshwater lake basins characterized by warm and humid climatic conditions. Following the death of algal organisms, the organic matter within these basins underwent deposition and transformation into oil shale of the Yanchang Formation under anaerobic reducing environments. In contrast, the oil shale of the Lucaogou Formation was formed through deposition by benthic algae and higher plant residues under the weak oxidation-reduction conditions within a brackish–saline lake in an arid–semi-arid climate.
- (3)
- According to the acid-generation mechanism of organic matter thermal evolution and the influence of diagenesis, the evolutionary pattern of organic acids is categorized into three stages. These three stages are, respectively, the immature stage, low maturity–mature stage, and high maturity–overmature stage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottardi, R.; Mason, S.L. Characterization of the natural fracture system of the Eagle Ford Formation (Val Verde County, Texas). AAPG Bull. 2018, 102, 1963–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M.; Zhou, J. Nanoscale pore structure characterization of the Bakken shale in the USA. Fuel 2017, 209, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.C.; Guo, X.B.; Li, Y.; Li, T.J.; Pan, Y.S.; Li, X.H. Pore Structure and Oil-bearing Properties of Mud Shale Reservoirs of Lucaogou Formation in Malang Sag, Santanghu Basin. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.Z.; Cao, J.; Shang, L.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, G.J. In situ occurrence of shale oil in micro-nano pores in Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2022, 44, 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Hou, J.G.; Dong, H.; Wu, G.Q.; Yan, L.; Zhang, L.W. Pore throat characteristics of fine-grained mixed deposits in shale oil reservoirs and their control on reservoir physical properties: A case study of the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Zhu, R.K.; Cui, J.G.; Cui, J.W. Characteristics of lacustrine shale porosity evolution, Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Pore formation and occurrence in the organicrich shales of the Triassic Chang-7 Member, Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 1, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Luo, X.R.; Lei, Y.H. Characterization of lacustrine shale pore structure: An example from the Upper-Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 27, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, J.H. Characteristics and significance of micron pores and micron fractures in shale oil reservoirs of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Gulong sag, Songliao Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2024, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, B.; Dai, C.C.; Hou, X.L.; Yang, L.; Wang, R. Geological heterogeneity of shale sequence and evaluation of shale oil sweet spots in the Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 846–856. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y. Pore characteristics and their evolution in Paleogene mud shales, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2015, 37, 566–574. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Sherwood, N.; Li, Z. Shale oil occurring between salt intervals in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 152, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, W.J. Microscopic pore characteristics of Sha-3 and Sha-4 shale and their accumulation significance in Liaohe Depression. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 35, 286–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Zhou, T.; Qiao, J.; Yang, G.L.; Zhao, G.H. Deep hydrothermalism of deep coarse-grained siliciclastic rocks and its geological significance: A case study of the 4th member of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Minfeng-Yanjia area, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 929–942. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Zhou, L.H.; Pu, X.G. Geological characteristics of shale rock system and shale oil exploration breakthrough in a lacustrine basin: A case study from the Paleogene 1st sub-member of Kong 2 Member in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.X. Geological characteristics and evaluation of continental shale oil in Biyang Sag of Nanxiang Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2013, 15, 663–671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.F.; Guo, Y.H.; Yang, Y.J. Shale reservoir diagenesis and its impacts on pores of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southeastern Chongqing. J. Palaeogeogr. 2016, 18, 843–856. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Lu, S.F.; Xue, H.T. Major controlling factors of poroperm characteristics of shale oil reservoirs in the Xingouzui Formation, Jianghan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Baruch, E.T.; Kennedy, M.J.; Lohr, S.C. Feldspar dissolution-enhanced porosity in Paleoproterozoic shale reservoir facies from the Barney Creek Formation (McArthur Basin, Australia). AAPG Bull. 2015, 99, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, T.; Bjorlykke, K. Organic acids from source rock maturation: Generation potentials, transport mechanisms and relevance for mineral diagenesis. Appl. Geochem. 1993, 8, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Meng, X.G.; Shen, Z.Z.; Yang, R.Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, F.L. Discovery and geochemical characteristics of Chang 7 source rocks from the eastern margin of a Triassic lacustrine basin in the Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 991–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.X.; Liu, X.Y. Characteristics and resource prospects of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.J.; Jia, C.Z.; Pang, X.Q. Upper Paleozoic total petroleum system and geological model of natural gas enrichment in Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Q.L.; Zhao, C.L. Potentials and prospects of shale oil-gas resources in major basins of China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Tian, T.; Li, J.L. Fault-fracture body characteristics and their effect on hydrocarbon distribution of Yanchang Formation in southwestern margin of Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2024, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Geochemical characteristics of shale in Yijun area, Ordos Basin. Ground Water 2021, 43, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F. Analysis of oil shale in the area of Qipan Town, Yijun County, Tongchuan City, Shaanxi Province, China. West-China Explor. Eng. 2019, 31, 111–112+115. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zou, Y.R.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.J. Paleoenvironment of organic-rich shale from the Lucaogou Fromation in the Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin, China. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2018, 8, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, K.P.; Chen, X. Reservoir condition analysis of Jurassic System in the east band of Fukang depression and the favorable area prediction. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2017, 12, 588–593. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, L.S.; Yin, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Du, X.D. Geological characteristics and exploration potential of shale oil of Permian Lucaogou Formation in hanging wall of Fukang fault zone, Junggar Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2023, 35, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.L.; Tian, J.J.; Wang, C.J.; Sun, H.M.; Feng, S.; Li, L. Characteristics and ore-controlling condition of oilshale in Southern margin area of Junggar Basin. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. (2000–2004) 2014, 34, 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 18602-2012; Rock Pyrolysis Analysis. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB/T 14506.30-2010; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Silicate Rocks Part 30: Determination of 44 Elements. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Carothers, W.W.; Kharaka, Y.K. Aliphatic acid anions in oil-field waters-Implications for origin of natural gas. AAPG Bull.-Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. 1987, 62, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.P.; Zhou, S.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, J.; Liu, M.M.; Chen, K.F. Distributions and evolution model of water-soluble organic acids for coals with different thermal maturations. Fuel 2021, 283, 118863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Vieth-Hillebrand, A.; Wilke, F.D.H.; Horsfiel, B. Characterization of water-soluble organic compounds released from black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 150–151, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Tang, D.Z.; Xu, H. Sedimentary characteristics of the oil shale in the upper permian lucaogou formation in dahuangshan southern margin of Jungar. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 29, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, N.; Shao, X.Z.; Zhu, G.Y. Geochemical characteristics and formation environment of source rocks of Triassic Chang 7 member in northern Pingliang area, Ordos Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2023, 35, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, Q.; Peng, J.L. Experimental Sudy on the Generation of Organic Acids from Source Rocks and Its Effect Factors. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2007, 25, 847–851. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Deng, X.Q.; Qi, Y.L. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks of M53 well and Chang-8 mem- ber oil-source in Pingliang exploration area, Ordos Basin. Geoscience 2020, 34, 800–811. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Deng, S.L.; Yao, Y. Study on Characteristics of Microscopic Composition of Source Rock Kerogen in Area A, Xinjiang. Adv. Geosci. 2021, 11, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Hu, G.; Teng, G.R. Organism assemblages in the Paleozoic source rocks and their implications. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 617–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.C.; Zhang, B.M.; Bian, L.Z. Development constraints of marine source rocks in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2005, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, G.R.; Liu, W.H.; Xu, Y.C.; Chen, J.F. A comprehensive geochemical delineation of highly evolved marine carbonate source rocks: A case study in the Ordos Basin. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 36, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- OuYang, S.Q.; Lyu, X.X.; Xue, N. Paleoenvironmental characteristics and source rock development model of Early-Middle Cambrian: A case of the Keping-Bachu area in the Tarim Basin. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. (Chin. Ed.) 2022, 51, 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Yu, X.H.; Han, B.Q. Geochemical characteristics of the 3rd member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongpu Depression and their geological implication. Geol. China 2010, 37, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiho, K. Global changes of Paleogene aerobic/anaerobic benthic foraminifera and deep-sea circulation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1992, 83, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Bird, D.A. Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in alkaline lakes from the western USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, J.K.; Xu, N.C.; Li, H.L. The Sr/Ba ratio response to salinity in clastic sediments of the Yangtze River Delta. Chem. Geol. 2021, 559, 119923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.F.; Freeman, K.H.; Lewan, M.D. δ13C of low-molecular-weight organic acids generated by the hydrous pyrolysis of oil-prone source rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2755–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.X.; Yao, S.P.; Lu, X.C.; Wu, H.G.; Sun, F.N.; Jin, J. Effects of organic matter evolution on oil reservoir property duringdiagenesis of typical continental shale sequences. Oil Gas Geol. 2019, 40, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Dong, D.L.; Zhen, X.J.; Yan, S.; Qun, L. Mechanism for the formation of natural fractures and their effects on shale oil accumulation in Junggar Basin, NW China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 254, 103973. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, D.Y.; Luo, Q.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, D.D.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Major factors controlling fracture development in the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation tight oil reservoir, Junggar Basin, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 146, 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Behar, F.; Vandenbroucke, M. Chemical modelling ofkerogen. Org. Geochem. 1987, 11, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, M. Pore evolution of shale oil reservoirs in Dongying Sag. Acta Pet. Sin. 2018, 39, 754–766. [Google Scholar]





| Conditions | Case I | Case II |
|---|---|---|
| Chromatographic column | Metrosep A Supp 17–250/4.0 | Metrosep Organic Acids-250/7.8 |
| Eluent | A: 6 mM NaOH, B: 5 mM Na2CO3 + 0.2 mM NaHCO3 | 2 mM H2SO4 + 100 mM LiCl |
| Flowrate | 0.6 mL/min | 0.5 mL/min |
| Columntemperature | 45 °C | 30 °C |
| WSOA types | Oxalate | Formate, acetate, propionate, butyrate, malonate, succinate |
| Well No. | Formation | Buried Depth/m | Formate (mg/L) | Acetate (mg/L) | Propionate (mg/L) | Butyrate (mg/L) | Oxalate (mg/L) | Malona te(mg/L) | Succinate (mg/L) | WSOAs (mg/L) | TOC/% | Permeability (mD) | Tmax (°C) | Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M20-1 | Chang73 | 2154.7 | 2.06 | 1.46 | 2.27 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.15 | 7.94 | 5.25 | 0.0001 | 448.00 | I |
| M20-2 | Chang73 | 2160.82 | 1.89 | 1.56 | 5.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 9.45 | 15.83 | 0.0012 | 444.00 | I |
| M20-3 | Chang73 | 2161.9 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 6.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 9.37 | 9.36 | 0.0011 | 442.00 | I |
| M20-4 | Chang73 | 2165 | 1.28 | 1.84 | 2.84 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 6.85 | 4.17 | 0.001 | 451.00 | I |
| M20-5 | Chang73 | 2170.3 | 1.58 | 1.12 | 2.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.28 | 7.25 | 2.16 | 0.001 | 451.00 | II2 |
| M20-6 | Chang73 | 2176.32 | 1.53 | 1.37 | 2.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.54 | 6.62 | 2.89 | 0.013 | 450.00 | II2 |
| M20-7 | Chang73 | 2177.6 | 1.02 | 1.22 | 2.22 | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 6.25 | 3.93 | 0.001 | 456.00 | II1 |
| M20-8 | Chang73 | 2179.6 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 2.45 | 0.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.09 | 7.24 | 3.21 | 0.001 | 446.00 | II1 |
| Fu50 | P2l | 5336.8 | 0.86 | 1.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.39 | 0.00 | 1.47 | 7.25 | 6.06 | 0.018 | 448.00 | II1 |
| Fu49-1 | P2l | 5624.6 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 5.18 | 0.00 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 8.96 | 3.05 | 0.011 | 462.00 | II1 |
| Fu49-2 | P2l | 5625.9 | 1.25 | 1.37 | 6.90 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 11.17 | 3.46 | 0.09 | 460.00 | II1 |
| KT5 | P2l | 5829 | 1.18 | 2.45 | 7.64 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.16 | 2.56 | 14.79 | 2.72 | 0.021 | 452.00 | II2 |
| KT3 | P2l | 6185.2 | 12.33 | 3.22 | 4.28 | 0.00 | 2.54 | 0.00 | 2.90 | 25.27 | 3.05 | 0.001 | 486.00 | III |
| Well No. | Buried Depth/m | Mn/Sr | Ba | δCe | V/(V + Ni) | V/Cr | Sr/Cu | Sr/Ba | δ13C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N55-10 | 2154.7 | 5.1 | 239.25 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 6.2 | 3.7 | 0.25 | −28.3 |
| N55-11 | 2161.9 | 4.9 | 101.87 | 0.94 | 0.74 | 5.4 | 4.6 | 0.24 | −29.8 |
| N55-12 | 2176.62 | 8.1 | 136.51 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 0.34 | −29.6 |
| N55-13 | 2177.3 | 5.8 | 95.95 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 6.7 | 1.4 | 0.23 | −28.7 |
| N55-14 | 2179.6 | 2.6 | 89.2 | 0.9 | 0.72 | 4.8 | 3.0 | 0.19 | −27.6 |
| Fu50 | 4336.8 | 1.55 | 119.0 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 2.63 | 18.1 | 4.07 | −34.76 |
| Fu49-1 | 5624.6 | 3.14 | 160.7 | 0.93 | 0.59 | 2.37 | 10.16 | 1.43 | −34.58 |
| Fu49-2 | 5625.9 | 1.91 | 234.1 | 0.89 | 0.67 | 2.89 | 6.3 | 1.36 | −33.04 |
| KT5-4 | 5829 | 1.9 | 234.1 | 0.85 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 6.8 | 1.4 | 34.98 |
| KT3 | 6185.2 | 3.70 | 511.5 | 0.9 | 0.81 | 2.58 | 9.1 | 0.84 | −38.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, G. Distribution, Origin, and Impact on Diagenesis of Organic Acids in Representative Continental Shale Oil. Processes 2024, 12, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12102092
Pang W, Li J, Zhou S, Li Y, Liu L, Wang H, Chen G. Distribution, Origin, and Impact on Diagenesis of Organic Acids in Representative Continental Shale Oil. Processes. 2024; 12(10):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12102092
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Wenjun, Jing Li, Shixin Zhou, Yaoyu Li, Liangliang Liu, Hao Wang, and Gengrong Chen. 2024. "Distribution, Origin, and Impact on Diagenesis of Organic Acids in Representative Continental Shale Oil" Processes 12, no. 10: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12102092
APA StylePang, W., Li, J., Zhou, S., Li, Y., Liu, L., Wang, H., & Chen, G. (2024). Distribution, Origin, and Impact on Diagenesis of Organic Acids in Representative Continental Shale Oil. Processes, 12(10), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12102092





