Abstract
Scheduling and optimization have a central place in the research area of computing because it is increasingly important to achieve fully automated production processes to adjust manufacturing systems to the requirements of Industry 4.0. In this paper, we demonstrate how an automated wet-etch scheduling problem for the semiconductor industry can be solved by constraint answer set programming (CASP) and its solver called clingcon. A successful solution to this problem is achieved, and we found that for all tested problems, CASP is faster and obtains smaller makespan values for seven of the eight problems tested than the solutions based on mixed integer linear programming and constraint paradigms. The considered scheduling problem includes a robot for lot transfers between baths. CASP is a hybrid approach in automated reasoning that combines different research areas such as answer set programming, constraint processing, and Satisfiability Modulo Theories. For a long time, exact methods such as constraint programming have displayed difficulties in solving real large-scale problem instances. Currently, the performance of state-of-the-art constraint solvers is comparatively better than a decade ago, and some complex combinatorial problems can be better solved. These theoretical and technical achievements open new horizons for declarative programming applications such as logistics.
1. Introduction
Real-time data generated at the shop-floor level and data derived from interconnected internet applications represent a high volume (many terabytes daily). In addition, these data have a rapid rate of change and come from a broad range of sources, meaning that some data would be structured, and others would be unstructured [1]. Although industrial production is a well-controlled process, the enormous amount of daily generated data makes it difficult to make decisions based on unstructured data. In addition, big data are characterized by a high volume, high velocity, and/or high variety of information assets that require new forms of processing to enable enhanced decision-making, insight discovery, and process optimization. Therefore, many industries are looking for semantic solutions in production process modeling. The advantage of the semantic approach is that data structuring to abstract entities is easier for humans to digest, guaranteeing correctness and accuracy in decision-making. Semantic data and reasoning are required, especially because intelligent behavior is expected [2,3]. To fill the gap in semantic data, many authors are proposing a methodology based on ontologies and reasoning for modeling a smart factory to provide self-organization, self-learning, and self-adaptation as well as the use of formal languages and mature reasoning that contributes to the fulfillment of Industry 4.0 [4,5].
Following that order of ideas, this study explores the applicability of methodologies and inference engines based on non-monotonic logic for solving scheduling and optimization problems in manufacturing systems. The use of this approach is justified because Industry 4.0 tends to the necessity to use semantic solutions to pass from the perspective of big data to knowledge. This transition is necessary to automate manufacturing systems. Thus, using an approach based on non-monotonic reasoning will facilitate the scheduler integration into other applications based on semantics, such as the planner and the software for context awareness.
Given the actual increasingly growing need to manufacture chips, it is obvious that it is important to dedicate efforts to solve some of the problems arising in the industry with more advanced technology [6]. One of the most important steps in the semiconductor manufacturing industry is the process of wet-etching wherein the circuits are printed on wafers [7,8]. This process is performed in an automated cell with one or more robots integrated to move lots between the machines. This problem is known as the automated wet-etch scheduling problem (AWSP or AWS problem). This problem has not been sufficiently studied, and the published results reveal that optimal solutions are not always found, and the efficiency can be improved. Taking into consideration the aspects before, it was decided to focus this research on how to solve the AWS problem with a robot problem using an approach based on Artificial Intelligence, called constraint answer set programming (CASP). The chosen problem corresponds to one of the main steps of the production in semiconductor manufacturing systems (SMSs), the scheduling of one manufacturing cell and its robot: the automated wet-etch.
As a result of this research, we report a successful optimal or near-optimal solution for the AWS problem of an SMS. This application includes a robot for lot transportation between the baths of the AWS-SMS. According to Crama and Van de Klundert [9], a robotic flow-shop such as the AWS is equivalent to a cluster tool, and both belong to the class of NP-complete problems.
The problem is solved using a hybrid approach based on answer set programming (ASP) and constraint programming (CP) [10,11,12,13,14]. This hybrid approach is known as constraint answer set programming (CASP). ASP is a declarative language for knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR), and its theoretical fundamentals are based on non-monotonic reasoning (NMR). ASP has been used to solve combinatorial knowledge-based problems in many different areas. Among the most outstanding applications are the decision-making system of a spacecraft [15], planning for the generation of equipment in a shipyard [16], phylogenetic systems [17], autonomous vehicles in Car Assembly [18], rescheduling for an operating room [19], diagnosis [20], and planning [21].
Unfortunately, classical ASP results are inconvenient for applications with large domains, such as most scheduling problems. The ASP limitation stems from the solving process, which is divided into two stages: grounding and solving. In the grounding stage, all variables are substituted by the constants of their respective domains. However, the grounding stage for large domains constitutes a bottleneck in the ASP solving process, because it can take an extremely long amount of time or, worse yet, turn the problem into an untreatable one. Therefore, CASP results in a more advantageous approach to the solution of the problem because CASP integrates ASP with constraint processing. Moreover, CASP was designed to model and solve constraints over large and even infinite domains through constraint solver systems specifically designed for that purpose [22]. Some of these solvers are clingcon [23] and EZCSP [24]. For a more detailed analysis of constraint solvers based on Satisfiability Modulo Theory (SMT) and ASP, see the investigation about this topic by Lierler et al. [25].
In this application, the scheduler was encoded in CASP, and the solutions were obtained using the solver clingcon 2.0.3 [26]. At this point, it is important to clarify that even though the original objective was to test the solution with data from a real company, this was not possible given the confidentiality politics of this type of business. Consequently, the alternative was to use a set of artificial data. For these purposes, the artificially created and published data by Bhushan and Karimi [27] were selected.
The contribution of this study is twofold. First, we report the successful application of a novel methodology and technology to solve a real problem occurring in a high-technology industry with an expensive process. Second, we show how a hybrid approach based on the CASP results is more adequate to treat problems with large domains, such as most scheduling problems in the industry. From the viewpoint of semiconductor manufacturing practice, the proposed solution in this paper provides an efficient way to obtain an optimized or near-optimized schedule for an AWS driven by a robot.
The proposed method was proven to be efficient and robust after several experiments in which it was tested with different configurations and input data.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 is devoted to a literature review related to both the main topic of this research, automated wet scheduling, and the literature regarding the methodologies applied to the solution of the actual research problem. Section 3 is dedicated to establishing the research motivation and formal description of the AWS problem. Section 4 shows the results of the experiments and compares and discusses these results with those obtained by other authors using other methodologies. Some concluding remarks complete the paper in Section 5.
2. Literature Review
Scheduling semiconductor manufacturing operations is a complicated problem because of various constraints such as sequence-dependent setup times, alternative machines, reentrancy, and complex product flows. SMSs have two more important characteristics: (a) the use of multi-clusters in the production process and (b) the inherent dynamism of its manufacturing due to its highly stochastic environment, where the occurrence of random events such as machine failures, the arrival of new urgent jobs, and the modification of a job during the execution time is common.
Even though an extensive amount of the scientific literature exists about typical problems occurring in an SMS, the purpose of this study is not to perform an extensive and detailed analysis of the whole literature in existence about it. Instead, a brief review of representative scheduling problems in SMSs is conducted, and then we focus our interest on reviewing the state of the art regarding the topic of the automated wet-etch scheduling problem.
2.1. Automated Wet-Etch Scheduling Problem
A recent paper on this topic is that by Ahn et al. [28], who solved a scheduling and optimization problem related to chip semiconductor selection, known as the die attach process. This process was formulated as a typical pick-and-place (PAP) problem. PAP is a well-known NP-hard problem that basically consists of finding the shortest path to pick good dies and place them in the strip. The problem’s solution was approached with a Q-learning method using two agents to find the shortest path.
Another typical problem in semiconductor manufacturing is the use of multi-cluster tools as wafer fabrication equipment. Zhu et al. [29] analyzed the scheduling of these tools. They focused their research on scheduling the close-down process subject to wafer residency constraints. Generally, such processes are caused by wafer lot switches as well as preventive and emergency maintenance. The nature of these processes is dynamic and noncyclic. These researchers proposed a linear program to determine the robot’s waiting time before unloading the wafers. In their study, they considered a single-arm process for two cluster tools and found that whenever there is always a feasible schedule for the steady state, it is possible to obtain an optimal solution for the close-down process.
Meanwhile, a typical characteristic of semiconductor production is re-entry. There is not much research about scheduling problems considering this complexity, but Li and Ma’s [30] study addressed not only a re-entrant job-shop scheduling problem but also integrated preventive maintenance planning into the scheduling. This optimization problem was solved using a hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm. They used simulation experiments to evaluate the proposed model. The results of the experiment showed that their model works better than other independent decision models because they obtained a maximum completion time that is smaller than that of the non-integrative models.
An example of dynamic scheduling in an SMS can be attributed to Ma et al. [31]. This study shows the development of a composite dispatching rule based on heuristic rules. The composite rule was obtained by exploring various states of a production line, such as the machine status and queue size. Dynamic scheduling was obtained using the support vector regression (SVR) approach. SVR obtained dynamic scheduling knowledge from optimized scheduling samples. Then, it dynamically obtained and used a composite dispatching rule to optimize the production performance.
Regarding surveys about case studies in an SMS, we can refer to Fuchigami and Rangel [32]. Other interesting papers about the surveys, challenges, and future directions of SMSs can be found in the papers by Mönch et al. [33], García-Mata et al. [34], Dequeant et al. [35], and Khakifirooz et al. [36]. A more recent study on the methodologies and techniques applied to solve SMSs has been given by Estrada-Jiménez et al. and Suvra-Das [5,37]. Unlike other older surveys, this review focuses on self-organization in smart manufacturing. The results show that at least 65% of the papers reviewed are focused on infrastructure development. This means that there exist various opportunities to apply methodologies and technologies based on Artificial Intelligence and that are indispensable to raise the abstraction level and are possible to take informed and/or automated decisions. That is especially true for complex systems such as SMSs.
Now, we describe the wafer-etching process and analyze the literature on the AWS problem. The most intensive capital of a modern SMS is wafer production, which consists of four phases and is also a key part of the production process. Wafer fabrication is performed by applying successive layers of silicone or gallium arsenide and circuit patterns of metal and wafer material. To complete the wafer fabrication, each layer requires a similar set of unit processes, such as deposition, photolithography, development, ion implantation, diffusion, oxidation, and etching. The scheduling problem for AWS and a transfer robot is related to two research areas: The first one focuses on the scheduling optimization problem for the transfer robot. The robot handles the lot transfer through machines. One generalization of this problem is known as the Hoist Scheduling Problem (HSP), and it is one of the most studied problems in Automated Manufacturing Systems (AMSs) because it represents a common problem arising in many automated systems in the industry [38]. HSPs are commonly found in automated electroplating lines, and numerous studies have been published about it. For example, Feng et al. [39] solved the Dynamic Hoist Scheduling Problem (DHSP) for multi-capacity re-entrant machines with a single hoist. This problem was approached with a method based on mixed integer programming (MIP). Meanwhile, Yan et al. [40] solved a similar problem for re-entrant workstations, but their optimization objective was dual, specifically reducing the cycle time and material handling cost simultaneously. To solve the optimization problem, the authors proposed a hybrid discrete differential evolution (DDE) algorithm.
The second area involved in this research is precisely the AWS scheduling problem itself. However, since this process requires at least one robot for lot transference, most research includes robot scheduling in the solution. This optimization problem has been solved by numerous methods that can be grouped into two categories: (a) specific algorithms and (b) generic methods. Initial attempts to obtain an optimized solution to the AWS scheduling problem can be traced back to Bhushan and Karimi [41], who used the MILP method. They reported a near-optimum two-step strategy capable of solving moderately sized problems with a ranking of four baths and 14 jobs. Karimi et al. [42] improved the solution by redefining an integer variable as a binary variable. Other authors reporting an optimized solution to the AWS problem with the exact MILP method are Aguirre et al. [43], who presented three methods for modeling and solving this problem. In this case, the solution included multiple robots. For smaller-sized cases, the authors developed a schedule that simultaneously generates job/bath assignments and schedules the transfer operations for the robot. Meanwhile, for medium-sized problems, a sequential method was proposed, where production activities were first scheduled, followed by robot operations for lot transference. In addition, they presented some ideas for solving the problem with multiple robots.
The most popular AI methods used for the AWS scheduling problem are of three classes: (a) metaheuristics, such as genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization, evolutionary algorithms, ant colony optimization, Tabu Search (TS), and Simulated Annealing (SA); (b) statistics: Monte Carlo methods and neural networks in different variants; and (c) rule-based methods: CP, ASP, and CASP [44].
Among the research reporting approaches based on AI methods to solve the AWS scheduling problem, one can mention the paper by Geiger et al. [45], which was one of the first cases to include a robot for lot transferences. The metaheuristic TS with two heuristics was jointly used to minimize the makespan Cmax: the profile fitting (PF) heuristic and the Nawaz–Enscore–Ham (NEH) heuristic. The authors reported that better results were achieved using NEH-TS. Later, Bhushan and Karimi [27] proposed a solution based on TS and SA combined with a new specific algorithm for the same problem.
Meanwhile, Rotondo et al. proposed an optimization model for sequencing batches of wafers outside a wet-etch tool and the scheduling of tool internal handler moves [27]. Unlike other authors, these studies address the application of a real manufacturing plant, where wet-etch tools’ internal mechanisms are not easy to modify because they are established by the tool vendor. Because of these limitations, they analyzed batch sequencing and scheduling as separate problems. The sequencing module combines an exact optimization approach based on an efficient permutation concept and a heuristic optimization approach based on GA.
However, only a few researchers have reported optimized solutions to the AWS scheduling problem using a combinatorial approach. One of them is Zeballos et al. [46] who reported a successful solution with CP combined with different research strategies. These authors reported experimental results with up to three robots, obtaining better results than those obtained by the MILP methodology combined with the Guided Variable Domain Reduction (GVDR) strategy. Similarly, Novas and Henning [47] reported another successful solution for the same problem using the CP methodology; however, they generalized the problem by implementing an innovative rolling horizon methodology that considers empty robot movements. According to Novas and Henning, robot unload times must be considered because they greatly affect the resultant schedule. Most recently, Hegyháti et al. [48] reported an optimal solution to an AWS scheduling problem with one and two robots using a different combinatorial approach. Specifically, they used an S-graph framework to schedule a multipurpose batch, proposing an extension to this framework to solve the AWS scheduling problem. The authors of [48] ultimately tested the implementation with different numbers of baths, jobs, and one and two robots. The maximum number of baths and jobs were six and four, respectively. Although the solution was tested with one and two robots, satisfactory results were obtained with only one robot because the second robot negatively affected the processing time.
2.2. ASP and CASP
Despite the enormous achievements of automated reasoners based on classical logic or monotonic logic, these reasoners are not expressive or practical enough to deal with incomplete and contradictory knowledge. Therefore, for more than 70 years, a way to deal with incomplete knowledge has been studied. In the 1980s, two successful semantic solutions based on non-monotonic reasoning were developed: the stable model semantic (SMS) [10] and well-founded semantics (WFS) [49]. These semantics are based on several types of non-monotonic logic, such as default logic, epistemic logic, and circumscription logic. In addition, both semantics have numerous extensions.
One of the most relevant features of the SME and WFS is their facility to design logical programs with the rule “denial by default”, also called negation as failure (NAF) or negation by default. The presence of NAF provides natural support to commonsense reasoning because it allows for the expression of exceptions, restrictions, and making intelligent deductions in the presence of incomplete knowledge.
The semantics of the stable model is based on the idea of accepting multiple minimal models (answer sets) as a description of the meaning of a program, unlike classical logic, in which a single model is accepted. These theoretical results led to the development of a novel paradigm of programming, commonly referred to as answer set programming (ASP) [50,51,52,53]. ASP is a paradigm of computation, in which logical theories (Horn clauses with negation by default) serve as specifications, and the solutions to problems are represented by a collection of models. ASP is a completely declarative language that has been designed to solve combinatorial problems. The most outstanding feature of ASP is that it allows one to easily represent default clauses. This characteristic allows for the representation and reasoning with debatable knowledge. ASP programs are not algorithms that describe how to solve a problem; a program is a formal description of the problem. The solution is completely found by the solver.
Another important point to consider is that nowadays, there are several inference machines for ASP. The oldest one is smodels, but the most recent ones, such as clasp, have [54] incorporated techniques from SAT and CSP technologies.
Answer set programs are defined by V = (P, D), where P is a set of predicates, and D is a set of facts or the domain of the problem. Predicates in P have an arity ≥0.
A problem can be encoded as a set of facts, rules, and constraints that describes the (candidate) solutions. An ASP program is a collection of rules of the form
where each and each are atoms, and n, m, k ≥ 0. The left- and right-hand sides of a clause are called the head and body, respectively. The head of a rule is a positive literal, and its body comprises literals (a literal is an atom a or its negation, denoted by not a). A rule without a body is a fact. A rule without a head is a constraint. In addition, the rules can be positive (n > 0), negative (m > 0), or both (n > 0 and m > 0). The symbol not represents default negation, also known as negation as failure, and it has a different meaning than the classical no symbol. For example, in the above general definition of an ASP rule, not b means that there is no evidence that b is true, but it does not mean that b is false. The term not b represents a belief, not a binary value true or false. For a clear and wider explanation about what ASP is, the papers by Januhen and Niemelä [53] and Lifschitz [54] are recommended.
A program is a set of safe rules. A rule is safe when every constraint variable occurring in a rule has been replaced by a term. The process of replacing the variables by terms is known as grounding, and it is conducted before the program is sent to the solver. If P is a ground positive program, meaning that the negative rules or section remains after the reduction operator has been applied. A unique answer set is defined as the smallest set of literals constructed from the atoms occurring in program P. The last definition can be extended to any ground program P containing negation by considering the reduct of P with respect to a set of atoms obtained by the Gelfond and Lifshitz’s operator [10,54,55], which is given by
In some ASP systems, such as clingo, language extensions such as choice rules, conditional choice rules, and aggregates are supported. Choice rules have the following form: Choice rules are used to describe a set of “potential solutions”.
Conditional rules are written as . For both rules, l and u ≥ 0 specify the lower and upper bounds, respectively; for the conditional rule, . Meanwhile, syntaxis aggregates have the form α {w1 : a1, …, wm : am, wm+1 : am+1, …, wn : an} ≺ k, where a represents a function mapping multisets Z to Z ∪ {+∞, −∞}, ≺ stands for the relation between Z ∪ {+∞, −∞} and Z, , are atoms, and are integers. Aggregates were designed to provide a general way to obtain a single value from a collection of input values. There are some other aggregates. In this solution, we used the count and minimum aggregates.
Furthermore, non-monotonic logic and ASP are very active and dynamic areas, where language extensions and better techniques for the development of solvers are constantly being proposed [23,56,57].
Meanwhile, there is currently a trend towards solving difficult problems through hybrid approaches, combining algorithms and systems from different AI subfields. The Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMTs) are a well-known example [58,59,60]. The objective of SMT is to satisfy the logical formulas of one or more different theories. Unfortunately, SMT problems belong to a very high complexity class. Hence, it is impossible to build an inference machine that can arbitrarily solve any SMT problem.
CASP is a recent and promising research area that integrates ASP and CP methodologies. It follows the SMT solving approach and combines the clasp ASP solver with the gecode CP. Additionally, CASP supports the modeling language gringo, which is the ASP grounder [12,13,14]. CASP improved the capacity of ASP to deal with large domains that occur in many practical problems such as scheduling and planning. For such domains, the grounding process is so time-consuming that it turns the problem into an untreatable one. However, CASP uses a different mechanism to model constraints over large domains based on non-Boolean constraints from the CP area, combining a simple modeling language with high performance [12,13,22].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Production Model
SMSs are among the largest and most high-tech industries in the world. This type of factory is a very capital-intensive business. The SMS process comprises four phases: wafer fabrication, wafer probe, assembly, and testing. One of the most complex operations is wet-etching, which is usually performed in a set of AWSs, and it is also the most intensive capital of the production process. The production processes are very complex and require up to 700 single processing steps and up to 3 months to produce. Typically, the production process comprises dozens of process flows, each of which requires more than 100 machines [33]. Many production models co-exist in an SMS, such as job-shop, flow-shop, and parallel machines. It is also necessary to deal with processes that can require batching or serial production, sequence-dependent setup times, tight due dates, no-wait operations, the reworking of a part of a wafer, and even more complex developments [61].
The AWS manufacturing process is carried out in batches and consists of the following processes and operations:
- (a)
- The wafer is covered with a thin uniform layer of silicon oxide (SiO2) or gallium arsenide (GaAs).
- (b)
- Portions of the wafer are selected and marked to form the circuit configuration (photolithography or photo-masking).
- (c)
- Etching is applied; it is a key step in the manufacturing of the wafer. This process is performed by one or more highly automated stations:
- (d)
- At these stations, the excess film of SiO2 or AsGa is eliminated in a series of chemical and deionizing baths.
- (e)
- The batches of AWS wafers are all of the same type and come from previous processing.
- (f)
- The lots are subject to processing in chemical and water baths arranged alternatively.
- (g)
- The batches are transferred by one or more robots between the baths. In the case study of this research, only one robot is considered for material transfer. Lot transference is performed by a robot on the order of milliseconds and can be different for each pair of baths.
- (h)
- The chemical baths follow a zero-wait storage policy and can never be used as temporal buffering (Zero Wait/No Intermediate Storage, ZW/NIS) because chemical overexposure can damage the wafers.
- (i)
- The water baths are used for storage (LS).
- (j)
- The processing time for each lot depends on the lot and bath.
- (k)
- In each bath, one lot can only be processed at a time.
- (l)
- It is assumed that the baths and the robot are never out of order.
This study reports a solution to the AWS scheduling problem using one robot. Once the schedule is obtained, an optimized solution is searched with the minimum makespan as the objective function. According to the production process, all jobs are processed sequentially on all baths, always starting at the first machine and ending at the last one. The jobs are uninterruptible.
3.2. Problem Definition
ASP is a language with many remarkable characteristics that make it suitable for solving a myriad of complex problems. However, there is one characteristic that distinguishes it: the ability to represent problems at an abstraction level, which is similar to a mathematical definition. Consequently, in this section, the problem encoding closely follows a formal definition of the problem.
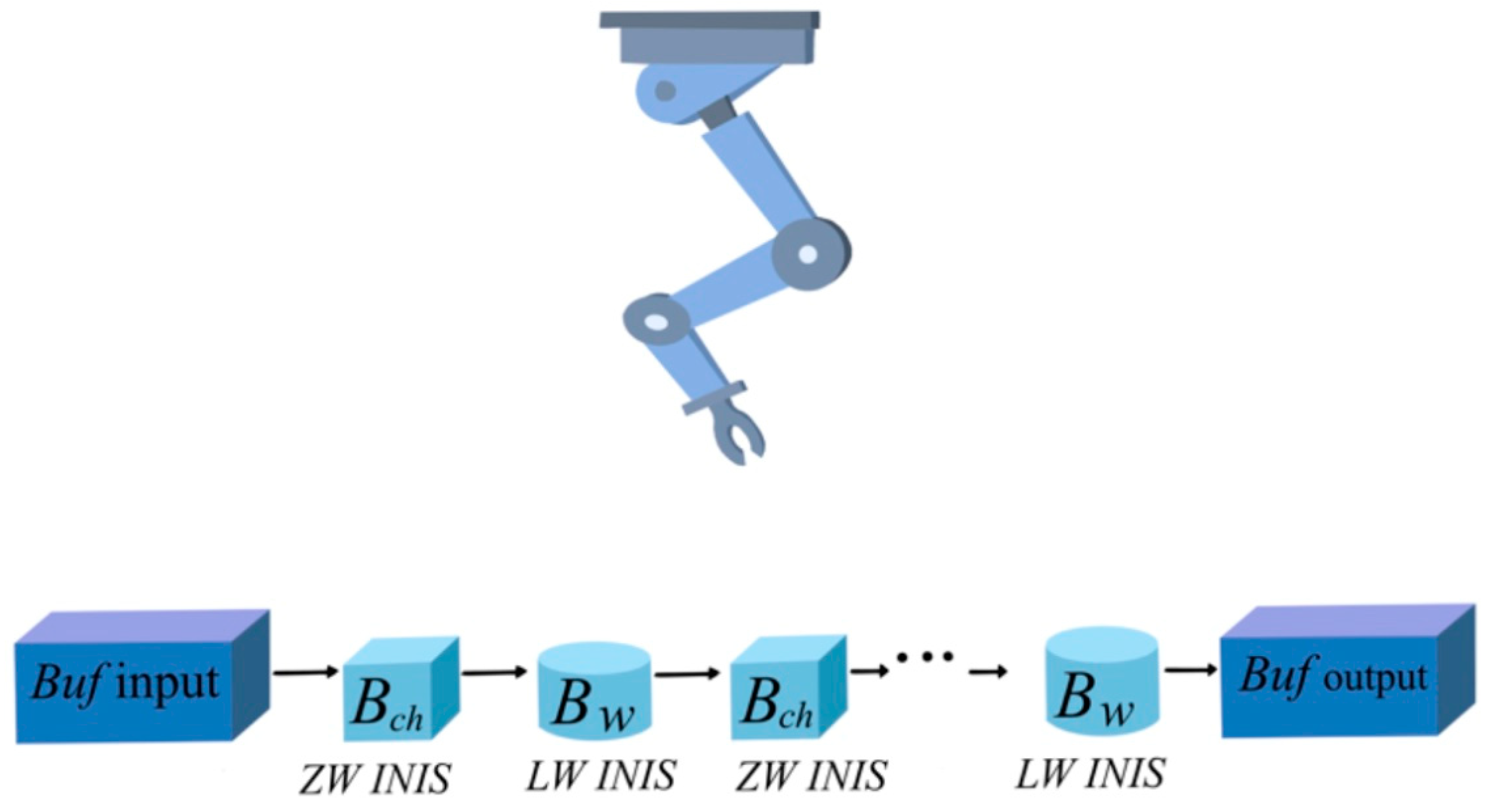
Since the AWS production process must fulfill strict constraints, known as ZW and Local Storage (LS) policies, modeling the AWS problem can be generalized to a serial flow-shop Multiproduct process with mixed intermediate storage policies (MIS). Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of a linear AWS with one robot.
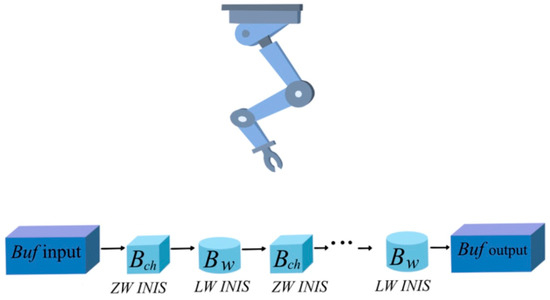
Figure 1.
Wafer-etching process with alternating chemical and water baths and one robot for lot transference.
3.3. Notations and Nomenclature
3.3.1. Indexes
j—lot;
b—bath;
r—robot;
s—start time;
c—completion time.
3.3.2. Sets
J—set of lots or job wafers with j ∈ J = {1, …, |J| − 1}.
T—set of discrete time slots t ∈ T = {0, …, |T| − 1}, where T is the scheduling period.
B—set of k renewable resources (k is the pre-established number of units of a resource that are available for each period of the planning horizon T). In this case, B is the set of baths, and each b ∈ B. The arrangement of the baths is alternating, starting with a chemical bath, followed by a water bath, where B = {Bch, Bw}; Bch = {B1, B3, B5, …, BK−1}; Bw = {B2, B4, B6,…, BK}; Bch ∩ Bw = ∅; Bch ∪ Bw = B.
R—is the set of robots for the transference of the jobs among baths r∈ R = {1, …, |R| − 1}. In this solution, only one robot was used.
Each job j has several properties:
The processing of job j in bath b is uninterruptible.
Usually, the processing times of each job j and each bath are different. The job’s duration identifies the time of residence of job j in bath b.
A solution contains the following assignments for each job j and each bath b:
- -
- the scheduled start time slot for j processing in bath b;
- -
- the scheduled completion time for j processing in bath b;
- -
- the bath assigned to job j;
- -
- the scheduled start time slot for robot r to transfer the job j from bath to bath
- -
- the scheduled completion time slot for robot r to finish the job transfer from bath to bath
- -
- the deadline for finishing the processing of all the jobs.
3.4. Constraints and Function Definitions
A formal description of this problem reduces it to a series of constraints that will be discussed later. First, a formal definition of a job is developed as follows: A job j is a pair <machines, dur>, where machines is a set of baths in which the jobs are processed, and dur is the processing time required to finish each job in each bath. J is the set of jobs and is defined by the pair <Λ, ORDER>, where Λ is the set of jobs and ORDER is a directed acyclic graph resulting from the Λ elements. Intuitively, ORDER describes the order in which the jobs must be processed. Each arc indicates that the processing of job must precede the processing of job . Given that the problem being solved is a flow-shop problem, the jobs must be sequentially processed, and consequently, the processing of job must be completed before job begins its processing. The constraints considered in the problem modeling are described in the following definitions.
Definition 1.
The interval between the start and completion of a job must match the job’s duration for each bath:
Definition 2.
The interval between the start and completion of a robot’s job transference must match the established robot’s duration transference among the baths:
Definition 3.
Some job must start in the first bath at time one.
Definition 4.
To detect an overlap among different jobs in the same bath, the following is considered:
Definition 5.
It is necessary to detect whether a job starts processing in the next bath before it finishes its processing in the actual bath and whether the batch has also been completely transferred to the next bath:
Definition 6.
It is also necessary to detect situations in which there is an overlap of the same job in continuous baths:
Definition 7.
To fulfill the constraint that jobs finishing in a chemical bath (chemical baths are odd) must immediately be transferred by the robot to the next bath, the following is considered. In the other cases, this solution must be deleted:
Definition 8.
This constraint deals with the case where a job processed in a chemical bath does not start its processing in the next bath immediately after finishing its processing in the chemical bath and finishes its transfer to the next water bath.
Definition 9.
There are two rules to detect when a robot is out of phase to perform the transference: one is to detect an out of phase in the chemical baths, and the second is to detect an out of phase for water baths. Here, we define the first one, which applies to a robot transfer from a chemical bath to a water bath:
Definition 10.
The second rule detects when the robot is out of phase, going from a water bath to a chemical bath:
Definition 11.
The next constraint was designed to detect an overlap among the robot transference from a water bath to the next one, and the robot transfer appears to overlap with another robot transfer starting in another bath that is not necessarily continuous:
Definition 12.
Unlike the previous definition, this constraint was designed to detect an overlap among the robot transfers from a chemical bath to a water bath, and it appears that the robot starts transferring a lot from a different one that is not the next one:
Definition 13.
In addition, there are two other cases where it is possible that there exists a third case of overlap in the use of the robot. In this last case, an overlap in the use of a robot transfer occurs among different jobs. This constraint can be expressed as follows:
Definition 14.
Another case related to overlap occurs when the robot starts transferring the lot before its processing in some bath has finished and additionally, there is an overlap among a different transference with the same robot but from the next bath:
Definition 15.
This constraint was designed to detect jobs that will finish after the deadline:
Definition 16.
There are cases where the robot starts to transfer the lot before this lot finishes its processing in the actual bath, and there is not enough time for the robot to finish the transfer before the deadline:
3.5. Encoding the Problem in CASP
As previously stated, the main objective of this research is to explore ASP capabilities to solve large problems, e.g., scheduling problems. Therefore, the first intent was to use plain ASP to encode the problem. The solver chosen was clingo 4.4. However, the set of combinations for these types of problems is extremely large. For example, in scheduling and planning problems, it is necessary to include time variables per time unit and for each variable combination to create the schedule or plan. Consequently, the bottleneck generated during the grounding step was the main obstacle to solving the complete problem, and it was only possible to obtain a partial solution of the problem with four jobs and four baths. Problems with input data beyond this size were untreatable using this approach. The obtained results are not outstanding considering that the problem under study is NP-hard [48]. On the other hand, the approach in CASP solvers is different and considerably reduces the computation time.
The combinatorial nature of the problem and the ASP difficulties during the grounding clearly showed that a different approach was required to solve the problem. The CASP approach was a natural selection to solve this problem because it is an extension of ASP and is capable of efficiently finding an optimal or near-optimal solution. In the next step, the problem was encoded according to the CASP extensions for ASP proposed by [12] and solved using the solver clingcon 2.0.3. The characteristics of the computer hardware used in the solution are as follows: intel i7 processor, 2.21 Ghz, 16 Gb memory, Ubuntu OS, 64 bits. For the problem in this study, it was assumed that the AWS is disposed linearly and has a single robot for batch transference (see Figure 1).
The processing times required for each job and each bath are defined for the next predicate using the following three parameters:
where j represents a job and is an integer with values in the range (1..n), b represents a bath in the range (1..k), and represents the processing times for job j in bath b. Note that the robot transfer times between the baths correspond to the predicate
where r represents the robot. In this case, only one robot was used; b represents a bath index in the range (1..k); mb, b + 1 represents the transfer time from bath b to bath b + 1.
duration(j, b, pjb)
tRobot(r, k, mb, b + 1),
The number of jobs, baths, and robots is given by the constants j, b, and r, respectively. The value ranges for each one are as follows:
bath(1..b). numBaths(b).
job(1..j). numJobs(j).
The time values were defined as global variables, with the constant deadline representing the time limit to finish all jobs.
$domain(1..deadline).
The problem was encoded conforming to the known methodology GENERATE, DEFINE and TEST. The GENERATE section is composed of two rules. One rule is used to create all combinations of the job, bath, and duration. The second rule in this section is used to generate the combinations including the jobs, baths, and processing times for the robot. It is important to clarify that in the next rules, P and P’ are variables related to the jobs, M and M’ are variables related to the baths, D and D’ are variables containing the job processing duration, and Tr and Tr’ are variables about the robot transference time for a given bath.
1{moveBatch(P, M, Tr) }1:- job(P), bath(M), tRobot(R, M, Tr).
1{do(P, M, D) }1:- job(M), bath(M), duration(P, M, D).
The combinations for the predicates moveBatch and do were transformed into global constraints using the operator distinct of clingcon as follows:
$distinct{iniJob(P, M): do(P, M, D)}.
$distinct{beginRobot(P, M): moveBatch(P, M, Tr)}.
In the DEFINE section, the problem constraint rules were implemented. The implementation in CASP of the selected constraints defined in Section 3.4 is shown next.
Rule (8) implements Definition 3. This rule is needed to ensure that in any solution, there exists one job initiating in the first bath at the first instance:
$count[iniJob(P, M) $==1: do(P, M, D): M==1] $==1.
To ensure the strict sequential processing of jobs in consecutive baths (Definition 5), this constraint is implemented in Rule (9). In this rule, the sequences do(P, M, D) and do(P, M’, D’) represent the assignment of job P to different baths M and M’, and the processing of job P in bath M precedes the processing of job P in bath M’. Also, M’ must be the bath that follows immediately after M:
badSeq(P, M, D, M’, D’):- do(P, M, D), do(P, M’, D’), moveBatch(P, M’, Tr), M’==M + 1, iniJob(P, M’) $<
(iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr).
(iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr).
A possible job overlap can be of two types: (a) jobs P and P’, where P ≠ P’ overlap in the same bath, or (b) the same job P is assigned to two different and sequential baths, M and M’, in overlapping times. The first case corresponds to Definition 4, and the second case corresponds to the Definition 6. The implementations appear in Rules (10) and (11), respectively:
overlapBJ(P, M, D, Tr, P’, D’):- tRobot(R, M, Tr), do(P, M, D), do(P’, M, D’), P != P’, iniJob(P, M) $<= iniJob(P’, M)
$and iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr $> iniJob(P’,M).
$and iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr $> iniJob(P’,M).
overlapJB(P, M, D, Tr, M’, D’):- moveBatch(P, M, Tr), do(P, M, D), do(J, M’, D’), M’==M+1,
iniJob(P, M) $<= iniJob(P, M’)
$and iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr $> iniJob(P, M’).
iniJob(P, M) $<= iniJob(P, M’)
$and iniJob(P, M) $+ D $+ Tr $> iniJob(P, M’).
The implementation of the NZW’s policy, expressed in Definition 8, consists of the following: as soon as a job P finishes processing in a chemical bath M, it must be transferred to the next bath M’, which is a water bath. If the transfer is not performed immediately, the wafer could suffer damage. This policy is implemented in Rule (12):
chemicalNZWrobot(P, M, D, Tr):- do(P, M, D), do(P, M’, D’), moveBatch(P, M, Tr), M\2 > 0, M’==M + 1,
beginRobot(P, M) $!= (iniJob(P, M) $+ D).
beginRobot(P, M) $!= (iniJob(P, M) $+ D).
In the TEST section, the heads of the previously implemented constraint rules in the DEFINE section are written as constraints in the ASP language. The constraint syntaxis in ASP are written as rules without heads semantically mean that those answer sets does not fulfill the problem constraints, and therefore, must be deleted of the solutions space. In this section, only the constraint rules related to Rules (9) to (12) are shown:
:- badSeq(P, M, D, M’, D’).
:- overlapJB(P, M, D, Tr, M’, D’).
:- overlapBJ(P, M, D, Tr, P’, D’).
:- chemicalNZWrobot(P, M, D, Tr).
Finally, makespan minimization is performed by the operator min:
$minimize{iniJob(P,Nb) $+ D $+ Tr: do(P, Nb, D)
: numBaths(Nb): moveBatch(P, M, Tr)}.
: numBaths(Nb): moveBatch(P, M, Tr)}.
Although there are many case studies in the scientific literature related to scheduling problems in SMSs, only a few have focused directly on the AWS problem. Various approaches have been attempted; however, no evidence has been found that the solution to the problem has been addressed using theories and techniques based on non-monotonic logic.
4. Results
4.1. Input Data
One main obstacle to the experiments was the access to the database of a real company. After performing an unsuccessful search for real data, a series of data was used that were artificially created and published by Bhushan and Karimi [27]. These data have also been used by other researchers, such as Zeballos et al. [46].
In this research, the solution of the AWS scheduling problem with one robot was first intended in plain ASP. The experimental results showed no solutions for more than four baths and four jobs. This unsuccessful experiment can be explained by the known grounding bottlenecks of ASP. Consequently, it was necessary to analyze and solve the problem using a hybrid approach. Specifically, the ASP extension for the selected CP was the one developed for the solver clingcon 2.0.3. This clingcon version uses the generic CP solver gecode 3.7.1 for the grounding step and clingo 3.0.4 for the solving step.
However, the direct use of these data was not possible in either ASP or CASP because they have values that belong to the set of real numbers, and ASP and CASP work exclusively with integers. To eliminate fractional values, job processing and robot transfer times were multiplied by 10. After the problem was solved, the obtained solution values were divided by ten to compare our results with those of Zeballos et al. and Bushan and Karimi [45,46].
The Design of the Experiment
For comparative purposes, this experiment was presented in a manner similar to that of Zeballos et al. [46], with only minor differences. The problem was solved on a computer with an Intel processor, Core i7CPU @ 2.21 GHz; memory 16.0 Gi.
Data contained in Table 1 and Table 2 were used to solve the problemas in the next way: Table 1 was used to solve problems P1 to P6 and P9. Data in Table 2 was used to solve Problem P7. Table 3 correspond to the robot transfer times used in all the problems. Table 4 identifies each one of the problems solved in this experiment, and the regarding results are shown in Table 5.

Table 1.
Processing times for problems P1–P6 and P9 (in seconds).

Table 2.
Processing times for problem P7 (in seconds).

Table 3.
Transference times for the robot (in seconds).

Table 4.
The identification of the solved problems.

Table 5.
The results obtained for problems P1–P7 and P9 with the hybrid CASP approach.
4.2. The Discussion of the Results
Analyzing the results of the experiments shown in Table 5 through the CASP approach, the results show that this approach is more suitable for solving problems with a huge number of combinations rather than plain ASP. With CASP, both the first and best solutions were found, except for the best solution of P6. However, with ASP, it was not possible to solve problems with more than four jobs and four baths.
Although ASP is a paradigm that has been successfully used for the solution of many complex problems involving incomplete reasoning, the experimental results obtained in this research show that ASP alone is inadequate for the solution of combinatorial optimization problems that involve a huge search space, as is the case for the AWS problem. This flaw in ASP results from the bottleneck that occurs during the grounding stage. To precisely overcome this disadvantage, some extensions such as CASP have been developed. CASP has a mechanism to enable modeling restrictions on huge domains, where these are processed in a different way than is typically conducted in ASP, thereby greatly reducing the grounding time.
To assess the quality of the obtained schedules, we compared the results obtained in this investigation with those obtained by other authors for the same AWS scheduling problem. In particular, Table 6 shows a comparison of our results obtained with the CASP/clingcon approach versus two other studies, which are as follows: (a) the results published by Zeballos et al. [46] with the CP+GVDR method and (b) the results published by Bhushan and Karimi [27] who used a MILP approach. The scheduling results, both for the baths and for the robot, are also graphically shown in Figure 2.

Table 6.
The results obtained for the AWS problem with a robot using three different approaches: MILP, CP+GVDR, and AWS + CSP (times in seconds) (a = impossible to test optimality within a time = 3600 s. NS = no solution found).
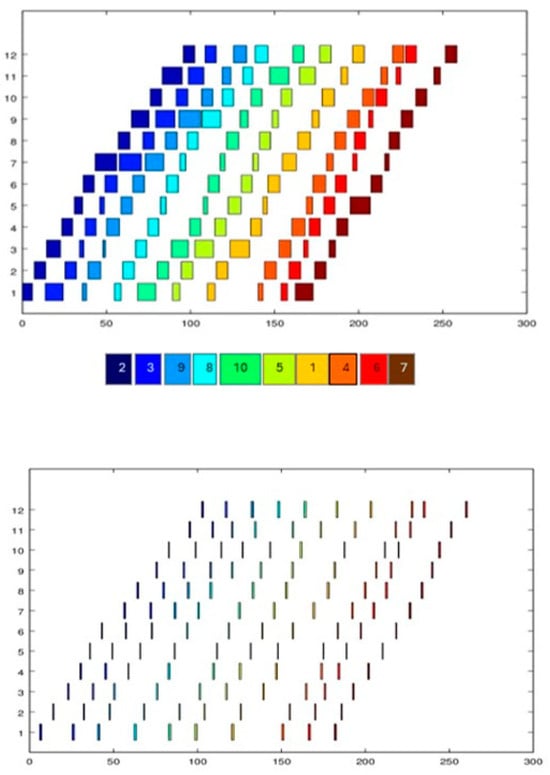
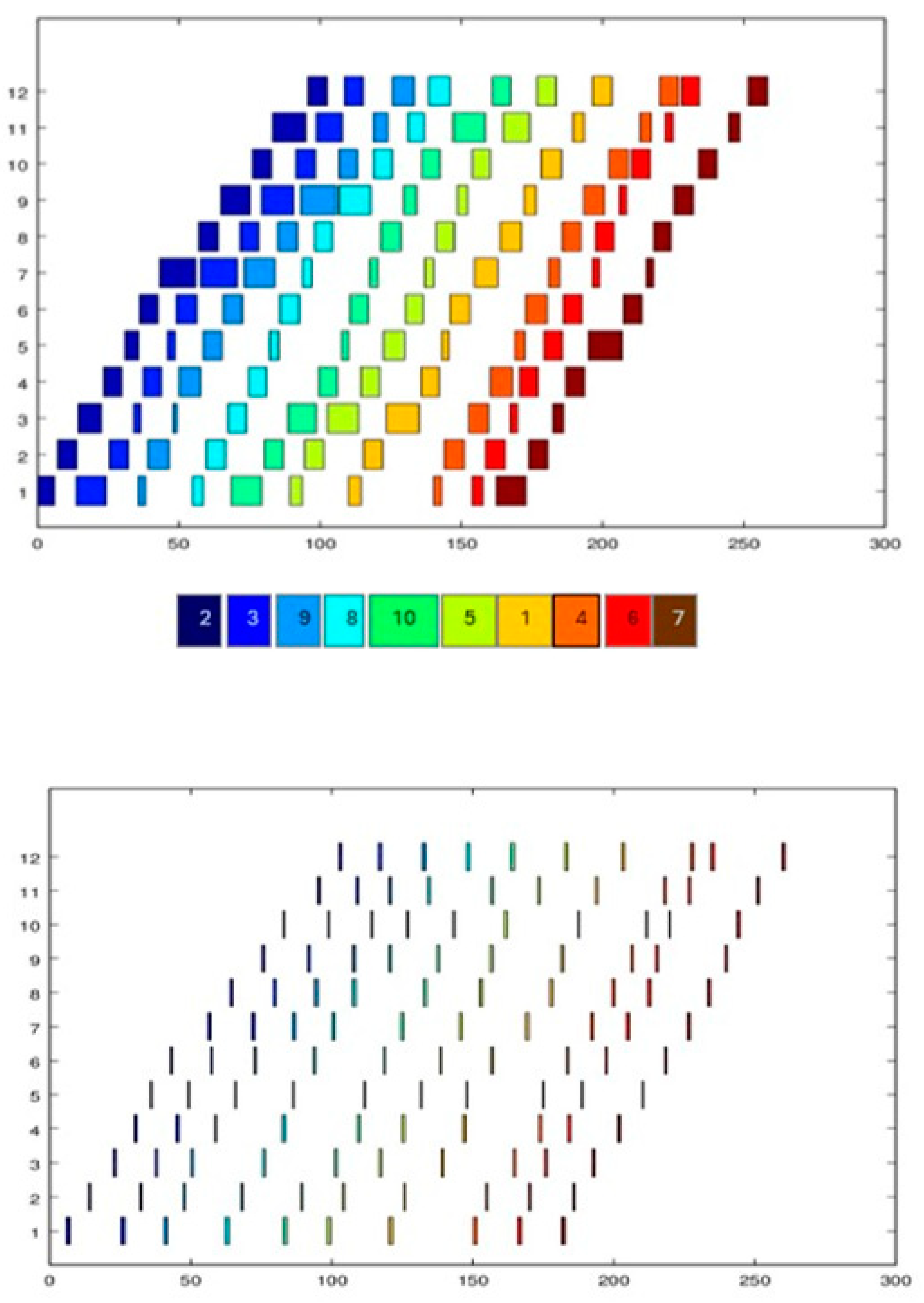
Figure 2.
Gantt graphics showing one of the best solutions for problem P9 (12 baths, 10 jobs). The superior graph corresponds to job scheduling, and the inferior graph corresponds to robot scheduling for the same problem.
Now, examining the results shown in Table 6, it can be observed that for both MILP and CP+GVDR, there are some cases in which the best makespan value cannot be obtained. Meanwhile, for CASP in all problems P1 to P9, the best solution was found efficiently. For the first solution, the minimum makespan obtained with CASP is very similar to the results obtained with CP+GVDR, but with CASP, in 75% of the cases, the makespan is better than with MILP and CP+GVDR (see the makespan values of problems P1, P3, P4, P5, and P7). However, determining the first solution, the efficiency of CP+GVDR is better than CASP, because in 75% of the cases, CP+GVDR has better times than CASP, and for MILP, only 12% of the cases are better than CASP. Meanwhile, CASP only has a better efficiency than MILP and CP+GVDR in 25% of the cases. Regarding the best solution, both approaches CASP and CP+GVDR obtained the same results in terms of the minimum makespan each for 50% of the cases. Finally, regarding the determination of the best solution, the CASP approach is clearly superior for all cases in terms of time performance compared with MILP and CP+GVDR. Moreover, it is possible to observe that the times used to obtain the best solution with CASP are smaller than those with MILP and CP+GVDR by up to two orders of magnitude in most cases. These results confirm the practical effectiveness of the CASP approach in solving complex scheduling problems with huge domains. It is also important to highlight that the CASP approach has better results for more difficult problems.
The scheduling results shown in Figure 2 let us infer that the resultant schedule is correct because it fulfills the constraints established during the modeling step, such as the zero-wait storage policy for chemical baths; each bath processes only one lot at a time, and there are no overlaps among the limited resources in this problem, that is, the baths and robot; the jobs are processed sequentially in each bath, fulfilling the flow-shop model corresponding to the problem description; and the scheduling robot is adjusted to transfer each lot from one bath to another according to the constraints established for this problem and following the processing transfer times of Table 3.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented a solution approach for the AWS scheduling problem in SMSs with one robot using CASP. These results indicate that one hybrid paradigm based on CASP is well placed for the solution of complex problems with huge domains, where the search space grows exponentially in relation to the input. The results obtained using the CASP approach are encouraging.
Meanwhile, it is true that for the first solution with CP+GVDR, for up to 70% of the cases, the results are better, both for the makespan value and for the CPU time. However, it turns out that for the best solution in 50% of the cases, CASP is better than MILP and CP+GVDR regarding the minimal value of the makespan. Additionally, it is true that CASP obtained the best performance in CPU time because for the best solution for 100% of the problems studied, the efficiency of CASP is better than that of CP+GVDR and MILP for one or more orders of magnitude. This means that CASP is highly competitive and can be used to solve problems of industrial size.
Meanwhile, the exploration of new approaches to solve scheduling problems is justified because they have taken a central place in multiple industries and businesses due to the increasing diversity in markets and products that demands better plans and more adjusted schedules. In addition, the exploration of new approaches and technologies is particularly important regarding technologies based on AI as in the case of the approach used in this research. AI technologies are indispensable for the design of Cyber Physical Systems (CPSs) and Internet 4.0 itself because the immense amount of data that it is generating every second in the manufacturing industry is unmanageable to take decisions. It is not only big data that pose problems to control the modern manufacturing systems; it is also the manufacturing environment which is highly dynamic and stochastic. All these characteristics of SMSs require a different approach capable of structuring all this information, turning it into knowledge, and being capable to reason with them.
Another additional advantage of using CASP instead of other different paradigms is the possibility of easily extending the model and its implementation, taking advantage of the non-monotonic characteristics of the ASP. Therefore, unexpected events, such as machine breakdowns or the arrival of urgent orders, can be included, and rescheduling can be solved with the same approach, especially now that a new clingcon solver with multi-shot capabilities has been released. Clingcon with multi-shot allows us to build hybrid systems with other paradigms such as Python, Lua, and Rust and also has capabilities of execution on incremental streaming. Hybrid solutions are indispensable to create interfaces between the reasoner and the physical system and the users.
The paradigm selected for solving this problem also facilitates the integration of the task scheduler into a general planner. In this way, both the planner and the scheduler can be fed with information coming from other manufacturing levels, such as sales, the warehouse, the chain of suppliers, or any other information related to the production process.
Future directions of this research include the solution of the problem using the updated clingcon language and its new solver. There are also plans to study how to represent the environment context of the production shop in clingcon. This representation is needed to link the physical system with a digital counterpart. Linking the monitoring of the environment with its context makes it possible to take better decisions based on knowledge more than only big data. Once the monitoring and the context awareness of the system is complete, it is also possible to automate the process of rescheduling. For all these future works, it is indispensable to use a hybrid system as the one based on CASP and Python or any other support imperative language. In conclusion, hybrid systems based on AI and other paradigms are expected to solve more complex problems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.G.-M. and L.B.; Methodology, C.L.G.-M.; Software, C.L.G.-M.; Validation, C.L.G.-M., L.B. and F.W.; Formal Analysis, C.L.G.-M.; Investigation, C.L.G.-M.; Data Curation, C.L.G.-M.; Original Draft Preparation, C.L.G.-M.; Review and Editing, C.L.G.-M., L.B. and F.W.; Visualization, C.L.G.-M.; Supervision, C.L.G.-M. and L.B.; Project Administration, C.L.G.-M.; Funding Acquisition, C.L.G.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Oks, S.J.; Jalowski, M.; Lechner, M.; Mirschberger, S.; Merklein, M.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Moeslein, K. Cyber-Physical Systems in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review, Categorization and Outlook. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C. Knowledge reasoning with semantic data for real-time data processing in smart factory. Sensors 2018, 18, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Garetti, M.; Tanca, L. Requirements and languages for the semantic representation of manufacturing systems. Comput. Ind. 2015, 81, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0: A review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Jimenez, L.A.; Pulikottil, T.; Nikghadam-Hojati, S.; Barata, J. Self-Organization in Smart Manufacturing—Background, Systematic Review, Challenges and Outlook. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 10107–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Cheang, B.; Lim, A. Problems and Solution Methods of Machine Scheduling in Semiconductor Manufacturing Operations: A Survey. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.J. A Method for Wafer Assignment in Semiconductor Wafer Fabrication Considerint Both Quality and Productivity Perspectives. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 52 Pt A, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, M.; Leng, T.; Albeshri, A. Optimal Cyclic Scheduling of Wafer-Residency-Time-Constrained Dual-Arm Cluster Tools by Configuring Processing Modules and Robot Waiting Time. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2023, 36, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crama, Y.; van de Klundert, J. Robotic Flowshop Scheduling Is Strongly NP-Complete; METEOR, Maastricht University School of Business and Economics: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1997; METEOR Research Memorandum No. 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfond, M.; Lifschitz, V. The Stable Model Semantics for Logic Programming. In Logic Programming, Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference and Symposium, Volume 2; Kowalksi, R., Boween, K.A., Eds.; Series in Logic Programming; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 1988; pp. 1070–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfond, M.; Lifschitz, V. Classical negation in logic programs and disjunctive databases. New Gener. Comput. 1991, 9, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, M.; Schaub, T. ASP modulo CSP: The clingcon system. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2012, 12, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banbara, M.; Kaufmann, B.; Ostrowski, M.; Schaub, T. Clingcon: The next generation. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2017, 17, 408–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebser, M.; Kaminski, R.; Kaufmann, B.; Schaub, T. Multi-shot asp solving with clingo. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2018, 19, 27–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.; Balduccini, M.; Gelfond, M.; Watson, R.; Barry, M. An A-prolog decision support system for the space shuttle. In Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages; Ramakrishnan, I.V., Ed.; PADL 2001; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 1990, pp. 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, F.; Grasso, G.; Alviano, M.; Manna, M.; Lio, V.; Liritano, S.; Leone, N. Team-building with answer set programming in the gioia-tauro seaport. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2012, 12, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E. Applications of answer set programming in phylogenetic systematics. In Logic Programming, Knowledge Representation, and Nonmonotonic Reasoning: Essays Dedicated to Michael Gelfond on the Occasion of His 65th Birthday, Vol. 6565 of LNCS; Balduccini, M., Son, T.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebser, M.; Obermeier, P.; Schaub, T.; Ratsch-Heitmann, M.; Runge, M. Routing Driverless Transport Vehicles in Car Assembly with Answer Set Programming. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2018, 18, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodaro, C.; Galtat, G.; Khan, M.K.; Maratea, M.; Porro, I. Operating Room (Re)Scheduling with Bed Management via ASP. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2021, 22, 220–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotawa, F.; Kaufmann, D. Model-based reasoning using answer set programming. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 16993–17011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Tran, S.; Pontelli, E.; Balduccini, M.; Schaub, T. Answer Set Planning: A Survey. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2023, 23, 226–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lierler, Y.Y.; Susman, B. Constraint Answer Set Programming versus Satisfiability Modulo Theories. In Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 1181–1187. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3060785 (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Gebser, M.; Ostrowski, M.; Schaub, T. Constraint answer set solving. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Logic Programming (ICLP), Pasadena, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2009; pp. 235–249. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-02846-5_22 (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Balduccini Balduccini, M. Representing constraint satisfaction problems in answer set programming. In Proceedings of the Working Notes of the Workshop on Answer Set Programming and Other Computing Paradigms (ASPOCP), Pasadena, CA, USA, 14 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lierler, Y. Constraint Answer Set Programming: Integrational and Translational (or SMT-based) Approaches. Theory Pract. Log. 2023, 23, 195–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebser, M.; Kaminski, R.; Kaufmann, B.; Ostrowski, M.; Schaub, T.; Thiele, S. A Users Guide to Gringo, Clasp, Clingo, and Iclingo. 2010. Available online: http://wp.doc.ic.ac.uk/arusso/wp-content/uploads/sites/47/2015/01/clingo_guide.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Bhushan, S.; Karimi, I.A. Heuristic algorithms for scheduling an automated wet-etch station. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2004, 28, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, G.; Park, M.; Park, Y.J.; Hur, S. Interactive Q-Learning Approach for Pick-and-Place Optimization of the Die Attach Process in the Semiconductor Industry. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4602052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, N. Close-down Process Scheduling of Wafer Residence Time-Constrained Multi-cluster Tools. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Q.; Ma, H.H. Integrating Preventive Maintenance Planning and Production Scheduling under Reentrant Job Shop. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 6758417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qiao, F.; Zhao, F.; Sutherland, J. Dynamic Scheduling of a Semiconductor Production Line Based on a Composite Rule Set. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, H.Y.; Rangel, S. A Survey of Case Studies in Production Scheduling: Analysis and perspectives. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 25, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönch, L.; Lars, L.; Fowler, J.W.; Dauzère-Pérès, S.; Mason, S.J.; Rose, O. A Survey of problems, solution techniques, and future challenges in scheduling semiconductor manufacturing operations. J. Sched. 2011, 14, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mata, C.L.; Márquez-Gutiérrez, P.R.; Burtseva, L. Rescheduling in Industrial Environments: Emerging Technologies and Forthcoming Trends. Int. J. Comb. Optim. Probl. Inform. 2015, 6, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dequeant, K.; Vialletele, P.; Lemaire, P.; Espinouse, M.L.A. Literature review on variability in semiconductor manufacturing: The next forward leap to Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Washington, DC, USA, 11–14 December 2016; pp. 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakifirooz, M.; Fathi, M.; Wu, K. Development of smart semiconductor manufacturing: Operations research and data science perspectives. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 108419–108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvra-Das, R. A Review of Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Quality Control in Semiconductor Production. Int. J. Comput. Eng. 2024, 5, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, A.M.; Méndez, C.A.; Garcia Sánchez, A.; Ortega-Mier, M.; Castro, P.M. General framework for automated manufacturing systems: Multiple hoists scheduling solution. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Che, A.; Chu, C. Dynamic Hoist Scheduling Problem with Multi-capacity Reentrant Machines: A Mixed Integer Programming Approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 87, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Wang, G.; Che, A.; Li, Y. Hybrid discrete differential evolution algorithm for biobjective cyclic hoist scheduling with reentrance. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 76, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, S.; Karimi, I.A. An MILP approach to automated wet-etch scheduling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, I.A.; Tan, Z.Y.L.; Bhushan, S. An improved formulation for scheduling an automated wet-etch station. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2004, 29, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.M.; Méndez, C.A.; Castro, P.M. A novel optimization method to automated wet-etch station scheduling in semiconductor manufacturing systems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Salleh, M.N.M.; Cheng, S.; Shi, Y. Metaheuristic research: A comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2018, 52, 2191–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, C.D.; Kempf, K.G.; Uzsoy, R. A Tabu search approach to scheduling an automated wet etch station. J. Manuf. Syst. 1997, 2, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, A.; Young, P.; Geraghty, J. Sequencing Optimisation for Makespan Improvement at Wet-Etch Tools. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015, 53, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos, L.J.; Castro, P.M.; Méndez, C.A. Integrated constraint programming scheduling approach for automated wet-etch stations in semiconductor manufacturing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novas, J.M.; Henning, G.P. Reactive scheduling framework based on domain knowledge and constraint programming. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 2129–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyháti, M.; Ösz, O.; Kovács, B. Combinatorial Approach for Scheduling Automated Wet-etch Stations. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Recent Achievements in Mechatronics, Automation, Computer Science and Robotics, Tirgu Mures, Romania, 6–7 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder, A.; Ross, A.K.; Schlipf, J.S. The well-founded semantics for general logic programs. J. ACM 1991, 38, 620–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, W. An Introduction to Answer Set Programming and Some of its Extensions. In Reasoning Web. Declarative Artificial Intelligence, 16th International Summer School 2020, Oslo, Norway, 24–26 June 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewka, G.; Eiter, T.; Truszczynski, M. Answer Set Programming at a Glance. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, M.; Cliffe, O.; De Vos, M. A pragmatic programmer’s guide to answer set programming. In Proceedings of the Software Engineering for Answer Set Programming (SEA09), Potsdam, Germany, 14 September 2009; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Janhunen, T.; Niemelä, I. The Answer Set Programming Paradigm. AI Mag. 2016, 37, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir, L. What is Answer Set Programming? Proc. Natl. Conf. Artif. Intell. 2008, 3, 1594–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Son, T.C.; Pontelli, E.; Le, T. Two applications of the ASP-prolog system: Decomposable programs and multi-context systems. In PADL 2014: Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Symposium on Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–20 January 2014; pp. 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalar, P.; Fandinno, J.; Schaub, T.; Wanko, P. On the Semantics of Hybrid ASP Systems Based on Clingo. Algorithms 2023, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, R.; Oliveras, A.; Tinelli, C. Solving SAT and SAT modulo theories: From an abstract Davis-Putnam-Logemann-Loveland procedure to DPLL(T). J. ACM 2006, 53, 937–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biere, A.; Heule, M.; Van Mareen, H.; Walsh, T. Handbook of Satisfiability. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, R.; Hubaux, A.; Ganesh, V.; Heymans, P. An SMT-based approach to automated configuration. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT), Manchester, UK, 30 June–1 July 2012; pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholany, M.M.S.; Ali, R.; Gebser, M. Hybrid ASP-Based Multi-objective Scheduling of Semiconductor Manufacturing Processes. In Logics in Artificial Intelligence—18th European Conference, JELIA 2023, Proceedings; Gaggl, S., Martinez, M.V., Ortiz, M., Ortiz, M., Eds.; (Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) Vol. 14281 LNAI); Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2023; pp. 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).