Abstract
This paper investigates the steady, two dimensional, and magnetohydrodynamic flow of copper and alumina/water hybrid nanofluid on a permeable exponentially shrinking surface in the presence of Joule heating, velocity slip, and thermal slip parameters. Adopting the model of Tiwari and Das, the mathematical formulation of governing partial differential equations was constructed, which was then transformed into the equivalent system of non-linear ordinary differential equations by employing exponential similarity transformation variables. The resultant system was solved numerically using the BVP4C solver in the MATLAB software. For validation purposes, the obtained numerical results were compared graphically with those in previous studies, and found to be in good agreement, as the critical points are the same up to three decimal points. Based on the numerical results, it was revealed that dual solutions exist within specific ranges of the suction and magnetic parameters. Stability analysis was performed on both solutions in order to determine which solution(s) is/are stable. The analysis indicated that only the first solution is stable. Furthermore, it was also found that the temperature increases in both solutions when the magnetic parameter and Eckert number are increased, while it reduces as the thermal slip parameter rises. Furthermore, the coefficient of skin friction and the heat transfer rate increase for the first solution when the magnetic and the suction parameters are increased. Meanwhile, no change is noticed in the boundary layer separation for the various values of the Eckert number in the heat transfer rate.
1. Introduction
Previous studies have proven that fluids play a vital role in enhancing the heat transfer rate in many engineering and industrial systems. It is also noticed from the previous literature that regular fluids, such as water, ethylene glycol, etc., must keep thermal conductivity low in order to improve the heat transfer rate. Many researchers have attempted to find new fluids that can further enhance the heat transfer rate. Choi and Eastman [1] were the first that introduced another kind of fluid known as “nanofluid” and claimed that the heat transfer rate of nanofluid outperformed that of regular fluids. Nanofluid can be defined as a mixture of nano-sized particles of solid in a base fluid. Later, many researchers worked on nanofluids experimentally and theoretically [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Consequently, these investigations lead to greater efforts to enhance the heat transfer rate, yet nobody can conclude and claim that a mixture of a particular type of base fluid with a particular kind of nanoparticle can produce the highest rate of heat transfer [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Continuous attempts have been made to improve the rate of heat transfer using various strategies. One of the approaches is mixing two different types of solid nanoparticle in a solitary base fluid, which produces a special kind of nanofluid known as hybrid nanofluid. This idea was initiated by Suresh et al. [15,16] by considering alumina and copper as the solid particles with a base fluid of water. Furthermore, they claimed that the rate of heat transfer of hybrid nanofluid is higher at the surface compared to that of simple fluid and nanofluid. Their discovery is a new research direction in fluid dynamics. Since then, numerous researchers have been focusing on hybrid nanofluid in their work and have discovered some interesting and promising results, as can be seen in these articles [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In 2016, Devi and Devi [23] contemplated the copper-alumina/water hybrid nanofluid numerically. They compared the numerical results of thermal conductivity with the experimental work of Suresh et al. [16] and found an astounding agreement between them. In the same year, the 3D magnetohydrodynamics MHD flow of hybrid nanofluid was considered by Devi and Devi [24], and their numerical results coincided with the experimental results obtained by Suresh et al. [15]. Because of these encouraging findings, the newly found thermophysical properties have been considered by many researchers in their studies, such as Das et al. [25], Mehryan et al. [26], Chamkha et al. [27], Hayat et al. [28], Saba et al. [29], Kumar and Sarkar [30], Kassai [31], and Ghalambaz et al. [32]. Recently, Waini et al. [33] considered the unsteady flow of hybrid nanofluid, by mixing copper and alumina (nanoparticles) with water (base fluid). They noticed that double solutions appeared in specific ranges of the unsteadiness parameter. Lund et al. [34] examined the steady flow of a hybrid nanofluid in the existence of a dissipation function effect and found double solutions. In addition, stability analysis on the solutions was done and demonstrated that only the first solution is stable. Meanwhile, the axisymmetric flow of electrically conducting hybrid nanofluid was inspected by Khashi’ie et al. [35], in whose work the occurrence of dual solutions is noticed within certain ranges of physical parameters. The stability analysis also specified that only the first solution is stable. Anuar et al. [36] showed the existence of dual solutions in the stagnation point-flow of water-based hybrid nanofluid with the velocity slip effect and concluded that a non-uniqueness of solutions exists over the exponentially shrinking surface. Their work was then continued by Waini et al. [37] by considering the effects of MHD and thermal radiation without stagnation point flow and slip effects. It was noticed that double solutions occur over the shrinking and stretching surfaces within specific ranges of the mass suction parameter.
Nowadays, fluid flow over the shrinking surface has gotten the attention of researchers who are intrigued to find the multiple solutions. There are greater possibilities for the existence of dual solutions when fluid is flowing on shrinking surfaces [38]. It appears that Miklavčič and Wang [39] are the main researchers that considered the flow of viscous fluid over the shrinking surface and reasoned that flow over the shrinking surface is not going to exist due to the unconfined vorticity. In order to keep the flow, sufficient suction on the surface is required. Afterwards, Fang et al. [40] examined viscous fluid flow over the shrinking sheet including the second slip parameter, and revealed that the impact of drag force can be decreased by applying higher mass suction on the surface. Meanwhile, Jahan et al. [41] analyzed the unsteady flow of nanofluid over the shrinking sheet and discovered double solutions. Hybrid nanofluid flow on the stretching/shrinking surface, with the effects of transpiration, was explored by Waini et al. [42]. It is also noticed from the previous literature that regular fluids, such as water, ethylene glycol, etc., must keep thermal conductivity low in order to improve the heat transfer rate [43,44]. Some current developments on nanofluids and hybrid nanofluids over the shrinking surface for multiple solutions can be seen in these articles [43,44,45,46,47].
A huge overview of the published work demonstrates that the effect of slip conditions on nanofluid flow has not been given a lot of consideration, especially on hybrid nanofluids. Numerous significant applications of fluids show boundary slip conditions, such as the perfecting of heart valves and inside cavities, and the cleaning of artificial heart valves [48]. It is worthwhile to state that the no-slip condition is not always valid in reality. In simple words, the velocity of the slip condition can be explained, as the fluid would not have zero velocity with regards to contact with the solid boundary. Similarly, a thermal slip condition can be explained. Andersson [49] is probably the first who introduced the concept of the slip effect on the boundary layer flow. Uddin et al. [50] examined nanofluid with the impacts of slip conditions and Darcian porous medium, and inferred that the temperature slip parameter has an inverse relationship with the temperature and velocity profiles. The MHD flow of a hybrid nanofluid in the presence of the slip condition was considered by Nadeem and Abbas [51], and they adopted the thermophysical properties of Devi and Devi [23,24] to solve the system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Using the same properties, Iftikhar et al. [52] also investigated the steady MHD flow of hybrid nanofluid with the slip condition. Based on published literature, it can be concluded that the thermophysical properties of Devi and Devi have been used broadly, as these properties match with the experimental results. Taking advantage of this situation, in this study, we also considered the thermophysical properties of Devi and Devi [23,24] in dealing with hybrid nanofluid, and anticipated that our results would help in understanding hybrid nanofluid effectively without having to conduct costly experimental studies.
This paper has three main objectives. First, to extend the work of Anuar et al. [36] and Waini et al. [37] by incorporating Joule heating effects with velocity and thermal slip conditions. By including the Joule heating effect, it’s very hard to find the solution due to the non-linearity in the temperature equations. Therefore, many researchers did not consider it in their study. Second, to obtain the maximum number of multiple solutions due to the existence of non-linearity. Third, to find a stable solution by performing stability analysis. According to the best of our knowledge, no such study has been contemplated previously. A 10% of volume fraction with a 0.1% ≤ ≤ 10% volume fraction was chosen for the numerical computation, and produced interesting results. It is expected that the current studies will provide good benefits to the researchers who are working on the hybrid nanofluid experimentally, and it is also expected that these results will reduce the cost of the experimental work in the future.
2. Mathematical Formulation
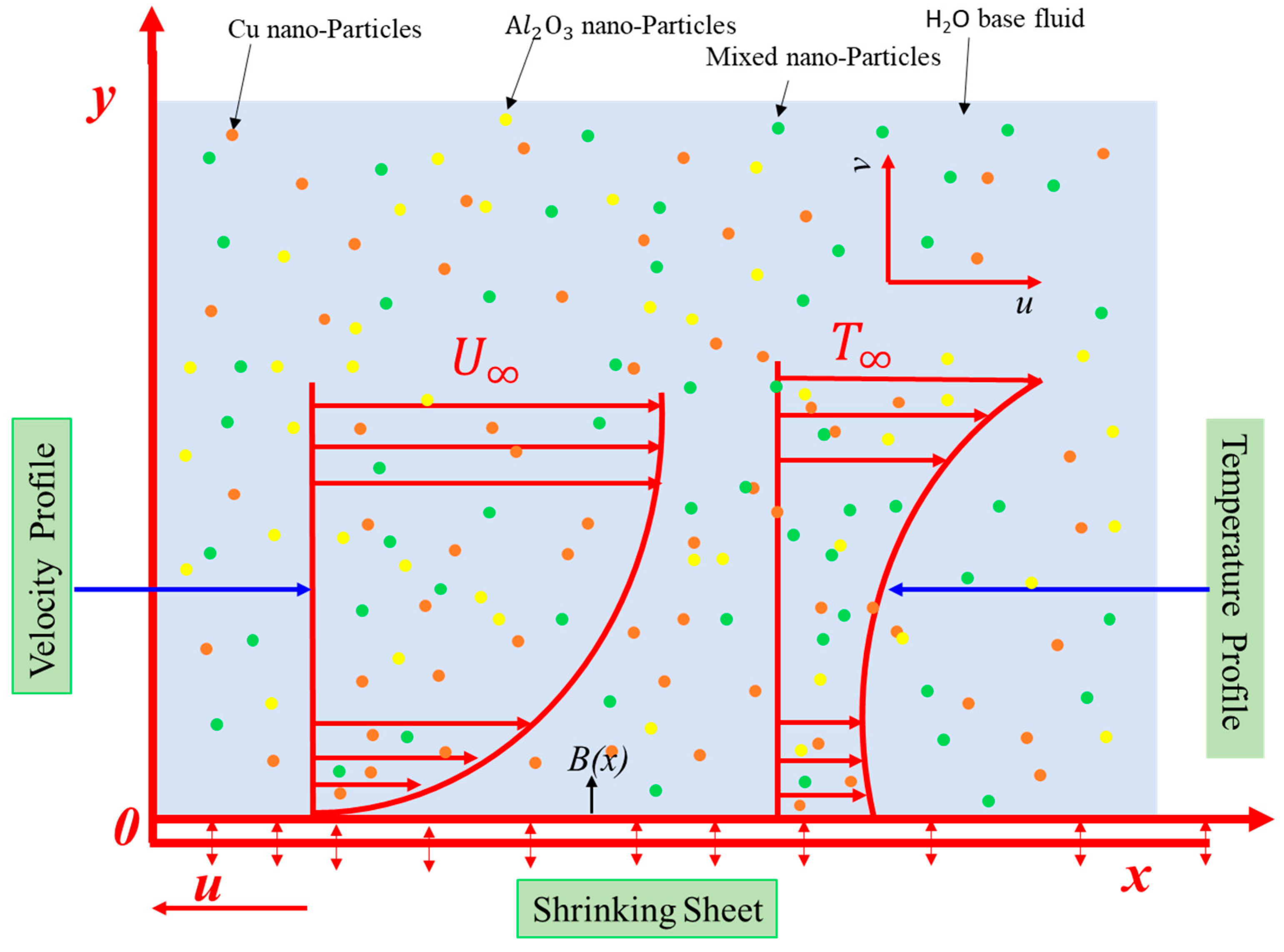
There have been considered the incompressible 2D, MHD, and steady boundary layer flow of hybrid nanofluid with the effects of Joule heating, velocity, and thermal slip conditions over the exponentially shrinking surface (see Figure 1) without the viscous dissipation effect. By considering all assumptions, the governing mass, momentum, and energy conservations can be expressed as [35,37]:
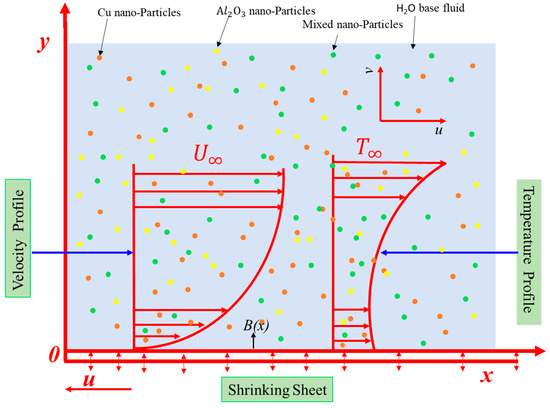
Figure 1.
A physical model and coordinate system.
The boundary conditions are [53]
Here, and are the corresponding velocities of the x-axis and y-axis; is the temperature of fluid; is the temperature of the surface and is explained as ; is the free stream temperature; is the magnetic field by the constant magnetic strength, ; and , and are the respective effective viscosity, density, heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity of hybrid nanofluid. Furthermore, is the velocity of the surface, is the velocity slip factor, is the thermal slip factor, and , where is the suction and blowing parameter.
Table 1 and Table 2 present the thermophysical properties of hybrid nanofluid, base fluid, and solid nanoparticles respectively. Furthermore, indicates the solid volume fraction of particles; the subscripts , and represent the hybrid nanofluid, copper, alumina, nanofluid, and regular base fluid respectively.

Table 1.
The thermophysical properties of hybrid nanofluid [34,37,54].

Table 2.
The thermophysical properties of nanoparticles and water [34,37,54].
The following variables of similarity transformation are used to reduce the system into ODEs [37]
where indicates the stream function explained as and that satisfy the Equation (1). By employing the similarity variables in Equation (7) into the Equations (2) and (3), we get
Along with the boundary conditions
where primes stand for the derivatives with respect to , is the Prandtl number, is the Eckert number, is the velocity slip parameter, and is the thermal slip parameter.
The important physical quantities of interest are the skin friction coefficient, Cf, and local Nusselt number, Nux, explained as
Applying similarity variables (5) yields
3. Stability Analysis
In order to perform the stability analysis of solutions of Equations (6) and (7) along with boundary conditions (9), the unsteady forms of the Equations (2) and (3) are required to test the features of the temporal stability analysis by introducing the new time-dependent dimensionless variable, . In this regard, the steps of Merkin [55], Lund et al. [56], and Weidman et al. [57] are adopted. Thus, we get
Equation (5) can take the following form with the new transformation variable of
By using Equation (14) into Equations (12) and (13), we get
Subject to boundary conditions
To check the stability of steady flow solutions where of satisfying the boundary value problem (6–9), we have
where is the unknown eigenvalue; during the process of finding of , it will generate the unlimited set of the eigenvalues, Furthermore, and are the small related values of and , where and can be obtained by setting = 0. Basically, these show the solutions of Equations (6) and (7). Accordingly, the flowing linear eigenvalue problems need to be solved.
Subject to the reduced boundary conditions
To get the smallest eigenvalue, , one of them, , is required to relax into an initial boundary condition, as suggested by Haris et al. [58]. In this problem, is relaxed to .
4. Results and Discussion
The system of non-linear ODEs (6–7) along boundary conditions (9) was solved by utilizing BVP4C in MATLAB programming. In order to get the solutions with good precision, we had to make some initial guesses at the initial mesh points by the changing of step-sizes. In the whole study, the tolerance was set at in order to get good accuracy in the solutions. Waini et al. [33] and Lund et al. [54] described this method in detail. As there exist two solutions, accordingly, more initial guesses were required to acquire the solution subject to fulfill boundary conditions asymptotically at . In the entire study, was selected as for both solutions.
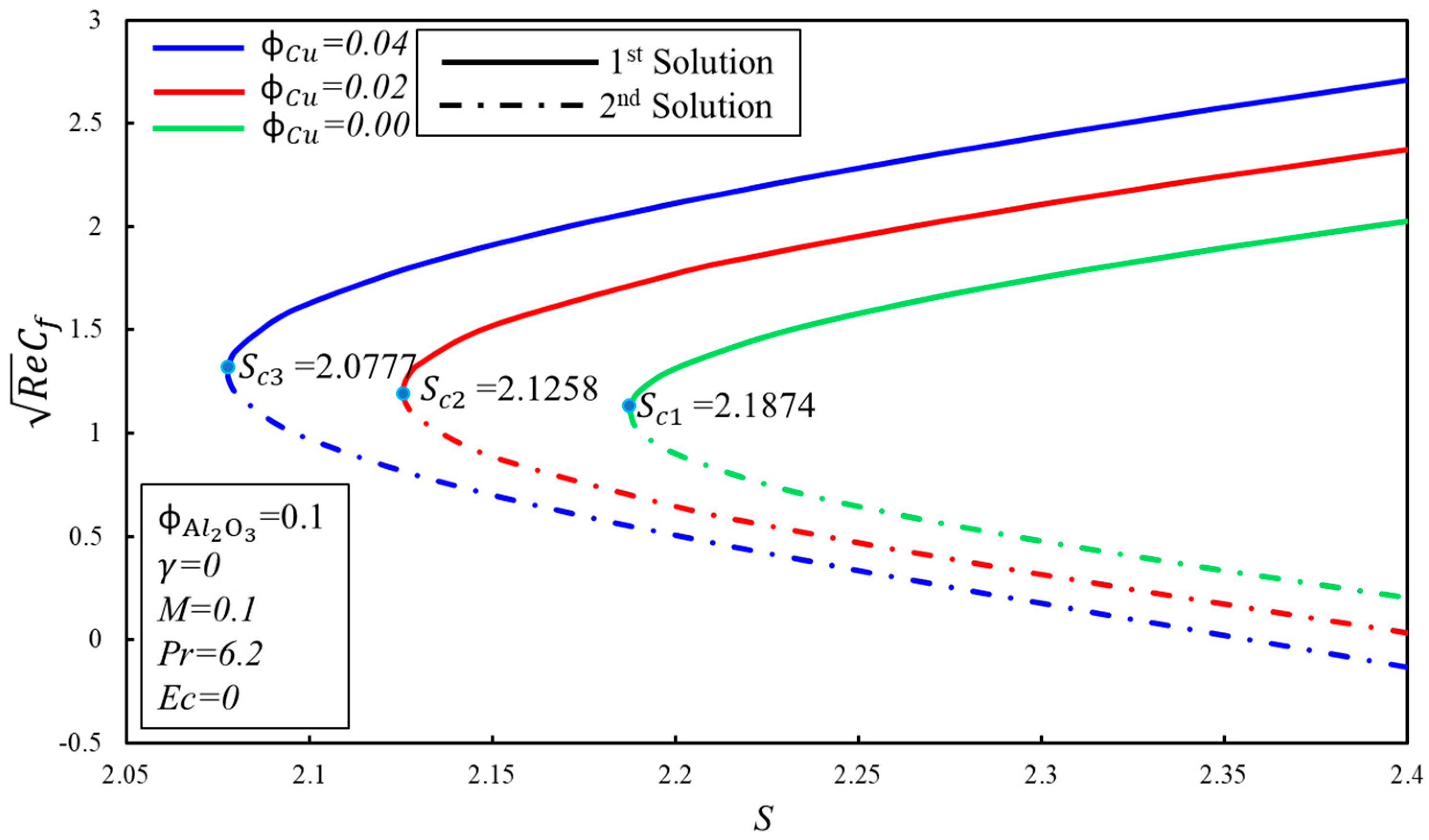
The numerical calculations were carried out for the various physical included parameters. In Figure 2, a graphical comparison of with Waini et al. [37] has been made for the validation of our numerical method, and shows an excellent agreement. The behavior of the graph and the critical values of the suction parameter, , are equivalent up to three decimal places, as referenced in the paper of Waini et al. [37] (alluding to Figure 2 of [37]). Henceforth, the present method can certainly be used, and the generated results are reliable and correct. Additionally, the numerical values of and for the different values of the magnetic parameter , the solid volume fraction of copper parameter (), the Prandtl and Eckert numbers, the Suction parameter , the velocity slip parameter , and the temperature slip parameter are given in Table 3 and Table 4.
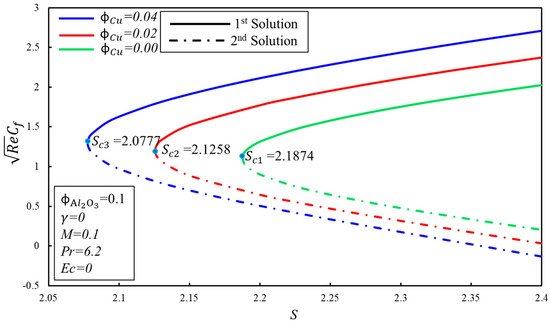
Figure 2.
A comparison of the variation of with Waini et al. [37].

Table 3.
The results of the surface where , and

Table 4.
The results of where and .
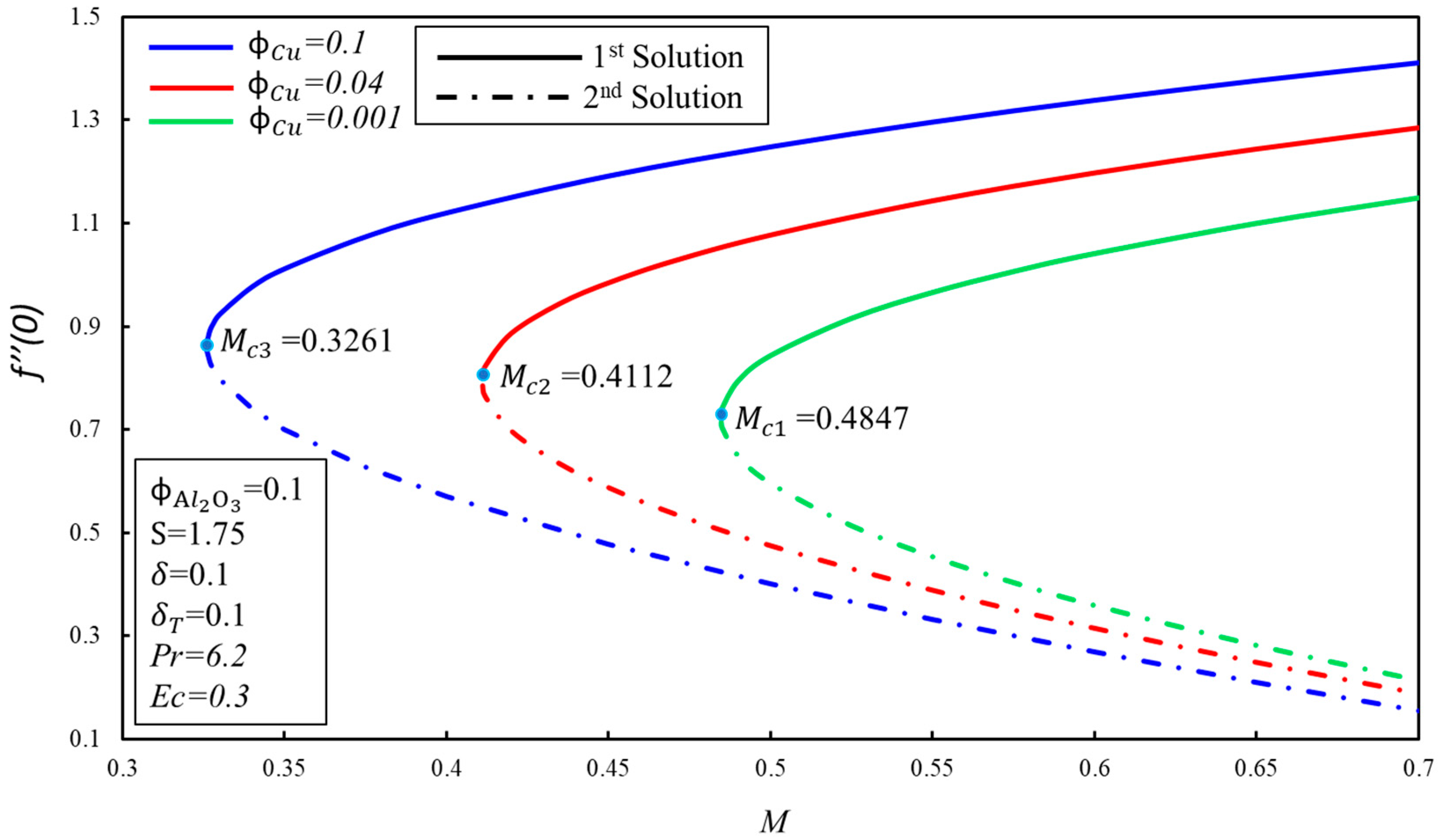
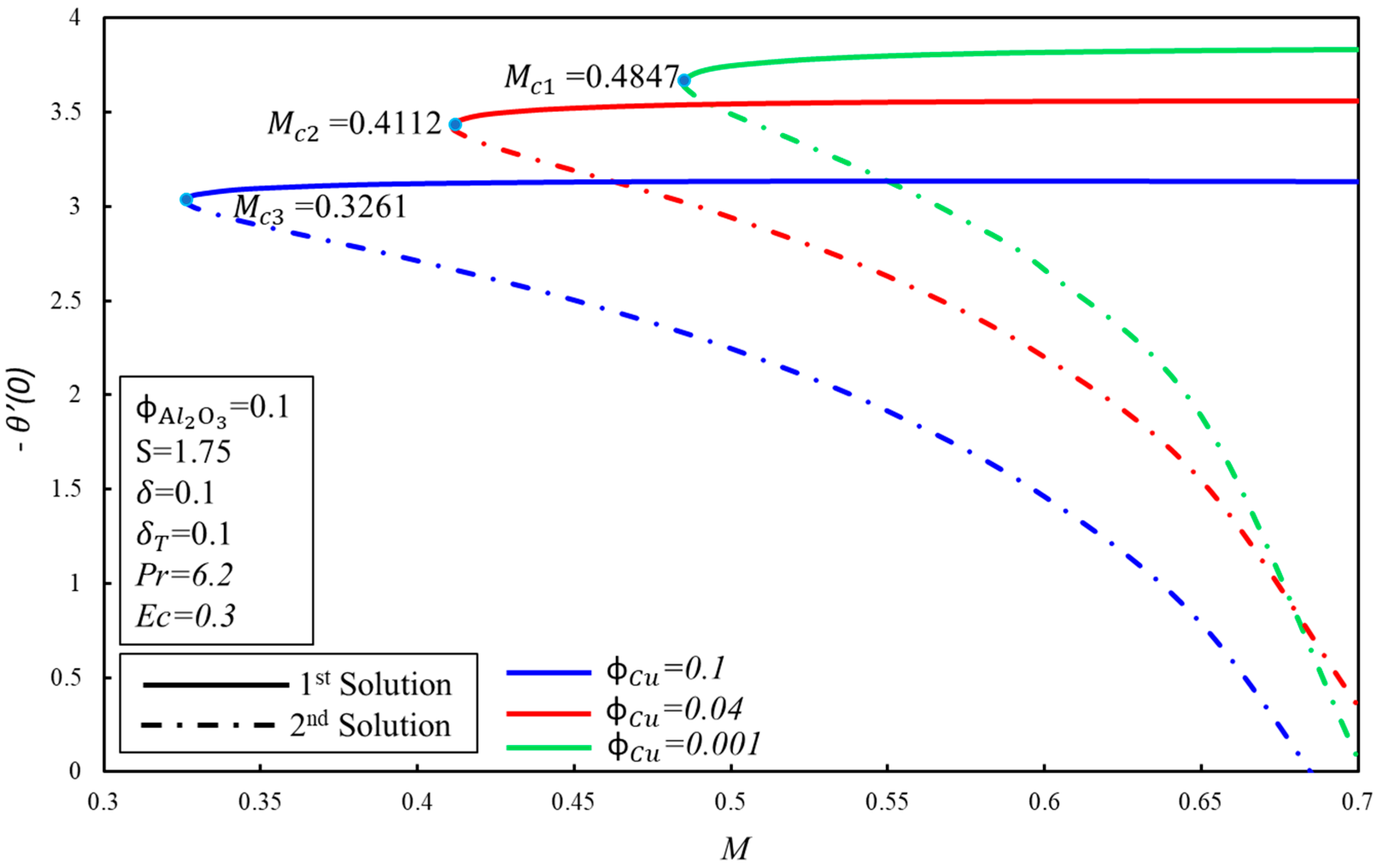
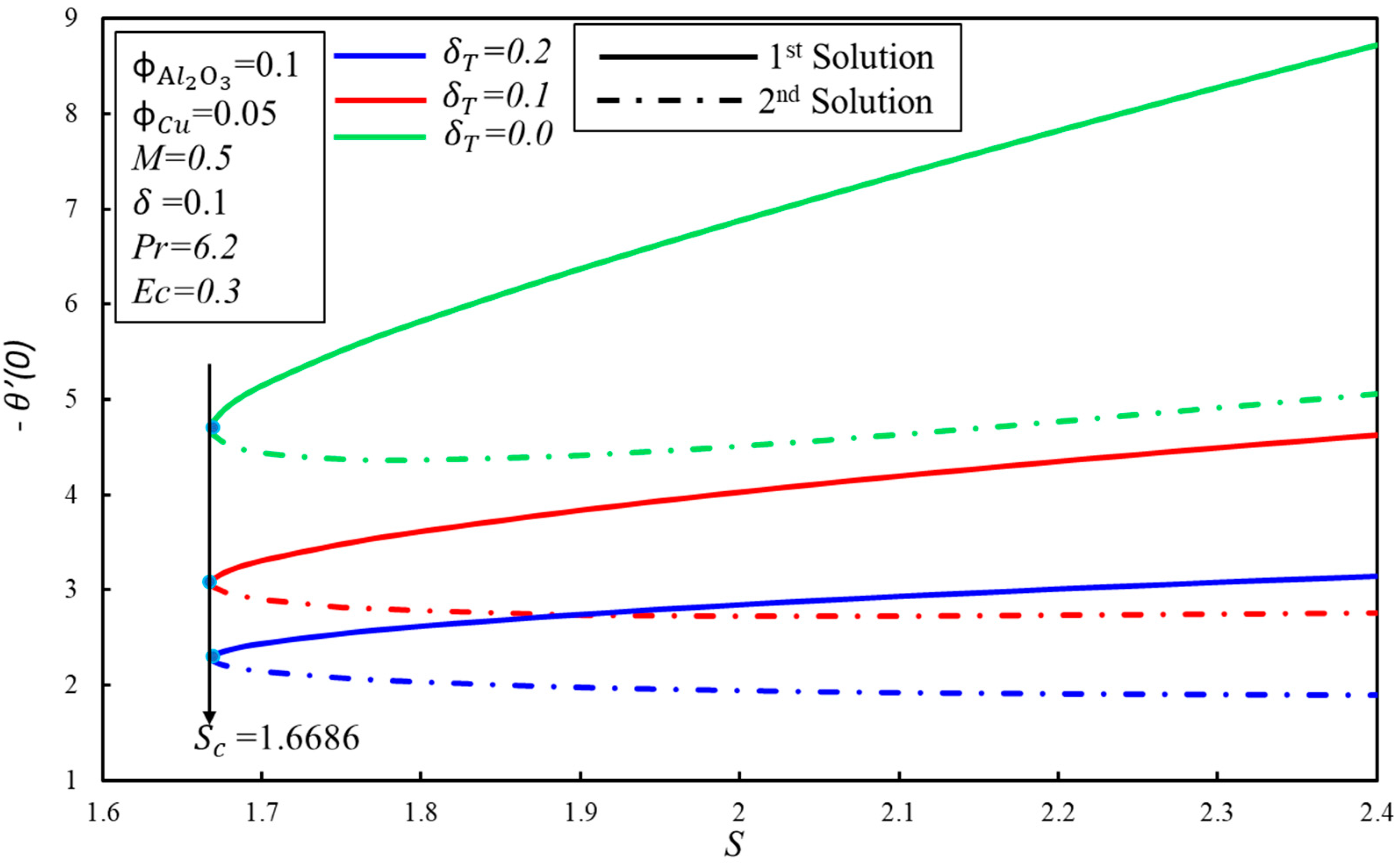
The effect of on the variation of and for the various values of magnetic parameter ( are illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4 separately. It is observed from these figures that dual solutions exist for Equations (6) and (7) along the boundary condition (9) in the specific ranges of . The respective critical values for and are and where solutions exist. There exist two ranges of solution which rely on the values of no solution exists when where , and dual solutions exist when . Furthermore, it is shown that decays with the increasing values of , which show the delay in the boundary layer separation. Physically, it is due to the fact that the higher impact of the magnetic number creates resistance in the fluid flow, and vorticity is smothered, as seen in the first solution. The skin friction coefficient, , and rate of heat transfer, , increase when the magnetic number, , increases for the first solution. These increments are due to the fact that the magnetic field creates the Lorentz force. On the other hand, they decline in the second solution.
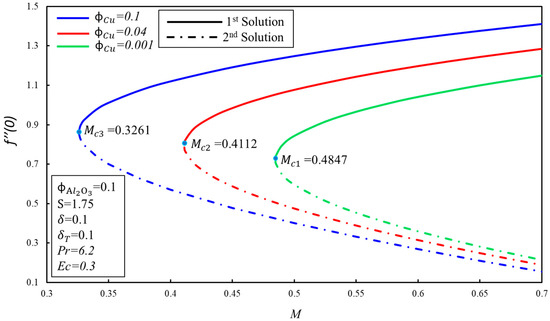
Figure 3.
The variation of with for various values of .
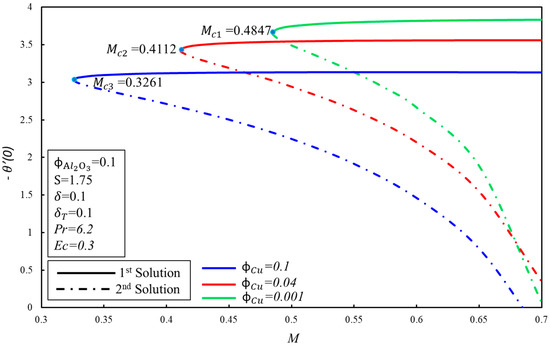
Figure 4.
The variation of with for various values of .
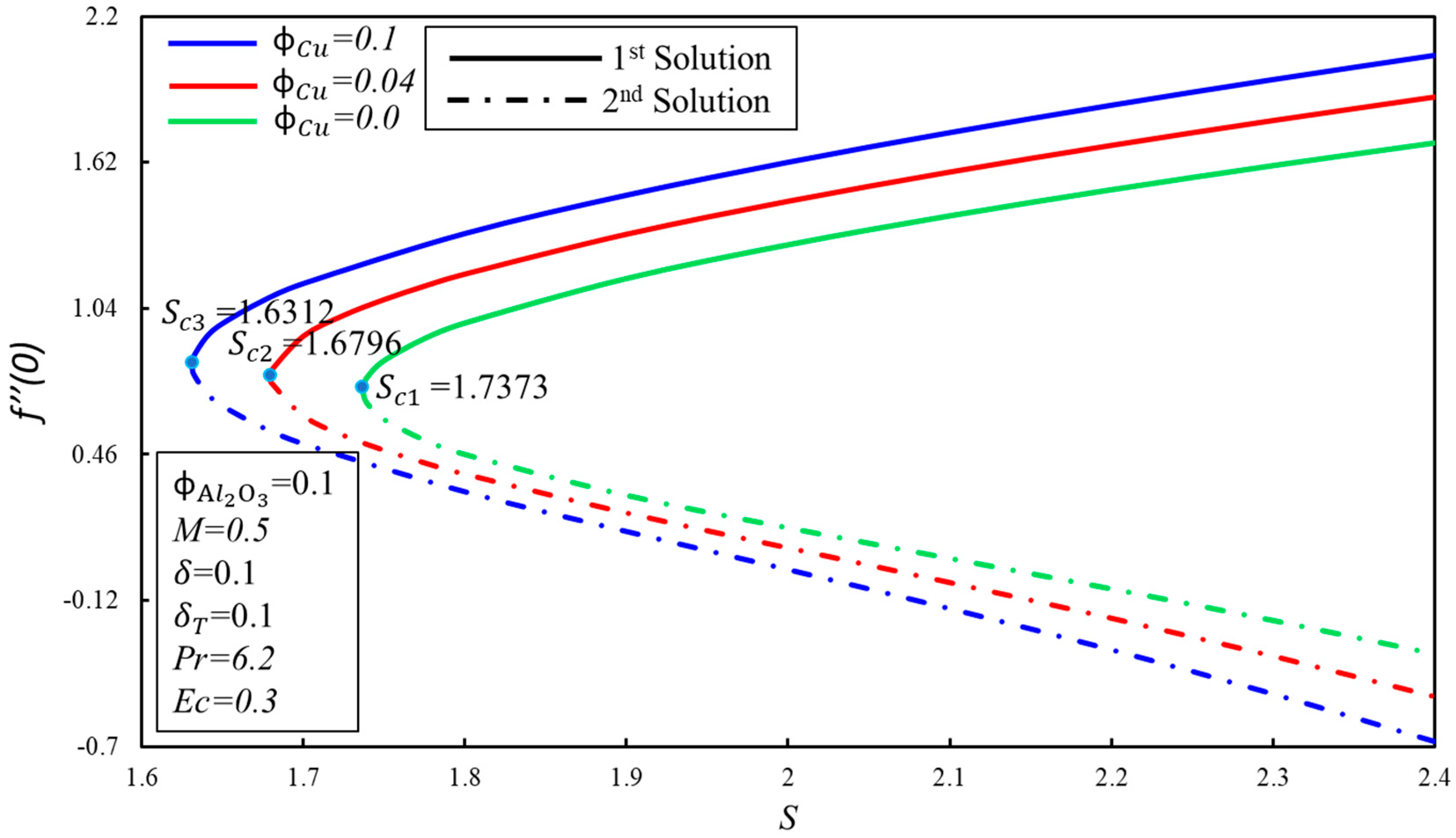
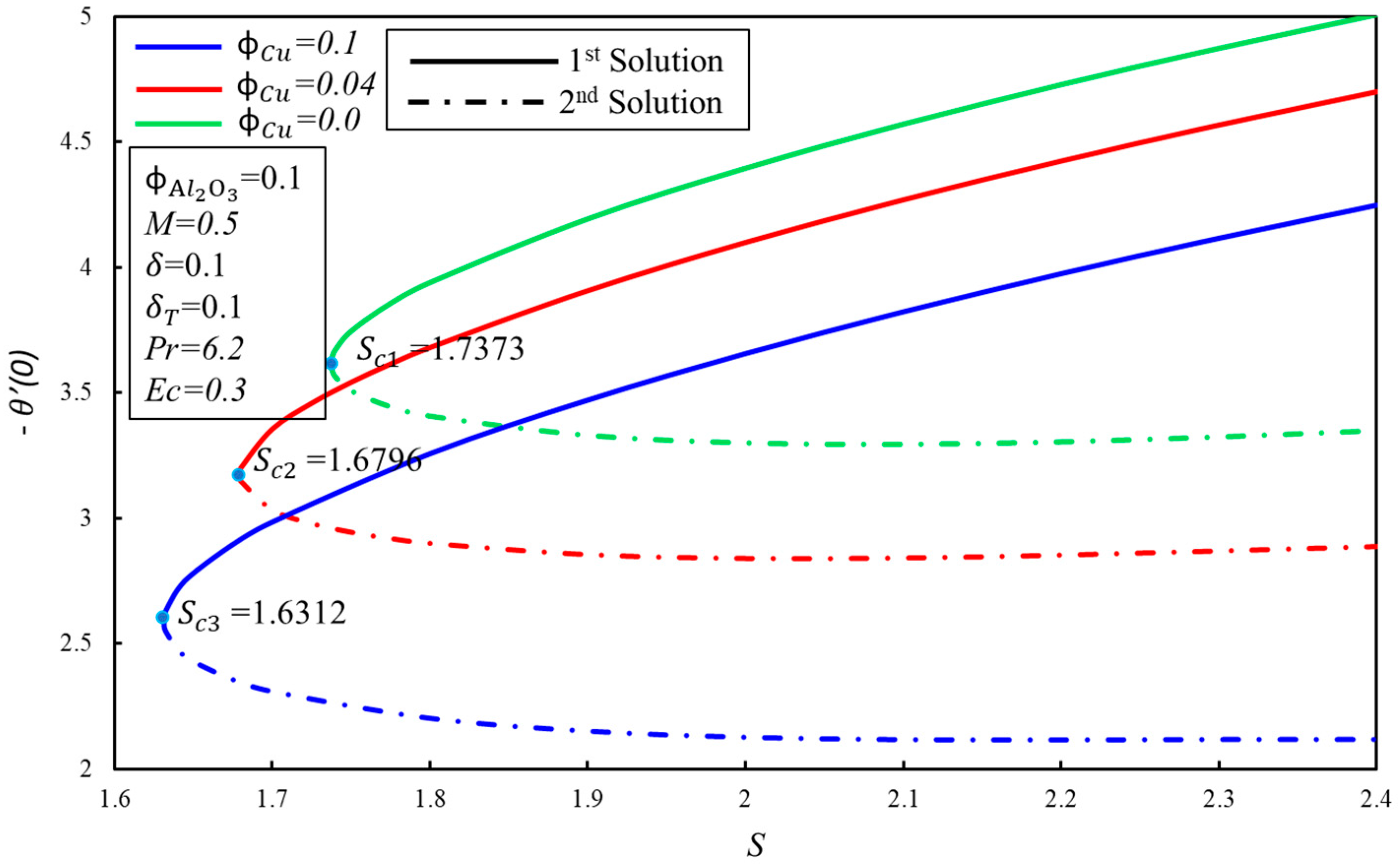
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the variation of skin friction coefficient, , and heat transfer rate, , against the suction parameter, , for fixed values of the solid volume fraction of copper, . When increases, the critical values of suction, , increment towards the left, which supports the delay in the boundary layer separation. The critical values of for and are , and respectively. Furthermore, the presence of dual solutions is conceivable when where , whereas no solution exits when . It is observed that for the fixed values of , the skin friction coefficient, , increases with the expanding of for the first solution, whereas the inverse trend is seen in the second solution. Moreover, the heat transfer rate, , increases when the suction parameter is increased, by keeping the fixed values of in the first solution. It can be explained as so: suction produces the drag force, which slows down the fluid flow, and as a result, the heat transfer rate increases. Meanwhile, the rate of heat transfer diminishes gradually in the second solution.
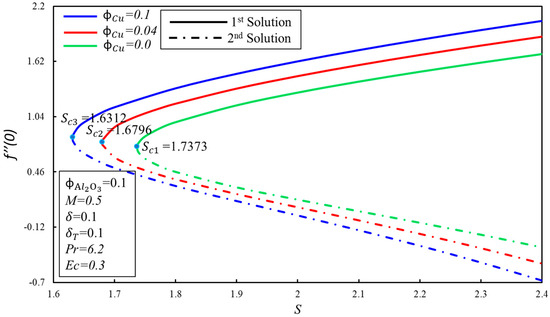
Figure 5.
The variation of with for various values of .
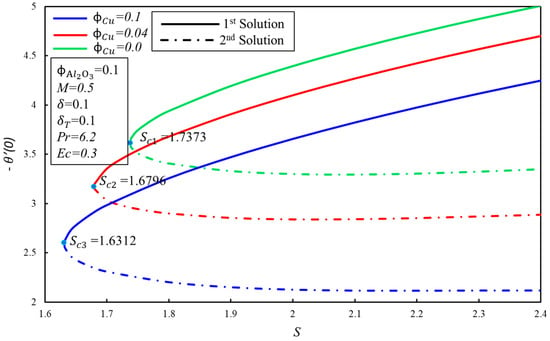
Figure 6.
The variation of with for various values of .
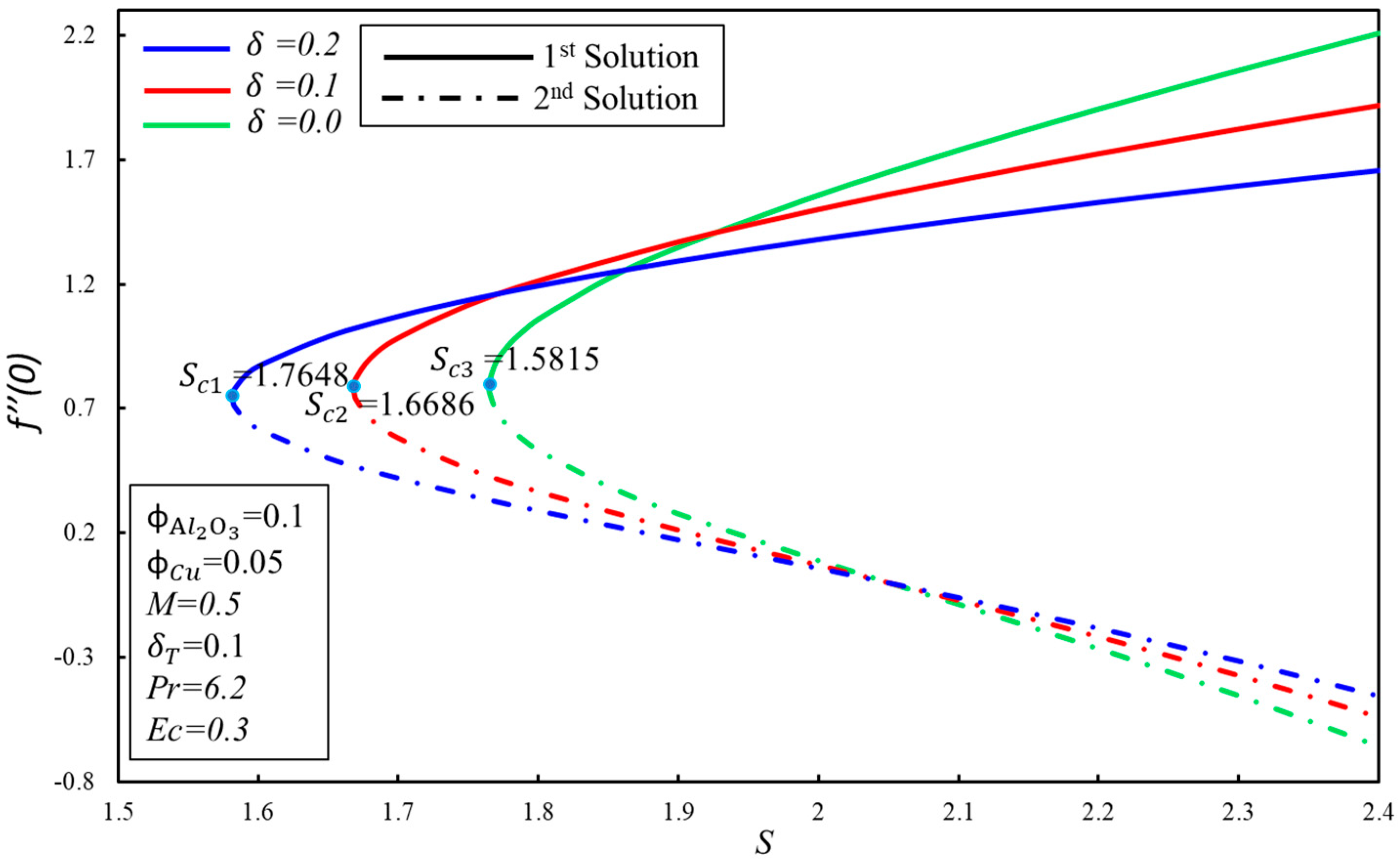
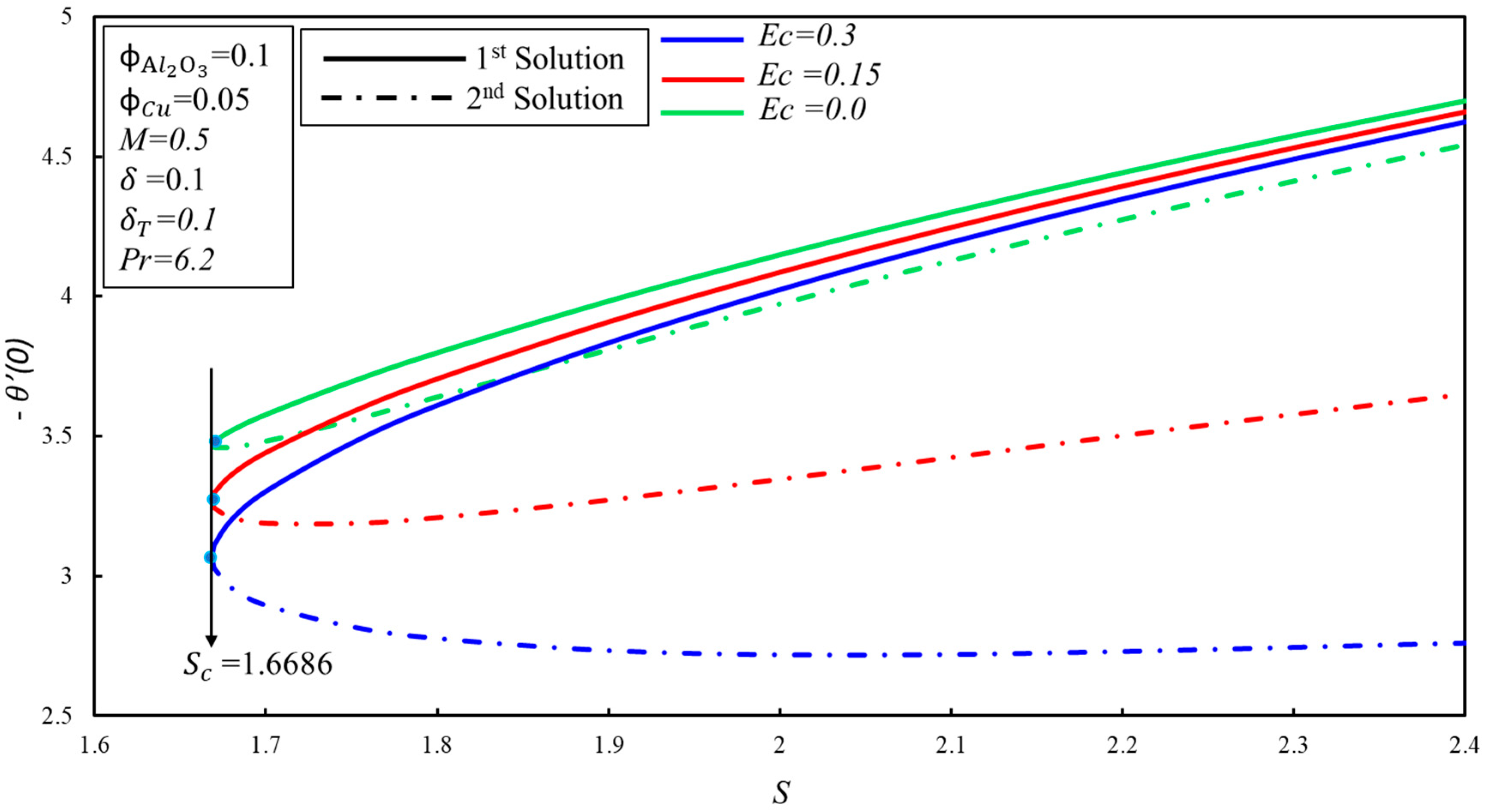
The effect of the velocity slip parameter, , on the skin friction coefficient, , for numerous values of is demonstrated in Figure 7. It is observed that the skin friction coefficient, , increases initially, and then decreases for the higher values of in the first solution; practically, it shows that the viscosity of the hybrid nanofluid enhances initially, and then starts to decrease after the intensive impact of the parameter in the boundary layer. However, a contradictory nature of the skin friction coefficient, , is noticed for the second solution. Moreover, the critical values of for the higher values of are , and where solutions exist, while no solution exists beyond these critical values. The effect of the Eckert number, , on the heat transfer rate, , is portrayed in Figure 8. The reduction of heat transfer is noticed in the two solutions as is enhanced. However, there is no effect of the higher values of on the delaying boundary layer separation, as the critical values of are the same. Dual solutions exist when and no solution exists when . It is worthwhile to mention that the effect of on is not important, as we have gotten the same values of for the higher values of . Figure 9 displays the variation of the heat transfer rate, , for numerous values of . The same behavior of is observed as it is demonstrated in Figure 8.
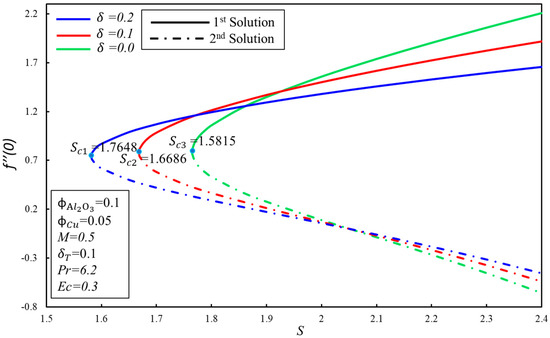
Figure 7.
The variation of with for various values of .
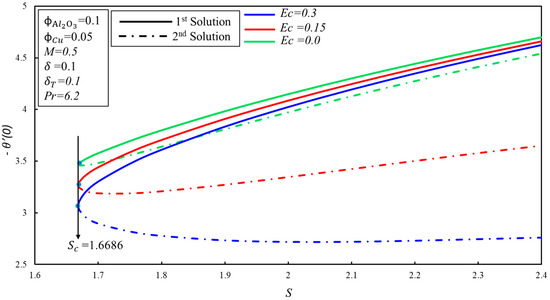
Figure 8.
The variation of with for various values of .
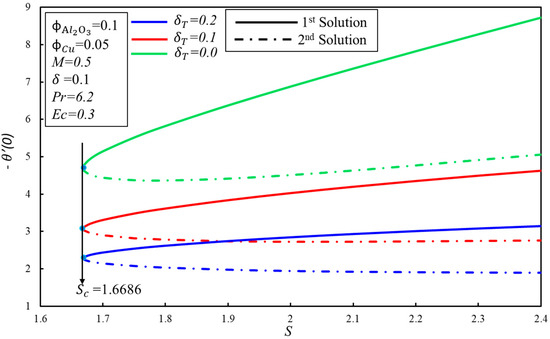
Figure 9.
The variation of with for various values of .
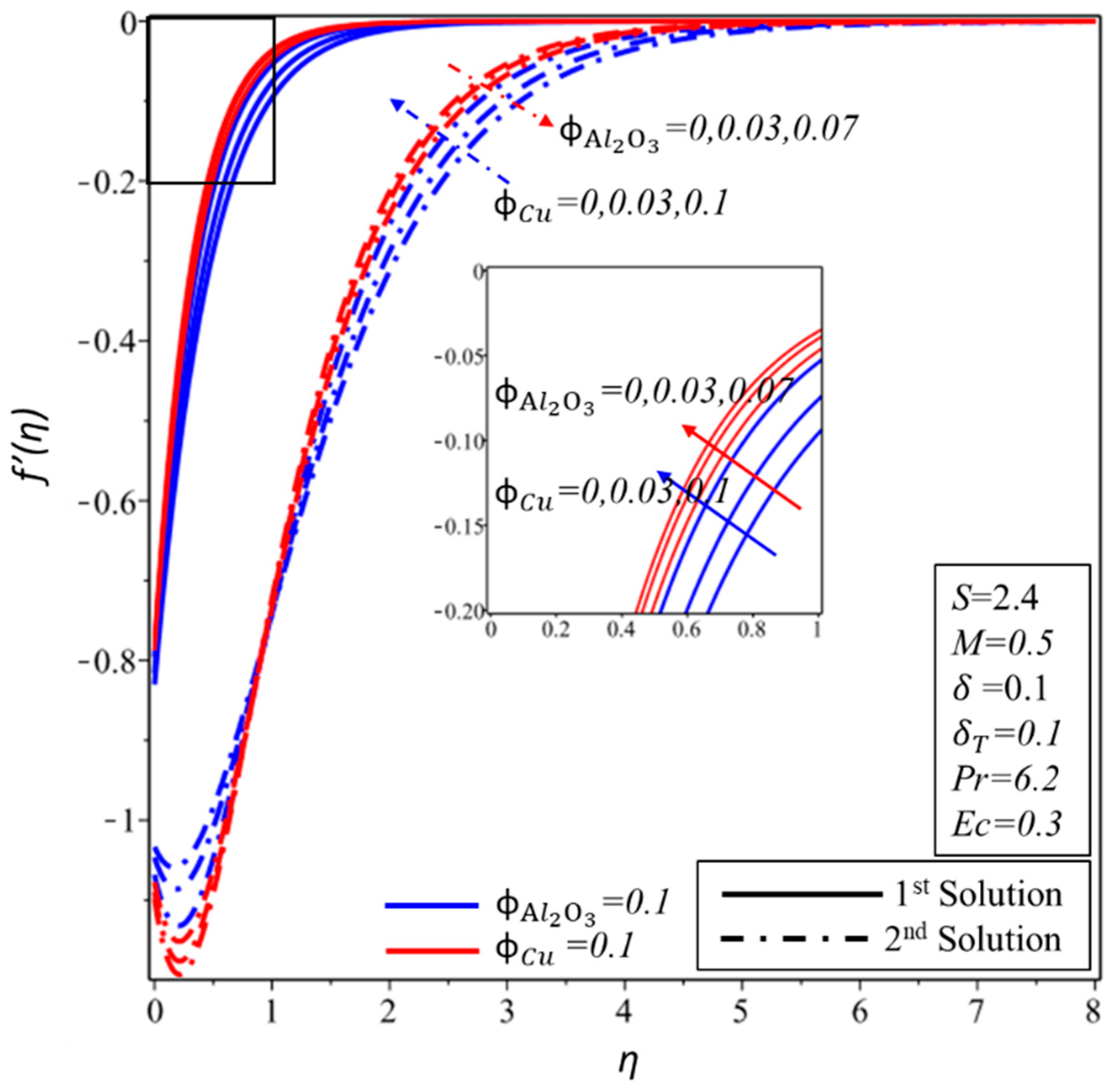
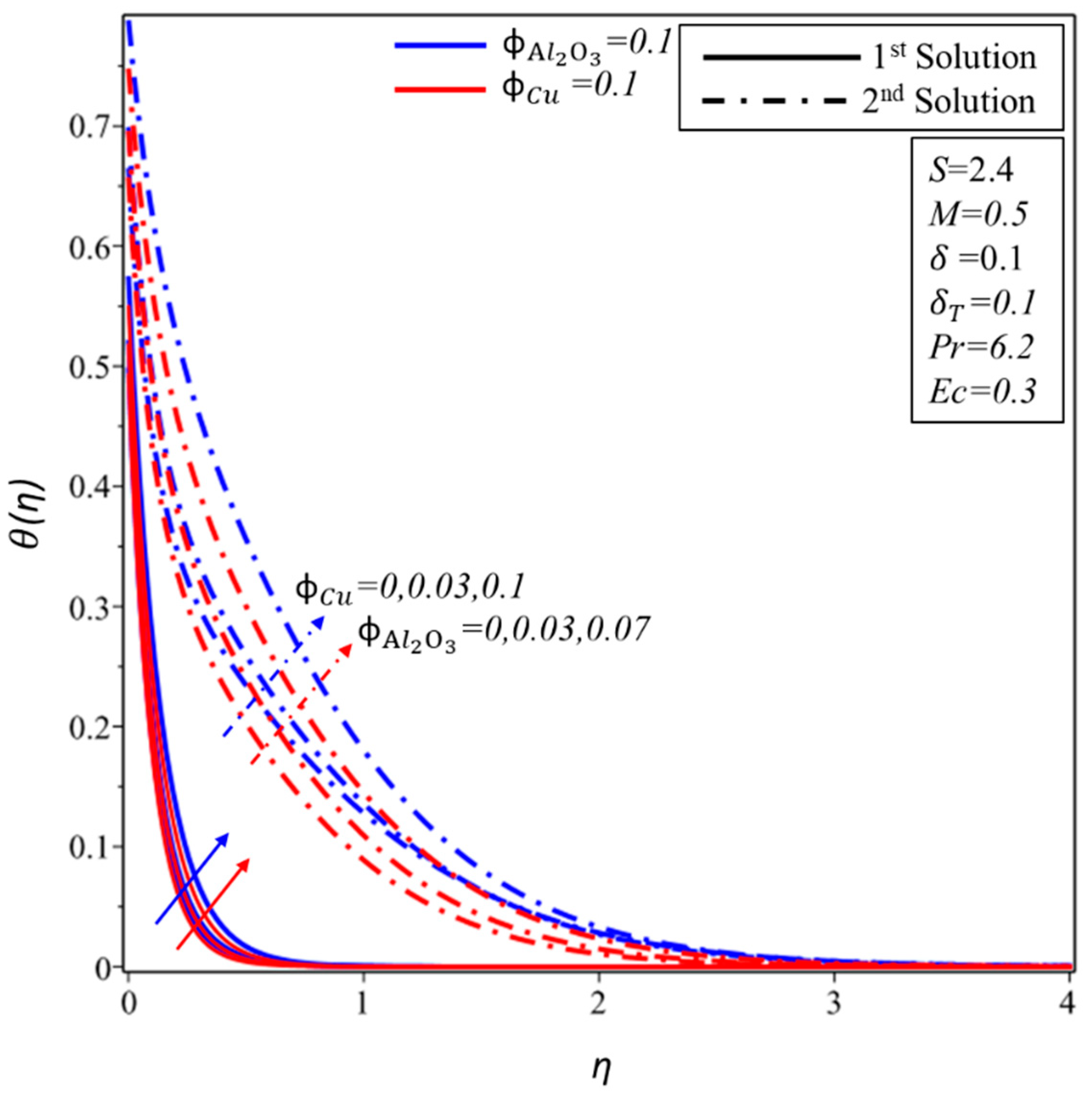
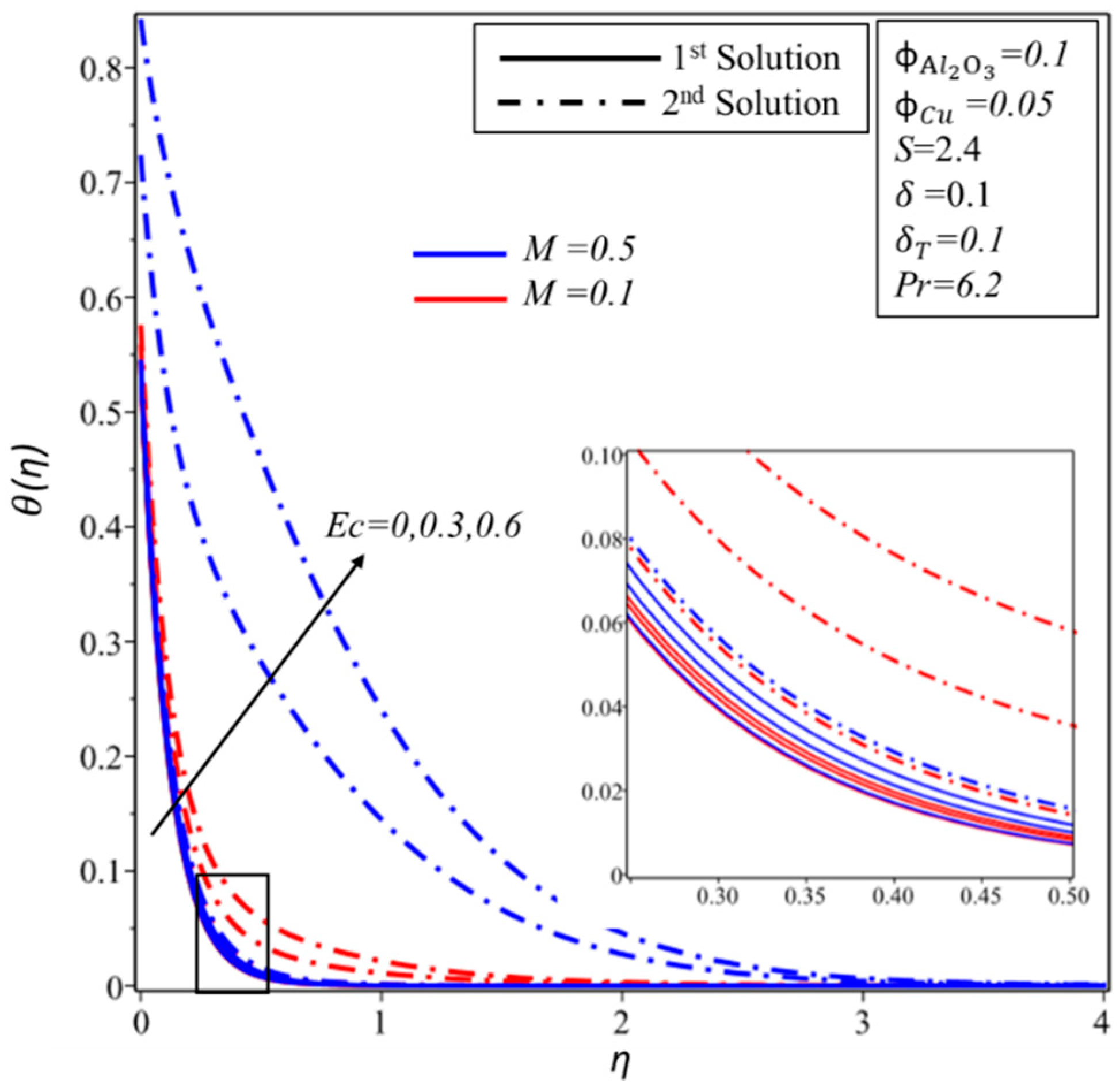
Figure 10 and Figure 11 show the effect of and on the velocity profile, , and temperature profile, . It is found that the velocity and thickness of the momentum boundary layer decrease for both solutions with increments in when is kept as a constant. In contrast, the momentum boundary layer becomes thicker in the subsequent solution when is increased for the fixed value of , while a reverse trend of velocity profile is noticed for the first solution. Furthermore, the thickness of the thermal boundary layer and the temperature distributions increase in both solutions with rising values of and . It is examined that by varying , values span a greater range of temperatures in the fluid flow from the surface as compared to ; this behaviour of the temperature profiles supports our assumptions of keeping fixed in the whole study. The thermal boundary layer thickness develops as the Eckert and magnetic numbers are increased in both solutions, as seen in Figure 12. This rising of the temperature is due to the higher kinetic energy, which is directly proportional to the Eckert number. Furthermore, the Lorentz force also causes the temperature of the fluid to spread from the surface towards the flow.
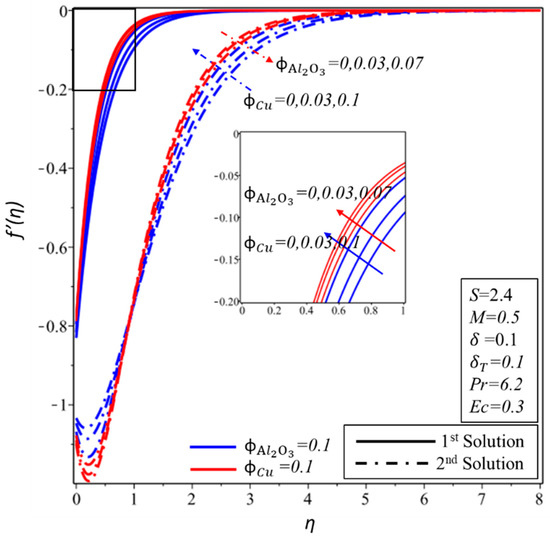
Figure 10.
The velocity profile, , for the various values of and .
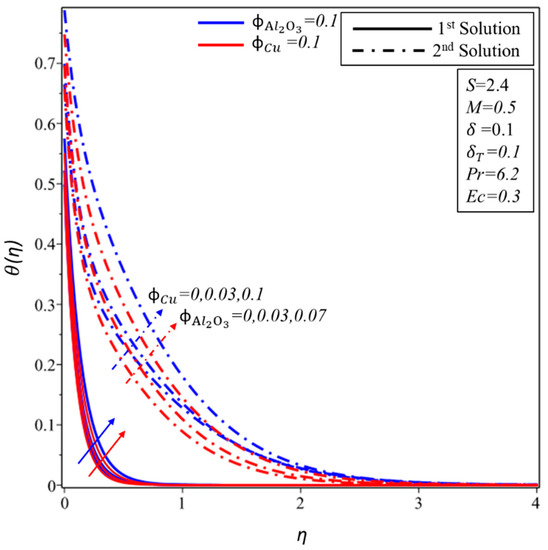
Figure 11.
The temperature profile, , for the various values of and .
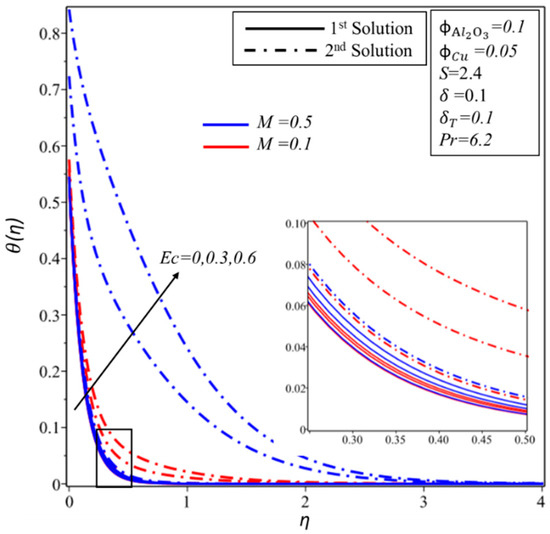
Figure 12.
The temperature profile, , for the various values of and .
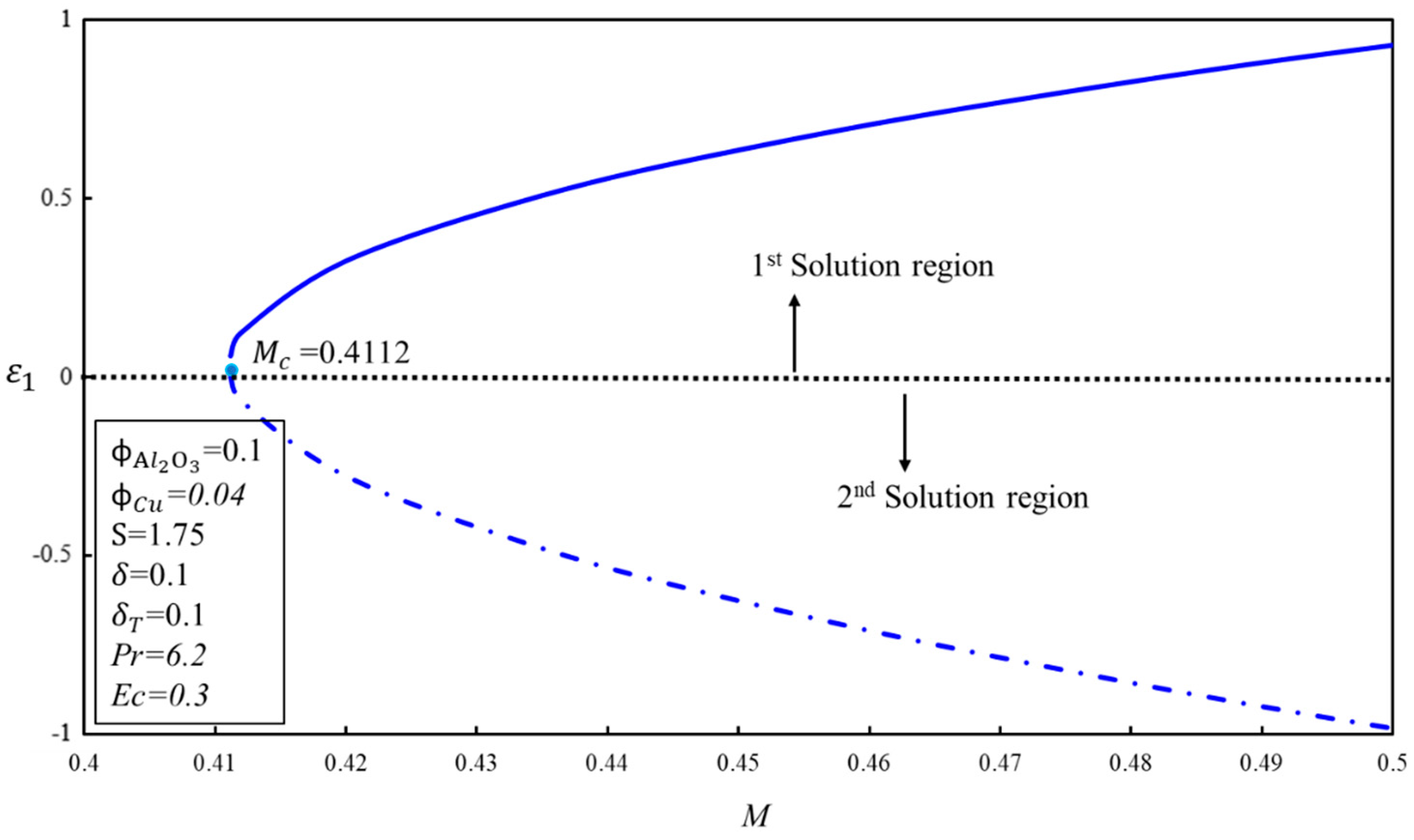
In order to indicate the physically realizable solution, the implementation of the stability analysis is necessary to conduct in the study when a non-uniqueness of solutions exists. Normally, the first solution is referred to as the physical solution, as it satisfies the far-field boundary condition, but it cannot be said which solution is the physical solution without performing the stability analysis of solutions. The indicated solution might be the second solution. Therefore, the performing of stability analysis of solutions should be considered to stop wrong predictions regarding the flow characteristics and solutions. In this study, the system of the eigenvalue problem (19–20) was solved with the help of BVP4C code in the MATLAB software in order to obtain the values of the smallest eigenvalue, . The signs of the smallest eigenvalue, , help to indicate a stable solution. If the sign of is positive, it is implied that the flow is stable and showing an initial growth of decay, while if it is negative, it means that the flow is unstable and indicates the initial growth of disturbance. Positive values of can be seen in the upper part of Figure 13, and negative values of in the lower part. Therefore, the first solution is stable and the second is unstable. Furthermore, it is also noticed that for both solutions when , which validates the current formulation of the problem and also proves that the real solution is the first solution.
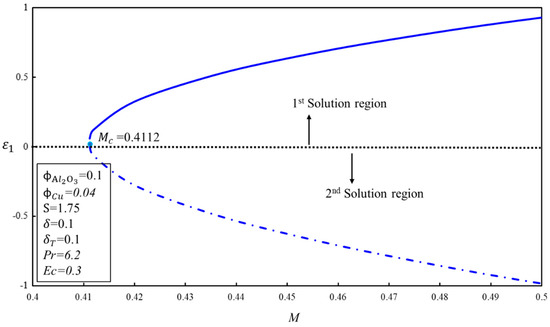
Figure 13.
The smallest eigenvalues, , for various values of .
5. Conclusions
The steady MHD flow of hybrid nanofluid with the effects of Joule heating and slip conditions has been investigated over the shrinking surface. After the transformation of the similarity variables, equations were solved by employing BVP4C. The pointwise conclusions of the present study are as follows:
- There exist two ranges of solution, namely dual solutions and no solution.
- Dual solutions do not exist beyond the critical values () of the parameters.
- The existence of dual solutions is possible in certain dimensions of the suction parameter .
- Due to the effect of Joule heating, the dual solutions also depend on certain ranges of the magnetic parameter, .
- The skin friction coefficient, , enhances for the first solution when the and parameters are increased, while reduces for the higher effect of the velocity slip factor, .
- The heat transfer rate, , reduces with increments in the Eckert number, , and the thermal slip parameter, ; however, Ec and do not affect the boundary layer separation.
- The temperature and thermal boundary layer thickness have direct relationships with for both solutions.
- Positive smallest eigenvalues indicate the initial decay of the disturbance, and that the flow becomes the stable flow.
- The stability analysis indicates that the real solution is the first solution.
Author Contributions
L.Y. derived the equations and generated the results. S.D. formulated the model and proofread the manuscript. I.K. discussed the results and checked the whole manuscript. I.A.M. wrote the paper. D.B. derived the equations of stability analysis. K.S.N. wrote the paper and checked the manuscript. E.-S.M.S. wrote the introduction section. H.S.A. run the stability program and generated the values. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University through the Research Group Project No. RGP-160.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding of this research through the Research Group Project No. RGP-160. The first and second authors are thankful to Liaquat Ali Lund who helped us a lot to conduct and complete this research.
Conflicts of Interest
This research received no external funding.
References
- Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; (No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135-29); Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1995.
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 106, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrajab, R.; Noghrehabadi, A.; Behbahani, M.; Hajidavalloo, E. An efficient enhancement in thermal conductivity of water-based hybrid nanofluid containing MWCNTs-COOH and Ag nanoparticles: Experimental study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Raza, M.; Ellahi, R. Influence of induced magnetic field and heat flux with the suspension of carbon nanotubes for the peristaltic flow in a permeable channel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.A.; Raza, M.; Mir, N.A.; Ellahi, R. Effects of different shapes of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Rohni, A.M. Stefan blowing and slip effects on unsteady nanofluid transport past a shrinking sheet: Multiple solutions. Heat Transf.—Asian Res. 2019, 48, 2047–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, U.; Khan, I.; Baleanu, D.; Nisar, K.S. Stability Analysis and Dual Solutions of Micropolar Nanofluid over the Inclined Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Convective Boundary Condition. Symmetry 2020, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Qasim, M.; Alderremy, A.A.; Noreen, S. Heat transfer enhancement using different shapes of Cu nanoparticles in the flow of water based nanofluid. Physica Scripta 2019, 95, 055209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Bhatti, M.M.; Ellahi, R.; Zeeshan, A.M.; Sait, S. Mathematical Analysis on an Asymmetrical Wavy Motion of Blood under the Influence Entropy Generation with Convective Boundary Conditions. Symmetry 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jaryani, P.; Amiri, A.; Rahimi, A.; Malekshah, E.H. Heat transfer and nanofluid flow of free convection in a quarter cylinder channel considering nanoparticle shape effect. Powder Technol. 2019, 346, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, J.; Moradikazerouni, A.; Shahsavar, A.; Afrand, M.; Salehipour, H.; Tran, M.D. Hydrothermal analysis of turbulent boehmite alumina nanofluid flow with different nanoparticle shapes in a minichannel heat exchanger using two-phase mixture model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 520, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Khan, I.; Rasool, G.; Sherif, E.S.M.; Sheikh, A.H. Influence of Single-and Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes on Magnetohydrodynamic Stagnation Point Nanofluid Flow over Variable Thicker Surface with Concave and Convex Effects. Mathematics 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Zhang, T.; Chamkha, A.J.; Shafiq, A.; Tlili, I.; Shahzadi, G. Entropy Generation and Consequences of Binary Chemical Reaction on MHD Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson Nanofluid Flow Over Non-Linearly Stretching Surface. Entropy 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Effect of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluid in heat transfer. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 38, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatundun, A.T.; Makinde, O.D. Analysis of Blasius flow of hybrid nanofluids over a convectively heated surface. In Defect and Diffusion Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 377, pp. 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattad, A.; Sarkar, J.; Ghosh, P. Hydrothermal performance of different alumina hybrid nanofluid types in plate heat exchanger. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhesh, D.; Kalaiselvam, S. Experimental analysis of hybrid nanofluid as a coolant. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Godini, A.; Sardari, P.T.; Toghraie, D.; Salehipour, H. Impact of variable fluid properties on forced convection of Fe3O4/CNT/water hybrid nanofluid in a double-pipe mini-channel heat exchanger. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, M. Novel uses of alumina/graphene hybrid nanoparticle additives for improved tribological properties of lubricant in turning operation. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Afrand, M.; Mehmandoust, B. Curve fitting on experimental data of a new hybrid nano-antifreeze viscosity: Presenting new correlations for non-Newtonian nanofluid. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 531, 120837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.A.; Devi, S.S.U. Numerical investigation of hydromagnetic hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with suction. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2016, 17, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.S.U.; Devi, S.A. Numerical investigation of three-dimensional hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with effecting Lorentz force subject to Newtonian heating. Can. J. Phys. 2016, 94, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Jana, R.N.; Makinde, O.D. MHD flow of Cu-Al2O3/Water hybrid nanofluid in porous channel: Analysis of entropy generation. In Defect and Diffusion Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 377, pp. 42–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mehryan, S.A.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Ghalambaz, M.; Chamkha, A.J. Free convection of hybrid Al2O3-Cu water nanofluid in a differentially heated porous cavity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Doostanidezfuli, A.; Izadpanahi, E.; Ghalambaz, M.J.A.P.T. Phase-change heat transfer of single/hybrid nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials over a heated horizontal cylinder confined in a square cavity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, A.U. Rotating flow of Ag-CuO/H2O hybrid nanofluid with radiation and partial slip boundary effects. Eur. Phys. J. E 2018, 41, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, F.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, U.; Waheed, A.; Rafiq, M.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Thermophysical analysis of water based (Cu–Al2O3) hybrid nanofluid in an asymmetric channel with dilating/squeezing walls considering different shapes of nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sarkar, J. Particle ratio optimization of Al2O3 -MWCNT hybrid nanofluid in minichannel heat sink for best hydrothermal performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 165, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M. Experimental investigation of carbon dioxide cross-contamination in sorption energy recovery wheel in ventilation system. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2018, 39, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalambaz, M.; Roşca, N.C.; Roşca, A.V.; Pop, I. Mixed convection and stability analysis of stagnation-point boundary layer flow and heat transfer of hybrid nanofluids over a vertical plate. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a stretching/shrinking sheet in a hybrid nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 136, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Seikh, A.H.; Sherif, E.S.M.; Nisar, K.S. Stability analysis and multiple solution of Cu–Al2O3/H2O nanofluid contains hybrid nanomaterials over a shrinking surface in the presence of viscous dissipation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 9, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashi’ie, N.S.; Arifin, N.M.; Nazar, R.; Hafidzuddin, E.H.; Wahi, N.; Pop, I. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Axisymmetric Flow and Heat Transfer of a Hybrid Nanofluid past a Radially Permeable Stretching/Shrinking Sheet with Joule Heating. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 64, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H.; Pop, I. Stagnation-Point Flow and Heat Transfer Over an Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Sheet in Hybrid Nanofluid with Slip Velocity Effect: Stability Analysis. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1366, p. 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow induced by an exponentially shrinking sheet. Chin. J. Phys. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Kadry, S.; Rho, S.; Mari, I.A.; Nisar, K.S. Effect of Viscous Dissipation in Heat Transfer of MHD Flow of Micropolar Fluid Partial Slip Conditions: Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavčič, M.; Wang, C. Viscous flow due to a shrinking sheet. Q. Appl. Math. 2006, 64, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Aziz, A. Viscous flow over a shrinking sheet with a second order slip flow model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Sakidin, H.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid: A revised model with stability and regression analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Transpiration effects on hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform shear flow. Alex. Eng. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S. Heat transfer enhancement with Ag-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M.; Simonson, C.J. Experimental effectiveness investigation of liquid-to-air membrane energy exchangers under low heat capacity rates conditions. Exp. Heat Transf. 2016, 29, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A. MHD micropolar nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretching/shrinking surface: Triple solutions. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A.; Khan, I. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces. Energies 2019, 12, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Effect of Suction/Injection on Stagnation Point Flow of Hybrid Nanofluid over an Exponentially Shrinking Sheet with Stability Analysis. CDF Lett. 2019, 11, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, M.; Khan, N.A. Slip effects on fractional viscoelastic fluids. Int. J. Differ. Equ. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.I. Slip flow past a stretching surface. Acta Mech. 2002, 158, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Bég, O.A.; Ismail, A.I. Radiative convective nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking sheet with slip effects. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2015, 29, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Abbas, N. On both MHD and slip effect in Micropolar Hybrid nanofluid past a circular cylinder under stagnation point region. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, N.; Rehman, A.; Sadaf, H.; Iqbal, S. Study of Al2O3/copper–water nanoparticle shape, slip effects, and heat transfer on steady physiological delivery of MHD hybrid nanofluid. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Lund, L.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Raza, J.; Bakouri, M.; Tlili, I. Stability analysis of Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Casson type nanofluid over an exponential sheet: Investigation of critical points. Symmetry 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Sherif, E.S.M. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of a Hybrid Nanofluid over a Stretching/Shrinking Sheet Executing MHD Flow. Symmetry 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Quadruple solutions of mixed convection flow of magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid over exponentially vertical shrinking and stretching surfaces: Stability analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 182, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).