Abstract
Tannic acid (TA), a prevalent polyphenolic contaminant in industrial effluents, significantly inhibits microbial activity in anaerobic digestion, thereby diminishing wastewater treatment efficiency. In this study, a sulfidized nano zero-valent iron (S-nZVI) composite incorporated into sludge biochar (SB), abbreviated as SB-S-nZVI, was synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method. The composite’s adsorption capacity for TA and its impact on anaerobic digestion were systematically evaluated. Experimental results showed that SB-S-nZVI achieved a TA removal efficiency of 99.31% under optimal conditions (S/Fe = 0.05, dosage = 0.3 g·L−1), with a maximum adsorption capacity of 337.08 mg·g−1. In anaerobic digestion, the addition of 0.03 g·L−1 SB-S-nZVI enhanced chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal by 3.32%, increased specific methanogenic activity by 62.66%, and improved the microbial community composition, particularly enriching hydrolytic bacteria (Georgenia) and methanogenic archaea (Methanosaeta). The mechanistic analysis revealed that the FeS protective layer of SB-S-nZVI inhibited nano zero-valent iron oxidation and facilitated chemisorption-driven TA removal. This study presents an innovative approach for the integrated treatment of TA-contaminated wastewater by combining adsorption, degradation, and energy recovery.
1. Introduction
Tannic acid (TA) is a plant-derived polyphenolic compound commonly found in wastewater from various industries, including paper manufacturing, food processing, and chemical production [1]. Due to its antimicrobial properties, TA negatively impacts microbial survival during the anaerobic digestion of paper mill wastewater. The antibacterial effects of plant polyphenols, such as TA, primarily disrupt cell wall integrity and increase membrane permeability, leading to intracellular material loss, cell death, and inhibited microbial growth and reproduction [2,3]. Additionally, TA inhibits acetoclastic methanogens, resulting in acetic acid accumulation and reduced anaerobic digestion efficiency [4,5]. High concentrations of TA in wastewater also promote the formation of organic acids and methane, significantly depleting dissolved oxygen levels, which can lead to aquatic hypoxia and the mortality of fish and shrimp, ultimately deteriorating water quality [6]. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop efficient methods for the degradation of tannic acid in wastewater.
Currently, tannins are primarily removed from wastewater through membrane filtration, chemical oxidation, biological treatment, and adsorption techniques [7,8]. Membrane filtration achieves up to 59% removal efficiency; however, its low selectivity and susceptibility to clogging result in high maintenance costs [9,10]. Chemical oxidation offers high removal efficiency (up to 50%) but may leave residual chemicals that disrupt subsequent wastewater treatment and pose environmental risks [11,12]. Biological methods can degrade 30–50% of recalcitrant organic pollutants but require strict acclimatization conditions, increasing operational costs [7,13,14]. Adsorption techniques are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability, yet conventional adsorbents often lack selectivity [6,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Sludge biochar (SB) has emerged as a promising adsorbent due to its highly porous structure and superior adsorption capacity, particularly for phenolic compounds [8,22,23].
However, unmodified sludge biochar is ineffective in removing certain small-molecule pollutants [24]. To enhance its reactivity and surface properties, biochar is often modified with iron-based nanoparticles [25,26,27,28], which leverage their reducing capabilities and strong adsorption affinity due to the characteristics of iron oxides [29,30,31]. S-nZVI further enhances biochar’s porosity, reactivity, and selectivity by forming a protective FeSₓ layer on the surface [32]. The incorporation of hydrophobic iron sulfides (FeS or FeS2), which possess lower band gaps than iron oxides, improves electron transfer from Fe⁰ to target compounds while minimizing electron transfer to water, thereby significantly increasing the material’s selectivity for specific contaminants [33,34,35,36,37,38]. Additionally, nZVI-loaded sludge biochar has been shown to enhance the methane production potential, increase daily methane yields, accelerate hydrolysis rates, stabilize anaerobic digestion processes, and reduce lag time [30,39]. Most existing studies focus on the individual functions of S-nZVI or biochar [8,17,23], such as adsorption or catalysis, without systematically analyzing their combined adsorption–degradation synergy in anaerobic processes. This study proposes an innovative strategy for the integrated treatment of TA-contaminated wastewater, leveraging adsorption, degradation, and energy recovery to enhance wastewater treatment efficiency.
In this study, an SB-S-nZVI composite was synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method, and its adsorption capacity for TA from wastewater, along with its impact on anaerobic digestion, was systematically investigated. The material’s morphology was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD), while its surface chemistry was analyzed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Adsorption kinetics were examined to evaluate the adsorption capacity for TA. Additionally, the effects of TA and SB-S-nZVI on anaerobic digestion were assessed, including microbial activity, extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) secretion, and microbial community dynamics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
TA, sodium hydroxide, sodium borohydride, sodium dithionite, ferrous sulfate, Macrogol 4000, anhydrous ethanol, and hydrochloric acid were obtained from Tianjin Zhiyuan Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China).
Excess-activated sludge and normal sludge were collected from a papermaking wastewater treatment plant in Guangxi. Due to the complex composition of high-yield pulp wastewater and the uncontrollable variables in long-term experiments, glucose was used as the carbon source, with TA added to the reactors. The synthetic wastewater composition was as follows: glucose (8.16 g·L−1), sodium bicarbonate (5.20 g·L−1), ammonium chloride (0.96 g·L−1), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (0.18 g·L−1), tannic acid (0.10 g·L−1), and trace elements such as zinc (0.03 g·L−1).
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of SB-S-nZVI
The synthesis of SB-S-nZVI followed a previously established method [40], with the step-by-step procedure schematically illustrated in Figure S1. Sludge biochar was prepared via high-temperature pyrolysis. Excess-activated sludge was pre-freeze-dried for 48 h and then passed through a 110-mesh sieve. A measured amount of dried sludge powder was carbonized in a tubular furnace, with the temperature gradually increased to 1200 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C·min−1 for 2 h. To remove dissolved oxygen, nitrogen was injected at a flow rate of 0.4 L·min−1 for 30 min. After the reaction, the powder was cooled to room temperature, and the resulting sludge biochar was collected and weighed to determine the biochar yield. The prepared sludge biochar was designated as SB1200. The sludge biochar yield (y) was calculated using the following equation:
where M0 and M1 are the masses of the sludge biochar before and after carbonization, respectively.
Sludge biochar-loaded S-nZVI composites were prepared using a one-step hydrothermal synthesis method. First, 1 g of the prepared sludge biochar was weighed, to which 50 mL of FeSO4 (1 mol·L−1) solution was added and an ultrasound was conducted for 1 h. Subsequently, 0.5 g of Macrogol 4000 was dissolved in 100 mL of water–ethanol mixture (4:1). This solution was mechanically stirred for 30 min (at a speed of 200 rpm), and 40 mL of NaBH4 (1 mol·L−1) and Na2S2O4 were then added successively at a rate of 2 drops per second. The stirring was continued for 1 h and nitrogen was introduced throughout the process. This solution was then sealed and stored after freeze-drying for 24 h. Composite modified materials with S/Fe molar ratios of 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, and 0.20 were prepared by controlling the amount of Na2S2O4. The prepared sludge-carbon loaded S-nZVI composites were named SB-S-nZVI0.01, SB-S-nZVI0.05, SB-S-nZVI0.10, SB-S-nZVI0.15, and SB-S-nZVI0.20.
2.2.2. Characterization of Adsorbents
A field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, HHT, Tokyo, Japan) was used in conjunction with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS, Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) to determine the composition and distribution of various elements on the surface of the sludge-based biochar. A transmission electron microscope (TEM, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) was used to observe the structure and morphology of the composite materials. An X-ray diffraction analyzer (XRD, BRUKER, Karlsruhe, Germany) was used to analyze the phase and crystal shape of the S-nZVI loaded with the sludge char. The surface elemental composition and semi-quantitative analysis of the sludge biochar were analyzed using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA). Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) was used to detect the active species during the degradation of TA.
2.2.3. Adsorption Degradation of TA
A single-factor experiment was conducted to investigate the effect of SB-S-nZVI dosage on the adsorption and degradation of TA, maintaining the pH between 6.0 and 7.0. The optimal conditions identified in this experiment were applied in subsequent tests.
We further evaluated the effect of the SB-S-nZVI dosage on the selective adsorption and degradation of TA. The SB-S-nZVI materials with different S/Fe ratios were weighed with concentrations of 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 g·L−1. A TA solution of 50 mL (100 mg·L−1) was transferred to the reactor for a constant-temperature reaction for 2 h (200 rpm). After the reaction, 1–2 mL of the supernatant was collected and filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane. Then, 1 mL of the supernatant was diluted 10 times with deionized water, and the absorbance of the diluent at 275 nm was determined using an ultraviolet (UV) spectrophotometer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The residual concentration was determined, and the removal rates of TA and adsorption capacity of the sludge biochar were calculated. The sludge biochar adsorption capacity Q (mg·g−1) and removal rates of TA η (%) were calculated as follows:
where C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium liquid concentrations (g·m−3), respectively, and v and m are the liquid volume (m3) and weight of the dried adsorbent used (kg), respectively.
2.2.4. Adsorption Kinetics Experiment and Adsorption Kinetics Model
For data on the adsorption kinetics, pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models were used for analysis and fitting. According to the experimental steps presented in Section 2.2.3, the sludge charcoal with the best adsorption performance was selected for kinetic exploration, and the gradient sampling times were 0, 5, 10, 15, 25, 40, 60, 85, 115, 150, and 200 min. The adsorption capacity of the adsorbent was calculated according to the same steps, and the data were analyzed and fitted using the pseudo-first-order (Equation (4)) and pseudo-second-order kinetic models (Equation (5)).
where qe and qt are the adsorption capacities at adsorption equilibrium and reaction time t, respectively; k1 and k2 are the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption constants, respectively; and t is the adsorption time.
2.2.5. Anaerobic Digestion Experiments
Five small anaerobic reactors were used in this study, with each reactor containing 150 mL of synthetic wastewater and 50 mL of anaerobic granular sludge, maintaining an influent pH of 6.0–7.0. The experimental setup is illustrated in Figure S2. The control group was conducted without SB-S-nZVI0.05 and tannic acid. In the experimental group, the reactors were designated CON (control group), TA (0.10 g·L−1 TA), TA-0.03SB (0.10 g·L−1 TA and 0.03 g·L−1 SB-S-nZVI0.05), TA-0.10SB (0.10 g·L−1 TA and 0.10 g·L−1 SB-S-nZVI0.05), and TA-0.17SB (0.10 g·L−1 TA and 0.17 g·L−1 SB-S-nZVI0.05). N2 was added to the reactors to remove oxygen. The produced gases were directed into a NaOH solution to absorb water vapor and CO2, with the remaining gas routed to an Automated Methane Potential Test System (AMPTS II, Nova Skantek, Lund, Sweden) for methane production measurement. The hydraulic retention time was 24 h. All anaerobic reactors were carried out in a constant temperature shaker at 37 ± 0.5 °C at 120 rpm. The chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency was measured once a day, specific methanogenic activity (SMA) was measured every 4 days, and EPS was measured every 5 days. Volatile suspended solids/total suspended solids (VSS/TSS) were determined on the 4th and 28th days of the reaction.
2.2.6. Anaerobic Digestion Analysis Method
The COD concentration was determined by rapid digestion spectrophotometry (COD rapid tester, Lianhua Technology Company, Beijing, China). SMA was calculated by one-dimensional linear fitting of the cumulative methanogenesis curve of sludge in the first 4 h, to obtain the methanogenesis rate K, using the following formula [41]:
where, K is the slope of the fitting line, and the unit is L·h−1; VSS is the average concentration of sludge biomass in the reactor, and the unit is mg·L−1; and V denotes the volume of the mixture in L. The VSS/TSS values were calculated by burning the carbonized sludge in a muffle furnace at 600 °C for 2 h based on its losses and ash weight [42]. The calculation formula for VSS, TSS, and ash is as follows:
where V is the volume of anaerobic granular sludge (unit: mL); VSS’s unit is g·L−1; and TSS’s unit is g·L−1. EPS was extracted by the NaOH-formaldehyde method [43,44]. Polysaccharides were determined by the anthrone-sulfuric acid method, glucose was used as the standard material, and protein and humus were determined by the modified Folin–Lowry method [45]. Characterization of EPS was performed using a three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectrometer (FL, F-7000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The content of cytochrome C in EPS was determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.2.7. Microbial Community Analysis for Anaerobic Digestion
To explore the effect of tannic acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on the microbial community structure of anaerobic granular sludge, the anaerobic granular sludge in the reactor was sequenced with high flux after 28 days of reaction. A microbial DNA library was created by Meiji Biotechnology (Shanghai, China) using the Illumina™ platform.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of SB-S-nZVI
3.1.1. Morphological Characterization of SB-S-nZVI
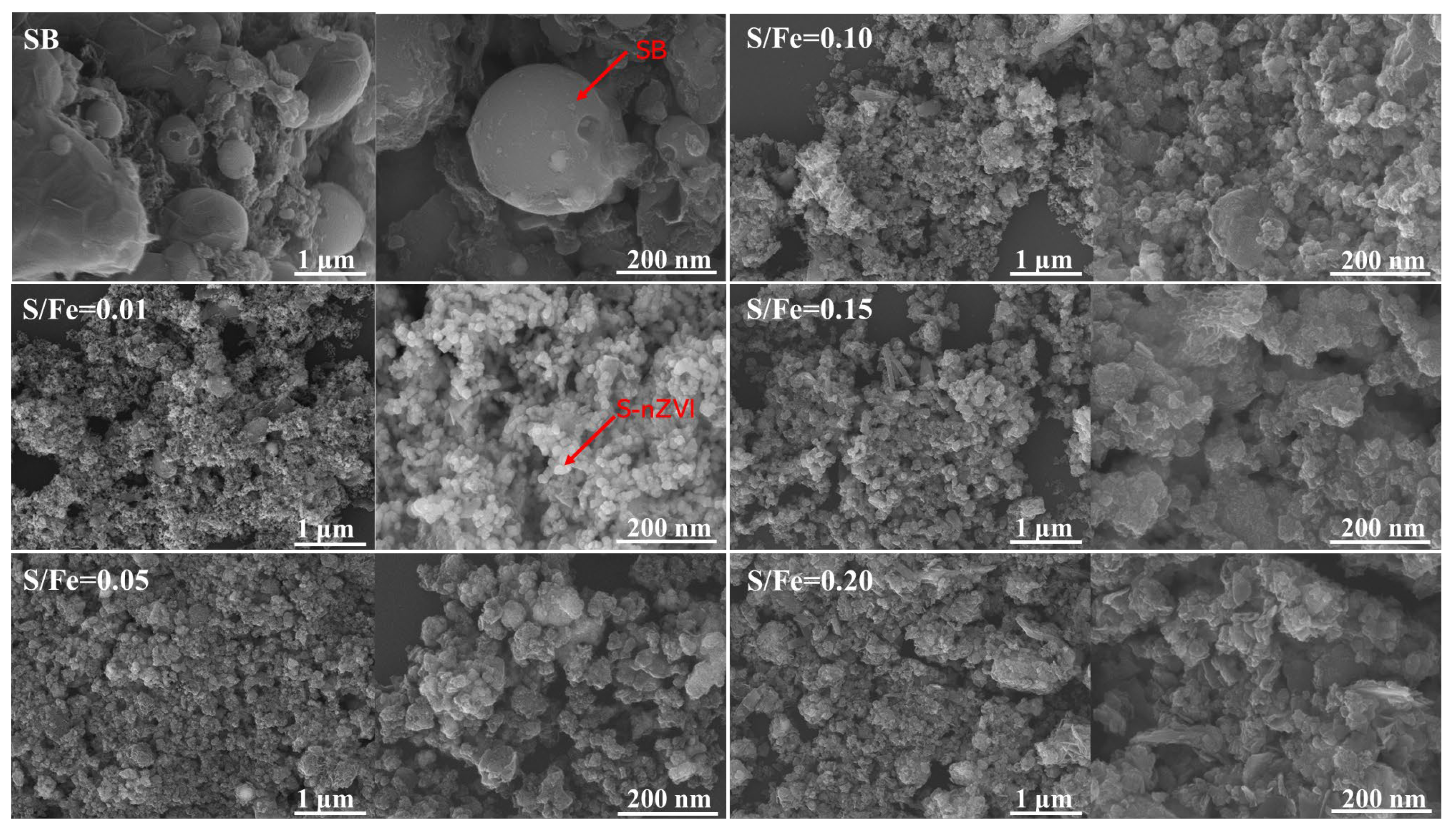
Figure 1 illustrates the FE-SEM images of sludge biochar loaded with S-nZVI, highlighting the material’s morphology at various scales. At both 1 μm and 200 nm resolutions, the pure SB exhibits a smooth and uniform carbon pellet structure, which provides a large surface area conducive to the adsorption of a wide range of pollutants. When the sulfur-to-iron ratio (S/Fe) is set at 0.01, the SB-S-nZVI particles are small and exhibit uniform size. However, as the sulfur content increases, while the iron content remains constant, the formation of ferrous sulfide and other sulfur-containing compounds on the particle surface also increases. This results in the nZVI particles becoming larger and less uniform, transitioning from a spherical to a more massive morphology. As shown in Figure 1, the particle size of S-nZVI expands with increasing sulfur content, likely due to the formation of a core-shell structure in which ferrous sulfide (FeS) encapsulates the zero-valent iron core. This core-shell structure enhances both the stability and reactivity of the material. Due to its highly reactive nature, nZVI is prone to oxidation upon exposure to oxygen. However, the FeS shell acts as a protective barrier, limiting contact between the zero-valent iron (ZVI) core and oxygen, thus significantly reducing oxidation rates [46]. This protective layer stabilizes the material, preserving its reactivity for extended periods. Consequently, the SB-S-nZVI composite demonstrates improved durability and sustained performance, making it highly effective for catalytic and adsorption applications, particularly in the context of environmental remediation.

Figure 1.
FE-SEM images of SB-S-nZVI with different S/Fe ratios.
The results of the EDS analysis are presented in Table S1. EDS provides a semi-quantitative elemental analysis, reflecting the surface distribution of elements. The data reveal that the sulfur content proportion on the surface gradually increases, aligning with the expected outcomes of the experiment. Conversely, the proportion of iron content decreases over time. This reduction is attributed to the increasing sulfur content, which diminishes the relative proportion of iron, despite the constant amount of iron added. The variation in the sulfur-to-iron ratio is primarily due to the added sulfur, rather than a change in the actual iron content. Additionally, the uneven distribution of nano zero-valent iron sulfide across the sample results in spatial variability in sulfur and iron concentrations, leading to some measurement discrepancies.
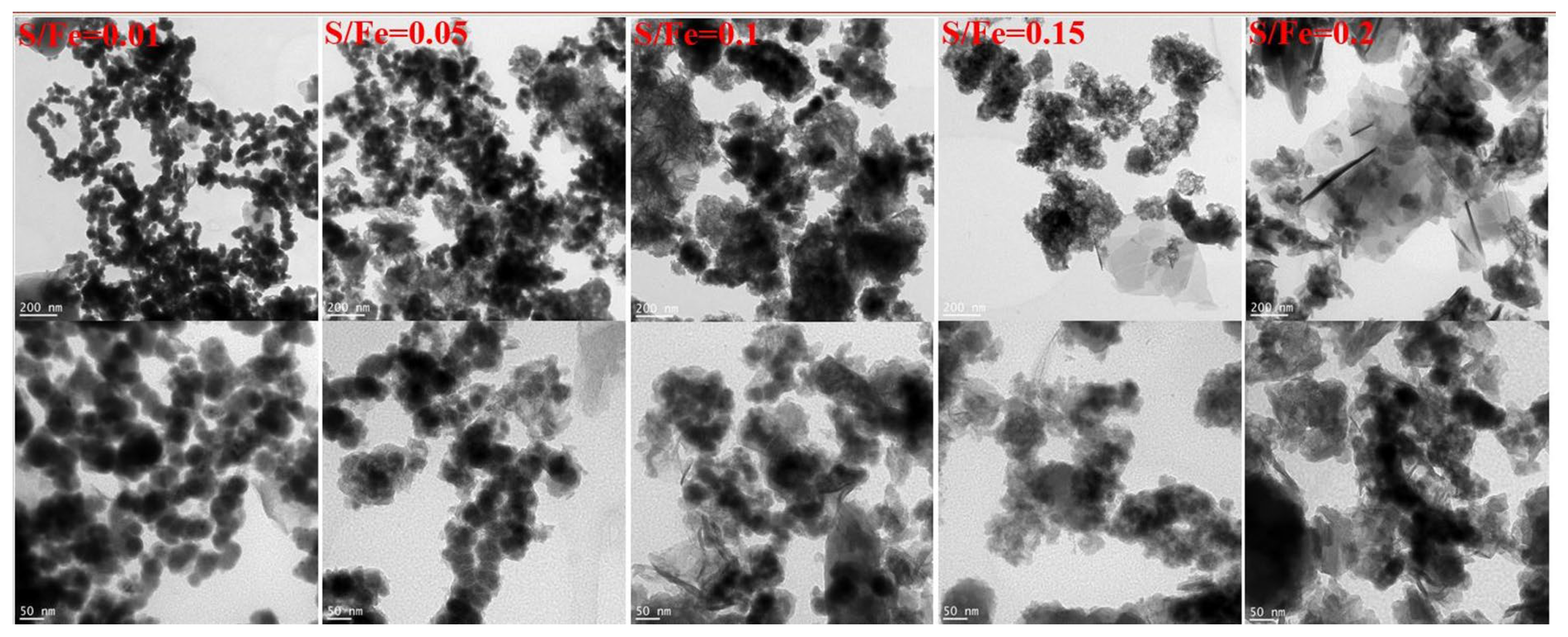
To examine the impact of sulfurization on the structure of nZVI, the synthesized SB-nZVI was analyzed using TEM to assess its morphology. As shown in Figure 2, at a sulfur-to-iron ratio (S/Fe) of 0.01, S-nZVI adopts a chain-like structure, with a layer of gray material attached to the outer surface of the black nZVI, which is likely a pyrite compound [47], confirming the successful synthesis of S-nZVI. At S/Fe = 0.05, the chain structure of S-nZVI becomes shorter, and the particle size increases. As sulfur content rises, the structure transitions from a chain-like to a block-like form. At S/Fe = 0.20, a few acicular structures are observed. This transformation can be attributed to the relatively low sulfur content at lower S/Fe ratios, resulting in limited FeS formation and the presence of a thin nZVI layer that promotes magnetic attraction and electrostatic interactions, thereby facilitating the chain structure. As the sulfur content increases, more FeS is formed, causing a flocculent surface on the nZVI particles, which reduces the magnetic interactions between them. Consequently, the chain structure diminishes and gives way to an amorphous block-like structure. The appearance of acicular structures is likely due to the formation of additional ferric sulfide compounds [46].

Figure 2.
TEM patterns of S-nZVI with different S/Fe ratios.
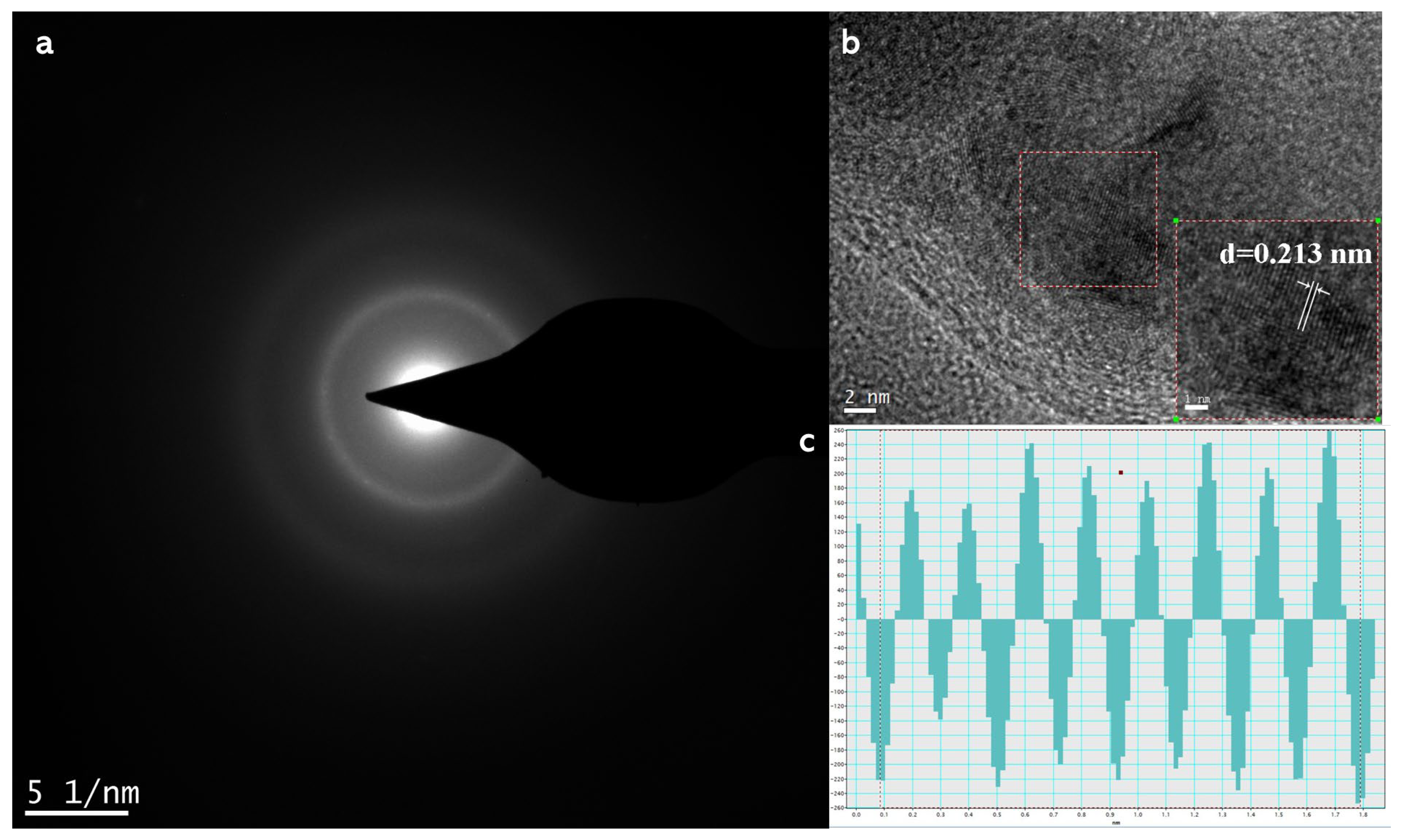
Figure 3 illustrates the microstructure of iron, with Figure 3a showing a diffuse ring pattern characteristic of nanocrystalline body-centered cubic (bcc) iron, corresponding to α-Fe [48]. Figure 3b demonstrates that the synthesized SB-nZVI exhibits crystallinity. Figure 3c provides a detailed diagram of the lattice particle size distribution from Figure 3b, obtained through measurement and analysis of the lattice images using Digital Micrograph (v 3.5). The measured lattice spacing was 0.213 nm, which corresponds to the α-Fe (110) plane [48].

Figure 3.
(a) Selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of nZVI particles characteristic of polycrystalline bcc iron; (b) iron lattice pattern; (c) intensity distribution of the lattice particle size in the specified region shown in (b).
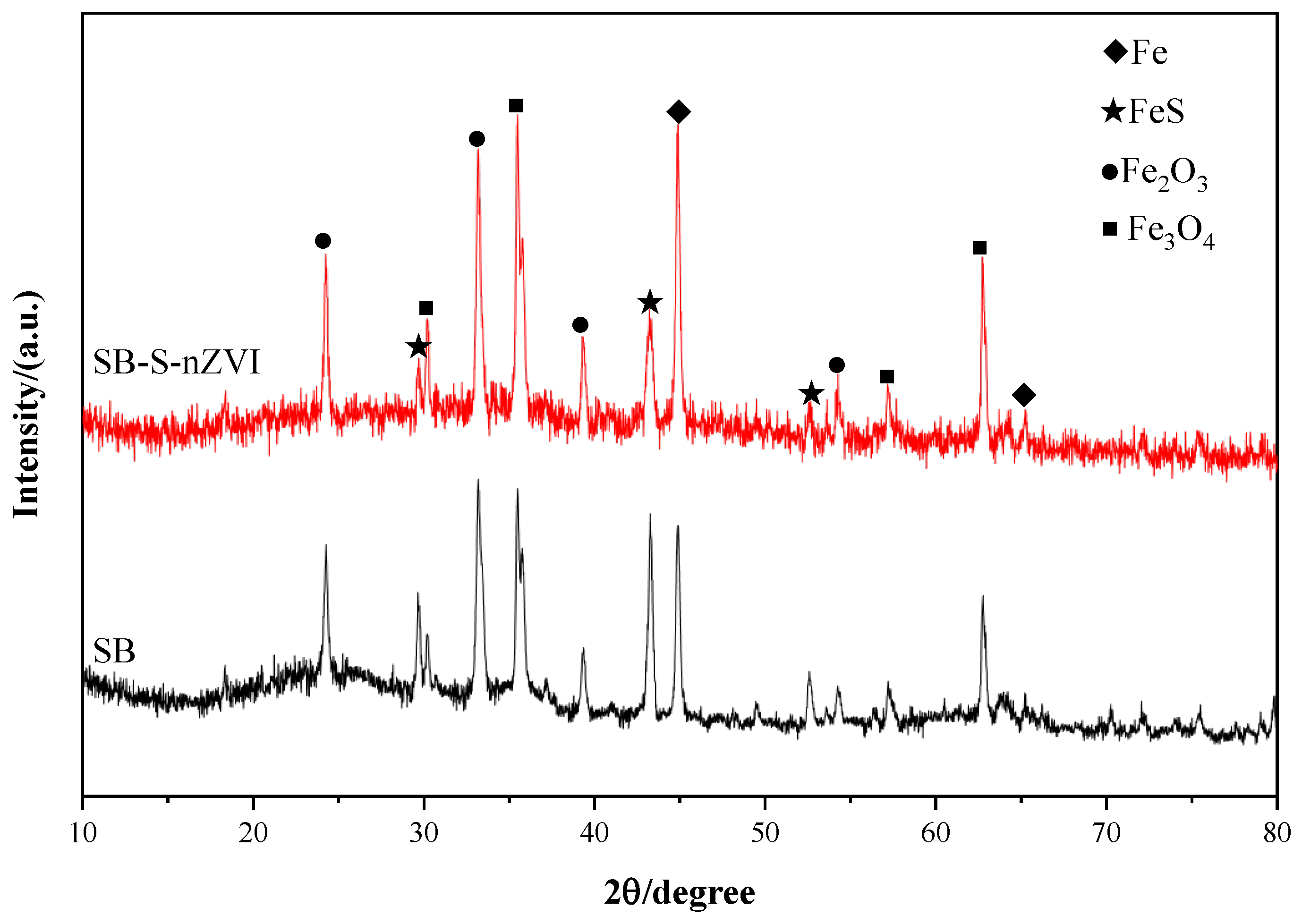
An X-ray diffractometer was used to further investigate the crystalline structure of the modified material, with phase analysis conducted using Jade (v 6.5). The diffraction patterns presented in Figure 4 show that SB-S-nZVI exhibits prominent peaks at 2θ = 44.82° and 64.57°, corresponding to the 110 and 200 crystal planes of Fe0, respectively, which is consistent with the TEM observations. Additionally, strong diffraction peaks at 2θ = 29.63°, 33.46°, 43.17°, and 52.57° correspond to the 200, 201, 202, and 220 planes of FeS [49], confirming the successful incorporation of sulfide nanoscale zero-valent iron onto sludge biochar. Furthermore, diffraction peaks for Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 were observed at 2θ = 35.13°, 71.82°, and 75.14°. These iron oxides are likely a result of the pyrolysis of sludge into SB at high temperatures. Notably, while corresponding diffraction peaks were observed in both SB and SB-S-nZVI, slight deviations in peak positions were detected. This shift is likely due to the reduction of iron ions in the interlayer during the process of loading SB onto S-nZVI, which increases the interlayer spacing and causes the diffraction peak positions to shift [50]. In summary, S-nZVI was successfully loaded onto sludge biochar with crystallinity, and the presence of nano-iron oxides can enhance the catalytic activity for pollutant degradation [51].

Figure 4.
XRD patterns of sludge biochar and nanoscale zero-valent iron loaded onto sludge biochar.
3.1.2. Surface Chemistry Characterization of SB-S-nZVI
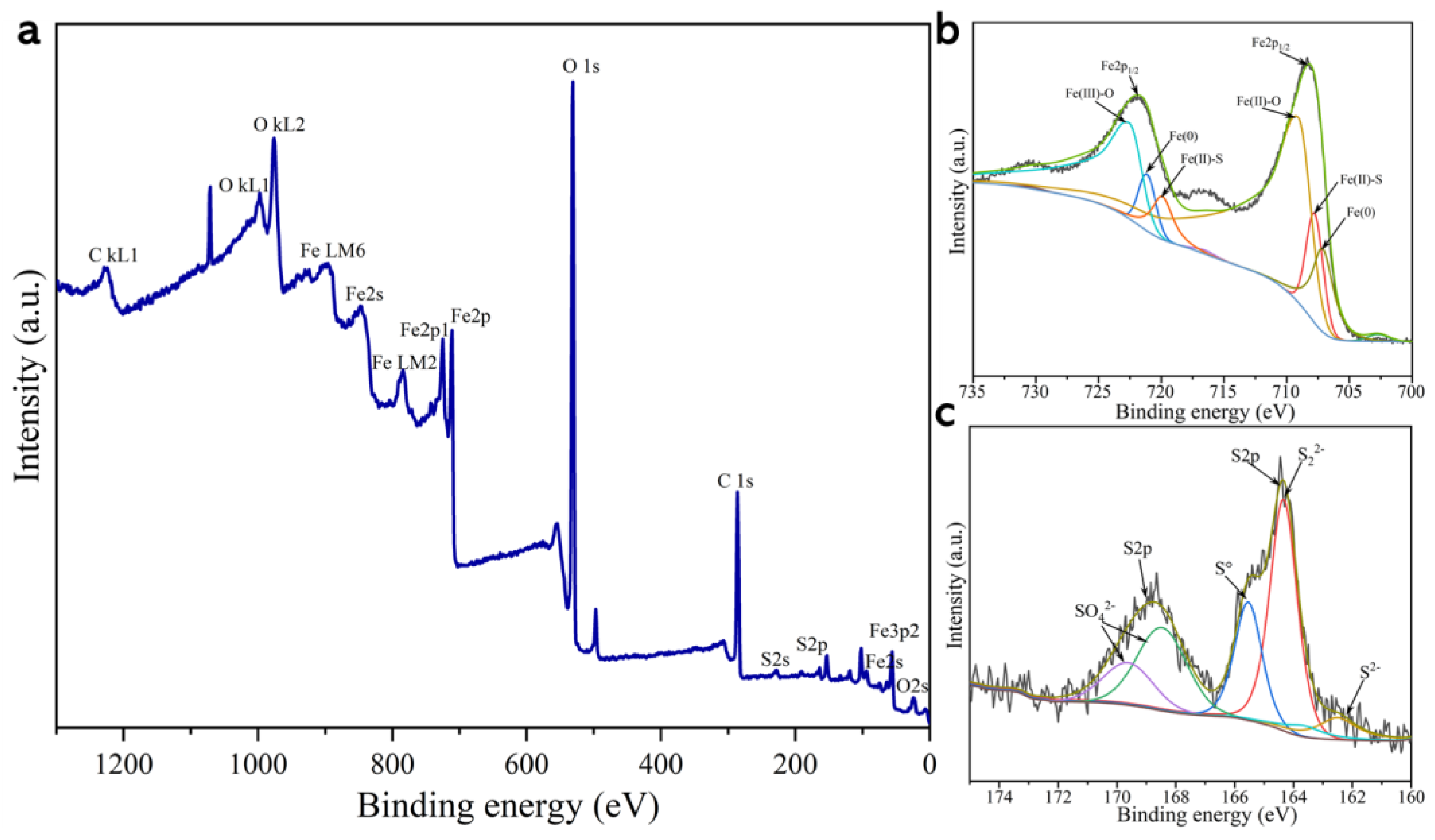
To further elucidate the surface chemical properties of SB-S-nZVI, XPS was employed to determine the chemical states of sulfur and iron on the material’s surface, with the results shown in Figure 5. Full-spectrum analysis revealed that the surface of SB-S-nZVI was enriched with carbon (C), oxygen (O), sulfur (S), iron (Fe), and other major elements, as illustrated in Figure 5a. The characteristic peaks observed at various binding energies correspond to the respective valence states of these elements. Notably, the Fe 2p spectra (Figure 5b) exhibit peaks at 707.20 and 721.20 eV, indicative of Fe (0), while peaks at 720.02 and 707.85 eV correspond to Fe (II)-S, and those at 722.75 and 709.25 eV are attributed to Fe (III)-O and Fe (II)-O, respectively [52]. The S 2p spectrum (Figure 5c) shows a characteristic peak at 162.5 eV, corresponding to S2−. The presence of Fe (0) and Fe (II)-S peaks in Figure 5b confirms the incorporation of FeS and nZVI onto the SB surface, suggesting successful loading of S-nZVI onto the sludge biochar. The observed iron oxide peaks may result from the reaction between a portion of the iron and oxygen during the XPS measurement, as well as from oxides formed during the preparation of the SB. Additional peaks at 169.61 and 168.55 eV in the S 2p spectrum, corresponding to SO42−, likely arise from residual by-products formed during the preparation of S-nZVI using FeSO4. Furthermore, peaks at 164.35 and 165.55 eV, attributed to polysulfides, suggest the presence of ferric sulfide compounds on the surface of SB-S-nZVI [53]. These compounds form a protective layer over the nZVI, extending its longevity. Additionally, the electrical conductivity of FeS enhances electron transfer, thereby promoting the reactivity of nZVI and sustaining its catalytic activity [52,54].

Figure 5.
XPS diagram of the sludge biochar loaded with S-nZVI. (a) Full-spectrum scanning surface of SB-S-nZVI; (b) Fe 2p XPS spectra of SB-S-nZVI; (c) S 2p XPS spectra of SB-S-nZVI.
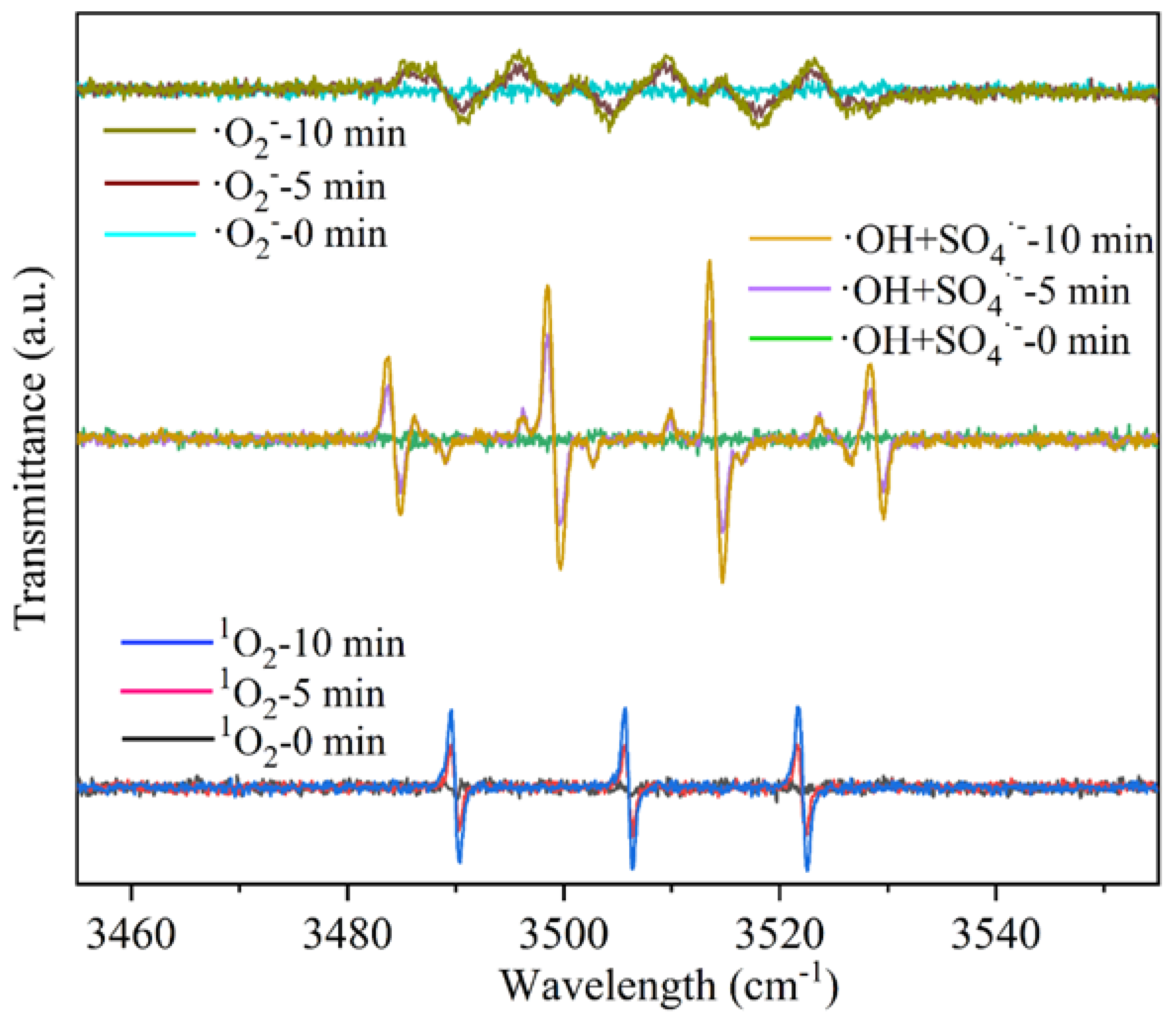
To investigate the active species involved in the degradation process, DMPO was employed as a free-radical trapping agent, and the active components in SB-S-nZVI were analyzed using an Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) spectrometer. The reactive species, including superoxide anion (·O2−), singlet oxygen (1O2), hydroxyl radical (·OH), and sulfate radical (SO4·−), were monitored at 0, 5, and 10 min under normal temperature and light conditions, as presented in Figure 6. At the initial stage of the reaction, no significant EPR signal was detected, indicating minimal release of ·O2−. However, at 5 min, a characteristic tetragonal signal for ·O2−, with an intensity ratio of 1:1:1:1, emerged. As the reaction progressed, the ·O2− signal exhibited only a slight increase and stabilized by 10 min. In contrast, both ·OH and SO4·− radicals displayed typical tetragonal patterns with a 1:2:2:1 intensity ratio after 5 min of reaction [51]. The intensity of the ·OH signal increased significantly with time, surpassing that of ·O2− and 1O2 by the 10th minute. Additionally, the 1O2 signal was also observed at 5 and 10 min, with the peak intensity gradually intensifying over the reaction period. The results indicate the presence of four distinct active components in SB-S-nZVI, consistent with previous findings [55]. Among these, 1O2, ·OH, and SO4·− played a dominant role in the degradation of TA. The rapid detection of these reactive species suggests the high catalytic potential of SB-S-nZVI for the efficient degradation of organic pollutants.

Figure 6.
EPR detection spectrum of SB-S-nZVI.
3.2. Adsorption of TA by SB-S-nZVI
3.2.1. Effect of SB-S-nZVI Dosage
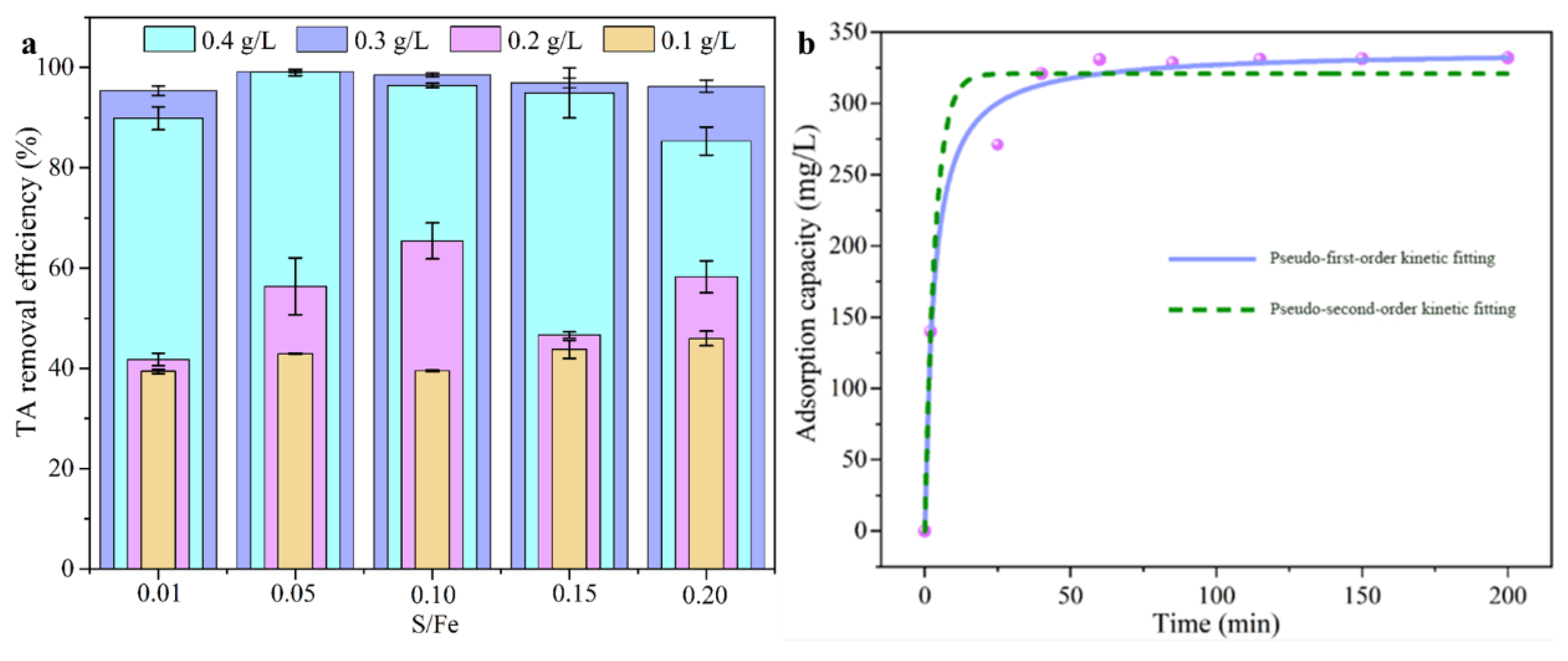
To investigate the impact of material dosage on the adsorption and degradation of TA, a single-factor experiment was conducted, as shown in Figure 7a. The removal efficiency of TA initially increased and then decreased with increasing dosage, reaching its maximum at an SB-S-nZVI concentration of 0.3 g·L−1. However, beyond this optimal dosage, the removal efficiency began to decline. This trend suggests that, at higher dosages, the number of adsorption sites increased, and an excess of FeS was involved in TA capture. When TA was fully adsorbed, some FeS did not fully react, remaining encapsulated by zero-valent iron, which led to its precipitation and diminished catalytic activity. Additionally, the S/Fe ratio at a fixed SB-S-nZVI dosage was found to influence TA removal. The most effective TA removal occurred at an S/Fe ratio of 0.05 with a dosage of 0.3 g·L−1. Deviations from this ratio had significant effects on the catalytic performance of zero-valent iron. An increase in sulfur content leads to greater sulfurization, more FeS formation, and less available zero-valent iron for reaction, resulting in higher hydrophobicity [56]. Consequently, TA cannot be effectively catalyzed and degraded. Conversely, a lower S/Fe ratio results in less FeS formation, leading to a higher amount of unreacted zero-valent iron. This excess iron, which is partially oxidized by dissolved oxygen, further limits its catalytic ability. In conclusion, the optimal conditions for TA adsorption and degradation were achieved with SB-S-nZVI at a dosage of 0.3 g·L−1 and a S/Fe ratio of 0.05, resulting in a TA removal rate of 99.31%.

Figure 7.
(a) Effect of SB-S-nZVI dosage on the tannic acid removal rate; (b) kinetic fitting of SB-S-nZVI0.05 for the adsorption of TA.
3.2.2. Kinetics of Tannic Acid Adsorption by SB-S-nZVI0.05
The kinetics of TA adsorption were investigated to elucidate the reaction rate and the nature of the adsorption process. To determine the rate-limiting step, the kinetic data were fitted to both pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models, as described by Equations (4) and (5). The model parameters and fitting results are presented in Figure 7b and Table 1. The adsorption of TA by SB-S-nZVI0.05 occurred in two distinct phases: a rapid adsorption phase followed by a slower degradation phase. During the initial 25 min, TA adsorption was rapid as the active sites on SB-S-nZVI0.05 were quickly occupied. The subsequent 35 min represented a slower phase, where adsorbed TA began to degrade, and the system approached equilibrium after 60 min. Notably, as shown in Table S1, the correlation coefficient (R2) for the pseudo-second-order model (R22) was significantly higher than that for the pseudo-first-order model (R21). Furthermore, the equilibrium adsorption capacity (q2e = 337.08 mg·g−1) derived from the pseudo-second-order model closely matched the experimental value and was higher than the value obtained from the pseudo-first-order model (q1e = 320.83 mg·g−1). These findings indicate that the adsorption of TA by SB-S-nZVI0.05 follows the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, suggesting that the adsorption process is primarily governed by chemical adsorption, with chemical interactions acting as the rate-limiting step. Table S2 compares the adsorption performance for TA removal in this study with other works conducted under different experimental conditions [14,16,17,18,19,20,21,57], demonstrating that the synthesized SB-S-nZVI0.05 exhibits superior adsorption performance for TA removal.

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters of TA adsorption by SB-S-nZVI0.05.
3.3. Effects of Tannic Acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on Anaerobic Digestion
3.3.1. Effects of Tannic Acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on Microbial Activity
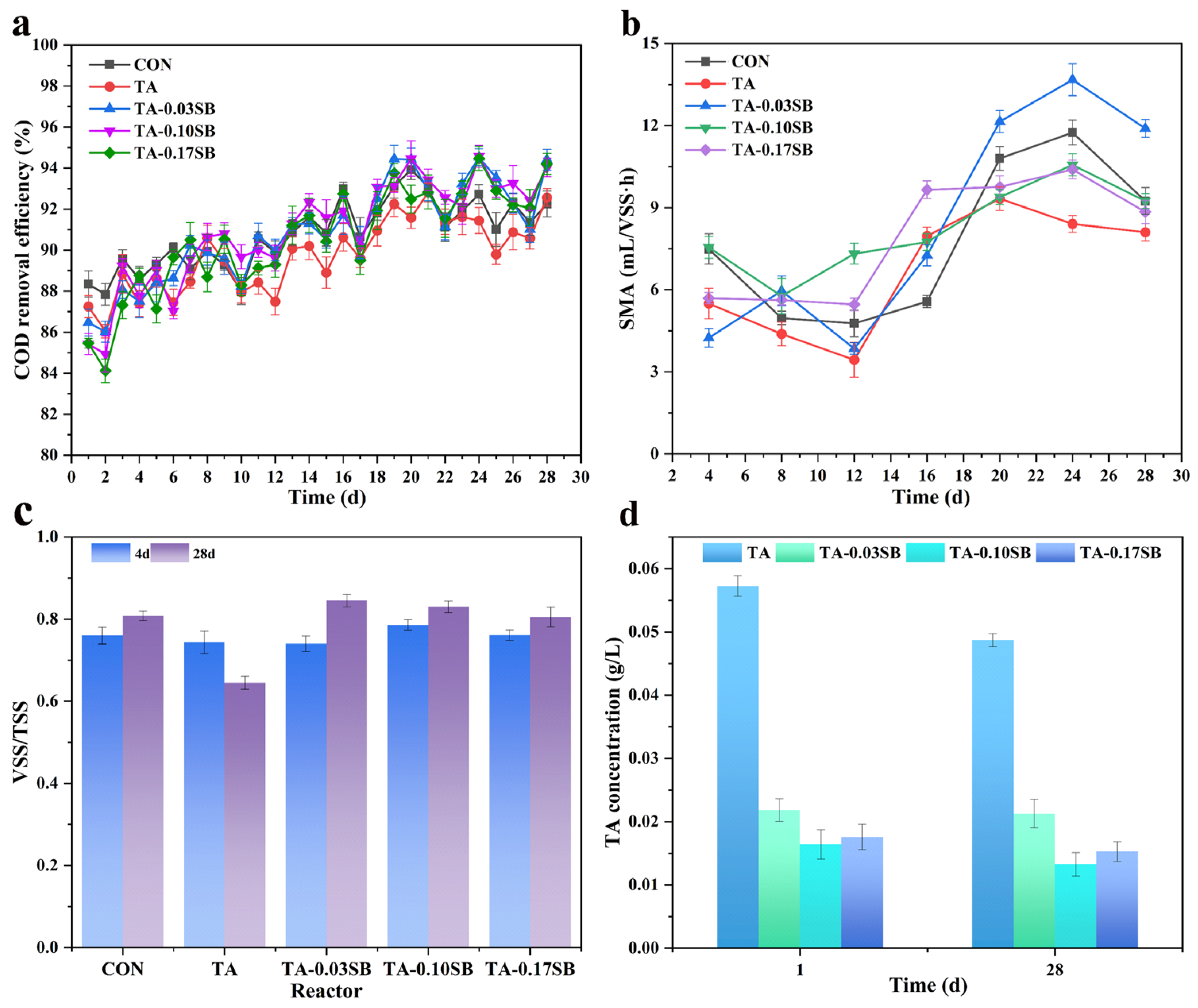
Figure 8a shows that the presence of SB-S-nZVI0.05 resulted in higher COD removal efficiency compared to both the CON and TA reactors, indicating its potential to enhance COD removal by anaerobic granular sludge. However, contrary to expectations, the highest COD removal efficiency was observed in the TA-0.03SB reactor, which showed a 3.32% improvement over the TA reactor. This suggests that COD removal efficiency is not directly proportional to the concentration of SB-S-nZVI0.05.

Figure 8.
Effects of tannic acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on anaerobic digestion: (a) COD removal efficiency, (b) SMA, (c) VSS/TSS, and (d) tannic acid concentration.
Figure 8b demonstrates that the SMA in the TA reactor was lower than in the CON reactor during both the early and late stages of the 28-day reaction cycle. On day 24, Compared to the control (CON) reactor, the SMA in the TA reactor decreased by 28.42%, while in the TA-0.03SB reactor, it increased by 16.43%. Notably, the SMA in the TA-0.03SB reactor was 62.66% higher than that in the TA reactor, indicating a positive effect of SB-S-nZVI0.05 on methanogenic activity. This is consistent with previous studies indicating that tannic acid concentrations ranging from 0.4 to 3.0 g·L−1 can inhibit up to 50% of methanogenic activity [58]. This suggests that tannic acid hindered the optimal functioning of the anaerobic digestion process. In contrast, the addition of SB-S-nZVI0.05 alleviated the inhibitory effects of tannic acid and stimulated methanogenic activity.
Figure 8c shows that the VSS/TSS ratio in the TA reactor was lower than that in the CON reactor, while the reactors containing SB-S-nZVI0.05 exhibited higher VSS/TSS ratios, with the TA-0.03SB reactor showing the highest ratio. The VSS/TSS ratio is commonly used as an indicator of microbial activity, suggesting that SB-S-nZVI0.05 mitigated the toxicity of tannic acid and protected microbial communities.
Finally, Figure 8d demonstrates that the TA-0.10SB reactor achieved the lowest tannic acid concentration (13.26 mg·L−1) and an 86.74% removal efficiency, compared to 48.69 mg·L−1 and 51.31% removal efficiency in the TA reactor. This demonstrates that the TA-0.10SB reactor exhibited superior performance in tannic acid removal, whereas the TA reactor showed relatively low tannic acid removal efficiency, indicating that the natural degradation of tannic acid by microorganisms was limited. This also reconfirms the adsorption capacity of SB-S-nZVI0.05 for TA.
The observed decrease in COD removal efficiency, VSS/TSS, and SMA in the TA reactor suggests that TA inhibited microbial growth, thereby disrupting the normal anaerobic digestion process. In contrast, the addition of SB-S-nZVI0.05 alleviated the inhibitory effects of tannic acid, thereby enhancing the anaerobic digestion process.
3.3.2. Effects of Tannic Acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on EPS Secretion
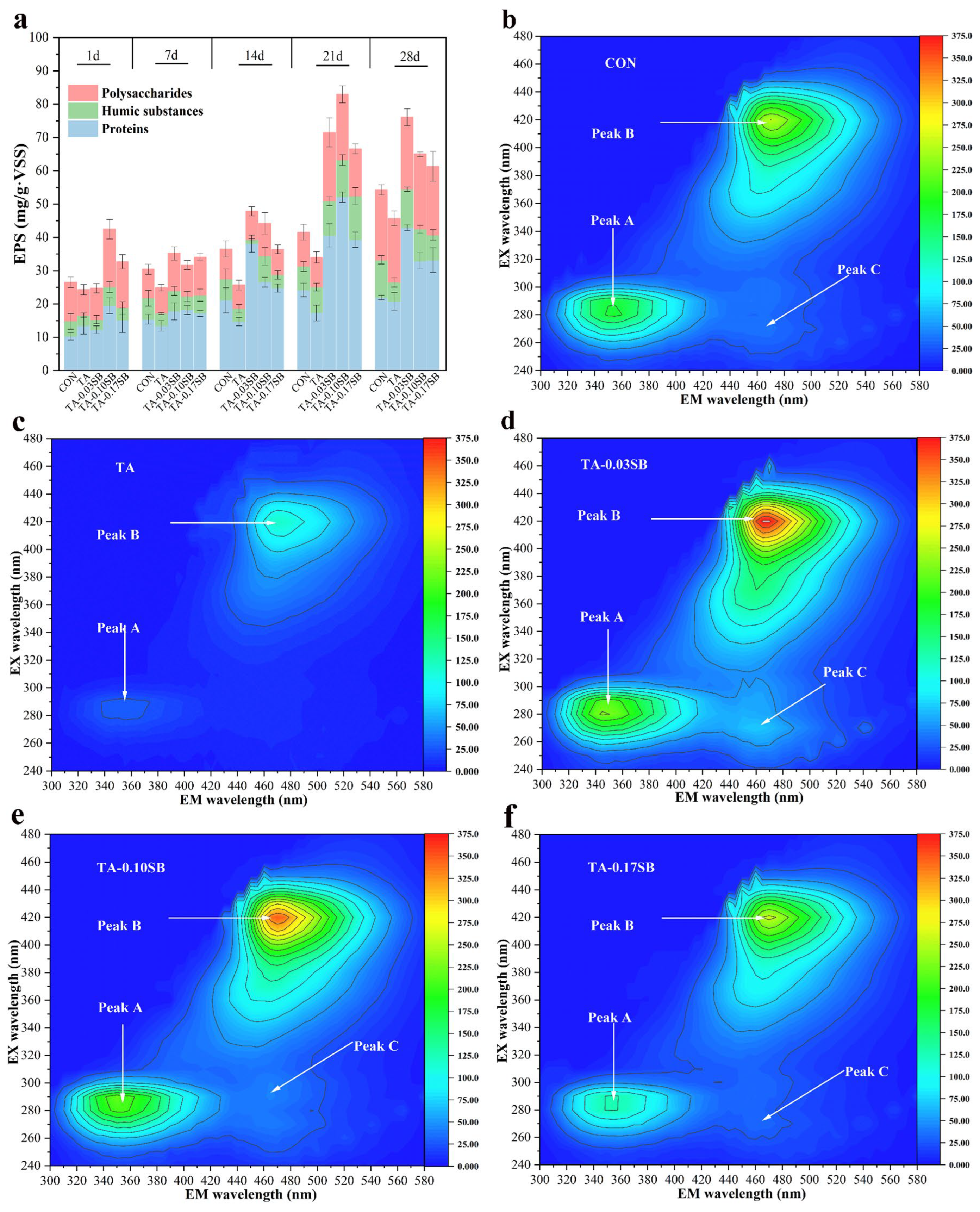
EPS quantification was performed by measuring the total polysaccharide, humic substance, and protein content. Figure 9a illustrates the effect of tannins and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on the EPS content in the reactor. EPS acts as a protective barrier for microorganisms and is important in maintaining the stability of anaerobic granular sludge [41]. On day 28 of the reaction, the EPS concentration in the CON reactor was measured at 54.24 mg·g−1 VSS. In contrast, the EPS concentration in the TA reactor was reduced by 8.54 mg·g−1 VSS compared to the CON reactor, suggesting that tannic acid inhibited microbial EPS secretion. On day 24, the highest EPS concentration, 82.96 mg·g−1 VSS, was recorded in the TA-0.10SB reactor, representing an increase of 48.92 mg·g−1 VSS relative to the TA reactor. EPS secretion in the TA reactor was significantly lower than in the CON reactor, confirming the inhibitory effect of tannic acid on EPS production. In contrast, reactors supplemented with SB-S-nZVI0.05 exhibited significantly higher EPS secretion than both the CON and TA reactors, suggesting that SB-S-nZVI0.05 facilitated EPS production. Additionally, EPS secretion in the CON, TA, and TA-0.03SB reactors exhibited a steady increase, consistent with previous studies [59,60]. This trend can be attributed to the availability of a sufficient carbon source and the limited consumption of EPS as an alternative carbon source by microorganisms. A distinct pattern of EPS secretion was observed in the TA-0.10SB and TA-0.17SB reactors, characterized by an initial increase followed by a subsequent decline. Unlike the continuous increase observed in other reactors, this decrease in EPS content over time may be attributed to the complete depletion of the primary carbon source, leading to the utilization of EPS as an alternative carbon source [61].

Figure 9.
Effects of tannic acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on EPS secretion: (a) change in EPS content, and (b–f) 3D-EEM analysis.
A 3D-EEM analysis was carried out at the end of the reaction cycle to detect and analyze EPS. Three characteristic peaks with different fluorescence intensities were observed in Figure 9b–f. Peak A (EX/EM: 290/350) was attributed to tryptophan protein, which was an important component of protein synthesis [62]. The peak intensity of the TA reactor was weak, indicating that tannic acid inhibited tryptophan protein synthesis. The peak intensities of the TA-0.03SB and TA-0.10SB reactors were slightly higher than that of the CON reactor, and the peak intensity of the TA-0.17SB reactor was lower than that of the CON reactor, which indicated that an appropriate amount of SB-S-nZVI0.05 was conducive to protein synthesis. Peak B (EX/EM: 420/470) was attributed to coenzyme F420, which played a vital role in the metabolic process of methanogens [63,64]. Coenzyme F420 was a carrier with low electron transfer. Studies have shown that the content of coenzyme F420 could indicate the activity of methanogens [65]. The peak intensity of coenzyme F420 in the reactors with SB-S-nZVI0.05 was higher than that in the TA and CON reactors, indicating that SB-S-nZVI0.05 promoted the formation of coenzyme F420 and indirectly promoted the process of methanogenesis. The peak intensity of the TA-0.03SB reactor was the highest, indicating that a low concentration of SB-S-nZVI0.05 could promote better methanogenesis. Peak C (EX/EM: 270/460) was attributed to humic acid compounds. The strength of Peak C was much lower than that of Peak A and Peak B, indicating that the content of humic acid compounds was low. The absence of Peak C was observed in the TA reactor, while the peak intensity in the added SB-S-nZVI0.05 reactors was higher than that in the CON reactor. Humic acid was shown to have promoted microbial extracellular DIET by virtue of its redox activity [66]. Thus, SB-S-nZVI0.05 could improve DIET efficiency by facilitating the generation of carriers.
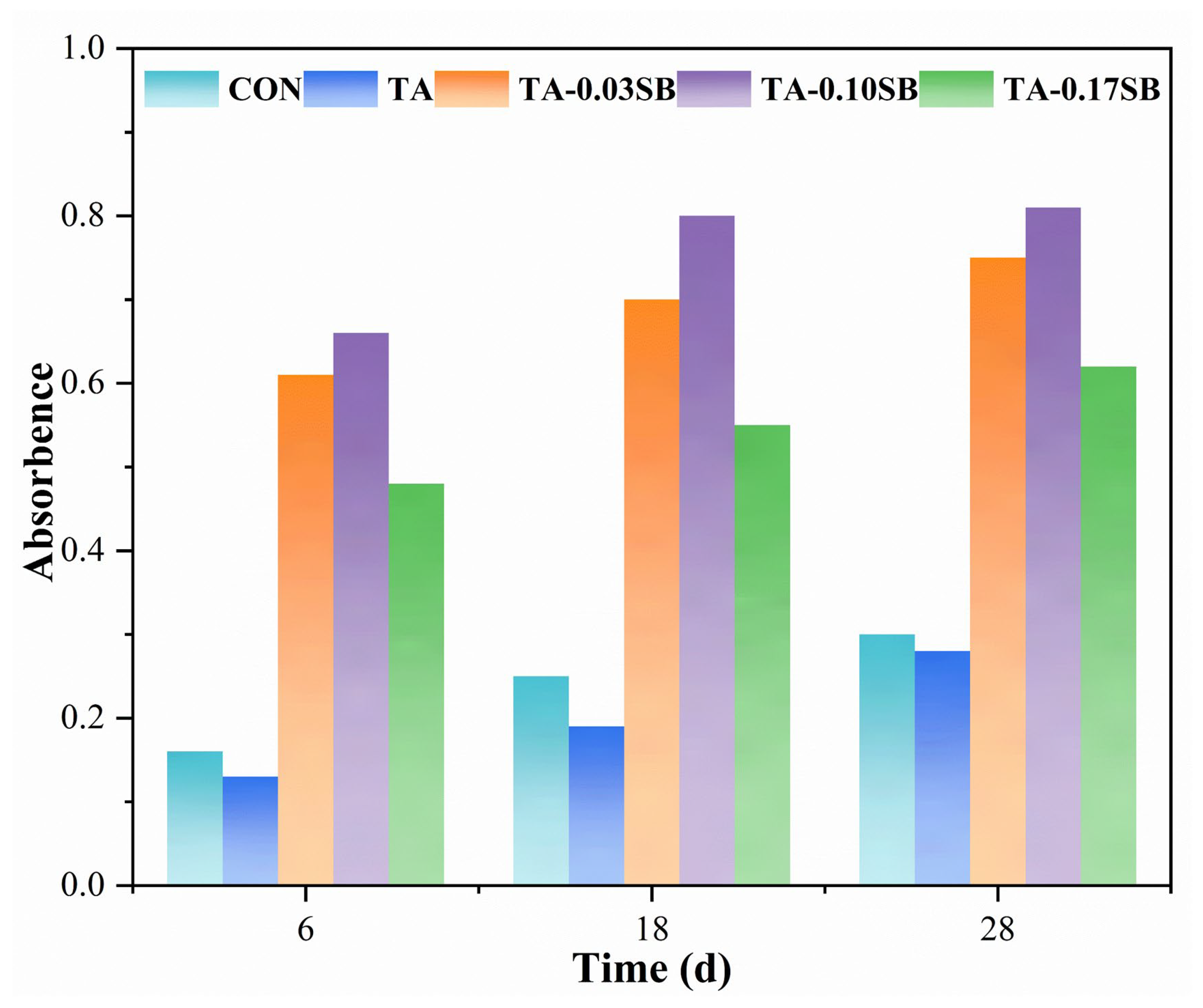
Figure 10 further demonstrates that the levels of C-type cytochromes were significantly higher in reactors supplemented with SB-S-nZVI0.05 compared to both the TA and CON reactors, suggesting that SB-S-nZVI0.05 promoted the formation of C-type cytochromes. As electrochemically active components of EPS, C-type cytochromes play a crucial role in facilitating extracellular electron transfer by serving as both electron donors and acceptors [67]. Specifically, they are essential for maintaining interactions between mutualistic bacteria and methanogens [61]. The significantly higher levels of C-type cytochromes in SB-S-nZVI0.05 treated reactors can be attributed to the superior electrical conductivity of SB-S-nZVI0.05, which may serve as a conductive medium for extracellular electron transfer, thereby enhancing microbial communication and promoting anaerobic digestion [68].

Figure 10.
Absorbance of C-type cytochrome at 419 nm in each reactor.
3.3.3. Effects of Tannic Acid and SB-S-nZVI0.05 on Bacterial and Archaeal Community
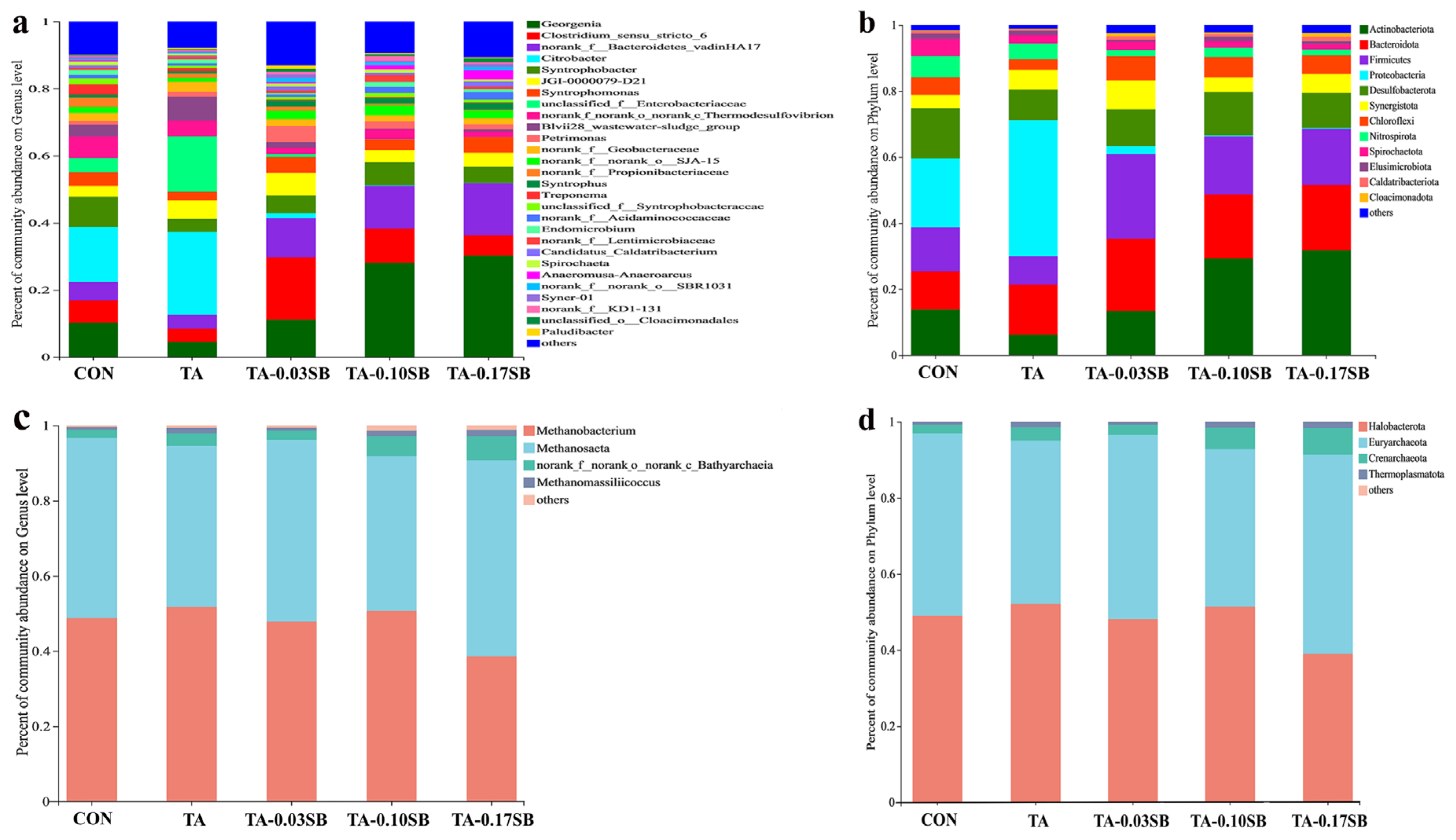
This study investigated the effects of TA and SB-C-NZVI on the structure of microbial communities. Figure 11a illustrates the bacterial community structure at the genus level, showing that the addition of SB-S-nZVI0.05 to the reactors increased the relative abundance of Georgenia, Clostridium sensu stricto 6, and norank f Bacteroidetes VadinHA17. These shifts promoted methane production and enhanced the anaerobic digestion process. In the CON reactor, Georgenia and Citrobacter were the dominant bacteria, while Citrobacter predominated in the TA reactor. Georgenia, a hydrolytic acidifying bacterium, facilitated hydrolysis during the initial stage of anaerobic digestion. The relative abundance of Georgenia was 10.29%, 4.51%, 11.18%, 28.06%, and 30.28% in the CON, TA, TA-0.03SB, TA-0.10SB, and TA-0.17SB reactors, respectively, indicating a significant enrichment with increasing SB- S-nZVI0.05 concentration. Clostridium sensu stricto 6 is known to degrade volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and promote methane production, contributing to system stability [69,70]. In the TA-0.03SB reactor, Clostridium sensu stricto 6 was most abundant (18.51%), whereas it was least abundant in the TA reactor (3.99%). This may result in the accumulation of VFAs in the TA reactor and thus inhibit methane production. Furthermore, increased SB- S-nZVI0.05 concentrations led to an enhanced relative abundance of norank f Bacteroidetes VadinHA17, a bacterium that can convert glucose to acetic acid and H2/CO2, promoting hydrogen and acetic acid production [71]. Additionally, Citrobacter, capable of utilizing tannic acid as its sole carbon source, showed growth at tannic acid concentrations as high as 5% (w/v) [72].

Figure 11.
Analysis of bacterial and archaeal composition: (a) analysis of bacteria at the genus level, (b) analysis of bacteria at the phylum level, (c) analysis of archaea at the genus level, and (d) analysis of archaea at the phylum level.
Figure 11b shows the bacterial community structure at the phylum level. Actinobacteriota, Bacteroidota, and Firmicutes were the predominant phyla in each reactor. Actinobacteriota and Bacteroidota are known for their roles in hydrolyzing and acidifying organic matter. Their combined relative abundance was 25.39%, 21.39%, 35.26%, 48.60%, and 51.56% in the CON, TA, TA-0.03SB, TA-0.10SB, and TA-0.17SB reactors, respectively, indicating that SB-S-nZVI0.05 significantly enriched the population of hydrolytic acidifying bacteria. In the TA-0.03SB reactor, Firmicutes were the dominant group, comprising 25.64% of the microbial community, contributing to the reduction of VFA accumulation and promoting methane production [69,70]. Firmicutes also have the ability to form biofilms on solid surfaces, enhancing their resistance to toxic substances [73]. The relative abundance of Chloroflexi was highest in the TA-0.03SB reactor (7.25%) and lowest in the TA reactor (3.23%). Chloroflexi plays a critical role in anaerobic digestion by secreting EPS and forming biofilms, thus protecting microorganisms [74].
Figure 11c presents the archaea community structure at the genus level, where Methanosaeta and Methanobacterium were the dominant genera across all reactors. Methanosaeta is an acetophilic methanogenic archaeon that produces methane from acetic acid, while Methanobacterium is a hydrogenotrophic methanogen, generating methane from H2 and CO2. The relative abundance of Methanosaeta was 47.93%, 42.87%, 48.37%, 41.18%, and 52.12% in the CON, TA, TA-0.03SB, TA-0.10SB, and TA-0.17SB reactors, respectively, whereas Methanobacterium accounted for 48.75%, 51.73%, 47.83%, 50.68%, and 38.62%, respectively. Interestingly, the relative abundance of Methanosaeta decreased in the TA and TA-0.10SB reactors but increased in the TA-0.03SB and TA-0.17SB reactors, while the relative abundance of Methanobacterium showed the opposite trend. The inverse relationship between these two methanogenic archaea suggests that tannic acid inhibited Methanosaeta growth. The addition of SB-S-nZVI0.05 mitigated the negative effects of tannic acid on Methanosaeta, thus enhancing methane production.
Figure 11d displays the phylum-level community structure of archaea, where Halobacterota and Euryarchaeota were the predominant phyla in each reactor. In the CON, TA, TA-0.03SB, TA-0.10SB, and TA-0.17SB reactors, Halobacterota accounted for 48.98%, 52.09%, 48.14%, 51.43%, and 39.05%, respectively, while Euryarchaeota accounted for 48.01%, 42.98%, 48.14%, 41.39%, and 52.32%, respectively. Compared to the CON reactor, Halobacterota increased by 3.11% in the TA reactor and decreased by 9.93% in the TA-0.17SB reactor. Halobacterota thrive in high-salt environments with nutrient deficiency, which leads to the death of other microorganisms, resulting in their relative increase [69]. In contrast, the proportion of Euryarchaeota increased by 4.01% in the TA-0.17SB reactor and decreased by 5.03% in the TA reactor. Euryarchaeota dominated the TA-0.17SB reactor, while Halobacterota was relatively less abundant, suggesting that the addition of SB-S-nZVI0.05 improved microbial community composition in the reactor.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the SB-S-nZVI adsorbent material was successfully synthesized using a one-step hydrothermal method. The mechanism by which this material treats TA-contaminated wastewater and promotes anaerobic digestion was systematically investigated. The key conclusions of this study are as follows:
The SB-S-nZVI0.05 adsorbent demonstrated a maximum TA removal efficiency of 99.31% at an optimal dosage of 0.3 g·L−1, and the maximum adsorption content of TA by SB-S-nZVI was found to be 337.08 g·mg−1.
Additionally, SB-S-nZVI0.05 effectively removed tannins while enhancing microbial degradation capacity and methane production. At a concentration of 0.03 g·L−1, SB-S-nZVI0.05 significantly increased SMA by up to 62.66%. Moreover, its application did not disrupt the microbial community composition or anaerobic digestion stability. Instead, SB-S-nZVI0.05 improved the microbial community structure, facilitating the enrichment of functional microorganisms.
These findings highlight the potential of SB-S-nZVI0.05 as a sustainable and effective adsorbent for enhancing anaerobic digestion processes, offering a promising strategy for improving wastewater treatment efficiency.
These findings underscore the potential of SB-S-nZVI0.05 as a sustainable and effective adsorbent for enhancing anaerobic digestion processes, offering a promising strategy for improving wastewater treatment efficiency. Future research could further assess the long-term stability of SB-S-nZVI in real industrial wastewater environments, particularly those with complex matrices containing high salts, heavy metals, and other contaminants. Moreover, exploring the synergistic integration of SB-S-nZVI with renewable energy technologies, such as anaerobic hydrogen–methane coupling systems, could foster the innovative development of integrated technologies focused on “pollution control, resource recovery, and low carbon emissions”.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13041084/s1, Table S1. Elemental analysis of the S-nZVI with different S/Fe ratios. Table S2. Comparison of different adsorbents for adsorption removal of tannic acid [14,16,17,18,19,20,21,57]. Figure S1. Step-by-step schematic diagram. Figure S2. Experimental setup diagram of anaerobic digestion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.G. and W.Z.; methodology, W.F.; software, L.L. and Y.Z. (Yunpeng Zhu); validation, K.J., S.Z. and K.Z.; formal analysis, Q.G.; investigation, Z.Q. and C.W.; resources, Z.W.; data curation, Q.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.G.; writing—review and editing, W.Z.; visualization, W.F.; supervision, L.L., Z.Q. and C.W.; project administration, Z.W.; funding acquisition, Z.W. and Y.Z. (Yuanyuan Zhao). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2022GXNSFAA035486 and 2023GXNSFGA026001), Guangxi Province Talent Project (GXR-1BGQ2424002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21868004), National Key Research and Development Plan Project (2022YFC2105500), and the Foundation of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control, College of Light Industry and Food Engineering (2023GXZZKF71).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Zhaodong Qiu and Congcong Wang were employed by the company Shandong Sun Paper Industry Joint Stock Co., Ltd. Author Yuanyuan Zhao was employed by the company Guangzhou Paper Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The companies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Li, W.W.; Li, X.D.; Zeng, K.M. Aerobic biodegradation kinetics of tannic acid in activated sludge system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 43, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Xu, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.G.; Shi, C.; Zhang, W.S.; Xia, X.D. Tannin-Rich Fraction from Pomegranate Rind Damages Membrane of Listeria monocytogenes. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efenberger-Szmechtyk, M.; Nowak, A.; Czyzowska, A. Plant extracts rich in polyphenols: Antibacterial agents and natural preservatives for meat and meat products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, F.R.; Hansen, M.J.; Feilberg, A.; Kümmel, S.; Nikolausz, M. Effect of tannic acid combined with fluoride and lignosulfonic acid on anaerobic digestion in the agricultural waste management chain. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, Q.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Yue, X.; et al. Synergetic effect of biochar and intermittent electricity stimulation on mitigating the adverse effects of tannic acid on anaerobic granular sludge in wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Jiang, L.; Wei, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L. Preparation of carbon/cobalt composite from phenolic resin and ZIF-67 for efficient tannic acid adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 287, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, S.; Ilyas, N.; Saeed, M.; Bibi, F.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Almalki, W.H. Treatment technologies for olive mill wastewater with impacts on plants. Environ. Res. 2022, 216, 114399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Tengku Yasim-Anuar, T.A.; Samsudin, M.H.; Mohd Yusoff, M.Z.; Zakaria, M.R.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Shirai, Y. Adsorption mechanism and effectiveness of phenol and tannic acid removal by biochar produced from oil palm frond using steam pyrolysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, E.O.; Ozer, A. Investigation of two ultrafiltration membranes for treatment of olive oil mill wastewater. Desalination 2009, 249, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Mirsaeedghazi, H.; Azarikia, F. Effect of the membrane processing on tannin removal from soluble fraction of Persian gum. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 8141–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorpas, A.A.; Costa, C.N. Combination of Fenton oxidation and composting for the treatment of the olive solid residue and the olive mile wastewater from the olive oil industry in Cyprus. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7984–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Enhanced removal of organics by permanganate preoxidation using tannic acid as a model compound–Role of in situ formed manganese dioxide. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammary, B.Y. Treatment of olive mill wastewater using an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Desalination 2005, 177, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Li, A.M.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y. Adsorption of tannic and gallic acids on a new polymeric adsorbent and the effect of Cu(II) on their removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Rajoria, P.; Rani, A. Adsorption of tannic acid from aqueous solution onto chitosan/NaOH/fly ash composites: Equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics and modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xing, Y. Adsorption of tannic acid from aqueous solution onto surfactant-modified zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 193, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıcı-Özdemir, Ç.; Önal, Y. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic adsorptions of the environmental pollutant tannic acid onto activated carbon. Desalination 2010, 251, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhan, Y. Adsorption of humic acid from aqueous solution onto unmodified and surfactant-modified chitosan/zeolite composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Ding, S.; Ma, H.; Ji, Y. Behaviors and mechanisms of tannic acid adsorption on an amino-functionalized magnetic nanoadsorbent. Desalination 2011, 273, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-Y.; Juang, R.-S. Adsorption of tannic acid, humic acid, and dyes from water using the composite of chitosan and activated clay. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2004, 278, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulia, D.; Leodopoulos, C.; Gimouhopoulos, K.; Rigas, F. Adsorption of humic acid on acid-activated Greek bentonite. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, N.; Masmoudi, M.A.; Megdiche, M.; Barakat, A.; Ellouze, M.; Chamkha, M.; Ksibi, M.; Sayadi, S. Biochar from olive mill solid waste as an eco-friendly adsorbent for the removal of polyphenols from olive mill wastewater. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 181, 384–398. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, C.; Phal, N.; Oh, J.; Chu, K.H.; Jang, M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of humic and tannic acids by adsorption–coagulation combined systems with activated biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Fe/S modified sludge-based biochar for tetracycline removal from water. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Simultaneous adsorption and dechlorination of pentachlorophenol from effluent by Ni-ZVI magnetic biochar composites synthesized from paper mill sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Chen, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Chromium (VI) removal from synthetic solution using novel zero-valent iron biochar composites derived from iron-rich sludge via one-pot synthesis. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chang, H.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, H. Efficient degradation of m-cresol during catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with biochar derived from the pyrolysis of persulfate-ZVI treated sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Yang, B.; Tian, Q.; Xu, H. Iron-based biochar derived from waste-activated sludge enhances anaerobic digestion of synthetic salty organic wastewater for methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.F.; Dai, M.; Naz, I.; Hao, X.Y.; Wei, X.X.; Rong, R.; Peng, C.S.; Ali, I. Carbothermal reduction synthesis of zero-valent iron and its application as a persulfate activator for ciprofloxacin degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Wang, P.; Meng, X.Y.; Ren, L.H. Performance and metagenomics analysis of anaerobic digestion of food waste with adding biochar supported nano zero-valent iron under mesophilic and thermophilic condition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liang, D.H.; Li, N. Conductive materials in anaerobic digestion: From mechanism to application. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.S.; Duan, L.F.; Dong, Y.M.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhao, S. Elemental sulfur generated in situ from Fe (III) and sulfide promotes sulfidation of microscale zero-valent iron for superior Cr (VI) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, H.; Lowry, G.V. Sulfidized Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Tuning the Properties of This Complex Material for Efficient Groundwater Remediation. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.N.; Boparai, H.K.; de Boer, C.V.; Chowdhury, A.I.A.; Kocur, C.M.D.; Austrins, L.M.; Herrera, J.; O’Carroll, D.M. Fate and transport of sulfidated nano zerovalent iron (S-nZVI): A field study. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Liu, X.T.; Noel, V.; Lou, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Henkelman, G.; Lowry, G.V. Sulfur Loading and Speciation Control the Hydrophobicity, Electron Transfer, Reactivity, and Selectivity of Sulfidized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Clark, E.A.; Henkelman, G.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G.V. Iron and Sulfur Precursors Affect Crystalline Structure, Speciation, and Reactivity of Sulfidized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13294–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangayayam, M.; Dideriksen, K.; Ceccato, M.; Tobler, D.J. The Structure of Sulfidized Zero-Valent Iron by One-Pot Synthesis: Impact on Contaminant Selectivity and Long-Term Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Schoonen, M.A.A. The absolute energy positions of conduction and valence bands of selected semiconducting minerals. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.C. Impact of biochar supported nano zero-valent iron on anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste: Methane production, performance stability and microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.N.; Li, B.Y.; Luo, L.; Zheng, Y.X.; Huang, L.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.L. Simultaneous adsorption and oxidation of antimonite onto nano zero-valent iron sludge-based biochar: Indispensable role of reactive oxygen species and redox-active moieties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.F.; Xian, P.; Yang, L.H.; Liu, X.; Zhan, L.H.; Bu, G.H. Effect of humic acid in leachate on specific methanogenic activity of anaerobic granular sludge. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2740–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, W.; Kindaichi, T.; Satoh, H.; Sasakawa, M.; Nakahara, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Okabe, S. Anaerobic treatment of municipal wastewater at ambient temperature: Analysis of archaeal community structure and recovery of dissolved methane. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5756–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.J.; Ding, Y.C.; Wang, M.Z.; Zhou, G.L.; Zheng, X.; He, H.Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Shen, D.S.; Shentu, J.L. Where are signal molecules likely to be located in anaerobic granular sludge? Water Res. 2014, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fr/olund, B.; Griebe, T.; Nielsen, P.H. Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 43, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Lowry, G.V. Distributing sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron onto phosphorus-functionalized biochar for enhanced removal of antibiotic florfenicol. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Wang, H.; Qi, L.; Cui, L.; Quan, G.; Yan, J. Production of activated biochar via a self-blowing strategy-supported sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron with enhanced reactivity and stability for Cr(VI) reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Zhang, W.X. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aspects of the core-shell structure and reactions with inorganic species in water. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 118, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaundal, J.B.; Goswami, Y.C.; Sharma, R. Optically Important Transparent Syndiotactic Polystyrene/FeS Composites Grown by Low Sol-gel Route. Orient. J. Chem. 2022, 38, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.-D.; Li, D.-C.; Qian, T.-T.; Jiang, H. Boosting the activity and environmental stability of nanoscale zero-valent iron by montmorillonite supporting and sulfidation treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Application of iron-based materials in heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zeng, L.; Wen, N.; Deng, D. Critical roles of sulfidation solvent in controlling surface properties and the dechlorination reactivity of S-nZVI. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Si, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, N. Sludge-derived biochar as efficient persulfate activators: Sulfurization-induced electronic structure modulation and disparate nonradical mechanisms. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 279, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Zhu, F. Microwave-assisted synthesis of magnetic surface molecular imprinted polymer for adsorption and solid phase extraction of 4-nitrophenol in wastewater. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Xi, S. Study on trends and performance of landfill research from 1999 to 2013 by using bibliometric analysis. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, B.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, L.; Carozza, J.C.; Yan, W.; Han, H.; Xu, C. Phase evolution of the surface iron (hydr) oxides to the iron sulfide through anion exchange during sulfidation of zero valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Ramachandran, M. Adsorptive removal of tannin from aqueous solutions by cationic surfactant-modified bentonite clay. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, G.; Diez, M.C. Methanogenic toxicity and continuous anaerobic treatment of wood processing effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 74, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.S.; Fang, H.H.P.; Furumai, H. Surface charge and extracellular polymer of sludge in the anaerobic degradation process. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; Guo, C.Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, S.F. Use of Extracellular Polymer Substance as an Additive to Improve Biogas Yield and Digestion Performance. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 12628–12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hu, A.D.; Ren, G.P.; Chen, M.; Tang, J.H.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhou, S.G.; He, Z. Enhancing sludge methanogenesis with improved redox activity of extracellular polymeric substances by hematite in red mud. Water Res. 2018, 134, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, K.C.; Leigh, J.A. Metabolic versatility in methanogens. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 29, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.Y.; Xu, Q.J.; Han, Z.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Tolerance of Aceticlastic Methanogenesis Enhanced by Magnetite under the Condition of Ammonia Stress. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.S.; He, P.P.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, L.L.; Lin, Y.; Mu, Y.; Yu, H.Q. Impact of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on the activity of anaerobic granular sludge: From macroscopic to microcosmic investigation. Water Res. 2017, 127, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S. Electron transfer at microbe-humic substances interfaces: Electrochemical, microscopic and bacterial community characterizations. Chem. Geol. 2017, 456, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M. Enhanced Sb(V) removal of sulfate-rich wastewater by anaerobic granular sludge assisted with Fe/C amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; Guo, C.Y.; Yao, M.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, S.F. Calcium ions affect sludge digestion performance via changing extracellular polymeric substances in anaerobic bioreactor. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 137, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.C.; Li, M.L.; Dang, W.H.; Zhu, K.L.; Chen, G.I.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.F.; Guo, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.W. Study on the mechanism of inhibiting the calcification of anaerobic granular sludge induced by the addition of trace signal molecule (3O-C6-HSL). Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryildiz, B.; Lukitawesa; Taherzadeh, M.J. Effect of pH, substrate loading, oxygen, and methanogens inhibitors on volatile fatty acid (VFA) production from citrus waste by anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Miyanaga, K.; Toyama, K.; Uy, D.; Tanji, Y. Changes in composition and microbial communities in excess sludge after heat-alkaline treatment and acclimation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Gunasekaran, P.; Lakshmanan, M. Biodegradation of tannic acid by Citrobacter freundii isolated from a tannery effluent. J. Basic Microbiol. 1999, 39, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, H.C.; Wyckoff, K.N.; He, Q. Linkages of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes populations to methanogenic process performance. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.L.; Wu, Y.R.; Wang, Z.W.; Fu, W.C.; Dang, W.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Ning, Y.; Wang, S.F. Improvement in calcified anaerobic granular sludge performance by exogenous acyl-homoserine lactones. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).