Fracture Competitive Propagation and Fluid Dynamic Diversion During Horizontal Well Staged Hydraulic Fracturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations for Hydraulic Fracture Propagation
2.1. Constitutive Equations for Porous Media
- (1)
- Fluid–solid coupling equations
2.2. Cohesion Model Control Equation
The Initiation and Extension of Cracks
- (1)
- Criteria for hydraulic fracture initiation and propagation
- (2)
- Fluid flow equation within hydraulic fractures
2.3. Horizontal Wellbore Flow
- (1)
- Pipe Element Model and Perforation Friction
- (2)
- Pipe Element Model—Wellbore Flow
3. Simulation Model and Verification
3.1. Geometric Model
3.2. Model Parameters
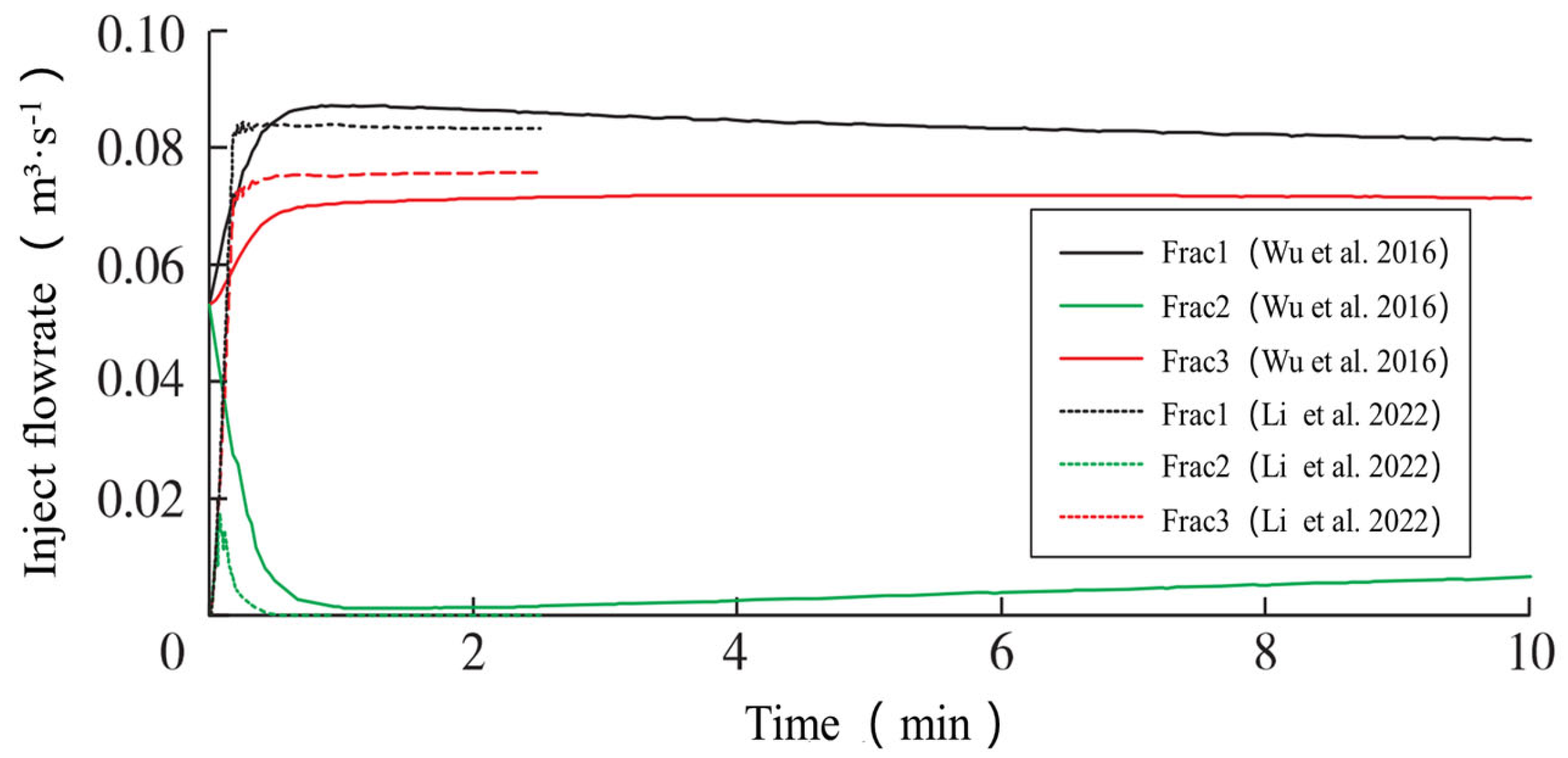
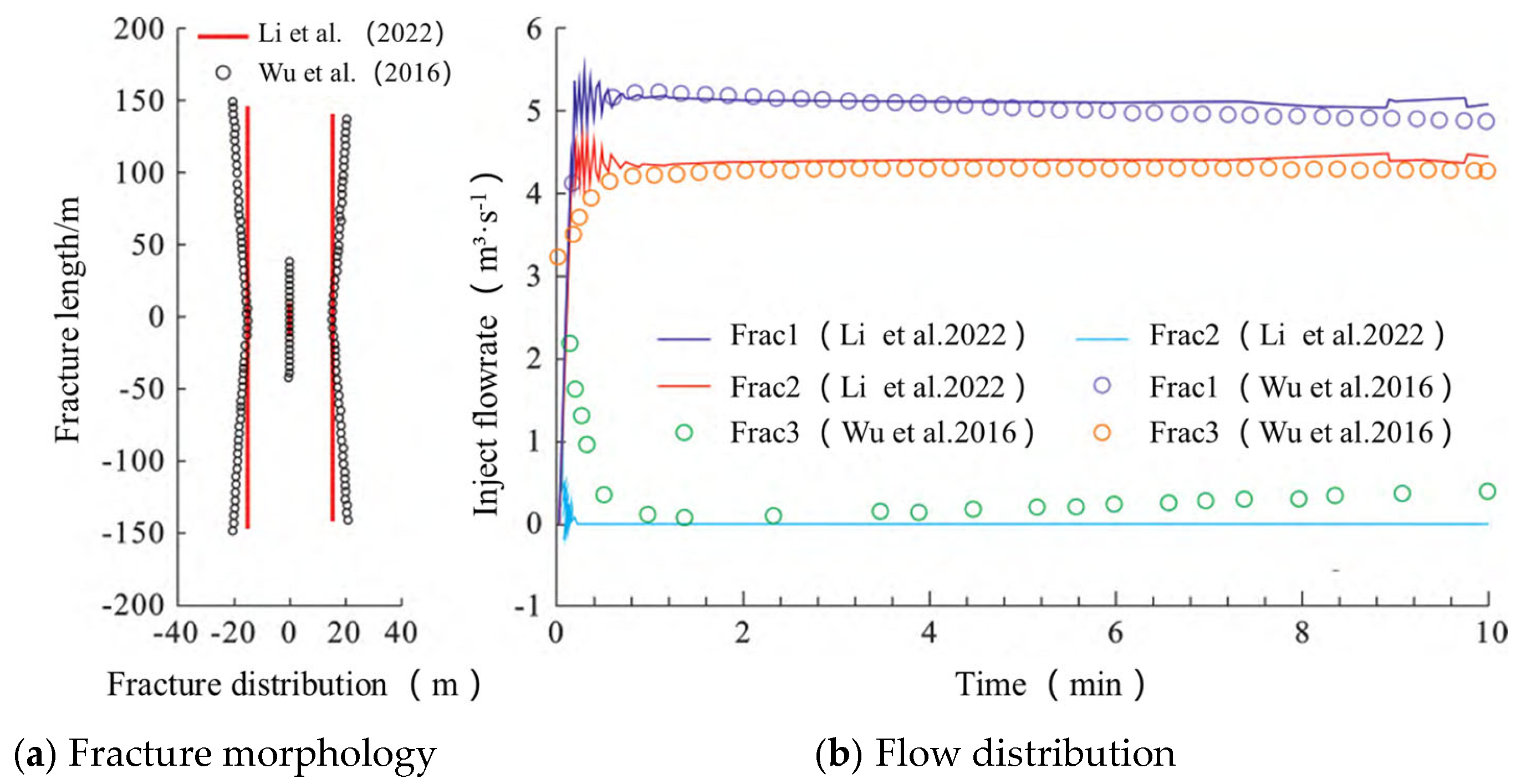
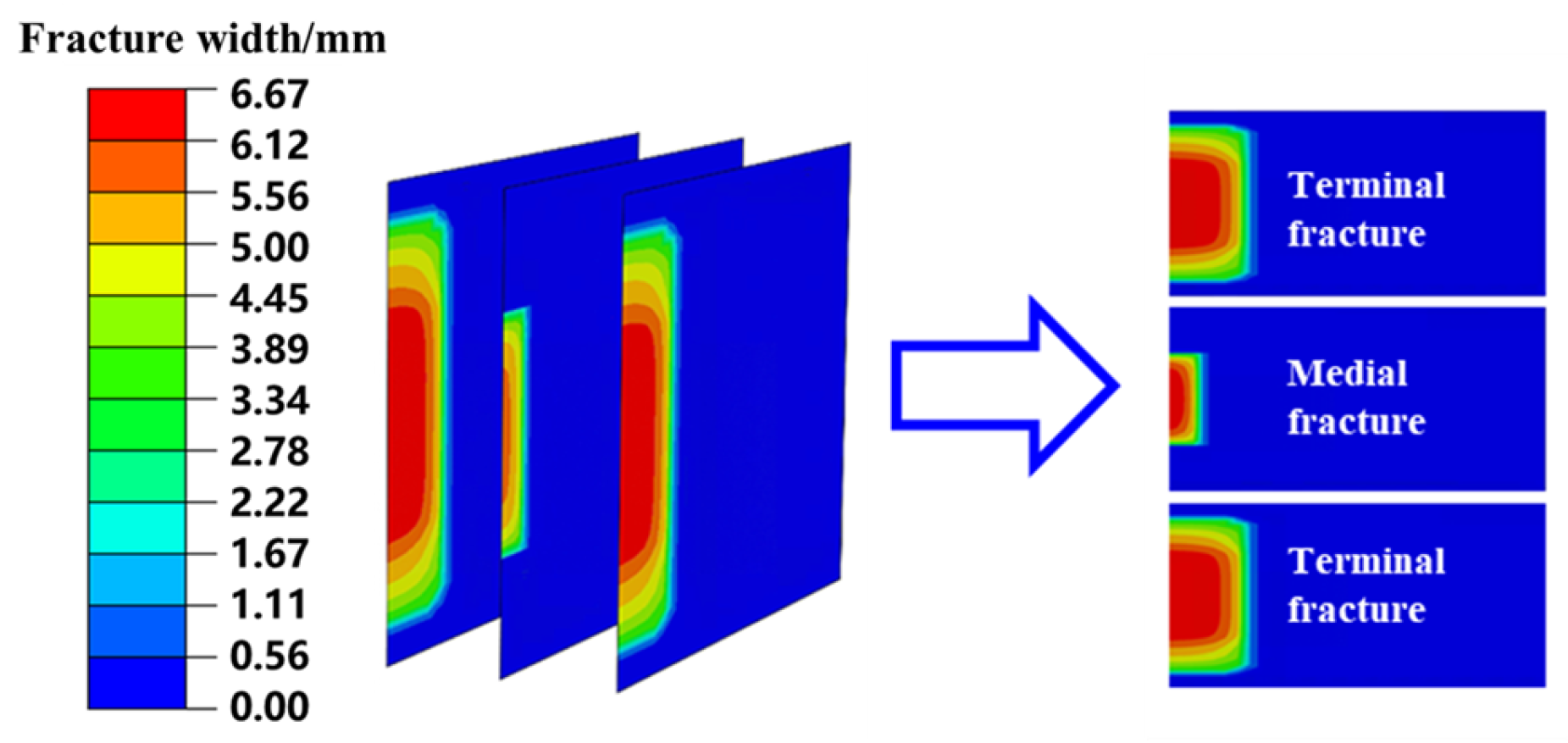
3.3. Model Validation
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Construction Factors
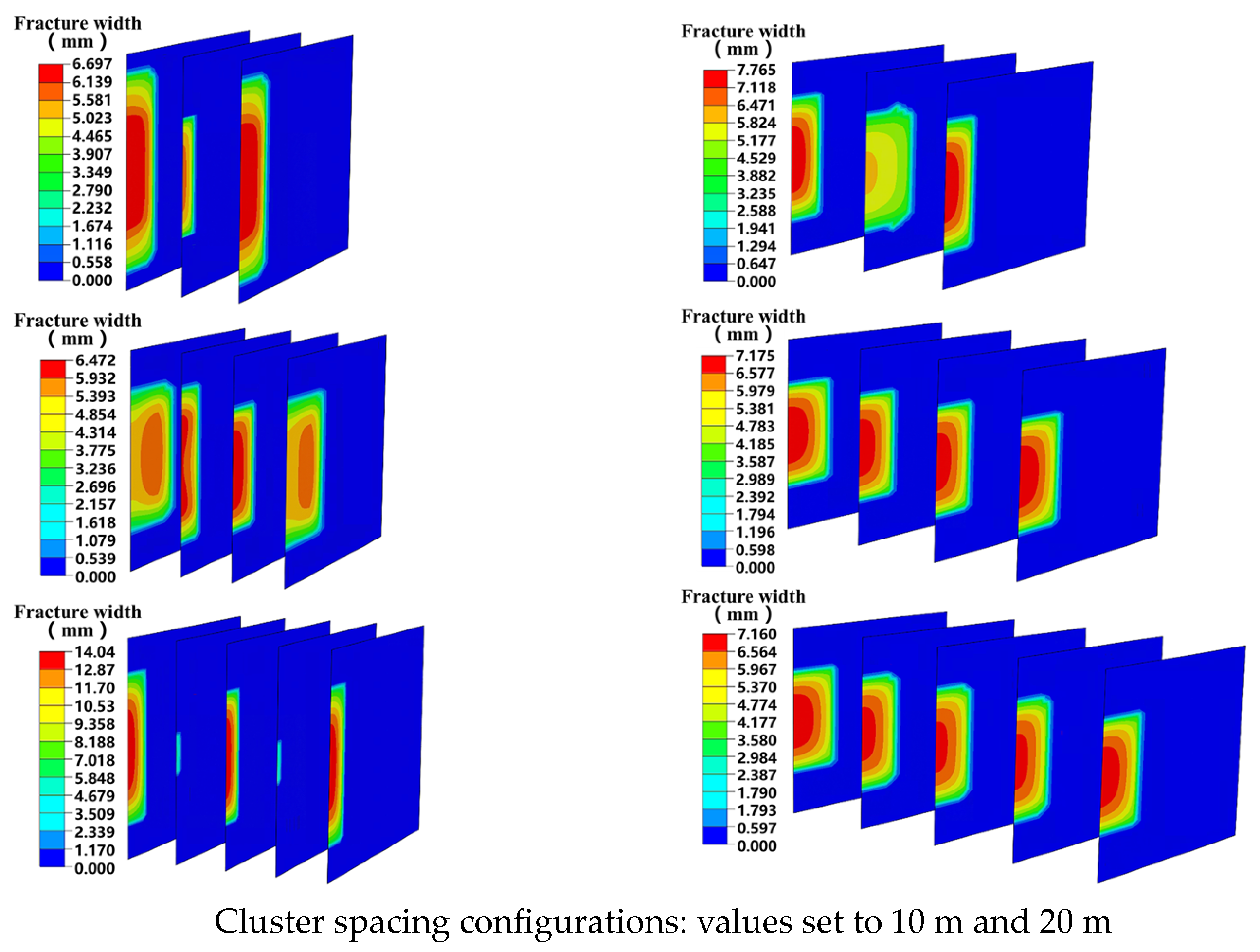
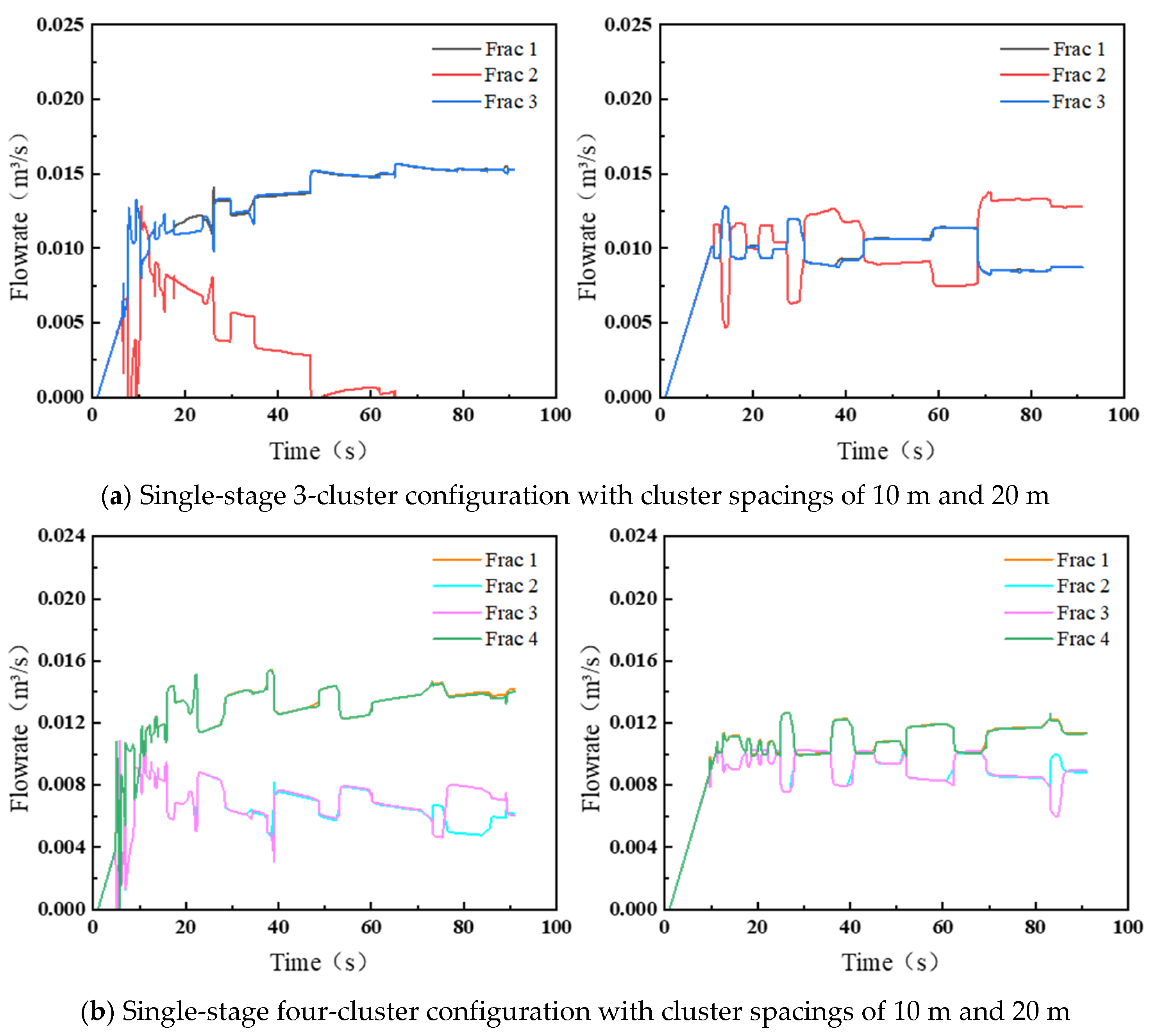
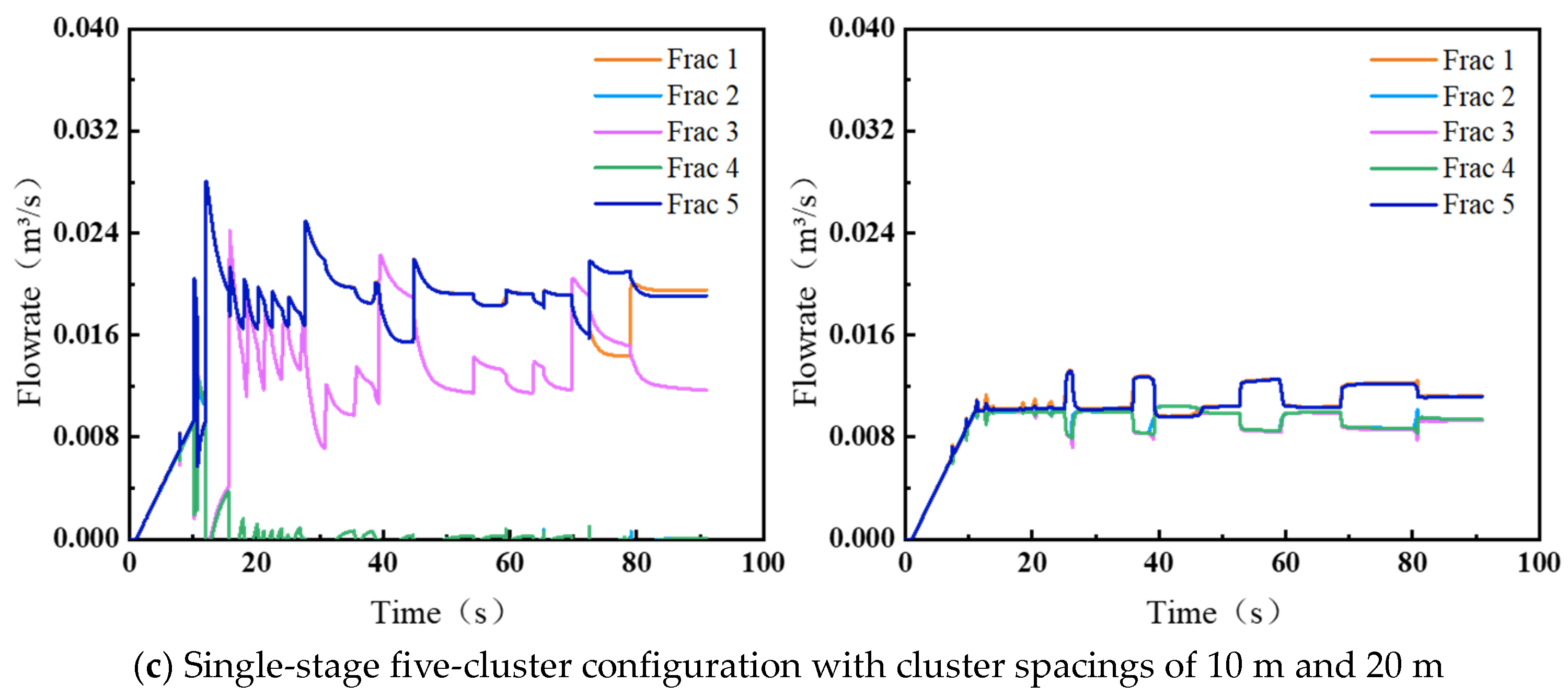
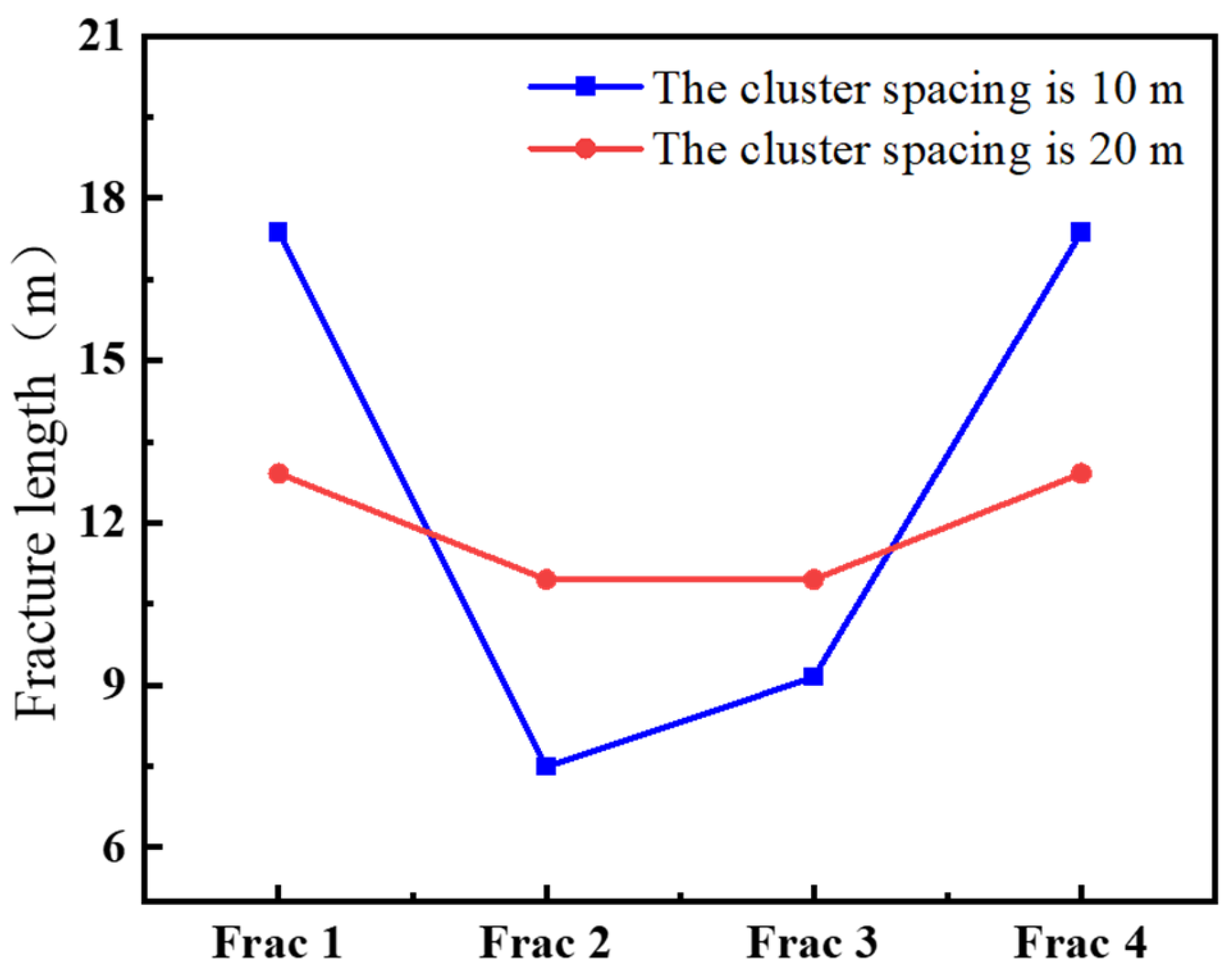
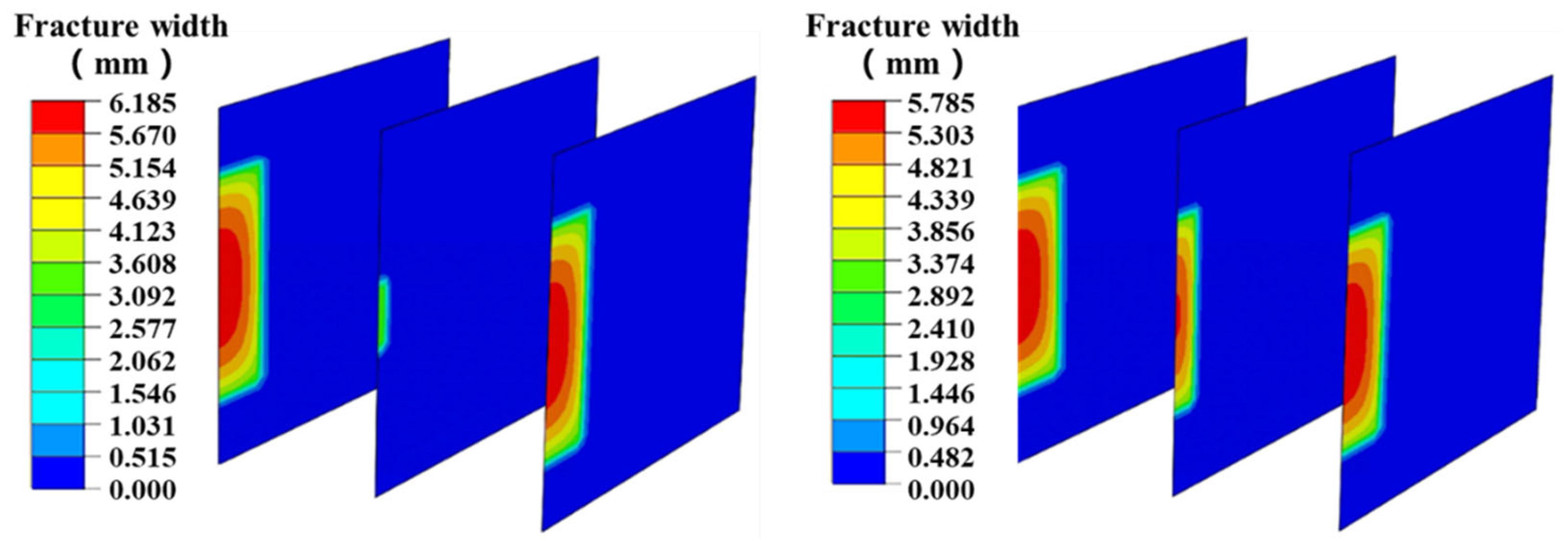
4.1.1. Number and Spacing of Clusters in a Single Segment
4.1.2. Perforation Friction
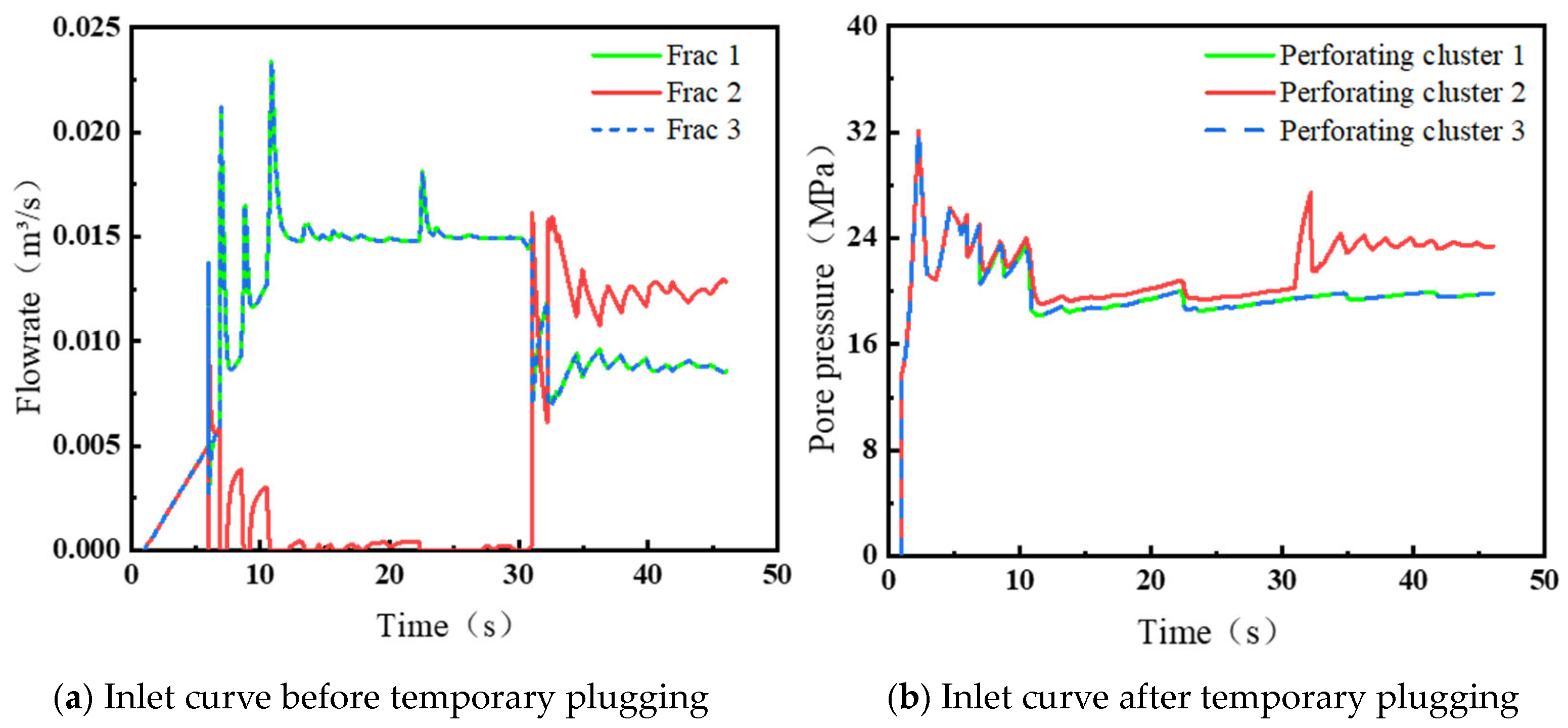
4.1.3. Temporary Blockage Parameters
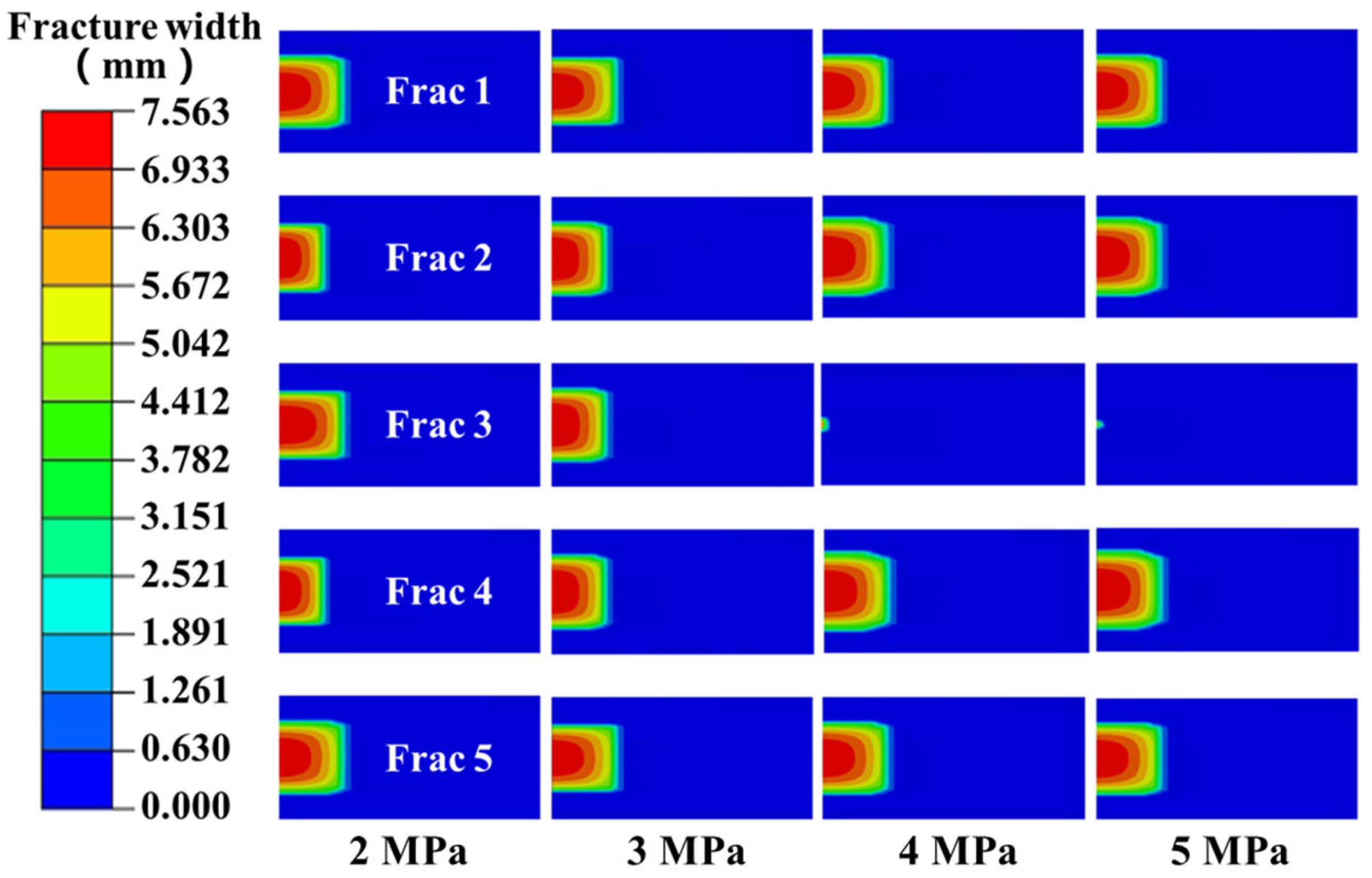
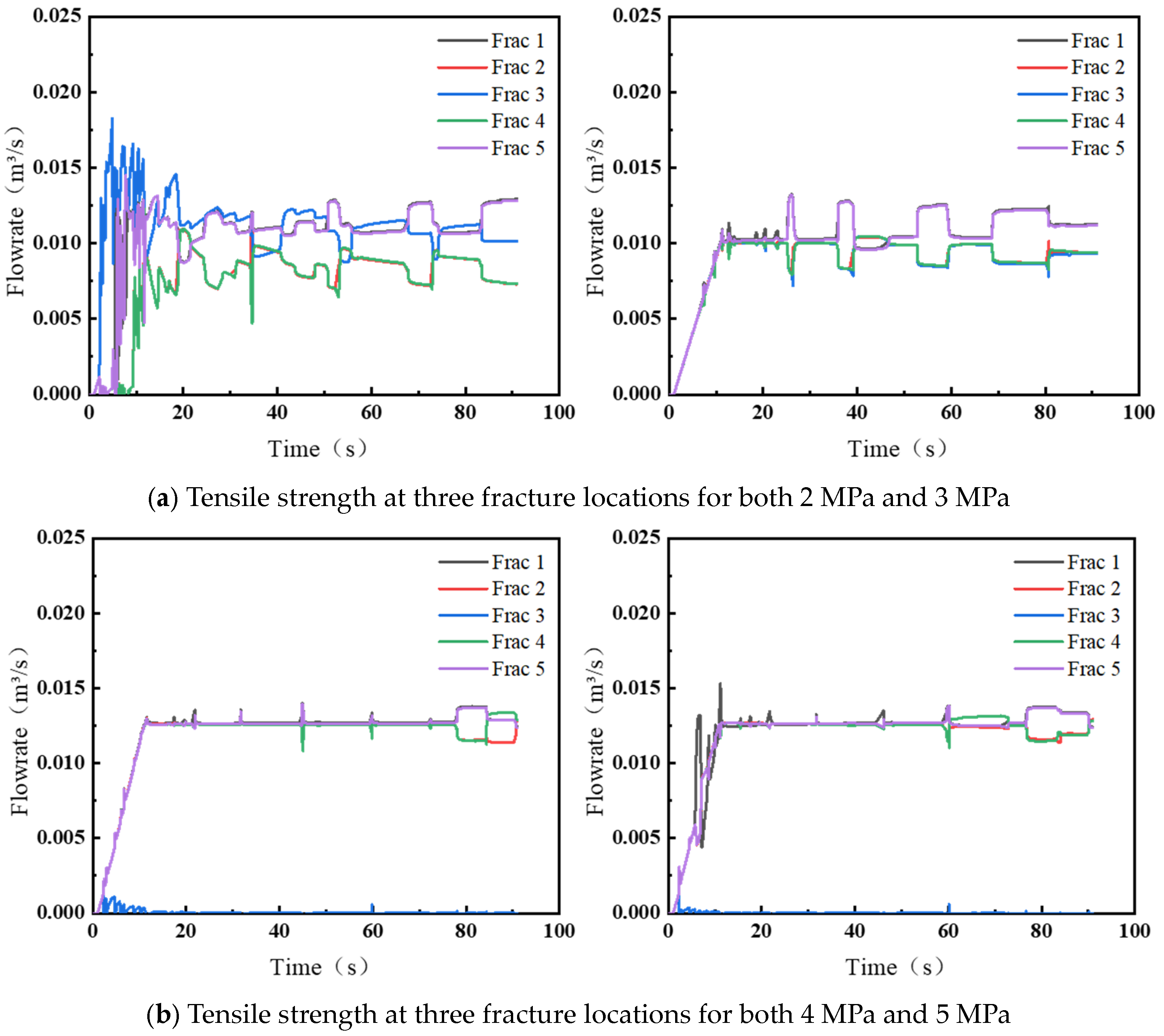
4.2. Differences in Mechanical Properties Between Clusters Within a Segment
5. Discussion and Analysis
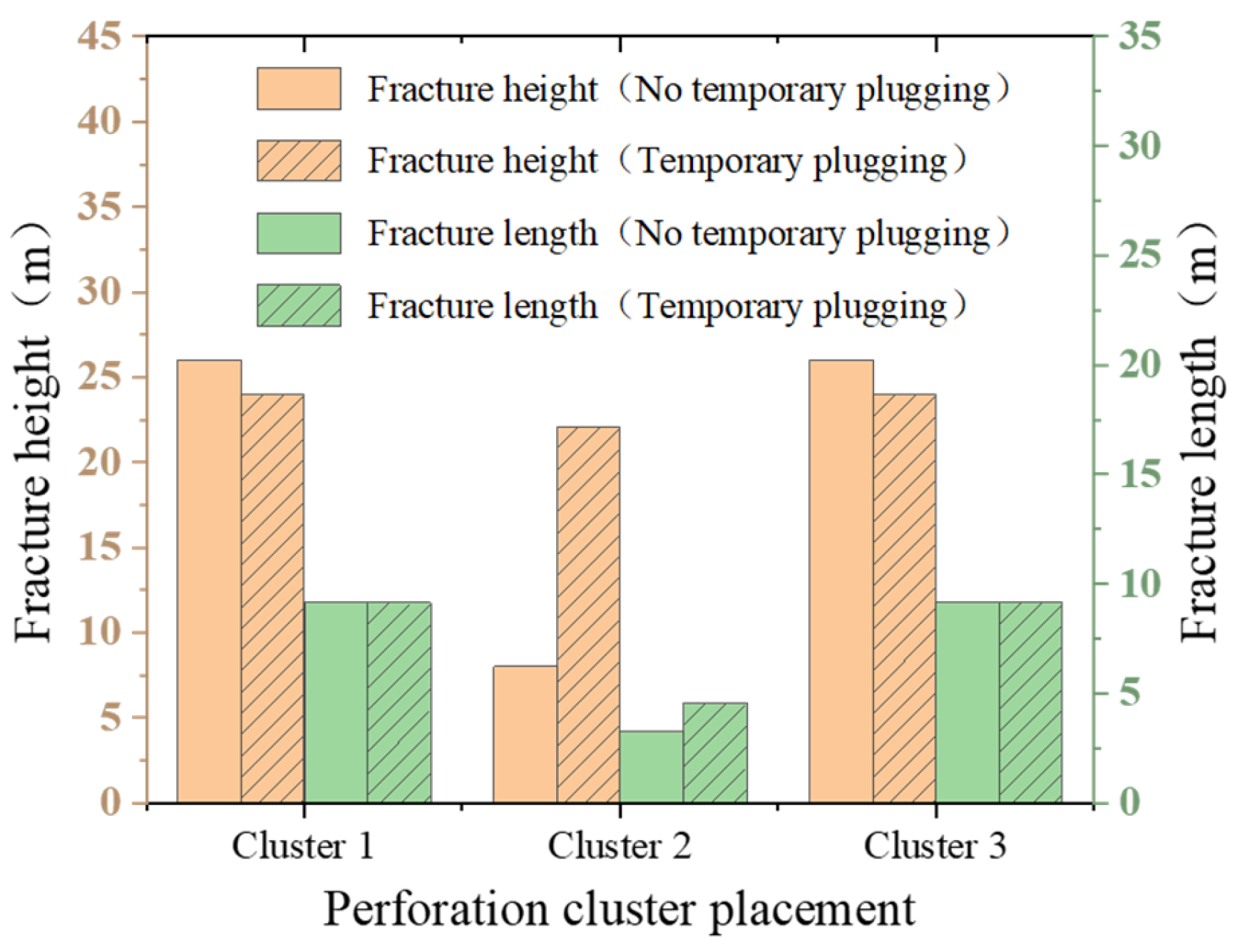
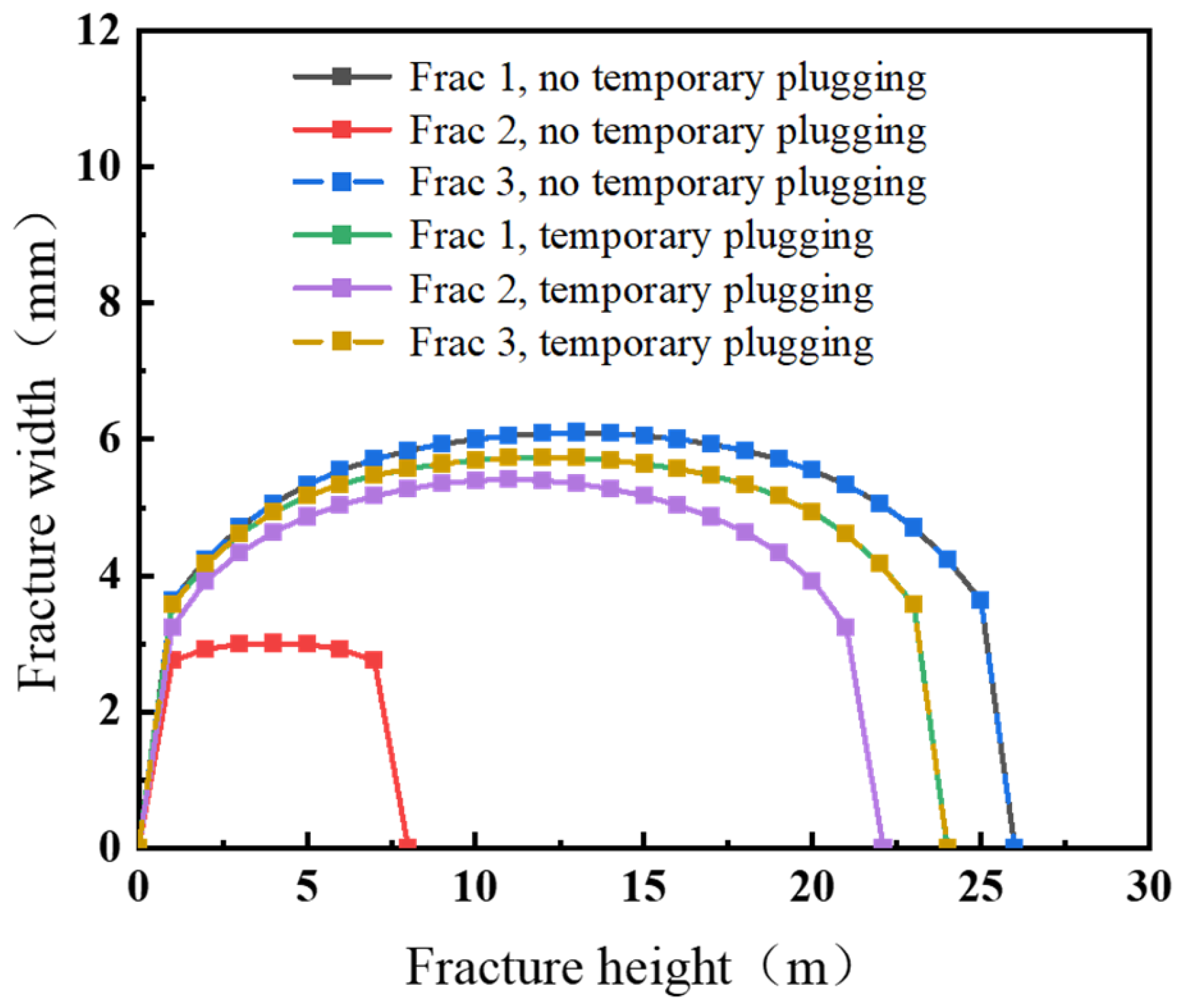
5.1. Quantitative Analysis of the Effectiveness of Temporary Block Fracturing Technology
5.2. Quantitative Analysis of the Degree of Difference in Fluid Inflow Through Cracks
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Increased fracture spacing mitigates stress shadow effects and improves fracture propagation uniformity. Expanding fracture spacing from 10 to 20 m enhances the propagation length of central fractures by 38.2% and elevates fracture width uniformity by 21.5%. Notably, the number of perforation clusters exhibits an optimal threshold, as excessive cluster proliferation may induce adverse operational effects.
- (2)
- Increasing perforation friction pressure (7.5 MPa) optimizes fluid allocation between edge and central fractures, suppressing fluid distribution imbalance. Under high-friction conditions, fracture propagation uniformity and stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) outperform those under low-friction scenarios, with fluid allocation progressively approaching equilibrium.
- (3)
- Temporary plugging fracturing technology enhances central fracture propagation capacity by dynamically adjusting fluid allocation and overcoming stress shadow effects. Post-plugging interventions reduce the fluid influx differentiation coefficient within the fracture system by 76% and increase the stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) by 32%.
- (4)
- The tensile strength heterogeneity between perforation clusters significantly governs fracture propagation and fluid allocation. When the tensile strength difference exceeds 1 MPa, perforation friction proves insufficient to equilibrate pressure allocation. By optimizing perforation cluster placement guided by well logging data, the effects of mechanical heterogeneity can be effectively controlled.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Research on chemical temporary plugging agent for deep reservoir fracturing: Progress and prospect. Nat. Gas Ind. 2025, 45, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Practice and understanding of volume fracturing technology for horizontal wells in Jimsar shale oil reservoir. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2024, 20, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, H.; Tu, K. Fracture parameter diagnostic method during staged multi-cluster fracturing based on distributed temperature sensing. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2025, 52, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Z. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional vertical fracture propagation model under the influence of bedding. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2024, 20, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, N.; Shen, G.; Chang, X.; Yu, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.; et al. Fracturing with Carbon Dioxide: From Microscopic Mechanism to Reservoir Application. Joule 2019, 3, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, K.; Deng, P.; Chen, B.; Shen, L.; Chen, Z. The impact of pressurization-induced decrease of capillary pressure and residual saturation on geological carbon dioxide storage. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 486, 144573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.K.; Waters, G.A.; Rylander, E.I. Evaluation of Production Log Data from Horizontal Wells Drilled in Organic Shales. In Proceedings of the SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 14 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, L.; Xiang, Y.; Cheng, N.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H. Numerical simulation of fracture propagation pattern in the presence of gravel. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2023, 19, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yan, T.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Sheng, S.; Zhou, F. The integrated simulation of fracture propagation and seepage studied by using a coupled phase field and fracture flow method. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2025, 10, 192–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Xi, Y.; Wang, C. Study on dynamic stress field of fracturing in horizontal wells of deep coal seams: A case study of Daning-Jixian block in Ordos Basin. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2025, 15, 310–323. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Research on the Fracture Propagation Law at the Deep Shale under Differentiated Perforation. Drill. Prod. Technol. 2025, 48, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.K.; Heinze, J.R.; Harris, C.D.; Davidson, B.M.; Wright, C.A.; Dunn, K.P. Optimizing Horizontal Completion Techniques in the Barnett Shale Using Microseismic Fracture Mapping. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 26 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshy, A. Dynamic Interaction within Multiple Limited Entry Fractures in Horizontal Wells: Theory, Implications and Field Verification. In Proceedings of the SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 3 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wheaton, B.; Miskimins, J.; Wood, D.; Lowe, T.; Barree, R. Integration of distributed temperature and distributed acoustic survey results with hydraulic fracture modeling; a case study in the Woodford Shale. Seg Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2015, 34, 4926–4927. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G.; Lilly, T.B.; Tymons, T.R. Improved Well Stimulation Through the Application of Downhole Video Analytics. In Proceedings of the SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 23 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe, R.; Acock, A.; Fisher, K.; Viswanathan, A.; Chadwick, C.; Reischman, R.; Wigger, E. Eagle Ford Completion Optimization Using Horizontal Log Data. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El Rabaa, W. Experimental Study of Hydraulic Fracture Geometry Initiated From Horizontal Wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, A. Hydraulic Fracturing Optimization; Experimental Investigation of Multiple Fracture Growth Homogeneity via Perforation Cluster Distribution. Doctoral Dissertation, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Germanovich, L.N.; Ring, L.M.; Astakhov, D.K.; Shlyapobersky, J.; Mayerhofer, M.J. Hydraulic fracture with multiple segments II. Modeling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1997, 34, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cai, B.; Geng, M.; Jia, A.; Weng, D.; Liang, T.; Zhang, F.; Wen, X.; Xiu, N. Three dimensional simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation based on vertical reservoir heterogeneity. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Mei, W.; Li, L.; Sun, Z.; An, Q.; Yang, Q.; Lu, M.; Yang, R. Propagation of hydraulic fractures in thin interbedded tight sandstones. Coal Geol. Explor. 2023, 51, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lecampion, B.; Desroches, J. Simultaneous initiation and growth of multiple radial hydraulic fractures from a horizontal wellbore. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2015, 82, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Olson, J.E. Simultaneous Multifracture Treatments: Fully Coupled Fluid Flow and Fracture Mechanics for Horizontal Wells. SPE J. 2014, 20, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Xu, G. The Effects of Perforation Erosion on Practical Hydraulic-Fracturing Applications. SPE J. 2017, 22, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, F.J.; Zou, Y.S.; Gao, L.Y.; Hu, J.; Gu, X.L. Numerical simulation method of fracture interaction during temporary plugging staged fracturing. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2018, 25, 506–509. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, S.; She, C.; Zheng, M.; Wang, D.; Lu, C.; Tang, X. Simulation of segmented multi-cluster fracturing fracture competitive propagation in horizontal wells considering flow allocation. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2025, 32, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Gu, M.Z.; Wang, T.Y.; Tian, S.C. Non-uniform perforation to balance multi-cluster fractures propagation and parameter optimization. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2024, 20, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Dong, Z.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Quantitative evaluation of frac hits based on shut-in pressure drop curve: Taking shale oil platform wells in Jimsar as an example. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2024, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Izadi, G.; Settgast, R.; Moos, D.; Baba, C.; Jo, H. Fully 3D Hydraulic Fracture Growth within Multi-Stage Horizontal Wells. In Proceedings of the 13th ISRM International Congress of Rock Mechanics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Olson, J.E. Mechanisms of Simultaneous Hydraulic-Fracture Propagation From Multiple Perforation Clusters in Horizontal Wells. SPE J. 2016, 21, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Olson, J.; Balhoff, M.T.; Yu, W. Numerical Analysis for Promoting Uniform Development of Simultaneous Multiple-Fracture Propagation in Horizontal Wells. Spe Prod. Oper. Prod. Oper. 2016, 32, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, A.; Detournay, E. An implicit level set method for modeling hydraulically driven fractures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2008, 197, 2858–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.J. The Finite Element Method: An Introduction with Partial Differential Equations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Chen, S.B.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, H.J. Hydraulic fracturing simulation technology of shale gas reservoir and application of extended finite element method. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Chen, W.; Yuan, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, J. 3-D numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing in a CBM reservoir. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 37, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jeffrey, R.G.; Zhang, X.; Kear, J. Finite-Element Simulation of a Hydraulic Fracture Interacting With a Natural Fracture. SPE J. 2017, 22, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Tan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Hydraulic fracture height growth law for deep coal measures shale reservoir. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2021, 28, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, T.J.; Ingraffea, A.R. A numerical procedure for simulation of hydraulically-driven fracture propagation in poroelastic media. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1990, 14, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Hydraulic fracture propagation in naturally fractured reservoirs: Complex fracture or fracture networks. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 68, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, J.B.; Conway, M.W. Effects of Perforation-Entry Friction on Bottomhole Treating Analysis. J. Pet. Technol. Pet. Technol. 1988, 40, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Sun, Z.; Llu, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, F.; Wang, B. Optimization of perforation friction during limited entry fracturing of Jimsar shale oil reservoir. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 37, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhou, F.; Yuan, L.; Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, G.; Han, S. Numerical modeling of multiple fractures competition propagation in the heterogeneous layered formation. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 3737–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, S.W. Friction-Factor Equation Spans All Fluid-Flow Regimes. 1977. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=PASCAL7860099142 (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z. Numerical simulation on staged multi-cluster and cross-layer fracturing of horizontal well in coal seam roof. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2022, 29, 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.H.; Zhou, F.J.; Huang, G.P. A finite element simulation method for multi-fracture propagation in horizontal wells based on fluid pipe element. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2022, 46, 105–112. [Google Scholar]








| The Interlayer | Reservoir | |
|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus/GPa | 28 | 25 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| Tensile strength /MPa | 5 | 3 |
| Effective stress (X, Y, Z)/MPa | 18/21/20 | 16/21/20 |
| Permeability | 1 × 10−7 | 1 × 10−7 |
| Porosity ratio | 0.0983 | 0.0983 |
| Viscosity/Pa·s | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B. Fracture Competitive Propagation and Fluid Dynamic Diversion During Horizontal Well Staged Hydraulic Fracturing. Processes 2025, 13, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072252
Yan Y, Wang Y, Li H, Wang Q, Wang B. Fracture Competitive Propagation and Fluid Dynamic Diversion During Horizontal Well Staged Hydraulic Fracturing. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072252
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yujie, Yanling Wang, Hui Li, Qianren Wang, and Bo Wang. 2025. "Fracture Competitive Propagation and Fluid Dynamic Diversion During Horizontal Well Staged Hydraulic Fracturing" Processes 13, no. 7: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072252
APA StyleYan, Y., Wang, Y., Li, H., Wang, Q., & Wang, B. (2025). Fracture Competitive Propagation and Fluid Dynamic Diversion During Horizontal Well Staged Hydraulic Fracturing. Processes, 13(7), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072252








