Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, and Propan-2-ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent (HDES) Preparation
2.3. HDES Characterization
2.4. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3. Results
3.1. HDES Characterization
3.2. Alcohol Separation from Hydroalcoholic Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shehata, M.; Unlu, A.; Sezerman, U.; Timucin, E. Lipase and Water in a Deep Eutectic Solvent: Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Studies of the Effects of Water-In-Deep Eutectic Solvents on Lipase Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8801–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pätzold, M.; Siebenhaller, S.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Syldatk, C.; Holtmann, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Efficient Solvents in Biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, O.G.; Castro, M.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Removing phenolic pollutants using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Lima, F.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep eutectic solvents: Overcoming 21st century challenges. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Alnashef, I.M.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Hashim, M.A. Glucose-based deep eutectic solvents: Physical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 178, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwamena, A.K. Recent advances in hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction. Separations 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panić, M.; Bubalo, M.C.; Redovniković, I.R. Designing a biocatalytic process involving deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Silva, S.A.M.E.; Ribeiro, B.D. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent as an inhibitor of metalloproteases (collagenase and elastase) in cosmetic formulation. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buarque, F.S.; Carniel, A.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Selective enzymes separation from the fermentation broth of Yarrowia lipolytica using aqueous two-phase system based on quaternary ammonium compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 124539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Sanglard, M.G.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Designer solvent ability of alcohols in aqueous biphasic systems composed of deep eutectic solvents and potassium phosphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-based eutectic mixtures: Hydrophobic low viscosity solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Su, E. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: The new generation of green solvents for diversified and colorful applications in green chemistry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Wong, W.F. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Current progress and future directions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Llorente, D.; Cañada-Barcala, A.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Águeda, V.I.; García, J.; Larriba, M. A review of the use of eutectic solvents, terpenes and terpenoids in liquid–liquid extraction processes. Processes 2020, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshatov, E.E.; Boltoeva, M.Y.; Folden, C.M. First evidence of metal transfer into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures: Indium extraction from hydrochloric and oxalic acids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4616–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; Van Spronsen, J.; Kroon, M.C.; Gallucci, F.; Van Sint Annaland, M.; Tuinier, R. A Search for Natural Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Natural Components. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.B.; Sardroodi, J.J.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.R. Structure and dynamics of thymol—Fatty acids based deep eutectic solvent investigated by molecular dynamics simulation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2022, 552, 113241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.B.; Sardroodi, J.J.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.R. Structure and dynamics of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents composed from terpene-fatty acids investigated by molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 114, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani Pour, S.; Sardroodi, J.J.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.R.; Pazuki, G. Investigation the effect of water addition on intermolecular interactions of fatty acids-based deep eutectic solvents by molecular dynamics simulations. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Dhattarwal, H.S.; Kashyap, H.K. An Overview of Structure and Dynamics Associated with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications in Extraction Processes. ChemPhysChem 2022, 23, e202200239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejrotti, S.; Antenucci, A.; Pontremoli, C.; Gontrani, L.; Barbero, N.; Carbone, M.; Bonomo, M. Critical Assessment of the Sustainability of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Case Study on Six Choline Chloride-Based Mixtures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 47449–47461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; Cieśliński, H.; Boczkaj, G. Deep eutectic solvents microbial toxicity: Current state of art and critical evaluation of testing methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Tripathi, M.; Lukk, T.; Karpichev, Y.; Gathergood, N.; Singh, B.N.; Thakur, V.K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Gupta, V.K. Biobased natural deep eutectic system as versatile solvents: Structure, interaction and advanced applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharepour, F.; Bakhshi, H.; Rahimnejad, M. Separation of ethanol azeotropic mixture using deep eutectic solvents in liquid-liquid extraction process. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.B.; Dwivedi, M.; Jha, D.; Kumar, R.; Sivagnanam, B.M. Azeotropic separation of isopropanol-water using natural hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Wazeer, I.; El Blidi, L.; Mulyono, S.; Hashim, M.A. Liquid-liquid separation of azeotropic mixtures of ethanol/alkanes using deep eutectic solvents: COSMO-RS prediction and experimental validation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Gautério, G.V.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Lemes, A.C.; Ribeiro, B.D. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Processes 2022, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; de Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Development of an ethanolic two-phase system (ETPS) based on polypropylene glycol 2000 + ethylene glycol + ethanol for separation of hydrophobic compounds. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2156–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjineci, N.; Boli, E.; Tzani, A.; Detsi, A.; Voutsas, E. Separation of the ethanol/water azeotropic mixture using ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 424, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.S.; Pereiro, A.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for azeotropic mixtures. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Guimarães, D.E.M.; Soares, C.M.F.; Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Ethanolic two-phase system formed by polypropylene glycol, ethylene glycol and/or ionic liquid (phase-forming or adjuvant) as a platform to phase separation and partitioning study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Molina, B.S.; Kroon, M.C. Aliphatic+ethanol separation via liquid-liquid extraction using low transition temperature mixtures as extracting agents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2015, 394, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Sebbah, T.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X. Terpenoid-capric acid based natural deep eutectic solvent: Insight into the nature of low viscosity. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakoudi, A.; Tsiouras, A.; Mourtzinos, I. Extraction of Lycopene from Tomato Using Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Jin, Y.; Jung, D.; Park, K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. In situ formation of thymol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Application to antibiotics analysis in surface water based on liquid-liquid microextraction followed by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Chua, B.L.; Chow, Y.H.; Chong, C.H. Development and characterisation of novel terpenoid-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for sustainable extraction of bioactive antioxidants from Rosmarinus officinalis L. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 388, 122792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Lima, F.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Circular Approach to Purify Water Contaminated with Ciprofloxacin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14739–14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, S.; Juneja, S.; Pandey, S. Water Miscibility, Surface Tension, Density, and Dynamic Viscosity of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Composed of Capric Acid, Menthol, and Thymol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 3400–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjalli, F.S.; Ahmad, O. Density of aqueous choline chloride-based ionic liquids analogues. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 647, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Pandey, S. Solvatochromic probe behavior within choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents: Effect of temperature and water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14652–14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.H.C.S.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Freire, C.S.R.; Marrucho, I.M. Production of lysozyme nanofibers using deep eutectic solvent aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Paul, N.; Naik, P.K.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Pattader, P.S.G.; Marrucho, I.M. Molecular dynamics insights and water stability of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents aided extraction of nitenpyram from an aqueous environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 7405–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Dubrovsky, I.; Kirichenko, S.; Bulatov, A. Behavior of quaternary ammonium salts and terpenoids-based deep eutectic solvents in aqueous phase. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 117987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Monteiro, N.V.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for purification of water contaminated with Bisphenol-A. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; Warrag, S.E.E.; Kroon, M.C. The Curious Case of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Story on the Discovery, Design, and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10591–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Xue, S.; Ren, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as pseudo-stationary phases in capillary electrokinetic chromatography: An explorative study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1213, 339936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Abranches, D.O.; Maximo, G.J.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Greener Terpene-Terpene Eutectic Mixtures as Hydrophobic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 17414–17423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From Phase Change Materials to Green Solvents: Hydrophobic Low Viscous Fatty Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, R.O.; Silva, L.P.; Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Liquefying Compounds by Forming Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Case Study for Organic Acids and Alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4174–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phenolic hydrogen bond donors in the formation of non-ionic deep eutectic solvents: The quest for type v des. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10253–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Shan, Y.; Wen, L.; Cao, X. Extraction of artemisinin using natural deep eutectic solvent selected by COSMO-RS. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 33, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.M.; Müller, S.; de Castilla, A.G.; Gurikov, P.; Matias, A.A.; Bronze, M.D.R.; Fernández, N. Physicochemical characterization and simulation of the solid–liquid equilibrium phase diagram of terpene-based eutectic solvent systems. Molecules 2021, 26, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.A.; Pereira, C.V.; Leonardo, I.C.; Fernández, N.; Gaspar, F.B.; Silva, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A. Terpene-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Systems as Efficient Solvents to Recover Astaxanthin from Brown Crab Shell Residues. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2246–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Formation of glassy phases and polymorphism in deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuniewski, M.; Paduszyński, K.; Domańska, U. (Solid + liquid) equilibrium phase diagrams in binary mixtures containing terpenes: New experimental data and analysis of several modelling strategies with modified UNIFAC (Dortmund) and PC-SAFT equation of state. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 422, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, A.; Sanjuan, A.; Bou-Ali, M.M.; Alonso, R.M.; Campanero, M.A. Physicochemical characterization of hydrophobic type III and type V deep eutectic solvents based on carboxylic acids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 392, 123431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, H.; Mostafa, A.; Alqarni, A.M.; Alsultan, R.; Al Shehab, Z.; Aljarrash, Z.; Al-Zawad, W.; Al-Kahlah, S.; Amir, M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction utilizing menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for simultaneous determination of sulfonamides residues in powdered milk-based infant formulas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štejfa, V.; Bazyleva, A.; Fulem, M.; Rohlíček, J.; Skořepová, E.; Růžička, K.; Blokhin, A.V. Polymorphism and thermophysical properties of L- and DL-menthol. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, G. Amplification of Hofmeister effect by alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7450–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.; Greaves, T.L.; Healy, T.W.; Drummond, C.J. The effect of structural modifications on the solution and interfacial properties of straight and branched aliphatic alcohols: The role of hydrophobic effects. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2015, 449, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.C.; Ramanan, R.N.; Tey, B.T.; Tan, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C.; Ooi, C.W. Purification of the recombinant enhanced green fluorescent protein from Escherichia coli using alcohol + salt aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, J. Separation of azeotropic mixtures (ethanol and water) enhanced by deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. Separation of isopropanol from its aqueous solution with deep eutectic solvents: Liquid–liquid equilibrium measurement and thermodynamic modeling. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Banerjee, T. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Lower Alcohols Using Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: Experiments and COSMO-SAC Predictions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumplido, M.A.P.; De la Torre, J.; Cerisuelo, J.P.; Chafer, A. Effect of the anion in phosphonium-based ionic liquids to recovery efficiently 2-propanol from an azeotropic mixture with water. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2023, 574, 113884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
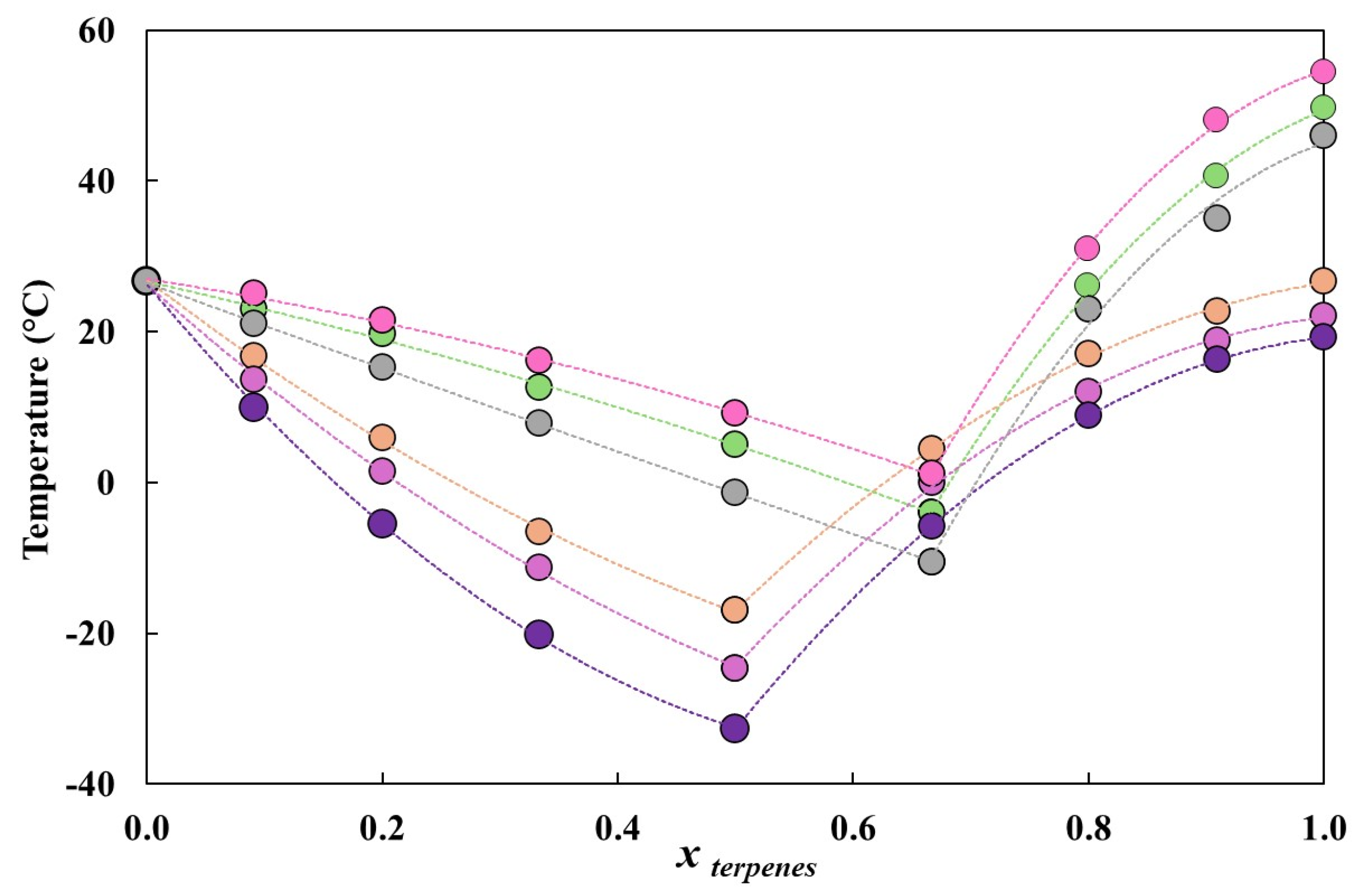
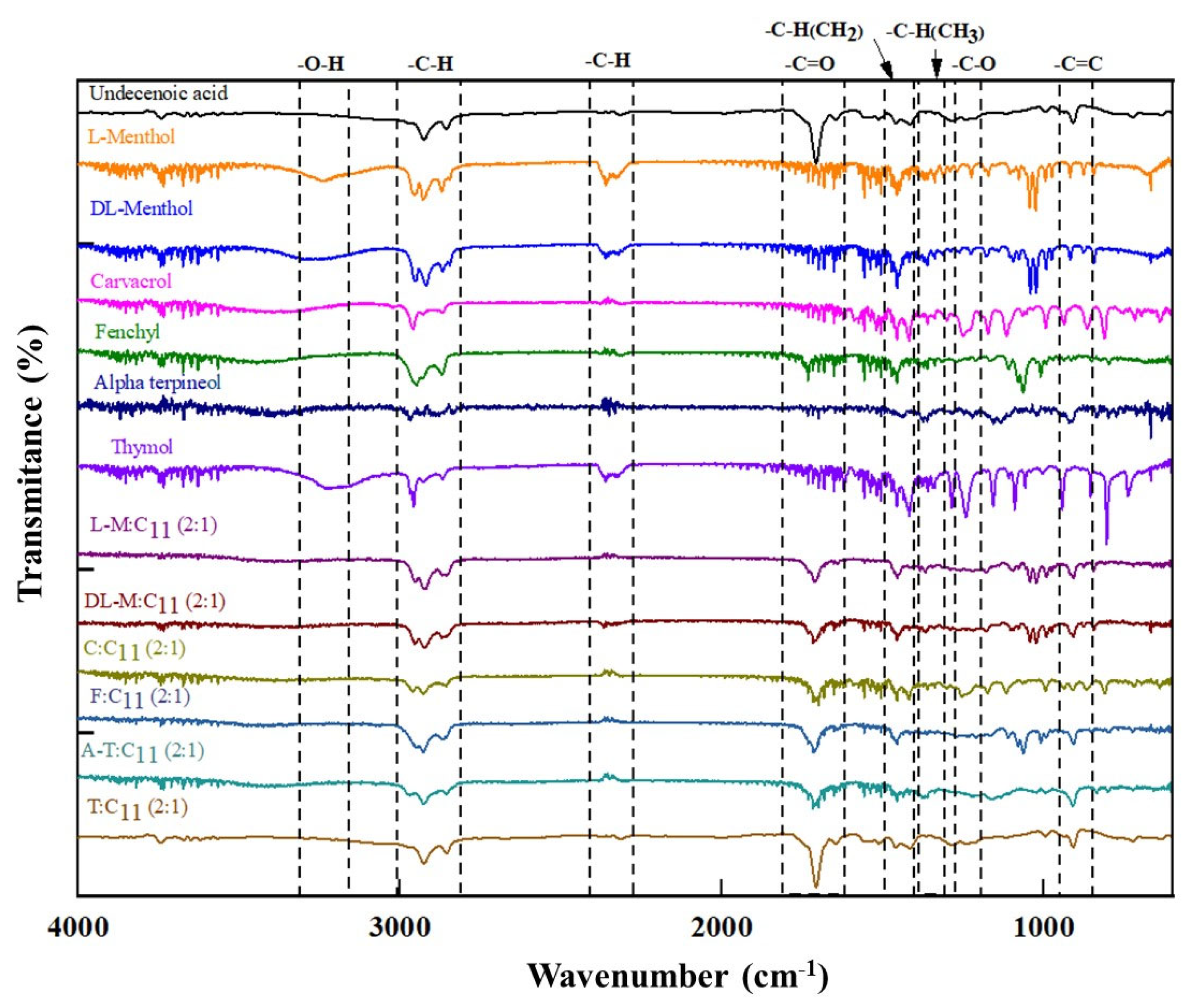

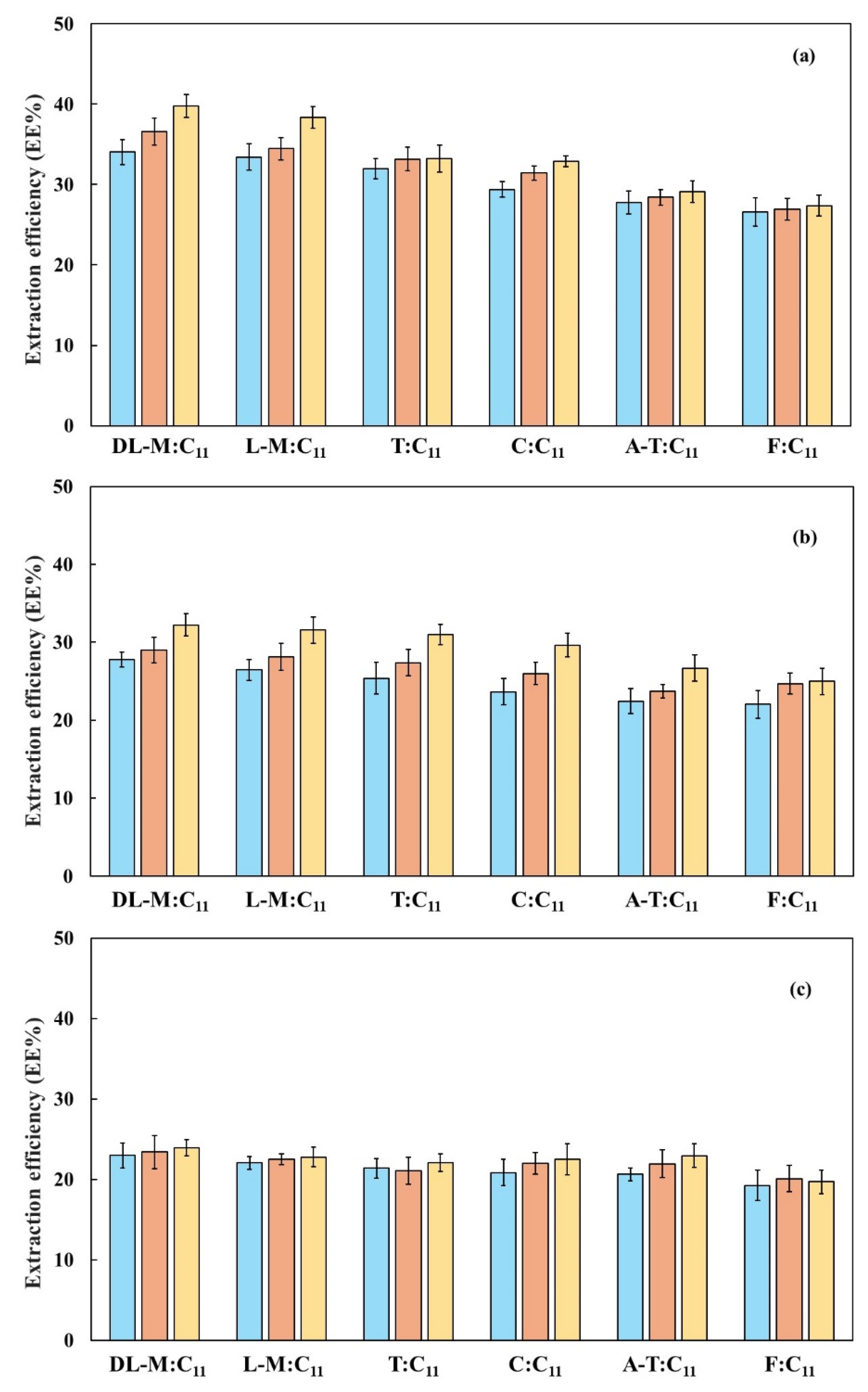
| HBA/HBD | Molecular Weight (g mol−1) | Water Solubility (mg L−1) | Catalog n° | CAS n° | Supplier | Purity [a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-undecenoic acid | 184.27 | 7.37 | 124672 | 112-38-9 | Sigma-Aldrich | 98% |
| DL-menthol | 156.27 | 420 | W266507 | 89-78-1 | Sigma-Aldrich | 99% |
| L-menthol | 156.27 | 490 | PHR1116 | 2216-51-5 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥99% |
| Carvacrol | 150.22 | 1250 | 282197 | 499-75-2 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥98% |
| Alpha-Terpineol | 154.25 | 7100 | 432628 | 98-55-5 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥96% |
| Thymol | 150.22 | 900 | T0501 | 89-83-8 | Sigma-Aldrich | 99% |
| Fenchyl alcohol | 154.25 | 461 | W248099 | 1632-73-1 | Sigma-Aldrich | ≥97% |
| Ethanol | 46.06 | totally miscible | 1211 | 64-17-5 | Isofar | 99.5% |
| propan-1-ol | 60.09 | totally miscible | 200-746-9 | 71-23-8 | Vetec | 99.5% |
| propan-2-ol | 60.09 | totally miscible | 190764 | 67-63-0 | Vetec | 99.5% |
| HBA (Molar Ratio) | Dried (ppm) | Saturated (ppm) | Log P (HBA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carvacrol (1:2) | 2149 ± 109 | 16,859 ± 84 | |
| Carvacrol (1:1) | 1438 ± 84 | 10,068 ± 109 | 3.08 |
| Carvacrol (2:1) | 780 ± 45 | 12,497 ± 168 | |
| Terpineol (1:2) | 3511 ± 118 | 19,566 ± 142 | |
| Terpineol (1:1) | 2069 ± 92 | 13,062 ± 107 | 2.79 |
| Terpineol (2:1) | 987 ± 67 | 15,089 ± 168 | |
| Thymol (1:2) | 1278 ± 127 | 13,008 ± 227 | |
| Thymol (1:1) | 934 ± 96 | 7250 ± 284 | 3.20 |
| Thymol (2:1) | 797 ± 36 | 10,018 ± 360 | |
| Fenchyl (1:2) | 4901 ± 126 | 20,864 ± 106 | |
| Fenchyl (1:1) | 2763 ± 68 | 15,648 ± 141 | 2.71 |
| Fenchyl (2:1) | 1168 ± 33 | 18,713 ± 136 | |
| DL-menthol (1:2) | 1373 ± 97 | 11,154 ± 70 | |
| DL-menthol (1:1) | 866 ± 36 | 7607 ± 175 | 3.28 |
| DL-menthol (2:1) | 631 ± 38 | 8795 ± 136 | |
| L-menthol (1:2) | 701 ± 68 | 12,919 ± 328 | |
| L-menthol (1:1) | 629 ± 30 | 8868 ± 136 | 3.28 |
| L-menthol (2:1) | 553 ± 27 | 10,160 ± 282 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Audeh, D.J.S.A.; Carniel, A.; Borges, C.P.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Buarque, F.S.; Ribeiro, B.D. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, and Propan-2-ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2024, 12, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061255
Audeh DJSA, Carniel A, Borges CP, Coelho MAZ, Buarque FS, Ribeiro BD. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, and Propan-2-ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions. Processes. 2024; 12(6):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061255
Chicago/Turabian StyleAudeh, Dalal J. S. A., Adriano Carniel, Cristiano Piacsek Borges, Maria Alice Zarur Coelho, Filipe Smith Buarque, and Bernardo Dias Ribeiro. 2024. "Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, and Propan-2-ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions" Processes 12, no. 6: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061255
APA StyleAudeh, D. J. S. A., Carniel, A., Borges, C. P., Coelho, M. A. Z., Buarque, F. S., & Ribeiro, B. D. (2024). Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, and Propan-2-ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions. Processes, 12(6), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061255










