Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Sustainable Farming Compartment with Evaporative Cooling System
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Sustainable Farming Compartment (SFC)
1.2. Evaporative Cooling System
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Prototype SFC
2.2. Dynamic Numerical Simulation of SFC
2.2.1. Governing Equations of Mathematical Model
2.2.2. Numerical Method
3. Results
3.1. Variation of Temperature and Humidity in a Controlled Condition
3.2. Variation of Temperature and Humidity during the Prototype SFC Test
3.3. Validation of Numerical Simulation
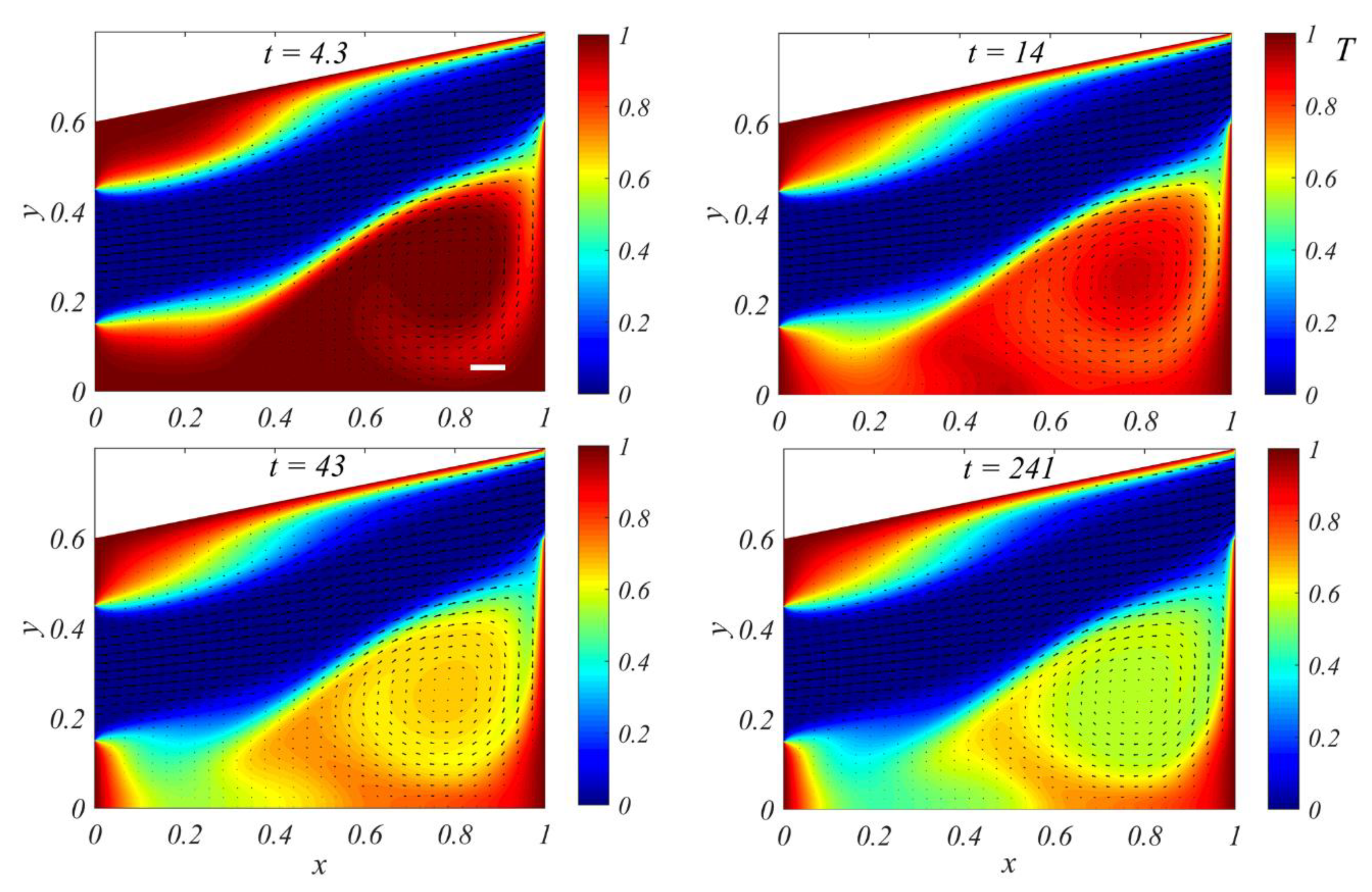
3.4. Comparisons of Temperature between Simulation and Experiment
4. Discussion
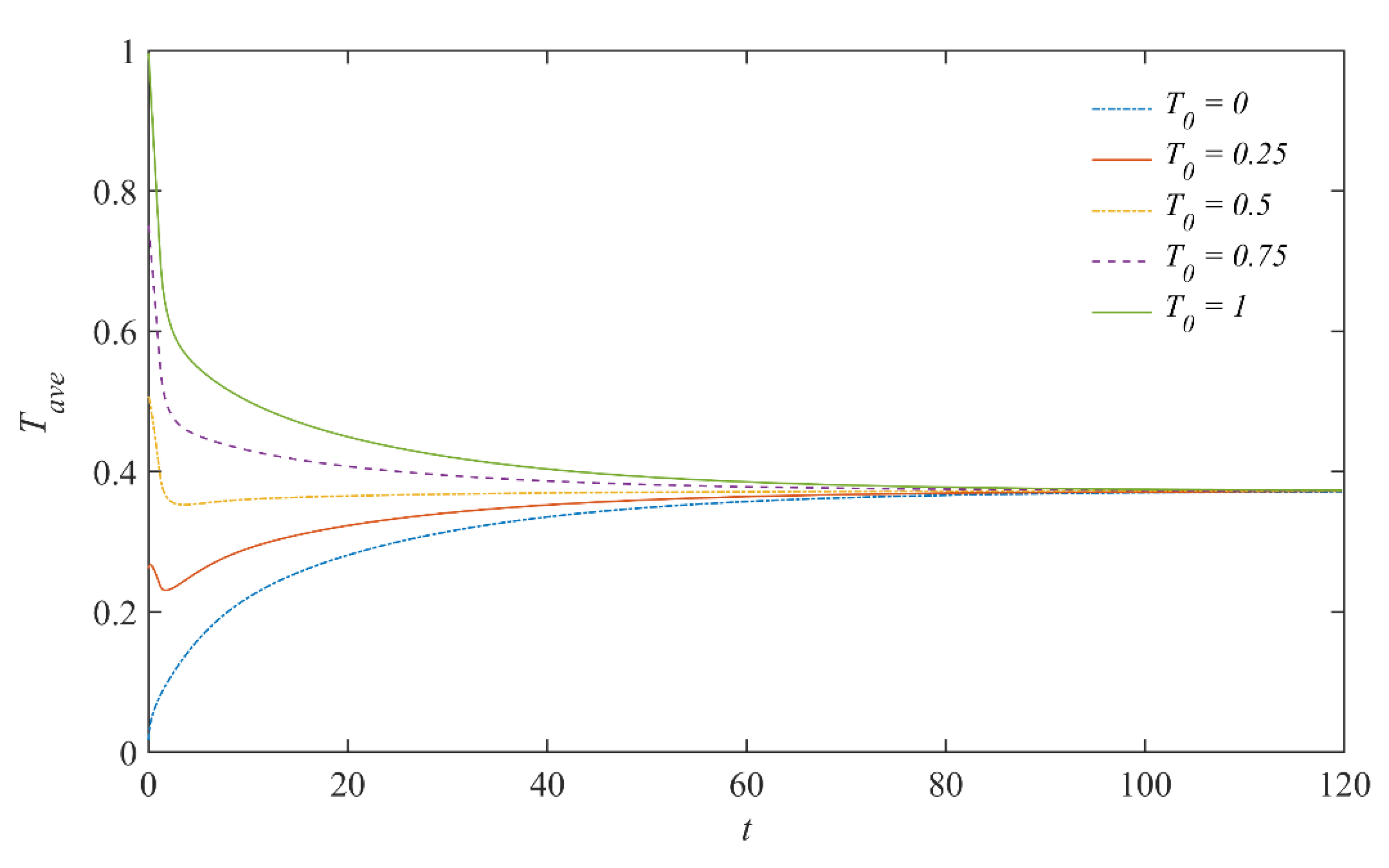
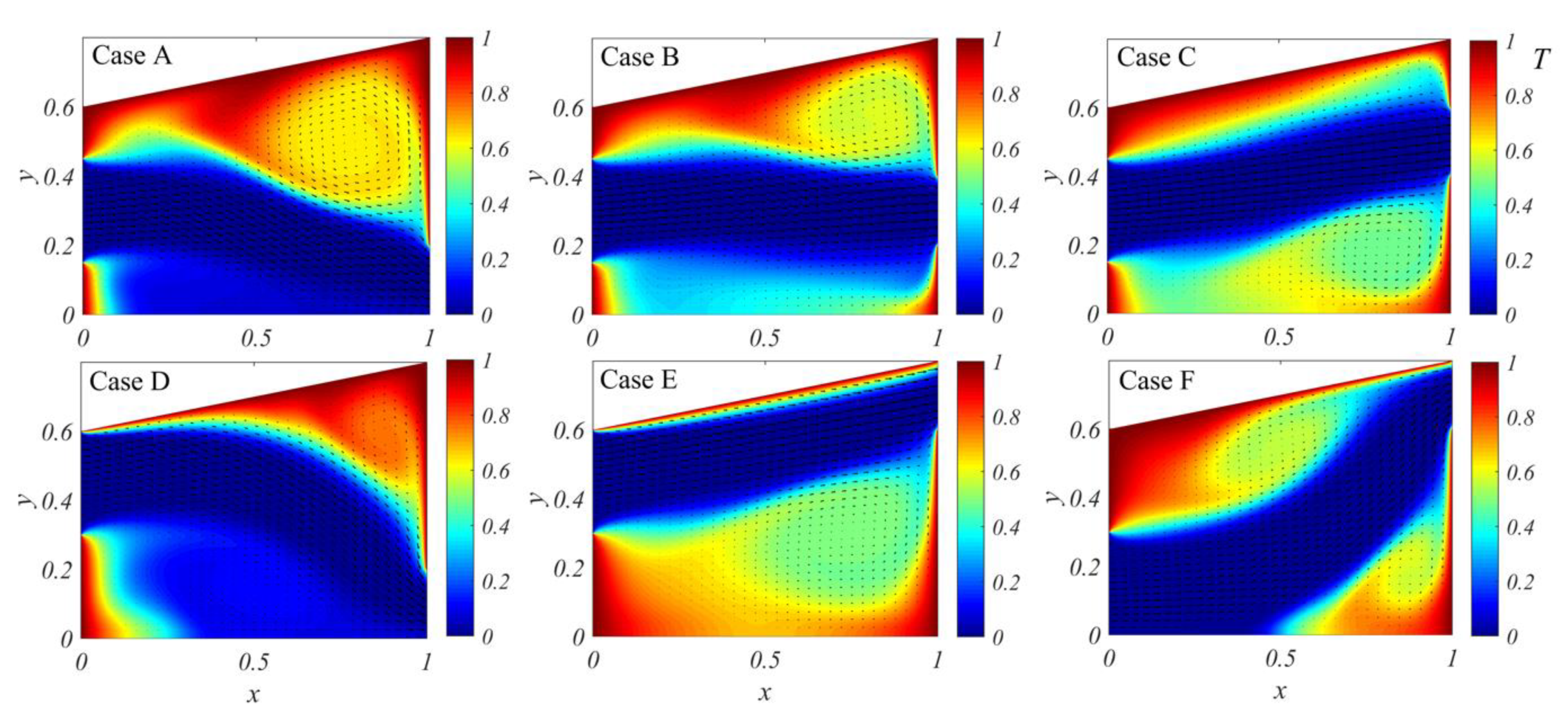
4.1. Numerical Parametric Studies on Inlet and Outlet Locations
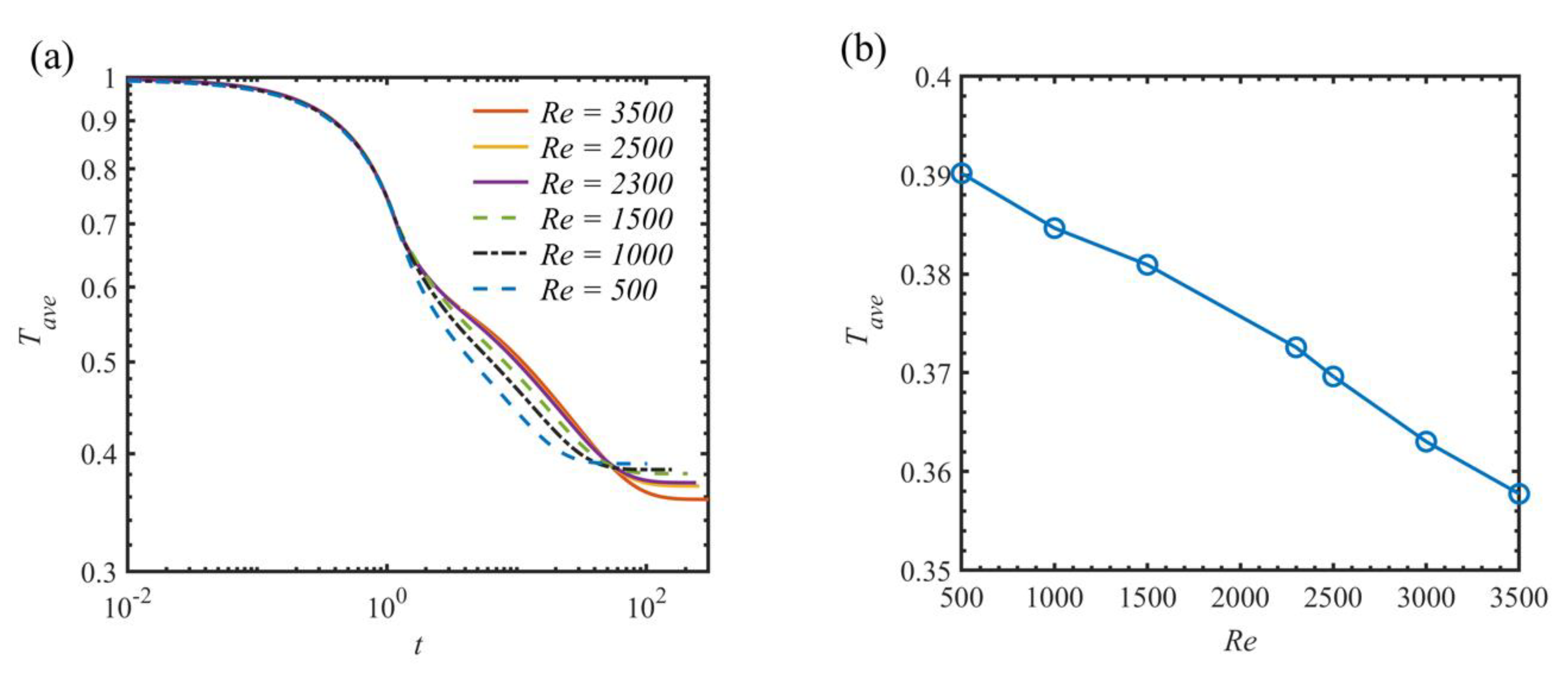
4.2. Numerical Parametric Studies on Reynolds Number
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNCCD. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification; UNCCD: Bonn, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfattah, M.A.; Dawoud, M.A.H.; Shahid, S.A. Soil and water management for combating desertification–towards the implementation of the United Nations Convention to combat desertification from the UAE perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Soil Degradation, Riga, Latvia, 17–19 February 2009; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfattah, M.A. Land degradation indicators and management options in the desert environment of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Soil Horiz. 2009, 50, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abahussain, A.A.; Abdu, A.S.; Al-Zubari, W.K.; El-Deen, N.A.; Abdul-Raheem, M. Desertification in the Arab region: Analysis of current status and trends. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 51, 521–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Reynolds, J.F.; Cunningham, G.L.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jarrell, W.M.; Virginia, R.A.; Whitford, W.G. Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science 1990, 247, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böer, B. An introduction to the climate of the United Arab Emirates. J. Arid Environ. 1997, 35, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAD. Maximizing recycled water use in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. In Annual Policy Brief; EAD: Abi Dhabi, UAE, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- “The National”, UAE. Available online: http://www.thenational.ae/uae/environment/plans-to-reuse-100-of-abu-dhabis-waste-water-in-four-years (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- Sahara Forest Project. 2017. Available online: https://www.saharaforestproject.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/SFP_-_Intro.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2017).
- Hatfield, J.L.; Prueger, J.H. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2015, 10, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.R.; Ebinuma, C.D.; Silveira, J.L. Experimental performance of a direct evaporative cooler operating during summer in a Brazilian city. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H. Theoretical analysis on heat and mass transfer in a direct evaporative cooler. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H. Numerical investigation on heat and mass transfer in a direct evaporative cooler. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabat, P.; Marchio, D.; Orphelin, M. Pre-Design and design tools for evaporative cooling. ASHRAE Trans. 2001, 107, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.; Shao, L.; Riffat, S.B. Performance of porous ceramic evaporators for building the cooling application. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsatitthanakorn, C.; Rerngwongwitaya, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Field experiments and economic evaluation of an evaporative cooling system in a silkworm rearing house. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarinejad, G.; Bozorgmehr, M.; Delfani, S.; Esmaeelian, J. Experimental investigation of two-stage indirect/direct evaporative cooling system in various climatic conditions. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljubury, I.M.A.; Ridha, H.D.A. Enhancement of evaporative cooling system in a greenhouse using geothermal energy. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperetti, A.; Tryggvason, G. Computational Methods for Multiphase Flow; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Harlow, F.H.; Welch, J.E. Numerical calculation of time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with a free surface. Phys. Fluids 1965, 8, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferziger, J.H.; Peric, M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Moin, P. Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 59, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.B.; Colella, P.; Glaz, H.M. A second-order projection method for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1989, 85, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Anthony, M.J. A run-around heat exchanger system to improve the energy efficiency of a home appliance using hot water. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Lakshminarayana, B.; Barnett, M. Low-Reynolds-number k-epsilon model for unsteady turbulent boundary-layer flows. AIAA J. 1993, 31, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasculli, A. CFD-FEM 2D Modeling of a local water flow. Some numerical results. Ital. J. Quat. Sci. 2008, 21, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pasculli, A. Viscosity variability impact on 2D laminar and turbulent poiseuille velocity profiles; characteristic-based split (CBS) stabilization. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Conference on Mathematics and Computers in Sciences and Industry (MCSI), Corfu, Greece, 25–27 August 2018; pp. 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- “World Weather Online”. Available online: https://www.worldweatheronline.com/ (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- Incropera, F.P.; Adrienne, S.L.; Theodore, L.B.; David, P.D. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]








| Type | Material | Thermal Conductivity W·m−1·K−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | Aluminum | 101.8 |
| Walls Bottom | Plexiglass Plywood | 0.20 0.16 |
| Roof | Plexiglass Styrene sheet | 0.20 0.033 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mousavi, M.S.; Mirfendereski, S.; Park, J.S.; Eun, J. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Sustainable Farming Compartment with Evaporative Cooling System. Processes 2019, 7, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110823
Mousavi MS, Mirfendereski S, Park JS, Eun J. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Sustainable Farming Compartment with Evaporative Cooling System. Processes. 2019; 7(11):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110823
Chicago/Turabian StyleMousavi, M. Sina, Siamak Mirfendereski, Jae Sung Park, and Jongwan Eun. 2019. "Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Sustainable Farming Compartment with Evaporative Cooling System" Processes 7, no. 11: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110823
APA StyleMousavi, M. S., Mirfendereski, S., Park, J. S., & Eun, J. (2019). Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Sustainable Farming Compartment with Evaporative Cooling System. Processes, 7(11), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110823








