ANN-Based Prediction and RSM Optimization of Radiative Heat Transfer in Couple Stress Nanofluids with Thermodiffusion Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What is the influence of the couple stress parameter on the flowing, temperature, and heat transference rate of the nanofluid?
- What role does the Dufour effect play in the heat transfer of the studied nanofluid?
- What is the effect of the accident on the movement of the nanofluid and the rates of heat transference because of the occurrence of thermal radiation?
- Does porosity play an essential role in the motion of the nanofluid and heat transference during its flow on the surface of a solid sphere?
- Are the flow and temperature of nanofluids affected by the presence of a velocity slippage condition?
2. Mathematical Formulations
3. Numerical Method and Validation
4. Optimization of the Important Physical Quantities
5. Results and Discussion
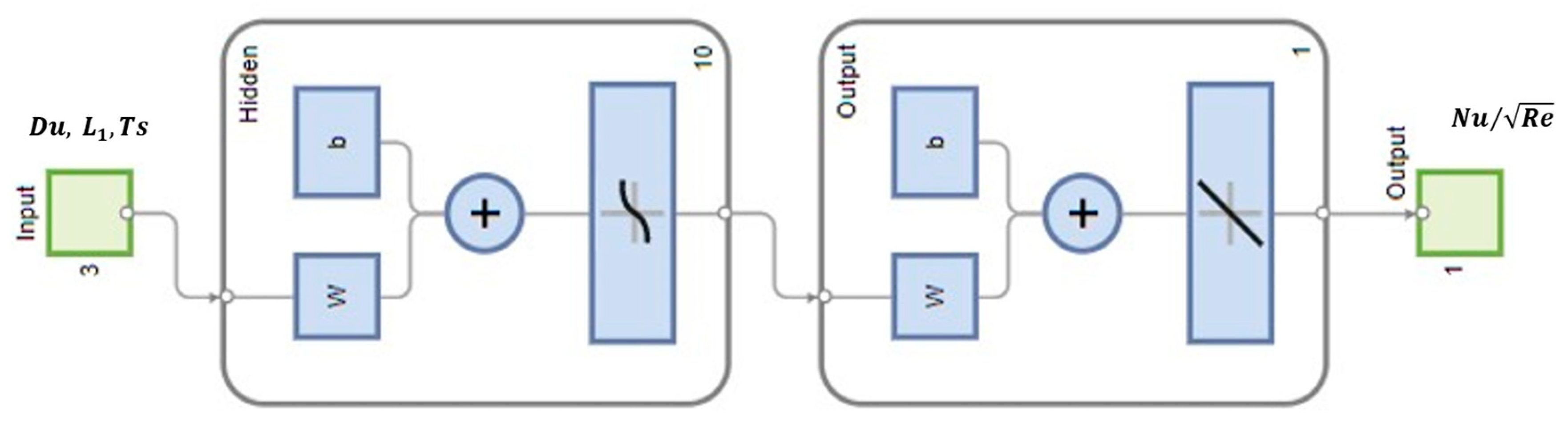
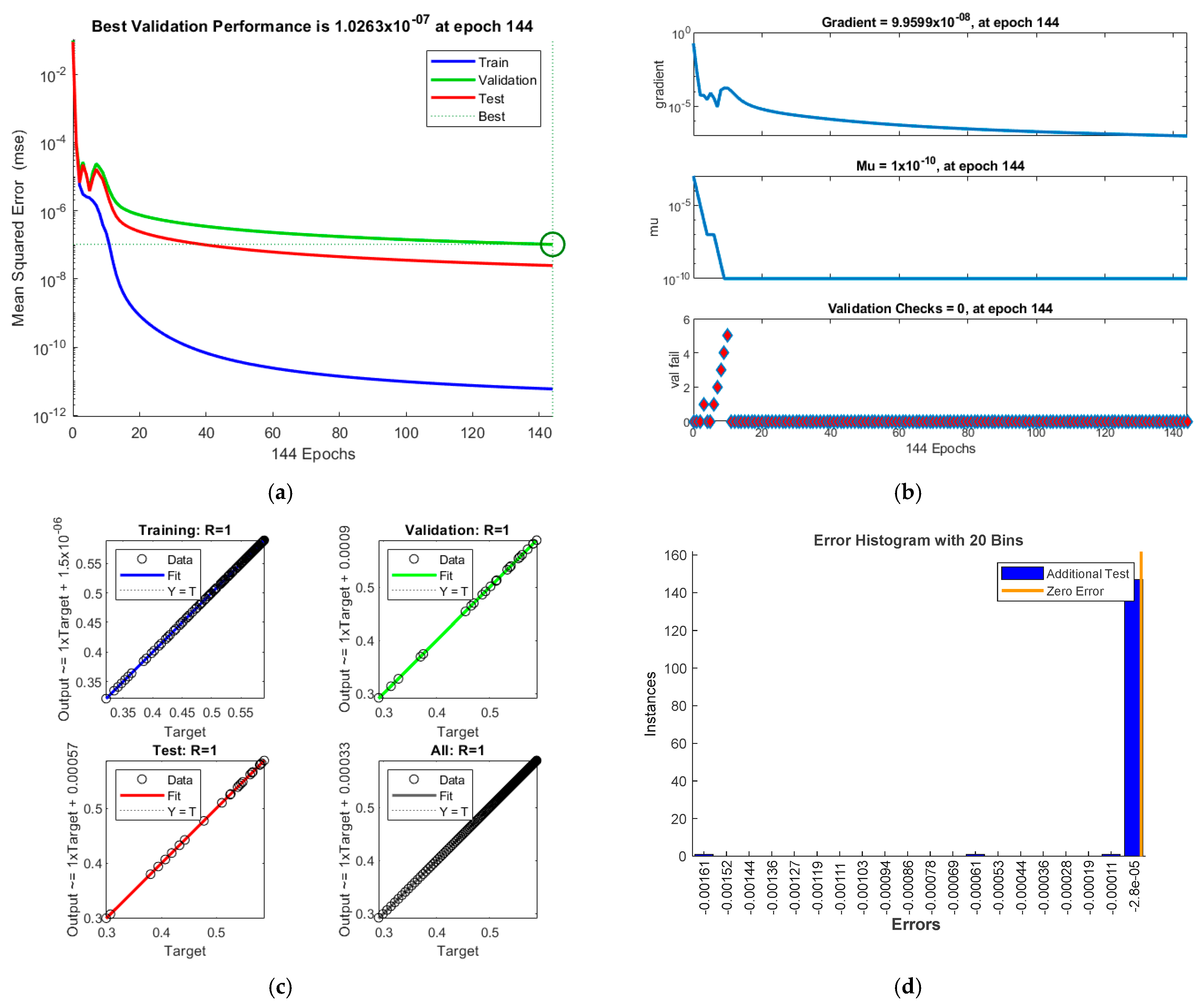
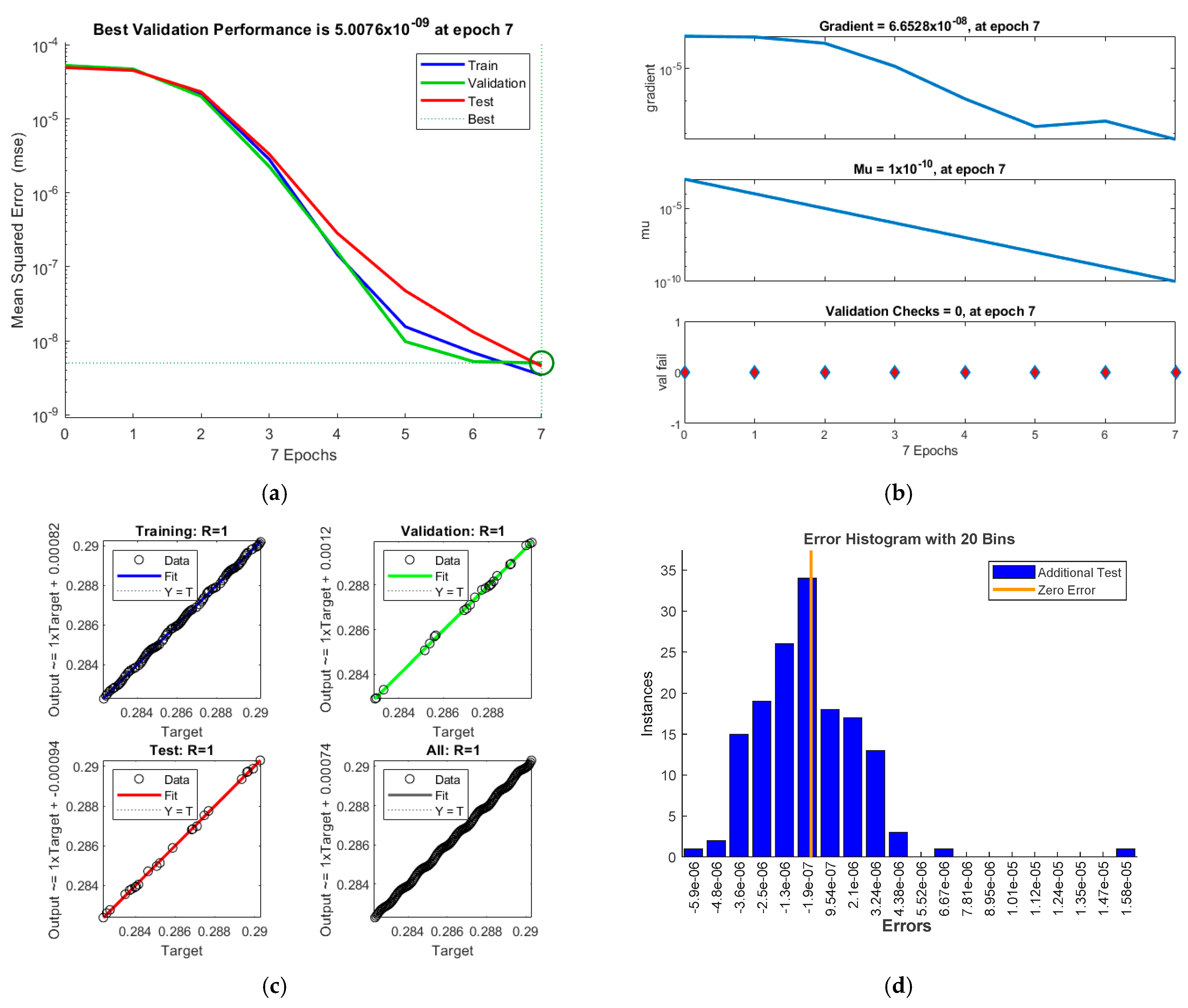
6. ANN Analyses
7. Concluding Remarks
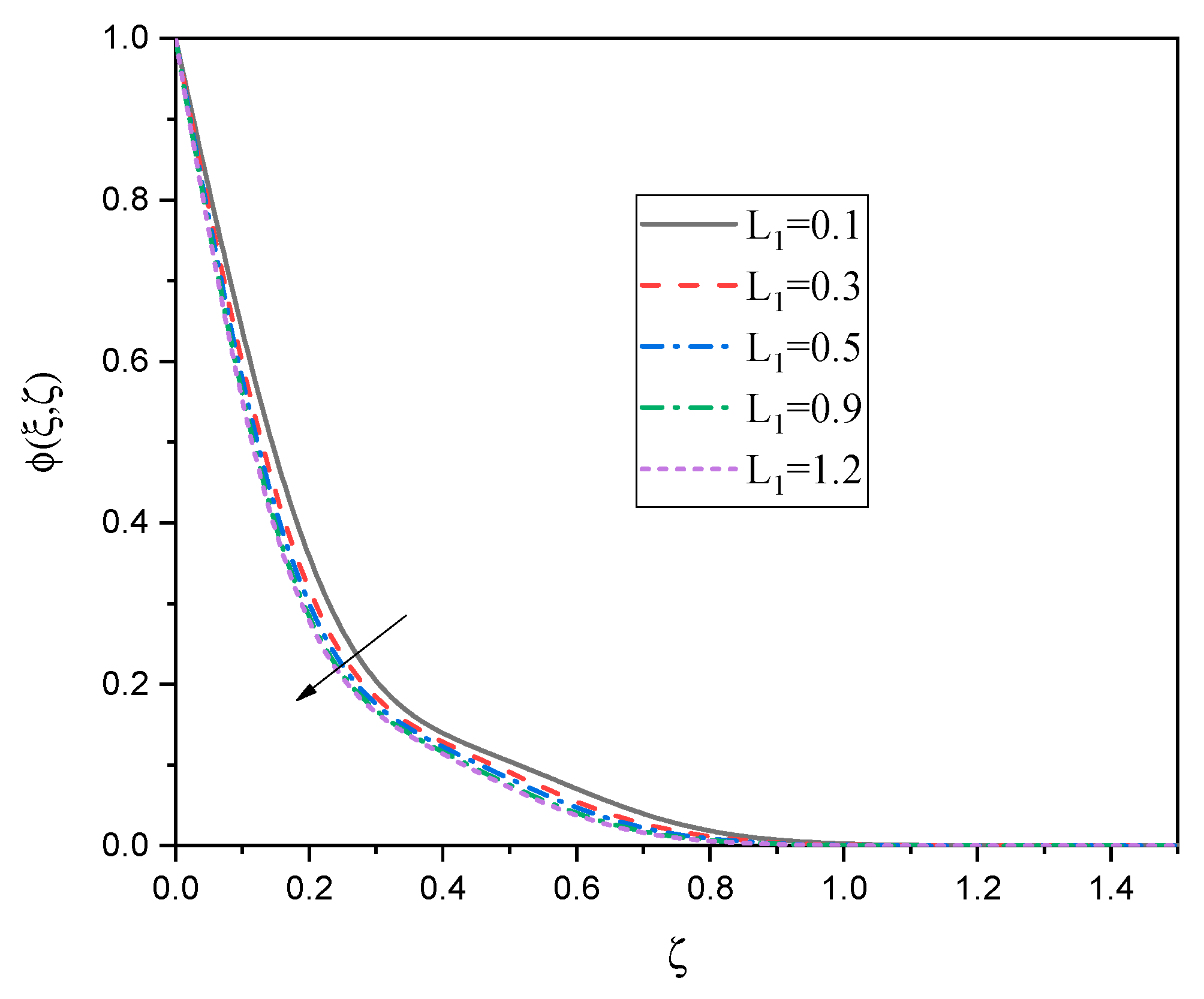
- The couple stress parameter causes an improvement in the gradients of the velocity, temperature, and concentration, and hence the skin friction. The values of the Nusselt number and Sherwood number increase significantly.
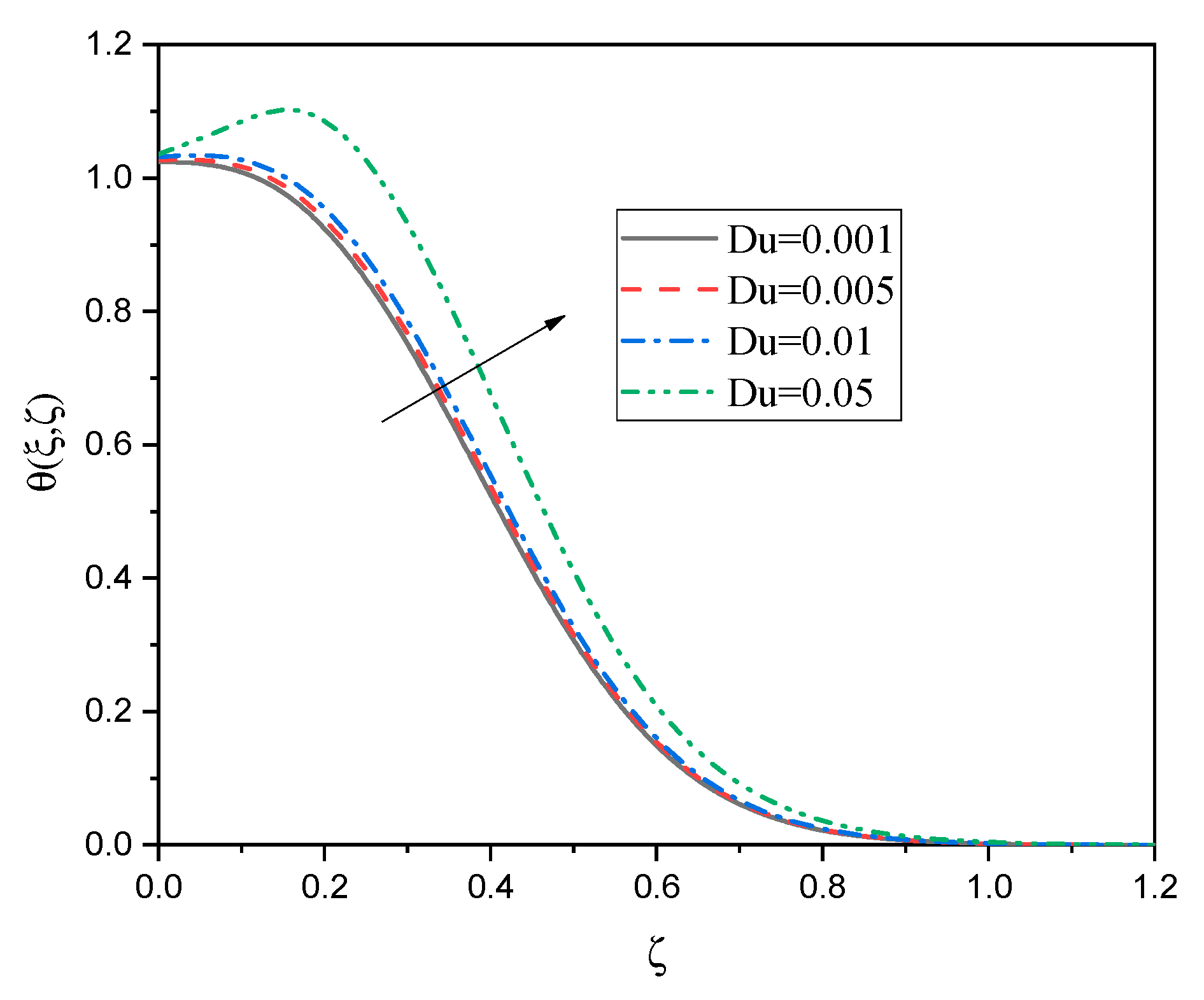
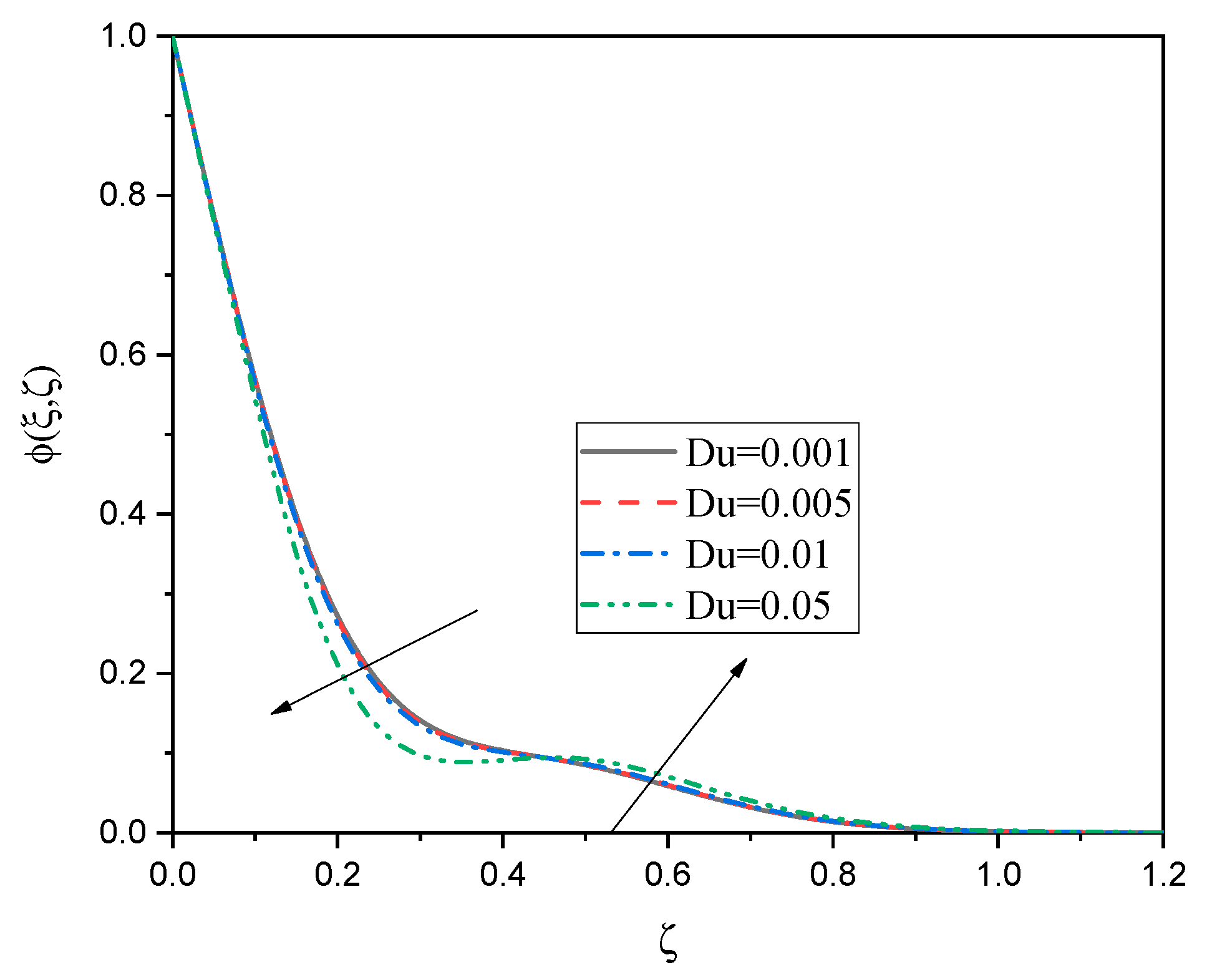
- A clear enhancement in the nanofluid temperature is obtained as the Dufour number is altered, while the heat transfer rate is decreasing.
- The slippage parameter in the case of the couple stress nanofluid flow gives higher velocity features, while both the temperature and concentration are reduced.
- For all values of = 0°, ≈ 30°) the thermal slip factor gives higher heat transfer rates.
- Good target values using ANN are obtained for all considered parameters, where R = 1.
- The mixed convection parameter causes the nanofluid velocity to increase significantly near the boundary layer due to friction and nanofluid pressure.
- The heat transfer from the sphere surface causes a slight temperature rise occurring near the boundary layer, but as distance increases, the temperature decreases due to heat dispersion and diffusion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brunton, S.L.; Noack, B.R.; Koumoutsakos, P. Machine learning for fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2020, 52, 477–508. [Google Scholar]
- Vinuesa, R.; Brunton, S.L.; McKeon, B.J. The transformative potential of machine learning for experiments in fluid mechanics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2023, 5, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, K.; Iaccarino, G.; Xiao, H. Turbulence modeling in the age of data. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 51, 357–377. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.; Kurzawski, A.; Templeton, J. Reynolds averaged turbulence modelling using deep neural networks with embedded invariance. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 807, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, M.; Fukami, K.; Zhang, K.; Nair, A.G.; Fukagata, K. Convolutional neural networks for fluid flow analysis: Toward effective metamodeling and low dimensionalization. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2021, 35, 633–658. [Google Scholar]
- Rabault, J.; Kuchta, M.; Jensen, A.; Réglade, U.; Cerardi, N. Artificial neural networks trained through deep reinforcement learning discover control strategies for active flow control. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 865, 281–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, H. Review of challenges and opportunities in turbulence modeling: A comparative analysis of data-driven machine learning approaches. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubair, S.; Ali, B.; Siddiqui, M.I.H. Neural network-based thermal analysis of stratified nanostructured materials with couple-stress nanofluid flow and gyrotactic microorganisms under exponential heating/cooling conditions. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 39, 2450438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Mushtaq, M.; Khan, M.I.; Farooq, U. Integrated artificial intelligence and non-similar analysis for forced convection of radially magnetized ternary hybrid nanofluid of Carreau-Yasuda fluid model over a curved stretching surface. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2024, 96, 1864–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Shatanawi, W.; Alharbi, W.G.; Shatnawi, T.A. AI-Neural Networking Analysis (NNA) of Thermally Slip Magnetized Williamson (TSMW) fluid flow with heat source. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 56, 104248. [Google Scholar]
- Swamy, H.K.; Ryu, D.; Kim, H.; Sankar, M.; Do, Y. Exploring bioconvection dynamics within an inclined porous annulus: Integration of CFD and AI on the synergistic effects of hybrid nanofluids, oxytactic microorganisms, and magnetic field. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 159, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Zamir, T.; Noor, T.; Muhammad, T.; Ali, M.R. Heat transfer enhancement using ternary hybrid nanofluid for cross-viscosity model with intelligent Levenberg-Marquardt neural networks approach incorporating entropy generation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 63, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.H.; Naidu, K.K.; Babu, B.H.; Raju, K.V.; Reddy, S.H.; Narayana, P.S. Numerical and neural network approaches to heat transfer flow in MHD dissipative ternary fluid through Darcy-Forchheimer permeable channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 60, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Thabet, E.N.; Abd-Alla, A.; Elhag, S. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) in an Electroosmosis-Controlled Darcy-Forchheimer flow for the Casson nanofluid model over stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 109, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A.; Gul, T.; Alotaibi, I.M.S.; Alghuried, A.; Alshomrani, A.S.; Alghuson, M. Artificial neural network analysis of the flow of nanofluids in a variable porous gap between two inclined cylinders for solar applications. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2024, 18, 2343418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Shatanawi, W.; Çolak, A.B. Neural networking-based analysis of heat transfer in MHD thermally slip Carreau fluid flow with heat generation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 54, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa, B.; Leela, V.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kamangar, S.; Bashir, M.N.; Ali, M.M. Integrated Neural Network based Simulation of Thermo Solutal Radiative Double-Diffusive Convection of Ternary Hybrid Nanofluid Flow in an Inclined Annulus with Thermophoretic Particle Deposition. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 62, 105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Aziz, A. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with a convective boundary condition. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transfer. Mar. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.; Layek, G. Magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow of nanofluid over an exponentially stretching permeable sheet. Phys. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 592536. [Google Scholar]
- Kakaç, S.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidur, R.; Leong, K.; Mohammed, H.A. A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1646–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Inc, M.; Tawfiq, F.M.; Bilal, M. Analytical analysis of 2D couple stress flow of blood base nanofluids with the influence of viscous dissipation over a stretching surface. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 39, 2450446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaloud, A.S.; Manai, L.; Tlili, I. Flow of couple stress nanofluid due to stretching surface with applications of induced magnetic field and variable thermal conductivity. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 57, 104356. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bilal, M.; Mir, A.; Kolsi, L.; Muhammad, T.; Ahmad, Z. Parametric simulation of couple-stress nanofluid flow subject to thermal and solutal time relaxation factors. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, R.; Kumar, N.N.; Basha, H. Lorentz force influenced entropy generation in couple stress squeezed hybrid-nanofluid flow: Application to cardiovascular hemodynamics. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, 85, 1254–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathyayani, G.; Rao, S.S.N. Influence of couple stress, radiation, and activation energy on MHD flow and entropy generation in Maxwell hybrid nanofluid flow over a flat plate, Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2024, 09544089241286741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, G. Optimization of heat transfer by nonlinear thermal convection flow past a solid sphere with Stefan blowing and thermal slip using Taguchi method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 141, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-hanaya, A.; Rashed, Z.; Ahmed, S.E. MHD Casson flow over a solid sphere surrounded by porous material in the presence of Stefan blowing and slip conditions. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 103, 402–412. [Google Scholar]

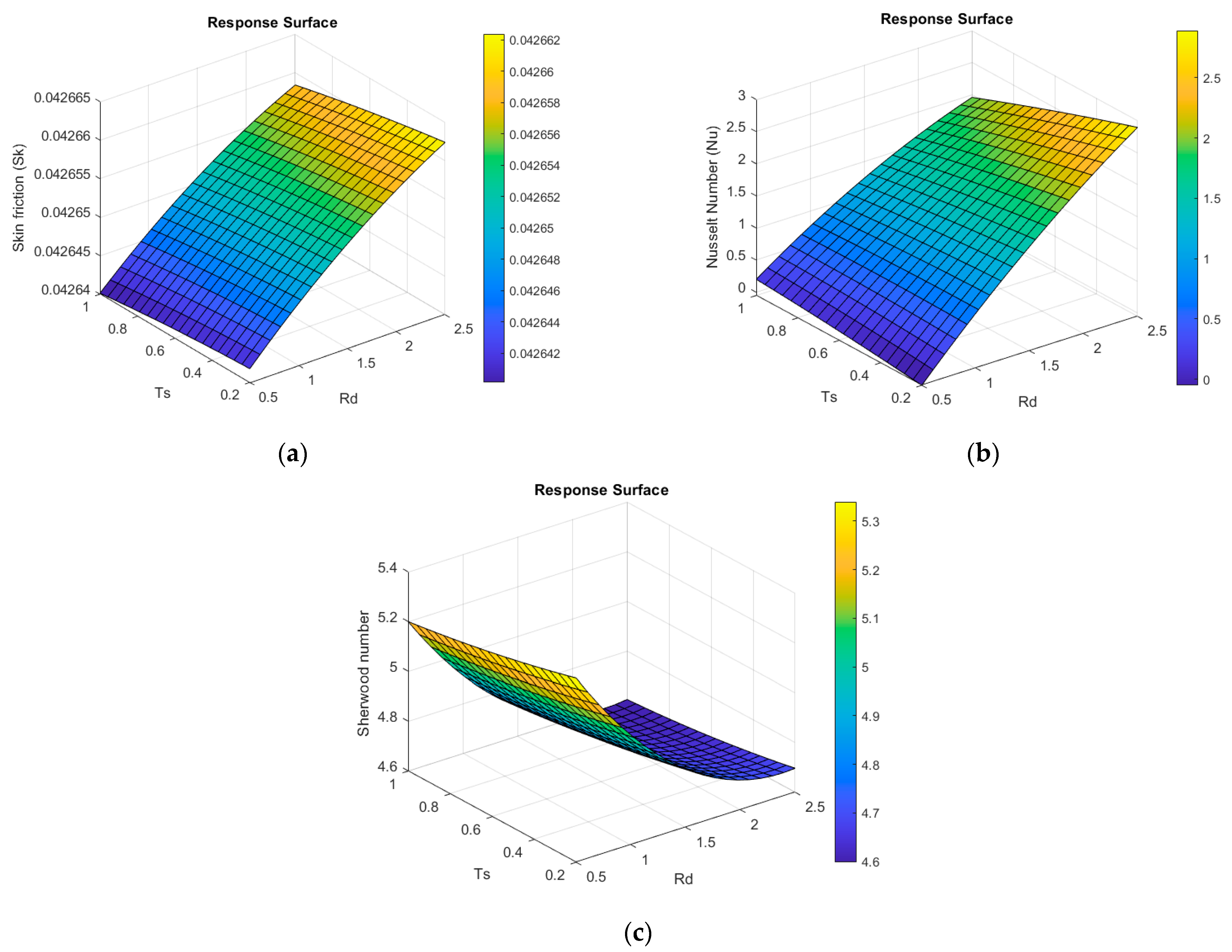


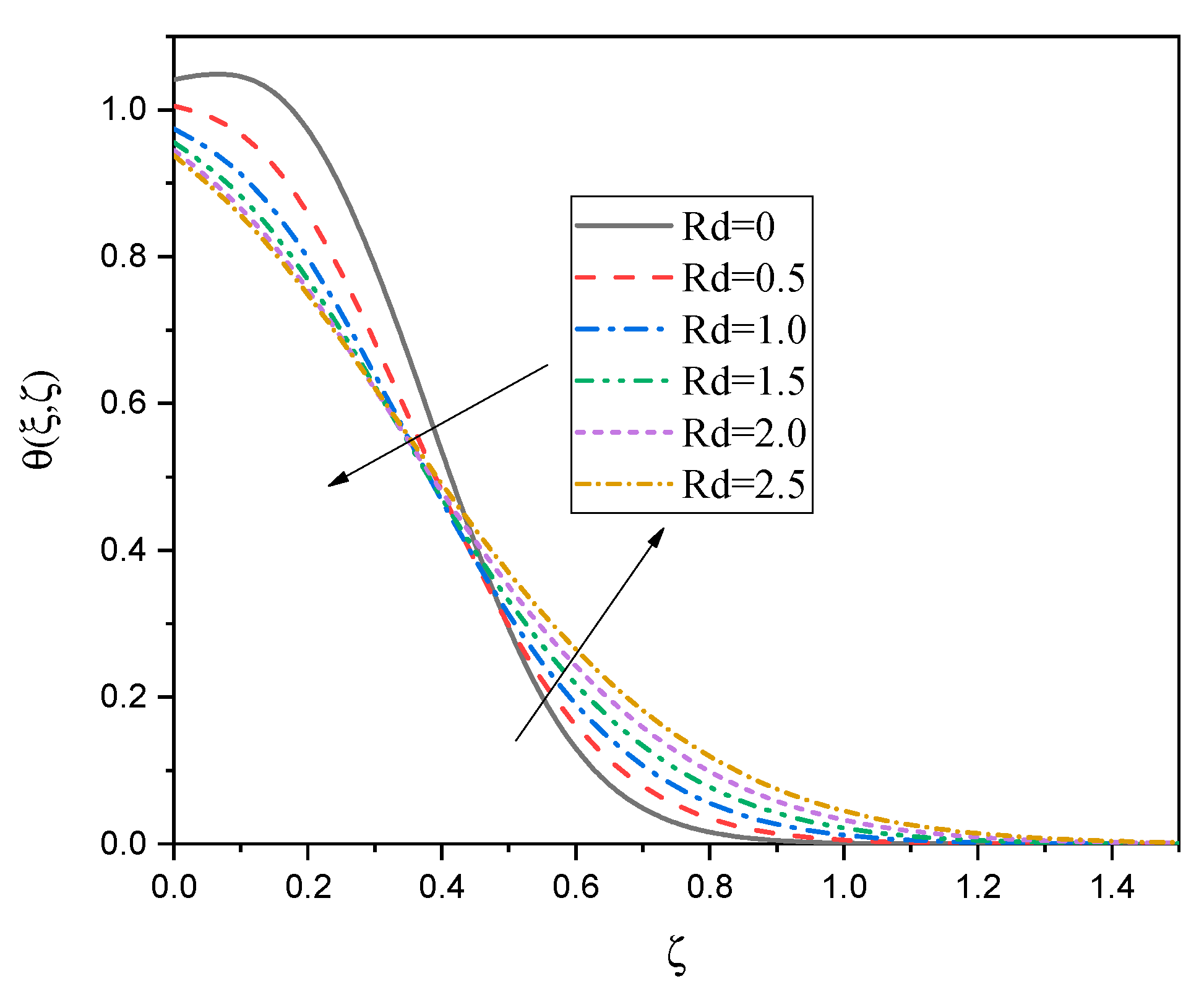


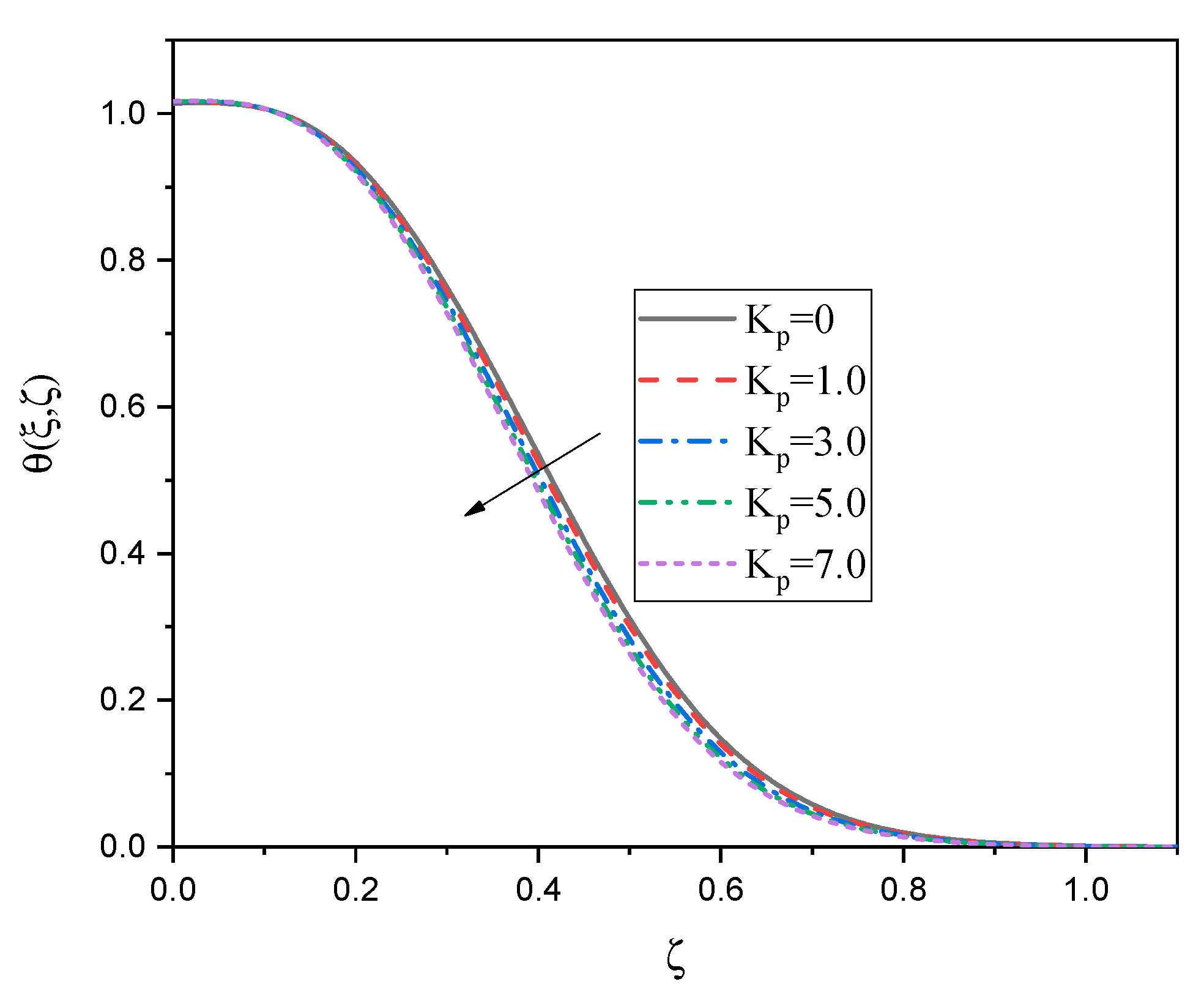



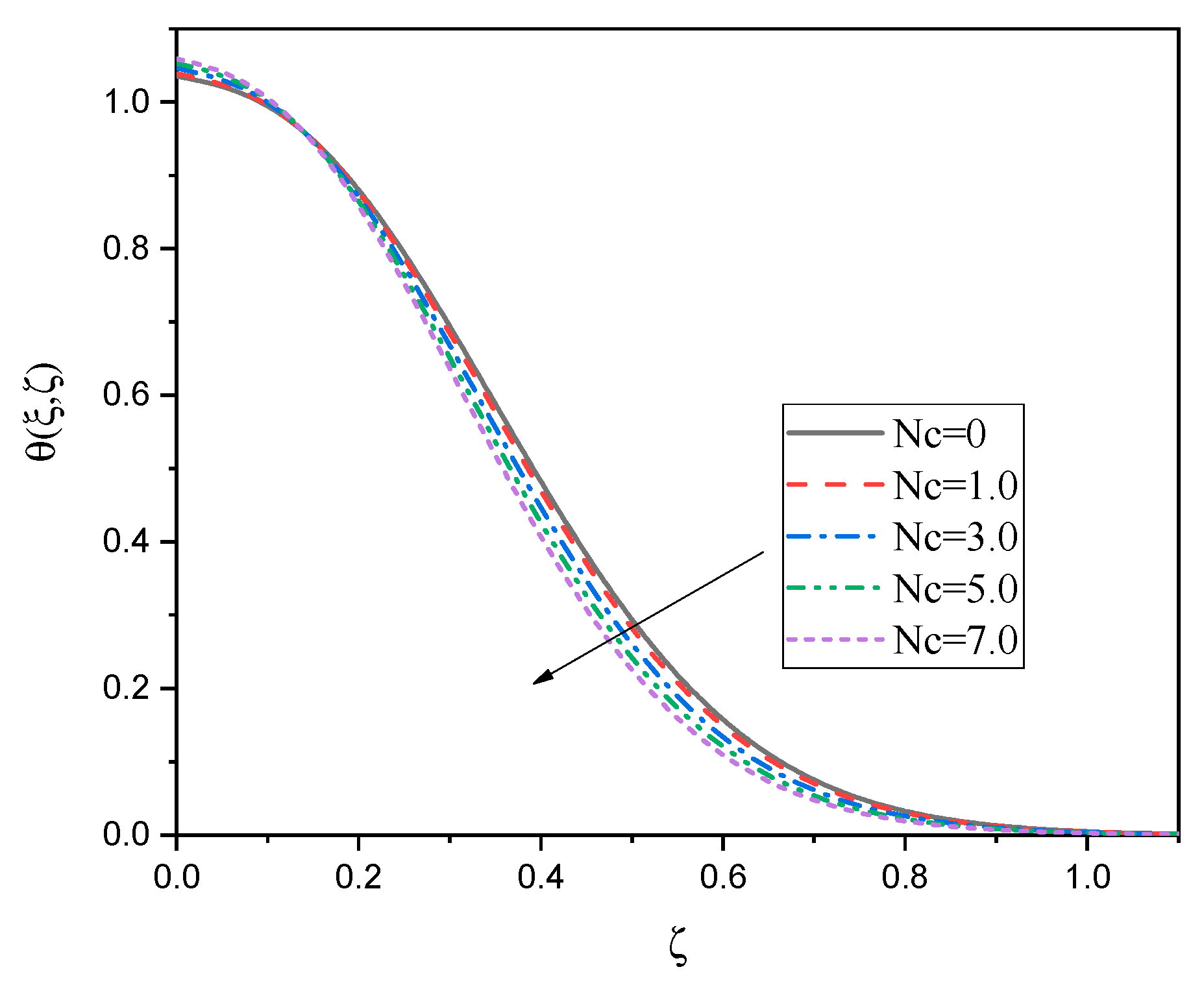
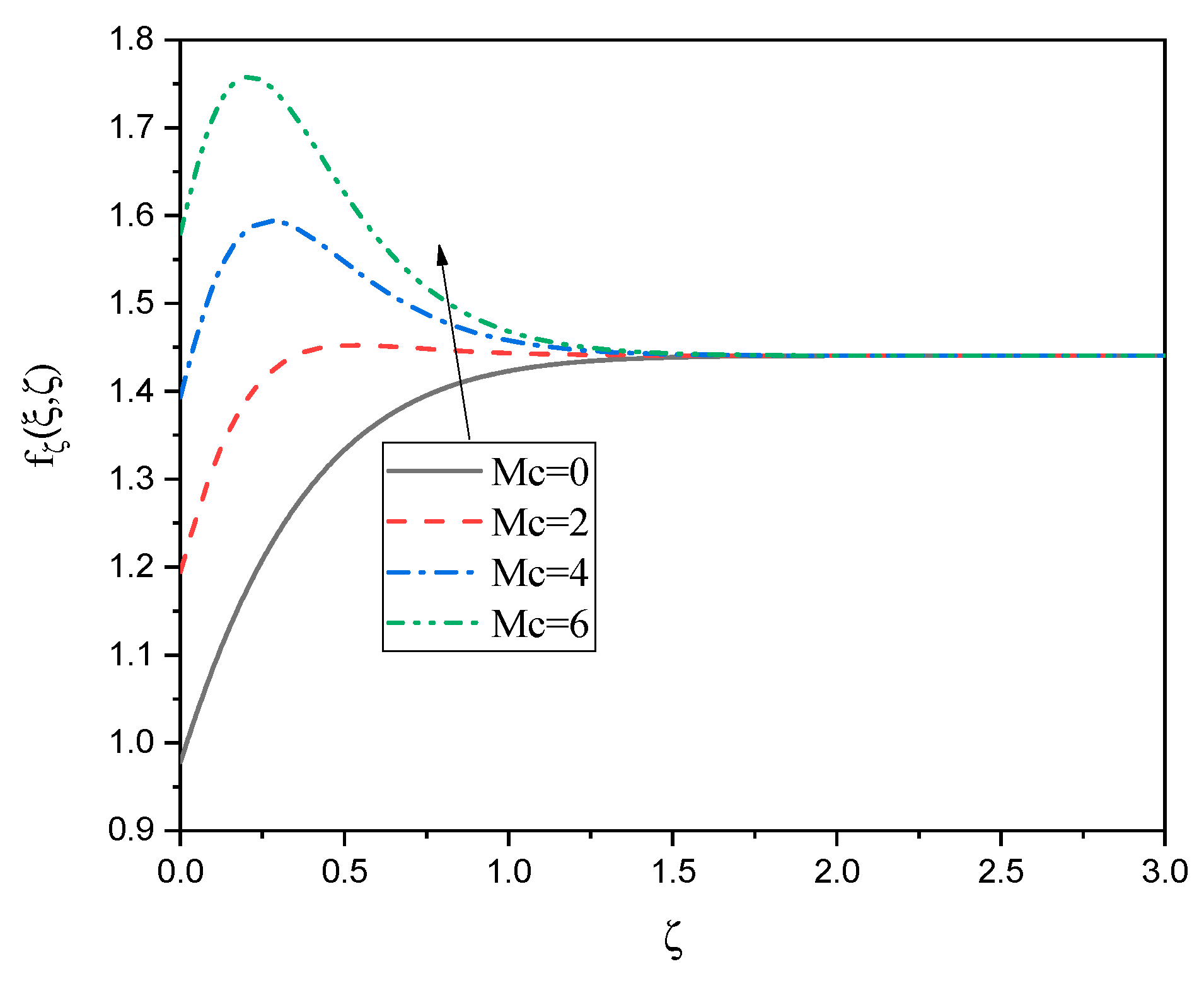



| 0.05 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0° | ≈30° | 0° | ≈30° | 0° | ≈30° | 0° | ≈30° | |
| Current examination (FDM) | 0.4895 | 0.4681 | 0.4632 | 0.4429 | 0.4134 | 0.3925 | 0.3151 | 0.2845 |
| Rana et al. [29] | 0.4945 | 0.4726 | 0.4757 | 0.4558 | 0.4185 | 0.3856 | 0.3070 | 0.2752 |
| Number of Observations | Error Degrees of Freedom | Root Mean Squared Error | R-Squared | Adjusted R-Squared | F-Statistic vs. Constant Model | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 10 | 1.77 × 10−6 | 1 | 1 | 6.88 × 107 | 9.38 × 10−38 | |
| 20 | 10 | 0.0428 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.04 × 103 | 1.2 × 10−13 | |
| 20 | 10 | 0.0178 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.24 × 103 | 4.92 × 10−14 | |
| Parameter | Range | Optimal Value | Maximum Predicted value | ||||
| 2.4465 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 0.042661 | 3.2683 | 6.3404 | ||
| 0.28362 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||||
| 0.30001 | 1.5 | 1.4501 | |||||
| = 0° | ≈ 30° | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.06977698 | 0.03887837 | 3.707143 | 0.10592010 | 0.050480790 | 3.515093 |
| 0.2 | 0.04872854 | 0.07098851 | 4.924491 | 0.07434244 | 0.078014410 | 4.645483 | |||
| 0.4 | 0.03684446 | 0.09982599 | 5.465102 | 0.05642097 | 0.103610300 | 5.156902 | |||
| 0.6 | 0.02947896 | 0.12161520 | 5.760536 | 0.04525443 | 0.123497700 | 5.439749 | |||
| 0.8 | 0.02452222 | 0.13789410 | 5.944762 | 0.03770974 | 0.138583300 | 5.617456 | |||
| 1.0 | 0.02097446 | 0.15030550 | 6.070081 | 0.03229433 | 0.150201800 | 5.738942 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.04872854 | 0.07098851 | 4.924491 | 0.07434218 | 0.001429891 | 4.677425 |
| 0.4 | 0.04929826 | 0.07024532 | 4.950215 | 0.07515649 | 0.000171984 | 4.699903 | |||
| 0.6 | 0.04985042 | 0.06954124 | 4.974950 | 0.07594646 | 0.001043702 | 4.721559 | |||
| 0.8 | 0.05038597 | 0.06887441 | 4.998767 | 0.07671350 | 0.002217169 | 4.742451 | |||
| 1.0 | 0.05090591 | 0.06824173 | 5.021716 | 0.07745889 | 0.003340965 | 4.762618 | |||
| 1.2 | 0.05141116 | 0.06763389 | 4.921647 | 0.07818382 | 0.004431233 | 4.782116 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04864383 | 0.07086869 | 4.922597 | 0.07421168 | 0.001447275 | 4.674675 |
| 0.04 | 0.04867213 | 0.07090594 | 4.923542 | 0.07425521 | 0.001441067 | 4.675590 | |||
| 0.07 | 0.04870033 | 0.07094505 | 4.924491 | 0.07429872 | 0.001434858 | 4.676510 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.04872854 | 0.07098851 | 4.925440 | 0.07434218 | 0.001429891 | 4.677425 | |||
| 0.13 | 0.04875658 | 0.07102577 | 4.926390 | 0.07438557 | 0.001424303 | 4.678342 | |||
| 0.16 | 0.04878458 | 0.07106550 | 4.921647 | 0.07442864 | 0.001421819 | 4.679263 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.04872950 | 0.22041360 | 4.857561 | 0.07434276 | 0.138431200 | 4.619795 |
| 0.004 | 0.04872916 | 0.17111870 | 4.879892 | 0.07434252 | 0.093193110 | 4.639070 | |||
| 0.007 | 0.04872881 | 0.12129860 | 4.902211 | 0.07434234 | 0.047514220 | 4.658291 | |||
| 0.010 | 0.04872854 | 0.07098851 | 4.924491 | 0.07434218 | 0.001429890 | 4.677425 | |||
| 0.013 | 0.04872820 | 0.02022522 | 4.946689 | 0.07434206 | 0.045005230 | 4.696422 | |||
| 0.016 | 0.04872793 | 0.03092984 | 4.968755 | 0.07434195 | 0.091746450 | 4.715243 | |||
| = 0° | ≈ 30° | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.03276736 | 0.2080947 | 5.603502 | 0.05024611 | 0.1089331 | 5.330424 |
| 0.4 | 0.03276723 | 0.2865276 | 5.554257 | 0.05024545 | 0.1697553 | 5.295525 | |||
| 0.6 | 0.03276706 | 0.3399973 | 5.502920 | 0.05024471 | 0.2238794 | 5.254621 | |||
| 0.8 | 0.03276696 | 0.3757719 | 5.451360 | 0.05024422 | 0.2676373 | 5.210441 | |||
| 1.0 | 0.03276686 | 0.3983062 | 5.401159 | 0.05024375 | 0.3008638 | 5.165130 | |||
| 1.2 | 0.03276689 | 0.4107288 | 5.353595 | 0.05024346 | 0.3245187 | 5.120429 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.00 | 0.03289593 | 0.2832164 | 6.070204 | 0.05044355 | 0.17013090 | 5.783751 | ||
| 0.05 | 0.03282977 | 0.2418788 | 5.834719 | 0.05034101 | 0.13647660 | 5.552588 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.03276736 | 0.2080947 | 5.603502 | 0.05024611 | 0.10893310 | 5.330424 | |||
| 0.15 | 0.03270887 | 0.1808442 | 5.378723 | 0.05015832 | 0.08654781 | 5.117743 | |||
| 0.20 | 0.03265417 | 0.1590929 | 5.162140 | 0.05007688 | 0.06845159 | 4.914959 | |||
| 0.25 | 0.03260312 | 0.1419081 | 4.954993 | 0.05000150 | 0.05390868 | 4.722321 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.03264627 | 0.1505862 | 5.295325 | 0.05006446 | 0.05994117 | 5.057343 |
| 0.3 | 0.03267049 | 0.1772648 | 4.884532 | 0.05010321 | 0.08666392 | 4.617199 | |||
| 0.6 | 0.03269696 | 0.2075794 | 4.437349 | 0.05014599 | 0.11707720 | 4.134715 | |||
| 0.9 | 0.03272603 | 0.2417639 | 3.948381 | 0.05019335 | 0.15139950 | 3.603085 | |||
| 1.2 | 0.03275821 | 0.2799947 | 3.411351 | 0.05024611 | 0.18974330 | 3.014307 | |||
| 1.5 | 0.03279386 | 0.3223301 | 2.819007 | 0.05030523 | 0.23205330 | 2.359058 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.03264496 | 0.2987385 | 5.386341 | 0.05006721 | 0.32856760 | 5.116513 |
| 0.5 | 0.03265417 | 0.1590929 | 5.162140 | 0.05007688 | 0.06845159 | 4.914959 | |||
| 1.0 | 0.03266549 | 0.9344965 | 4.924056 | 0.05009235 | 0.79299910 | 4.684390 | |||
| 1.5 | 0.03267317 | 1.7042140 | 4.775386 | 0.05010327 | 1.52531400 | 4.536570 | |||
| 2.0 | 0.03267819 | 2.4235270 | 4.682597 | 0.05011062 | 2.21391900 | 4.442980 | |||
| 2.5 | 0.03268168 | 3.0952270 | 4.621521 | 0.05011568 | 2.85833900 | 4.380822 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsemiry, R.D.; Ahmed, S.E.; Eid, M.R.; Elsaid, E.M. ANN-Based Prediction and RSM Optimization of Radiative Heat Transfer in Couple Stress Nanofluids with Thermodiffusion Effects. Processes 2025, 13, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041055
Alsemiry RD, Ahmed SE, Eid MR, Elsaid EM. ANN-Based Prediction and RSM Optimization of Radiative Heat Transfer in Couple Stress Nanofluids with Thermodiffusion Effects. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041055
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsemiry, Reima Daher, Sameh E. Ahmed, Mohamed R. Eid, and Essam M. Elsaid. 2025. "ANN-Based Prediction and RSM Optimization of Radiative Heat Transfer in Couple Stress Nanofluids with Thermodiffusion Effects" Processes 13, no. 4: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041055
APA StyleAlsemiry, R. D., Ahmed, S. E., Eid, M. R., & Elsaid, E. M. (2025). ANN-Based Prediction and RSM Optimization of Radiative Heat Transfer in Couple Stress Nanofluids with Thermodiffusion Effects. Processes, 13(4), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041055









