Actuator Fault Estimation for Distributed Interconnected Lipschitz Nonlinear Systems with Direct Feedthrough Inputs
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Actuator fault estimation is investigated for interconnected systems with direct feedthrough terms. By constructing an augmented state vector composed of original system states and actuator faults, an augmented descriptor system is established. An observer is designed for the augmented interconnected system which can achieve a simultaneous estimate of system states and actuator faults.
- (ii)
- An additional control term is used to mitigate the influence from the process uncertainties to the estimation error dynamics, ensuring a robustness of the estimation performance.
- (iii)
- (iv)
- In the proposed design, there are no constraints on the fault conditions in principle. Therefore, the proposed fault estimation algorithm can diagnose a wide range of faults occurring in engineering systems.
- (v)
- To the best of our knowledge, this study would be a very pioneering work to explicitly handle actuator fault estimation for distributed interconnected systems with direct feedthrough input terms.
2. System Model and Preliminaries
- (i)
- The direct feedthrough input term is considered in this paper where the matrix of the direct feedthrough input is a non-zero matrix. In many engineering systems such as aircraft systems [40] and three-shaft gas turbine engine systems [41], the direct feedthrough input matrix is full-column rank. Therefore, in this study, the direct feedthrough input matrix is assumed to be full-column rank. The distribution matrix of the additive actuator fault acting on the system output, that is is usually the same as , or partial columns of . As a result, one can assume is full of column rank in this study.
- (ii)
- The bound of the process uncertainty is assumed to be known for the analysis. However, in practical scenarios, the designer can choose a sufficiently large observer parameter to achieve a robust estimation performance.
- (iii)
- The nonlinear function is assumed to be globally Lipschitz. is the Lipschitz constant which quantifies how much the output of the nonlinear function changes with respect to its input so that the change rate of the function is bounded. However, the proposed results in this study can be applied to local Lipschitz systems. More details on Lipschitz systems can be found in [38,39].
3. Fault Estimation for Nonlinear Distributed Systems
- , ,
- , ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ;
- ,
- ,
- ,
- , ,
- (i)
- Construct an augmented descriptor distributed interconnected system in the form of (4), and the system matrices are defined in (3).
- (ii)
- Calculate matrices , , , and using (9a)–(9d).
- (iii)
- Solve the linear matrix inequalities (14), (50), and (51) simultaneously to obtain and One can then calculate , , and
- (iv)
- Implementing the distributed fault estimation observer (18) and (19), one can have a simultaneous estimate of system states and actuator fault signals in the form of (54) and (55).
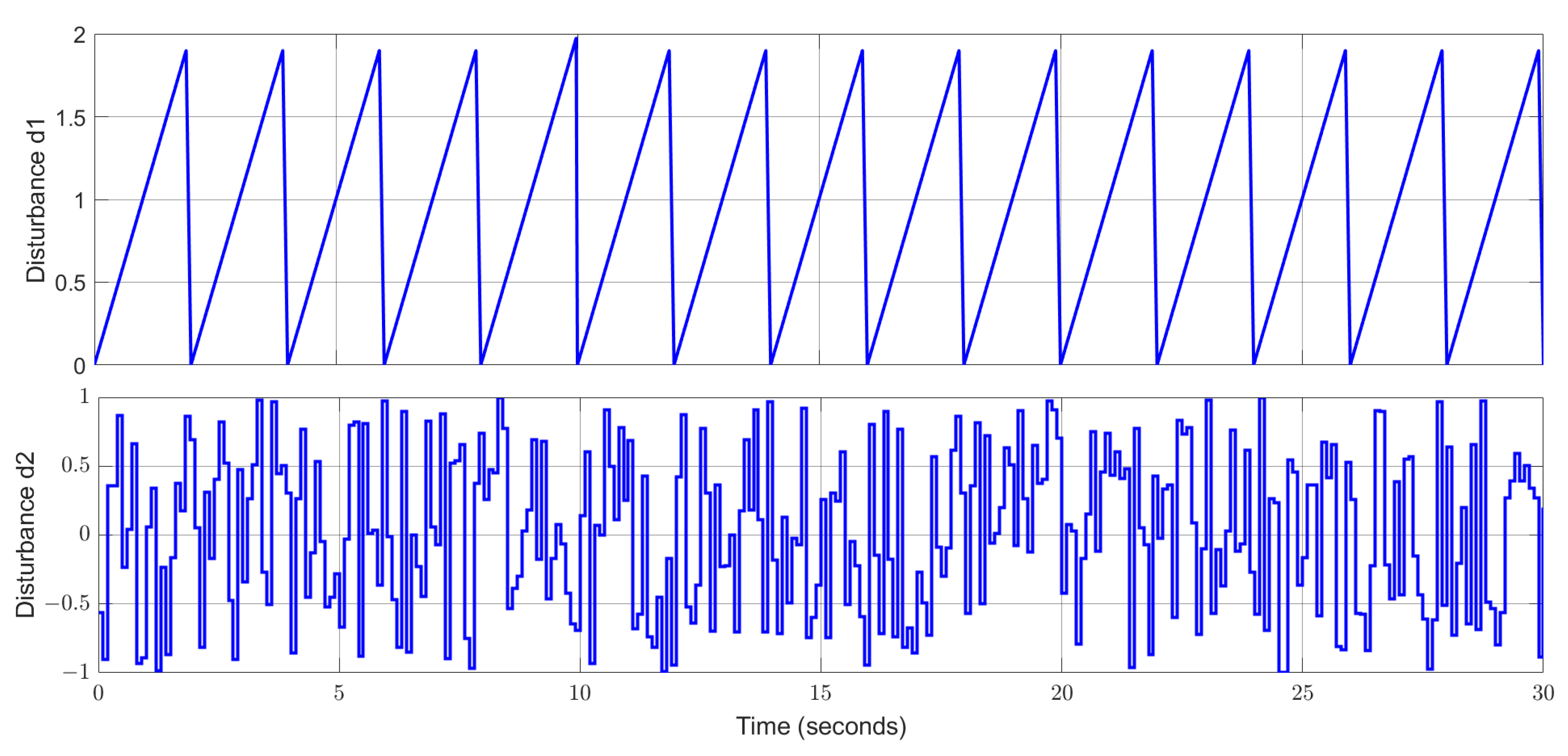
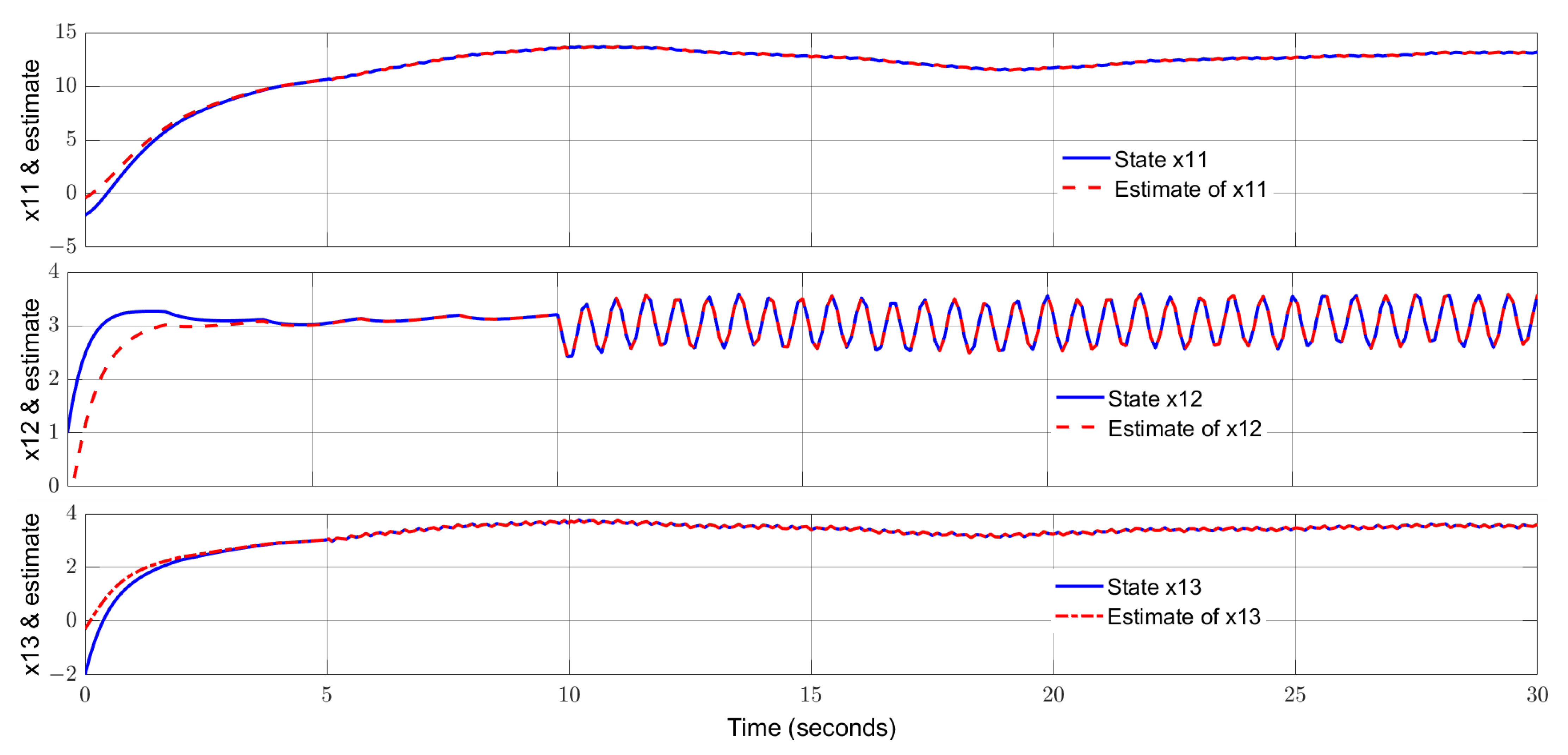
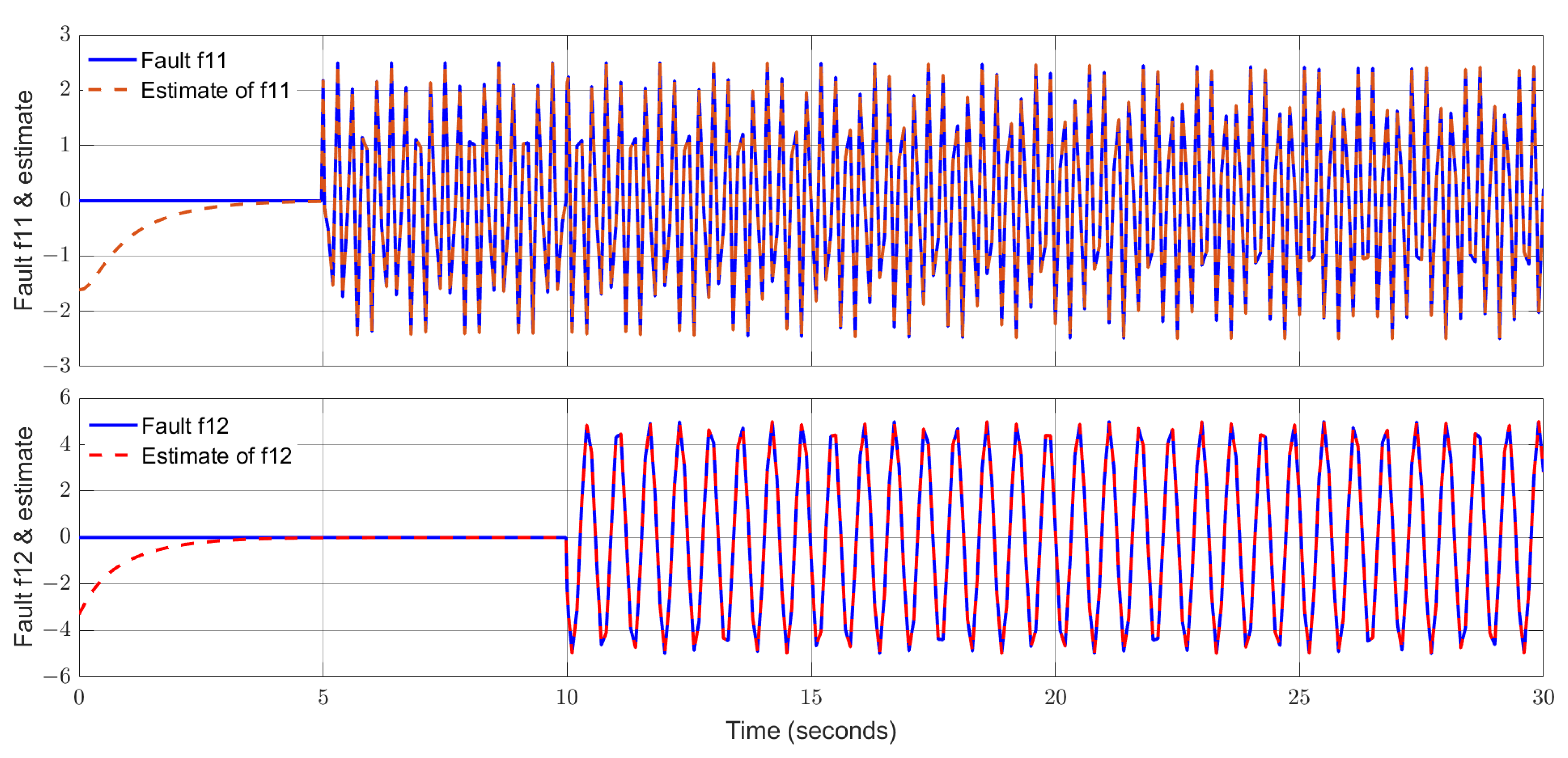
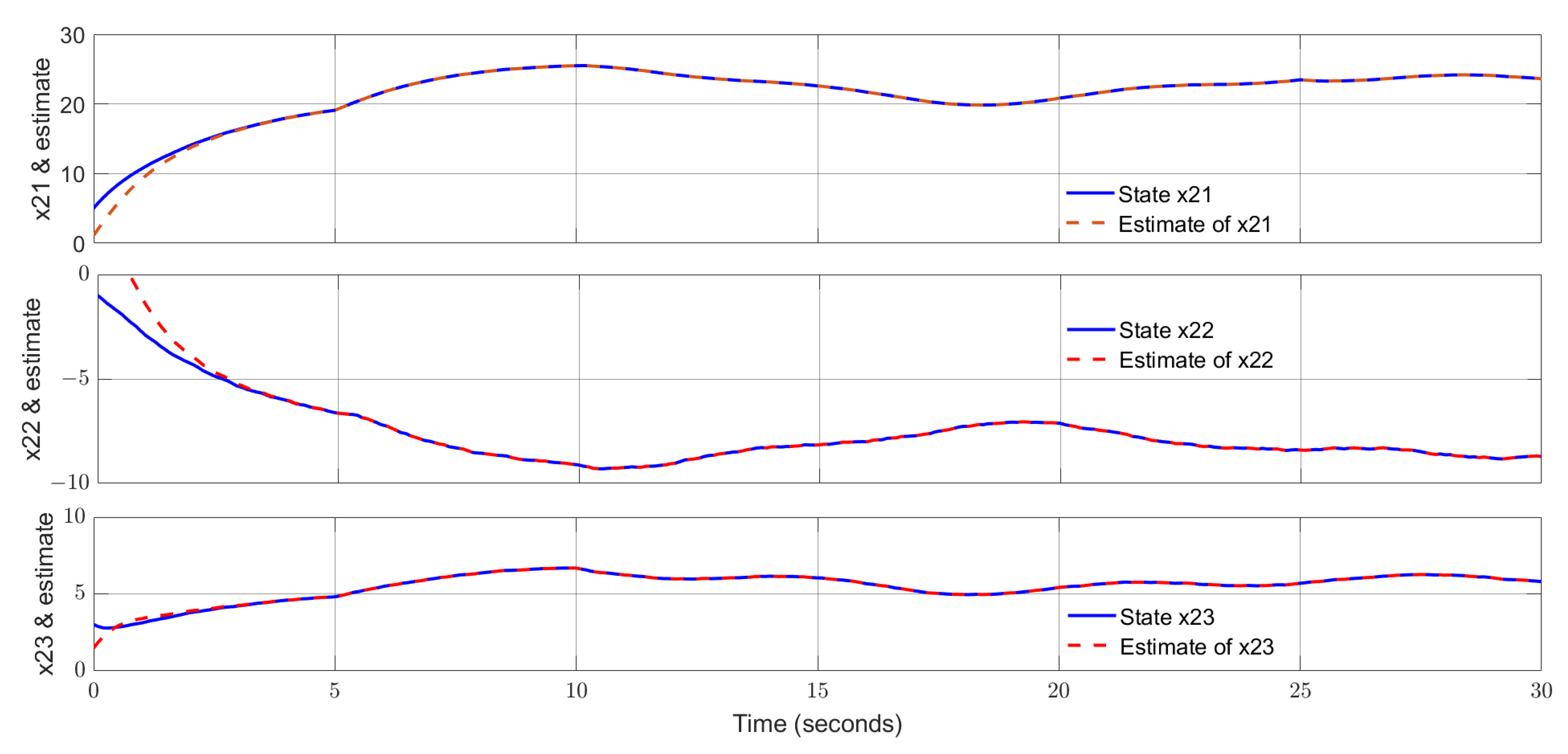
4. Simulation Study and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Study
4.2. Discussion for Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.-W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. Fault reconstruction approach for saturated dynamic systems using adaptive estimation and optimization. ISA Trans. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Huang, H. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on adaptive denoising residual network. Processes 2025, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, F.; Zeng, Y.; Qian, J. Fault diagnosis of hydro-turbine via the incorporation of Bayesian algorithm optimized CNN-LSTM neural network. Energy 2024, 290, 130326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yu, J.; Tian, L.; Yin, C. Data-driven fault diagnosis of PEMFC water management with segmented cell and deep learning technologies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 67, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Du, J.; Cong, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L. Fault diagnosis for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles based on signal decomposition and two-dimensional feature clustering. Green Energy Intell. Transp. 2022, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, J.; Shi, S.; Cai, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, P. Fault diagnosis techniques for electrical distribution network based on artificial intelligence and signal processing: A review. Processes 2025, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, D. A Survey of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis toward integrated O&M for wind turbines. Energies 2019, 12, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Pula, R. Methods of photovoltaic fault detection and classification: A review. Energy Rep. 2002, 8, 5898–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.; EL-Koujok Poulin, B.; Amazouz, M.; Yacout, S. Fault diagnosis in industrial chemical processes using interpretable patterns based on logical analysis of data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 95, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tan, H.; Yang, C.; Yan, H. A review of fault diagnosis methods for key systems of the high-speed train. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yan, X.; Yang, K.; Zhao, J.; Sheng, C.; Yuan, C. Review of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis for marine power systems. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2021, 3, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Fu, F.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y. Fault diagnosability evaluation for interconnected large-scale cyber–physical systems. Automatica 2025, 173, 112090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, G. Interconnected dynamic systems: An overview on distributed control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2013, 33, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Butcher, A. Decentralized estimation of spacecraft relative motion using consensus extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, L. Distributed fault detection for large-scale interconnected systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2023, 18, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boem, F.; Carli, R.; Farina, M.; Ferrari-Trecate, G.; Parisini, T. Distributed fault detection for interconnected large-scale systems: A scalable plug & play approach. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2019, 6, 800–811. [Google Scholar]
- Baroumand, S.; Zaman, A.; Mihaylova, L.S. Attack detection and fault-tolerant control of interconnected cyber-physical systems against simultaneous replayed time-delay and false-data injection attacks. IET Control Theory Appl. 2023, 17, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boem, F.; Gallo, A.J.; Raimondo, D.M.; Parisini, T. Distributed fault-tolerant control of large-scale systems: An active fault diagnosis approach. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2020, 7, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, X.; Yan, R.; Deng, R.; Zhou, D. Distributed sensor fault diagnosis for a formation of multi-vehicle systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 791–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ho, D. Proportional multiple-integral observer design for descriptor systems with measurement output disturbances. IEE Control Theory Appl. 2004, 151, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedher, A.; Benothman, K.; Maquin, D.; Benrejeb, M. State and sensor faults estimation via a proportional integral observer. In Proceedings of the 6th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices, Djerba, Tunisia, 23–26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Ding, S.; Ma, Y. Robust fault estimation approach and its application in vehicle lateral dynamic systems. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 2007, 28, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, H. Descriptor observer approaches for multivariable systems with measurement noises and application in fault detection and diagnosis. Syst. Control Lett. 2006, 55, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Swain, A.; Nguang, S.; Nasiri, A. Estimation of actuator and sensor faults for nonlinear systems using a descriptor system approach. In Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z. Estimation and compensation for Lipschitz nonlinear discrete-time systems subjected to unknown measurement delays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5950–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoort, M.; Veluvolu, K.C.; Rath, J.; Djemai, M. Adaptive sensor and actuator fault estimation for a class of uncertain Lipschitz nonlinear systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2016, 30, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Gao, Z.-W.; Liu, Y. Sensor fault reconstruction using robustly adaptive unknown-input observers. Sensors 2024, 24, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.; Bu, X. Robust sliding-mode observer-based sensor fault estimation, actuator fault detection and isolation for uncertain nonlinear systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2015, 13, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Qasem, O. Full-order reduced-order observers for linear parameter-varying systems with one-sided Lipschitz nonlinearities disturbances using parameter-dependent Lyapunov function. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 5541–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, Z.-W.; Liu, Y. Monitoring and reconstruction of actuator and sensor attacks for Lipschitz nonlinear dynamic systems using two types of augmented descriptor observers. Processes 2024, 12, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ma, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W. Fast actuator and sensor fault estimation based on adaptive unknown input observer. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Chen, M.; Yan, X. Distributed fault estimation and fault-tolerant control of interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Xie, X. Distributed observer-based robust fault estimation design for discrete-time interconnected systems with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 6737–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Man, J.; Song, S.; Ahn, C. Finite-time fault estimation and tolerant control for nonlinear interconnected distributed parameter systems with Markovian switching channels. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, G. Decentralized fuzzy fault estimation observer design for discrete-time nonlinear interconnected systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, K. Unknown observer-based distributed fault estimation of discrete-time nonlinear interconnected systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhao, Z. Plug-and-play robust distributed fault estimation for interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemouche, A.; Boutayeb, M. On LMI conditions to design observers for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. Automatica 2013, 49, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Han, Z. A note on observers for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2002, 47, 1751–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Breikin, T.; Wang, H. High-gain estimator and fault-tolerant design with application to a gas turbine dynamic system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2007, 15, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanek, B.; Edelmayer, A.; Szabo, Z.; Bokor, J. Bridging the gap between theory and practice in LPV fault detection for flight control actuators. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 31, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D. Time-invariant descriptor systems. Automatica 1978, 14, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. PD observer parametrization design for descriptor systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2005, 342, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Moysis, L.; Gupta, M.; Fragulis, G.; Volos, C. Observer design for nonlinear descriptor systems: A survey on system nonlinearities. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 43, 2853–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, W. Sliding-mode observers for nonlinear systems with unknown inputs and measurement noise. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2013, 11, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, G.; Ho, D.; Li, Y. Distributed estimation and control for discrete time-varying interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 67, 2192–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corless, M.; Tu, J. State and input estimation for a class of uncertain systems. Automatica 1998, 34, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; El Ghaoui, L.; Feron, E.; Balakrishnan, V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Feron, E.; El Ghaoui, L. History of linear matrix inequalities in control theory. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 June–1 July 1994; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. The Schur Complement and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ravat, A.; Dhawan, A.; Tiwari, M. LMI and YALMIP: Modelling and optimization toolbox in MATLAB. In Advances in VLSI, Communication, and Signal Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Vito, D.; Kron, M.; Lafontaine, J.; Lovera, M. A Matlab toolbox for LMI-based analysis and synthesis of LPV/LFT self-scheduled H∞ control systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Aided Control System Design, Yokohama, Japan, 8–10 September 2010; pp. 1397–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, S.; Petres, Z.; Baranyi, P. TP tool—A MATLAB toolbox for TP model transformation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium of Hungarian Researchers on Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Budapest, Hungary, 15–17 November 2007; pp. 483–495. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, A.; Kuczmann, M. Extending the TPTool MATLAB toolbox with LMI based observer and disturbance rejection design. Results Control Optim. 2023, 13, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Poznyak, A.; Orlov, Y.; Polyakov, A. Road Map for Sliding Mode Control Design; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Park, J.; Chen, C. Second-order sliding mode controller design with output constraint. Automatica 2020, 112, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, S.; Joo, Y. Decentralized observer-based integral sliding mode control design of large-scale interconnected systems its application to doubly fed induction generator-based wind farm model. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 33, 5758–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Get Started with Simulink; R2024b; Mathworks: Natick, MA, USA, 2024.
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Shi, P.; Pan, J. Distributed fault estimation design of interconnected systems with external disturbances. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, K. Fault diagnosis based on adaptive observer for interconnected systems. Control Eng. China 2020, 27, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, K. Distributed fault estimation observer design for a class of interconnected nonlinear systems. Control Decis. 2019, 34, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Dai, H.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.; Chai, Y.; Zheng, W. Fault estimation for switched interconnected nonlinear systems with external disturbances via variable weighted iterative learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Brief 2023, 70, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fault Estimation Approaches for Interconnected Systems | Advantages | Limits |
|---|---|---|
| Augmented Luenberger distributed observer [32] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for low-frequency fault signals, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance and ability to suppress the external disturbances. | It is not applicable to estimate high-frequency actuator fault signals. Disturbance attenuation ability is relatively limited compared with disturbance decoupling techniques. Neither a nonlinear term nor direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Descriptor distributed observer [33] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for both low-frequency and high-frequency actuator fault signals, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance and ability to suppress the external disturbances. | Disturbance attenuation ability is relatively limited compared with disturbance decoupling techniques. Neither a nonlinear term nor direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Fuzzy proportional and integral distributed observer [35] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for low-frequency actuator fault signals with robustness against uncertainties. | It is not applicable to reconstruct a very high-frequency actuator fault signal. Disturbance attenuation ability is relatively limited compared with disturbance decoupling techniques. No direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Nonlinear augmented unknown input distributed observer [36] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for low-frequency fault signals, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance and ability to suppress the external disturbances. | It is not applicable to reconstruct a very high-frequency actuator fault signal. No direct feedthrough input term is considered in interconnected systems. |
| Augmented unknown input distributed observer 1 [37] | Robust actuator fault estimation can be achieved for low-frequency fault signals. Process disturbances are decoupled, and the measurement noise is attenuated by LMI optimization to ensure robustness. | It is not applicable to reconstruct high-frequency actuator fault signals. Neither a nonlinear term nor direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Augmented unknown input distributed observer 2 [59] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved particularly for low-frequency fault signals, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance. | It is not applicable to reconstruct a very high-frequency actuator fault signal. Neither a nonlinear term nor direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Adaptive distributed observer [60] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved particularly for low-frequency fault signals. | Robustness against uncertainty is not taken into account. The estimation capability for a high-frequency fault signal is questionable. Neither a nonlinear term nor direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Nonlinear augmented Luenberger distributed observer [61] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for low-frequency fault signals, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance and ability to suppress the external disturbances. | Disturbance attenuation ability is relatively limited compared with disturbance decoupling techniques. It is not applicable to reconstruct a high-frequency actuator fault signal. No direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| Nonlinear iterative learning disturbed observer [62] | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for both low-frequency and high-frequency fault signals. The robustness is discussed. | Disturbance attenuation ability is relatively limited compared with disturbance decoupling technique. No direct feedthrough input term is considered in the interconnected system. |
| The proposed observer technique in this paper | Actuator fault estimation can be achieved for both low-frequency and high-frequency fault signals. The process disturbance is removed by using a nonlinear control term, and regional pole constraints are used to enhance the transient performance. Lipschitz nonlinear terms are considered. A direct feedthrough input term is included in the interconnected system. | Further work needs to be done to extend the approach to more complex systems such as interconnected systems with high nonlinearities. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, L.; Gao, Z.-W.; Liu, Y. Actuator Fault Estimation for Distributed Interconnected Lipschitz Nonlinear Systems with Direct Feedthrough Inputs. Processes 2025, 13, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051283
Fang L, Gao Z-W, Liu Y. Actuator Fault Estimation for Distributed Interconnected Lipschitz Nonlinear Systems with Direct Feedthrough Inputs. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051283
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Ling, Zhi-Wei Gao, and Yuanhong Liu. 2025. "Actuator Fault Estimation for Distributed Interconnected Lipschitz Nonlinear Systems with Direct Feedthrough Inputs" Processes 13, no. 5: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051283
APA StyleFang, L., Gao, Z.-W., & Liu, Y. (2025). Actuator Fault Estimation for Distributed Interconnected Lipschitz Nonlinear Systems with Direct Feedthrough Inputs. Processes, 13(5), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051283







