Enhancing Heavy Metal Removal and Stabilization in River Sediment by Combined Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Pretreatment Methods
2.2. Sequential Extraction Test Procedures of Heavy Metals
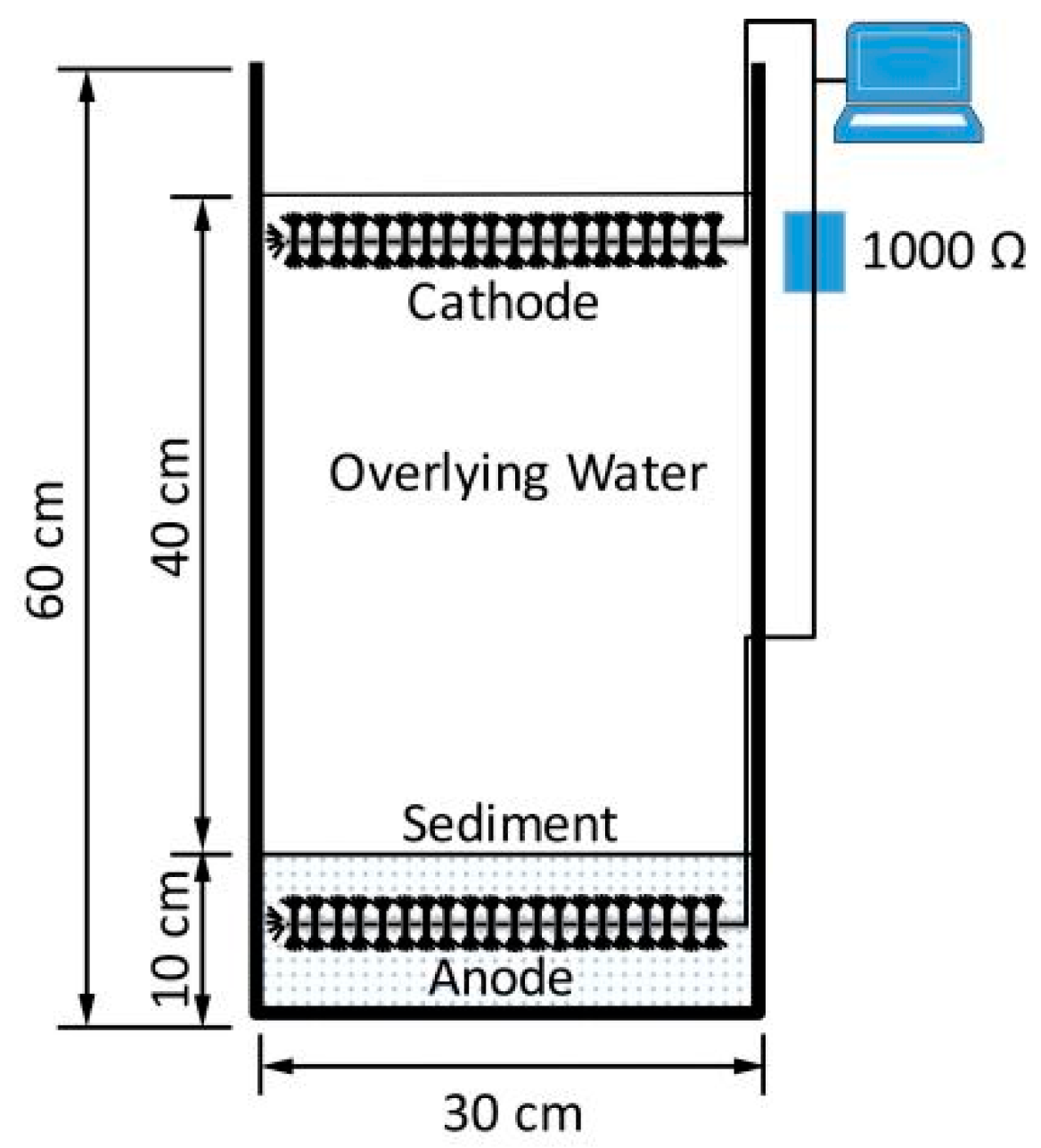
2.3. Construction and Operation of Bioreactors
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Characterization of Anode Microbial Community
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Removal of Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.2. Speciation Changes in Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.3. Effect of Sediment Organic Matter Degradation on Heavy Metals
3.4. Electricity Generation
3.5. Microbial Communities Analysis in Sediments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Cai, Z.; Han, B.; Qian, T.; Zhao, D. An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation. Water Res. 2016, 100, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K. Remediation of Heavy Metal(Loid)s Contaminated Soils—To Mobilize or to Immobilize? J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.J.; Luo, S.L.; Liang, C.; Xiao, X.; Xi, Q.; Wei, W.; Zeng, G.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by Growing Hyperaccumulaor Endophytic Bacterium Bacillus Sp. L14. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8599–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Ming, C.; Jia, W. Remediation of contaminated soils by enhanced nanoscale zero valent iron. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, E.; Donner, E.; Lombi, E.; Turner, A.; Zhao, F.-J.; McGrath, S.P. In Situ Fixation of Metal(loid)s in Contaminated Soils: A Comparison of Conventional, Opportunistic, and Engineered Soil Amendments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13501–13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Díaz, M.; Pérez-Sanz, A.; Vicente, M.Á.; Lobo, M.C. Immobilisation of Pb and Zn in Soils Using Stabilised Zero-valent Iron Nanoparticles: Effects on Soil Properties. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Investigation of heavy metal (Cu, Pb, Cd, and Cr) stabilization in river sediment by nano-zero-valent iron/activated carbon composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Fang, Z.; Tsang, P.E.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by biochar-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjee, P.; Amarasiriwardena, D.; Xing, B. Antimony adsorption by zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI): Ion chromatography–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (IC-ICP-MS) study. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.Y. Simultaneous removal of heavy metals and biodegradation of organic matter with sediment microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 53433–53438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lin, X.; Xia, C.; Sun, G.; Lian, Y.; Xu, M. Enhancing the bioremediation by harvesting electricity from the heavily contaminated sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabutey, F.T.; Ding, J.; Zhao, Q.; Antwi, P.; Quashie, F.K.; Tankapa, V.; Zhang, W. Pollutant removal and bioelectricity generation from urban river sediment using a macrophyte cathode sediment microbial fuel cell (mSMFC). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 148, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, E.; Bossa, N.; Wiesner, M.R.; Gunsch, C.K. A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI): Behavior, transport and impacts on microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, C.; Serov, A.; Narvaez Villarrubia, C.W.; Stariha, S.; Babanova, S.; Schuler, A.J.; Artyushkova, K.; Atanassov, P. Double-chamber microbial fuel cell with a non-platinum-group metal Fe-N-C cathode catalyst. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Xu, X.; Lu, K.; Li, X. Effects of the presence of nanoscale zero-valent iron on the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls and total organic carbon by sediment microbial fuel cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wu, X. Removal and Changes of Sediment Organic Matter and Electricity Generation by Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells and Amorphous Ferric Hydroxide. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2014, 28, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Machado, K.A.A.; Spencer, W.; Kloas, M.; Toffolon, C.Z. Metal fate and effects in estuaries: A review and conceptual model for better understanding of toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Misra, V.; Singh, R.P. Removal of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Mohan, S.V.; Lens, P.N.L. Metals removal and recovery in bioelectrochemical systems: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 195, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Deng, H.; Zhao, F. Remediation of mercury contaminated soils—A review. Soil Sediment Contam. 2016, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Lim, M.; Hwang, Y.S. Potential environmental implications of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for environmental remediation. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2014, 29, e2014022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S.; Skousen, J.; Kim, D.-G.; Jin, S. Accelerated metolachlor degradation in soil by zerovalent iron and compost amendments. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Dong, H.; Guan, X.; Ren, Q.; Lv, X.; Jin, X. Simple combination of oxidants with zero-valent-iron (ZVI) achieved very rapid and highly efficient removal of heavy metals from water. Water Res. 2016, 88, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M.; Eltayeb, M.A.H.; Potgieter-Vermaak, S.S.; Van Grieken, R.; Potgieter, J.H. Assessment of heavy metals pollution in Sudanese harbours along the Red Sea Coast. Microchem. J. 2007, 87, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Pan, G. Immobilization of arsenic in soils by stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron, iron sulfide (FeS), and magnetite (Fe₃O₄) particles. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Díaz, M.; Díez-Pascual, S.; González, A. A nanoremediation strategy for the recovery of an As-polluted soil. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, M.; Banerjee, D.K. Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for heavy metal partitioning in mine tailings. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.C.W.; Lo, I.M.C. Competitive Cu and Cd sorption and transport in soils: A combined batch kinetics, column, and sequential extraction study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6655–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Elliott, D.W.; Zhang, W. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: Materials and engineering aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2006, 31, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, H.K.; Joseph, M.; Carroll, O.; Denis, M. Cadmium (Cd(2+)) removal by nano zerovalent iron: Surface analysis, effects of solution chemistry and surface complexation modeling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 6210–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, F.; Tian, Q.; Nie, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Fang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S. A highly porous animal bone-derived char with a superiority of promoting nZVI for Cr(VI) sequestration in agricultural soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, M.; Ding, J.; Zhang, W. Biodegradation of organic matter and anodic microbial communities analysis in sediment microbial fuel cells with/without Fe(III) oxide addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueye, M.T.; Di Palma, L.; Allahverdiyev, G.; Bavasso, I.; Petrucci, E.; Stoller, M.; Vilardi, G. The Influence of Heavy Metals and Organic Matter on Hexavalent Chromium Reduction by Nano Zero Valent Iron in Soil. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 47, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.T.; Wan, J.; Tokunaga, T. Kinetic stability of hematite nanoparticles: The effect of particle sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, D.; Song, T.; Ouyang, P.; Xie, J. Effects of the presence of sheet iron in freshwater sediment on the performance of a sediment microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16566–16571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. Salinity and conductivity amendment of soil enhanced the bioelectrochemical degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Temsah, Y.S.; Sevcu, A.; Bobcikova, K.; Cernik, M.; Joner, E.J. DDT degradation efficiency and ecotoxicological effects of two types of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water and soil. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Farrukh, M.A. Antibacterial activity of green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Lawsonia inermis and Gardenia jasminoides leaves extract. J. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, H.D.; Miller, G.S.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Sowers, K.R. Dehalorespiration with polychlorinated biphenyls by an anaerobic ultramicrobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ševců, A.; El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J.; Černík, M. Oxidative stress induced in microorganisms by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacca, M.L.; Fajardo, C.; Costa, G.; Lobo, C.; Nande, M.; Martin, M. Integrating classical and molecular approaches to evaluate the impact of nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on soil organisms. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.C.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Okada, D.Y.; Delforno, T.P.; Gomes, P.C.F.L.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Varesche, M.B.A. Analysis of a microbial community associated with polychlorinated biphenyl degradation in anaerobic batch reactors. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Pb | Cr | As | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw sediment (k/kg dw) | 1.15 ± 0.11 | 2.04 ± 0.09 | 0.92 ± 0.05 |
| Overlying water (mg/L) | 0.067 ± 0.014 | 0.096 ± 0.011 | 0.035 ± 0.008 |
| Sample-ID | Seq-Num | OTUs-Num | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw sediment | 40,825 | 6569 | 27,034.12 | 17,729.03 | 7.11 | 0.0024 | 0.94 |
| BR1 | 37,255 | 6322 | 25,987.65 | 17,065.11 | 7.04 | 0.0031 | 0.95 |
| BR2 | 36,354 | 5895 | 22,198.67 | 15,934.82 | 6.89 | 0.0065 | 0.92 |
| BR3 | 35,643 | 6119 | 24,876.32 | 16,087.75 | 7.01 | 0.0033 | 0.95 |
| BR4 | 36,102 | 6043 | 24,257.08 | 16,113.34 | 6.99 | 0.0041 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Wu, M.; Ren, G. Enhancing Heavy Metal Removal and Stabilization in River Sediment by Combined Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells. Processes 2025, 13, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041235
Xu X, Wu M, Ren G. Enhancing Heavy Metal Removal and Stabilization in River Sediment by Combined Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041235
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xun, Mingsong Wu, and Guoling Ren. 2025. "Enhancing Heavy Metal Removal and Stabilization in River Sediment by Combined Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells" Processes 13, no. 4: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041235
APA StyleXu, X., Wu, M., & Ren, G. (2025). Enhancing Heavy Metal Removal and Stabilization in River Sediment by Combined Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells. Processes, 13(4), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041235






