Optimal Design of a Carbon Dioxide Separation Process with Market Uncertainty and Waste Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
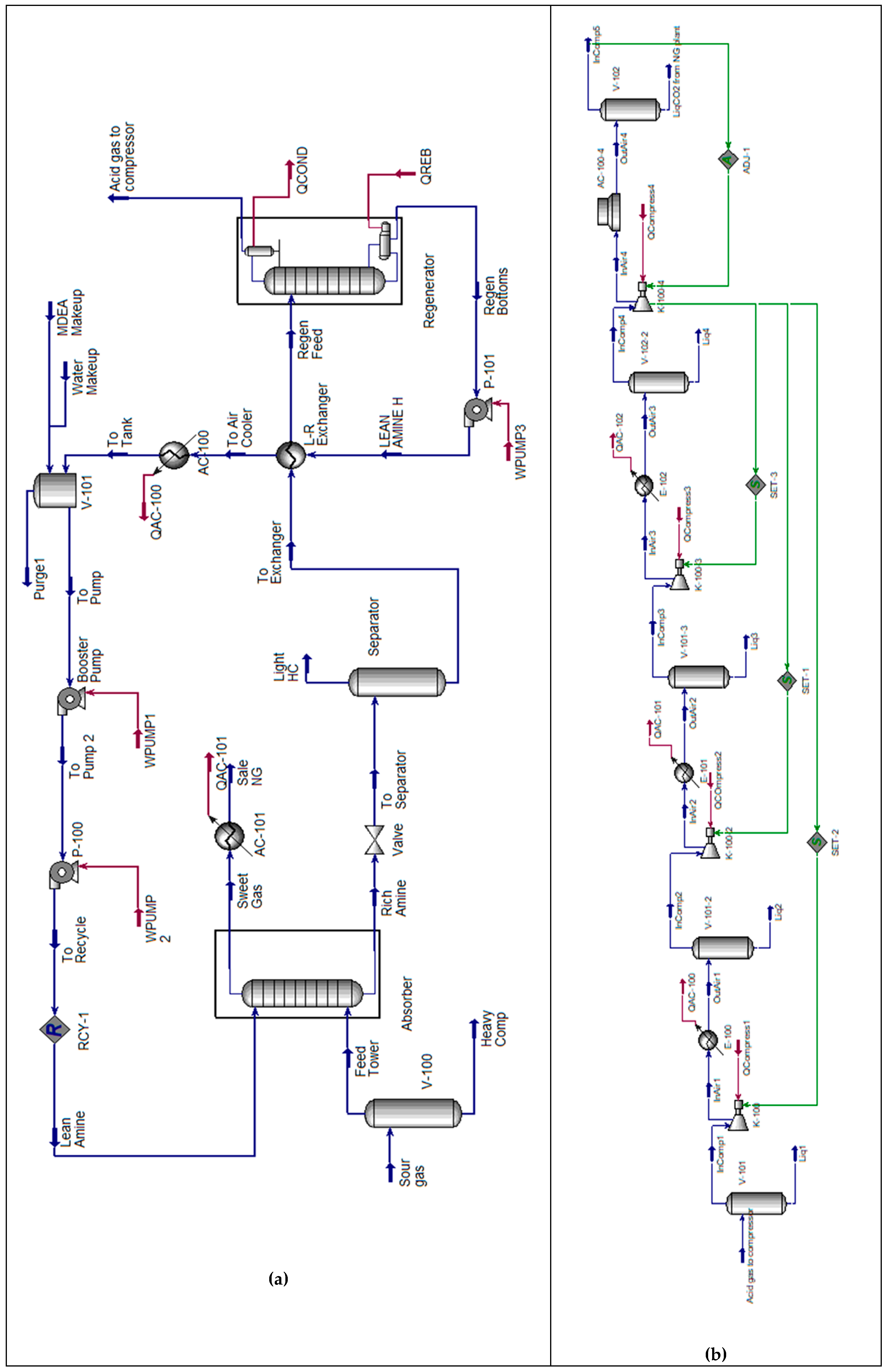
2. Process Description
3. Methods
3.1. Simulation Base Case
3.2. Predictive Concept Design
3.2.1. Development of Econometric Models
3.2.2. Formulation of the Economic Optimization
3.3. Waste Reduction Algorithm
4. Results
4.1. Simulation Output
4.2. Economic Scenarios
4.2.1. Correlation
4.2.2. Econometric Models
4.3. Optimal Economic and Environmental Friendly Design
4.3.1. DEP4 Cumulated
4.3.2. Economic Optimal
4.3.3. Minimal Environmental Risks
5. Conclusions and Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roussanaly, S.; Grimstad, A.-A. The Economic Value of CO2 for EOR Applications. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 7836–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haszeldine, R.S. Carbon capture and storage: How green can black be? Science 2009, 325, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, I.W.; Lee, A.; Middleton, P.; Lowe, C.; Imbus, S.W.; Miracca, I. CO2 Capture Project: Initial Results. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Health, Safety, and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Calgary, AB, Canada, 29–31 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mumford, K.A.; Wu, Y.; Smith, K.H.; Stevens, G.W. Review of solvent based carbon-dioxide capture technologies. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brush, R.M.; Davitt, H.J.; Aimar, O.B.; Arguello, J.; Whiteside, J.M. Immiscible CO2 flooding for increased oil recovery and reduced emissions. In Proceedings of the SPE/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Tulsa, Oklahoma, 3–5 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzetti, M.J.; Skagestad, R.; Mathisen, A.; Eldrup, N.H. CO2 from natural gas sweetening to kick-start EOR in the North Sea. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 7280–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, H.J. Scaling up carbon dioxide capture and storage: From megatons to gigatons. Energy Econ. 2011, 33, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-H.; Yun, D.; Binns, M.; Yeo, Y.-K.; Kim, J.-K. Conceptual process design of CO2 recovery plants for enhanced oil recovery applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14385–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chávez-Rodríguez, M.; Varela, D.; Rodrigues, F.; Salvagno, J.B.; Köberle, A.C.; Vasquez-Arroyo, E.; Raineri, R.; Rabinovich, G. The role of LNG and unconventional gas in the future natural gas markets of Argentina and Chile. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 45, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzo, R.; Dyner, I.; Arango, S.; Larsen, E.R. Regulation and development of the Argentinean gas market. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolas, D.A.; Frangopoulos, C.A.; Gialamas, T.P.; Tsahalis, D.T. Operation optimization of an industrial cogeneration system by a genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 1997, 38, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.M. Conceptual Design of Chemical Processes; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 1110. [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen, G. Industrial best practices of conceptual process design. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepiacci, P.; Depetri, V.; Manca, D. A systematic approach to the optimal design of chemical plants with waste reduction and market uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 102, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, D.; Grana, R. Dynamic conceptual design of industrial processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, H.; Bare, J.C.; Mallick, S.K. Pollution prevention with chemical process simulators: The generalized waste reduction (WAR) algorithm—Full version. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1999, 23, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.P.; Ruiz, E.L.A.; Erdmann, E. Energy requirements, GHG emissions and investment costs in natural gas sweetening processes. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Erdmann, E. Potencialidad el EOR con CO2 en reservorios de baja permeabilidad de la cuenca Neuquina. In Congreso de Produccion y Desarrollo de Reservas; Instituto Argentino del Petroleo y Gas: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mores, P.; Scenna, N.; Mussati, S. Post-combustion CO2 capture process: Equilibrium stage mathematical model of the chemical absorption of CO2 into monoethanolamine (MEA) aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Scharp, R.; Cabezas, H. The waste reduction (WAR) algorithm: Environmental impacts, energy consumption, and engineering economics. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, E.; Ruiz, L.A.; Martínez, J.; Gutierrez, J.P.; Tarifa, E. Endulzamiento de gas natural con aminas. Simulación del proceso y análisis de sensibilidad paramétrico. Avances en Ciencias e Ingeniería. 2012, 3, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Green, D.W.; Perry, R.H. Chemical Engineers’ Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, W.A.; Berrouk, A.S. Using mixed tertiary amines for gas sweetening energy requirement reduction. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2013, 11, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Malayeri, M.; kharaji, A.G.; Shariati, A. Feasibility study, simulation and economical evaluation of natural gas sweetening processes—Part 1: A case study on a low capacity plant in iran. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 20, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.P.; Benitez, L.A.; Ale Ruiz, E.L.; Erdmann, E. A sensitivity analysis and a comparison of two simulators performance for the process of natural gas sweetening. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lagtah, N.M.; Al-Habsi, S.; Onaizi, S.A. Optimization and performance improvement of Lekhwair natural gas sweetening plant using Aspen HYSYS. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvamsdal, H.; Jakobsen, J.; Hoff, K. Dynamic modeling and simulation of a CO2 absorber column for post-combustion CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prölss, K.; Tummescheit, H.; Velut, S.; Åkesson, J. Dynamic model of a post-combustion absorption unit for use in a non-linear model predictive control scheme. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behroozsarand, A.; Zamaniyan, A. Multiobjective optimization scheme for industrial synthesis gas sweetening plant in GTL process. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2011, 20, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øi, L.E.; Bråthen, T.; Berg, C.; Brekne, S.K.; Flatin, M.; Johnsen, R.; Moen, I.G.; Thomassen, E. Optimization of configurations for amine based CO2 absorption using Aspen HYSYS. Energy Procedia 2014, 51, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.P.; Erdmann, E.; Manca, D. Multi-objective optimization of a CO2-EOR process from the sustainability criteria. In 28th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering; Elsevier: Graz, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Honeywell. UniSim Design; Honeywell International Inc.: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.; GadelHak, Y. Correlating the additional amine sweetening cost to acid gases load in natural gas using Aspen Hysys. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 17, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ortega, C.E.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Gómez-Castro, F.I.; Hernández, S.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Rong, B.-G.; Errico, M. Design, optimization and controllability of an alternative process based on extractive distillation for an ethane–carbon dioxide mixture. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2013, 74, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, D. A methodology to forecast the price of commodities. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Karimi, I.A., Srinivasan, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1306–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, D. Modeling the commodity fluctuations of OPEX terms. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2013, 57, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepiacci, P.; Manca, D. Economic assessment of chemical plants supported by environmental and social sustainability. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar]
- EIA. US Energy Information Administration. 2018. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/ (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Ministry-of-Energy. Reporte de Produccion. 2017; Presidencia de la Nacion Argentina. Available online: https://www.se.gob.ar/ (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Wiggins, S.; Etienne, X.L. Turbulent times: Uncovering the origins of US natural gas price fluctuations since deregulation. Energy Econ. 2017, 64, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Deng, Z.; Xia, Y.; Fu, M. A new sampling method in particle filter based on Pearson correlation coefficient. Neurocomputing 2016, 216, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Rodgers, J.; Nicewander, W.A. Thirteen ways to look at the correlation coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Salleh, F.H.; Arif, S.M.; Zainudin, S.; Firdaus-Raih, M. Reconstructing gene regulatory networks from knock-out data using Gaussian Noise Model and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 59, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancey, C.P.; Reidy, J. Statistics without Maths for Psychology; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D.; Cabezas, H. Designing sustainable processes with simulation: The waste reduction (WAR) algorithm. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1999, 23, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, A.A.; Mandagarán, B.A.; Campanella, E.A. Análisis del Impacto Ambiental de la Recuperación de Metanol en la Producción de Biodiesel usando el Algoritmo de Reducción de Desechos WAR. Inf. Tecnol. 2010, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, W.M.; van Baten, J.; Martin, T. Implementation of the waste reduction (WAR) algorithm utilizing flowsheet monitoring. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B. EORI’s Economic scoping model. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual EORI Casper CO2 Conference, Enhanced Oil Recovery Institute, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY, USA, 9 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzetto, F.; Ortiz-Gutiérrez, R.A.; Manca, D.; Bezzo, F. Strategic design of bioethanol supply chains including commodity market dynamics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10305–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, D. Price model of electrical energy for PSE applications. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 84, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, D. A methodology to forecast the price of electric energy. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 679–684. [Google Scholar]











| Component | Model |
|---|---|
| CO2 | |
| MDEA |
| Component | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG | 0.0362 | −0.0285 | 1.2205 | - | 0.1918 | 0.0705 |
| CO2 | 0.0033 | 0.0078 | 1.4167 | −0.4870 | 0.0606 | 0.0074 |
| MDEA | 0.1124 | 0.9731 | 0 | −0.0171 | 0.0126 | 0.0002 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutierrez, J.P.; Erdmann, E.; Manca, D. Optimal Design of a Carbon Dioxide Separation Process with Market Uncertainty and Waste Reduction. Processes 2019, 7, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060342
Gutierrez JP, Erdmann E, Manca D. Optimal Design of a Carbon Dioxide Separation Process with Market Uncertainty and Waste Reduction. Processes. 2019; 7(6):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060342
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutierrez, Juan Pablo, Eleonora Erdmann, and Davide Manca. 2019. "Optimal Design of a Carbon Dioxide Separation Process with Market Uncertainty and Waste Reduction" Processes 7, no. 6: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060342
APA StyleGutierrez, J. P., Erdmann, E., & Manca, D. (2019). Optimal Design of a Carbon Dioxide Separation Process with Market Uncertainty and Waste Reduction. Processes, 7(6), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060342




