The Optimization of the Rear Guide Vane of a Bulb Tubular Pump Based on Orthogonal Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methodology and Verification
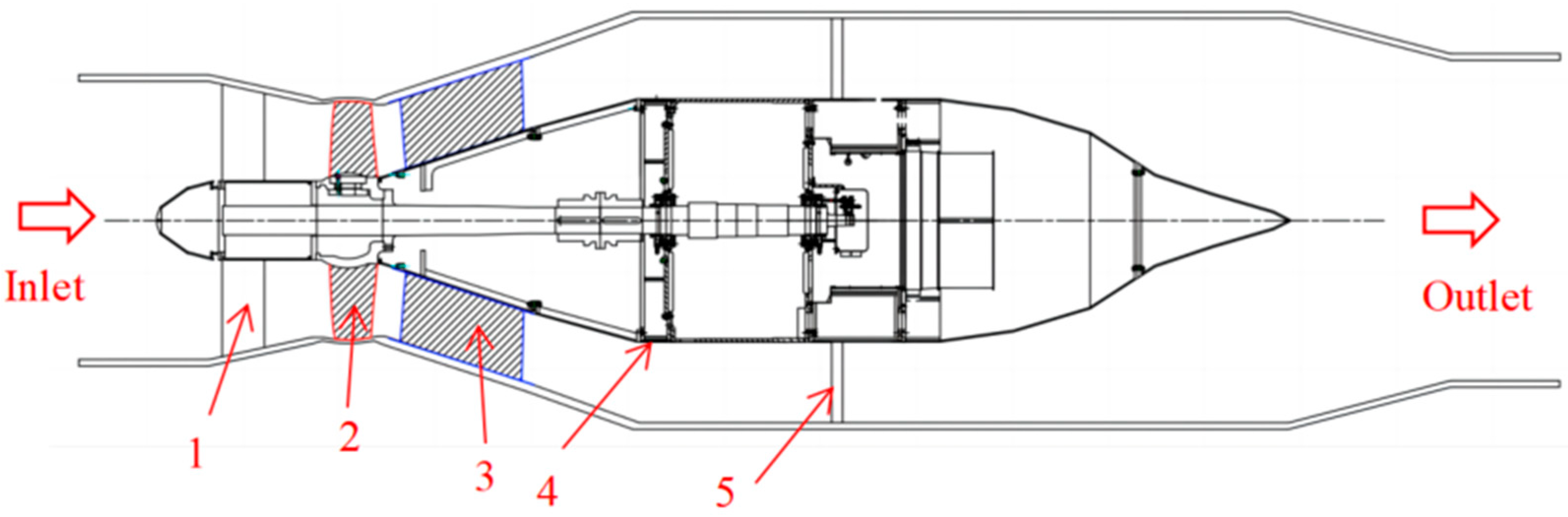
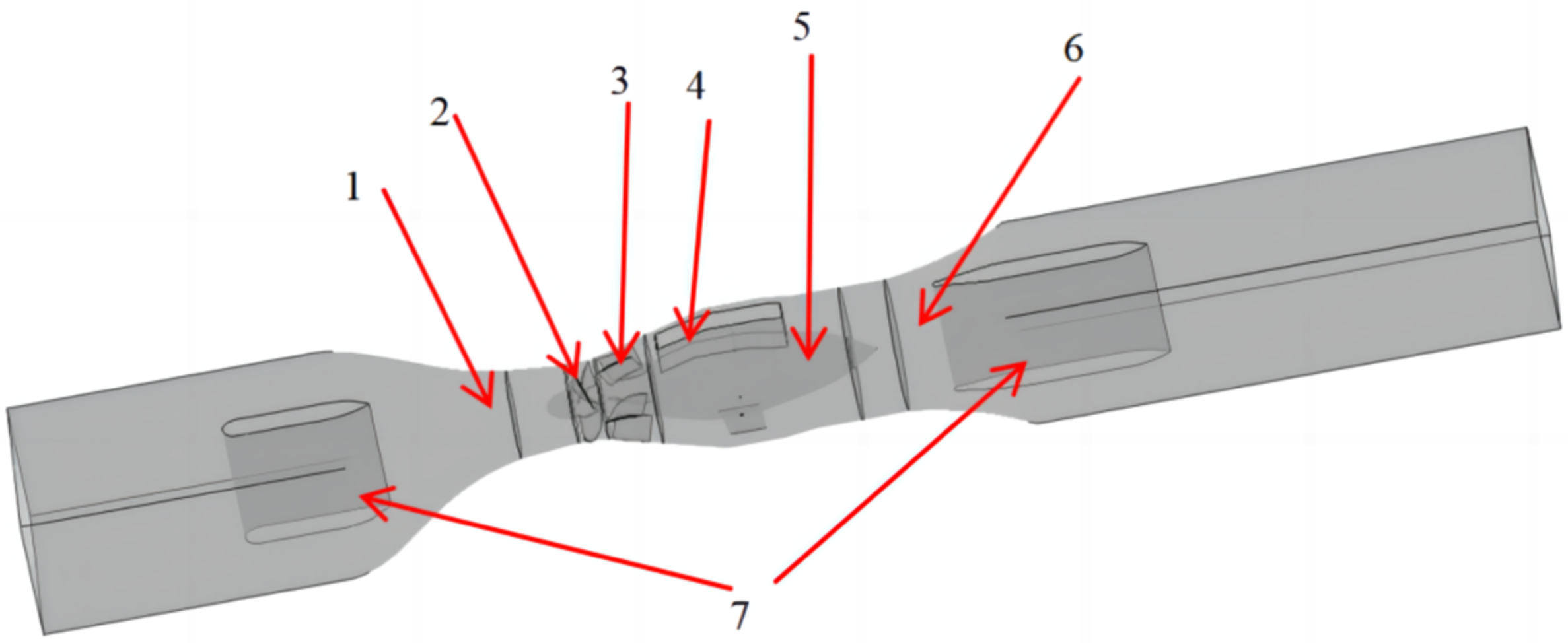
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Numerical Simulation Method
2.2.1. Governing Equations
- (1)
- Continuity equation
- (2)
- N-S equation
- (3)
- Energy equation
2.2.2. Turbulence Model
2.2.3. Entropy Production Theory
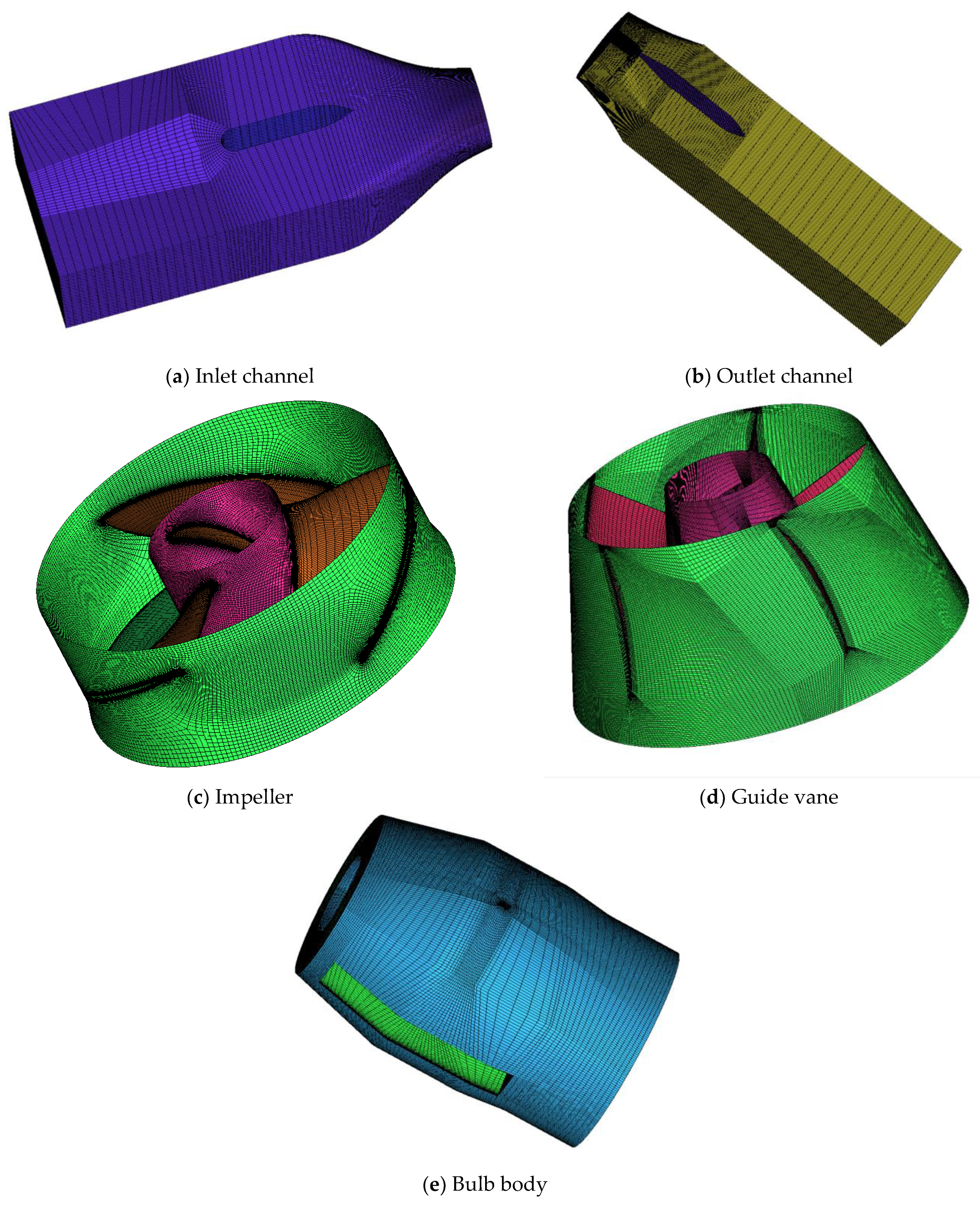
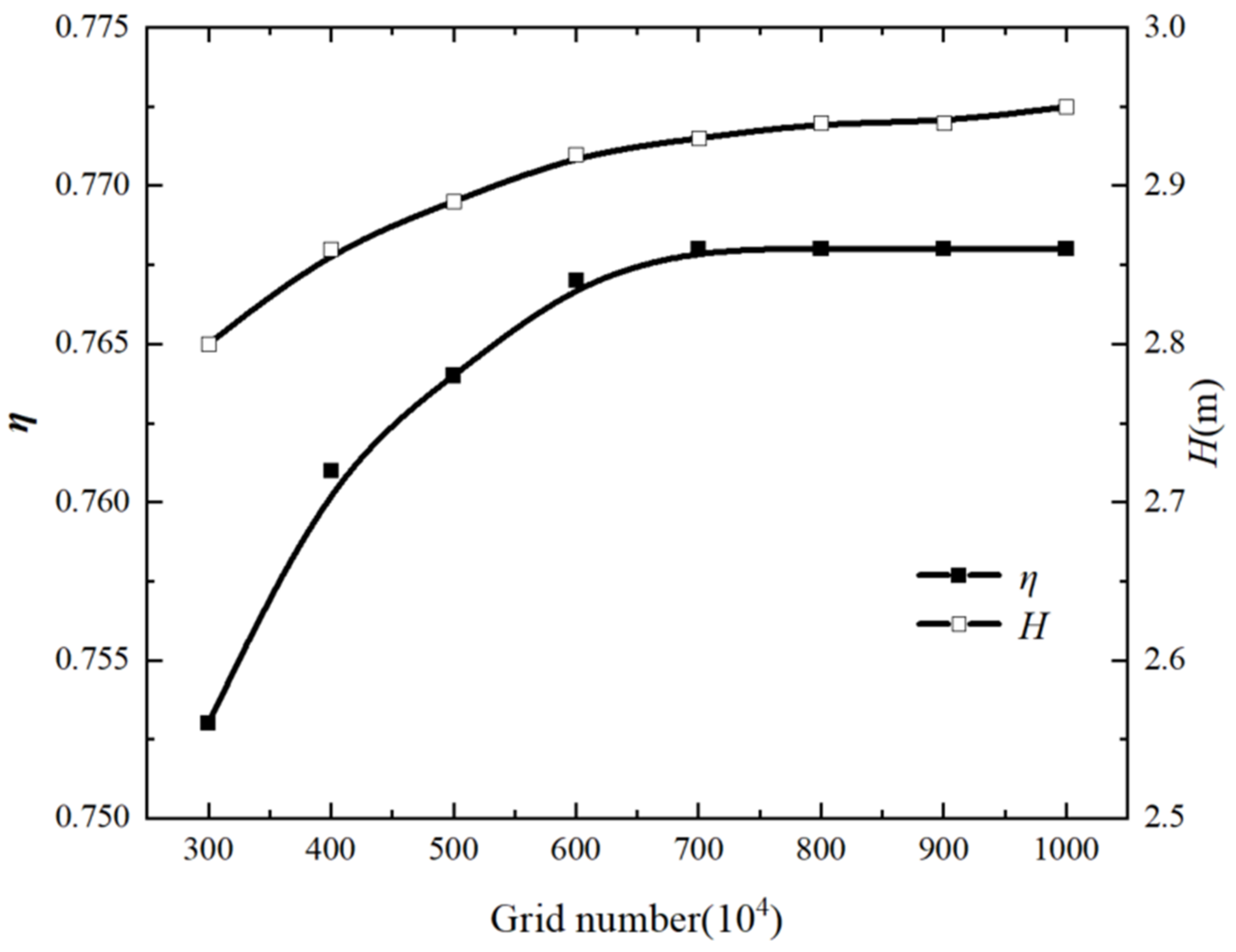
2.2.4. Mesh Generation
2.2.5. Boundary Condition for Numerical Simulations
2.3. Model Test
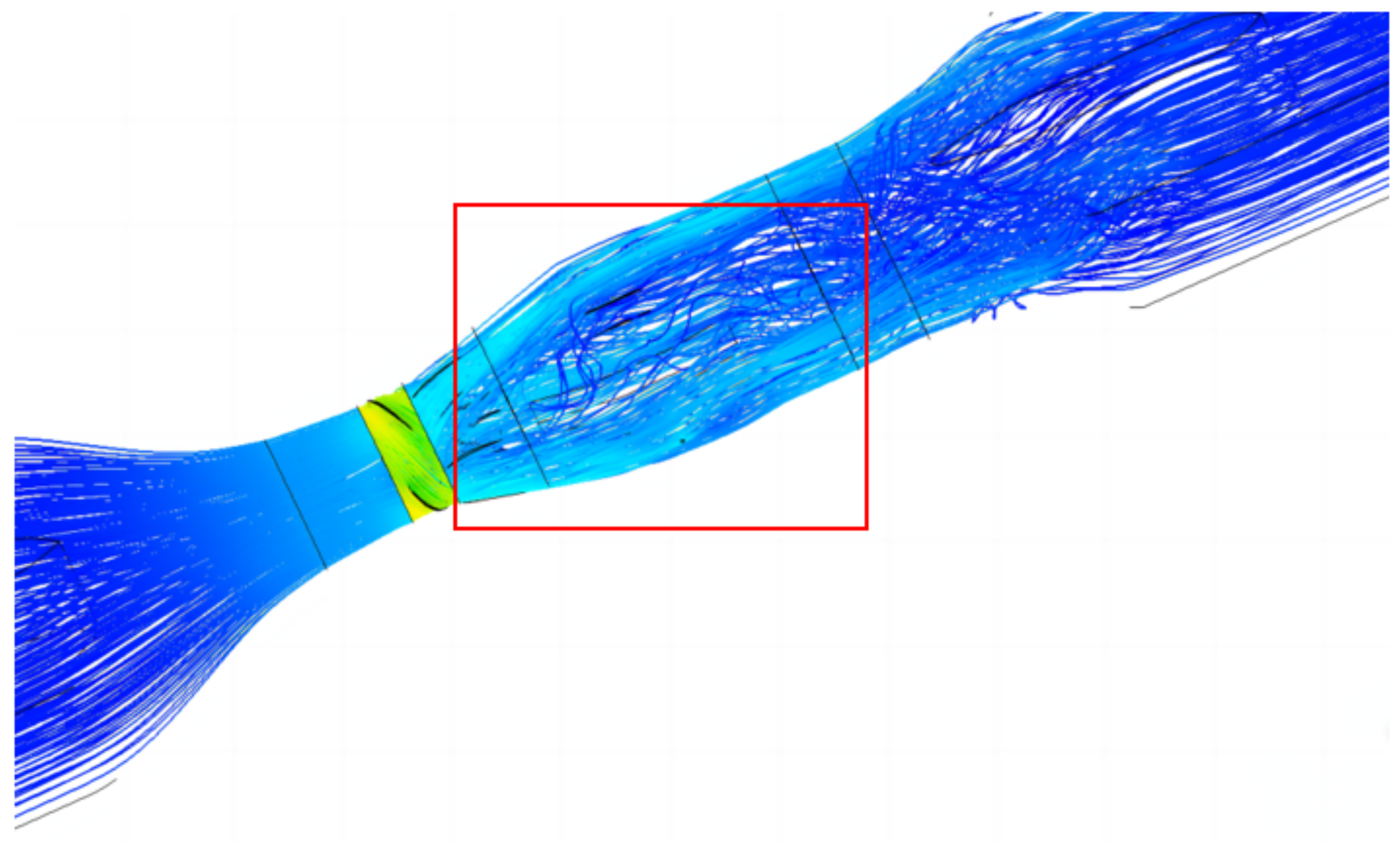
2.4. Internal Flow Analysis
3. Methodology
3.1. Orthogonal Test
3.2. Numerical Calculation Results and Range Analysis
3.2.1. Numerical Calculation
3.2.2. Range Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
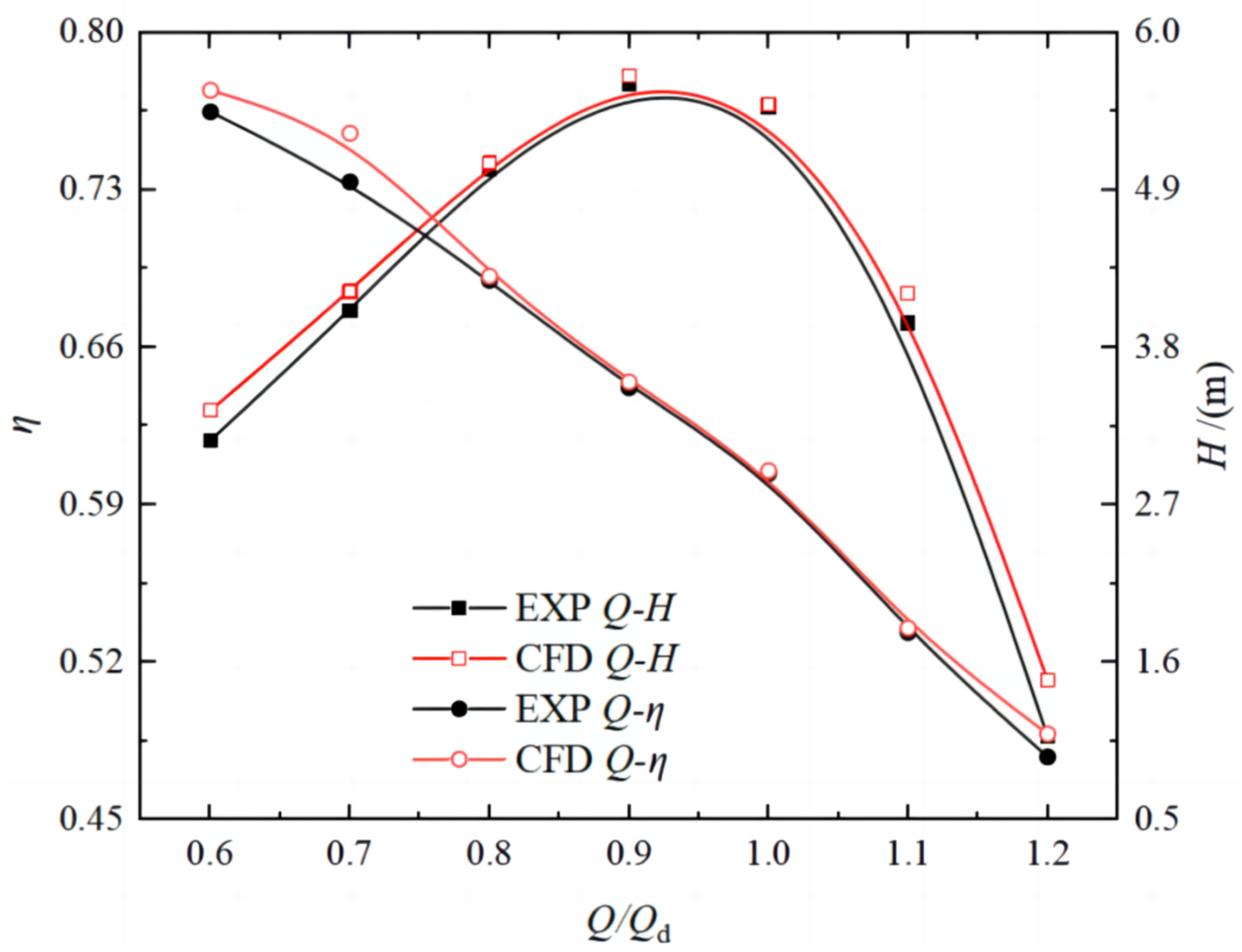
4.1. Comparative Analysis of the External Characteristics
4.2. Internal Flow Contrast Analysis
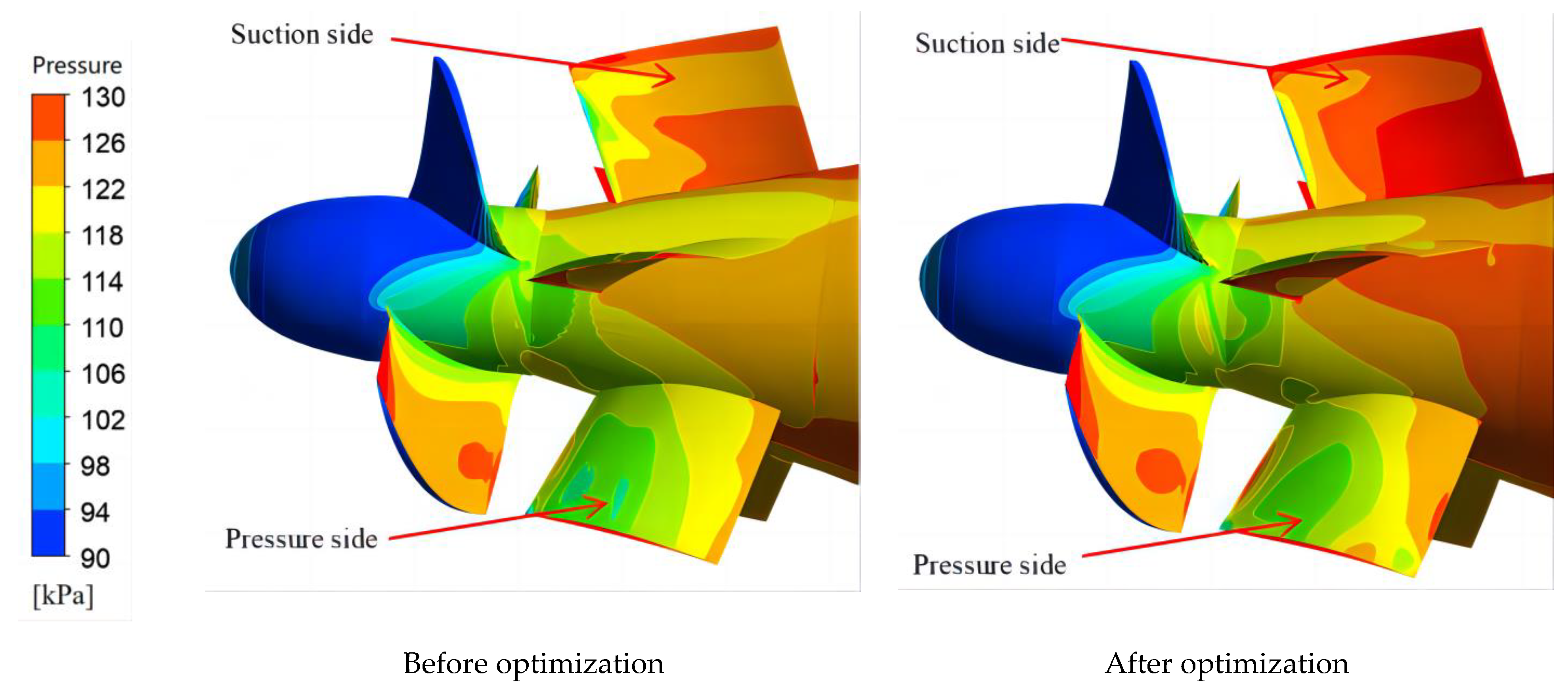
4.2.1. Pressure Analysis
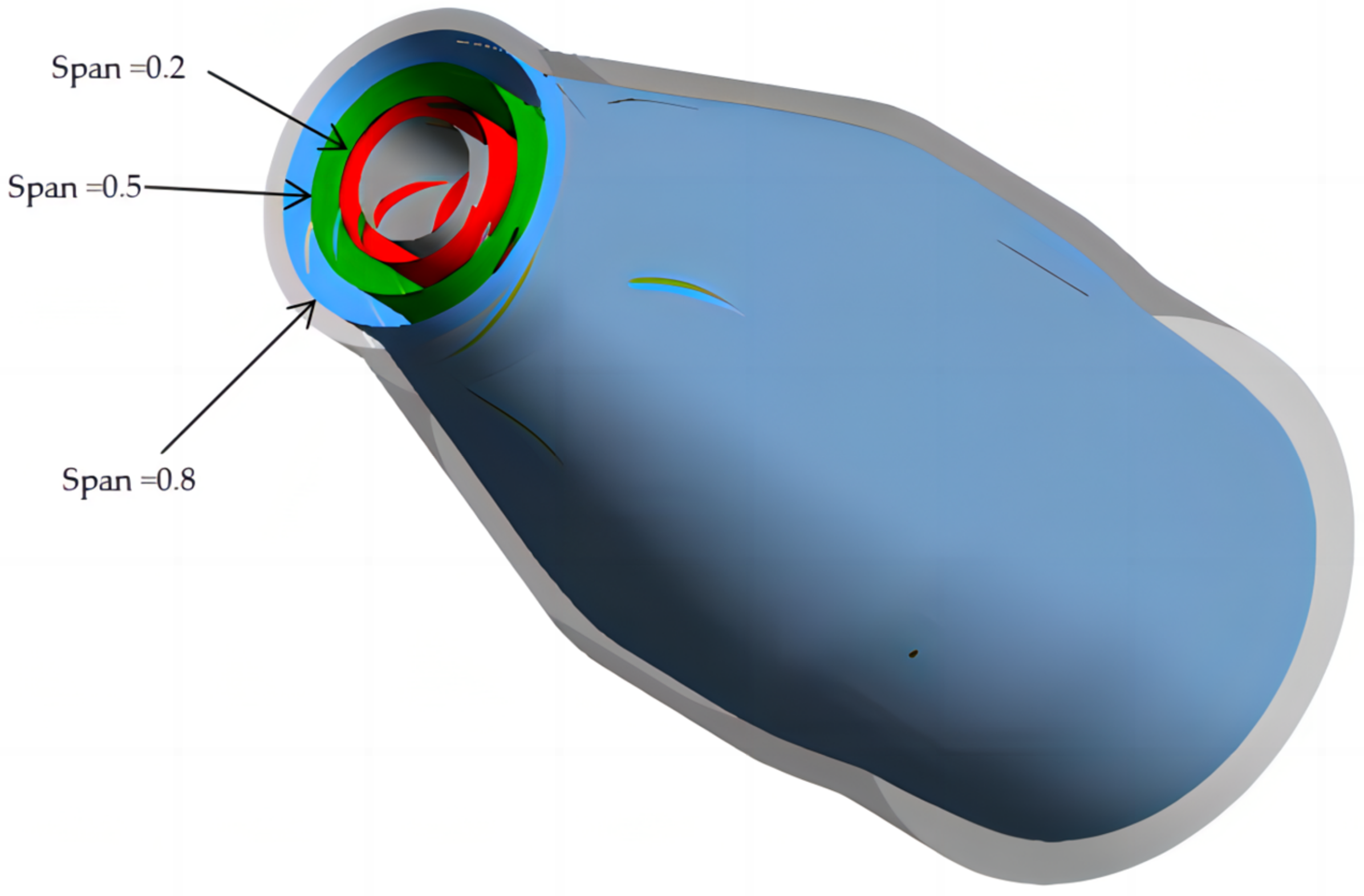
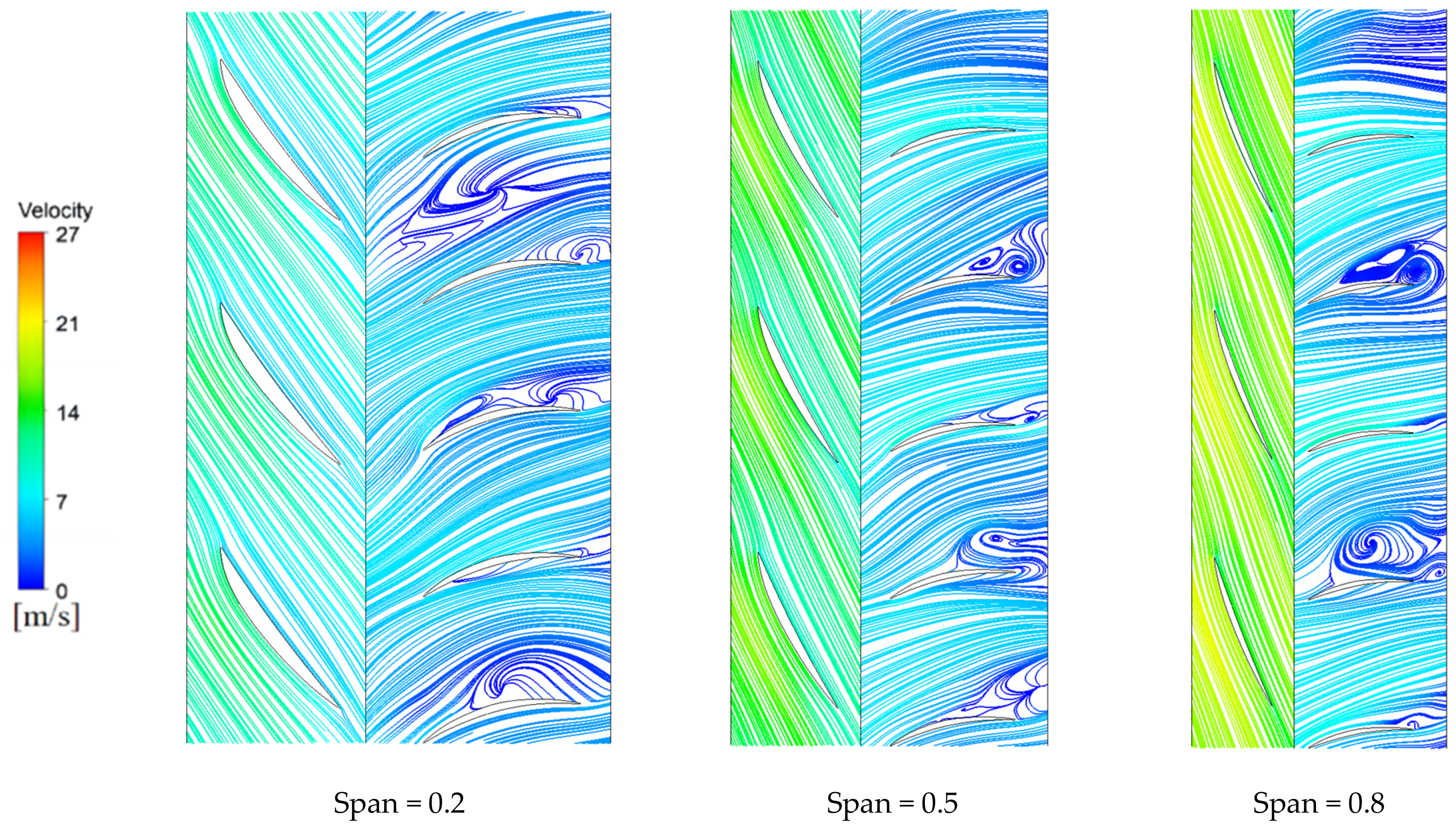
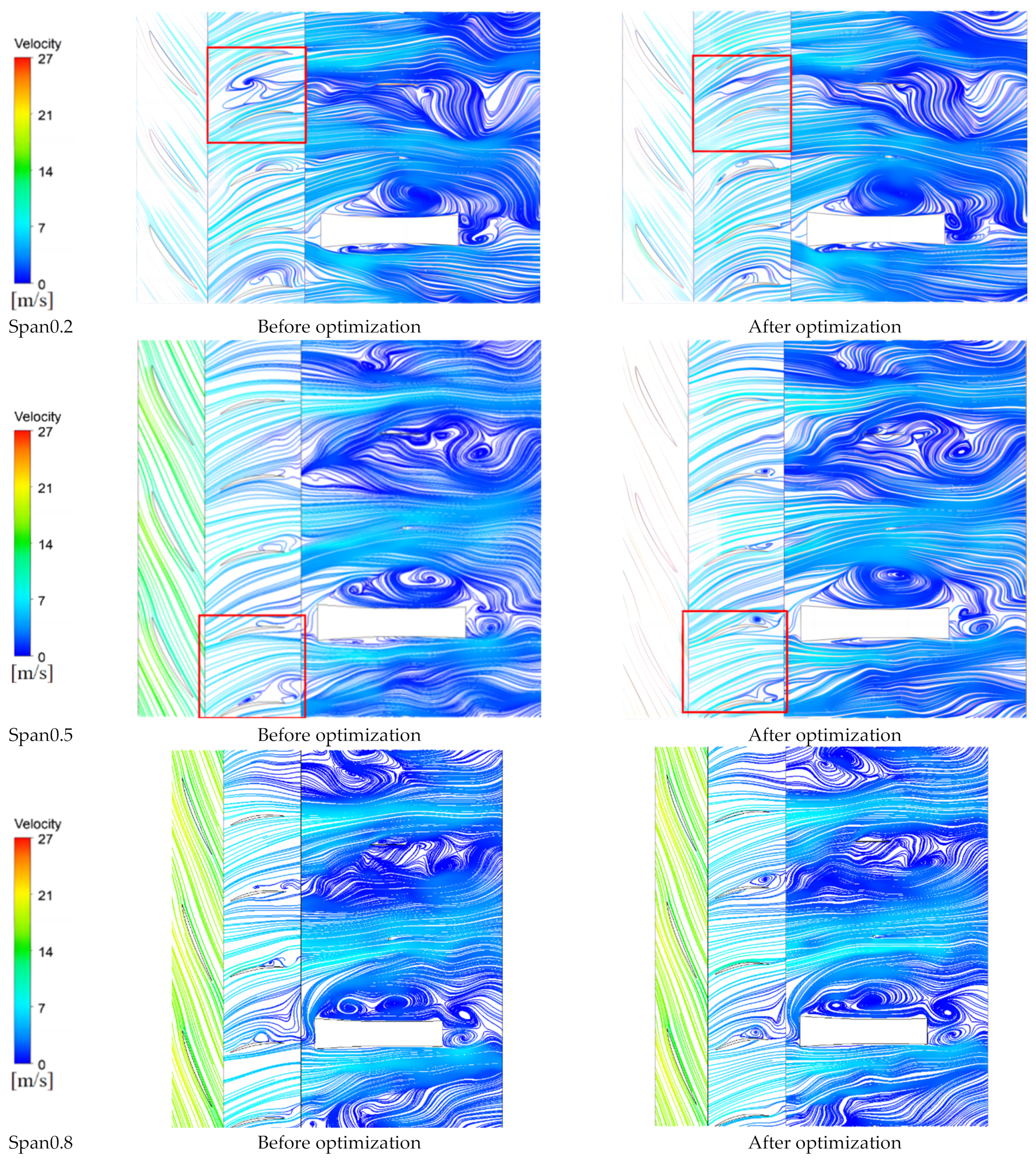
4.2.2. Streamline Analysis
4.2.3. Entropy Production Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Selection of Key Parameters—Five design parameters that significantly influence the pump’s external characteristics are chosen as factors for the orthogonal experiment, with each factor set at three levels. An L27 orthogonal table is constructed, and the design schemes in the table are numerically simulated.
- (2)
- Range Analysis and Optimal Design—A range analysis is performed to evaluate the influence of each factor on the test results. The optimal combination, according to the analysis, is a wrap angle (φ) of 16°, a rim inlet angle of 99°, a hub inlet angle of 90°, a hub outlet angle of 89°, and a rim outlet angle of 93°. Numerical calculations under three operating conditions show a hydraulic efficiency increase of 0.7% at a low flow rate, 0.88% at the design flow rate, and 1.1% at a high flow rate.
- (3)
- Flow Field and Energy Loss Analysis—The internal flow field under standard working conditions is analyzed, comparing the pressure distribution and streamline turbulence. The entropy generation theory is introduced to assess energy loss within the impeller, guide vane, and bulb body. The optimized design improves pressure distribution and reduces flow separation, thereby minimizing unnecessary energy loss.
- (4)
- Outlook—Due to limited resources and other reasons, this study does have its limitations. Although the role of structures such as the water barrier pier and the support body is considered in the computational domain model, only the guide vane is optimized. Additionally, the unstable flow near the support body also highlights that the optimization space is large. In a follow-up study, the guide vane and other flow components such as the bulb body can be matched and optimized.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffstaedt, J.P.; Truijen, D.P.K.; Fahlbeck, J.; Gans, L.H.A.; Qudaih, M.; Laguna, A.J.; De Kooning, J.D.M.; Stockman, K.; Nilsson, H.; Bricker, J.D.; et al. Low-head pumped hydro storage: A review of applicable technologies for design, grid integration, control and modelling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 158, 112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Muhirwa, A.; Maxime, B. Energy loss mechanisms of transition from pump mode to turbine mode of an axial-flow pump under bidirectional conditions. Energy 2022, 257, 124630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yuan, Y.; Jiao, H.; Tang, F.; Cheng, L.; Yang, F.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, J. Numerical investigation and experiment on pressure pulsation characteristics in a full tubular pump. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, H.; Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Shi, W. Numerical simulation and experimental study on the comparison of the hydraulic characteristics of an axial-flow pump and a full tubular pump. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z.; Cao, B. Investigation and optimization into flow dynamics for an axial flow pump as turbine (PAT) with ultra-low water head. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 314, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Binama, M.; Dai, J. Transient characteristics during power-off process in a shaft extension tubular pump by using a suitable numerical model. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, C. Multi-disciplinary optimization design of axial-flow pump impellers based on the approximation model. Energies 2020, 13, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Tan, L.; Han, B.; Han, S. Multi-parameter optimization design of axial-flow pump based on orthogonal method. Energies 2022, 15, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Ma, S.B.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H. Influence of inflow directions and setting angle of inlet guide vane on hydraulic performance of an axial-flow pump. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Z.; Cheng, Q. Performance improvement of an axial-flow pump with inlet guide vanes in the turbine mode. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2020, 234, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.; Gao, B.; Alubokin, A.A.; Zhou, W.; Shi, J. Numerical investigation on the unsteady vortical structure and pressure pulsations of a centrifugal pump with the vaned diffuser. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2022, 98, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; An, C.; Zhu, R.; Chen, J. Research on hydrodynamics of high velocity regions in a water-jet pump based on experimental and numerical calculations at different cavitation conditions. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 045124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.; Choi, B.L.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, G.S.; Sun, S.; Kim, J.H. Multiobjective hydraulic optimization of the diffuser vane in an axial flow pump. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 075125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chai, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Xing, J.; Yan, B.; Cheng, Y.; Han, Y. Numerical simulation and model test of the influence of guide vane angle on the performance of axial flow pump. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 015129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Chen, T.; Wu, D.Z.; Wang, L.Q. Multi-point optimization on the diffuser of an axial flow pump. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 022011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tong, S.; Shu, Z.; Cao, X.E. Investigating the hydraulic performance of slanted axial flow pumps using an enstrophy dissipation-based hybrid optimization approach. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 057117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, P.; Ni, D.; Gong, X.; He, B.; Zhu, R. Investigation on the Impact of Trailing Edge Stacking Styles on Hydraulic Performance in the Multistage Submersible Pump Space Diffuser. Processes 2023, 11, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qiu, G.; Pei, J.; Pavesi, G.; Tai, G.; Yuan, S. Effect of return channel on performance and pressure fluctuation of pump turbine. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 105129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lv, F.; Li, F.; Ji, D.; Shi, W.; Lu, W.; Lu, L. Comparison of energy performance of shaft tubular pump device at two guide vane inlet angles. Processes 2022, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J. Effects of distance between impeller and guide vane on losses in a low head pump by entropy production analysis. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fang, M.; Pan, J.; Tao, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W.; Xiao, R. Guide vane profile optimization of pump-turbine for grid connection performance improvement. Energy 2023, 274, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Xia, S.; Li, Q. Influence of guide vane slope on axial-flow hydraulic performance and internal flow characteristics. Energies 2022, 15, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, L.; Jiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C. Analysis of internal flow characteristics and entropy generation of low head bulb tubular pump. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1183086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, R.; van Esch, B.B. Numerical study of the energy loss in the bulb tubular pump system focusing on the off-design conditions based on combined energy analysis methods. Energy 2022, 258, 124794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Han, Y.; Xu, P.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, F.; Chen, Y.; Xue, M.; Chai, Y. Experimental study and numerical simulation of internal flow dissipation mechanism of an axial-flow pump under different design parameters. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cheng, L.; Xu, W.; Lei, S. Study on the Influence of Tip Clearance on Cavitation Performance and Entropy Production of an Axial Flow Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Li, S.; Cheng, L.; Sun, T.; Zhang, B.; Jiao, W. Experiment on Influence of Blade Angle on Hydraulic Characteristics of the Shaft Tubular Pumping Device. Processes 2022, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, F.; Tang, F.; Xu, T. Numerical analysis of energy loss in stall zone for full tubular pump based on entropy generation theory. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Lu, W.; Xu, B.; Xu, L.; Lu, L. Study of Energy Loss Characteristics of a Shaft Tubular Pump Device Based on the Entropy Production Method. Entropy 2023, 25, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Pei, J. Energy characteristics of full tubular pump device with different backflow clearances based on entropy production. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhot, V.; Orszag, S.A.; Thangam, S.; Gatski, T.B.; Speziale, C.G. Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1992, 4, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Flow Passage Component | Geometric Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Impeller | Hub diameter | 1600 mm |
| Hub ratio | 0.37 | |
| Impeller outlet diameter | 4300 mm | |
| Number of blades | 3 | |
| Inlet diameter | 4520 mm | |
| Outlet diameter | 5520 mm | |
| Blade tip clearance | 5 mm | |
| Guide vane | Guide vane diffusion angle | 13.4° |
| Number of blades | 5 | |
| Blade setting angle | 0° |
| Factors and Levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels | Factors | ||||
| /(°) | /(°) | /(°) | /(°) | /(°) | |
| 1 | 89 | 89 | 97 | 93 | 14 |
| 2 | 90 | 90 | 98 | 94 | 15 |
| 3 | 91 | 91 | 99 | 95 | 16 |
| Schemes | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/(°) | B/(°) | C/(°) | D/(°) | E/(°) | |
| 1 | 89 | 97 | 89 | 93 | 14 |
| 2 | 89 | 97 | 90 | 94 | 15 |
| 3 | 89 | 97 | 91 | 95 | 16 |
| 4 | 89 | 98 | 89 | 94 | 16 |
| 5 | 89 | 98 | 90 | 95 | 14 |
| 6 | 89 | 98 | 91 | 93 | 15 |
| 7 | 89 | 99 | 89 | 95 | 15 |
| 8 | 89 | 99 | 90 | 93 | 16 |
| 9 | 89 | 99 | 91 | 94 | 14 |
| 10 | 90 | 97 | 90 | 95 | 16 |
| 11 | 90 | 97 | 91 | 93 | 14 |
| 12 | 90 | 97 | 89 | 94 | 15 |
| 13 | 90 | 98 | 90 | 93 | 15 |
| 14 | 90 | 98 | 91 | 94 | 16 |
| 15 | 90 | 98 | 89 | 95 | 14 |
| 16 | 90 | 99 | 90 | 94 | 14 |
| 17 | 90 | 99 | 91 | 95 | 15 |
| 18 | 90 | 99 | 89 | 93 | 16 |
| 19 | 91 | 97 | 91 | 94 | 15 |
| 20 | 91 | 97 | 89 | 95 | 16 |
| 21 | 91 | 97 | 90 | 93 | 14 |
| 22 | 91 | 98 | 91 | 95 | 14 |
| 23 | 91 | 98 | 89 | 93 | 14 |
| 24 | 91 | 98 | 90 | 94 | 16 |
| 25 | 91 | 99 | 91 | 93 | 16 |
| 26 | 91 | 99 | 89 | 94 | 14 |
| 27 | 91 | 99 | 90 | 95 | 15 |
| Schemes | H/m | /% | Schemes | H/m | /% | Schemes | H/m | /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.974 | 77.25 | 2 | 2.974 | 77.34 | 3 | 2.98 | 77.45 |
| 4 | 2.99 | 77.62 | 5 | 2.97 | 77.24 | 6 | 2.977 | 77.41 |
| 7 | 2.972 | 77.38 | 8 | 2.988 | 77.59 | 9 | 2.974 | 77.29 |
| 10 | 2.987 | 77.58 | 11 | 2.975 | 77.25 | 12 | 2.977 | 77.4 |
| 13 | 2.977 | 77.4 | 14 | 2.975 | 77.41 | 15 | 2.971 | 77.24 |
| 16 | 2.974 | 77.3 | 17 | 2.975 | 77.41 | 18 | 2.997 | 77.68 |
| 19 | 2.977 | 77.36 | 20 | 2.982 | 77.49 | 21 | 2.975 | 77.24 |
| 22 | 2.97 | 77.24 | 23 | 2.97 | 77.24 | 24 | 2.983 | 77.5 |
| 25 | 2.984 | 77.54 | 26 | 2.975 | 77.31 | 27 | 2.975 | 77.41 |
| Index | A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head H/m | 26.799 | 26.801 | 26.808 | 26.817 | 26.758 | |
| 26.808 | 26.783 | 26.803 | 26.799 | 26.774 | ||
| 26.791 | 26.814 | 26.787 | 26.782 | 26.876 | ||
| 2.978 | 2.978 | 2.979 | 2.98 | 2.973 | ||
| 2.979 | 2.976 | 2.978 | 2.978 | 2.975 | ||
| 2.977 | 2.979 | 2.976 | 2.976 | 2.986 | ||
| R | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.013 | |
| Index | A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
/% | 696.57 | 696.36 | 696.61 | 696.6 | 695.36 | |
| 696.67 | 696.3 | 696.6 | 696.53 | 696.35 | ||
| 696.33 | 696.91 | 696.36 | 696.44 | 697.86 | ||
| 77.4 | 77.373 | 77.401 | 77.4 | 77.262 | ||
| 77.408 | 77.367 | 77.4 | 77.392 | 77.372 | ||
| 77.37 | 77.434 | 77.373 | 77.382 | 77.54 | ||
| R | 0.038 | 0.067 | 0.028 | 0.018 | 0.278 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Meng, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, R.; Yao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, W. The Optimization of the Rear Guide Vane of a Bulb Tubular Pump Based on Orthogonal Tests. Processes 2025, 13, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010264
Wang K, Meng X, Wang T, Jiang R, Yao W, Zhang M, Wang W, Wang W. The Optimization of the Rear Guide Vane of a Bulb Tubular Pump Based on Orthogonal Tests. Processes. 2025; 13(1):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010264
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kuilin, Xiaomin Meng, Tao Wang, Rongrong Jiang, Wang Yao, Mengru Zhang, Wentong Wang, and Wenjie Wang. 2025. "The Optimization of the Rear Guide Vane of a Bulb Tubular Pump Based on Orthogonal Tests" Processes 13, no. 1: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010264
APA StyleWang, K., Meng, X., Wang, T., Jiang, R., Yao, W., Zhang, M., Wang, W., & Wang, W. (2025). The Optimization of the Rear Guide Vane of a Bulb Tubular Pump Based on Orthogonal Tests. Processes, 13(1), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010264







