Simple Alternatives to PID-Type Control for Processes with Variable Time-Delay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Fractional Order Controller with Adaptive Law
- if , then
- if , then
- if , then
- if , then
- if , then
- if , then
3. Realization of Fractional-Order Controllers
- Step 1: Discretize FOC using a generating function.This function has been proposed as an interpolation between Euler and Tustin discretization rules:with the weighting parameter and being the sampling period, with special cases for (Euler discretization) and for (Tustin discretization).
- Step 2: Calculate the frequency response of the obtained discrete-time fractional-order system.This is done by substituting with .
- Step 3: Calculate the impulse response of the discrete-time fractional-order system.This step employs the inverse Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), which converts the previously computed frequency domain response into a time domain response.
- Step 4: Identify a rational discrete time transfer function that produces a similar impulse response as that obtained from the inverse FFT.
4. Stability of Fractional-Order Controllers
5. Integer-Order Controllers for Time Delay Systems
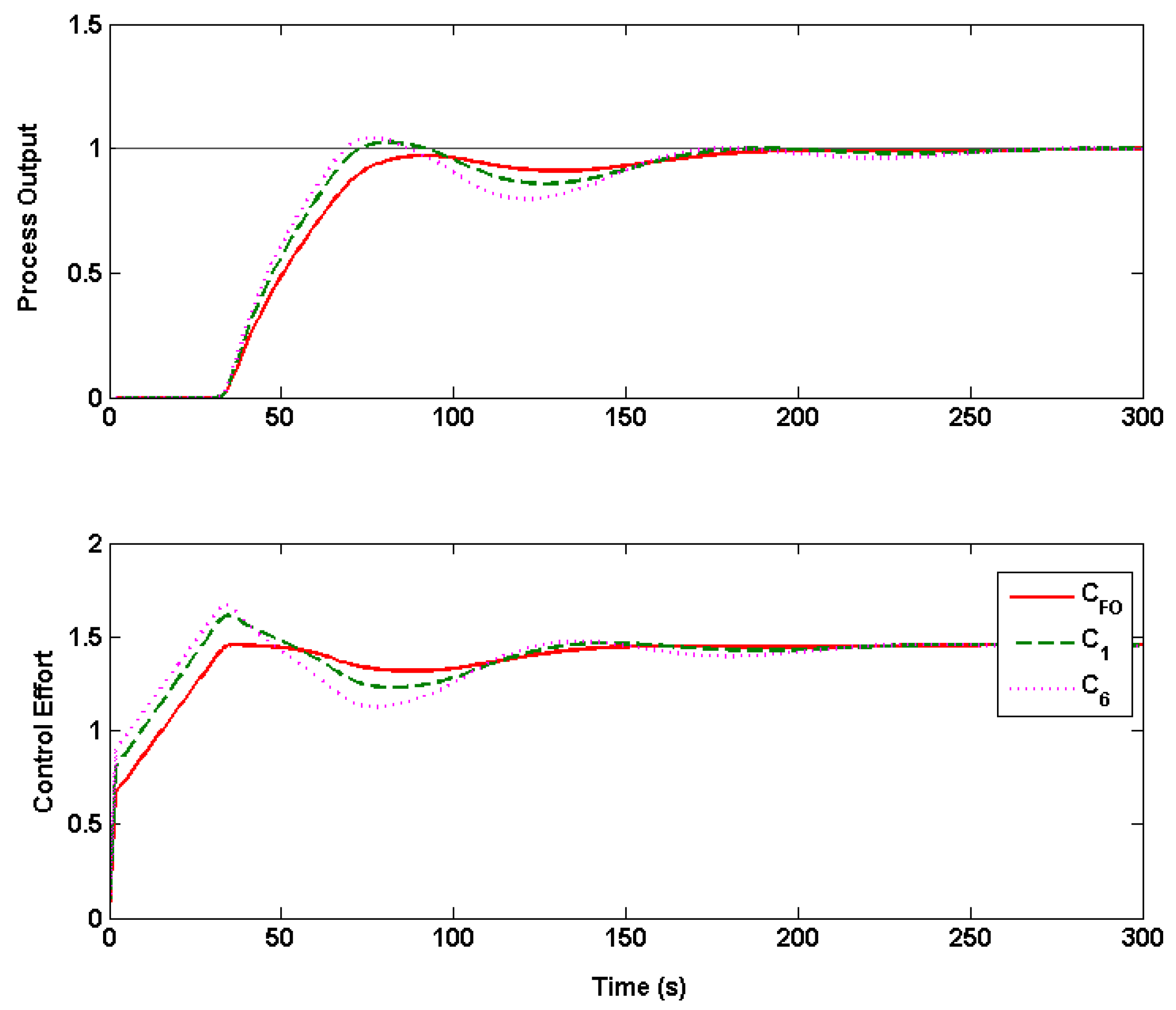
6. Case Studies of Variable Time Delay Processes
6.1. Case Study 1: Quality Control in Continuous Steel Casting
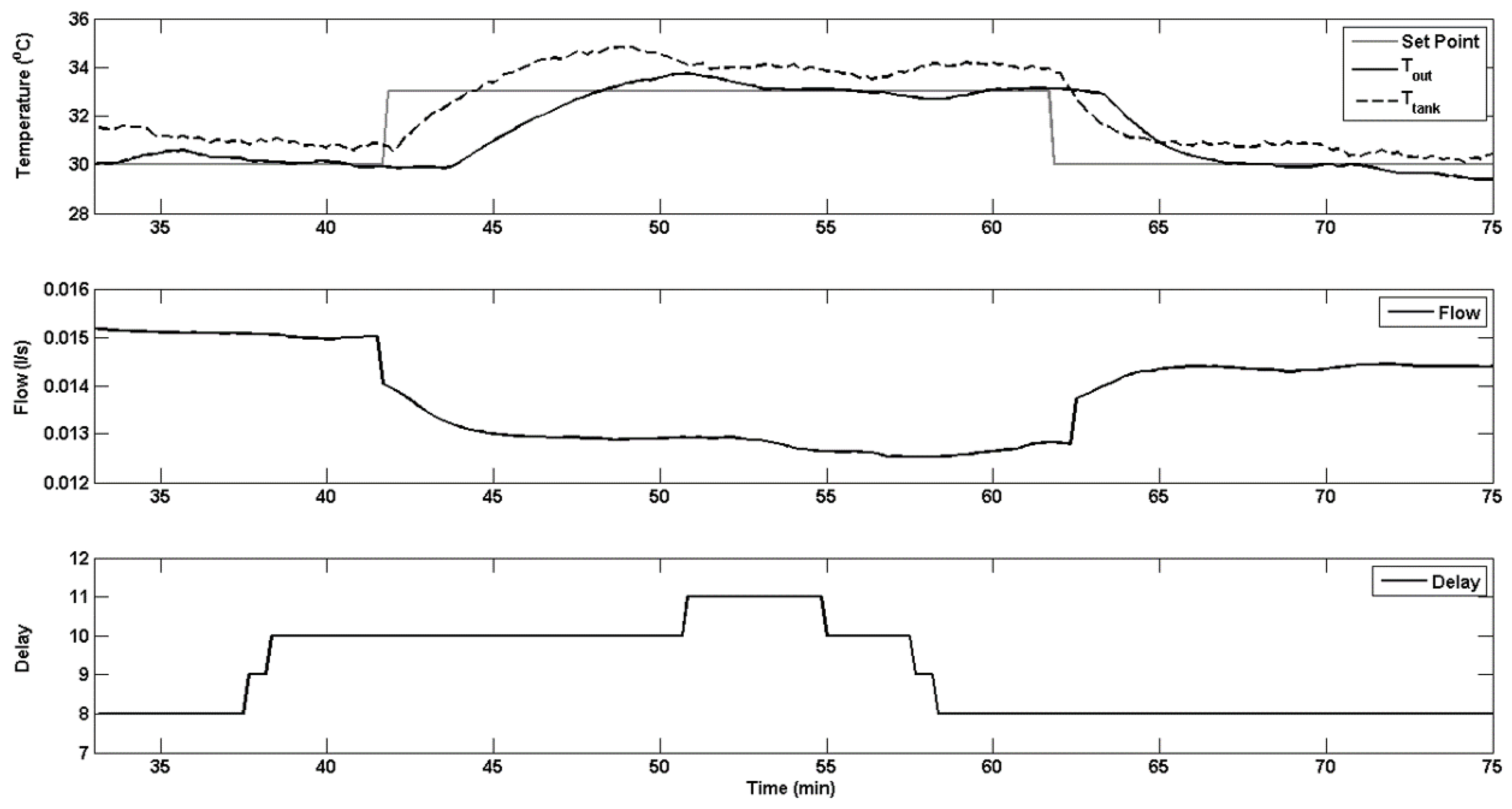
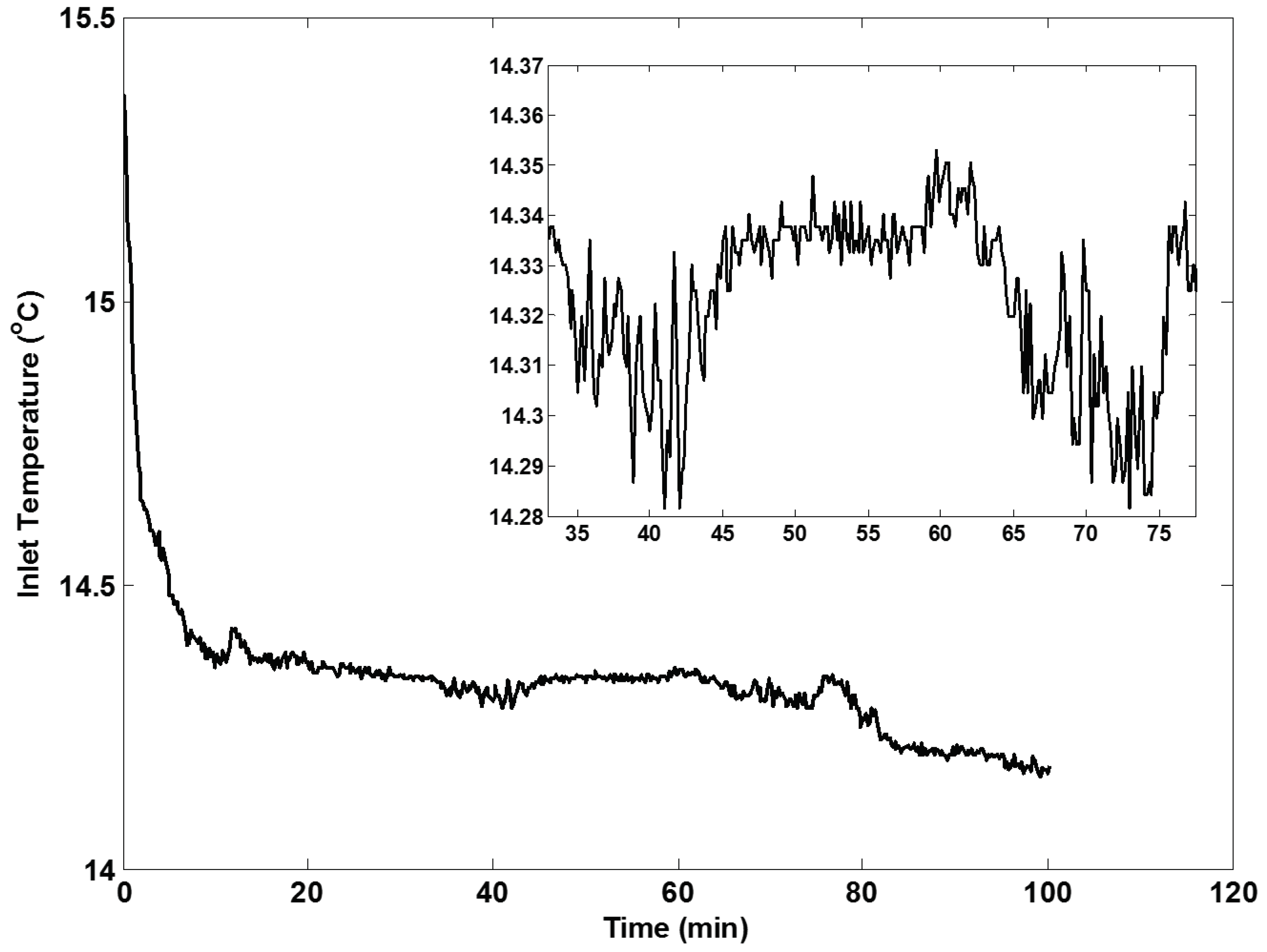
6.2. Case Study 2: Temperature Control
6.2.1. Real-Time Implementation
- Design and test the controller in MATLAB/Simulink;
- Create an Embedded function with the designed controller;
- Create and configure the dynamic-link library (dll);
- Define the path in the LabVIEW interface;
- Select and configure the parameters of the inputs and outputs function in call library functions;
- Define the path to save data, save the VI project, and test the controller.
6.2.2. Real-Time Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Starr, K.; Petersen, H.; Bauer, M. Control loop performance monitoring—ABB’s experience over two decades. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aström, K.J.; Hägglund, T. Advanced PID Control; Instrument Society of America: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Hasimoto, I. Present status and future needs: The view from Japanese industry. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Chemical Process Control, Padre Island, TX, USA, 17–22 February 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, T. A survey on industry impact and challenges thereof. IEEE Control Syst. 2017, 37, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer M, I. Craig, Economic assessment of advanced process control—A survey and framework. J. Process Control 2008, 18, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional-order systems and PIλDμ-controllers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1999, 44, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, I.; Dorcak, L.; Kostial, I. Control quality enhancement by fractional order controllers. Acta Montan. Slovaca 1998, 3, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tepljakov, A.; Alagoz, B.; Yeroglu, C.; Gonzalez, E.; Hosseinnia, H.; Petlenkov, E. FOPID controllers and their industrial applications: A survey of recent results. In Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Fei, S. Analysis of actuator rate limit effects on first-order plus time-delay systems under fractional order proportional integral control. In Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Oustaloup, A. La Dérivation non Entière: Théorie, Synthèse et Applications; Hermes: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.; Craig, I. CRONE control system design toolbox for the control engineering community: Tutorial and case study. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2008, 18, 2–18. [Google Scholar]
- van Duist, L.; van der Gigten, G.; Toten, D.; Saikumar, N.; Hosseinnia, H. FLOreS—Fractional Order Loop Shaping MATLAB Toolbox. In Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Cech, M. Web based fractional PID controller design: www.pidlab.com. In Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 563–568. [Google Scholar]
- Normey-Rico, J. Control of Dead-Time Processes; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sbarciog, M.; De Keyser, R.; Cristea, S.; de Prada, C. Nonlinear predictive control of processes with variable time delay. A temperature control case study. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Part of IEEE MCSC, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, C.; Ionescu, C.; De Keyser, R.; Dulf, E. Robustness evaluation of fractional order control for varying time delay processes. Signal Image Video Process. 2012, 6, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Ionescu, C.; Keyser, R.D. Time delay compensation for the secondary processes in a multivariable carbon isotope separation unit. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, I.; Vinagre, B. Practical application of digital fractional order controller to temperature control. Acta Montan. Slovaka 2002, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Åström, K.; Hägglund, T. Revisiting the Ziegler-Nichols step response method for PID control. J. Process Control 2004, 14, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nise, N. Control Systems Engineering; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.; De Keyser, R. The next generation of relay-based PID autotuners (PART1): Some insights on the performance of simple relay-based PID autotuners. In Proceedings of the IFAC Conference on Advances in PID Control (PID’12), Brescia, Italy, 28–30 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vilanova, R.; Visioli, A. PID Control in the Third Millenium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Monje, C.; Vinagre, B.; Feliu, V.; Chen, Y. Tuning and auto-tuning of fractional order controllers for industry applications. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monje, C.; Chen, Y.; Vinagre, B.; Xue, D.; Feliu, V. Fractional-order Systems and Controls: Fundamentals and Applications. In Advances in Industrial Control; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Keyser, R.; Muresan, C.; Ionescu, C. A novel auto-tuning method for fractional order PI/PD controllers. ISA Trans. 2016, 62, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keyser, R.; Muresan, C.I.; Ionescu, C.M. An efficient algorithm for low-order direct discrete-time implementation of fractional order transfer functions. ISA Trans. 2018, 74, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.; Park, J.H. A novel Lyapunov functional for stability of time-varying delay systems via matrix-refined-function. Automatica 2017, 80, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keyser, R.; Ionescu, C. FRtool: A frequency response tool for CACSD in Matlab. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Aided Control Systems Design, Munich, Germany, 4–6 October 2006; pp. 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Skogestad, S. Simple analytic rules for model reduction and PID controller tuning. J. Process Control 2003, 13, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimholt, C.; Skogestad, S. Should we forget the Smith Predictor? In Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Dekemele, K.; Ionescu, C.; Doncker, M.D.; Keyser, R.D. Closed loop control of an electromagnetic stirrer in the continuous casting process. In Proceedings of the European Control Conference, Aalborgh, Denmark, 29 June–1 July 2016; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vinagre, B.; Chen, Y.; Petráš, I. Two direct Tustin discretization methods for fractional-order differentiator/integrator. J. Frankl. Inst. 2003, 340, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Notation | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| water density | 1 | kg/ℓ | |
| time constant of the tube transfer function | 11.1 | - | |
| specific heat coefficient of water | 4186 | J/(kg C) | |
| gain of the tube transfer function | 0.95 | - | |
| Q | amount of heat | 2000 | W |
| inlet temperature | 12 | C | |
| sampling period | 4 | s | |
| V | volume of the tank | 0.35 | ℓ |
| volume of the tube | 1.7 | ℓ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Copot, D.; Ghita, M.; Ionescu, C.M. Simple Alternatives to PID-Type Control for Processes with Variable Time-Delay. Processes 2019, 7, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030146
Copot D, Ghita M, Ionescu CM. Simple Alternatives to PID-Type Control for Processes with Variable Time-Delay. Processes. 2019; 7(3):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030146
Chicago/Turabian StyleCopot, Dana, Mihaela Ghita, and Clara M. Ionescu. 2019. "Simple Alternatives to PID-Type Control for Processes with Variable Time-Delay" Processes 7, no. 3: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030146
APA StyleCopot, D., Ghita, M., & Ionescu, C. M. (2019). Simple Alternatives to PID-Type Control for Processes with Variable Time-Delay. Processes, 7(3), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030146







