Study on Evaluation of the Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure Model and Prediction of Adsorbed Gas Content in Deep Coalbed Methane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sample and Methods
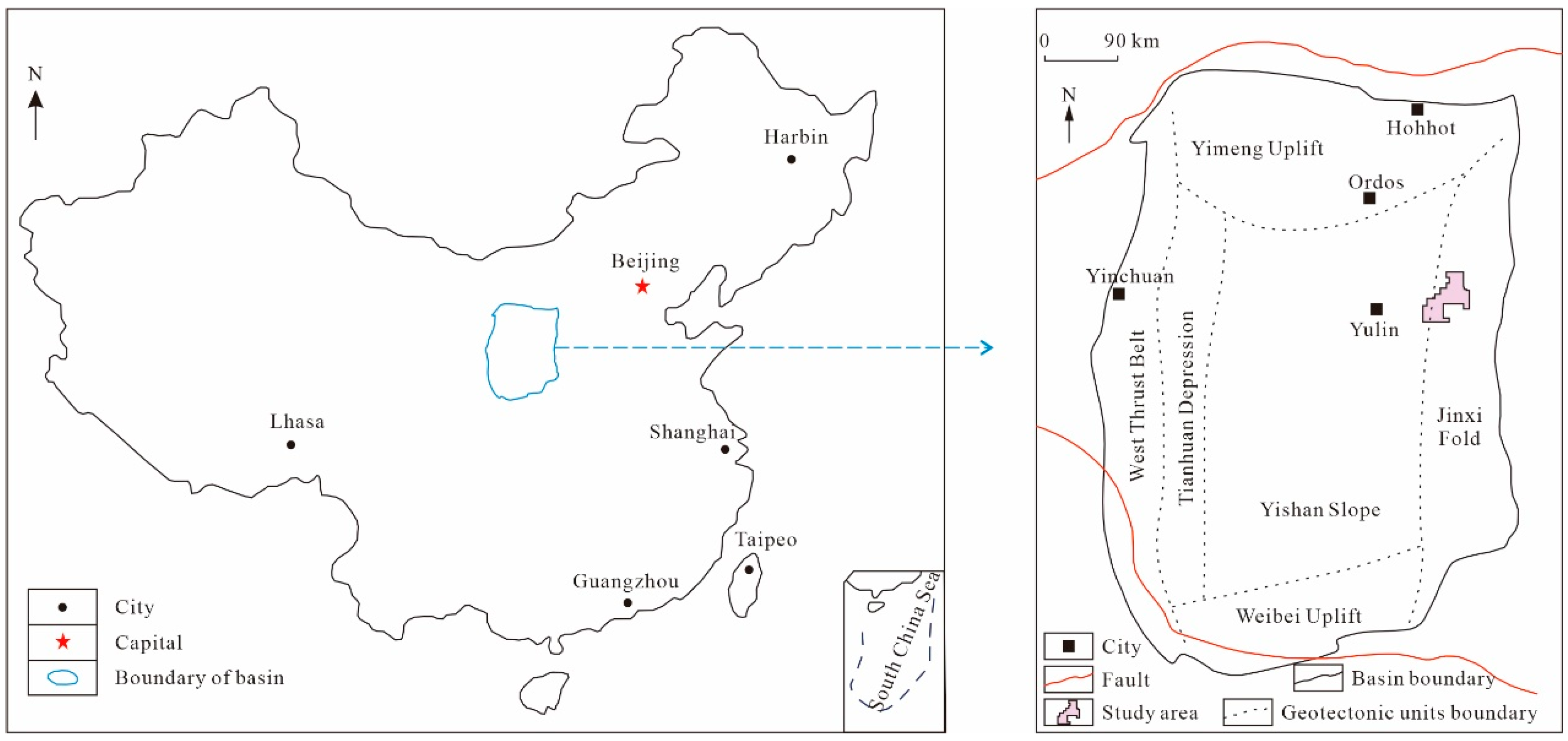
2.1. Geological Setting
2.2. Coal Sample Characterization
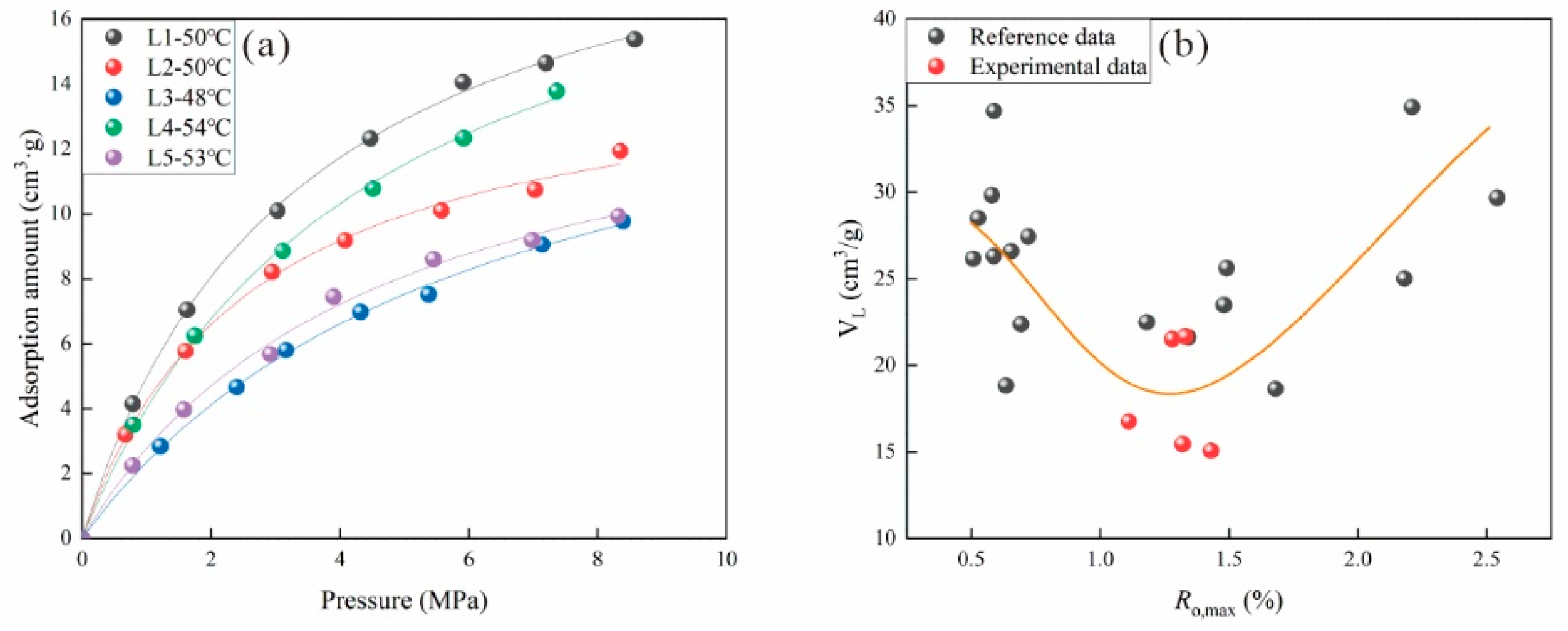
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
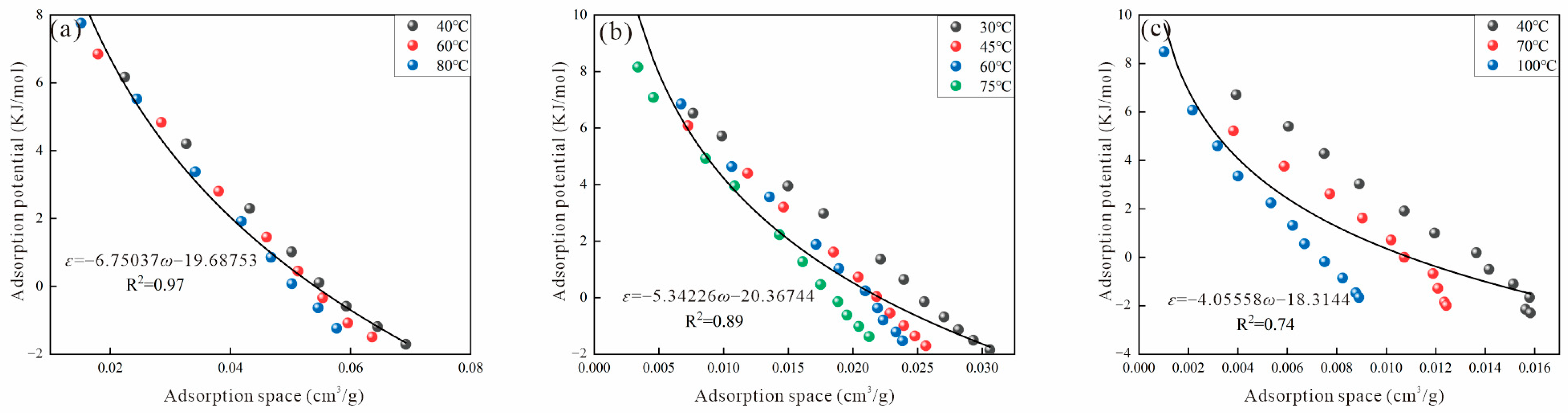
2.4. Adsorption Potential and Adsorption Space
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Factors Influencing Adsorption Behavior
3.1.1. Effect of Coal Rank on Adsorption Behavior
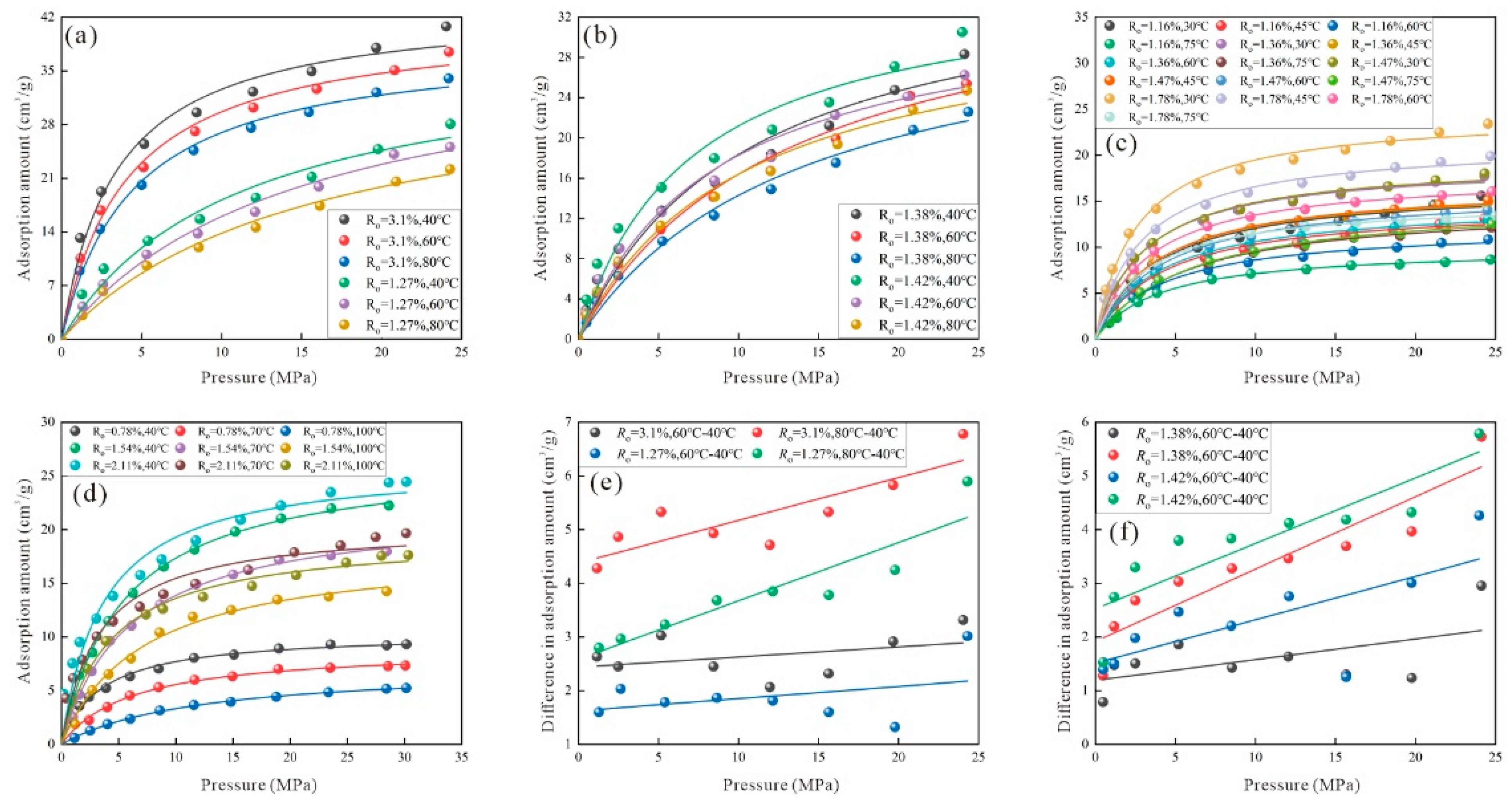
3.1.2. Effects of Pressure and Temperature on Adsorption Behavior
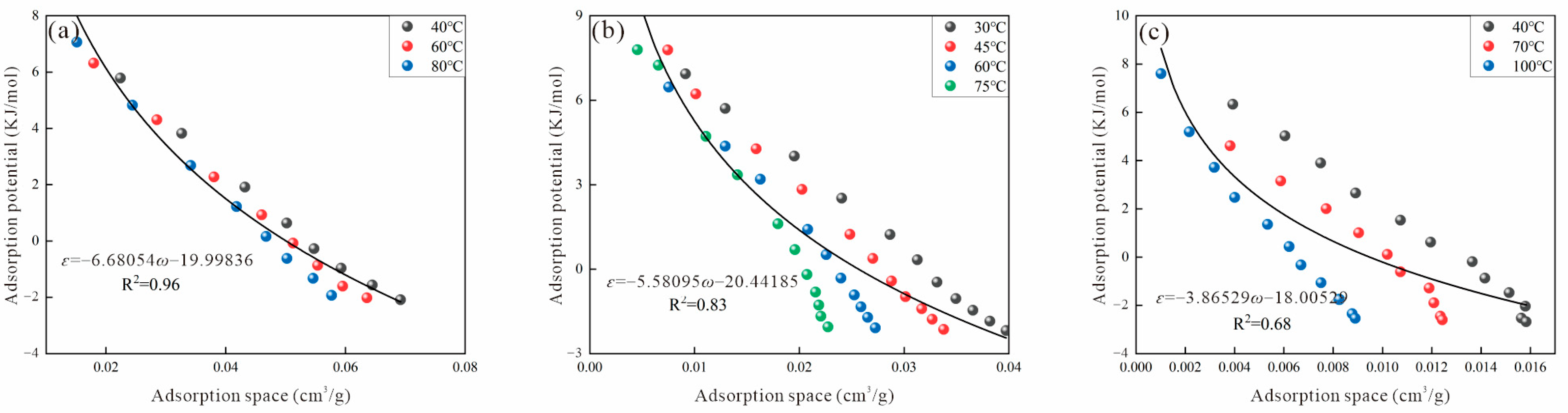
3.2. Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure
3.2.1. Dubinin Method
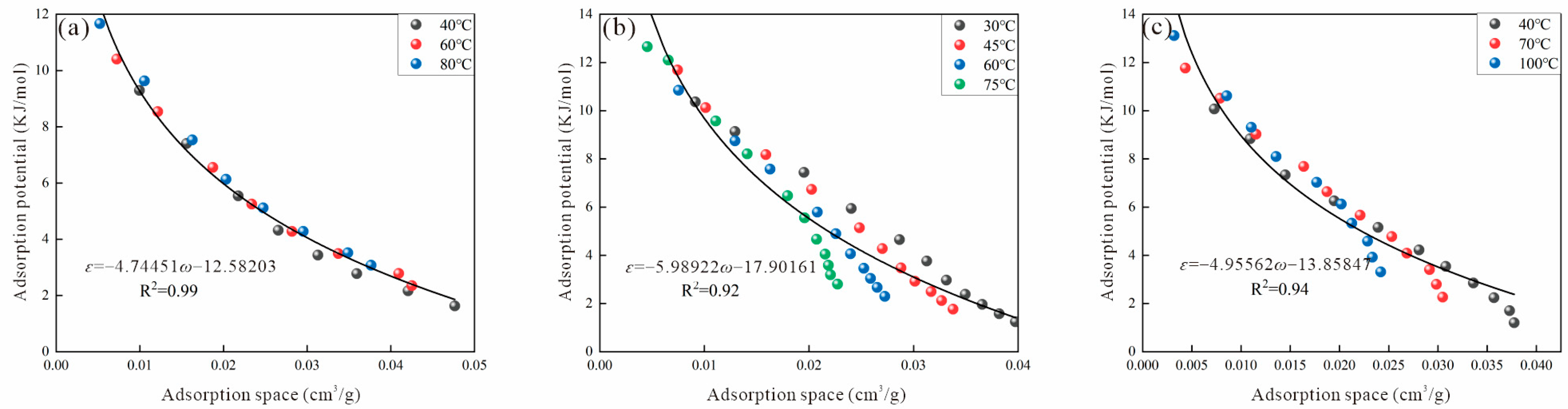
3.2.2. Reid Method
3.2.3. Antoine Method
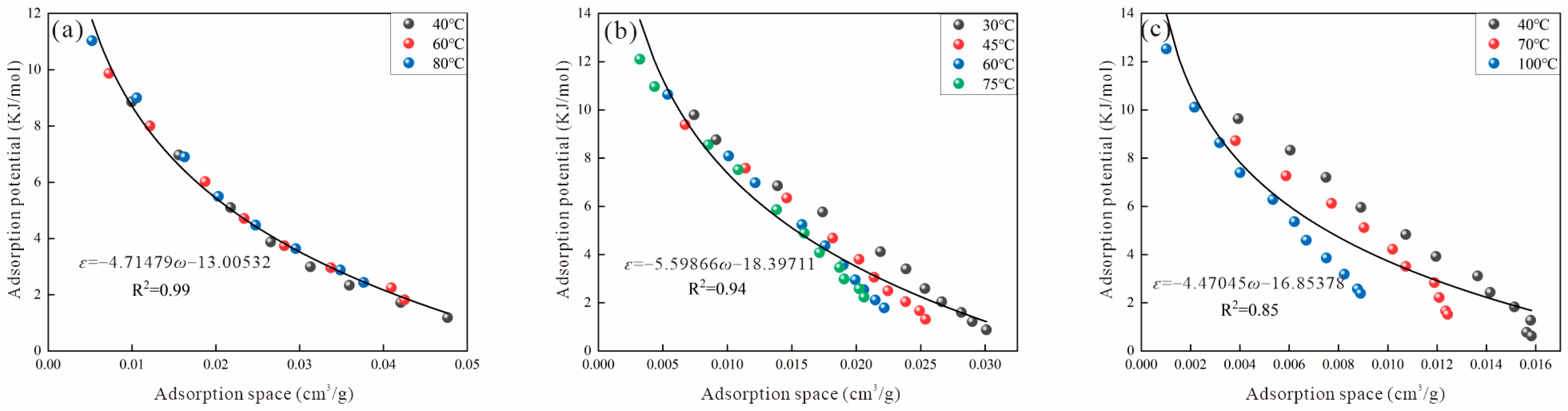
3.2.4. Astakhov Method
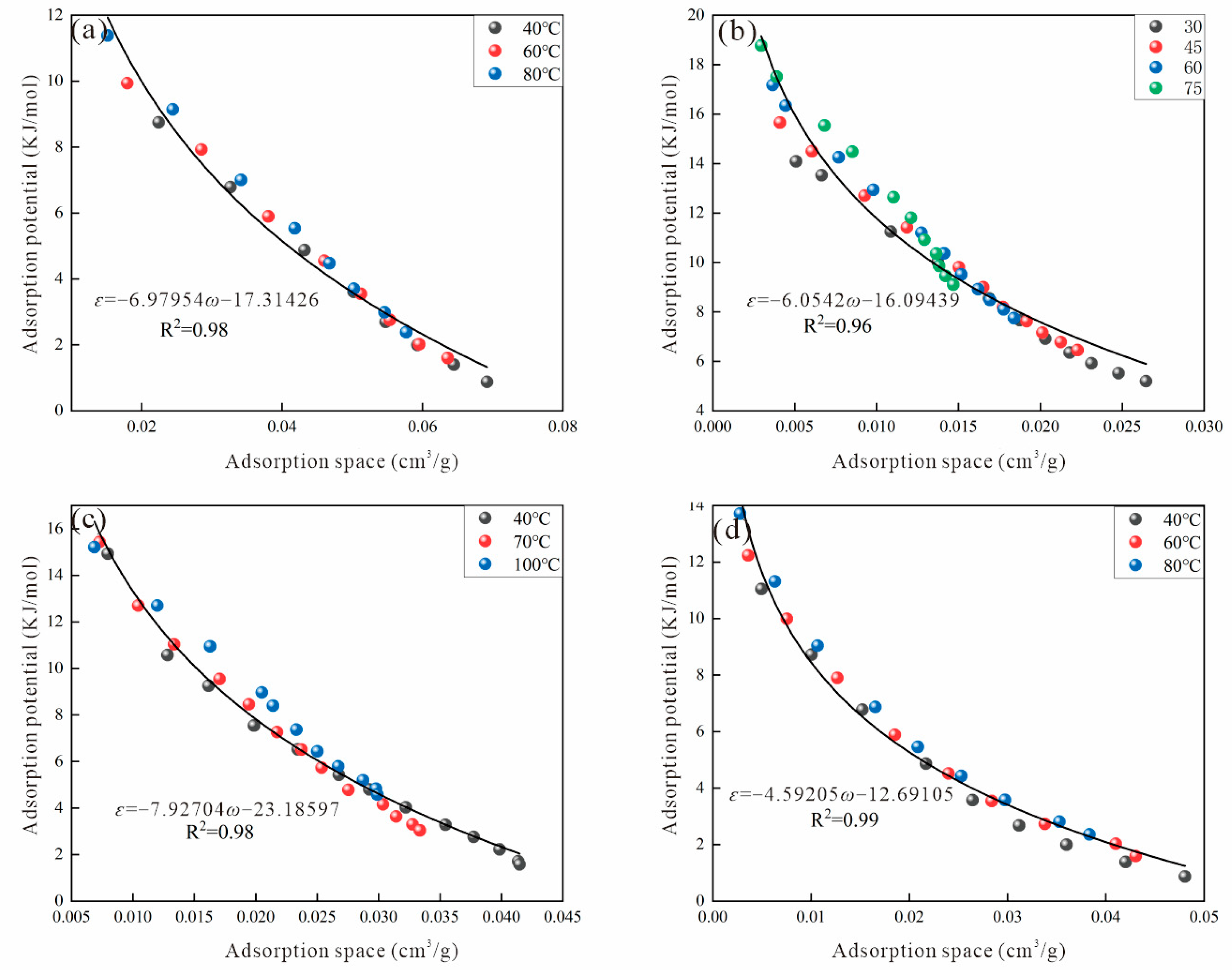
3.2.5. Amankwah Method
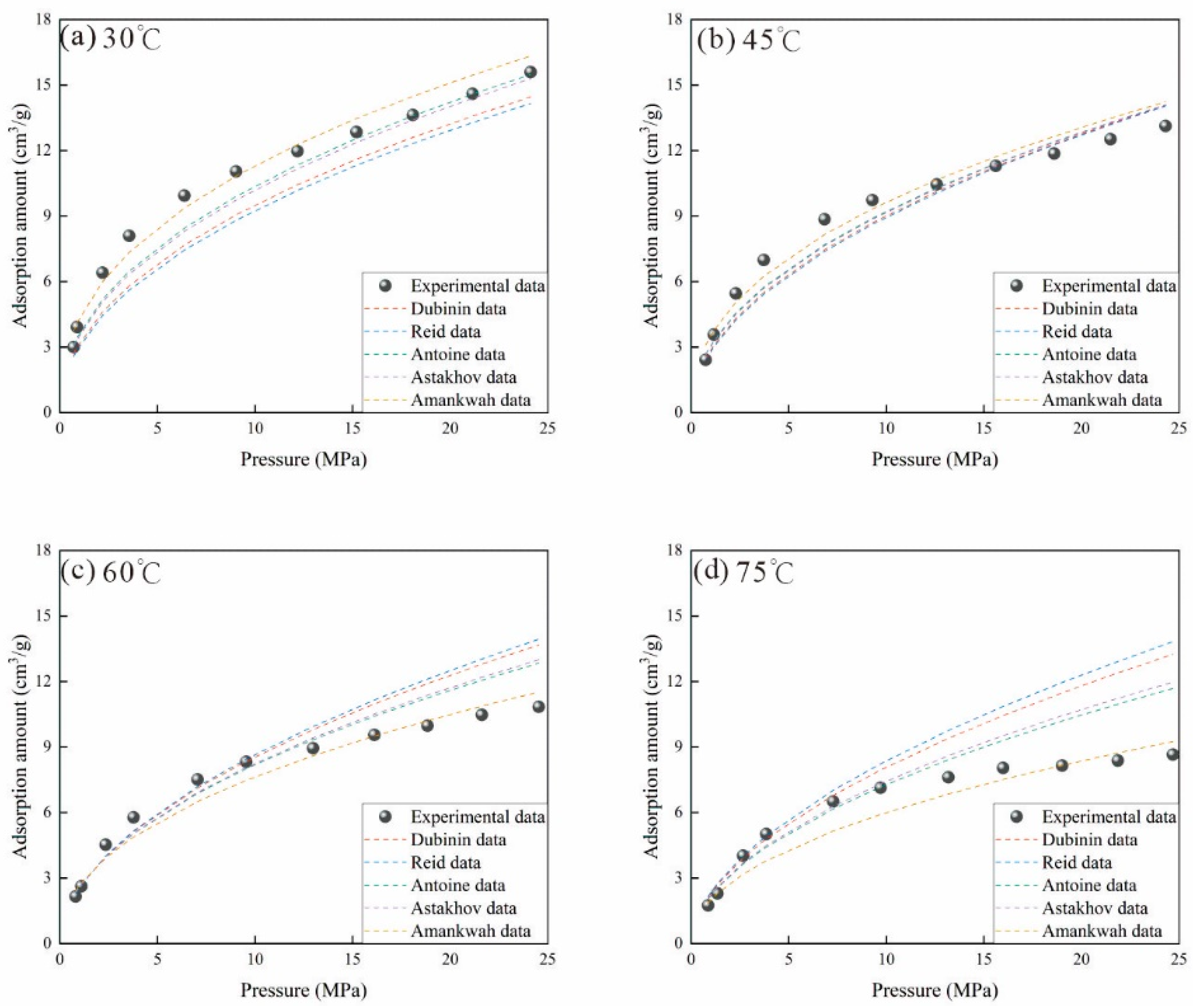
3.2.6. Error Analysis of Different Methods
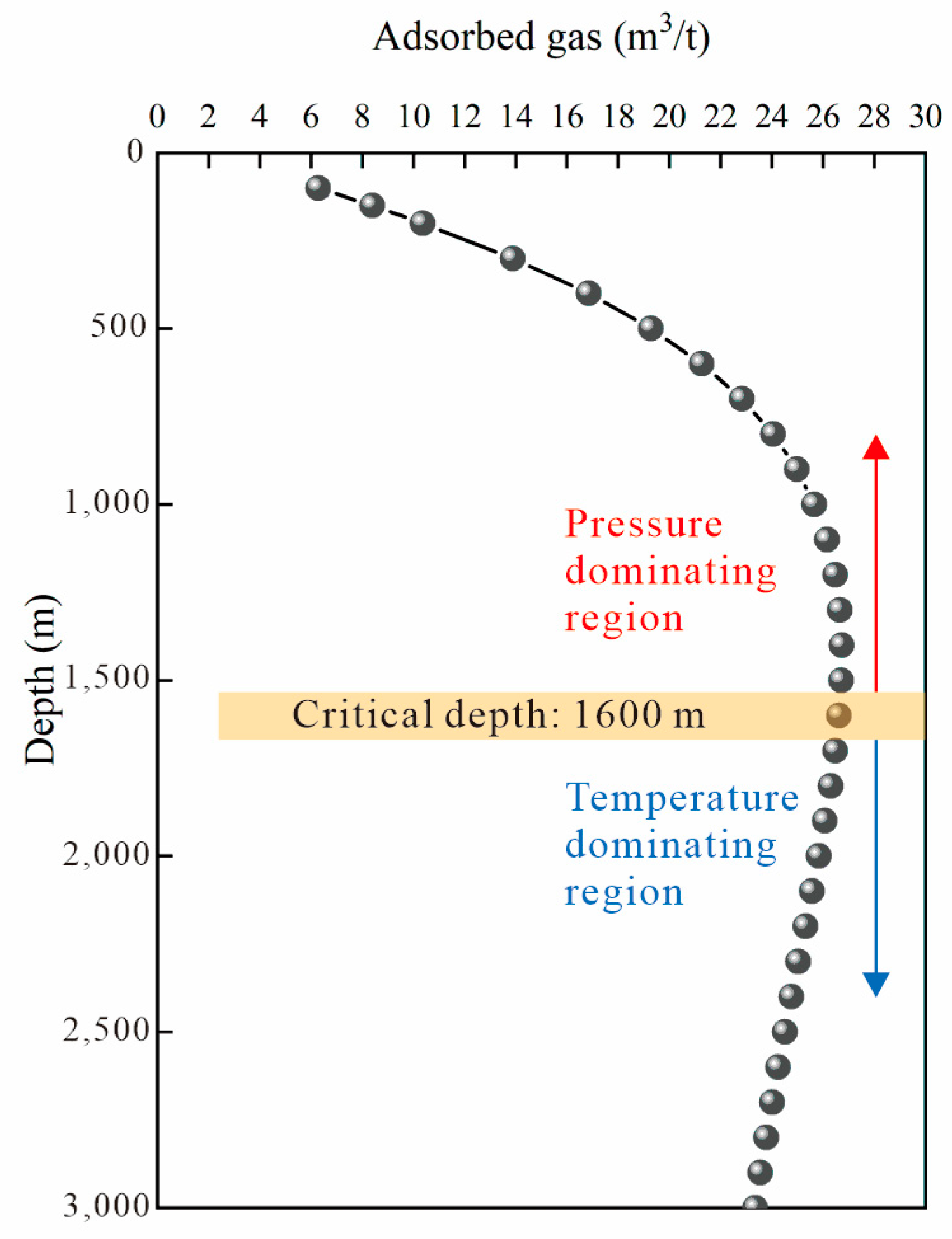
3.3. Adsorbed Gas Content Prediction and Application
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The adsorption capacity of deep coalbed methane is influenced by a combination of temperature, pressure, and coal rank. As pressure increases, the inhibitory effect of temperature on methane adsorption becomes more pronounced, and this inhibitory effect is further enhanced with higher coal ranks.
- (2)
- Although various virtual saturation vapor pressure models can be used to calculate methane adsorption amount, only the adsorption characteristic curve obtained by the Amankwah model aligns with actual physical principles and exhibits the smallest ARE and MSE. Therefore, the Amankwah model provides a reliable method for predicting adsorbed gas content.
- (3)
- The adsorbed gas prediction model based on adsorption potential theory indicates that there is a critical depth for adsorbed gas in the middle Linxing Block, which is approximately 1600 m. Above this critical depth, the adsorption capacity is primarily influenced by pressure, making it conducive to the formation of adsorbed gas reservoirs. Below this critical depth, the adsorption capacity is mainly affected by temperature and free gas has certain conditions for formation, causing free gas-containing reservoirs to form more easily.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X. Reservoir forming characteristics and favorable area evaluation of deep coalbed methane in Daning-Jixian Block. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Jiang, B.; Xue, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H. Coalbed methane emissions and drainage methods in underground mining for mining safety and environmental benefits: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 127, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, O.; Fisne, A. A comprehensive study on methane adsorption capacities and pore characteristics of coal seams: Implications for efficient coalbed methane development in the Soma Basin, Turkiye. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 6355–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkreuth, W.; Levandowski, J.; Weniger, P.; Krooss, B.; Prissang, R.; da Rosa, A.L. Coal characterization and coalbed methane potential of the Chico-Loma Coalfield, Parana Basin, Brazil—Results from exploration borehole CBM001-CL-RS. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2024, 38, 1589–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicca, M.M.; Kalkreuth, W.; Rosa, A.L.; Simao, G.; Levandowski, J.; Silva, T.F.; Anzolin, H.M. Effect of diabase intrusion on the CBM-bearing coalfields of southern Brazil: A review. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 119, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.C.; Flores, R.M. Developmental geology of coalbed methane from shallow to deep in Rocky Mountain basins and in Cook inlet Matanuska basin, Alaska, USA and Canada. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 241–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, R.E.; Kuuskraa, V.A. Deep coal seams: Potential for long-term natural-gas supplies. J. Pet. Technol. 1995, 47, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Song, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bo, D.; Liu, S.; Hao, J. Main controlling factor of coalbed methane enrichment area in southern Qinshui Basin, China. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2024, 14, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wu, C.; Huo, Z.; Zhao, Q. Productivity characteristics and controlling factors of coalbed methane vertical well in a coal block of Qinshui Basin. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2024, 42, 856–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hou, W.; Xiong, X.; Xu, B.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Feng, K.; Yun, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. The status and development strategy of coalbed methane industry in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qin, Y.; Tang, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A comprehensive review of deep coalbed methane and recent developments in China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2023, 279, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Yang, S.; Tang, S.; Tao, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, A.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, T. Advance on exploration-development and geological research of coalbed methane in the Junggar Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2412–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tao, S.; Sun, B.; Tang, S.; Chen, S.; Wen, Y.; Ye, J. Genesis and accumulation mechanism of external gas in deep coal seams of the Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2024, 286, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhen, H.; et al. Theoretical and technological difficulties and countermeasures of deep CBM exploration and development in the eastern edge of Ordos Basin. Coal Geol. Explor. 2023, 51, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q. Progress and study on exploration and production for deep coalbed methane. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Tao, S.; Li, S.; Tang, S.; Chen, S.; Zong, P.; Dong, Y. Differences in geological conditions of deep and shallow coalbed methane and their formation mechanisms. Coal Geol. Explor. 2024, 52, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tonnsen, R.R.; Miskimins, J.L. Simulation of deep-coalbed-methane permeability and production assuming variable pore-volume compressibility. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2011, 50, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, B.; Wang, K.; Wen, H.; Yang, R.; Huang, Z. Extreme massive hydraulic fracturing in deep coalbed methane horizontal wells: A case study of the Linxing Bloc, eastern Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.; Mehana, M. Coalbed methane characterization and modeling: Review and outlook. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Wang, L.; Naveen, P.; Longinos, S.N.; Hazlett, R.; Ojha, K.; Panigrahi, D.C. Influence of competitive adsorption, diffusion, and dispersion of CH4 and CO2 gases during the CO2-ECBM process. Fuel 2023, 358, 130065. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Dou, W.; Du, L.; Zhang, B.; Luo, B.; Yang, M.; et al. Quantitative Prediction of Deep Coalbed Methane Content in Daning-Jixian Block, Ordos Basin, China. Processes 2023, 11, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Deng, Z.; Fu, X.; Yin, K. A Study on Three-Phase Gas Content in Coal Reservoirs and Coalbed Methane-Water Differential Distribution in the Western Fukang Mining Area, Xinjiang, China. Acs Omega 2021, 6, 3999–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, P.; Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.; Yang, J. Evaluation and correction of prediction model for free gas content in deep coalbed methane: A case study of deep coal seams in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Ma, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Study on gas content variation and main controlling of low-rank coal in Huanglong Jurassic coalfield. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2023, 41, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Zhang, S.; Tang, S.; Xin, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, B. Re-cognition of adsorption phase density and adsorption phase volume: Insights from methane adsorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shao, L.; Hou, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yao, M.; Zhang, J. Methane adsorption characteristics and its influencing factors of the medium-to-high rank coals in the Anyang-Hebi coalfield, northern China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2019, 37, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhapkar, P.V.; Pradhan, S.P.; Chandra, D.; Hazra, B.; Vishal, V. Systematic pore characterization of sub-bituminous coal from Sohagpur Coalfield, central India using gas adsorption coupled with X-ray scattering and high-resolution imaging. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 9297–9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpensuppanimit, P.; Mohammad, S.A.; Robinson, R.L.; Gasem, K.A.M. Modeling the temperature dependence of supercritical gas adsorption on activated carbons, coals and shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 138, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y. Study on the methane adsorption characteristics of coal with heterogeneous potential wells. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2020, 23, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, G. Adsorption capacity, adsorption potential and surface free energy of different structure high rank coals. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, D.; Sun, X.; Wang, H. Quantitative characterization of the evolution of in-situ adsorption/free gas in deep coal seams: Insights from NMR fluid detection and geological time simulations. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2024, 285, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Prediction Model for Isothermal Adsorption Curves Based on Adsorption Potential Theory and Adsorption Behaviors of Methane on Granular Coal. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, E.; Zacharia, R.; Chahine, R.; Benard, P. Modified potential theory for modeling supercritical gas adsorption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9137–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, X.; Liang, L. Study on the Pseudo-saturation Vapor Pressure of the Methane on Shales. J. Southwest Pet. University. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2015, 37, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Liu, D.; Vandeginste, V.; Cai, Y.; Sun, F. Thermodynamic energy change and occurrence mechanism of multiple fluids in coal reservoirs. Energy 2023, 283, 129089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; Guo, H. Prediction of methane adsorption capacity in different rank coal at low temperature by the Polanyi-based isotherm model. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1384–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liao, J.; Ye, D.; Chen, R. Study of the methane adsorption characteristics in a deep coal reservoir using adsorption potential theory. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Jia, S.; Ye, X.; Long, Y. The adsorption model of the adsorption process of CH4 on coal and its thermodynamic characteristics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Sun, Q.; Geng, S.; Wang, S.; Xue, S.; Ding, X. Distribution pattern and geological evolution of combustion metamorphic rocks in the northeast margin of Ordos Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Franceschi, M.; Duan, X.; Li, K.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, Z. Petrography, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry of Combustion Metamorphic Rocks in the Northeastern Ordos Basin, China: Implications for the Origin of “White Sandstone”. Minerals 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Sang, S.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, H. Natural Gas Accumulation Characteristics in the Linxing Area, Ordos Basin, NW China: Revealed from the Integrated Study of Fluid Inclusions and Basin Modeling. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 8695497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Gao, J.; Du, J.; Wu, J.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J. Multilayer coal-derived gas enrichment mechanism and whole gas bearing system model: A case study on the Linxing Block along the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chao, W.; Du, J.; Yang, Q.; Mi, H.; Zhang, S. Breakthrough, future challenges and countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin: A case study of Linxing-Shenfu block. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 8899-2008; Method of Determining Maceral Group Composition and Mineral of Coal. China Coal Industry Association: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 212-2008; Proximate Analysis of Coal. China Coal Industry Association: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 6948-2008; Method of Determining Microscopically the Reflectance of Vitrinite in Coal. China Coal Industry Association: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Lu, G.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Quan, F.; Tamehe, L. Variation of Surface Free Energy in the Process of Methane Adsorption in the Nanopores of Tectonically Deformed Coals: A Case Study of Middle-Rank Tectonically Deformed Coals in the Huaibei Coalfield. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7155–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanyi, M. The Potential Theory of Adsorption. Science 1963, 141, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amankwah, K.; Schwarz, J. A modified approach for estimating pseudo-vapor pressures in the application of the dubinin-astakhov equation. Carbon 1995, 33, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, N.; Qiu, Y. Methane adsorption interpreting with adsorption potential and its controlling factors in various rank coals. Processes 2020, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godyn, K.; Dutka, B. The impact of the degree of coalification on the sorption capacity of coals from the Zofiowka Monocline. Arch. Min. Sci. 2018, 63, 727–746. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Xie, Y.; Pan, X.; Pang, J.; Zhou, L. Gas analysis of deep coalbed methane and its geological model for development in Linxing Block. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1634–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Theory and Method for Compatibility Evaluation of Joint Deep Coalbed Methane an Tight Sandstone Gas Production: In a Case of Member C2b~P1t in Linxing Block; China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C. Deep Coalbed Methane Accumulation and Reservoiring in Linxing Area, Eastern Ordos Basin, China; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S. Storage-Seepage Mechanism and Development Features of Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoir; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Tang, D.; Pan, Z.; Xu, H.; Tao, S.; Liu, Y.; Ren, P. Geological conditions of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China: Implications for coalbed methane development. Int. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 53, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Cui, B.; Huang, D.; Xie, X. Evaluation of deep high-rank coal seam gas content and favorable area division based on GIS: A case study of the South Yanchuan block in Ordos Basin. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2022, 40, 1151–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Qi, S.; Gao, W.; Sun, K. Study on the relationship between chemical structure evolution and gas generation of coal. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2017, 28, 863–872. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jin, C.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Sun, P.; Meng, Z.; An, L. Coalbed methane adsorption capacity related to maceral compositions. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2020, 38, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qin, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, J. Adsorption Behavior of Deep Coalbed Methane Under High Temperatures and Pressures. Geol. J. China Univ. 2013, 19, 648–654. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W. Characterization of Coalbed Methane Accumulation and Reservoir under the Background of Magma Invasion in Linxing District; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhao, J. Key parameters identification for deep coalbed methane reservoir in Linxing block of eastern Ordos Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Huangfu, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Y. Gas oversaturation in deep coals and its implications for coal bed methane development: A case study in Linxing Block, Ordos Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1031493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Ro (%) | Maceral Composition (%) | Proximate Analysis (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | L | I | M | Mad | Ad | Vdaf | FCad | ||
| L1 | 1.28 | 53.6 | 0 | 30.2 | 16.2 | 0.62 | 24.5 | 33.96 | 40.92 |
| L2 | 1.43 | 62.7 | 0 | 20.7 | 16.6 | 0.59 | 23.27 | 25.05 | 51.09 |
| L3 | 1.11 | 58.2 | 2.8 | 27.0 | 12 | 0.50 | 20.52 | 29.97 | 49.01 |
| L4 | 1.33 | 83.6 | — | 9.2 | 7.2 | 0.52 | 10.54 | 26.41 | 62.52 |
| L5 | 1.32 | 48.6 | 2.6 | 24.8 | 24 | 0.75 | 24.78 | 27.02 | 47.45 |
| k | R2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ro = 3.1% | Ro = 1.27% | Ro = 0.78% | Ro = 1.54% | Ro = 2.11% | Ro = 1.16% | Ro = 1.36% | Ro = 1.47% | Ro = 1.78% | Ro = 1.38% | Ro = 1.42% | |
| 2 | 0.9781 | 0.9342 | 0.7011 | 0.8939 | 0.8896 | 0.8452 | 0.8778 | 0.8958 | 0.8034 | 0.9213 | 0.9322 |
| 3 | 0.9889 | 0.9434 | 0.7912 | 0.9368 | 0.9248 | 0.8835 | 0.9158 | 0.9321 | 0.8486 | 0.9259 | 0.9388 |
| 4 | 0.9891 | 0.9419 | 0.8625 | 0.959 | 0.9463 | 0.9139 | 0.944 | 0.9576 | 0.8862 | 0.9242 | 0.9391 |
| 5 | 0.9797 | 0.9306 | 0.9135 | 0.9624 | 0.9541 | 0.9361 | 0.9625 | 0.9725 | 0.9157 | 0.9166 | 0.9334 |
| 6 | 0.9621 | 0.9113 | 0.9454 | 0.9505 | 0.9495 | 0.9304 | 0.9651 | 0.9677 | 0.913 | 0.9037 | 0.9223 |
| 7 | 0.9381 | 0.8856 | 0.9611 | 0.9273 | 0.9343 | 0.9572 | 0.9729 | 0.9745 | 0.951 | 0.8865 | 0.9066 |
| 8 | 0.9093 | 0.8554 | 0.9642 | 0.8966 | 0.9107 | 0.9574 | 0.9668 | 0.9643 | 0.9577 | 0.8655 | 0.887 |
| 9 | 0.8773 | 0.8223 | 0.9581 | 0.8617 | 0.8812 | 0.9519 | 0.9551 | 0.9484 | 0.9584 | 0.8417 | 0.8644 |
| 10 | 0.8433 | 0.7875 | 0.9457 | 0.8249 | 0.8478 | 0.9418 | 0.939 | 0.9285 | 0.9539 | 0.8158 | 0.8395 |
| Optimal k value | 3.2149 | 2.9126 | 7.8968 | 5.0298 | 5.3601 | 7.8637 | 6.9213 | 6.4175 | 8.9537 | 2.8841 | 3.3443 |
| Samples | T/°C | ARE/% | MSE/cm3/g | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dubinin | Reid | Antoine | Astakhov | Amankwah | Dubinin | Reid | Antoine | Astakhov | Amankwah | ||
| Ro = 3.1% | 40 | 4.51 | 6.44 | 4.49 | 5.77 | 3.94 | 1.49 | 1.91 | 1.54 | 1.70 | 1.22 |
| 60 | 5.60 | 5.70 | 5.30 | 5.56 | 5.21 | 1.50 | 1.57 | 1.29 | 1.45 | 1.27 | |
| 80 | 6.49 | 7.40 | 5.64 | 5.36 | 5.54 | 2.04 | 2.63 | 1.33 | 1.41 | 1.31 | |
| Ro = 1.16% | 30 | 15.93 | 18.40 | 8.11 | 9.27 | 7.03 | 1.53 | 1.75 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.62 |
| 45 | 9.48 | 9.95 | 8.61 | 8.77 | 7.72 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.67 | |
| 60 | 11.83 | 12.62 | 9.95 | 10.28 | 9.57 | 1.38 | 1.51 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.83 | |
| 75 | 23.43 | 26.63 | 15.63 | 16.94 | 13.38 | 2.30 | 2.63 | 1.45 | 1.60 | 1.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, W.; Jia, T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Chao, W.; Li, S.; Liu, Z. Study on Evaluation of the Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure Model and Prediction of Adsorbed Gas Content in Deep Coalbed Methane. Processes 2024, 12, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091837
Peng W, Jia T, Zhang S, Wu J, Chao W, Li S, Liu Z. Study on Evaluation of the Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure Model and Prediction of Adsorbed Gas Content in Deep Coalbed Methane. Processes. 2024; 12(9):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091837
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Wenchun, Tengfei Jia, Songhang Zhang, Jian Wu, Weiwei Chao, Shilong Li, and Zizhen Liu. 2024. "Study on Evaluation of the Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure Model and Prediction of Adsorbed Gas Content in Deep Coalbed Methane" Processes 12, no. 9: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091837
APA StylePeng, W., Jia, T., Zhang, S., Wu, J., Chao, W., Li, S., & Liu, Z. (2024). Study on Evaluation of the Virtual Saturated Vapor Pressure Model and Prediction of Adsorbed Gas Content in Deep Coalbed Methane. Processes, 12(9), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091837






