A Novel Consensus Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Using Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Categorical Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Concepts
2.1. Three Basic Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Algorithms
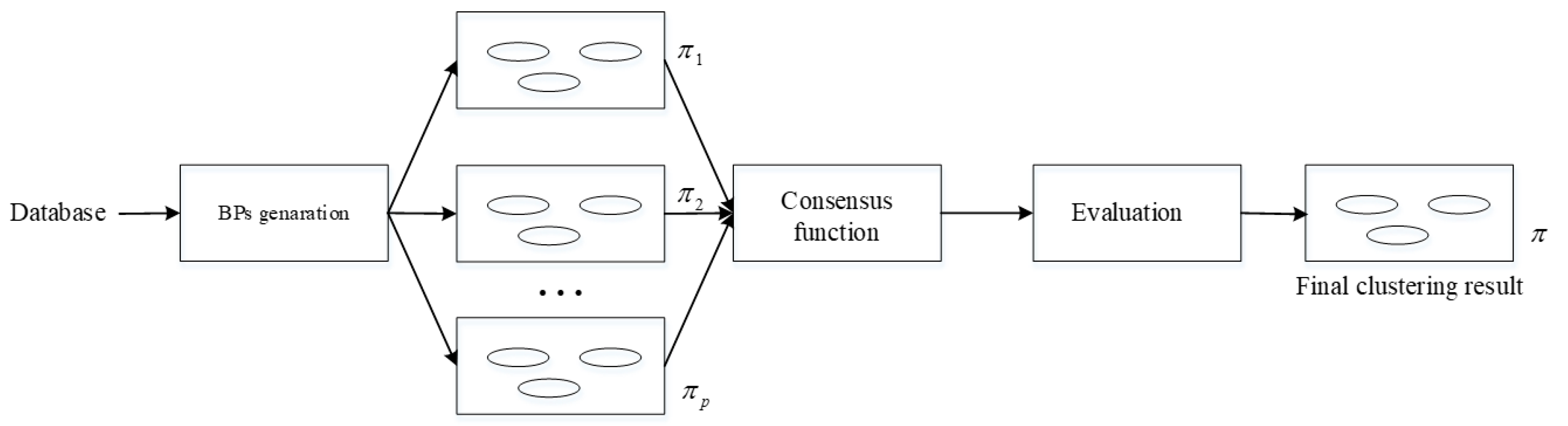
2.2. Consensus Clustering
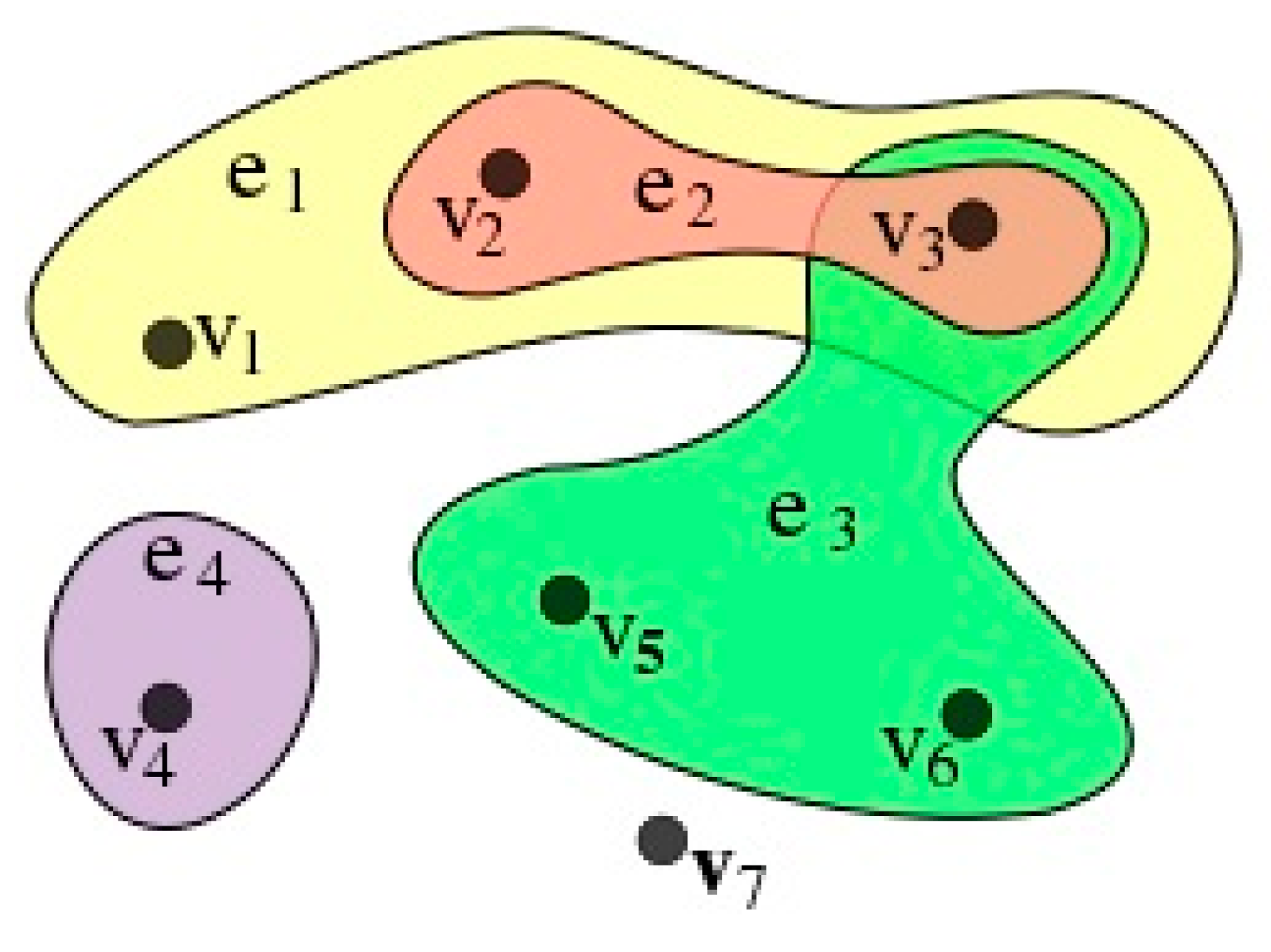
2.3. Chain and Hypergraph Structure
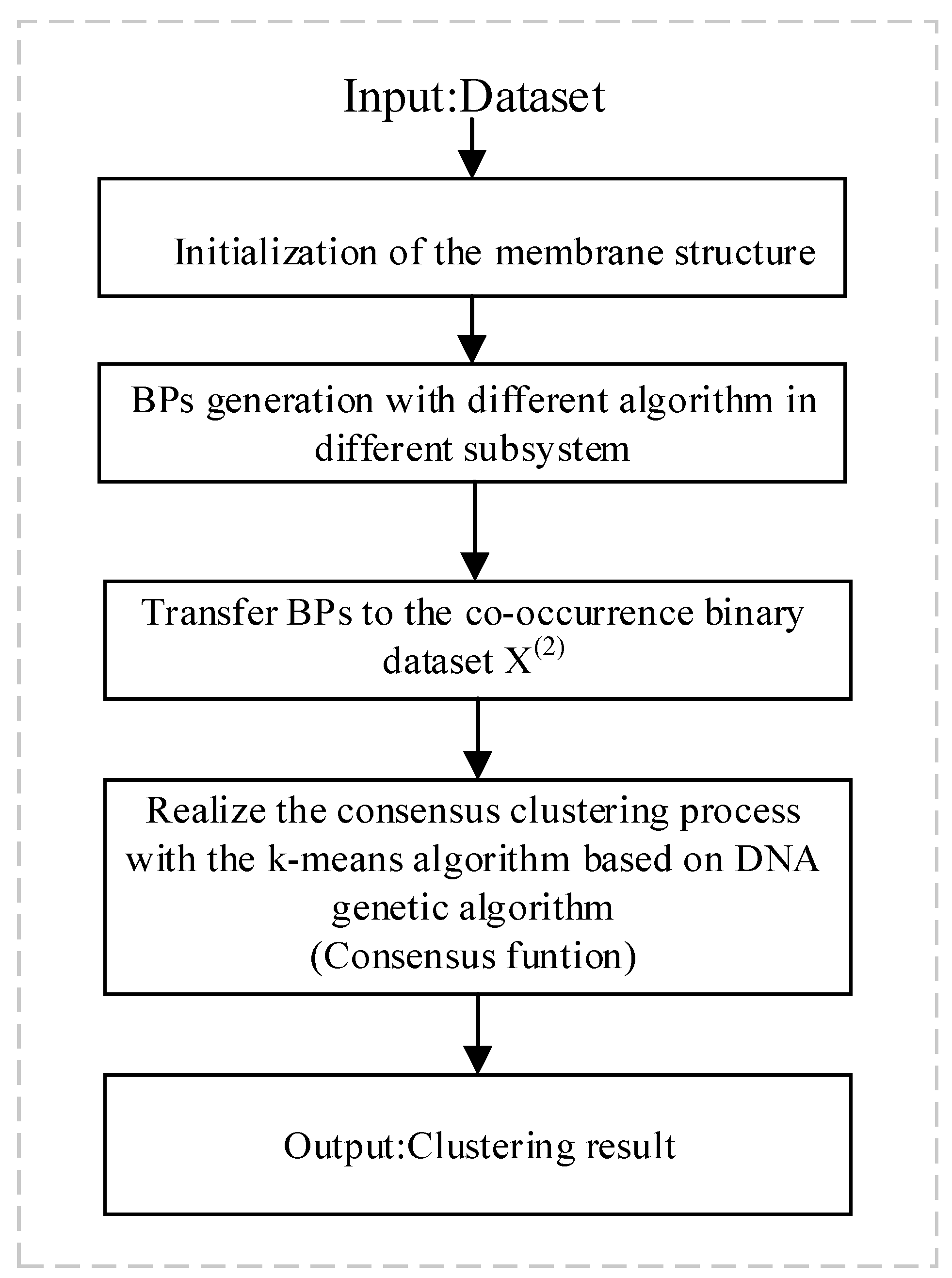
3. Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Consensus Clustering (DCHP-FCC)
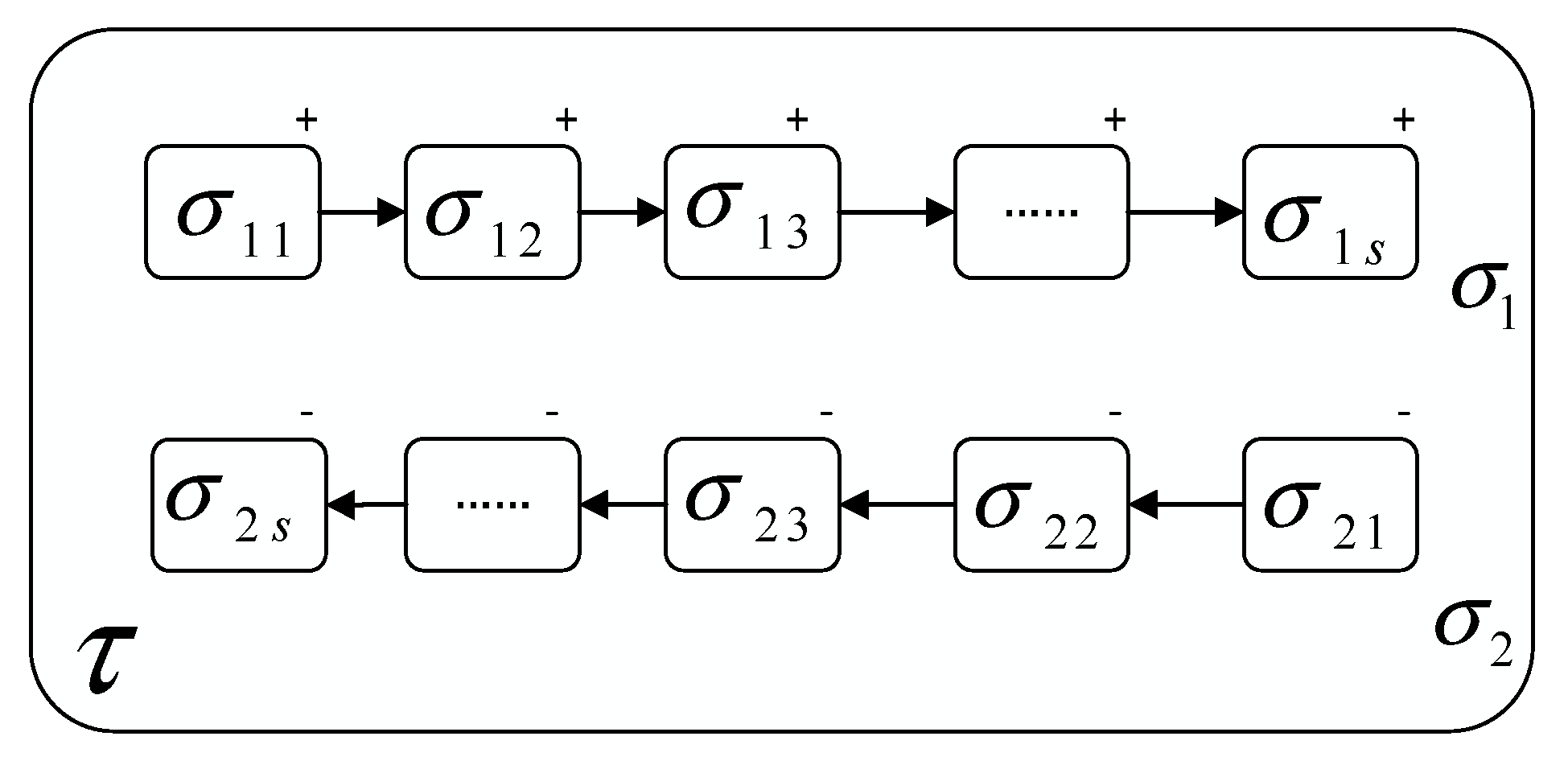
3.1. Membrane Structure of the DCHP System
- is the finite set of objects;
- represents the structure of the membrane. It includes the structure of the chain membrane, hyper-membrane and consensus membrane;
- are objects in , which represent the initial multisets objects in membranes at the beginning of the calculation; we denote the number of chain membrane is , the number of hyper-membrane is and the number of membrane in consensus system is . . means the membrane has no object.
- is the subsystem which is used to generate the basic partition of clustering. In this system, three subsystems execute three kind of clustering algorithm, respectively.
- is the consensus clustering membrane, which is used to generate the final clustering result.
- is the output membrane of the system .
3.2. The Consensus Clustering Realized with the DCHP System
3.2.1. Reaction Chain-Hypergraph P System in Subsystem
3.2.2. Local Communication Membrane System
3.2.3. Consensus System
4. Experiments and Discussions
4.1. Data Sets and Parameter Settings
4.2. Evaluation Metric
4.3. Experiment Results and Analysis
4.4. Significance Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z. Extensions to the k-means algorithm for clustering large data sets with categorical values. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Das, S. Categorical fuzzy k-modes clustering with automated feature weight learning. Neurocomputing 2015, 166, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. A Moving Shape-based Robust Fuzzy K-modes Clustering Algorithm for Electricity Profiles. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 187, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Rastogi, R.; Shim, K. ROCK: A robust clustering algorithm for categorical attributes. Inf. Syst. 2000, 25, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, V.; Gehrke, J.; Ramakrishnan, R. CACTUS-clustering categorical data using summaries. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGKDD Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–18 August 1999; pp. 7–83. [Google Scholar]
- Barbara, D.; Li, Y.; Couto, J. COOLCAT: An entropy-based algorithm for categorical clustering. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM ‘02), Mclean, VA, USA, 4–9 November 2002; pp. 582–589. [Google Scholar]
- Andritsos, P.; Tsaparas, P.; Miller, R.J.; Sevcik, K.C. LIMBO: A scalable algorithm to cluster categorical data. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), Heraklion, Greece, 14–18 March 2004; pp. 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Liang, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, X. A weighting k-modes algorithm for subspace clustering of categorical data. Neurocomputing 2013, 108, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Maulik, U.; Bandyopadyay, S. Multiobjective genetic algorithm-based fuzzy clustering of categorical attributes. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 13, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Kuo, R.J.; Chien, C.H.; Quyen, N.T.P. Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm using fuzzy membership chromosome for categorical data clustering. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 30, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Li, F.; Liang, J.; Liu, B.; Dang, C. Space structure and clustering of categorical data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, L. Many-objective fuzzy centroids clustering algorithm for categorical data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 96, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, X.; Deng, S. Squeezer: An efficient algorithm for clustering categorical data. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2002, 17, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Cheung, Y.; Liu, J. A new distance metric for unsupervised learning of categorical data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, R.; Tian, P.; Wen, A.; Liu, W.; Jiao, L. An intuitionistic fuzzy possibilistic C-means clustering based on genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–19 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.J.; Nguyen, T.P.Q. Genetic intuitionistic weighted fuzzy k-modes algorithm for categorical data. Neurocomputing 2019, 330, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhu, S. Kernel-based multiobjective clustering algorithm with automatic attribute weighting. Soft Comput. 2017, 22, 3685–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naouali, S.; Salem, S.B.; Chtourou, Z. Uncertainty mode selection in categorical clustering using the Rough Set Theory. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 159, 113555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, M.; Datta, S.; Lorenz, D. Variance estimation in tests of clustered categorical data with informative cluster size. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2020, 29, 3396–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, N.; Suresh Ghana Dhas, C. High-performance link-based cluster ensemble approach for categorical data clustering. J. Supercomput. 2020, 76, 4556–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Diao, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Yao, J.; Chang, C.; Lv, G. From whole to part: Reference-based representation for clustering categorical data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pǎun, G. Computing with Membranes. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2000, 61, 108–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Alhazov, A.; Su, H.; Song, B. Local synchronization on asynchronous tissue P systems with Symport/Antiport Rules. IEEE Trans. NanoBioence 2020, 19, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Mario, J. Spiking neural P systems with inhibitory rules. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 188, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Pan, L. The computation power of spiking neural P systems with polarizations adopting sequential mode induced by minimum spike number. Neurocomputing 2020, 401, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, P. A novel image thresholding method based on membrane computing and fuzzy entropy. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. Appl. Eng. Technol. 2013, 24, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, H. Fault diagnosis model of power systems based on adaptive fuzzy spiking neural P systems. Chin. J. Electron. 2016, 23, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Peng, H.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.J.; Wang, T. Weighted fuzzy spiking neural P systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 21, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, C.; Pan, L. Tissue-like P systems with evolutional symport/antiport rules. Inf. Sci. 2017, 378, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Yi, K.; Zhang, G.; Dong, J.; Huang, Z. Automatic Implementation of Fuzzy Reasoning Spiking Neural P Systems for Diagnosing Faults in Complex Power Systems. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, X. Novel coupled DP system for fuzzy C-means clustering and image segmentation. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Wang, N. A Complex Chained P System Based on Evolutionary Mechanism for Image Segmentation. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xue, A. Communication P systems on simplicial complexes with applications in cluster analysis. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Liu, X.Y. Logic Operation in Spiking Neural P System with Chain Structure. In Frontier and Future Development of Information Technology in Medicine and Education; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Kong, D.T.; Hu, J.Y.; Qu, J.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Xue, J. Hybrid Chain-Hypergraph P Systems for Multiobjective Ensemble Clustering. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143511–143523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Wu, J.; Yang, Z. A genetic fuzzy k-Modes algorithm for clustering categorical data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, M.; Liu, X. An Improved Consensus Clustering Algorithm based on Cell-Like P Systems with Multi-Catalysts. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 154502–154517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiulio, C.; Violeta, L. Graphs and Hypergraphs. In Applications of Hyperstructure Theory; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, T.W.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, M.H. Efficient Searching of Subhypergraph Isomorphism in Hypergraph Databases. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data & Smart Computing, Shanghai, China, 15–18 January 2018; pp. 739–742. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, J.; Bernhard, S. Learning with Hypergraphs: Clustering, Classification, and Embedding. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19, Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 19, pp. 1601–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, E. Dual Hypergraph Regularized PCA for Biclustering of Tumor Gene Expression Data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 31, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Xiong, H.; Cao, J.; Chen, J. K-means-based consensus clustering: A unified view. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 27, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, D.; Graff, C. UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Shang, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, F.; Jiang, L.; Stolkin, R. Multi-objective artificial immune algorithm for fuzzy clustering based on multiple kernels. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 50, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset | # of Instance | # of Attributes | # of Classes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean-small | 47 | 35 | 4 |
| Spect Heart | 267 | 22 | 2 |
| Tic-tac-toe | 958 | 9 | 2 |
| Voting | 435 | 16 | 2 |
| Breast cancer | 286 | 9 | 2 |
| Zoo | 101 | 17 | 7 |
| Mushroom | 8124 | 22 | 2 |
| UCI Datasets | DCHP-FCC (BPs = 90) | DCHP-FCC (BPs = 60) | DCHP-FCC (BPs = 30) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARI | ACC | F | ARI | ACC | F | ARI | ACC | F | ||
| Soybean-small | Mean | 0.9338 | 0.9149 | 0.9052 | 0.9676 | 0.9567 | 0.9505 | 0.9228 | 0.8950 | 0.8853 |
| Std. | 0.0069 | 0.0112 | 0.0140 | 0.0044 | 0.0078 | 0.0102 | 0.0086 | 0.0145 | 0.0180 | |
| Algorithm | Parameters | Description | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| FKM | The number of clusters | Random select in | |
| WFKM/IWFKM | The number of clusters | Random select in | |
| GFKM | The number of clusters | Random select in | |
| Pop_size | Population size | 100 | |
| Max_iter | Maximum number of generations | 100 | |
| Pm | Mutation parameter | 0.01 | |
| Consensus clustering | The number of clusters | Real number of clusters | |
| Iteration stopping criteria | |||
| Pc | Crossover parameter | 0.7 | |
| Pm1 | Mutation parameter | 0.01 |
| UCI Datasets | DCHP-FCC | FKM | WFKM | GFKM | IWFKM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean-small | ARI | 0.97 ± 0.004 | 0.86 ± 0.006 | 0.88 ± 0.010 | 0.89 ± 0.009 | 0.87 ± 0.006 |
| ACC | 0.96 ± 0.008 | 0.83 ± 0.009 | 0.86 ± 0.015 | 0.86 ± 0.013 | 0.85 ± 0.010 | |
| F | 0.95 ± 0.010 | 0.80 ± 0.012 | 0.84 ± 0.021 | 0.84 ± 0.017 | 0.83 ± 0.015 | |
| Spect Heart | ARI | 0.75 ± 0.002 | 0.50 ± 4 × 10−5 | 0.50 ± 2 × 10−5 | 0.51 ± 0.001 | 0.50 ± 4 × 10−5 |
| ACC | 0.79 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.79 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.79 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.79 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.79 ± 5 × 10−32 | |
| F | 0.74 ± 0.002 | 0.63 ± 0.000 | 0.63 ± 0.000 | 0.63 ± 0.003 | 0.63 ± 0.000 | |
| Tic-tac-toe | ARI | 0.52 ± 0.000 | 0.51 ± 0.000 | 0.50 ± 3 × 10−5 | 0.52 ± 0.001 | 0.51 ± 5 × 10−5 |
| ACC | 0.65 ± 2 × 10−31 | 0.65 ± 4 × 10−5 | 0.65 ± 2 × 10−31 | 0.66 ± 0.000 | 0.65 ± 2 × 10−31 | |
| F | 0.59 ± 0.001 | 0.57 ± 0.001 | 0.55 ± 0.001 | 0.60 ± 0.002 | 0.56 ± 0.001 | |
| Voting | ARI | 0.78 ± 0.000 | 0.75 ± 0.000 | 0.75 ± 3 × 10−6 | 0.75 ± 0.000 | 0.75 ± 2 × 10−6 |
| ACC | 0.88 ± 0.000 | 0.86 ± 0.000 | 0.85 ± 1 × 10−6 | 0.86 ± 0.000 | 0.85 ± 1 × 10−6 | |
| F | 0.88 ± 0.000 | 0.86 ± 0.000 | 0.85 ± 1 × 10−6 | 0.86 ± 0.000 | 0.85 ± 1 × 10−6 | |
| Breast cancer | ARI | 0.51 ± 1 × 10−4 | 0.50 ± 6 × 10−6 | 0.50 ± 3 × 10−5 | 0.51 ± 7 × 10−4 | 0.50 ± 6 × 10−6 |
| ACC | 0.70 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.70 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.70 ± 5 × 10−32 | 0.71 ± 5 × 10−5 | 0.70 ± 5 × 10−32 | |
| F | 0.58 ± 8 × 10−4 | 0.56 ± 3 × 10−4 | 0.55 ± 7 × 10−4 | 0.59 ± 0.002 | 0.54 ± 4 × 10−4 | |
| Zoo | ARI | 0.90 ± 0.000 | 0.87 ± 0.001 | 0.87 ± 0.002 | 0.89 ± 0.002 | 0.86 ± 0.001 |
| ACC | 0.87 ± 0.000 | 0.84 ± 0.002 | 0.83 ± 0.003 | 0.84 ± 0.002 | 0.83 ± 0.003 | |
| F | 0.78 ± 0.004 | 0.74 ± 0.005 | 0.73 ± 0.008 | 0.77 ± 0.004 | 0.72 ± 0.006 | |
| Mushroom | ARI | 0.81 ± 1 × 10−31 | 0.67 ± 0.014 | 0.70 ± 0.014 | 0.68 ± 0.016 | 0.67 ± 0.018 |
| ACC | 0.89 ± 2 × 10−31 | 0.76 ± 0.017 | 0.80 ± 0.014 | 0.74 ± 0.015 | 0.76 ± 0.017 | |
| F | 0.89 ± 2 × 10−31 | 0.76 ± 0.015 | 0.79 ± 0.014 | 0.77 ± 0.016 | 0.76 ± 0.019 |
| UCI Datasets | DCHP-FCC vs. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FKM | WFKM | GFKM | IWFKM | |
| Soybean-small | 0.9 × 10−8(+) | 5.0 × 10−5(+) | 3.0 × 10−4(+) | 6.6 × 10−6(+) |
| Spect Heart | 5.7 × 10−27(+) | 1.0 × 10−23(+) | 5.1 × 10−22(+) | 1.1 × 10−23(+) |
| Tic-tac-toe | 7.0 × 10−14(+) | 1.8 × 10−14(+) | 3.5 × 10−10(+) | 8.5 × 10−5(+) |
| Voting | 6.1 × 10−9(+) | 1.8 × 10−12(+) | 1.5 × 10−6(+) | 6.9 × 10−13(+) |
| Breast cancer | 6.6 × 10−4(+) | 0.0077(+) | 0.3373(−) | 3.1 × 10−4(+) |
| Zoo | 0.0092(+) | 0.0033(+) | 0.3104(−) | 0.0020(+) |
| Mushroom | 3.4 × 10−7(+) | 2.6 × 10−5(+) | 5.1 × 10−6(+) | 4.9 × 10−6(+) |
| UCI Datasets | DCHP-FCC vs. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FKM | WFKM | GFKM | IWFKM | |
| Soybean-small | 2.9 × 10−7(+) | 1.1 × 10−4(+) | 8.4 × 10−4(+) | 2.2 × 10−5(+) |
| Spect Heart | - | - | - | - |
| Tic-tac-toe | - | - | - | - |
| Voting | 7.2 × 10−9(+) | 1.2 × 10−12(+) | 1.8 × 10−6(+) | 4.3 × 10−13(+) |
| Breast cancer | - | - | - | - |
| Zoo | 5.5 × 10−4(+) | 0.0027(+) | 0.0060(+) | 4.8 × 10−5(+) |
| Mushroom | 0.0414(+) | 0.5516(−) | 0.1215(−) | 7.9 × 10−6(+) |
| UCI Datasets | DCHP-FCC vs. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FKM | WFKM | GFKM | IWFKM | |
| Soybean-small | 4.3 × 10−7(+) | 2.0 × 10−4(+) | 8.7 × 10−4(+) | 1.1 × 10−4(+) |
| Spect Heart | 1.9 × 10−14(+) | 3.7 × 10−14(+) | 1.2 × 10−9(+) | 8.1 × 10−13(+) |
| Tic-tac-toe | 0.0540(−) | 6.0 × 10−6(+) | 0.5474(−) | 1.1 × 10−4(+) |
| Voting | 6.8 × 10−9(+) | 1.1 × 10−12(+) | 1.6 × 10−6(+) | 3.9 × 10−13(+) |
| Breast cancer | 9.7 × 10−4(+) | 1.9 × 10−4(+) | 0.3499(−) | 1.7 × 10−6(+) |
| Zoo | 0.0374(+) | 0.0280(+) | 0.3151(−) | 0.0023(+) |
| Mushroom | 2.3 × 10−6(+) | 8.8 × 10−5(+) | 1.0 × 10−5(+) | 6.6 × 10−6(+) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Liu, X. A Novel Consensus Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Using Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Categorical Data. Processes 2020, 8, 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101326
Jiang Z, Liu X. A Novel Consensus Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Using Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Categorical Data. Processes. 2020; 8(10):1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101326
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhenni, and Xiyu Liu. 2020. "A Novel Consensus Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Using Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Categorical Data" Processes 8, no. 10: 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101326
APA StyleJiang, Z., & Liu, X. (2020). A Novel Consensus Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering Using Coupling DNA-Chain-Hypergraph P System for Categorical Data. Processes, 8(10), 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101326





