Abstract
The rapid development of new energy vehicles and Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs) has significantly mitigated urban air pollution. However, the disposal of spent LIBs presents a considerable threat to the environment. Recycling these waste LIBs not only addresses the environmental issues but also compensates for resource shortages and generates substantial economic benefits. Current recycling processes primarily focus on the extraction of valuable metals, often overlooking the treatment of residual waste post-extraction. This project targets the iron phosphate (FePO4) derived from waste lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery materials, proposing a direct acid leaching purification process to obtain high-purity iron phosphate. This purified iron phosphate can then be used for the preparation of new LFP battery materials, aiming to establish a complete regeneration cycle that recovers lithium carbonate and iron phosphate from waste LFP materials for the production of LFP. The study investigates process parameters such as acid types and concentrations, leaching time, and the number of leaching cycles. The results demonstrate that, after purification, the levels of impurity metals decrease while the iron content increases correspondingly. Under optimized experimental conditions, the dilute sulfuric acid leaching rates of Al, Cu, Ca, and Ni reached 36.0%, 51.4%, 89.5%, and 90.9%, respectively. Furthermore, hydrothermal treatment in dilute phosphoric acid achieved leaching rates of 87.9%, 85.8%, 98.4%, and 99.1% for Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni, respectively. The microstructure characterization revealed significant changes in phase and grain morphology during the leaching process in dilute phosphoric acid, which are likely associated with the liberation of impurity atoms from the lattice. These findings indicate that acid leaching is highly effective in removing impurities from the iron phosphate recycled from waste LIBs.
1. Introduction
China has led the world in the production and sales of new energy vehicles (NEVs) for nine consecutive years, with market penetration rates soaring from 0.022% in 2010 to 25.6% in 2022 [1,2]. In recent years, spurred by the “Dual Carbon” target, the NEV industry in China has experienced rapid growth, significantly increasing the demand for power batteries. The country’s NEV sector maintained robust growth from January to May 2024, with NEV production reaching 3.93 million units, up 30.7% year-on-year, while sales rose by 32.5% to 3.9 million units [2]. Power batteries typically reach the end of their life after 8 to 10 years due to capacity decay and performance degradation. It is projected that by 2025, China will have accumulated over 2 million tons of retired power batteries, a figure expected to rise to 7.8 million tons by 2030. Globally, the LIB recycling market is forecasted to reach $15.5 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% [3,4].
Recycling waste LIBs is crucial not only for recovering valuable metals but also for mitigating environmental pollution risks. Properly purified and refined recovered materials can be reused in the production of new batteries, thus contributing to a circular economy [5,6]. Currently, two main approaches are used to manage scrapped power batteries from electric vehicles: cascade utilization and disassembly for recycling. Cascade utilization is applied when the battery capacity drops to 80% of its initial level, making it unsuitable for electric vehicles but viable for other applications, such as energy storage systems and smaller power supplies. When battery performance further declines to below 50%, disassembly and electrode material recycling becomes necessary [7].
In a typical recycling process, LIBs undergo discharging, crushing, and component separation [8,9]. The “black mass”, which includes transition metals and lithium-containing cathodes, is further processed using chemical methods, primarily hydrometallurgy, pyrometallurgy, and biological metallurgy [10,11]. Among these, hydrometallurgy is the most widely used technique due to its lower energy consumption, reduced emissions, higher recovery efficiency, and high product purity. This process typically involves two stages: leaching and separation. Initially, black powders are treated in an acidic solution with reducing agents, converting metals from their solid form into soluble ions [12,13]. Various acids, both inorganic (e.g., sulfuric, hydrochloric, and nitric acids) and organic (e.g., citric, tartaric, and oxalic acids), are used to optimize the leaching process. Subsequently, the dissolved metals are selectively separated and purified through ion exchange, solvent extraction, chemical precipitation, or electrodeposition [14,15,16,17]. In response to growing environmental concerns, circular hydrometallurgy processes have been proposed, incorporating energy-efficient and resource-efficient steps to minimize reagent consumption and waste production [18].
LFP batteries, known for their safety, long lifespan, and low cost, are a preferred power source for NEVs, currently accounting for 74.0% of total installed capacity. The recycling of waste LFP batteries has garnered significant research attention over recent decades. For instance, Liu et al. developed an efficient oxidation process using NaClO to recover Li from waste LFP batteries, achieving a Li recovery efficiency of up to 99.8% under optimal leaching conditions. They also successfully resynthesized high-performance LiFePO4/C using the recovered products [19]. Qiu et al. reported a green, closed-loop method to recycle waste LFP, achieving a Li recovery efficiency of 97.6% with properly adjusted oxidation leaching parameters. They also reproduced LiFePO4 cathode materials, which exhibited excellent cycling stability and rate performance [20].
Current recycling processes typically focus on the extraction of valuable lithium from waste LFP while paying less attention to the recovery and utilization of iron due to its lower economic value. However, as evidenced by the examples mentioned above, there is a growing need to use recycled materials to reproduce LFP and reintegrate them into battery production, thereby completing the regeneration cycle. In fact, iron phosphate recovered from waste LFP can potentially be used as a raw material for synthesizing LFP through high-temperature solid-phase methods, thus creating a closed-loop, value-added system. Zeng [21] developed a novel organic acid leaching and advanced oxidation method, successfully separating and purifying lithium salts and iron phosphate. Additionally, the recovered Li2CO3 was combined with FePO4 as a lithium source to regenerate LFP cathode materials. Similarly, Kumar [22] and Jin [23] reported that, after acid leaching and dissolution of waste lithium iron phosphate cathode materials, selective precipitation of LiCO3 and FePO4 was carried out, followed by regeneration into LFP cathode materials.
However, the recycling process inevitably introduces metal impurities such as Li, Na, Ca, Mg, Mn, Ni, and Al into the residue after valuable lithium extraction. Therefore, further purification of the iron phosphate residue post-lithium extraction is of significant research importance to fully recycle and reuse all components of waste LFP. Typically, lithium extraction slag is dissolved using acids, bases, or oxidants, followed by chemical precipitation to obtain high-purity iron phosphate [24,25,26]. Liu Q. [27] optimized the dissolution conditions for lithium-extracted tailings using hydrochloric acid, studying the leaching kinetics with the aim of high-value recycling of these tailings from lithium iron phosphate battery waste. Liu X. [28] conducted an experimental study involving hydrochloric acid leaching, iron powder replacement for copper removal, and hydrolysis and chemical precipitation for the removal of titanium and aluminum, ultimately synthesizing iron phosphate for batteries. Liu H. [29] invented a method for recovering and preparing battery-grade iron phosphate from waste potassium iron phosphate lithium extraction residues, which involved acid solution leaching, filtration, initial purification with salicylic acid, pH coarse precipitation, and further purification processes.
Lithium extraction slag constitutes over 95% of the mass fraction of LiFePO4, and its complete dissolution would require a large amount of chemicals. However, if the impurity elements in the slag can be selectively extracted while the major component, FePO4, remains in solid form, the acid usage can be significantly reduced. In fact, selective leaching/extraction is commonly used in wet metallurgy and solid waste recycling, where valuable metals are leached and utilized, leaving inexpensive components in the waste residue [30,31,32,33]. This method is also applied to recycle lithium from waste LFP battery materials, leaving FePO4 in the slag [34,35]. Similarly, selective leaching/extraction may continue to be used for lithium extraction slag, but with the aim of obtaining high-purity iron phosphate rather than leaching precious metals. Yang selectively leached impurity metals such as Cu and Ni using a phosphoric acid and hydrochloric acid mixture (H3PO4/HCl molar ratio = 3:1), leaving iron and phosphorus in the leaching residue [36]. The removal efficiency of metal impurities reached 97%, while the main elements Fe and P remained below 2%. Thermodynamic evaluation illustrated that Mn, Cu, Ni, and other elements were soluble in the phosphoric acid mixture, while FePO4 remained in solid form.
Great Power Energy Co., Ltd., one of the largest lithium-ion battery manufacturers in China, has been engaged in battery recycling and reuse for many years. The company has established the Henan Province New Energy Waste Resource Recycling Technology Research Center in collaboration with Huanghuai University, and founded Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd., dedicated to lithium-ion battery recycling. We have encountered the issue of low purity iron phosphate after lithium extraction, which hinders its use by downstream battery material manufacturers. This study focuses on iron phosphate derived from the lithium extraction process at Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd., and aims to develop a simple acid leaching purification process using single acids to obtain high-purity iron phosphate.
2. Experimental Design
Recycled iron phosphate powders were supplied by Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd. Sulfuric acid (Analytical Reagent, 95.0–98.0%), phosphoric acid (Analytical Reagent, ≥85.0%), and ethanol (Analytical Reagent, ≥95.0%) were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Deionized water was prepared in our laboratory.
First, an elemental analysis was conducted on the recycled iron phosphate powders received from Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd., Zhumadian city in Henan province, China. The elemental contents of Fe, Al, Ca, Cu, Ni, K, and Mg, as measured by ICP, were 23.04%, 1.50%, 0.19%, 0.37%, 0.22%, 0.14%, and 0.09%, respectively. Based on the analysis results, we selected Al, Cu, Ca, and Ni as the impurity elements for experimental calibration and compared their removal efficiency under various conditions by measuring their residual content.
Concentrated sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid were diluted to a concentration of 1 mol/L for subsequent use. The diluted acids and deionized water, measured using a graduated cylinder, along with the iron phosphate powders, measured using an electronic balance, were combined in a beaker and stirred thoroughly. The reaction solution was then subjected to various heat treatments. The resulting solid powders were obtained by varying the acid types and concentrations, leaching temperature and time, and the number of leaching cycles.
The size and morphology of the prepared samples were examined using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, JSM-6700F, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). Elemental content was analyzed with an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Optima 8300, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The leaching rate of each element was calculated using the following formulas:
where m is the mass of the sample taken when analyzing the sample, in g; V0 is the volume of the solution after digestion, in L; f is the dilution factor; C0 is the concentration of the element in the test solution, in mg/L; C1 is the concentration of the original solution of the sample digestion solution, in mg/L, C1 = C0 × f; Cx is the final result of the measured element, in mg/kg; W(%) is the final test result of the measured element. E(%) is the leaching rate of the measured impurity element.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dilute Sulfuric Acid Leaching
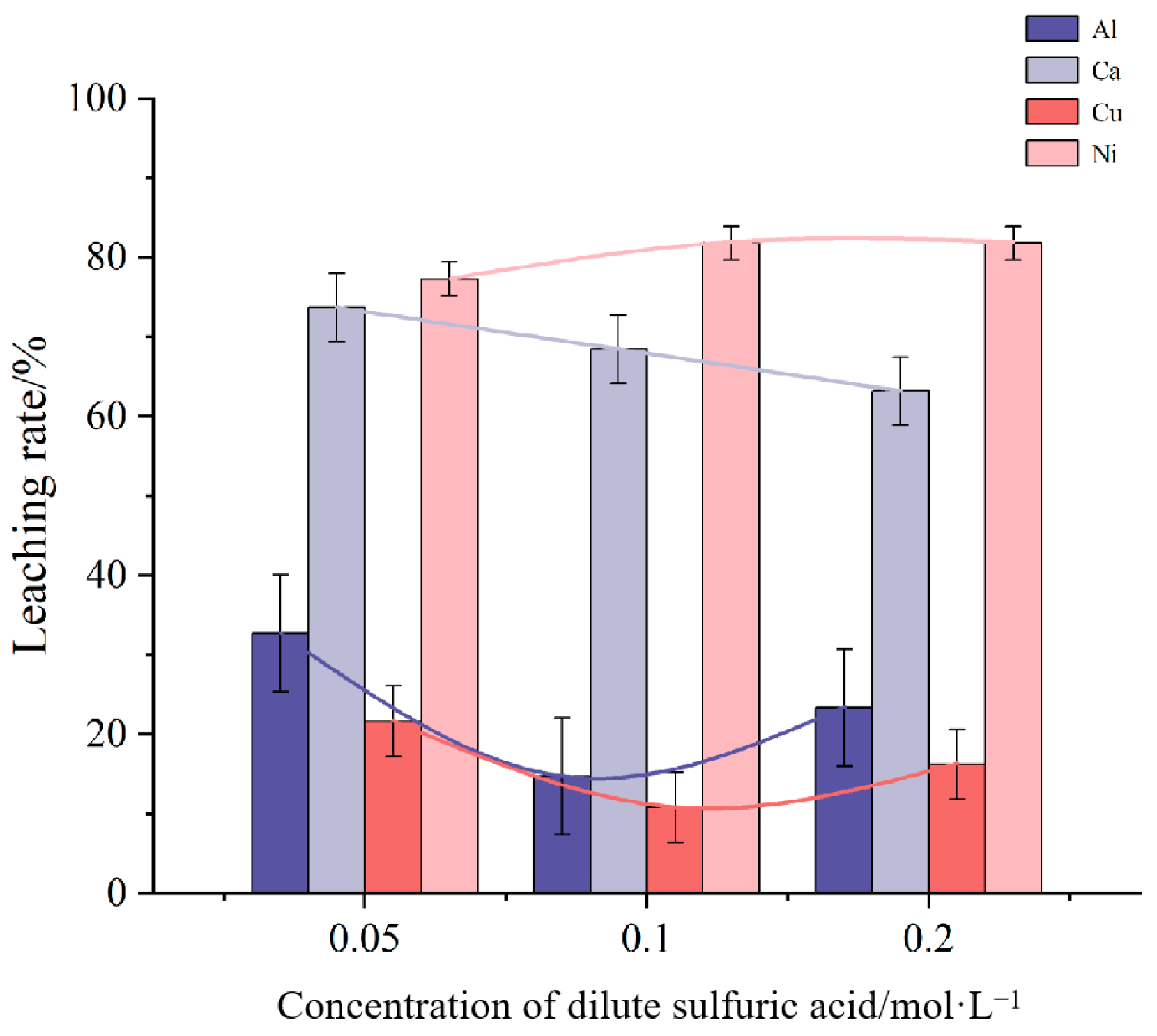
Figure 1 illustrates the effect of dilute sulfuric acid concentration on the leaching rates of impurity elements Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni. The mixture was heated and stirred at room temperature. The results indicate that as the concentration of dilute sulfuric acid increases, the leaching rates of Al and Cu initially decrease and then increase, while the leaching rate of Ca consistently decreases. The leaching rate of Ni, however, remains relatively stable throughout the concentration range. The analysis shows that the highest leaching rates for Al, Ca, and Cu impurities occur at a sulfuric acid concentration of 0.05 mol/L. Nevertheless, to minimize solvent usage in potential industrial applications, a concentration of 0.2 mol/L was chosen for further experiments.
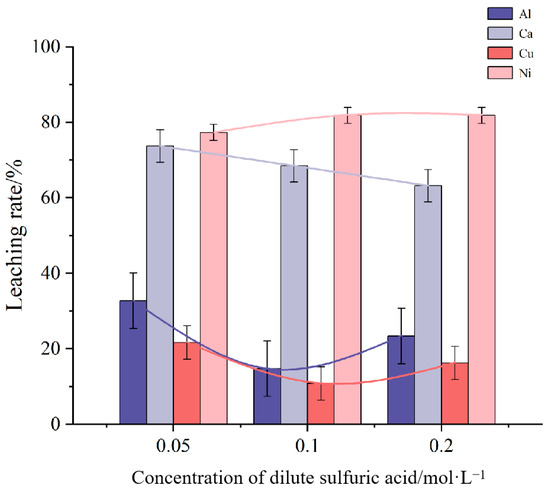
Figure 1.
Influence of dilute sulfuric acid concentration on leaching rate of impurity elements.
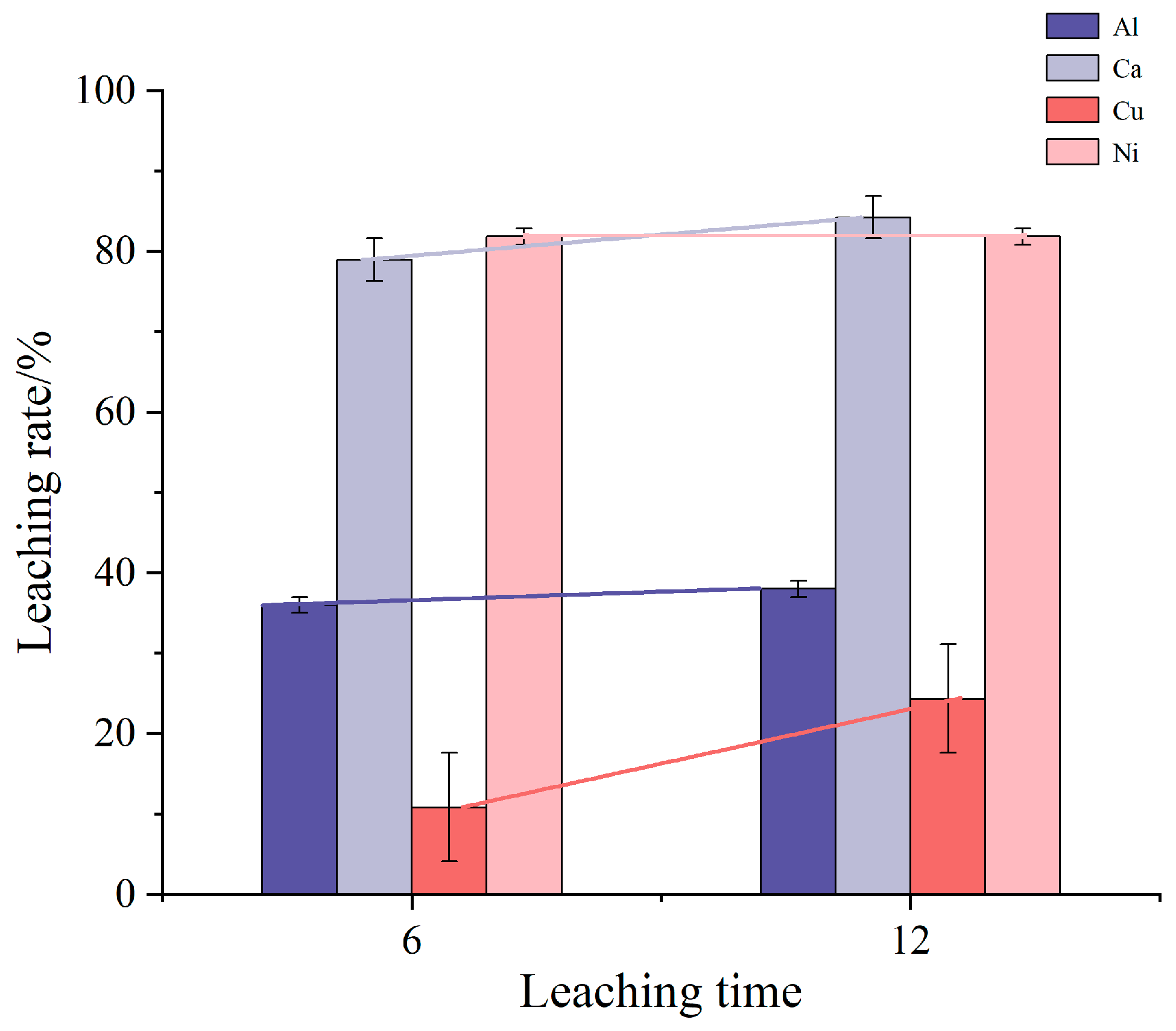
Figure 2 depicts the impact of leaching time on the leaching rates of impurity elements Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni. In this experiment, the concentration of the leaching solution was maintained at 0.2 mol/L, with only the leaching time varying across different groups. The mixture was heated and stirred at room temperature. The results indicate that as the leaching time extends, the leaching rates of Al, Ca, and Cu increase, with Cu showing the most significant increase over prolonged periods, while Al shows a comparatively smaller increase. The limited solubility of Al under these conditions suggests that extending the leaching time does not significantly enhance Al removal. Meanwhile, the Ni content exhibits minimal change with prolonged leaching time, indicating that Ni dissolution has likely reached saturation, and alternative methods are required to further increase its dissolution.
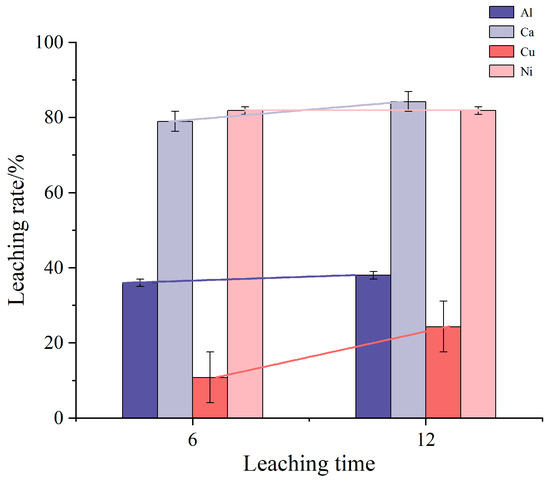
Figure 2.
Influence of leaching time on leaching rate of impurity elements.
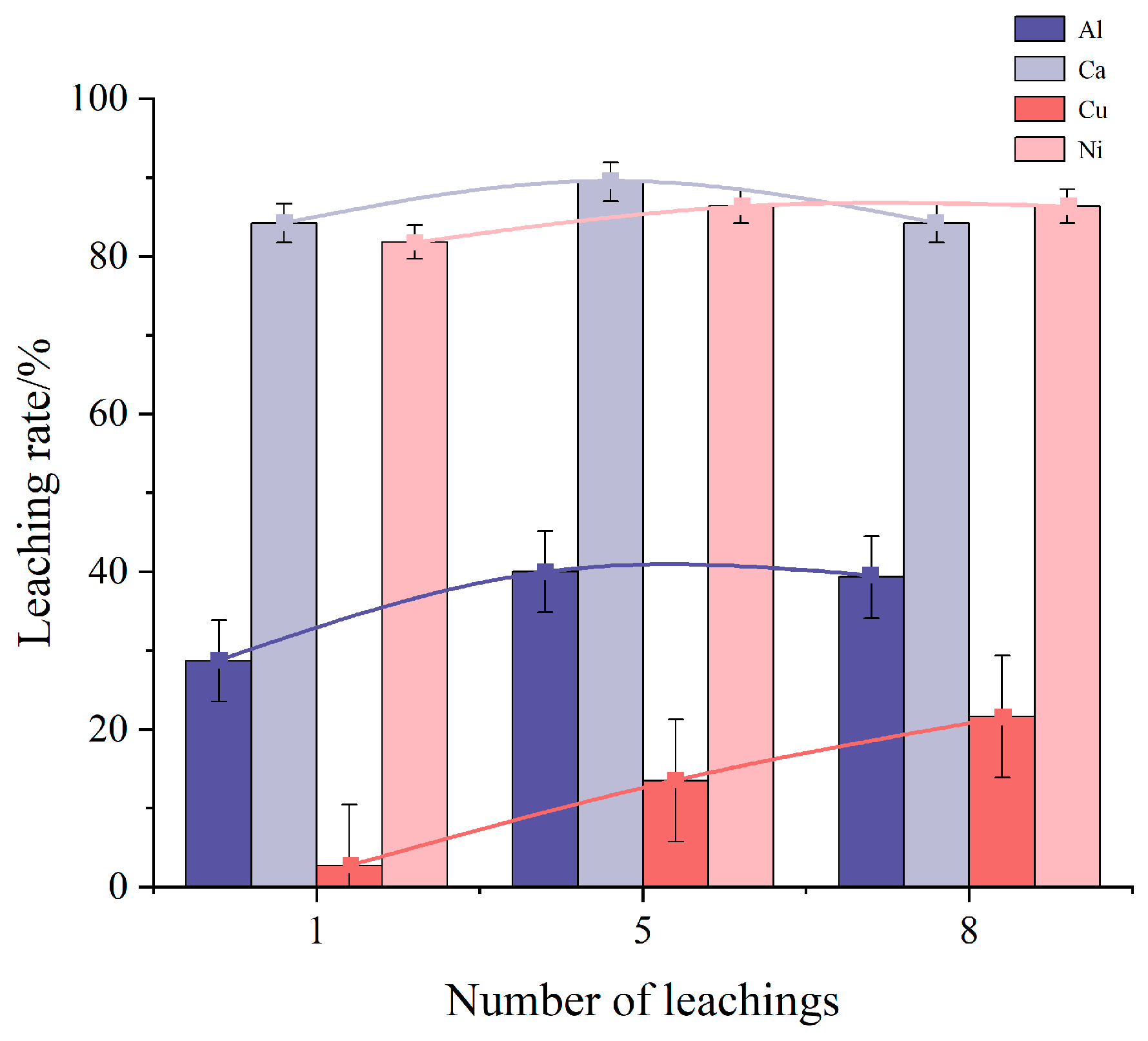
Figure 3 illustrates the effect of the number of leaching rounds on the leaching rates of impurity elements Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni. As the number of leaching rounds increases, the leaching rate of Al initially rises and then falls, reaching a maximum of 40% at five rounds. The leaching rates of Cu and Ni, on the other hand, continue to increase with more leaching rounds, achieving maximum rates of 21.62% and 86.37%, respectively. For the Ca element, the maximum leaching rate of 89.47% is observed at five leaching rounds. The observed trend suggests that the dissolution of other impurity elements may influence the dissolution of Ca, leading to a decrease in its leaching rate as the number of leaching rounds increases. In contrast, the leaching rates of Cu and Ni continue to rise with additional rounds.
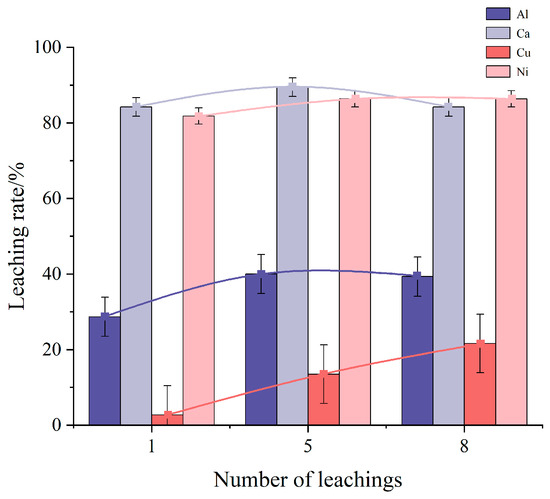
Figure 3.
Influence of leaching round numbers on the impurity element leaching rate.
To enhance the overall leaching rate of impurity elements, we first ball milled the raw materials and then subjected them to a high-temperature, high-pressure hydrothermal reaction at 120 °C for 12 h. This treatment resulted in a significant increase in the leaching rates of Ca, Cu, and Ni. Under optimized conditions using ball milling-assisted hydrothermal treatment, the leaching rates for Al, Cu, Ca, and Ni with dilute sulfuric acid were 36.0%, 51.4%, 89.5%, and 90.9%, respectively, demonstrating that acid leaching is highly effective in removing impurities during the recovery of iron phosphate from spent batteries. To further improve purification efficiency, we subsequently conducted the experiment using phosphoric acid in place of sulfuric acid as the leaching solution (Table 1).

Table 1.
Optimized experimental results with dilute sulfuric acid leaching.
3.2. Dilute Phosphoric Acid Leaching
Phosphoric acid was used instead of sulfuric acid, offering a fundamentally different approach from traditional acid leaching and presenting a novel purification route. During the dissolution and re-crystallization process, metal impurities such as Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni are released. Table 2 shows the leaching rates of these measured impurities. It was observed that, with increasing temperature, the leaching rates of Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni initially increase and then decrease. Consequently, the optimal leaching temperature for these elements was found to be 200 °C, where the leaching rates reached their maximum values of 65.07% for Al, 84.74% for Ca, 96.76% for Cu, and 96.36% for Ni.

Table 2.
Influence of leaching temperature on leaching rate of impurity elements.
Table 3 presents the effect of the filling degree of the hydrothermal autoclave on the leaching rates of the measured impurity elements. The filling degree refers to the ratio of the liquid volume to the total volume of the inner tank of the hydrothermal autoclave. This parameter is closely related to the system’s supercritical conditions, such as the pressure at a given temperature, which can significantly influence the reaction process.

Table 3.
Influence of filling degree of a hydrothermal kettle on leaching rate of impurity elements.
It was observed that the leaching rates generally decrease as the filling degree increases. The highest leaching rates for Al, Ca, Cu, and Ni were achieved at a filling degree of 25%, with values of 87.9%, 85.8%, 98.4%, and 99.1%, respectively. These results are comparable to previously reported leaching efficiencies of 99.53% for Ni and 98.08% for Cu [30]. The loss of Fe during the leaching process was also analyzed by measuring the Fe content in the leaching solution, and the loss rate of Fe was calculated using the following formula:
where µ represents the loss rate of Fe as a mass percentage; is the mass of the sample taken when analyzing the sample, in g; V is the total volume of the filtered filtrate (in L); E0 is the original Fe content in the samples used for the acid leaching experiments as a mass percentage; and CFe is the final concentration of Fe measured in the solution (in mg/L). The calculated Fe loss for the sample with the highest leaching rate is 0.22%, which is lower than previously reported results of 0.3% [30]. This reduction in iron loss not only increases the yield of iron phosphate products but also lowers waste management costs under similar conditions. Based on the calculation method outlined in Table 4, the acid consumption and acid usage costs associated with the three elements (Fe, Cu, and Ni, present in both this study and the comparative literature) decreased by 5.12%. Additionally, the reduction in iron loss allows for an increase in iron phosphate product yield and a reduction in waste management costs under the same conditions.

Table 4.
Economic analysis compared the selective leaching method with a complete dissolution process.
Furthermore, a preliminary analysis was also conducted to compare the acid consumption and economic feasibility with that of a complete dissolution process. Detailed calculations are provided in Table 4.
It was observed that the acid consumption decreased significantly from 12.796 mol/kg to 0.444 mol/kg when both acids were treated as monobasic acids. Correspondingly, the cost of acid usage dropped from 0.436 CNY/kg to 0.085 CNY/kg, despite the fact that the less expensive hydrochloric acid (32%, 300 CNY/t) was used for complete dissolution, whereas the more costly phosphoric acid (85%, 5000 CNY/t) was employed for selective leaching.
3.3. Microstructure Characterization
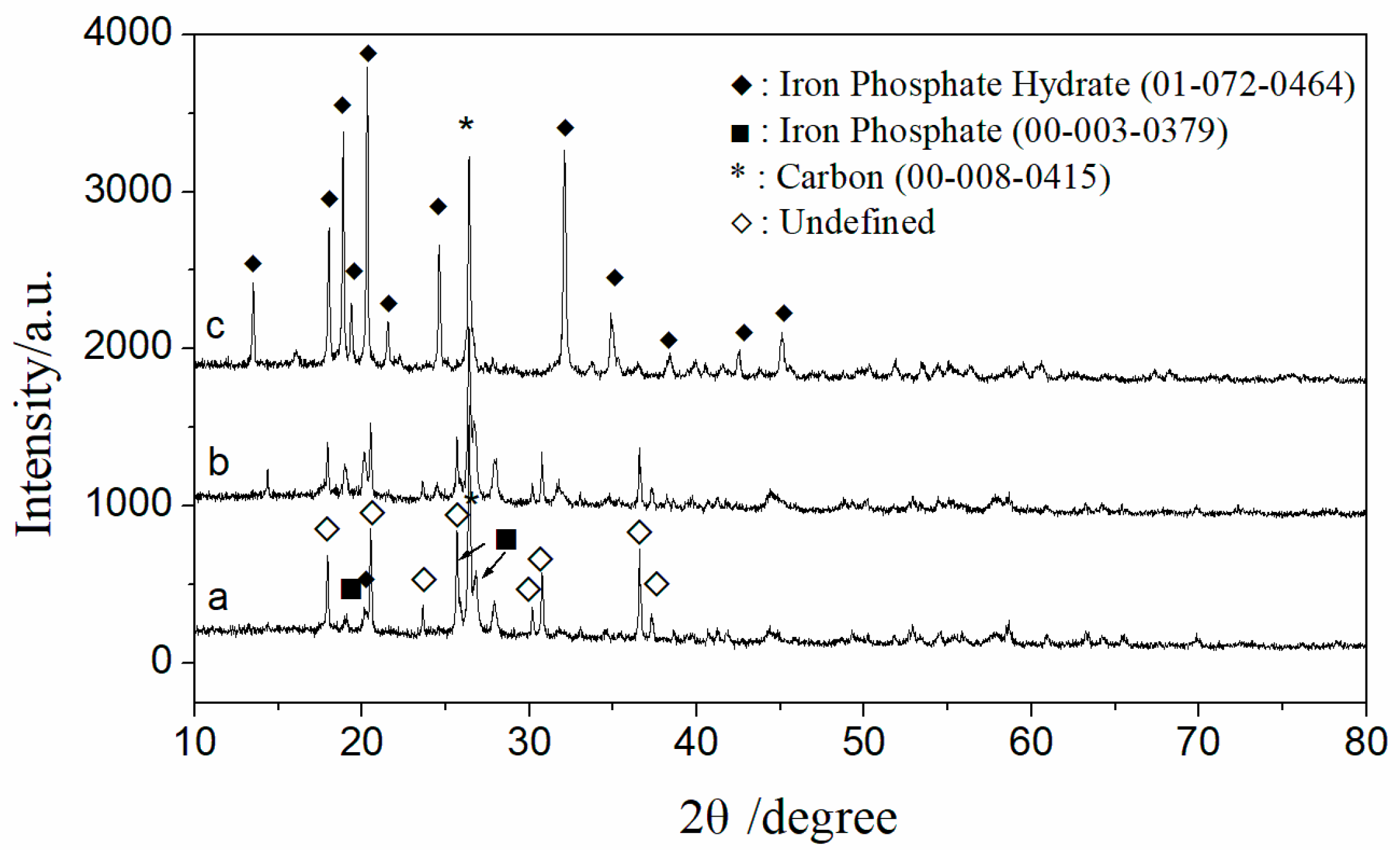
Figure 4 presents the typical XRD patterns of the samples: as received (a), purified with sulfuric acid (b), and purified with phosphoric acid (c). The XRD pattern of the received sample shows quite chaotic diffraction peaks. In addition to the characteristic peaks of carbon, iron phosphate, and iron phosphate hydrate, the other main diffraction peaks align with those of iron manganese phosphate (ICDD: 00-034-0134) in the database. However, according to the ICP detection results of the raw materials, manganese content is very low, ranking after Fe, Cu, Ni, Al, Ca, Mg, and K. Therefore, it cannot be conclusively identified as iron manganese phosphate, despite the match in the diffraction pattern. Instead, the crystal structure resembling that of iron manganese phosphate is likely due to the presence of residual impurity metal ions such as Cu, Ni, Al, Ca, and Mg in the iron phosphate.
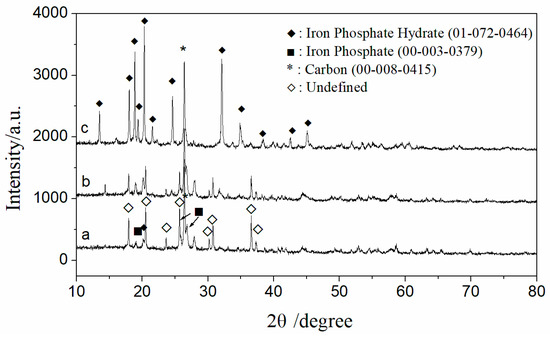
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the samples as received (a) and post-treatment ((b) with sulfuric acid; (c) with phosphate acid).
The main diffraction peaks in the XRD pattern of the sample purified with phosphoric acid (c) match those of iron phosphate hydrate (ICDD: 01-072-0464). During the acid leaching process, the crystal structure transitions from one similar to iron manganese phosphate to a hydrated iron phosphate structure, with a significant reduction in impurity element content, as confirmed by ICP characterization results. This change can reasonably be attributed to the liberation of impurity atoms from the lattice.
The XRD pattern of the sample purified with sulfuric acid (b) exhibits characteristics that lie between those of the as-received sample (a) and the sample purified with phosphoric acid (c). This indicates that while the dilute sulfuric acid leaching method is effective in removing impurities from iron phosphate recycled from waste LIBs, the dilute phosphoric acid leaching method achieves better purification efficiency. The carbon in the sample was left untreated, as it was suggested by a company representative that the residual carbon may have a beneficial effect on the subsequent synthesis of lithium iron phosphate or could be more easily removed during the synthesis process.
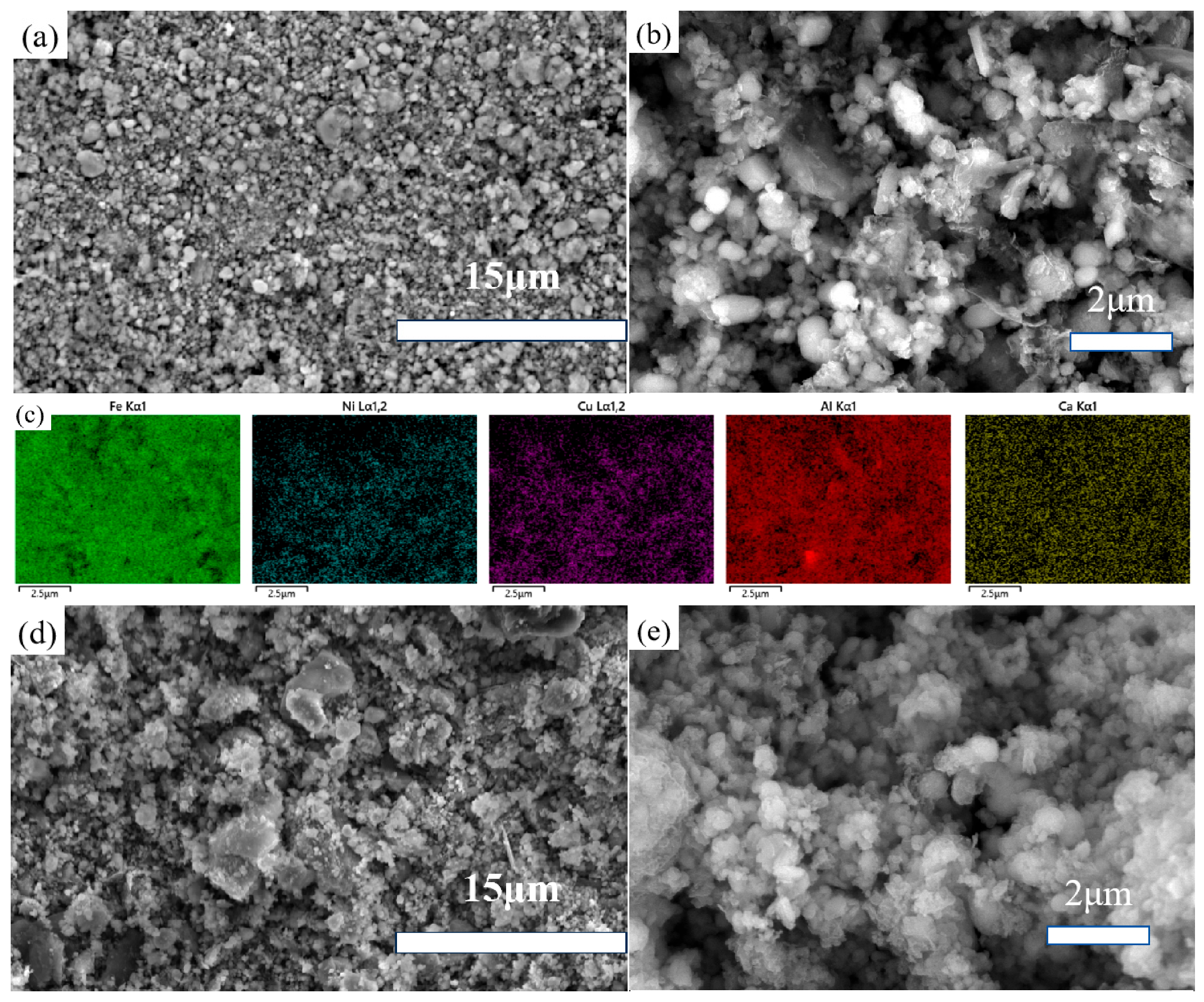
The as-received powders and processed samples were dried for SEM morphological observation. As shown in Figure 5a,b, the as-received powders consist of micro-sized aggregates. Figure 5c presents the colored EDS mapping of the elements examined in this study.
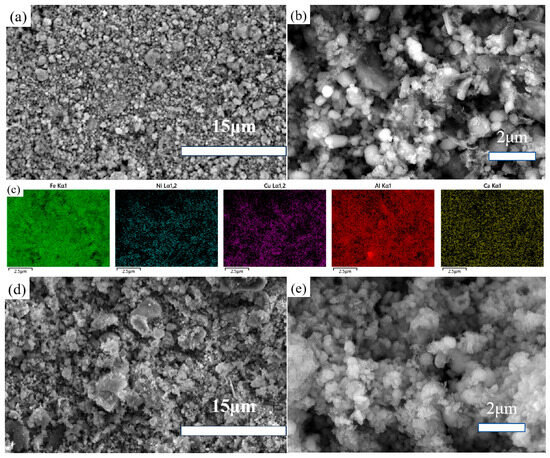
Figure 5.
FESEM images of the as-received powders (a–c) and ball-milled samples (d,e).
Figure 5d,e depict the ball-milled powders, where larger aggregates are observed in the low-magnification SEM images compared to the as-received samples. This is likely due to the fact that ball milling reduces particle size, leading to finer particles that are more prone to aggregation during the filtration and drying process because of hydrogen bonding. Figure 5e, at higher magnification, provides a detailed view showing that the ball-milled powders have indeed become smaller. By reducing particle size, grinding enhances mass transfer during the acid leaching process. Therefore, ball milling was considered as a method to improve the leaching efficiency of impurity elements.
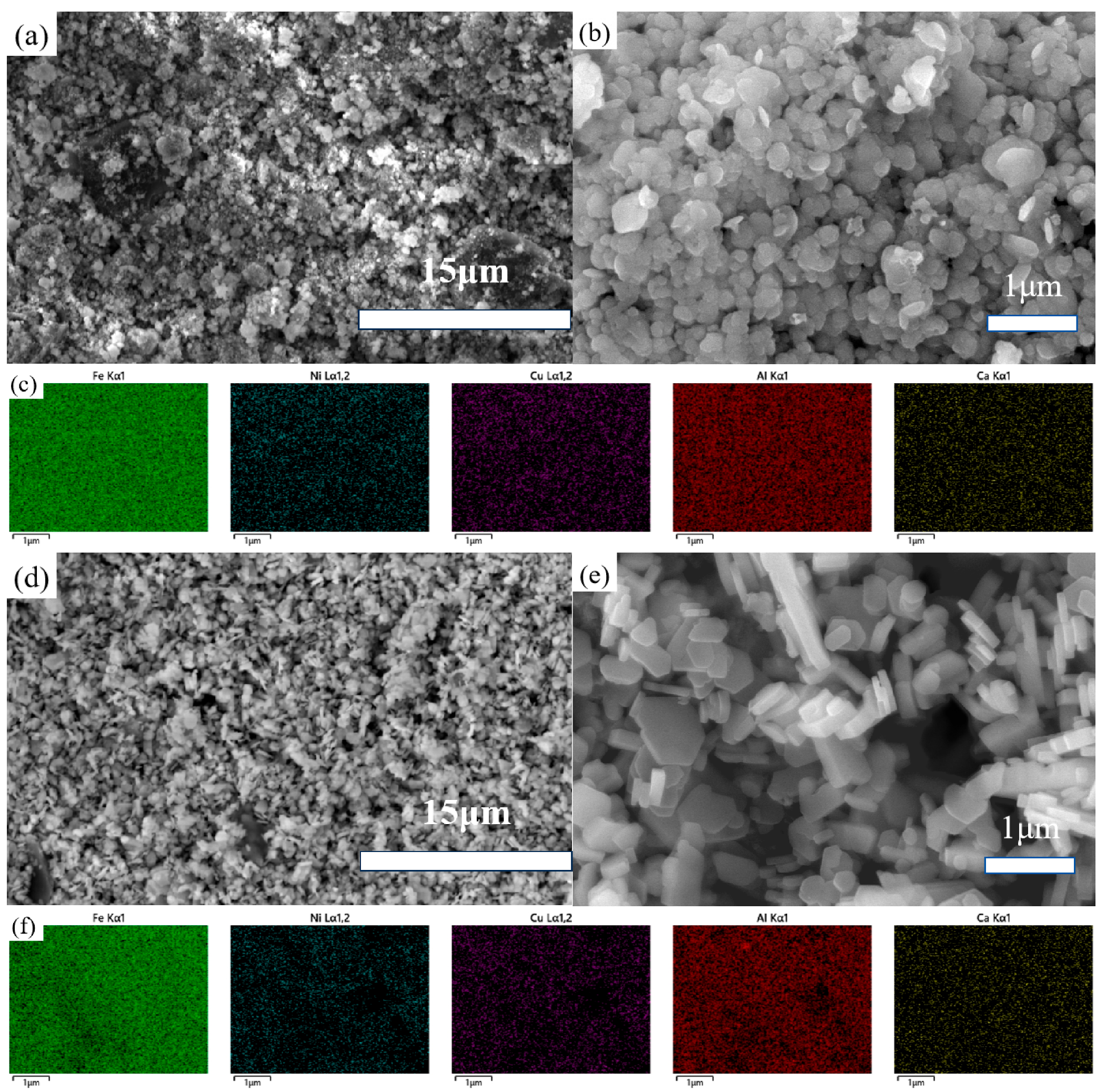
Figure 6 presents the FESEM images of the samples obtained after sulfuric acid leaching and phosphoric acid leaching.
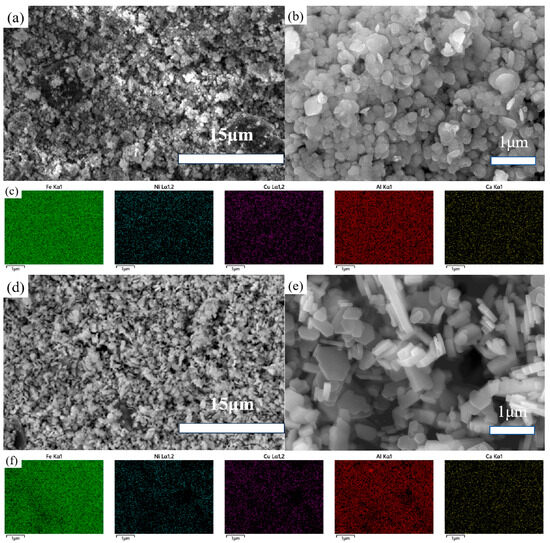
Figure 6.
FESEM images of the samples obtained after sulfuric acid leaching (a,b) and phosphoric acid leaching (d,e) and their colored EDS maps (c,f).
In Figure 6a,b, the samples treated with sulfuric acid leaching show a similar morphology and size compared to the untreated samples, with an improvement in overall uniformity and the elimination of particularly fine particles. In contrast, Figure 6d,e reveal that the samples subjected to hydrothermal treatment in diluted phosphoric acid exhibit even greater uniformity in size, with the edges of each particle becoming more distinct. As previously mentioned, hydrothermal treatment in diluted phosphoric acid differs fundamentally from traditional simple acid leaching. The dissolution and re-crystallization processes during hydrothermal treatment lead to more uniform particles and improved crystallization.
4. Conclusions
This project focused on the purification of iron phosphate obtained from waste LFP battery materials after lithium extraction, proposing a direct acid leaching process to achieve high-purity iron phosphate for the subsequent preparation of LFP battery materials. The study’s findings indicate that the purification process effectively reduced impurity metal elements while correspondingly increasing the iron content. Specifically, under optimized experimental conditions, the dilute sulfuric acid leaching rates for aluminum (Al), copper (Cu), calcium (Ca), and nickel (Ni) were 36.0%, 51.4%, 89.5%, and 90.9%, respectively. Furthermore, hydrothermal treatment in dilute phosphoric acid yielded leaching rates of 87.9% for Al, 85.8% for Ca, 98.4% for Cu, and 99.1% for Ni. The microstructure characterization demonstrated that the dilute phosphoric acid leaching process achieved a good purification effect, attributed to the liberation of impurity atoms from the lattice. Overall, this work demonstrated the effectiveness of acid leaching in removing impurities from FePO4 recovered from waste LFP batteries, highlighting its potential for use in recycling and reusing battery materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B., W.S. and X.Z.; methodology, L.B., F.Y. and G.L.; investigation, G.L., Y.F. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B., G.L. and H.O.; writing—review and editing, Y.L. and W.S.; visualization, L.B. and Y.F.; supervision, F.Y.; project administration, L.B.; funding acquisition, L.B. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by the China Central Guidance on Local Science Technology Development Fund of Henan Province (Z20221343028), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (242300420256), the Scientific and Technological Research Projects of Henan Province (232102231001), and the Tianzhong Talent Program in Huanghuai University.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Wenbin Sun was employed by the company Henan Great Power Energy Co., Ltd. Author Xiaomao Zeng was employed by the company Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The Henan Great Power Energy Co., Ltd. and Henan Great Power Recycling Technology Co., Ltd. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ning, T.; Lu, B.; Ouyang, X.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, J. Prospect and sustainability prediction of China’s new energy vehicles sales considering temporal and spatial dimensions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 142926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhua. China’s Installed Capacity of Power Batteries Sees Growth in First 5 Months. Available online: https://english.www.gov.cn/archive/statistics/202406/16/content_WS666eda66c6d0868f4e8e8319.html (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Yang, T.; Luo, D.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Enabling Future Closed-Loop Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Direct Cathode Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2203218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, K.; Gong, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P. Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 materials via a green and economical one-step hydrothermal process. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, F.; Tedjar, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Houlachi, G.; Bouchard, P.; Demopoulos, P.G.; Zaghib, K. Progress and Status of Hydrometallurgical and Direct Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Materials 2020, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Su, X.; An, L. Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Song, W.J. Electrode material recovery mode and analysis of economic lithium-ion power battery. Adv. New Renew. Energy 2018, 6, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville, R.; Shaw-Stewart, J.; Goodship, V.; Rowson, N.; Kendrick, E. A Review of Physical Processes Used in the Safe Recycling of Lithium Ion Batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W. Recent Advances in Pretreating Technology for Recycling Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Li, L. Bioleaching mechanism of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion battery by the mixed culture of acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Vereda-Alonso, C.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Towards Sustainable Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Advancements in Circular Hydrometallurgy. Processes 2024, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, L.; Yang, S. A novel recycling process of LiFePO4 cathodes for spent lithium-ion batteries by deep eutectic solvents. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, U.; Joshi, B.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Hydrometallurgical Routes to Close the Loop of Electric Vehicle (EV) Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs) Value Chain: A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 950–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, P.; Ning, P.; Li, Q. Recovery of Valuable Metals from Mixed Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Multi-Step Directional Precipitation. RSC Adv. 2020, 11, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; He, Y. Lithium Recycling and Cathode Material Regeneration from Acid Leach Liquor of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery via Facile Co-Extraction and Co-Precipitation Processes. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, Z. Recovery of Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Precipitation and Electrodialysis Techniques. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. The Twelve Principles of Circular Hydrometallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P.; Meng, Q.; Yang, X. Efficient oxidation approach for selective recovery of lithium from cathode materials of spent LiFePO4 batteries. JOM 2022, 74, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.J.; Zhang, B.C.; Xu, Y.L.; Hu, J.G.; Deng, W.T.; Zou, G.Q.; Hou, H.S.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.H.; et al. Enabling the sustainable recycling of LiFePO4 from spent lithium-ion batteries. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.H. Study on Green Recovery and Regeneration of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Material for Decommissioned Power Battery. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.; Shen, X.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J. Selective recovery of Li and FePO4 from spent LiFePO4 cathode scraps by organic acids and the properties of the regenerated LiFePO4. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Jing, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Facile and efficient recovery of lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries via air oxidation-water leaching at room temperature. Green Chem. 2021, 24, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Ma, X. A Method for Resource Recovery and Preparation of Battery Grade Iron Phosphate from Iron Phosphate Waste Residue. CN Patent 118387848 A, 26 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. A Method for Recycling Lithium Iron Phosphate Extraction Waste to Prepare Battery Grade Iron Phosphate. CN Patent 118221086 A, 21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Y.; Xue, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Selective Recovery of Li and Fe from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by an Environmentally Friendly Mechanochemical Approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11029–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, J.; Qiu, T. Recovery of lithium-extracted tailings from Lithium iron phosphate battery waste and preparation of iron phosphate. Rare Met. Cem. Carbides 2022, 50, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Xiao, S.; Huang, T.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J. Purification of iron phosphate waste generated zfter recycling of spent batteries. Min. Metall. Eng. 2024, 44, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Mu, J.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Wu, S.; Kuang, G. Method for Recovering and Preparing Battery Grade Iron Phosphate from Waste Lithium Iron Phosphate Extraction Residue. CN Patent 115611253 A, 22 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Trucill, P.; Lancia, A.; D’Amore, D.; Brancato, B.; Di Natale, F. Selective leaching of precious metals from electrical and electronic equipment through hydrometallurgical methods. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Haruna, B.; Luo, Z.; Muhammad, M.A.; Tang, J.; Kuva, J.; Koivula, R.; Bao, H.; Xu, J. Selective Separation of Lithium from Leachate of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Zirconium Phosphate/Polyacrylonitrile Composite: Leaching and Sorption Behavior. Batteries 2024, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Lee, M.S.; Nguyen, T.H. Ball Milling Treatment of Black Dross for Selective Dissolution of Alumina in Sodium Hydroxide Leaching. Processes 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shen, C.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, C. Extraction of Vanadium from the Spent Residuum Catalysts by Fenton-like Reaction Followed with Alkaline Leaching. Processes 2023, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, G.Q. Deep eutectic solvent-assisted selective extraction of valuable metals from waste lithium-ion batteries. AIChE J. 2024, 70, e18394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, J.L.; Wu, X.S.; Zeng, L.; Guan, W.J.; Cao, Z.Y.; Li, Q.G.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wu, S.X. Novel approach to recycling of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using hydrometallurgy, focused on preferential extraction of lithium. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 431, 139645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Fang, D.F.; Yi, G.P.; Gao, Z.; Shao, P.H.; Liu, C.L.; Luo, X.B.; Luo, S.L. Closed-loop regeneration of battery-grade FePO4 from lithium extraction slag of spent Li-ion batteries via phosphoric acid mixture selective leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 431, 133232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).