Is Recycling Always the Best Option? Environmental Assessment of Recycling of Seashell as Aggregates in Noise Barriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goal and Scope
- -
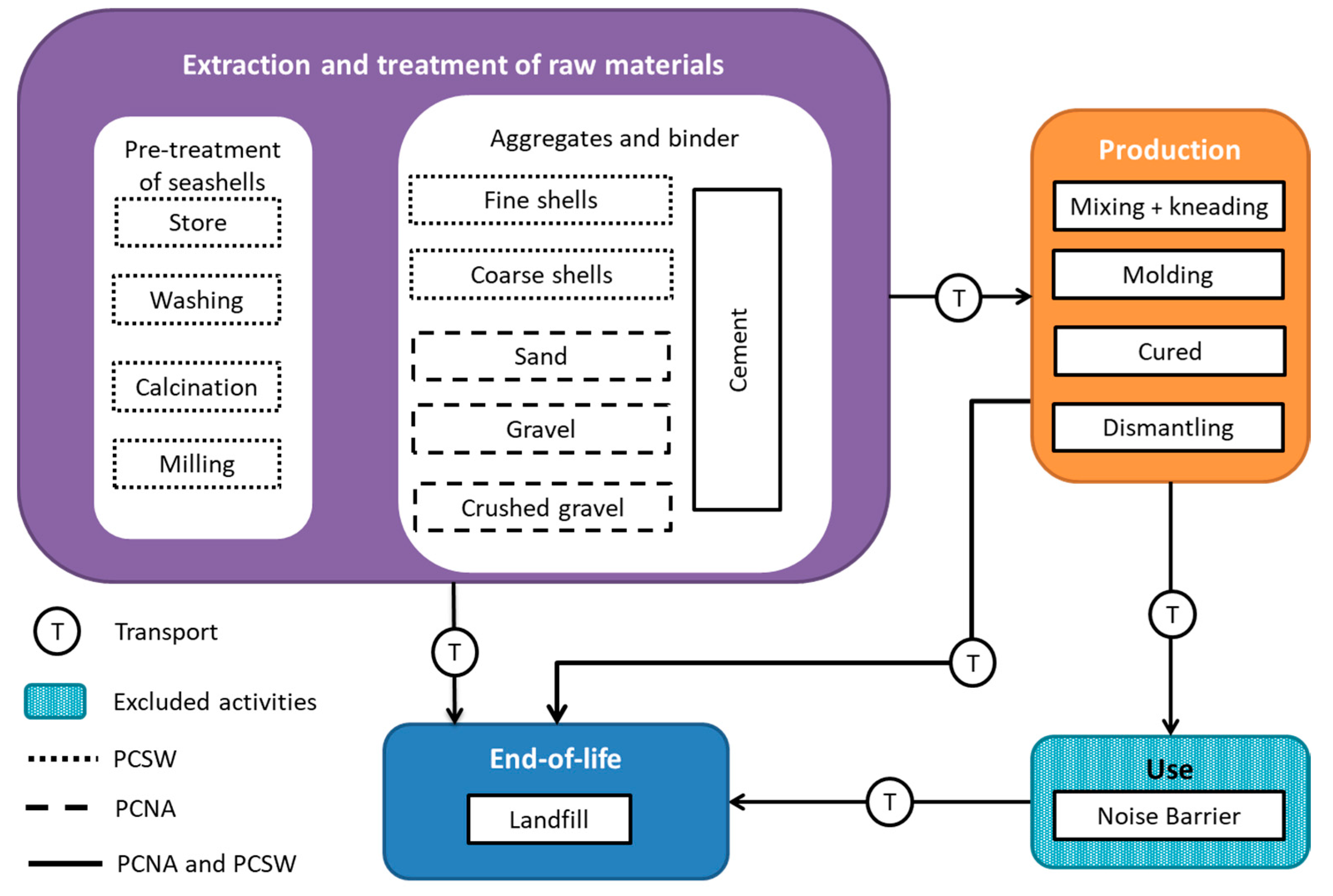
- Extraction and treatment of raw materials:
- Cement.
- Natural aggregates (sand, gravel and crushed gravel) for PCNA.
- Seashell waste for PCSW, which needs a pre-treatment consisting of storing, washing, calcination, and milling to obtain fine and coarse aggregates.
- -
- Production of the noise barrier:
- Mixing and kneading: Cement and aggregates or seashell waste are mixed with water.
- Molding: Concrete is molded (see Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials (SI)).
- Cured: Hardening process.
- Dismantling: Removal from the mold where the mixture is supported.
- -
- -
- End-of-life. Landfilling of the waste from the extraction and treatment of raw materials, the production process, and the end-of-life of the noise barrier.
- -
- Transport. It includes the transport of the seashell waste to the pre-treatment facility, of the raw materials to the noise barrier factory, of the porous concrete panel to the location of use, and of the waste to the landfill.
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory
2.2.1. Raw Materials
2.2.2. Production
2.2.3. End-of-Life
2.2.4. Transport
2.3. Sensitivity Analysis
2.4. Environmental Impact Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of PCNA and PCSW
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estanqueiro, B.; Dinis Silvestre, J.; De Brito, J.; Duarte Pinheiro, M. Environmental life cycle assessment of coarse natural and recycled aggregates for concrete. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2016, 22, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Arcidiacono, C.; Bezama, A.; Ioppolo, G.; Winans, K.; Koutinas, A.; Gallego-Schmid, A. Sustainability issues of by-product and waste management systems to produce building material commodities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Arcidiacono, C.; Bezama, A.; Ioppolo, G.; Winans, K.; Koutinas, A.; Gallego-Schmid, A. Sustainability issues of by-product and waste management systems, to produce building material commodities: A comprehensive review of findings from a virtual special issue. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Arenas, C.; Arroyo Torralvo, F.; Leiva, C. Sustainable management of spent fluid catalytic cracking catalyst from a circular economy approach. J. Waste Manag. 2020, 110, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Leiva, C.; Navarrete, B.; Vilches, L.F. Synthetic slag production method based on a solid waste mix vitrification for the manufacturing of slag-cement. Materials 2019, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallego-Schmid, A.; Chen, H.M.; Sharmina, M.; Mendoza, J.M.F. Links between circular economy and climate change mitigation in the built environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.C.; Jha, M.K.; Kim, B.S. Resource recycling of superalloys and hydrometallurgical challenges. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4671–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Srivastava, R.R.; Jun, M.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.C. Hydrometallurgical recycling of surface-coated metals from automobile-discarded ABS plastic waste. J. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, R.; Ilyas, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Ghaffar, A. Resource recovery of critically-rare metals by hydrometallurgical recycling of spent lithium ion batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 49, 4671–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei, R.K.; Maroufi, S.; Assefi, M.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Thermal isolation of a clean alloy from waste slag and polymeric residue of electronic waste. Processes 2020, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaimes, G.G.; Vora, N.; Chopra, S.S.; Landis, A.E.; Khanna, V. Design of sustainable biofuel processes and supply chains: Challenges and opportunities. Processes 2015, 3, 634–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, W. Sustainability of aggregates in construction. In Sustainability of Construction Materials, 2nd ed.; Khatib, J.M., Ed.; Elselvier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 181–207. [Google Scholar]
- Sreebha, S.; Padmalal, D. Environmental impact assessment of sand mining from the small catchment rivers in the Southwestern Coast of India: A case study. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BOE. Law 7/1992, de 24 de July, about River Fishing, of Comunidad Autónoma de Galicia, BOE 1992, Pages 34618 to 34625. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es-ga/l/1992/07/24/7 (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Hill, A.R.; Dawson, A.R.; Mundy, M. Utilisation of aggregate materials in road construction and bulk fill. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2001, 32, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Union Européenne des Producteurs de Granulat (UEPG). Stadistic. 2018. Available online: http://www.uepg.eu/statistics/estimates-of-production-data/data-2015 (accessed on 23 July 2018).
- Arenas, C.; Luna-Galiano, Y.; Leiva, C.; Vilches, L.F.; Arroyo, F.; Villegas, R.; Fernández-Pereira, C. Development of a fly ash-based geopolymeric concrete with construction and demolition wastes as aggregates in acoustic barriers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Ye, Y. Properties of recycled aggregate concrete prepared with scattering-filling coarse aggregate process. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Yap, S.P.; Lee, S.C. Green concrete partially comprised of farming waste residues: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandni, T.J.; Anand, K.B. Utilization of recycled waste as filler in foam concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Chen, X. Sustainability: Don’t waste seafood waste. Nature 2015, 524, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cong, X.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wang, C. Scalable recycling of oyster shells into high purity calcite powders by the mechanochemical and hydrothermal treatments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Li, X. Recycling of shell wastes into nanosized calcium carbonate powders with different phase compositions. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 92, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xia, M.; Li, H.; Chen, T.; Ye, Y.; Zheng, H. Bivalve Shell: Not an abundant useless waste but a functional and versatile biomaterial. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2502–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, P.; Mármol, I.; Morales, J.; Sánchez, L. Use of limestone obtained from waste of the mussel cannery industry for the production of mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.I.; Yi, S.T.; Leem, Y.M. Effect of oyster shell substituted for fine aggregate on concrete characteristics: Part I. Fundamental properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.I.; Kim, M.Y.; Park, H.G.; Yi, S.T. Effect of partial replacement of sand with dry oyster shell on the long-term performance of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Park, S.; Lee, K.; Park, J. Oyster shell as substitute for aggregate in mortar. Waste Manag. Res. 2004, 22, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewuyi, P.; Adegoke, T. Exploratory study of periwinkle shells as coarse aggregates in concrete works. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization (EN). Tests for Chemical Properties of Aggregates—Part 1: Chemical Analysis; EN 1744-1; EN: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Felipe-Sesé, M.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; Corpas-Iglesias, F.A. The use of solid residues derived from different industrial activities to obtain calcium silicates for use as insulating construction materials. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 3019–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, D.; Cavallo, D. Mechanical behavior of concretes made with non-conventional organic origin calcareous aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Li, L.G.; Lai, Z.; Kwan, A.; Chen, P.; Ng, P.L. Effects of crushed oyster shell on strength and durability of marine concrete containing fly ash and blastfurnace slag. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 25, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lertwattanaruk, P.; Makul, N.; Siripattarapravat, C. Utilization of ground waste seashells in cement mortars for masonry and plastering. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, E.; Fan, J.; Xiong, G. Properties of cement-based bricks with oyster-shells ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, R.A.F.; De Galindro, B.M.; Helpa, C.F.; Soares, S.R. The recycling of oyster shells: An environmental analysis using Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 106, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribarren, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Implementing by-product management into the life cycle assessment of the mussel sector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Environmental noise guidelines for the European region. Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics; World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union (EC). Directive 2002/49/Ec of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 June 2002 relating to the assessment and management of environmental noise. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, L189, 12–25. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32002L0049andfrom=EN (accessed on 3 June 2020).
- Kotzen, B.; English, C. Book Environmental Noise Barriers—A Guide to Their Acoustic and Visual, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Peceño, B.; Arenas, C.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Leiva, C. Substitution of coarse aggregates with mollusk-shell waste in acoustic-absorbing concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galician Statistical Institute (IGE). Production of Marine Aquaculture in Galicia. 2017. Available online: https://www.ige.eu/web/mostrar_actividade_estatistica.jsp?idioma=esandcodigo=0301004 (accessed on 12 June 2018).
- Eurostat. Catches—Major Fishing Areas (from 2000 Onwards). 2019. Available online: https://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=fish_ca_mainandlang=en (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- International Standards Organization (ISO). Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework, ISO 14040; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- International Standards Organization (ISO). Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines, ISO 14044; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ACH. Noise Barriers. Available online: http://www.barrieresach.com/pantallas-barreras-acusticas-ACH (accessed on 18 August 2019).
- Pan Rodo. Noise Barriers. Available online: https://www.obralia.com/dir/minisites/catalogos/419295/catalogo.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2018).
- European Committee for Standardization (EN). Road Traffic Noise Reducing Devices—Test Method for Determining the Acoustic Performance—Part 1: Intrinsic Characteristics of Sound Absorption under Diffuse Sound Field Conditions; EN 1793-1; EN: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno Ruiz, E.; Valsasina, L.; Brunner, F.; Symeonidis, A.; FitzGerald, D.; Treyer, K.; Bourgault, G.; Wernet, G. Documentation of Changes Implemented in Ecoinvent Data 3.1; Ecoinvet: Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission (EC). Commission Decision on the European List of Waste (COM 2000/532/EC). Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 50, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Galvez-Martos, J.L.; Styles, D.; Schoenberger, H.; Zeschamar-Lahl, B. Construction and demolition waste best management practice in Europe. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, M.C.; Bello, P.M.; Bao, M.; Torrado, J.J. From waste to commodity: Transforming shells into high purity calcium carbonate. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Maps. Distances. 2020. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/ (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Mercante, I.T.; Bovea, M.D.; Ibáñez-Forés, V.; Arena, A.P. Life cycle assessment of construction and demolition waste management systems: A Spanish case study. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2012, 17, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and of the Council (EC). Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2007 on Type Approval of Motor Vehicles with Respect to Emissions from Light Passenger and Commercial Vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on Access to Vehicle Repair and Maintenance Information. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2007/715/oj (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Barros, C.; Bello, P.; Valiño, S.; Bao, M.; Arias, J. Odours prevention and control in the shell waste valorisation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on EcoTopia Science (ISETS07), Nagoya, Japan, 23–25 November 2007; pp. 890–895. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. Structure/mechanical behavior relationships in crossed-lamellar seashells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 25, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahari, F.; Aniza, N. Cockle shell as an alternative construction material for artificial reef. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creativity and Innovation for Sustainable Development, Sarawak, Malaysia, 12–14 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F.; Carro-López, D. Performance of mussel shell as aggregate in plain concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 570–583. [Google Scholar]
- PRé Consultants. SimaPro 8.0.4.LCA Software and Database Manual; PRé Consultants, B.V.: Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, J.B.; Gorrèe, M.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Kleijn, G.R.; van Oers, R.L.; Wegener, L.; Sleeswijk, A.; Suh, S.; Udo de Haes, H.A.; et al. Life Cycle Assessment, an Operational Guide to the ISO Standards. Part 2a; Guide Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Fresh-state performance of recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, G.; Sharmina, M.; Mendoza, J.M.F.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Azapagic, A. Developing and implementing circular economy business models in service-oriented technology companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.M.F.; Sharmina, M.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Heyes, G.; Azapagic, A. Integrating backcasting and eco-design for the circular economy: The BECE framework. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 21, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, J.M.F.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Azapagic, A. Building a business case for implementation of a circular economy in higher education institutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission (EC). Towards a Circular Economy: A Zero Waste Programme for Europe. 2014. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/circular-economy/pdf/circular-economy-communication.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2020).
- Kalmykova, Y.; Sadagopan, M.; Rosado, L. Circular economy—From review of theories and practices to development of implementation tools. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Segoloni, E.; Blasi, F.; Di Maria, F. Low-molecular-weight phenols recovery by eco-friendly extraction from Quercus spp. wastes: An analytical and biomass-sustainability evaluation. Processes 2020, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Parameters | PCNA | PCSW |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction and treatment of raw materials | ||
| Pre-treatment of seashells1 | ||
| Seashell waste (kg) | - | 301.8 |
| Propane (kg) | - | 6.3 |
| Diesel (g) | - | 140.0 |
| Aluminum sulphate (g) | - | 7.2 |
| Chlorine dioxide (g) | - | 1.8 |
| Water (kg) | 280.0 | |
| Electricity, low voltage (kWh) | - | 29.4 |
| Aggregates and cement | ||
| Gravel (kg) | 48.0 | - |
| Sand (kg) | 96.0 | - |
| Crushed gravel (kg) | 69.1 | |
| Fine shells (kg) | - | 90.4 |
| Coarse shells (kg) | - | 90.4 |
| Cement (kg) | 35.2 | 45.2 |
| Production | ||
| Water (kg) | 14.6 | 27.1 |
| Electricity (low voltage) (kWh) | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| End-of-life | ||
| Landfill (including waste from raw material treatment, production and end-of-life) (kg) | 262 | 240 |
| Transport | ||
| Seashell waste to pre-treatment facility (tkm) | - | 3.02 |
| Raw materials to the factory (tkm) | 11.2 | 18.5 |
| From factory to use place (tkm) | 52.4 | 48.6 |
| From use place to landfill (tkm) | 1.0 | 0.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peceño, B.; Leiva, C.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Gallego-Schmid, A. Is Recycling Always the Best Option? Environmental Assessment of Recycling of Seashell as Aggregates in Noise Barriers. Processes 2020, 8, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070776
Peceño B, Leiva C, Alonso-Fariñas B, Gallego-Schmid A. Is Recycling Always the Best Option? Environmental Assessment of Recycling of Seashell as Aggregates in Noise Barriers. Processes. 2020; 8(7):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070776
Chicago/Turabian StylePeceño, Begoña, Carlos Leiva, Bernabé Alonso-Fariñas, and Alejandro Gallego-Schmid. 2020. "Is Recycling Always the Best Option? Environmental Assessment of Recycling of Seashell as Aggregates in Noise Barriers" Processes 8, no. 7: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070776
APA StylePeceño, B., Leiva, C., Alonso-Fariñas, B., & Gallego-Schmid, A. (2020). Is Recycling Always the Best Option? Environmental Assessment of Recycling of Seashell as Aggregates in Noise Barriers. Processes, 8(7), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070776







