Study on Multi-Scale Cloud Growth Characteristics of Frustoconical Dispersal Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation Method
2.1. Governing Equation
2.1.1. The Initial Breakup of Cloud Materials
2.1.2. The Dispersal of Cloud Particles
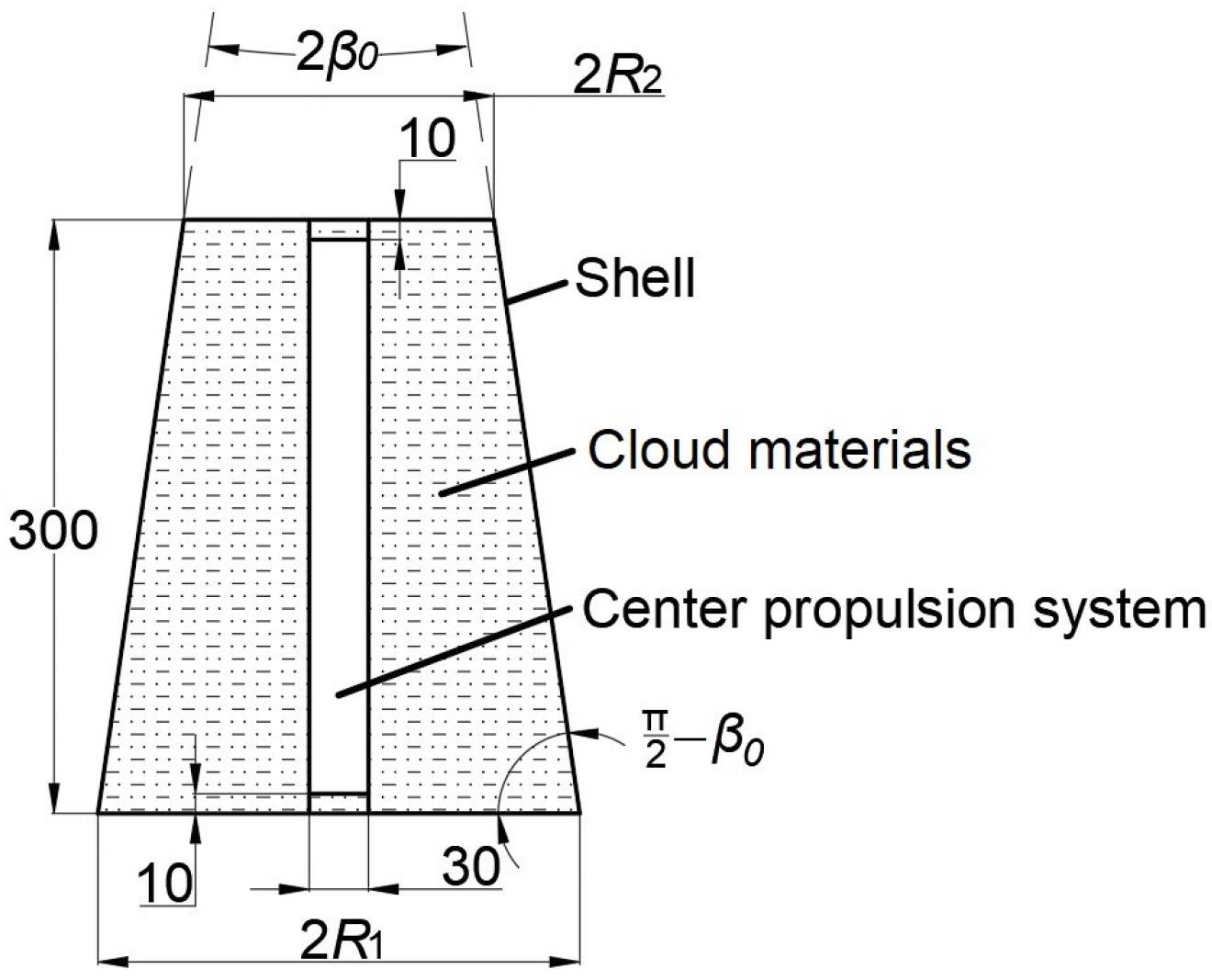
2.2. Geometry and Parameters
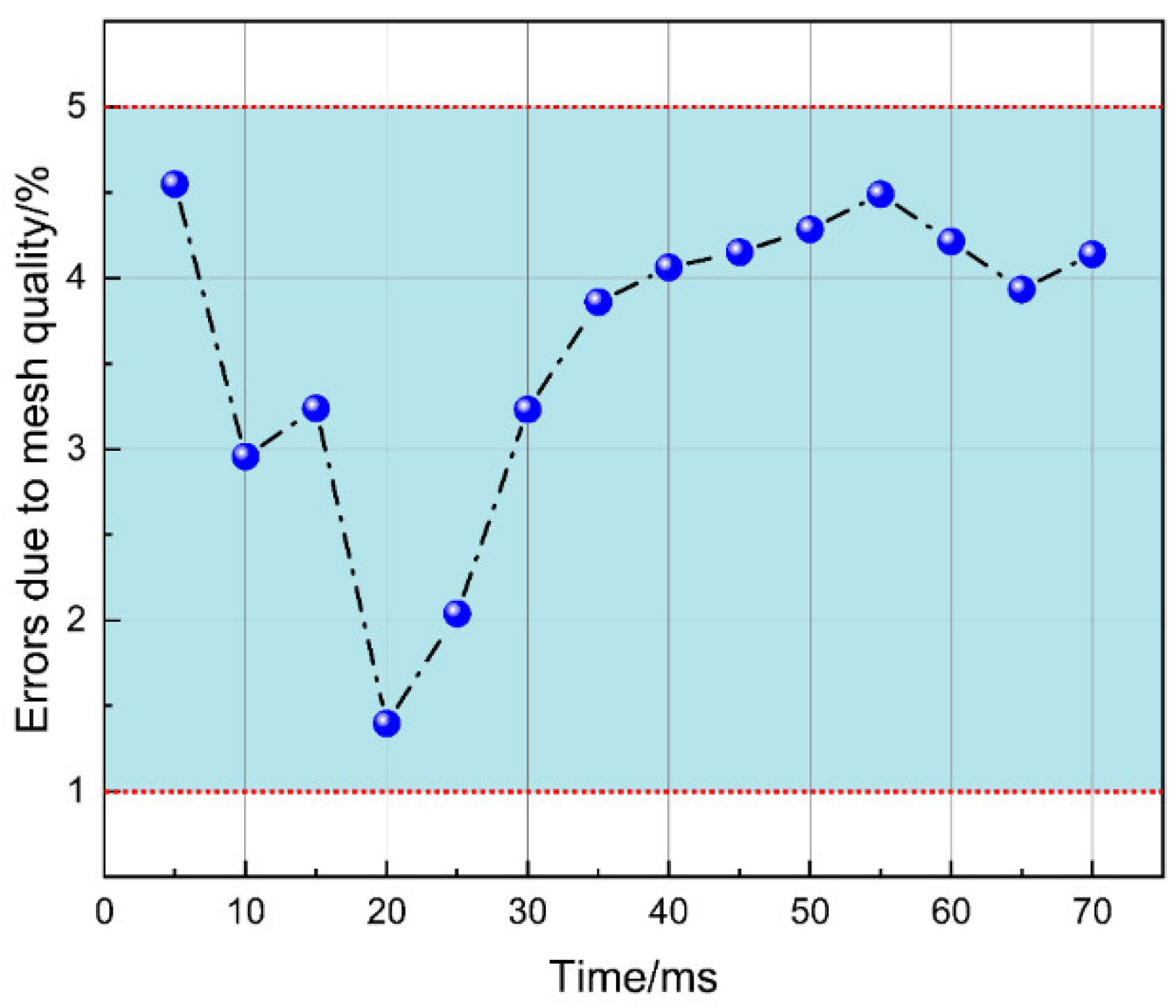
2.3. Mesh Information
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macroscopic Characteristics of Cloud
3.1.1. Cloud Size
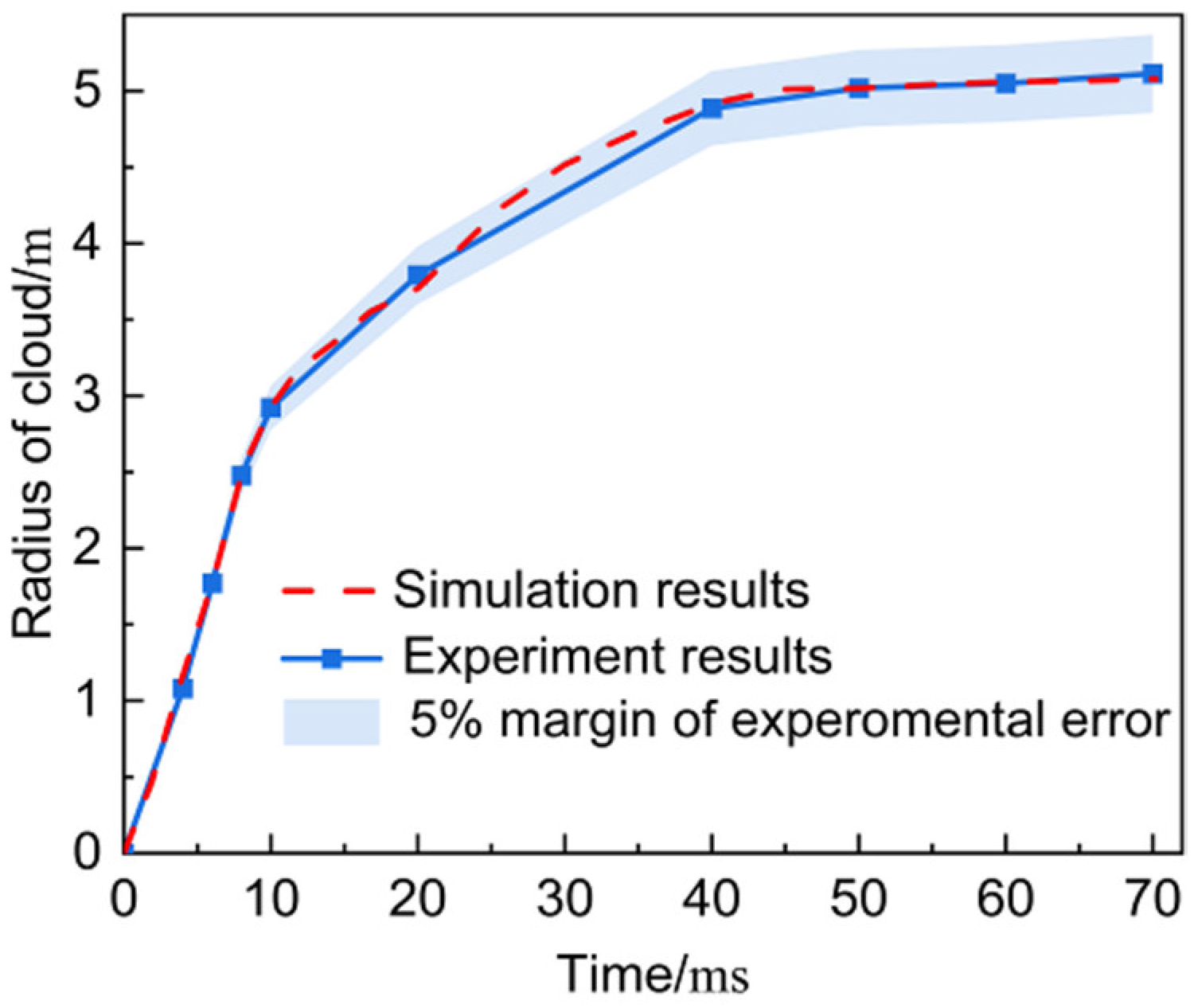
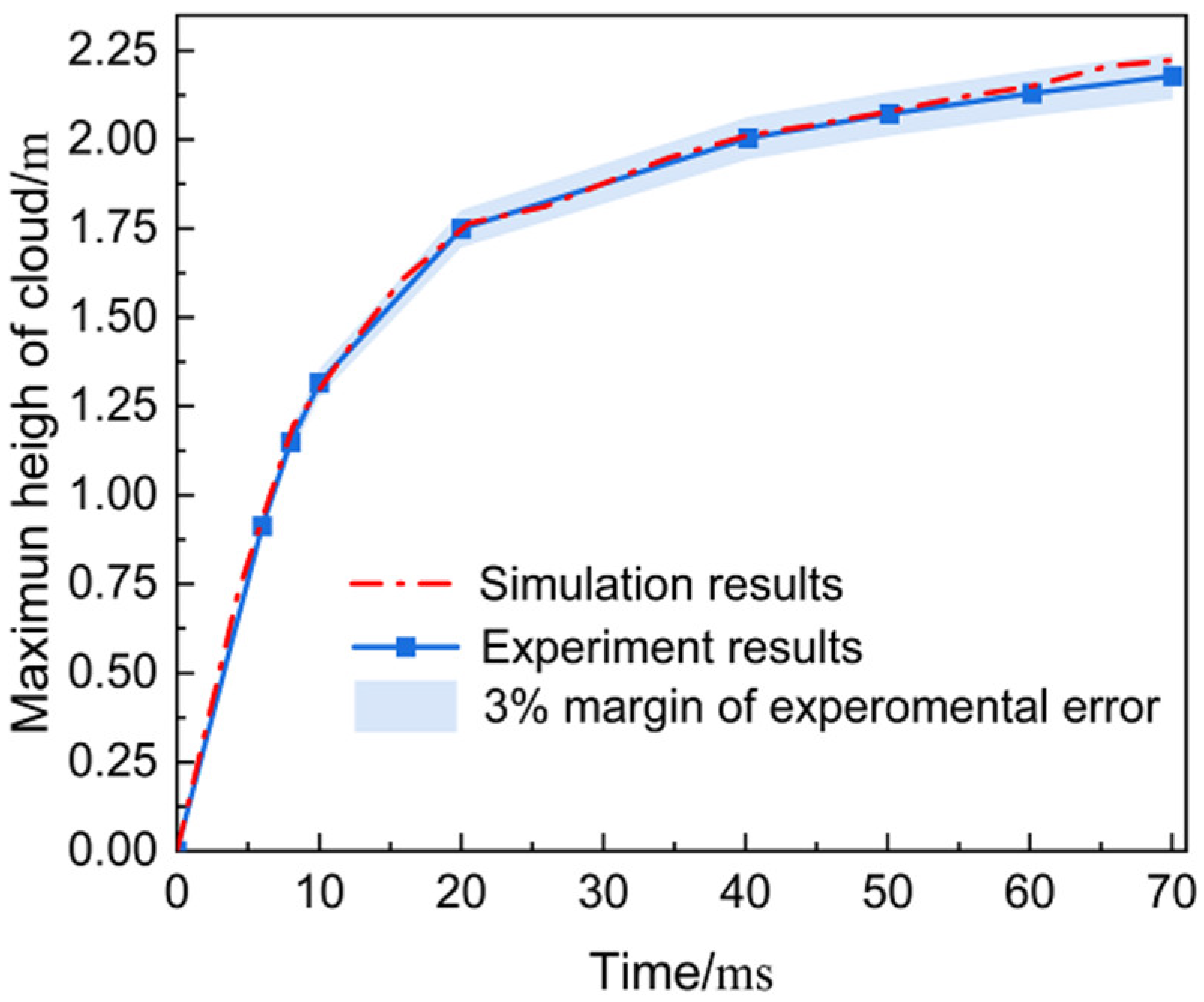
3.1.2. Reliability Verification
3.2. Mesoscopic Characteristics of Cloud
3.2.1. Cloud Particle Size Distribution
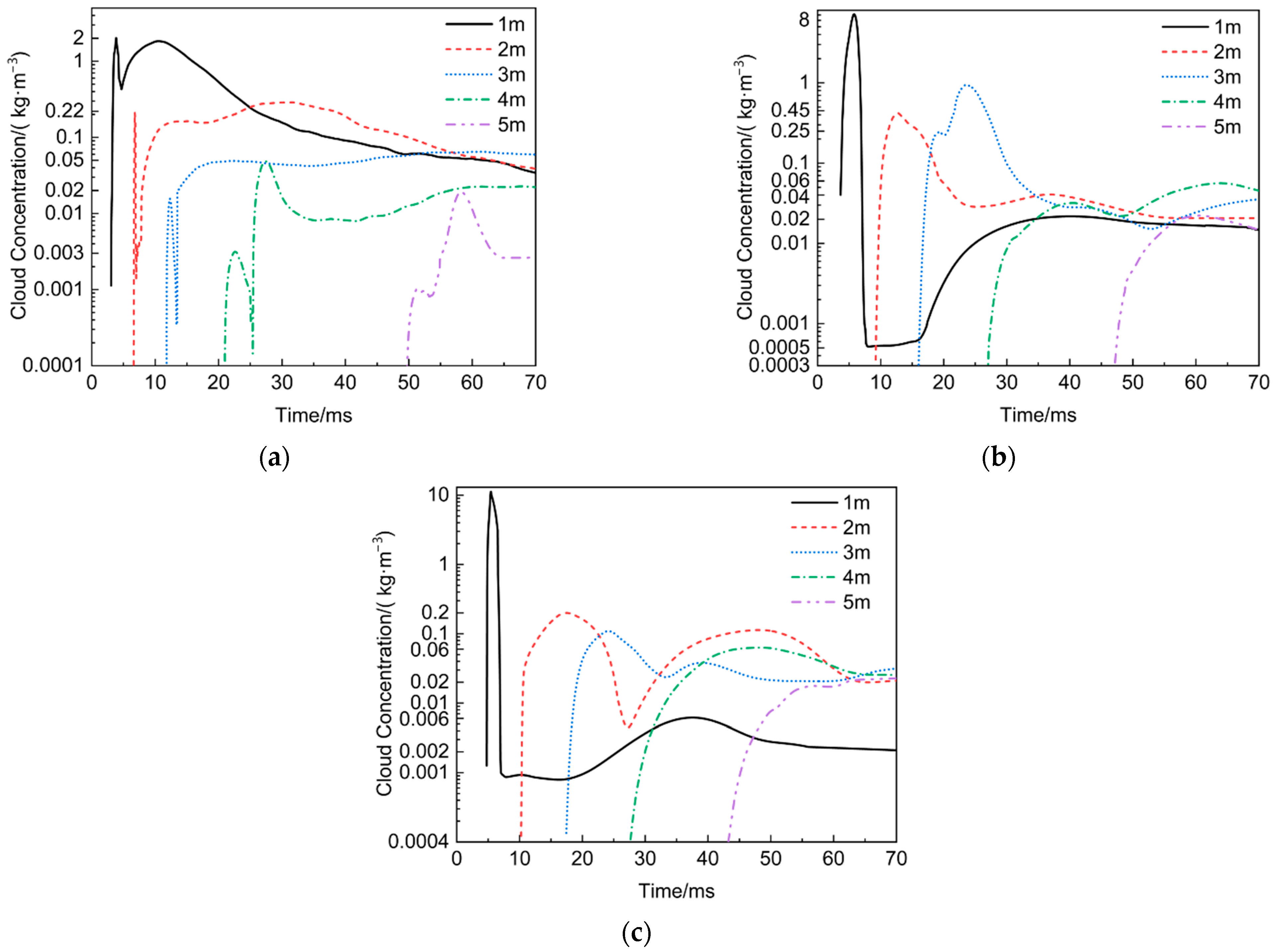
3.2.2. Cloud Concentration Distribution
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Conducting a multiscale analysis of cloud dispersal behaviors to investigate the mechanisms behind cloud growth.
- (2)
- Constructed a multiscale coupling mechanism for cloud dispersal.
- (3)
- Established an internal particle collision aggregation model for the cloud.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiba, Z.; Sono, T.J.; Mostert, F.J. Implications of fine water mist environment on the post-detonation processes of a PE4 explosive charge in a semi-confined blast chamber. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Yun, Y.; Chen, G.; Feng, M.; Li, Y. Investigation on thermokinetic suppression of ammonium polyphosphate on sucrose dust deflagration: Based on flame propagation, thermal decomposition and residue analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; LI, H. Numerical simulation over the impact of the cloud status on the detonation pressure field. J. Saf. Environ. 2013, 13, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezi, G.; Dancygier, A.N. Numerical study of velocity distribution of fragments caused by explosion of a cylindrical cased charge. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Study on concentration distribution and detonation characteristics for non-axisymmetric fuel dispersal. Def. Technol. 2023, 31, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, C.H.; Li, J.P. Influence of shell structure on dispersing velocity of fuel-air mixture. Acta Armamentarii 2017, 38, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, D.; Gregoire, Y.; Petel, O.; Goroshin, S.; Zhang, F. Particle Jet Formation during Explosive Dispersal. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 91109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. A Whole Explosive Dispersion Process Prediction Model for Fuel Clouds. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2020, 45, 950–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.F.; Yin, J.T.; He, C.; Liu, Y. Effect of Shell Shape on Dispersal Cloud Size of the FAE. J. North Univ. China 2018, 39, 672–676+701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Jia, B.; Shi, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S. Fuel Movement Characteristics of Cone-Shaped FAE Device at the Initial Stage of Spreading. Explos. Mater. 2021, 50, 30–34+39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.R. Near-Field Dispersal Modeling for Liquid Fuel-Air Explosives; Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM): Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.W. Far-Field Dispersal Modeling for Fuel-Air-Explosive Devices; Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM): Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Apparao, A.; Rao, C.R.; Tewari, S.P. Studies on formation of unconfined detonable vapor cloud using explosive means. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, X. Numerical study on the dynamic fracture of explosively driven cylindrical shells. Def. Technol. 2022, 27, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qiang, H.; Miao, G.; Gao, W. Numerical simulation of fuel dispersal into cloud and its combustion and explosion with smoothed discrete particle hydrodynamics. Acta Phys. Sin. 2015, 64, 110202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fostiropoulos, S.; Strotos, G.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Gavaises, M. Numerical investigation of heavy fuel oil droplet breakup enhancement with water emulsions. Fuel 2020, 278, 118381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, R.C.; Zhang, F. Jetting instability mechanisms of particles from explosive dispersal. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 500, 152012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, X.; Ren, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yan, X. The mechanism of liquid dispersing from a cylinder driven by central dynamic shock loading. Def. Technol. 2021, 17, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Du, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q. Flame behavior, shock wave, and instantaneous thermal field generated by unconfined vapor-liquid propylene oxide/air cloud detonation. Def. Technol. 2023, 25, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ripley, R.; Yoshinaka, A.; Findlay, C.; Anderson, J.; Rosen, B. Large-scale spray detonation and related particle jetting instability phenomenon. Shock. Waves 2014, 25, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, Q. Molecular dynamics study on the dislocation evolution mechanism of temperature effect in nano indentation of FeCoCrCuNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Technol. 2023, 39, 2299903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, C.; Du, Y. Molecular dynamics study on dynamic mechanical behaviour of FeCoCrCuNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Technol. 2023, 38, 2200660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.Y. Numerical simulation for movement of inert particles dispersed by explosive. Acta Armamentarii 2010, 31, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Bai, C. Computational Analysis of Dispersion Process of Explosively Driven Solid Fuel. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2005, 2, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Launder, B.E.; Launder, D.B. Mathematical Models of Turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 57, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, S.; Li, D. Numerical Simulation of Dispersal Process of Solid-liquid Mixed Fuel. Acta A Rmamenta RII 2014, 35, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samirant, M.; Smeets, G.; Baras, C.; Royer, H.; Oudin, L.R. Dynamic Measure in Combustible and Detonable Aerosols. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1989, 14, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Russo, P.; Sanchirico, R.; Di Benedetto, A. CFD simulations of dust dispersion in the 20 L vessel: Effect of nominal dust concentration. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 27, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Song, X.; Li, B. Calculation of Fuel Cloud Radius Based on Dimensional Analysis. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2021, 42, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, Q. Study on concentration and turbulence of solid-liquid FAE in dispersal process. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, E.; Li, J. Predictive Model for Concentration Distribution of Explosive Dispersal. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2085–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Density /(kg·m−3) | Tensile Strength /MPa | Bulk Sound Velocity /(m·s−3) | Viscosity Coefficient /(Pa·s) | Initial Pressure /MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shell | 7800 | 235 | - | - | - |
| Cloud material | 1952 | 0.1 | - | 0.01 | - |
| Air | 1.225 | - | - | 1.8 × 10−5 | 0.1 |
| Minimum Mesh Size /mm | Mesh Divergence Rate | Maximum Mesh Size /mm | Total Radius of Calculated Area /mm | Maximum Number of Meshes | Time Step /ms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The divergent mesh | 3 | 1.05 | 100 | 10,000 | 34,170 | 0.1 |
| The uniform mesh | 3 | 1 | 3 | 10,000 | 69,367 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Li, Q.; Jiang, C.; Du, Y. Study on Multi-Scale Cloud Growth Characteristics of Frustoconical Dispersal Devices. Processes 2024, 12, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071316
Zhou W, Li Q, Jiang C, Du Y. Study on Multi-Scale Cloud Growth Characteristics of Frustoconical Dispersal Devices. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071316
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Weizhi, Qiang Li, Chunlan Jiang, and Ye Du. 2024. "Study on Multi-Scale Cloud Growth Characteristics of Frustoconical Dispersal Devices" Processes 12, no. 7: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071316
APA StyleZhou, W., Li, Q., Jiang, C., & Du, Y. (2024). Study on Multi-Scale Cloud Growth Characteristics of Frustoconical Dispersal Devices. Processes, 12(7), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071316






