Modeling the Effect of Channel Tapering on the Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution Characteristics of Interdigitated Flow Fields in Redox Flow Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
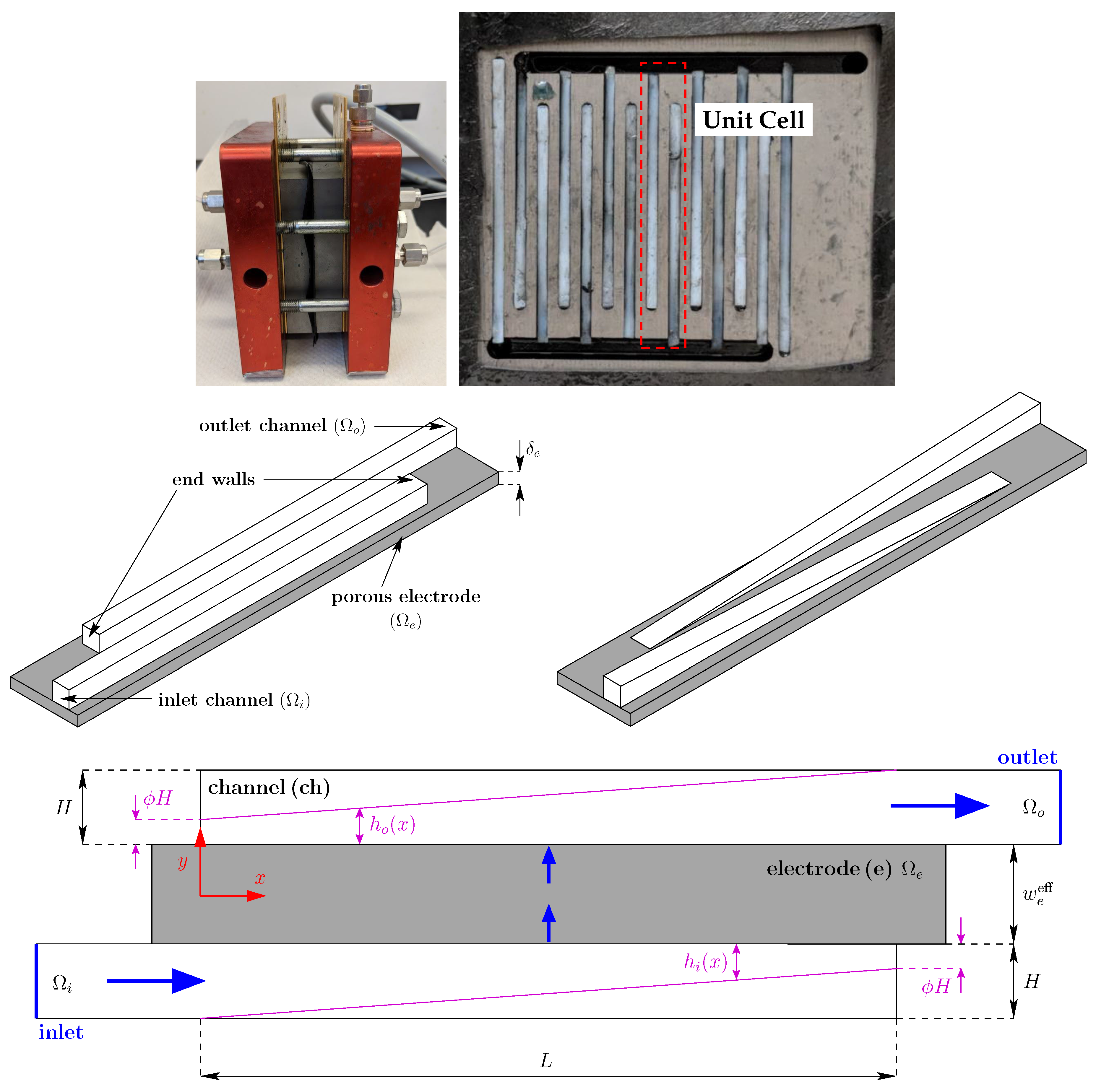
2. Mathematical Model
3. Experimental
4. Discussion of Results
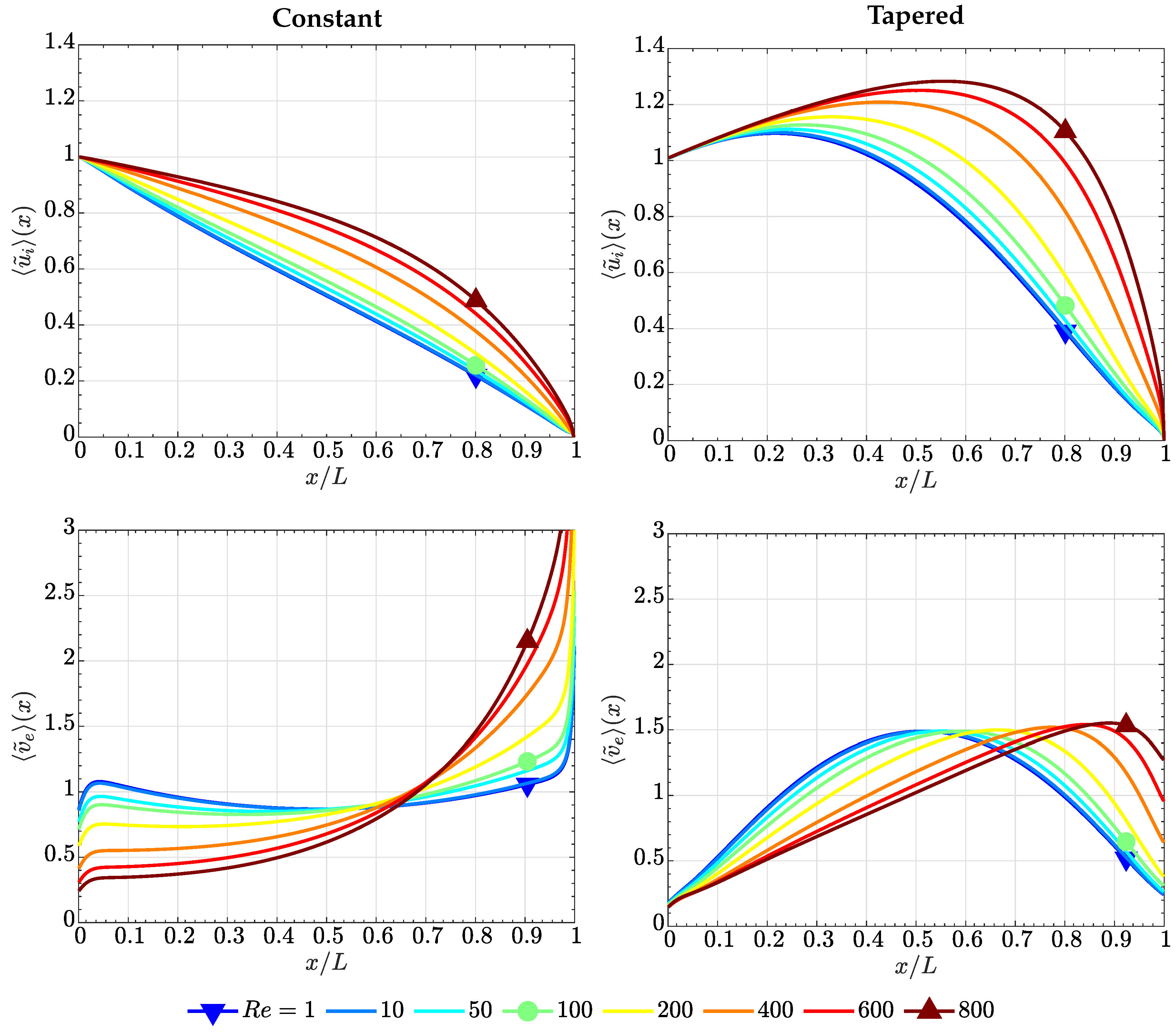
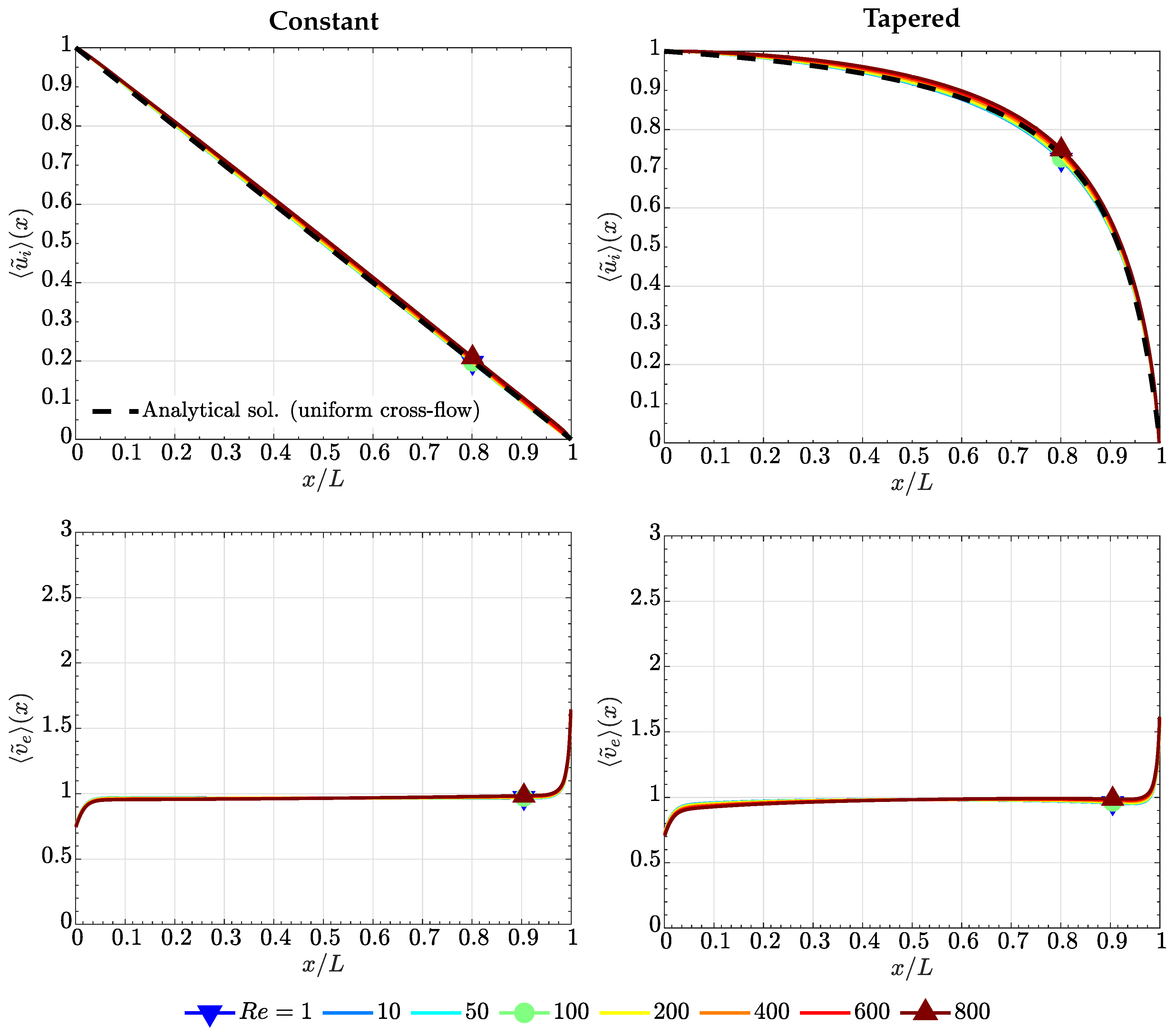
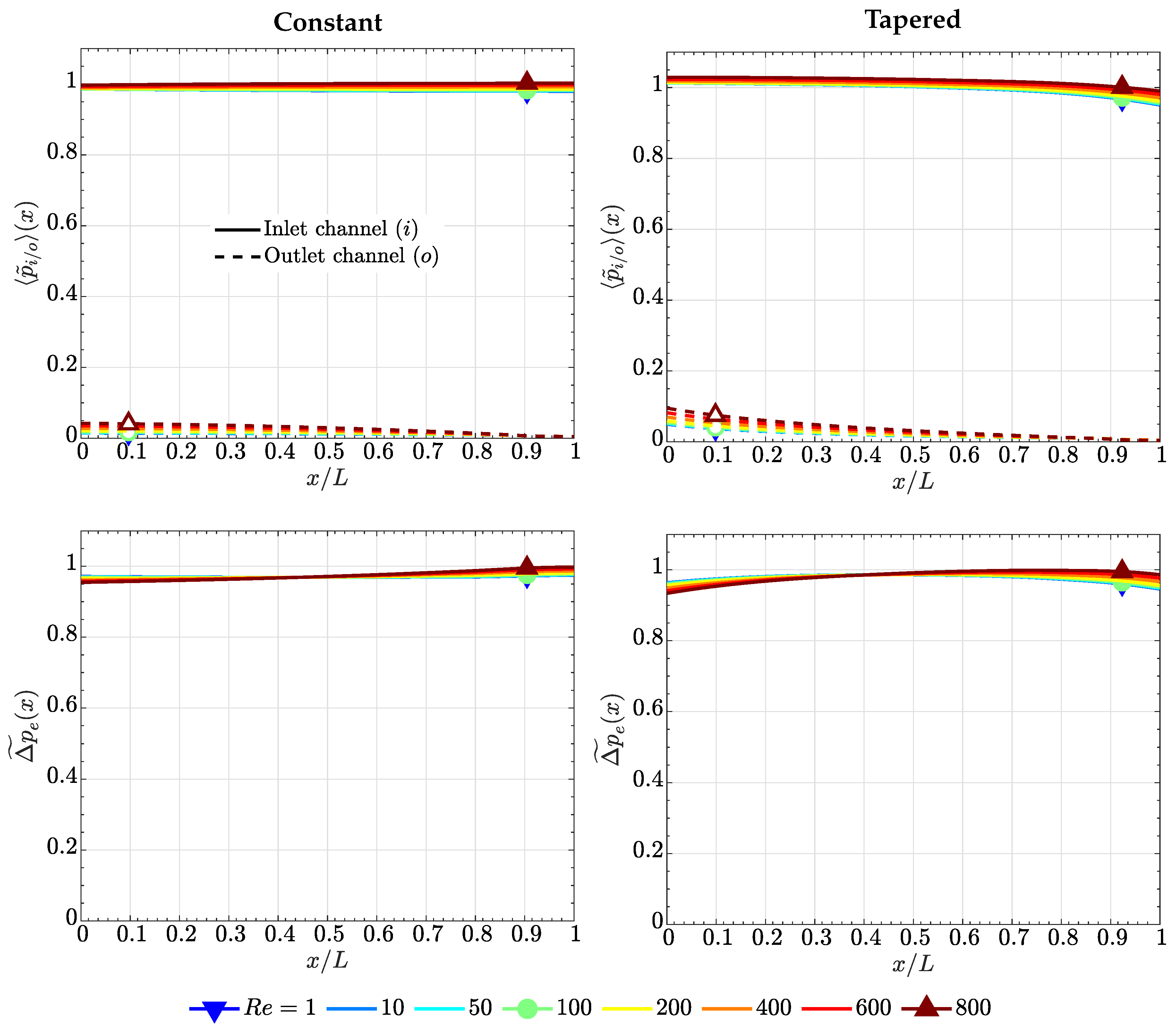
4.1. Case of High Electrode Permeability, ()
4.2. Case of Low Electrode Permeability, ()
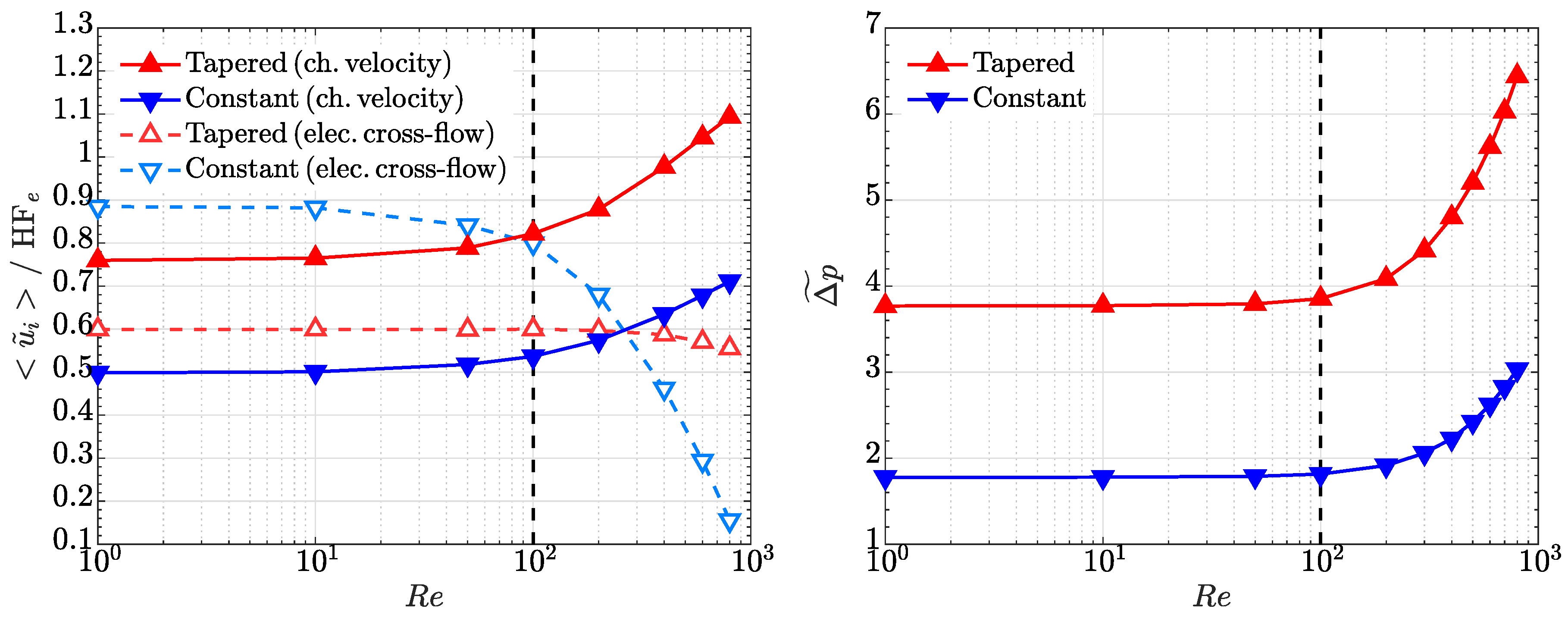
4.3. Comparison with the Lubrication Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| C | dimensionless coefficient in Equation (A10) |
| D | dimensionless coefficient in Equation (A10) |
| h | local channel height/ |
| H | initial height/ |
| homogeneity factor defined in Equation (16) | |
| integral defined in Equation (A13) | |
| integral defined in Equation (A13) | |
| K | absolute permeability/ |
| integral defined in Equation (A13) | |
| L | length/ |
| number of channel segments | |
| p | pressure/ |
| Q | feed flow rate/ |
| flow rate per unit length in the spanwise direction/ | |
| Reynolds number of the flow in the channels | |
| momentum source term/ | |
| u | axial velocity in x-direction/ |
| superficial velocity vector/ | |
| U | inlet velocity/ |
| v | transverse velocity in y-direction/ |
| w | width/ |
| x | x-coordinate/ |
| y | y-coordinate/ |
| Greek letters | |
| exponent in Equation (25) | |
| dimensionless governing parameter in Equation (8) | |
| dimensionless governing parameter in Equation (8) | |
| thickness/m | |
| variation | |
| dimensionless parameter in Equation (Appendix A) | |
| porosity | |
| dimensionless governing parameter in Equation (8) | |
| dynamic viscosity/ | |
| dimensionless parameter defined in Equation (A14) | |
| density/ | |
| tapering parameter in Equation (1) | |
| spatial region | |
| Subscripts | |
| channel | |
| e | electrode |
| f | fiber |
| i | inlet |
| n | index |
| o | outlet |
| reference | |
| flow-field rib | |
| Superscripts | |
| c | convective |
| effective | |
| v | viscous |
Appendix A. Lubrication Model
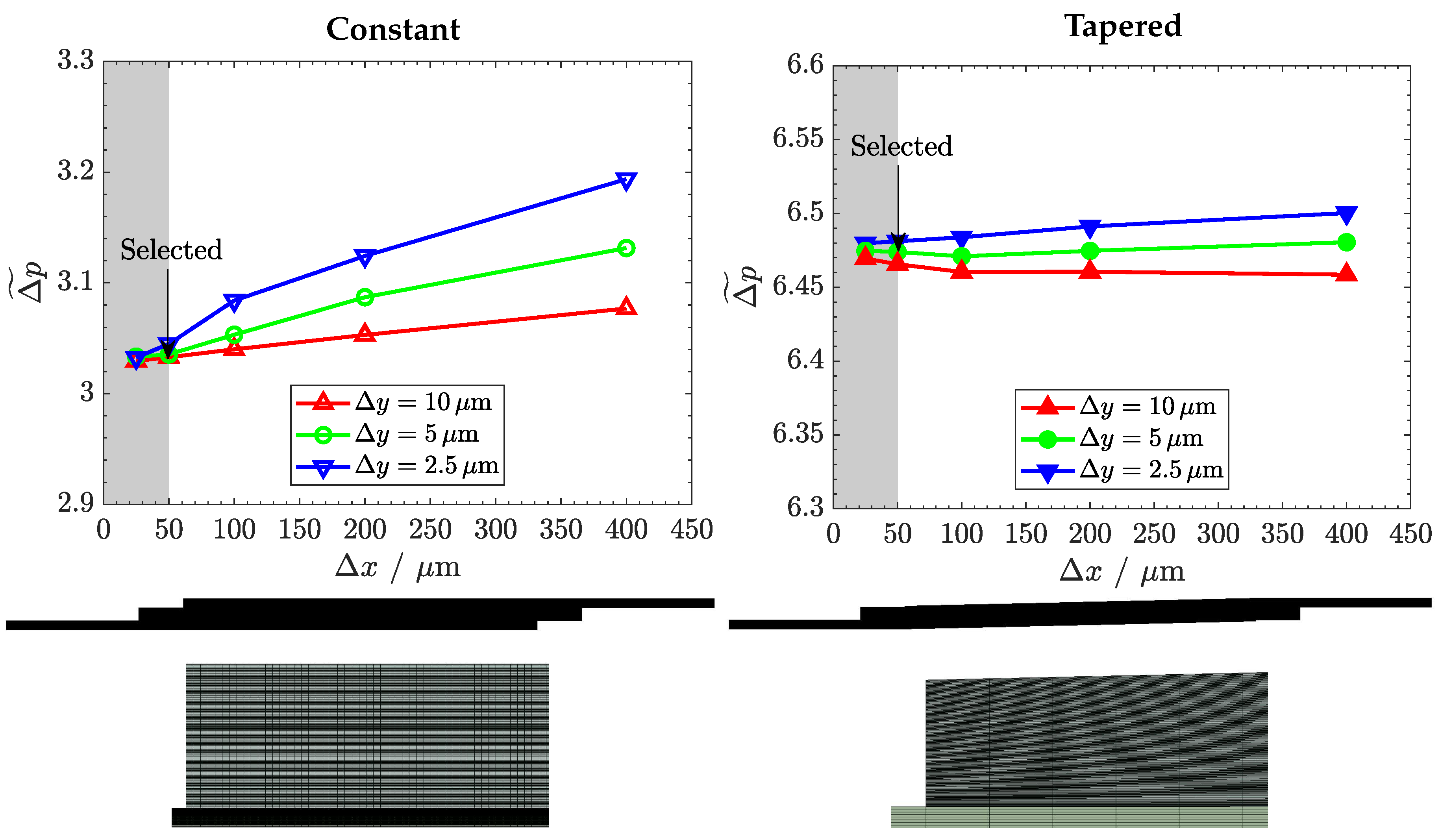
Appendix B. Mesh Independency Study and Streamlines


References
- Williams, J.H.; DeBenedictis, A.; Ghanadan, R.; Mahone, A.; Moore, J.; Morrow III, W.R.; Price, S.; Torn, M.S. The Technology Path to Deep Greenhouse Gas Emissions Cuts by 2050: The Pivotal Role of Electricity. Science 2012, 335, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugolo, J.; Aziz, M.J. Electricity Storage for Intermittent Renewable Sources. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7151–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, C.R.; Vrubel, H.; Amstutz, V.; Peljo, P.; Toghill, K.E.; Girault, H.H. Redox Flow Batteries, Hydrogen and Distributed Storage. Chimia 2015, 69, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soloveichik, G.L. Flow Batteries: Current Status and Trends. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11533–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Liu, J. Progress and Directions in Low-Cost Redox-Flow Batteries for Large-Scale Energy Storage. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.L.; Weber, A.Z. Advanced Redox-Flow Batteries: A Perspective. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A5064–A5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knehr, K.W.; Agar, E.; Dennison, C.R.; Kalidindi, A.R.; Kumbur, E.C. A Transient Vanadium Flow Battery Model Incorporating Vanadium Crossover and Water Transport through the Membrane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A1446–A1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hickner, M.A.; Agar, E.; Kumbur, E.C. Optimized Anion Exchange Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7559–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.Z.; Mench, M.M.; Meyers, J.P.; Ross, P.N.; Gostick, J.T.; Liu, Q. Redox Flow Batteries: A Review. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1137–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, P.A.; Agar, E.; Dennison, C.R.; Kumbur, E.C. Modeling of Ion Crossover in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries: A Computationally-Efficient Lumped Parameter Approach for Extended Cycling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A5244–A5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoglan, T.C.; Pahari, S.K.; Hamel, A.; Howland, R.; Cappillino, P.J.; Agar, E. Operando Spectroelectrochemical Characterization of a Highly Stable Bioinspired Redox Flow Battery Active Material. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A1745–A1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, M.; Dennison, C.R.; Jin, X.; Liu, F.; Agar, E. Elucidating Effects of Faradaic Imbalance on Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Performance: Experimental Characterization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A3844–A3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, A.; Agar, E.; Dennison, C.R.; Kumbur, E.C. On the Quantification of Coulombic Efficiency for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries: Cutoff Voltages vs. State-of-charge Limits. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 35, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, Y.A.; Aaron, D.S.; Mench, M.M. Coupled Membrane Transport Parameters for Ionic Species in All-Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, E.; Rychcik, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Investigation of the V(V)/V(IV) System for Use in the Positive Half-Cell of a Redox Battery. J. Power Sources 1985, 16, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Modification of Graphite Electrode Materials for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Application-I. Thermal Treatment. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, E.; Benjamin, A.; Dennison, C.R.; Chen, D.; Hickner, M.A.; Kumbur, E.C. Reducing Capacity Fade in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries by Altering Charging and Discharging Currents. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentil, S.; Reynard, D.; Girault, H.H. Aqueous Organic and Redox-Mediated Redox Flow Batteries: A Review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 21, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, R.M.; Perry, M.L. The Influence of Electrode and Channel Configurations on Flow Battery Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A1381–A1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, M.; Zackin, B.I.; Sabarirajan, D.C.; Taspinar, R.; Artyushkova, K.; Liu, F.; Zenyuk, I.V.; Agar, E. Impact of Corrosion Conditions on Carbon Paper Electrode Morphology and the Performance of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A353–A363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner-Cuenca, A.; Penn, E.E.; Oliveira, A.M.; Brushett, F.R. Exploring the Role of Electrode Microstructure on the Performance of Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2230–A2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, A.M.; Clement, J.T.; Veith, G.M.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Mench, M.M. High Performance Electrodes in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries through Oxygen-Enriched Thermal Activation. J. Power Sources 2015, 294, 33–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, J.; Pezeshki, A.; Clement, J.T.; Aaron, D.; Mench, M.M. Architecture for Improved Mass Transport and System Performance in Redox Flow Batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 351, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhao, T.S.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, X.L.; Zhang, Z.H. In-situ investigation of hydrogen evolution behavior in vanadium redox flow batteries. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xi, J.; Qiu, X.; Guan, T.; He, Y. In situ mapping of activity distribution and oxygen evolution reaction in vanadium flow batteries. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, N.; Eifert, L.; Banerjee, R.; Köble, K.; Faragó, T.; Zuber, M.; Bazylak, A.; Zeis, R. Visualization of electrolyte flow in vanadium redox flow batteries using synchrotron X-ray radiography and tomography – Impact of electrolyte species and electrode compression. J. Power Sources 2019, 439, 227071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, C.R.; Agar, E.; Akuzum, B.; Kumbur, E.C. Enhancing Mass Transport in Redox Flow Batteries by Tailoring Flow Field and Electrode Design. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A5163–A5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuzum, B.; Alparslan, Y.C.; Robinson, N.C.; Agar, E.; Kumbur, E.C. Obstructed Flow Field Designs for Improved Performance in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2019, 49, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Prahl, J.M.; Alexander, J.I.D.; Savinell, R.F. Redox Flow Batteries with Serpentine Flow Fields: Distributions of Electrolyte Flow Reactant Penetration into the Porous Carbon Electrodes and Effects on Performance. J. Power Sources 2018, 384, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, F.; Lu, F.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, X.; Xiang, B. A Hierarchical Interdigitated Flow Field Design for Scale-up of High-Performance Redox Flow Batteries. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.; Darling, R.M. Modeling Flow Distribution and Pressure Drop in Redox Flow Batteries. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 3746–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.L.; Milshtein, J.D.; Hinricher, J.J.; Brushett, F.R. Quantifying the Impact of Viscosity on Mass-Transfer Coefficients in Redox Flow Batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, K.V.; Forner-Cuenca, A.; Mularczyk, A.; Eller, J.; Brushett, F.R. Elucidating the Nuanced Effects of Thermal Pretreatment on Carbon Paper Electrodes for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44430–44442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, K.M.; Marschewski, J.; Ebejer, N.; Ruch, P.; Cotta, R.M.; Michel, B.; Poulikakos, D. Mass Transport Enhancement in Redox Flow Batteries with Corrugated Fluidic Networks. J. Power Sources 2017, 15, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Zhao, T.S.; An, L.; Zeng, Y.K.; Wei, L. Critical Transport Issues for Improving the Performance of Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 339, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milshtein, J.D.; Barton, J.L.; Carney, T.J.; Kowalski, J.A.; Darling, R.M.; Brushett, F.R. Towards Low Resistance Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A2487–A2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, D.S.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Z.; Grim, G.M.; Papandrew, A.B.; Turhan, A.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Mench, M.M. Dramatic Performance Gains in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries through Modified Cell Architecture. J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derr, I.; Przyrembel, D.; Schweer, J.; Fetyan, A.; Langner, J.; Melke, J.; Weinelt, M.; Roth, C. Electroless Chemical Aging of Carbon Felt Electrodes for the All-Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB) Investigated by Electrochemical Impedance and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salaberri, P.A.; Gostick, J.T.; Zenyuk, I.V.; Hwang, G.; Vera, M.; Weber, A.Z. On the limitations of volume-averaged descriptions of gas diffusion layers in the modeling of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. ECS Trans. 2017, 80, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; García-Salaberri, P.A.; Zenyuk, I.V. The impact of reaction on the effective properties of multiscale catalytic porous media: A case of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Transport Porous Med. 2019, 128, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; García-Salaberri, P.A.; Zenyuk, I.V. Bridging Scales to Model Reactive Diffusive Transport in Porous Media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 013524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, T.S.; Leung, P.K. Numerical Investigations of Flow Field Designs for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, L.T.; Jayanti, S. Hydrodynamic Analysis of Flow Fields for Redox Flow Battery Applications. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2014, 44, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Koenig, G.M., Jr. A carbon-free lithium-ion solid dispersion redox couple with low viscosity for redox flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 323, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, X.; Xi, J. Broad temperature adaptability of vanadium redox flow battery–Part 1: Electrolyte research. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, M.R.; Wong, A.A.; Aziz, M.J. The Effect of Interdigitated Channel and Land Dimensions on Flow Cell Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A2625–A2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.J.; Tummino, J.J. High-Performance Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries with Graphite Felt Electrodes. J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Fang, Q.; Gu, S.; Li, S.F.Y.; Yan, Y. Nonaqueous redox-flow batteries: Organic solvents, supporting electrolytes, and redox pairs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3515–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhao, T.S.; Shi, L.; Shu, J.B. Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Mass Transfer Coefficients for Chemically Reactive Flows in Porous Media. J. Heat Transf. 2018, 140, 052601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.D.R.; Jervis, R.; Tranter, T.G.; Sadeghi, M.A.; Brett, D.J.L.; Shearing, P.R.; Gostick, J.T. Mass transfer in fibrous media with varying anisotropy for flow battery electrodes: Direct numerical simulations with 3D X-ray computed tomography. Chem Eng. Sci. 2019, 196, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salaberri, P.A.; Zenyuk, I.V.; Shum, A.D.; Hwang, G.; Vera, M.; Weber, A.Z.; Gostick, J.T. Analysis of representative elementary volume and through-plane regional characteristics of carbon-fiber papers: Diffusivity, permeability and electrical/thermal conductivity. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2018, 127, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostick, J.T.; Fowler, M.W.; Pritzker, M.D.; Ioannidis, M.A.; Behra, L.M. In-plane and through-plane gas permeability of carbon fiber electrode backing layers. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qu, Z.G.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yang, W.W. Experimental study on the performance of a vanadium redox flow battery with non-uniformly compressed carbon felt electrode. Appl. Energy 2018, 213, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, J.; García-Salaberri, P.A.; Kok, M.D.R.; Jervis, R.; Shearing, P.R.; Brandon, N.; Brett, D.J.L. X-ray Micro-Computed Tomography of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells: What is the Representative Elementary Area? J. Electrochem. Soc 2020, 167, 013545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salaberri, P.A.; Vera, M.; Iglesias, I. Modeling of the anode of a liquid-feed DMFC: Inhomogeneous compression effects and two-phase transport phenomena. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasbi, A.; García-Salaberri, P.A.; Chen, J.; Talukdar, K.; Sanchez, D.G.; Ersal, T. Through-the-membrane transient phenomena in PEM fuel cells: A modeling study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F3154–F3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Zhao, T.S.; Zeng, Y.K.; An, L.; Wei, L. A highly permeable and enhanced surface area carbon-cloth electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Y.; Tao, W.Q.; Zelenay, P.; Mukundan, R.; Kang, Q. Pore-scale study of multiphase reactive transport in fibrous electrodes of vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 248, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschewski, J.; Brenner, L.; Ebejer, N.; Ruch, P.; Michel, B.; Poulikakos, D. 3D-printed fluidic networks for high-power-density heat-managing miniaturized redox flow batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.; Thomsen, E.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.; Koeppel, B.; Sprenkle, V. Performance of a low cost interdigitated flow design on a 1 kW class all vanadium mixed acid redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Shen, S.; Yan, X.; Zhu, F.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of height/width-tapered flow fields on the cell performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23107–23117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancusi, E.; Fontana, É.; Augusto Ulson de Souza, A.; Guelli Ulson de Souza, S.M.A. Numerical study of two-phase flow patterns in the gas channel of PEM fuel cells with tapered flow field design. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Yan, W.M.; Soong, C.Y.; Chen, F.; Chu, H.S. Reactant gas transport and cell performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with tapered flow field design. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Kerkhof, P.J.A.M. Dynamic behavior of liquid water transport in a tapered channel of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathode. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3076–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.D.R.; Khalifa, A.; Gostick, J.T. Multiphysics Simulation of the Flow Battery Cathode: Cell Architecture and Electrode Optimization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1408–A1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, S.; Suzuki, T. Modeling and Simulation of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery with Interdigitated Flow Field for Optimizing Electrode Architecture. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 020553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shahgaldi, S.; Alaefour, I.; Xu, Q.; Li, X. Gas permeability of catalyzed electrodes in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Appl. Energy 2018, 209, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, A.M.; Sacci, R.L.; Delnick, F.M.; Aaron, D.S.; Mench, M.M. Elucidating effects of cell architecture, electrode material, and solution composition on overpotentials in redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 229, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.A.; Aziz, M.J.; Rubinstein, S. Direct Visualization of Electrochemical Reactions and Comparison of Commercial Carbon Papers in operando by Fluorescence Microscopy Using a Quinone-Based Flow Cell. ECS Trans. 2017, 77, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Forner-Cuenca, A.; Oluwadamilola, O.T.; Vladimir, Y.; Brushett, F.R.; Brandon, N.P.; Gu, S.; Cai, Q. Elucidating effects of cell architecture, electrode material, and solution composition on overpotentials in redox flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2020, 447, 227249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic channel length | L | 4 cm, 10 cm |
| Reference inlet/outlet channel height | H | 1 mm |
| Effective channel-to-channel distance | 1.5 mm | |
| Electrode permeability | – | |
| Density | ||
| Dynamic viscosity | ||
| Inlet velocity (volume flow rate) | U () | 1–800 (1–800) |
| CFD Model Constant/Tapered | Lubrication Model Constant/Tapered | Relative Variation/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.80/4.64 | 1.84/4.69 | 2.22/1.08 | ||
| 1.78/4.62 | 1.84/4.69 | 3.37/1.51 | ||
| 1.05/1.51 | 1.08/1.55 | 2.86/2.65 | ||
| 1.03/1.49 | 1.08/1.55 | 4.85/4.00 | ||
| 1.01/1.03 | 1.01/1.05 | 0/1.94 | ||
| 1.00/1.00 | 1.01/1.05 | 1.00/5.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Salaberri, P.A.; Gokoglan, T.C.; Ibáñez, S.E.; Agar, E.; Vera, M. Modeling the Effect of Channel Tapering on the Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution Characteristics of Interdigitated Flow Fields in Redox Flow Batteries. Processes 2020, 8, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070775
García-Salaberri PA, Gokoglan TC, Ibáñez SE, Agar E, Vera M. Modeling the Effect of Channel Tapering on the Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution Characteristics of Interdigitated Flow Fields in Redox Flow Batteries. Processes. 2020; 8(7):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070775
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Salaberri, Pablo A., Tugba Ceren Gokoglan, Santiago E. Ibáñez, Ertan Agar, and Marcos Vera. 2020. "Modeling the Effect of Channel Tapering on the Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution Characteristics of Interdigitated Flow Fields in Redox Flow Batteries" Processes 8, no. 7: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070775
APA StyleGarcía-Salaberri, P. A., Gokoglan, T. C., Ibáñez, S. E., Agar, E., & Vera, M. (2020). Modeling the Effect of Channel Tapering on the Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution Characteristics of Interdigitated Flow Fields in Redox Flow Batteries. Processes, 8(7), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070775







