Thermodynamic Analysis of a Compact System Generating Hydrogen for Mobile Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactions and Equilibrium Constants
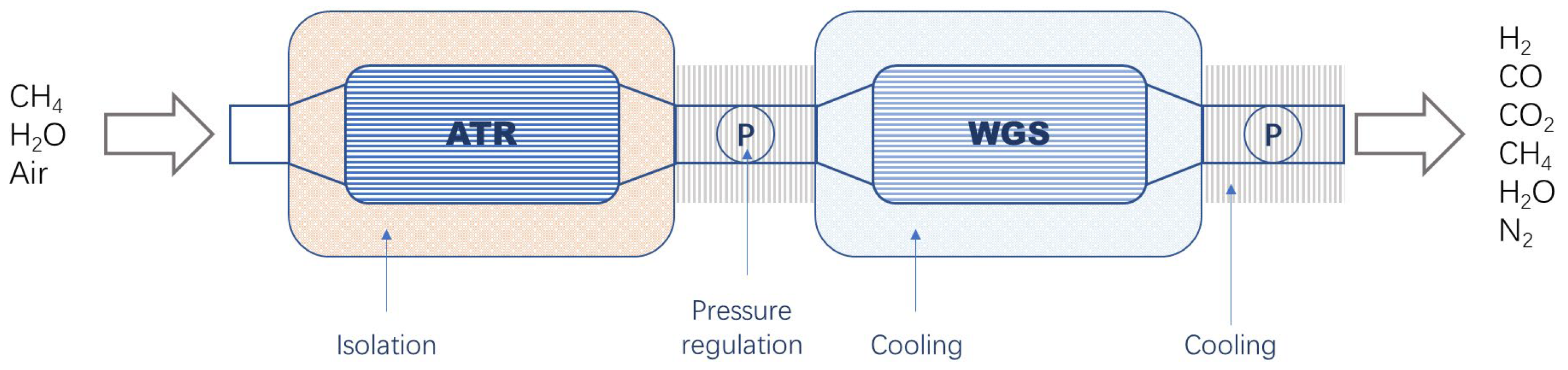
2.2. System Description
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Analysis of Autothermal Reformer (ATR)
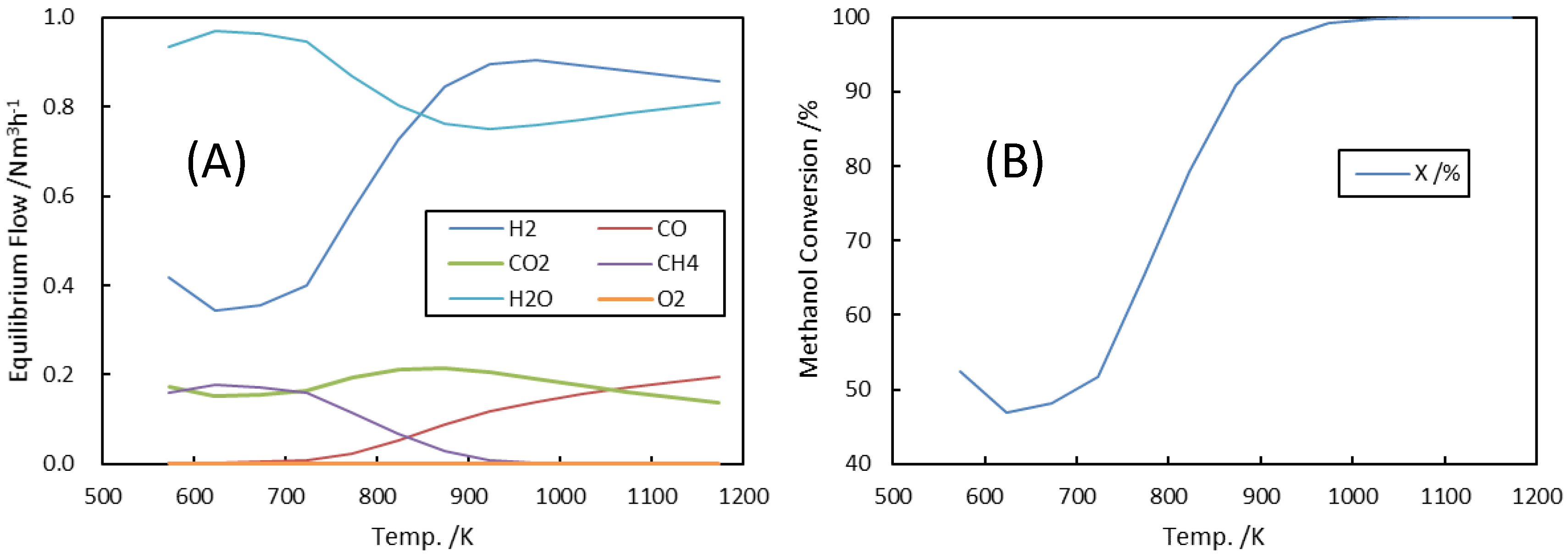
3.1.1. Equilibrium Flow at ATR Exit
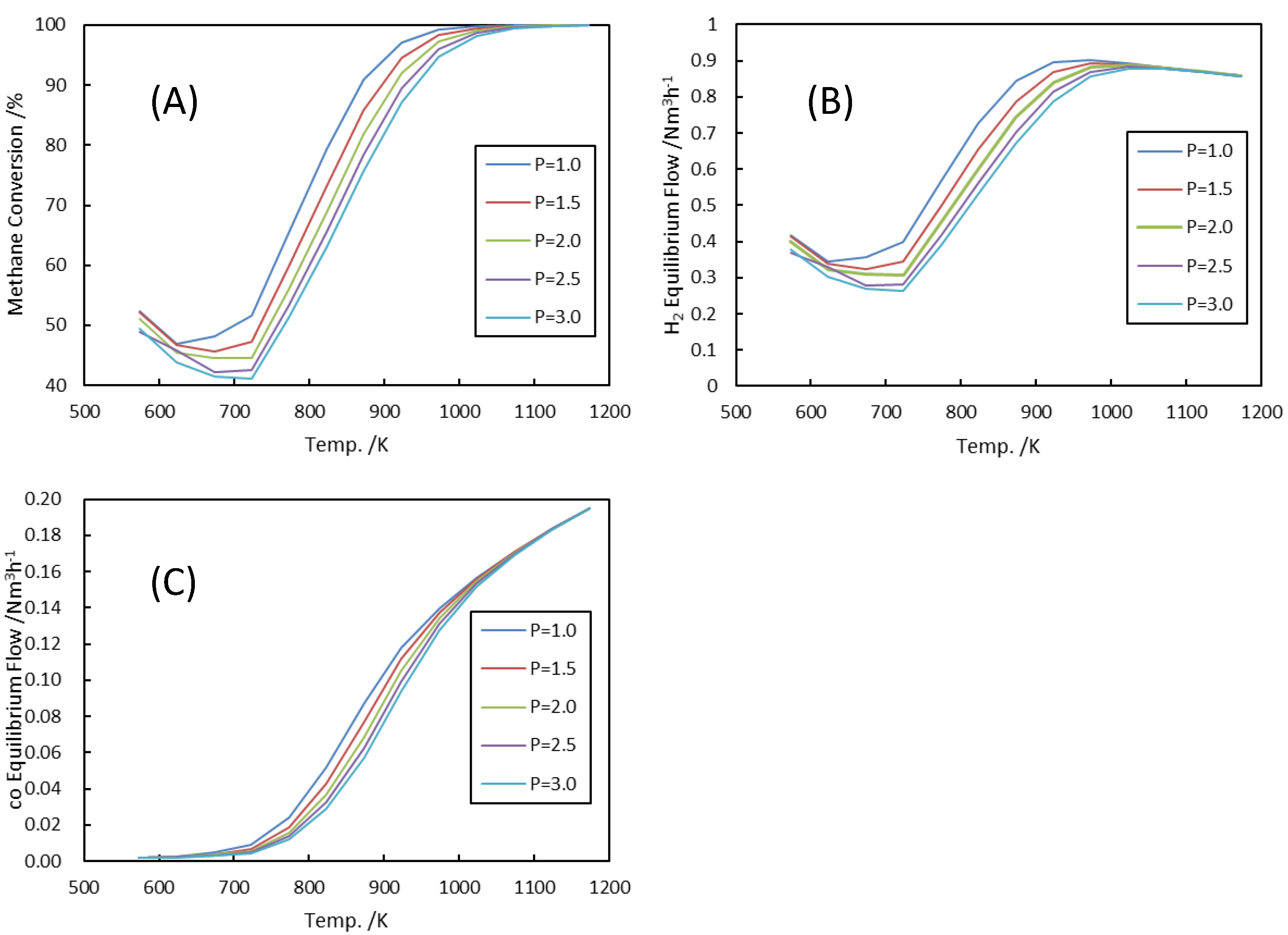
3.1.2. ATR Exit Pressure
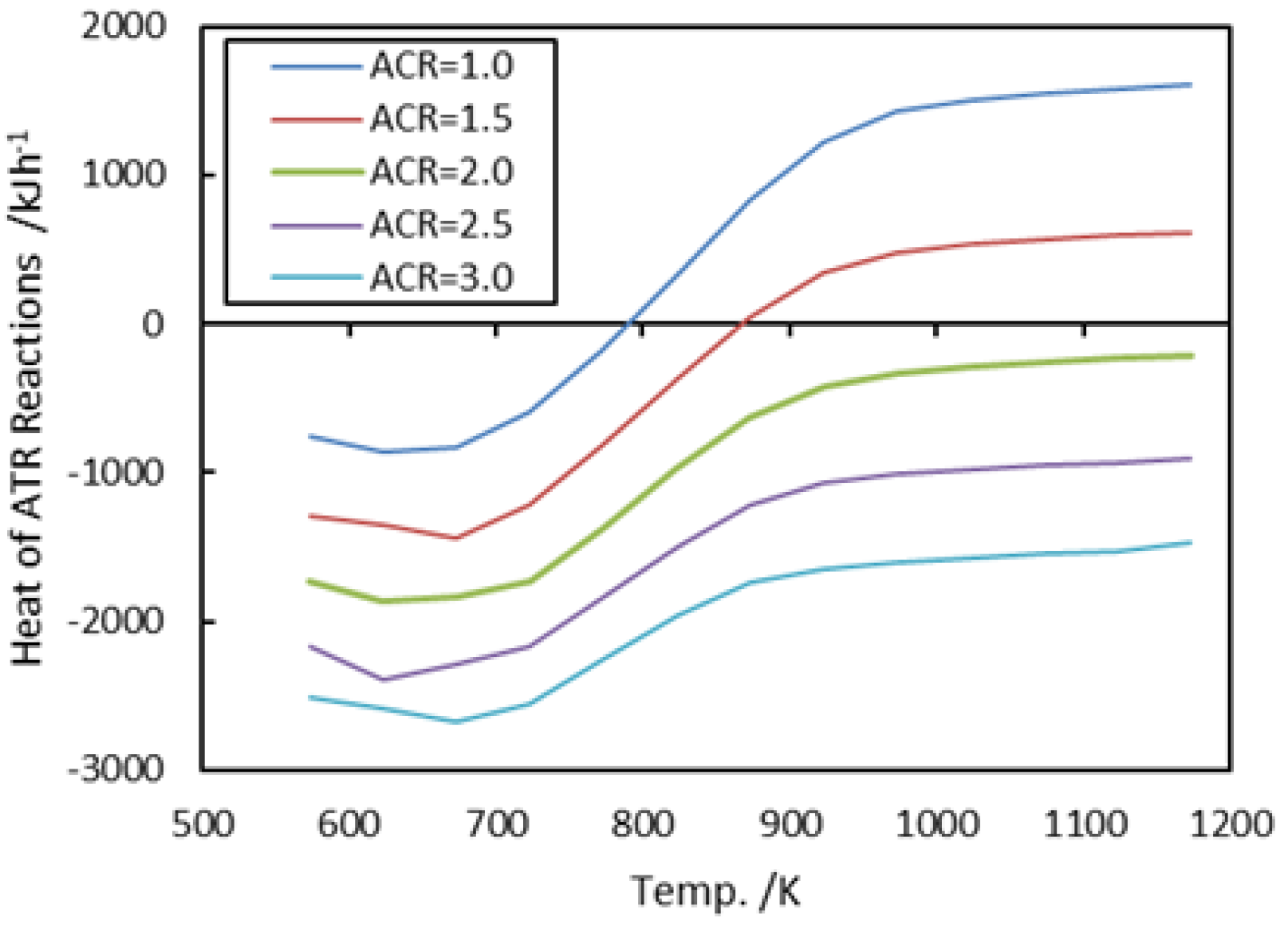
3.1.3. Air-to-Carbon Ratios (ACR)
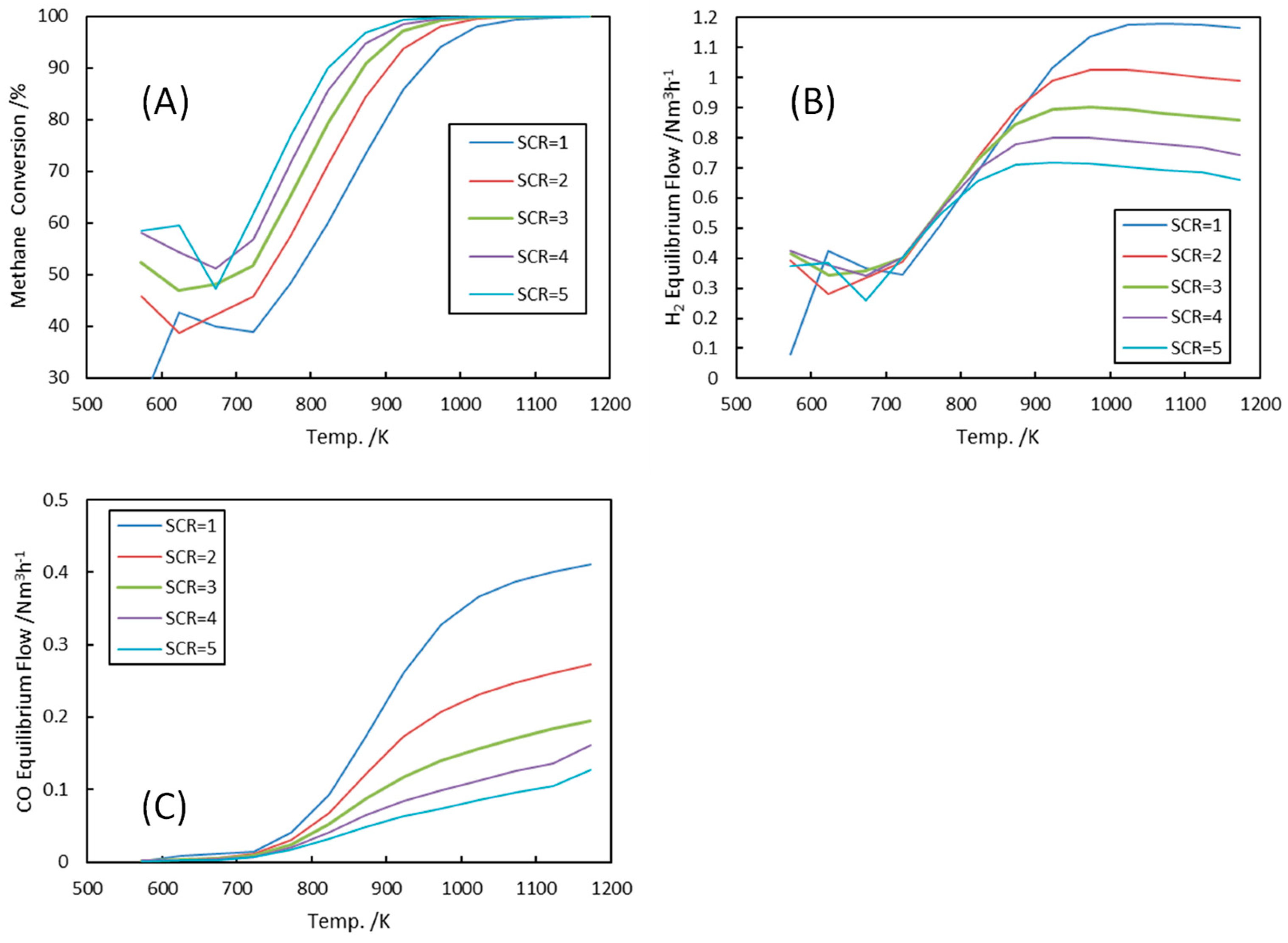
3.1.4. Steam-to-Carbon Ratios (SCR)
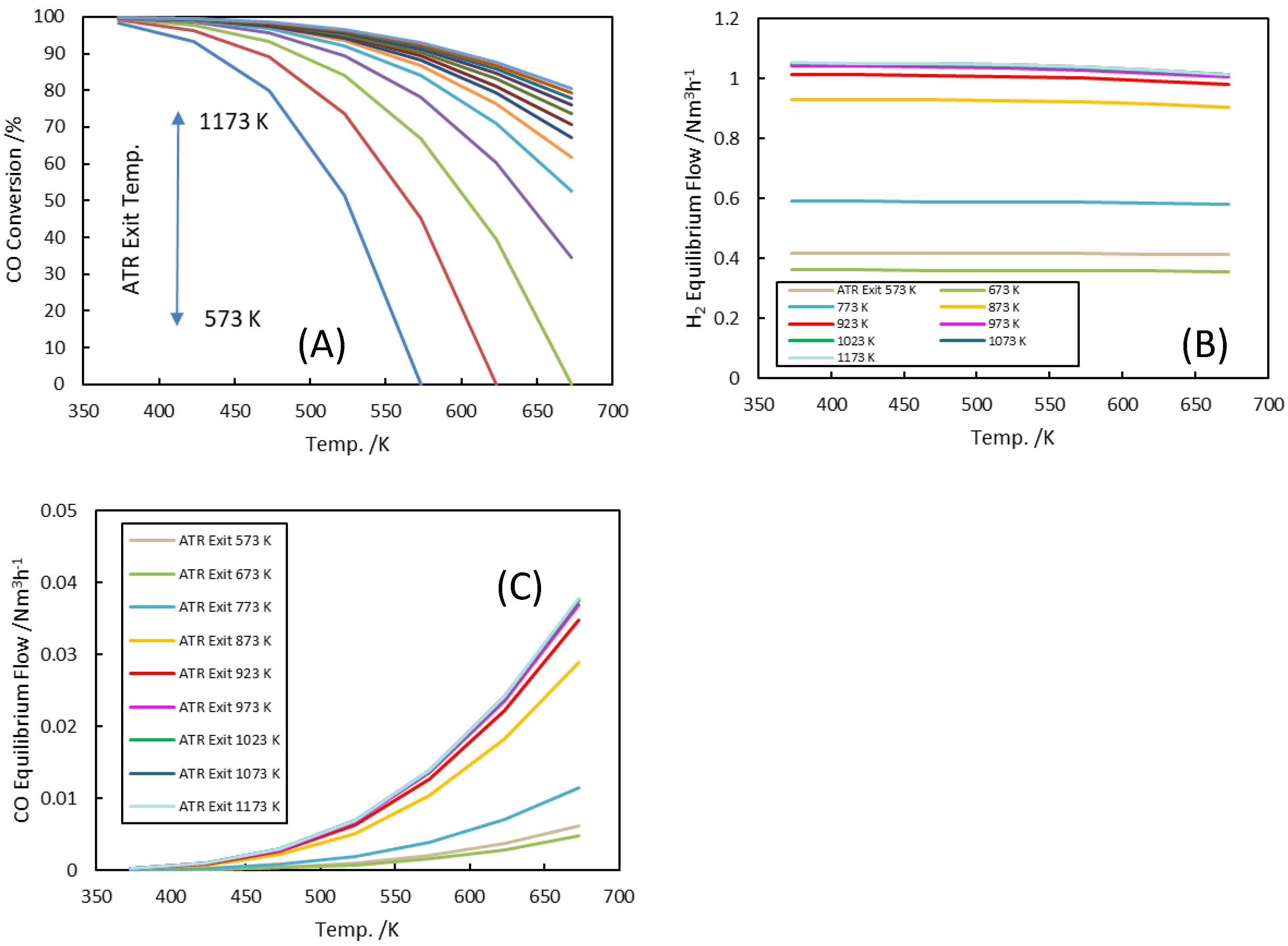
3.2. Water–Gas Shift (WGS) Reactor
3.3. Material and Heat Efficiency
3.4. Issues and Solutions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hui, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Akhtar, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dai, B.; Yu, J. Comprehensive review of development and applications of hydrogen energy technologies in China for carbon neutrality: Technology advances and challenges. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 315, 118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Toksha, B.; Rahaman, M. A Critical Review on Hydrogen Based Fuel Cell Technology and Applications. Chem. Rec. 2024, 24, e202300295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Recent development of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies: A review. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 8421–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, S.; Osterloh, F.E.; Wang, X.; Mallouk, T.E.; Maeda, K. Photocatalytic water splitting. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Qin, F.; Khalid, F.; Suo, G.; Zahra, T.; Chen, Z.; Javed, Z. Essential parts of hydrogen economy: Hydrogen production, storage, transportation and application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 210, 115196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Acar, C. Review and evaluation of hydrogen production methods for better sustainability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11094–11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hook, J.P. Methane-Steam Reforming. Catal. Rev. 1980, 21, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megía, P.J.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Calles, J.A.; Carrero, A. Hydrogen Production Technologies: From Fossil Fuels toward Renewable Sources. A Mini Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 16403–16415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Ge, Y.; Gao, R.; Yang, J.; Li, A.; Xie, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Asakura, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Thermal catalytic reforming for hydrogen production with zero CO2 emission. Science 2025, 387, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R. Catalytic Steam Reforming. In Catalysis: Science and Technology; Anderson, J.R., Boudart, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; Volume 5, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J. Steam reforming of hydrocarbons. A historical perspective. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Bao, X., Xu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 147, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.; Rostrup-Nielsen, T. Large-Scale Hydrogen Production. CATTECH 2002, 6, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, C.; Soliman, I.; Panthi, D.; Tandler, P.; Fatani, O.; Ghulamullah, N.A.; Marasinghe, D.; Farhath, M.; Madhujith, T.; Conrad, K.; et al. A comprehensive review on hydrogen production, storage, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10900–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagdougui, H.; Sacile, R.; Bersani, C.; Ouammi, A. Chapter 4—Hydrogen Storage and Distribution: Implementation Scenarios. In Hydrogen Infrastructure for Energy Applications; Dagdougui, H., Sacile, R., Bersani, C., Ouammi, A., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnakar, R.R.; Gupta, N.; Zhang, K.; van Doorne, C.; Fesmire, J.; Dindoruk, B.; Balakotaiah, V. Hydrogen supply chain and challenges in large-scale LH2 storage and transportation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 24149–24168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.; Sehested, J.; Nørskov, J.K. Hydrogen and synthesis gas by steam- and CO2 reforming. In Advances in Catalysis; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 47, pp. 65–139. [Google Scholar]
- Szablowski, L.; Wojcik, M.; Dybinski, O. Review of steam methane reforming as a method of hydrogen production. Energy 2025, 316, 134540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distel, M.M.; Margutti, J.M.; Obermeier, J.; Nuß, A.; Baumeister, I.; Hritsyshyna, M.; Weiß, A.; Neubert, M. Large-Scale H2 Storage and Transport with Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier Technology: Insights into Current Project Developments and the Future Outlook. Energy Technol. 2025, 13, 2301042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntepe, A.; Erkan, S.; Olgar, M.A.; Çelik, S.; Zan, R. Investigating surface area and hydrogen pressure effects on LiH and NaH. J. Solid State Chem. 2024, 330, 124483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, P.; Jiao, F.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Han, D.; Liu, Q. An Efficient Integrated System for Methanol Steam Reforming to Produce Hydrogen Coupled with PEMFC Power Generation. J. Therm. Sci. 2025, 34, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, A.L. Hydrogen generation from natural gas for the fuel cell systems of tomorrow. J. Power Sources 1996, 61, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalis, A. A comprehensive review of fuel cell-based micro-combined-heat-and-power systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 105, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kou, Y.; Liang, W.; Bieerke, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z. Fuel Cell-Based Distributed Robust Optimal Scheduling for Combined Heat and Power Supply. Electronics 2024, 13, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimm, D.L.; Lam, C.-W. The combustion of methane on platinum—Alumina fibre catalysts—I: Kinetics and mechanism. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1980, 35, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapellucci, R.; Giordano, L. Steam, dry and autothermal methane reforming for hydrogen production: A thermodynamic equilibrium analysis. J. Power Sources 2020, 469, 228391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashchenko, D. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis of steam methane reforming based on a conjugate solution of material balance and law action mass equations with the detailed energy balance. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoz, A.; Olgun, H.; Ozdogan, S. Reforming options for hydrogen production from fossil fuels for PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 154, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, A.; Vogel, B.; Hübner, P. Reforming of natural gas-hydrogen generation for small scale stationary fuel cell systems. J. Power Sources 2002, 105, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megía, P.J.; Rocha, C.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Carrero, A.; Calles, J.A.; Madeira, L.M.; Soria, M.A. Thermodynamic Comparison between Conventional, Autothermal, and Sorption-Enhanced Bio-oil Steam Reforming. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, M.H.; de Croon, M.H.J.M.; van der Schaaf, J.; Cobden, P.D.; Schouten, J.C. Modeling and analysis of autothermal reforming of methane to hydrogen in a fixed bed reformer. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimm, D.L. Catalysts for the control of coking during steam reforming. Catal. Today 1999, 49, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, F.; Gómez, T. Efficiency and economics of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1997, 22, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Subramanian, K.A. Enhancement of efficiency and power output of hydrogen fuelled proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell using oxygen enriched air. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 6067–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Guan, Y.; Reinecke, A. Characterizing hydrogen-fuelled pulsating combustion on thermodynamic properties of a combustor. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamel, N.; Li, X. Transient analysis of carbon monoxide poisoning and oxygen bleeding in a PEM fuel cell anode catalyst layer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-López, V.F.; Mason, T.; Shearing, P.R.; Brett, D.J.L. Carbon monoxide poisoning and mitigation strategies for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells—A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 79, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, B.; Hafttananian, M.; Khamani, S.; Ramiar, A.; Ranjbar, A.A. Poisoning of proton exchange membrane fuel cells by contaminants and impurities: Review of mechanisms, effects, and mitigation strategies. J. Power Sources 2019, 427, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengaard, H.S.; Nørskov, J.K.; Sehested, J.; Clausen, B.S.; Nielsen, L.P.; Molenbroek, A.M.; Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R. Steam Reforming and Graphite Formation on Ni Catalysts. J. Catal. 2002, 209, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusini, E.; Casapu, M.; Zimina, A.; Doronkin, D.E.; Störmer, H.; Barthe, L.; Belin, S.; Grunwaldt, J.-D. Structural Changes of Ni and Ni–Pt Methane Steam Reforming Catalysts During Activation, Reaction, and Deactivation Under Dynamic Reaction Conditions. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7463–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Ding, S.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Y. Catalytic performance of Ni catalysts for steam reforming of methane at high space velocity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, P.; Kumar, A.; Khraisheh, M. A review of recent advances in water-gas shift catalysis for hydrogen production. Emergent Mater. 2020, 3, 881–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Chand, R.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Mishra, P.K. Performance of water gas shift reaction catalysts: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Qin, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, X.; Gao, Z.; Peng, M.; Huang, F.; Xiao, D.; Wen, X.; Wang, N.; et al. Fully-exposed Pt-Fe cluster for efficient preferential oxidation of CO towards hydrogen purification. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostom, S.; Symonds, R.; Hughes, R. Cu-BTC and Zeolite-5A-Modified Cu-BTC MOFs for High-Pressure and Moderate-Temperature H2 Purification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 11207–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Hydrogen purification by Mg alloy hydrogen adsorbent. Adsorption 2022, 28, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.; Dybkjaer, I.; Christiansen, L.J. Steam Reforming Opportunities and Limits of the Technology. In Chemical Reactor Technology for Environmentally Safe Reactors and Products; de Lasa, H.I., Doğu, G., Ravella, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 249–281. [Google Scholar]

| Reactions | /kJ mol−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Steam reforming | CH4 + H2O ←→ CO + 3 H2 | 206 |
| (2) | Water–gas shift | CO + H2O ←→ CO2 + H2 | −41 |
| (3) | Partial oxidation | CH4 + 1.5 O2 ←→ CO + 2 H2O | −519 |
| (4) | Total oxidation | CH4 + 2 O2 ←→ CO2 + 2 H2O | −803 |
| (5) | Dry reforming | CH4 + CO2 ←→ 2 CO + 2 H2 | 247 |
| (6) | Steam reforming | CH4 + 2 H2O ←→ CO2 + 4 H2 | 165 |
| (7) | Combustion | H2 + 0.5 O2 ←→ H2O | −394 |
| (8) | Combustion | CO + 0.5 O2 ←→ CO2 | −172 |
| (9) | Boudouard reaction | CO ←→ 0.5 C + 0.5 CO2 | −86 |
| (10) | Decomposition | CH4 ←→ C + 2 H2 | 75 |
| Reactions | Equilibrium Constant K | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Steam reforming | CH4 + H2O ←→ CO + 3 H2 | K1 = exp (−26,830/T + 30.114)/atm2 |
| (2) | Water–gas shift | CO + H2O ←→ CO2 + H2 | K2 = exp (4400/T − 4.036) |
| (3) | Partial oxidation | CH4 + 1.5 O2 ←→ CO + 2 H2O | Complete |
| Reactants | Products | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction 1 | CH4 | + | 1.5 O2 | ←→ | CO | + | 2 H2O |
| Feed/mol h−1 | 0.21 | 0 | |||||
| Equilibrium | 0 | ||||||
| Reaction 2 | CH4 | + | H2O | ←→ | CO | + | 3 H2 |
| Feed/mol h−1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Equilibrium | |||||||
| Reaction 3 | CO | + | H2O | ←→ | CO2 | + | H2 |
| Feed/mol h−1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Equilibrium | |||||||
| H2 | CO | CO2 | CH4 | H2O | O2 | N2 | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2462 | 0.7385 | 0.1292 | 0.4862 | 1.6000 |
| Fraction | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.1538 | 0.4615 | 0.0808 | 0.3038 | 1.0000 | |
| ATR Exit at 923 K | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.6268 | 0.0813 | 0.1603 | 0.0045 | 0.5950 | 0.0000 | 0.4862 | 1.9540 |
| Fraction | 0.3208 | 0.0416 | 0.0820 | 0.0023 | 0.3045 | 0.0000 | 0.2488 | 1.0000 | |
| WGS Exit at 473 K | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.7064 | 0.0017 | 0.2399 | 0.0045 | 0.5153 | 0.0000 | 0.4862 | 1.9540 |
| Fraction | 0.3615 | 0.0009 | 0.1228 | 0.0023 | 0.2637 | 0.0000 | 0.2488 | 1.0000 |
| H2 | CO | CO2 | CH4 | H2O | O2 | N2 | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2462 | 0.7385 | 0.1292 | 0.4862 | 1.6000 |
| Fraction | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.1538 | 0.4615 | 0.0808 | 0.3038 | 1.0000 | |
| ATR Exit at 973 K | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.6259 | 0.0955 | 0.1495 | 0.0012 | 0.6025 | 0.0000 | 0.4862 | 1.9607 |
| Fraction | 0.3192 | 0.0487 | 0.0762 | 0.0006 | 0.3073 | 0.0000 | 0.2479 | 1.0000 | |
| WGS Exit at 423 K | Flow/Nm3h−1 | 0.7208 | 0.0006 | 0.2444 | 0.0012 | 0.5076 | 0.0000 | 0.4862 | 1.9607 |
| Fraction | 0.3676 | 0.0003 | 0.1246 | 0.0006 | 0.2589 | 0.0000 | 0.2479 | 1.0000 |
| η (Fuel) | Q1 /kJ h−1 | Q(ATR) /kJ h−1 | Q2 /kJ h−1 | Q(WGS) /kJ h−1 | Banlance /kJ h−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 (ATR 923K, WGS 473K) | 0.97 | 1341 | −860 | −480 | −146 | −145 |
| Case 2 (ATR 973K, WGS 423K) | 0.99 | 1341 | −809 | −415 | −174 | −57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, Q.; Yang, X.; Liang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Thermodynamic Analysis of a Compact System Generating Hydrogen for Mobile Fuel Cell Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051273
Lang Q, Yang X, Liang K, Liu Y, Zhang Y. Thermodynamic Analysis of a Compact System Generating Hydrogen for Mobile Fuel Cell Applications. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Qiaolin, Xiaobo Yang, Ke Liang, Yang Liu, and Yang Zhang. 2025. "Thermodynamic Analysis of a Compact System Generating Hydrogen for Mobile Fuel Cell Applications" Processes 13, no. 5: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051273
APA StyleLang, Q., Yang, X., Liang, K., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Thermodynamic Analysis of a Compact System Generating Hydrogen for Mobile Fuel Cell Applications. Processes, 13(5), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051273








