Abstract
Water kefir is a non-dairy fermented beverage that ferments water kefir grains in a sucrose solution. These grains harbor a diverse microbiota, including lactic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria, and yeast species. The composition of water kefir is primarily influenced by cultivation conditions and the microbiota profile of the grains, resulting in fermentation metabolites such as ethanol, lactic acid, mannitol, acetic acid, glycerol, and other organic acids. However, this microbial diversity can vary depending on the origin of the grains, the fermentation substrate, and environmental conditions. As it is a potentially beneficial product for health, interest in kefir consumption has increased in recent years. Specific legislation for water kefir is still scarce, and despite potentially probiotic microorganisms, water kefir is not classified as a probiotic, but it fits the definition of a potentially functional food due to its health benefits. Studies demonstrate the potential health benefits of water kefir in terms of anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and intestinal health effects. However, industrial-scale production and starter cultures have not yet been developed. This study aims to comprehensively review water kefir, exploring its potential health benefits, fermentation process, microbial diversity, and regulatory aspects.
1. Introduction
In recent years, consumer demand for nutritionally rich foods that support health and enhance quality of life has significantly increased [1]. Due to the growing awareness of the health benefits of probiotics, there is a rising interest in foods containing microorganisms with probiotic properties, with fermented foods gaining particular attention [2].
Dairy-based fermented foods remain the most prevalent among fermented foods. However, plant-based alternatives have garnered significant interest, whether due to health issues, such as people with allergies related to protein in cow’s milk or lactose intolerance, or the growing number of vegans [1,3]. Thus, within the group of non-dairy fermented foods, we have water kefir [4].
Water kefir is obtained by fermenting water kefir grains inoculated in a sucrose solution, with brown sugar being the primary fermentation agent [4]. The fermented beverage obtained is carbonated, cloudy, mildly alcoholic, and sweet. Its composition is determined mainly by the cultivation conditions and the microbiological profile of the grains, with the main fermentation byproducts including ethanol, lactic acid, mannitol, acetic acid, glycerol, and other organic acids [5,6]. The great variability in the microbiological composition of this fermented beverage makes it difficult to include it as a probiotic beverage, creating an important area that needs to be explored [7].
The health benefits of water kefir consumption may stem from its beneficial microorganisms, fermentation metabolites (organic acids and oligosaccharides), or their synergistic effects. However, studies on water kefir are scarce, and further research is needed to fully understand its potential health benefits [8]. Associated with this, it is necessary to explore and identify the microorganisms found in water kefir so that we can understand its composition, favoring the formulation of specific legislation for this beverage and the complete understanding of the real benefits associated with health [9,10]. Additionally, studies are needed on alternatives for preserving the microorganisms present in this beverage, and other products need to be made available to the consumer that are practical without losing the benefits. Therefore, the major gaps that need to be filled are based on conducting clinical studies with humans to verify the real effect of water kefir on human metabolism, and the development of starter cultures, facilitating the standardized determination of the microbial diversity of water kefir, and legislation [8].
In this context, this study aims to conduct a review of water kefir, exploring the fermentation process that occurs in the production stage of this beverage, the microorganisms identified, the potential health benefits, and the current regulatory aspects. For this purpose, a search of the current literature was carried out using the following keywords: water kefir, sweet kefir, tibicos, tibi, and non-dairy kefir.
2. Origin, Composition, and Production Process
The origin of water kefir is mostly unknown, unlike that of milk kefir. There is no documented region of origin for water kefir. Still, the first scientific report was published in 1889, which related the use of kefir grains in beer made with ginger by soldiers in the Crimean War in 1855 [5,11]. In 1989 in Mexico, water kefir was described as a microbial community called “tibi”. Other reports relating the use of water kefir were made in Mexico, France, Italy, and Germany; however, they used different names for the grains, such as tibicos, tibi, sweet kefir, Piltz, and kefir di Frutti, among others [5,11,12]. The consumption of water kefir is more common in countries as Russia, South America, and Eastern Europe, where it is traditional [7,11]. Information on availability suggests that water kefir is produced and consumed across several continents. This indicates a widespread and growing interest in this fermented beverage. Future research and market analysis may provide more concrete production.
The structure of water kefir grains is formed by α-D-(1→6)-linked glucopyranosyl residues with (1→3) connected side chains. The grains range in size from 5 to 20 mm in diameter, are irregular in shape, translucent, have a fragile structure, and are insoluble in water. The color of water kefir grains ranges from whitish to gray. Still, it can be influenced by the fermentation material, for example, the color of the fruits or vegetables, or the type of sugar used [11,13,14,15,16].
The grains can be reused for multiple fermentations through back-slopping, or by transferring them from a previous batch to a fresh substrate for a new fermentation [11,12]. Several fruits and vegetables, including soy, ginger, carrot, apple, pineapple, grape, kiwi, pear, melon, strawberry, pomegranate, tomato, and coconut, have been used as fermentation substrates, offering options for diversification and nutritional enhancement [5,17,18,19].
The resulting fermented beverage is carbonated, slightly cloudy, mildly alcoholic, and sweet. The grain cultivation conditions and microbiological profile primarily influence its composition. The main fermentation byproducts include ethanol, lactic acid, mannitol, acetic acid, glycerol, and other organic acids [5,6]. Thus, the beverage obtained after the fermentation process is composed of microorganisms (a symbiotic community of bacteria and yeasts), 2% lactic acid, 1% acetic acid, small amounts of alcohol resulting from the fermentation process (1%), and carbon dioxide, and the initial sugar content is reduced by half. Studies show that the concentration of microorganisms in the beverage may vary due to previously mentioned factors. The proportion of lactic acid bacteria ranges from 2.8 × 104 to 9 × 107 CFU/mL, acetic acid bacteria from 7 × 102 to 3.2 × 106 CFU/mL, and yeasts from 4.7 × 105 to 4.8 × 107 CFU/mL. The beverage resulting from the fermentation process contains various aromatic compounds, including isoamyl acetate, ethyl acetate, and ethyl octanoate, among others [11,20].
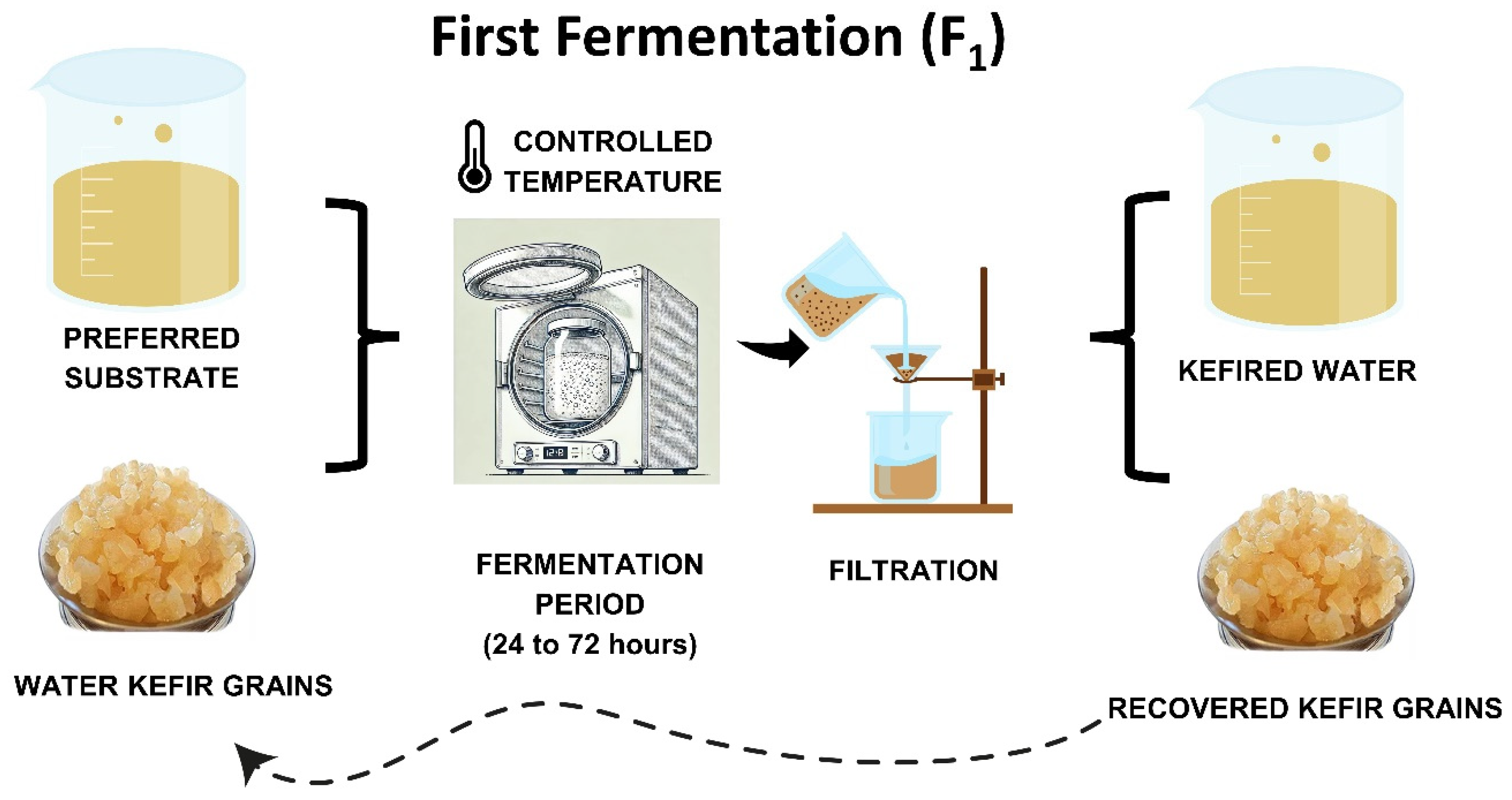
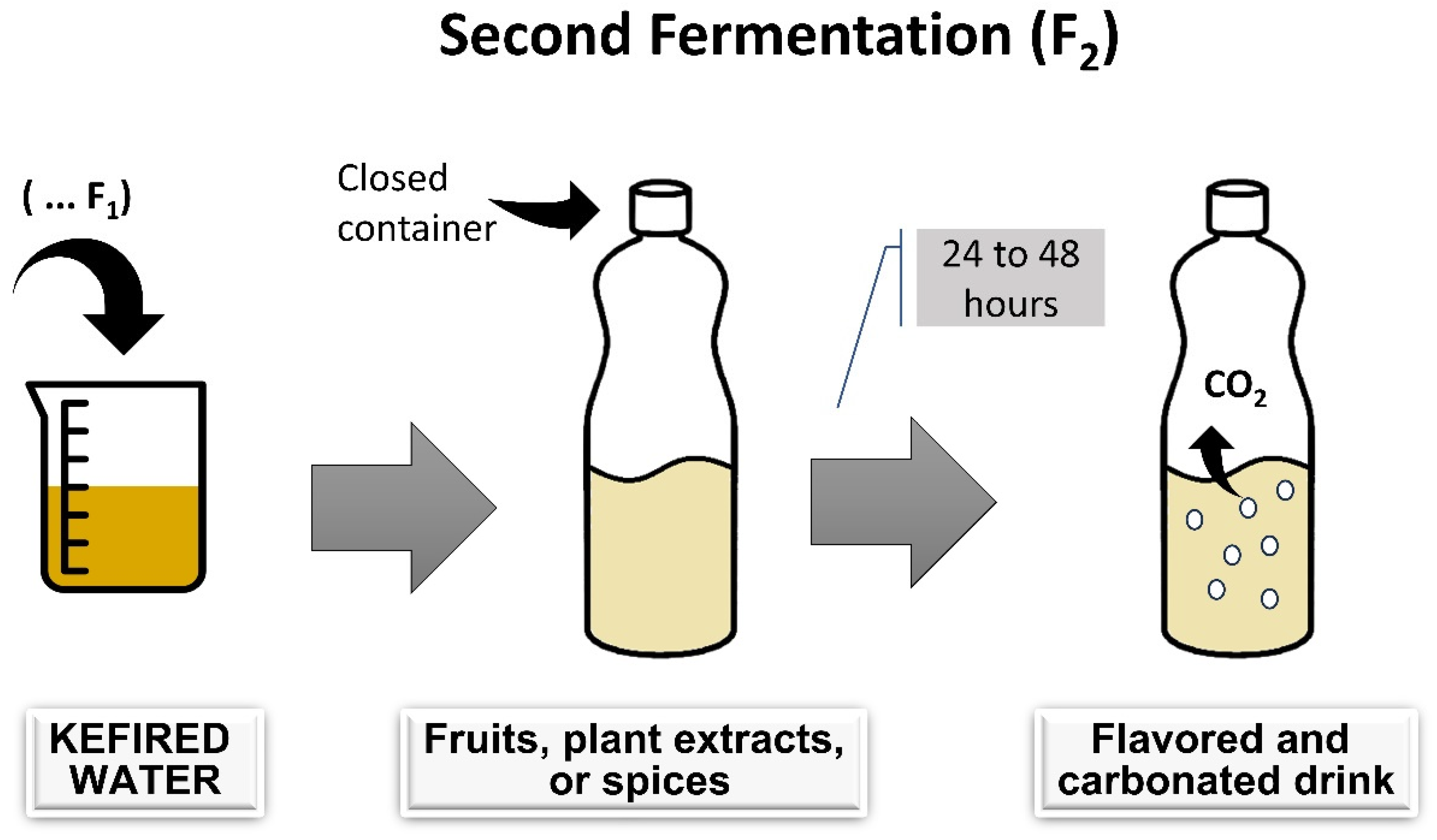
Fermentation is typically spontaneous, involving water kefir grains in a sucrose solution. Traditionally, water kefir fermentation occurs by incubating the mixture at 20–25 °C in a dark environment for 24–72 h, using 6–30% sugar and 6–20% water kefir grains [14,21]. Standardized starter cultures are uncommon, and water kefir is usually produced domestically, making it more challenging to standardize the beverage [11]. After separating the water kefir grain from the fermented liquid, the liquid can be consumed as is or used in a second fermentation to enhance flavor and naturally carbonate the drink [5,22]. Figure 1 and Figure 2 summarize the water kefir production process.
Figure 1.
Stages of water kefir production: first fermentation process.
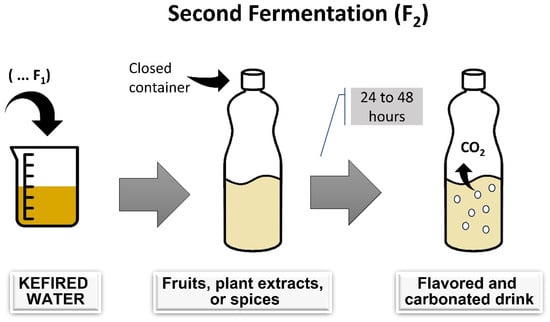
Figure 2.
Stages of water kefir production: second fermentation process.
Water kefir has been growing in popularity due to its potential health benefits. For this reason, studies have been carried out to obtain new products that are easier to apply and meet the needs of the consumer market for more practical foods. Among these is the development of powdered water kefir. A study demonstrated that microorganisms were preserved in water kefir even after the freeze-drying process, maintaining the product’s characteristics and showing the versatility of water kefir [23]. Additionally, water kefir is a refreshing and carbonated beverage and can be an alternative to replacing the consumption of soft drinks, which are nutritionally poor products. Thus, kefir could be a beverage that appeals to consumers due to its organoleptic characteristics, while also offering added nutritional value. Furthermore, research has been conducted to use water kefir as an ingredient in the formulation of other products to enhance nutritional value by providing more potentially beneficial microorganisms [24].
3. Regulatory Aspects
Several studies have reported that fermented foods offer potential health benefits, as the International Scientific Association for Probiotic and Prebiotic (ISAPP) reported. Still, they cannot be classified as probiotic foods. Although kefir contains microorganisms in its composition, to be considered probiotic, the species responsible for the beneficial effects must be isolated and identified, and their action must be scientifically proven. Additionally, it is difficult to determine whether the beneficial effects of consuming fermented foods are related to microorganisms, the food matrix, or a combination of both, associated with the fact that changes in the microbial species may occur over the shelf life of fermented foods, making it difficult to determine the composition of microorganisms in fermented foods accurately. Therefore, traditional fermented foods must use the term “containing live and active bacterial cultures” [4,25].
Water kefir is regulated in some countries and is commonly marketed as a “traditional beverage”. In Brazil, legislation regarding fermented beverages does not include specific regulatory provisions for water kefir, and regulations focus exclusively on milk kefir, as established in the Technical Regulation for the Identity and Quality of Fermented Milk. There is no specific legislation for non-dairy fermented products. Still, it is determined that fermented products must maintain their activity and abundant viability in the product throughout their shelf life. Previous legislation determined that the total bacterial count must reach at least 107 CFU/mL for LAB and at least 104 CFU/mL for yeasts in vegetable beverages. However, the current legislation only determines the quantity of microorganisms that must be mentioned and effective [26]. In Japan, kefir can be marketed as a functional beverage, but it must meet the Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) criteria if it claims to confer health benefits [9].
Although not classified as a probiotic food, water kefir demonstrates notable health-benefiting activity, aligning with the definition of functional food. Functional foods are natural or processed foods that contain biologically active compounds that offer clinically proven health benefits in defined, effective, and non-toxic quantities. These benefits are supported by specific biomarkers for preventing, managing, or treating chronic diseases or their symptoms [27]. Thus, water kefir is a potentially functional food due to its characteristics and potential health benefits [4,21].
4. Fermentation Dynamics of Water Kefir
Water kefir presents a challenging environment, rich in sugar and low in nitrogen (amino acids), making cooperation among the microbial community crucial. During fermentation, the metabolic activities of yeast and bacteria produce various compounds that contribute to the aroma and functional properties of the final products. When microorganisms in water kefir grow under optimal conditions, dextran—the main structural component of kefir grains—is synthesized, increasing grain biomass [5,11,28].
The water kefir fermentation process starts aerobically and gradually becomes anaerobic as oxygen is consumed and/or eliminated by the carbon dioxide produced by the yeasts [11,28]. Sucrose is metabolized into ethanol, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, acetic acid, mannitol, vitamins (e.g., B vitamins), amino acids (e.g., arginine), glycerol, esters, and other organic acids. In this way, the sucrose concentration decreases by up to 98% in the first 24 h of fermentation [10,11,29].
In the common dynamics of water kefir fermentation, yeasts such as Saccharomyces, Zygotorulaspora and Dekkera hydrolyze sucrose through an extracellular β-D-fructofuranosidase (invertase), producing glucose and fructose. These monosaccharides are absorbed by the yeast cells through facilitated diffusion. Yeast uses these sugars for its metabolism and ethanol production, making them available to the bacteria. The ethanol concentration increases linearly until it exceeds 10% of the total volume. However, the ethanol level decreases as it is converted into acetic acid by acetic acid bacteria during fermentation [11,30].
Although lactic acid bacteria are more abundant in the grains, yeast-driven metabolic activity predominates during water kefir fermentation. Some studies suggest a potential relationship between the CO2 released by the yeast and the stimulation of lactic acid bacteria. In the early stage of fermentation, small amounts of CO2 may stimulate the growth of lactic acid bacteria, producing organic acids that acidify the medium and can be used by yeast as an energy source [14].
Other microbial interactions may occur during kefir fermentation. However, separate cultures of microbial kefir grains do not grow in sugar solution or have decreased biochemical activity, making studying the microbial interactions involved in kefir fermentation even more challenging [5].
5. Microbial Diversity of Water Kefir
The microbiota of water kefir grains includes various species of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeast. Each gram of water kefir grain contains approximately 108 colony-forming units (CFU) of LAB, 106–108 CFU of AAB, and 106–107 CFU of yeast [6,31]. LAB are primarily represented by the genus Lactobacillus, AAB by the Acetobacter genus, and yeasts by the Saccharomyces, Zygosaccharomyces, and Brettanomyces genera. The dominant species and their prevalence in studies can vary based on several factors, including the substrate used and fermentation conditions. Additionally, the origin of the grains and diversity of the samples studied can influence the species commonly isolated [6,29]. The composition and frequency of microbial species, and the concentration of bioproducts, depend on the carbon and energy sources available during fermentation, which also affects grain granulation and microbial growth [32].
Different species within water kefir exhibit symbiotic relationships, surviving and propagating by sharing their bioproducts as energy sources or growth-stimulating factors. It has been shown that the composition of the water kefir beverage differs in proportion to the grains from which it is obtained, depending on the type of fermentation substrate used [5]. The beverage’s composition can also vary during successive fermentations, even when the same grain is used on each substrate [33].
Since the discovery of these organisms and the subsequent development of molecular tools, significant steps have been taken to identify the variety of yeasts and bacteria involved in water kefir fermentation. Numerous studies on the microbiology of water kefir have been conducted across different countries [28]. Table 1 presents a microbiological diagnosis of the different species identified in water kefir from different countries.

Table 1.
Microorganisms identified in water kefir.
A metagenomic study using the Shotgun technique in water kefir demonstrated Lactobacillus, Oenococcus, and Bifidobacterium as the main bacterial genera, and Saccharomyces and Dekkera as the main yeast genera. Additionally, it showed a possibly novel Lactobacillus species related to L. hordei and L. mali, and a novel Oenococcus sp., Candidatus O. aquikefiri [37].
A recent study using water kefir from Brazil demonstrated a greater abundance of Zymomonas mobilis, followed by Sporolactobacillus spathodeae and Liquorilactobacillus satsumensis. Regarding fungi, Lachances fermentati was the most present, followed by Wickerhamomyces anomalus [23].
Microorganisms with potential probiotic properties isolated from water kefir include Lactobacillus acidophilus LA15, Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus B-30892, Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1, L. kefiranofaciens DN1, L. lactis WH-C1, Lactobacillus mali APS1, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei CIDCA 8339, and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MA2 [4,45,46].
Knowing the composition of microorganisms present in water kefir is extremely important. It helps in understanding the composition of this beverage, how these microorganisms can act, and their relationship with consumer benefits. It also helps standardize specific legislation for water kefir. Thus, a major gap that needs to be filled is the determination of starter cultures, which would favor greater standardization of the microbial diversity in water kefir.
6. Potential Health Benefits of Water Kefir
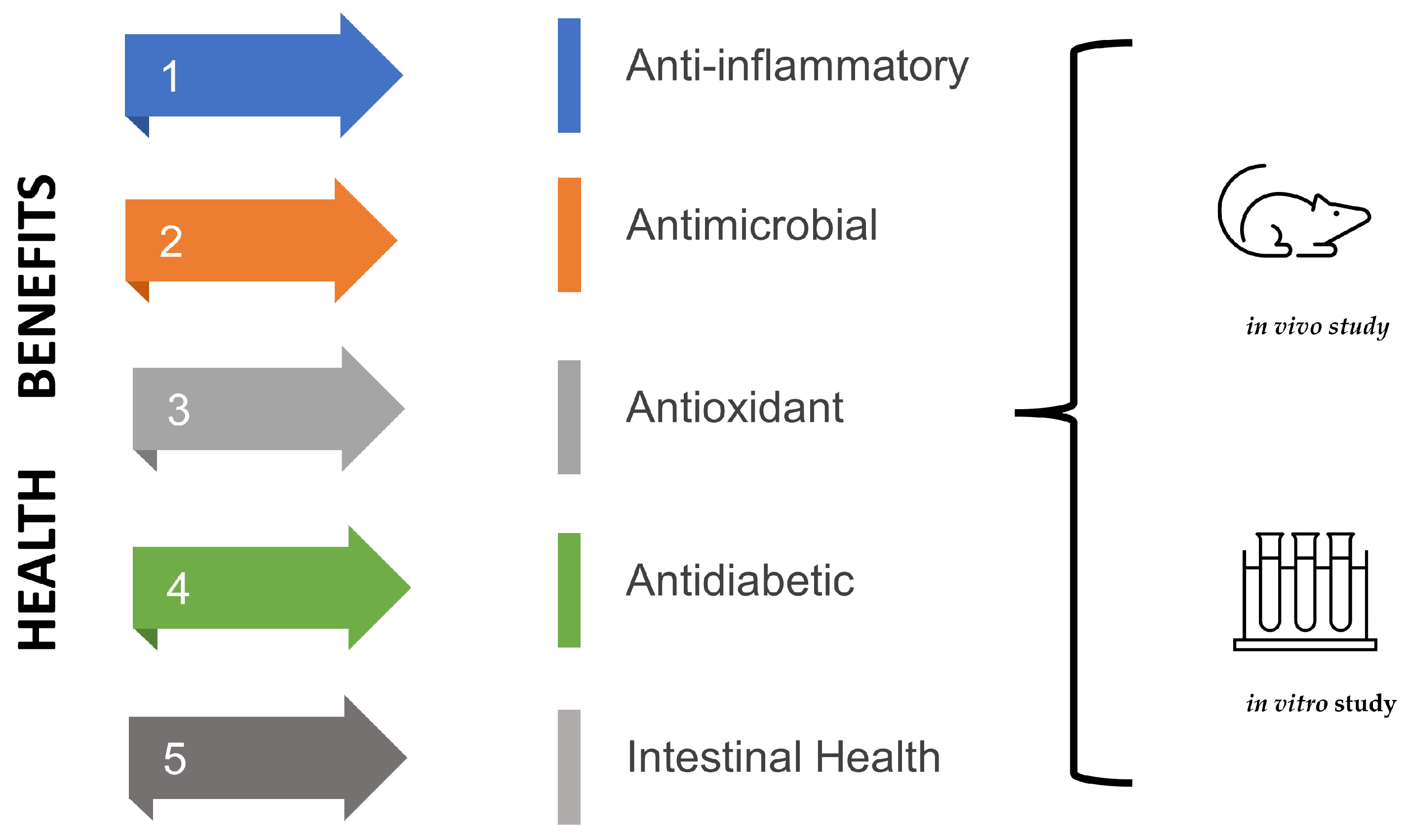
Fermented products, including water kefir, can provide beneficial effects (Figure 3) when consumed due to the content of beneficial microorganisms or compounds produced by these microorganisms [4]. Unlike milk kefir, few studies have evaluated the potential health benefits of water kefir, especially in humans. Despite this, studies demonstrate the benefits of water kefir, highlighting anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and intestinal health-promoting effects [4,13].
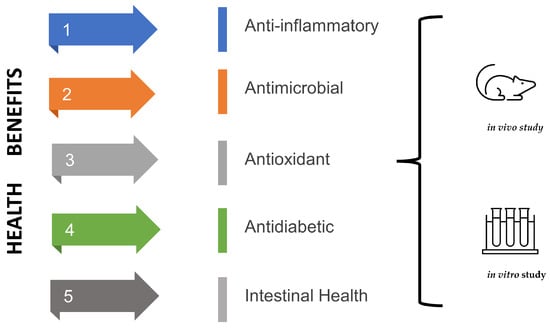
Figure 3.
Health benefits of water kefir based on in vivo and in vitro studies.
Antidiabetic effects have been associated with water kefir, where administration to Wistar rats improved glucose levels and lipid profiles [47]. An in vitro study with cells demonstrated α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (50–80%) by water kefir [45]. Experiments with mice evaluating the administration of L. paracasei isolated from water kefir grains demonstrated that after 14 weeks, the experimental group presented less insulin intolerance and alteration of genes involved in glucose homeostasis [46].
Furthermore, administering water kefir for 2 weeks enhanced systemic antioxidant activity in mice, demonstrated by an increase in the activity of the enzymes superoxide dismutase and catalase. With this antioxidant activity, water kefir showed the ability to reduce gastric ulcers and improve protein oxidation in mice [48]. Water kefir also exhibits potential antimicrobial effects related to the compounds produced during fermentation, such as the production of organic acids, which reduce pH, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms [28].
The potential beneficial effects of water kefir are linked to intestinal health. After administering water kefir to rats, it was found to have a protective effect against inflammation-induced intestinal barrier disruption. This effect was associated with an increased production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and Bifidobacterium species, and a reduction in excess proteolytic fermentation compounds [20]. SCFAs (propionate, butyrate, and acetate) are metabolites that the intestinal microbiota produces. They help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, exert an anti-inflammatory effect, and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria [49].
Studies demonstrate the beneficial action of water kefir in improving intestinal microbiota composition. Microorganisms isolated from water kefir administered to rats increased the number of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Lactobacillus, and Prevotella, and decreased that of Proteobacteria and Enterobacteriaceae. This selective alteration of the intestinal microbiota may be linked to the ability of probiotic strains to co-aggregate and form a protective barrier that prevents pathogenic bacteria from colonizing the epithelial surface. Additionally, these strains can produce antimicrobial substances, such as bacteriocins [50,51]. In animals supplemented with potentially probiotic microorganisms, improvements in the intestinal mucosal barrier were observed, which led to a decrease in translocation from the gastrointestinal tract to the bloodstream. This also reduced the production of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) associated with allergic reactions. The suppression of IgE occurred through the upregulation of Cd2, Stat4, and Ifnr expression, which induced a balanced Th1/Th2 response, increased the regulatory population of CD4(+) and CD25(+) T cells, and reduced the activity of CD19(+) B cells [52].
Despite the numerous benefits associated with the consumption of water kefir, it should be considered that in some situations, water kefir, as well as other fermented beverages, may not be recommended, such as for pregnant women, since the fermentation process results in the formation of alcohol [10,11,14]. Still, the beverage obtained has a considerable sugar content, which should be included in the diet of people with diabetes with caution. As discussed, water kefir is mainly produced in an artisanal manner, without rigorous industrial processes, which means that contamination can occur during the artisanal production process of water kefir [8].
Despite in vitro studies and animal model research demonstrating the potential benefits of consuming water kefir, clinical studies with humans are extremely important to establish its real effects on human metabolism. However, given the possible evidence of water kefir in relation to various pathological clinical conditions, water kefir may be classified as a probiotic food in the future. It could be utilized to prevent and treat various diseases [45].
7. Final Considerations and Future Perspectives
Water kefir is a potential functional food associated with health benefits and can meet the market demand for vegan foods. The fermented beverage obtained is principally composed of microorganisms, acetic acid, lactic acid, and ethanol. Microbiological diversity is influenced by the origin of the grains and the fermentation process, among other factors. Additionally, there is an urgent need to intensify research in starter cultures for water kefir production to enable the transition from artisanal to industrial production and allow for the standardized identification of microorganisms present in this beverage.
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed substantially to the work reported. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, Brazil), grant number 306063/2022-0.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Postgraduate Program in Food Science and Technology, Center of Agricultural Sciences and Engineering, Federal University of Espírito Santo, and to the Department of Food Science and Technology, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis 88034-001, Santa Catarina, Brazil, for their partnership and support in our research on water kefir.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Manoj, P.M.; Mohan, J.R.; Khasherao, B.Y.; Shams, R.; Dash, K.K. Fruit based probiotic functional beverages: A review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojikon, F.D.; Kasimin, M.E.; Molujin, A.M.; Gansau, J.A.; Jawan, R. Probiotication of Nutritious Fruit and Vegetable Juices: An Alternative to Dairy-Based Probiotic Functional Products. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Arpitha, S.; Das, C.; Laishram, R.; Sasi, M.; Kumar, S.; Maheshwari, C.; Krishnan, V.; Kumari, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; et al. Research trends and approaches for the nutritional and bio-functionality enhancement of fermented soymilk. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 107, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, M.B.; dos Santos, D.C.; de Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Ores, J.d.C.; Takeuchi, K.P.; Lemes, A.C. A review of nondairy kefir products’ characteristics and potential human health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorda, F.A.; Pereira, G.V.d.M.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; Vandenberghe, L.P.d.S.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, biochemical, and functional aspects of sugary kefir fermentation—A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkir, E.; Yilmaz, B.; Sharma, H.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Ozogul, F. Challenges in water kefir production and limitations in human consumption: A comprehensive review of current knowledge. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.F.; Moure, M.C.; Quiñoy, F.; Esposito, F.; Simonelli, N.; Medrano, M.; León-Peláez, Á. Water Kefir, a Fermented Beverage Containing Probiotic Microorganisms: From Ancient and Artisanal Manufacture to Industrialized and Regulated Commercialization. Futur. Foods 2022, 5, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Gómez-Sala, B.; O’Connor, E.M.; Kenny, J.G.; Cotter, P.D. Global regulatory frameworks for fermented foods: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 902642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzirri, U.G.; Loizzo, M.R.; Aiello, F.; Prencipe, S.A.; Restuccia, D. Non-dairy kefir beverages: Formulation, composition, and main features. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Wilkinson, S.; Daenen, L.; Arendt, E.K. An update on water kefir: Microbiology, composition and production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 345, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidoux, M.; Brillouet, M.; Quemener, B. Characterization of the polysaccharides from a Lactobacillus brevis and from sugary kefir grains. Biotechnol. Lett. 1988, 10, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Gökırmaklı, Ç.; Greene, A.K. A comparison of milk kefir and water kefir: Physical, chemical, microbiological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, D.; De Vuyst, L. Microbial Species Diversity, Community Dynamics, and Metabolite Kinetics of Water Kefir Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinas, M.; Horisberger, M.; Bauer, H. The structural organization of the Tibi grain as revealed by light, scanning and transmission microscopy. Arch. Microbiol. 1980, 128, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldherr, F.W.; Doll, V.M.; Meißner, D.; Vogel, R.F. Identification and characterization of a glucan-producing enzyme from Lentilactobacillus hilgardii TMW 1.828 involved in granule formation of water kefir. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, O.; Randazzo, W.; Miceli, A.; Guarcello, R.; Francesca, N.; Erten, H.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Characterization of kefir-like beverages produced from vegetable juices. LWT 2016, 66, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Fernandes, M.; Lima, F.S.; Rodrigues, D.; Handa, C.; Guelfi, M.; Garcia, S.; Ida, E.I. Evaluation of the isoflavone and total phenolic contents of kefir-fermented soymilk storage and after the in vitro digestive system simulation. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Corona, O.; Guarcello, R.; Francesca, N.; Germanà, M.A.; Erten, H.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Development of new non-dairy beverages from Mediterranean fruit juices fermented with water kefir microorganisms. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, M.; Börner, R.A.; Ghyselinck, J.; Verstrepen, L.; De Medts, J.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Boulangé, C.L.; Priour, S.; Marzorati, M.; Damak, S. Water kefir and derived pasteurized beverages modulate gut microbiota, intestinal permeability and cytokine production in vitro. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendón, M.D.; Bengoa, A.A.; Iraporda, C.; Medrano, M.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Water kefir: Factors affecting grain growth and health-promoting properties of the fermented beverage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, R.S.; Ressutte, J.B.; Hata, N.N.; Henrique-Bana, F.C.; Guergoletto, K.B.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Spinosa, W.A. Quality and shelf life assessment of a new beverage produced from water kefir grains and red pitaya. LWT 2021, 140, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, K.V.; Zanetti, V.C.; Camelo-Silva, C.; Alexandre, L.A.; da Silva, A.C.; Verruck, S.; Teixeira, L.J.Q. Powdered water kefir: Effect of spray drying and lyophilization on physical, physicochemical, and microbiological properties. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 5, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, V.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Flores, C. Unlocking Innovations: Exploring the Role of Kefir in Product Development. Curr. Food Sci. Technol. Rep. 2024, 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instrução Normativa Nº 46, de 23 de Outubro de 2007. Available online: https://www.cidasc.sc.gov.br/inspecao/files/2019/09/INSTRUÇÃO-NORMATIVA-N-46-de-23-de-outubro-de-2007-Leites-Fermentados.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Gur, J.; Mawuntu, M.; Martirosyan, D. FFC’s Advancement of Functional Food Definition. Funct. Foods Heal. Dis. 2018, 8, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cufaoglu, G.; Erdinc, A.N. An alternative source of probiotics: Water kefir. Food Front. 2023, 4, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, D.; Aerts, M.; Vandamme, P.; De Vuyst, L. Oxygen and diverse nutrients influence the water kefir fermentation process. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Torres, A.; Gutiérrez-Ambrocio, S.; Heredia-Del-Orbe, P.; Villa-Tanaca, L.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C. Inferring the role of microorganisms in water kefir fermentations. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Bechtner, J.; Behr, J.; Eisenbach, L.; Geißler, A.J.; Vogel, R.F. Lifestyle of Lactobacillus hordei isolated from water kefir based on genomic, proteomic and physiological characterization. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-L.; Huang, Y.-L.; Chen, M.-J. Effects of cow’s and goat’s milk as fermentation media on the microbial ecology of sugary kefir grains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, R.R.; Koyanagi, T.; Peláez, A.L.; De Antoni, G.; Enomoto, T. Changes in Microbiota During Multiple Fermentation of Kefir in Different Sugar Solutions Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, P.P.L.G.; Silva, M.R.; Santos, L.F.P.; Nunes, I.L.; Magalhães-Guedes, K.T. Production of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) kefir fermented beverage flavored with cocoa (Theobroma cacao) powder. Braz. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 13, e5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Hou, Q.; Hui, W.; Kwok, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Assessment of the microbial diversity of Chinese Tianshan tibicos by single molecule, real-time sequencing technology. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, R.R.; Yamamoto, S.; Sasaki, T.; Michihata, T.; Mahmoud, A.-H.; Koyanagi, T.; Enomoto, T. Microbiological and functional characterization of kefir grown in different sugar solutions. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verce, M.; De Vuyst, L.; Weckx, S. Shotgun metagenomics of a water kefir fermentation ecosystem reveals a novel oenococcus species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Azi, F.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Xing, G.; Dong, M. Quality and metagenomic evaluation of a novel functional beverage produced from soy whey using water kefir grains. LWT 2019, 113, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azi, F.; Tu, C.; Rasheed, H.A.; Dong, M. Comparative study of the phenolics, antioxidant and metagenomic composition of novel soy whey-based beverages produced using three different water kefir microbiota. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, V.P.L.; Ziegler, L.-M.; Vogel, R.F.; Ehrmann, M. Bifidobacterium tibiigranuli sp. nov. isolated from homemade water kefir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.; Scapini, T.; Camargo, A.F.; Bonatto, C.; Stefanski, F.S.; de Jesus, E.P.; Diniz, L.G.T.; Bertan, L.C.; Maldonado, R.R.; Treichel, H. Development of fermented beverage with water kefir in water-soluble coconut extract (Cocos nucifera L.) with inulin addition. LWT 2021, 145, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Tan, J.; Börner, R.; Zhang, S.; Priour, S.; Lima, A.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Cotter, P.; Duboux, S. A temporal view of the water kefir microbiota and flavour attributes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerlikaya, O.; Akan, E.; Kinik, Ö. The metagenomic composition of water kefir microbiota. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 30, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; Fernández, L.A.; Díaz, M.L.; Pérez, M.; Corona, M.; Reynaldi, F.J. Microbiological and chemical characterization of water kefir: An innovative source of potential probiotics for bee nutrition. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2023, 55, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.Y.; Utra, U.; Ahmad, R.; Rather, I.A.; Park, Y.-H. Evaluation of probiotic potential and anti-hyperglycemic properties of a novel Lactobacillus strain isolated from water kefir grains. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, N.; Mohamad, N.E.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, C.L.; Masarudin, M.J.; Abd-Aziz, S.; Izham, M.N.M.; Kumar, M.R.; Hussin, Y.; Alitheen, N.B. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Isolated from Malaysian Water Kefir Grains. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 16, 2161–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayadi, M.; Al Jawfi, Y.; Belarbi, M.; Soualem-Mami, Z.; Merzouk, H.; Sari, D.C.; Sabri, F.; Ghalim, M. Evaluation of Anti-Hyperglycemic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Water Kefir as Probiotic on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2014, 4, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsoni, R.M.P.; Moraes, F.d.S.A.; de Rezende, M.S.; da Silva, C.L.; de Andrade, T.U.; Brasil, G.A.; de Lima, E.M. Pretreatment with water kefir reduces the development of acidified ethanol-induced gastric ulcers. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 58, e191046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, K.; Venkidasamy, B.; Samynathan, R.; Nagella, P.; Rebezov, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Ponomarev, E.; Bouyahya, A.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Short-chain fatty acid: An updated review on signaling, metabolism, and therapeutic effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 2461–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, N.; Chen, M. Sugary Kefir Strain Lactobacillus mali APS1 Ameliorated Hepatic Steatosis by Regulation of SIRT-1/Nrf-2 and Gut Microbiota in Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1700903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, I.-B.; Kim, H.; Song, K.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Seo, K.-H. Modulation of gut microbiota and increase in fecal water content in mice induced by administration of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens DN1. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M. The Antiallergic Effect of Kefir Lactobacilli. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H244–H253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).