A Simplified and Optimized Chemical Mechanism for Combustion of n-Pentane at Atmospheric Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simplified and Optimized Mechanism
2.1. DRGEPSA
2.2. Temperature Sensitivity
2.3. Species Change Degree
2.4. Flow Rate Sensitivity
2.5. Optimization Analysis
3. Verification and Discussion
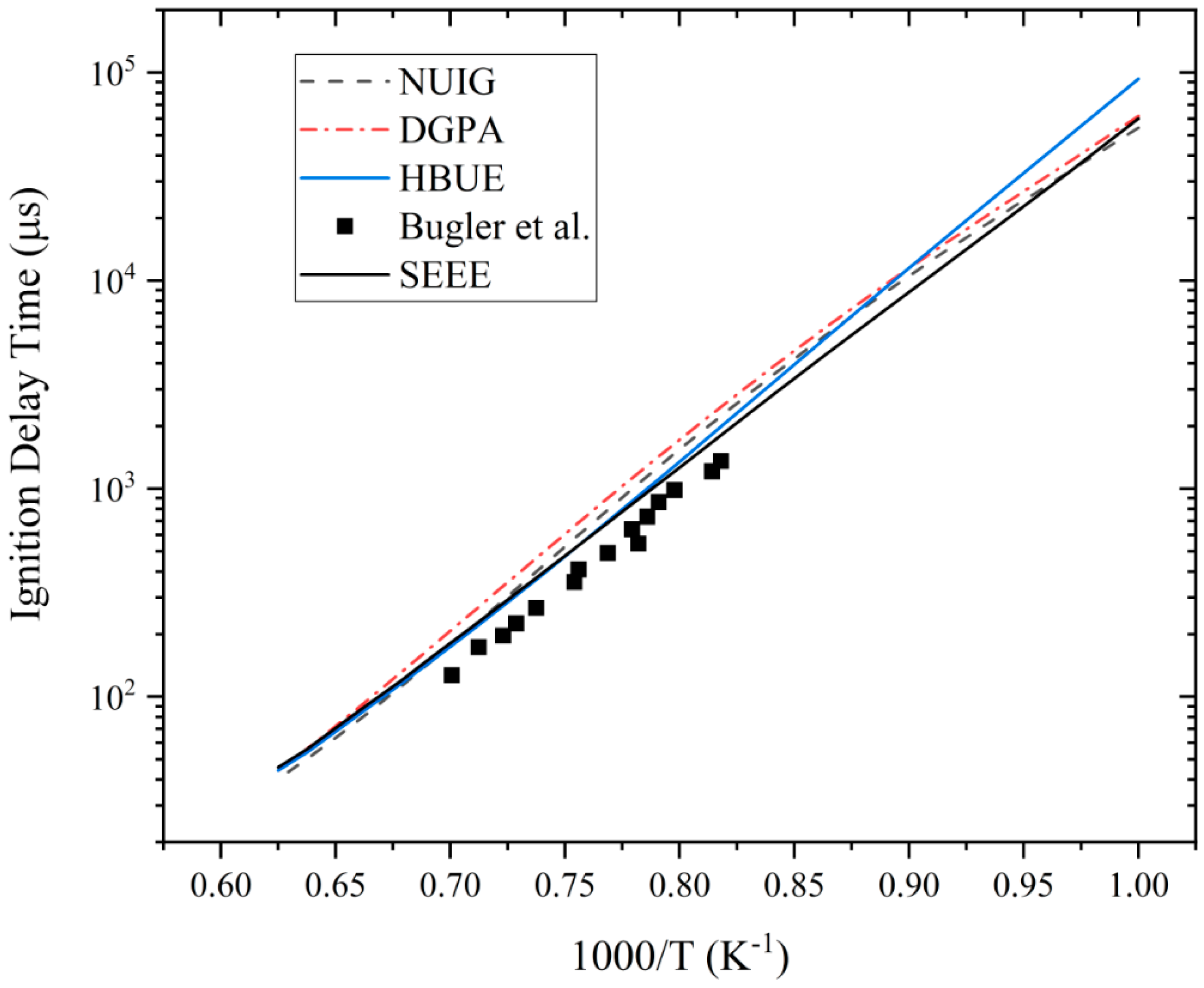
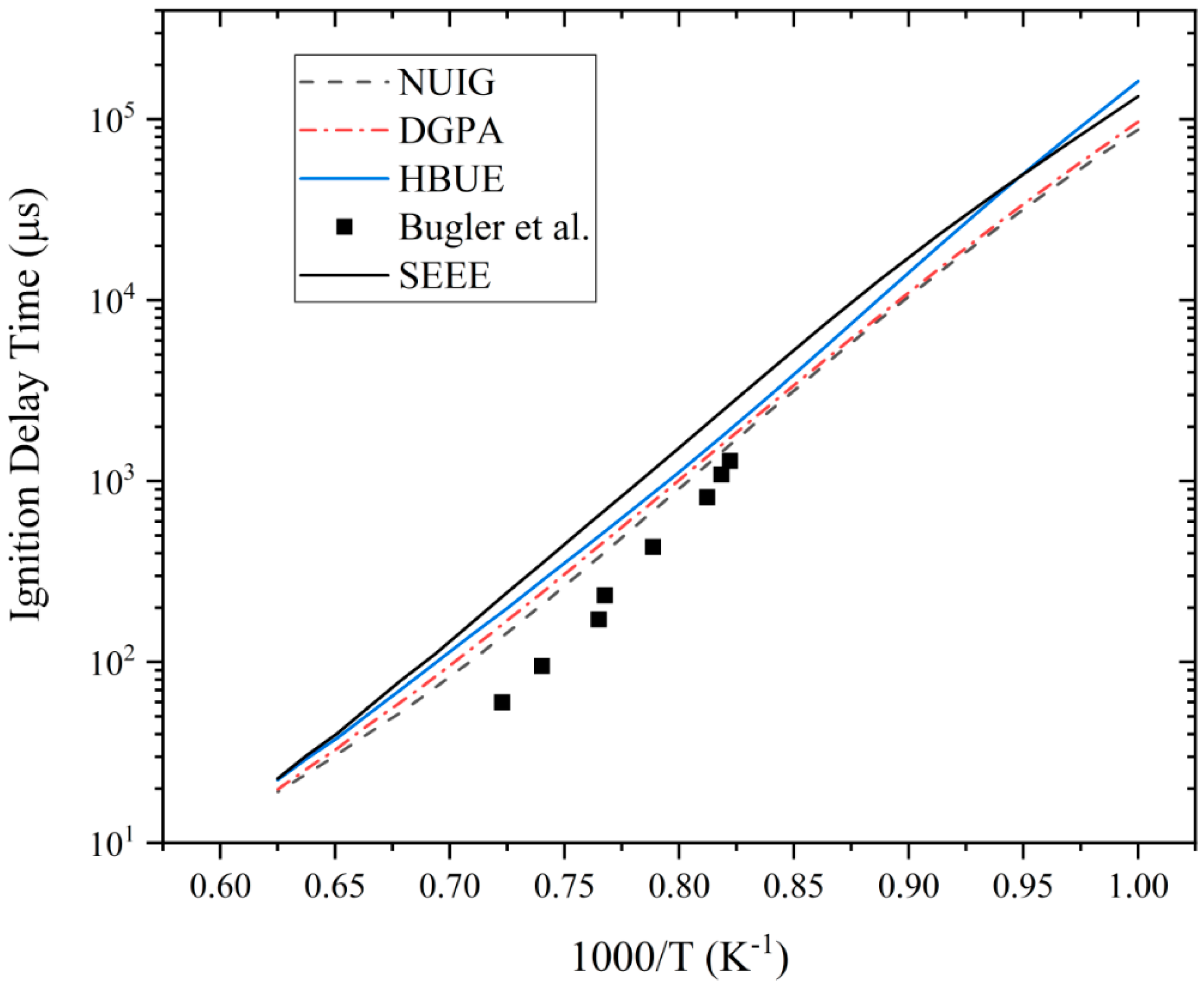
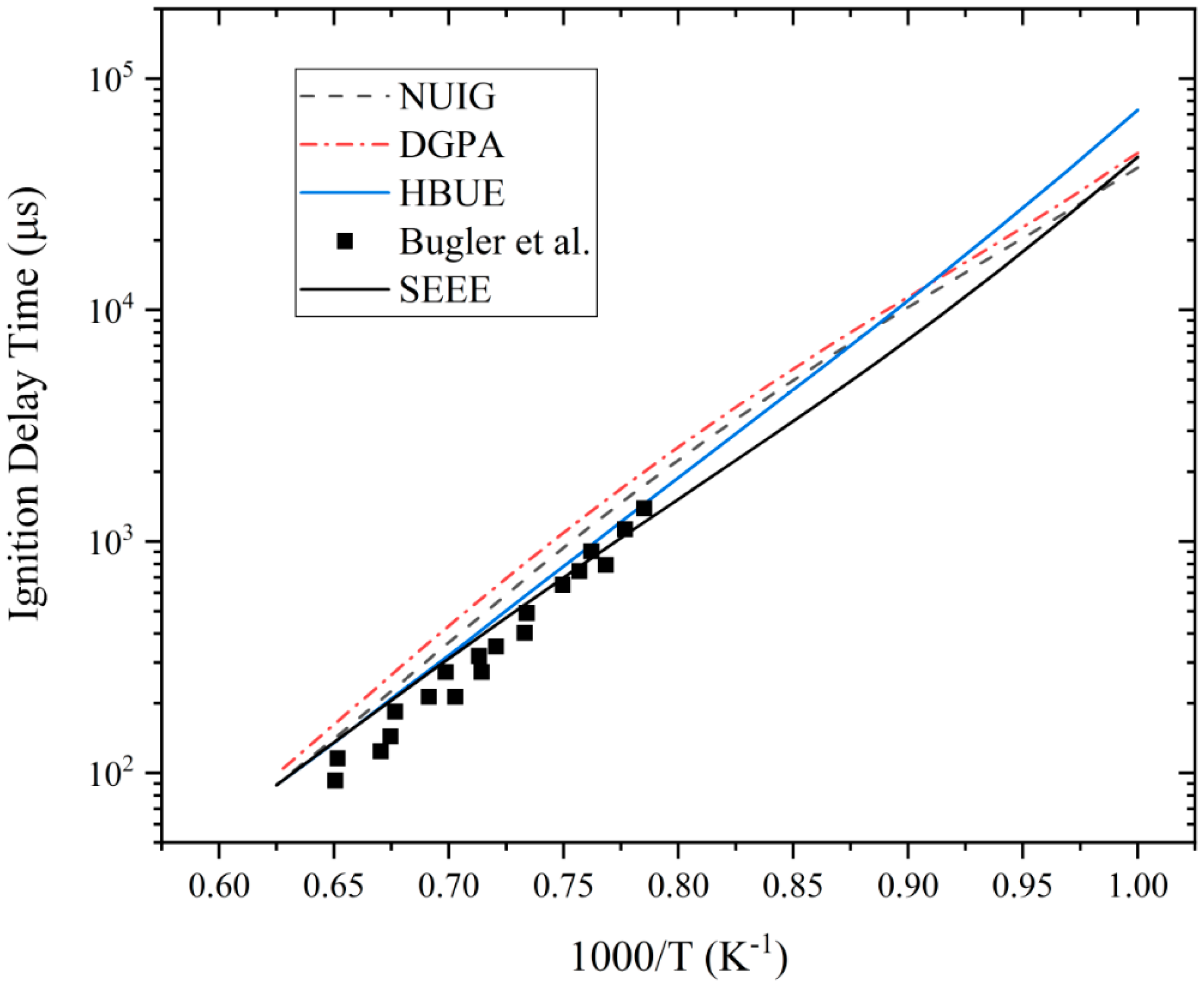
3.1. Ignition Delay Time
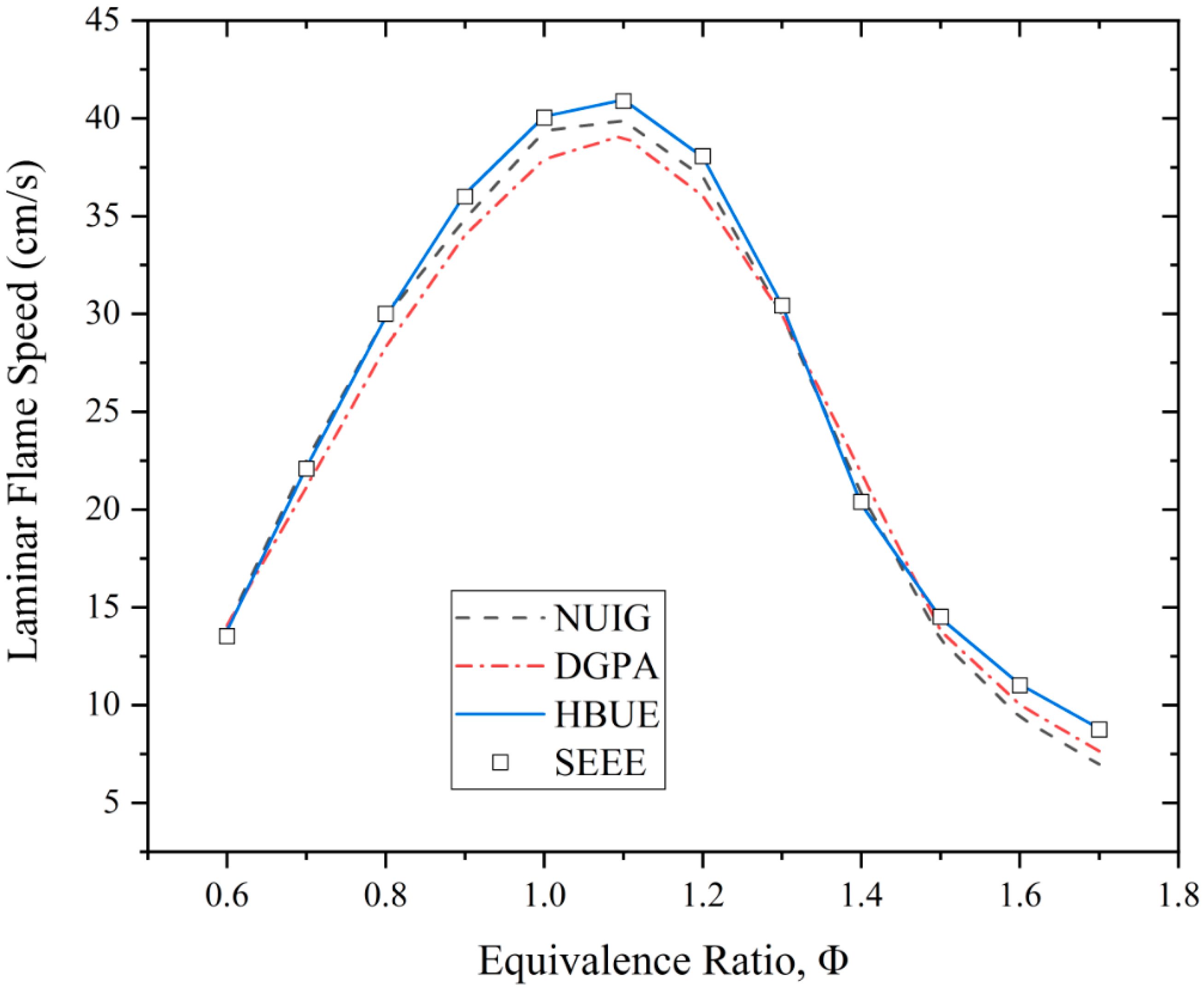
3.2. Laminar Flame Speed
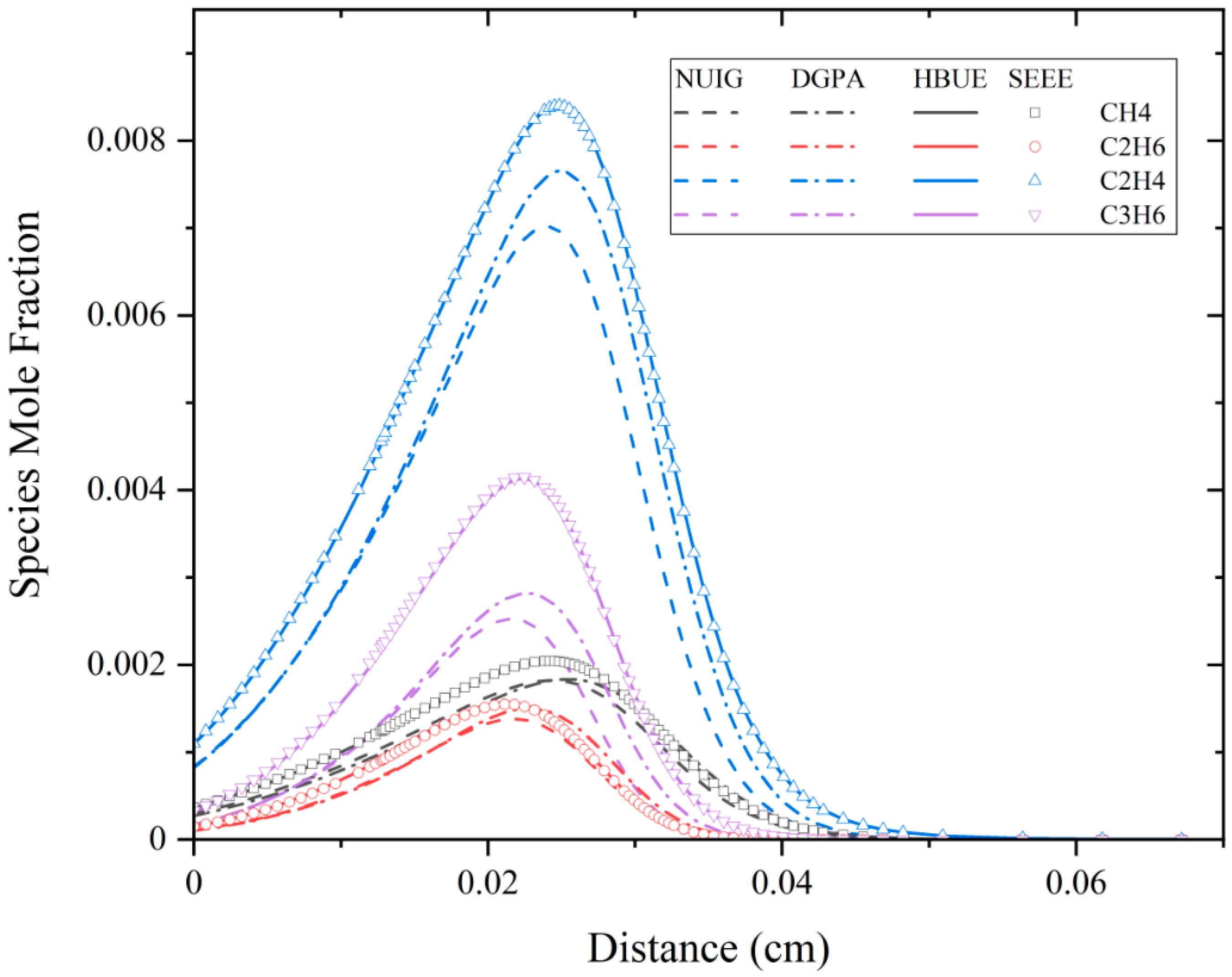
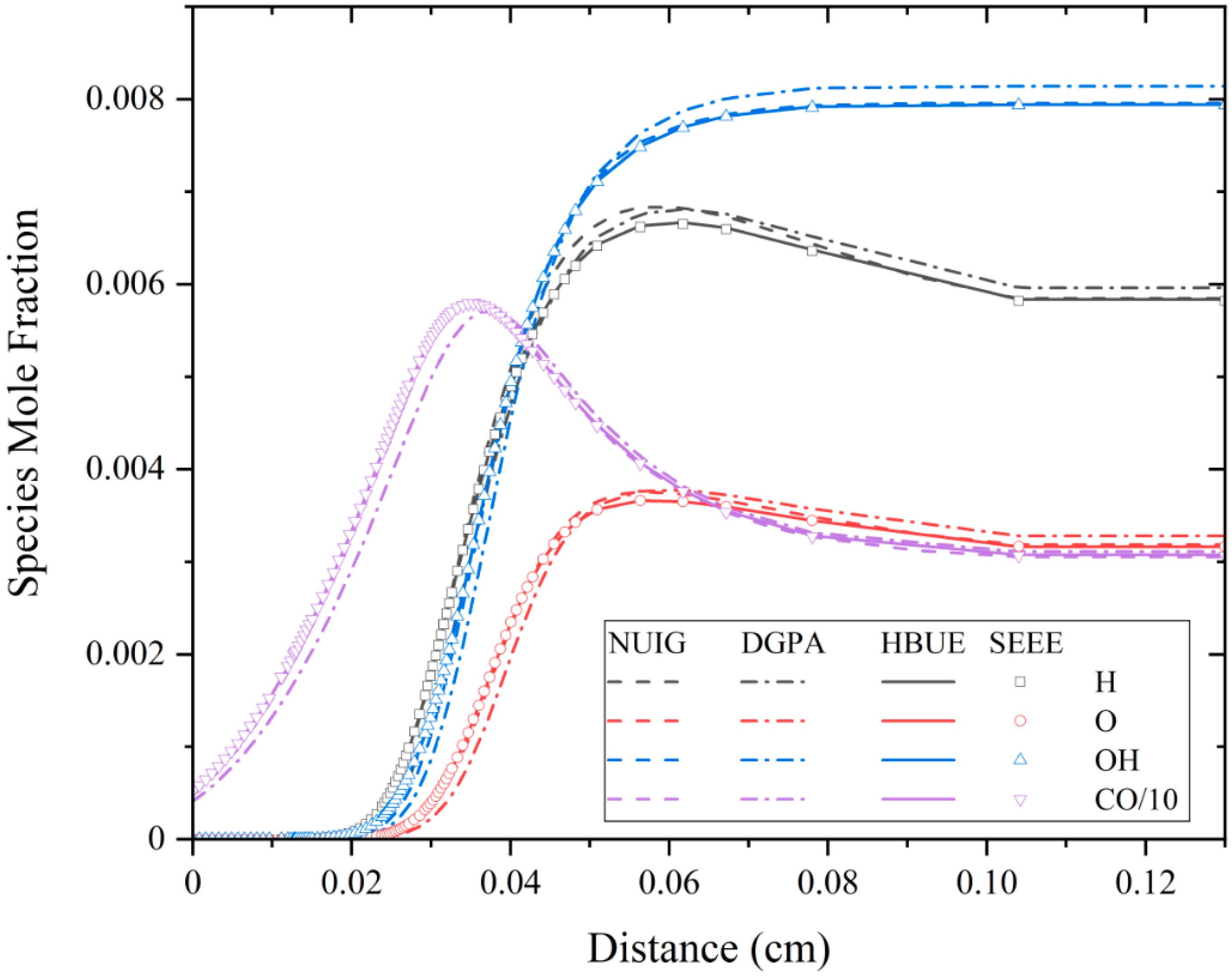
3.3. Species Mole Fraction
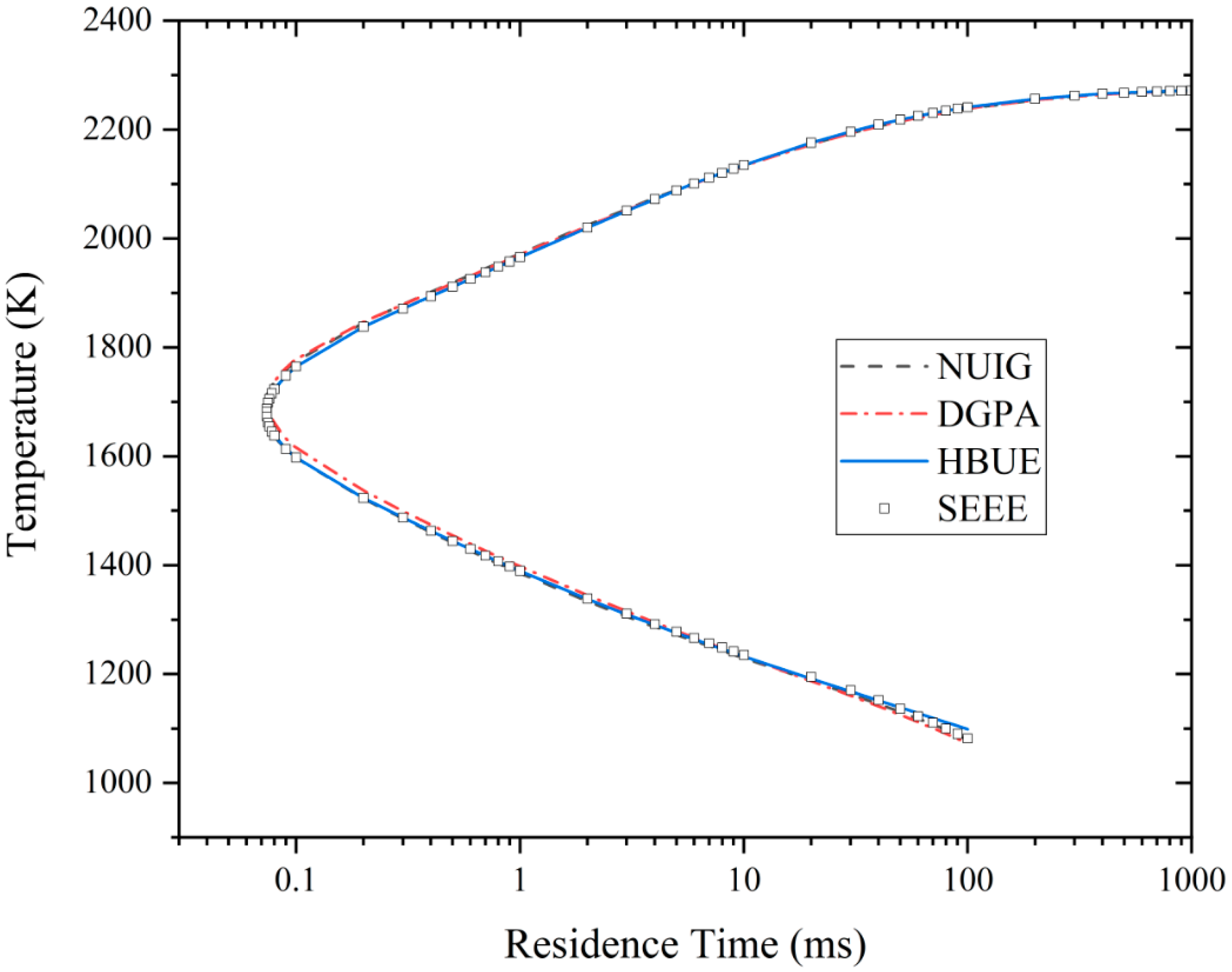
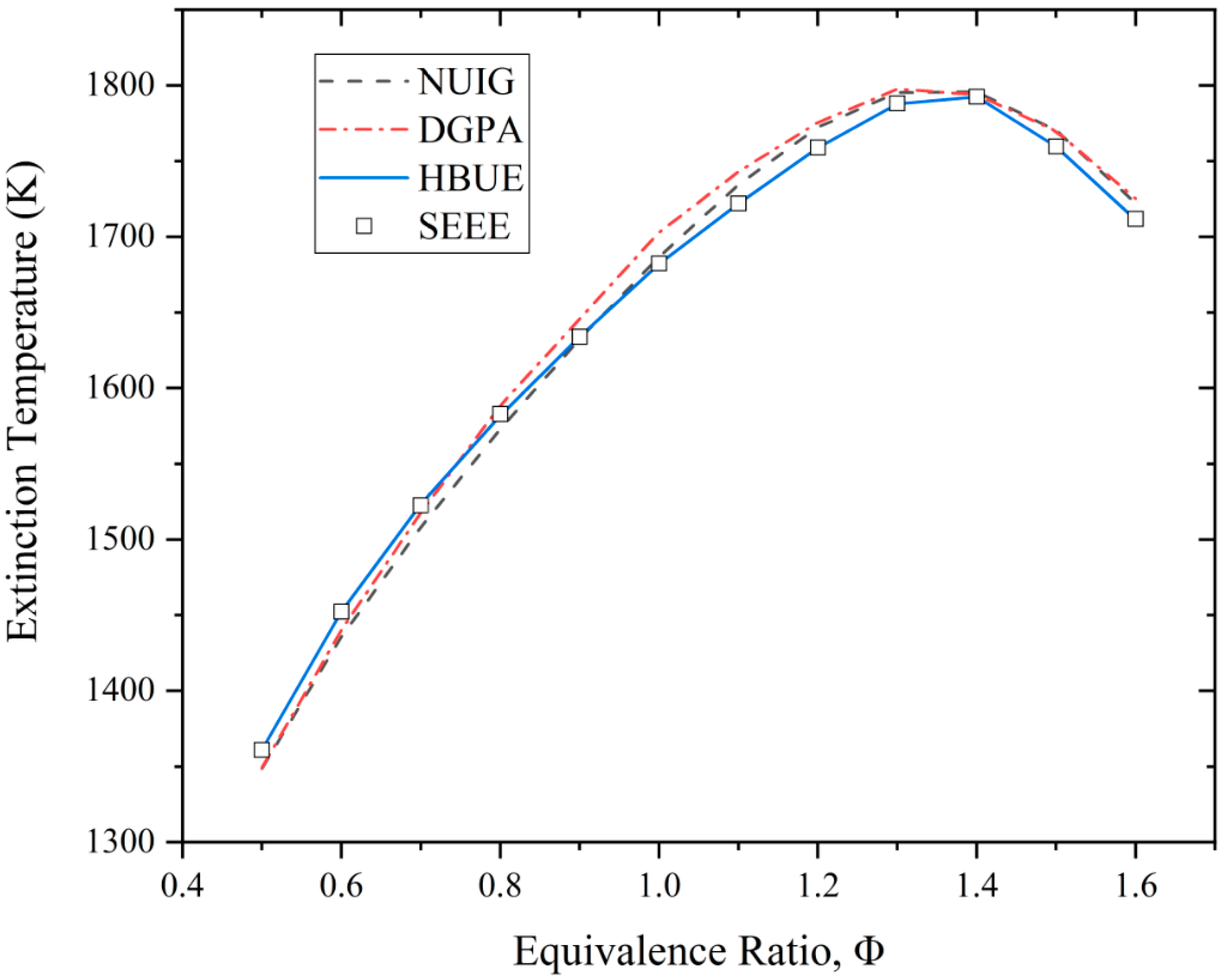
3.4. Extinction Residence Time
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, F.; Zhong, B. Skeletal Mechanism Generation Based on Eigenvalue Analysis Method. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2012, 28, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiong, C.; Qi, J.; Hou, L. Research on Combustion Characteristics of Air–Light Hydrocarbon Mixing Gas. Processes 2020, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.H.; Kinnear, C. The mechanism of combustion of pentane in the gas phase between 250 and 400 C. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1971, 13, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.; Simmons, R. The low-temperature combustion of n-pentane. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1969, 12, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.K.; Pitz, W.J.; Thornton, M.M.; Malte, P.C. A kinetic modeling study of n-pentane oxidation in a well-stirred reactor. Combust. Flame 1988, 72, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakir, A.; Belumam, M.; Boettner, J.; Cathonnet, M. Kinetic study of n-pentane oxidation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1991, 77, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugler, J.; Marks, B.; Mathieu, O.; Archuleta, R.; Camou, A.; Grégoire, C.; Heufer, K.A.; Petersen, E.L.; Curran, H.J. An ignition delay time and chemical kinetic modeling study of the pentane isomers. Combust. Flame 2016, 163, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhukov, V.; Sechenov, V.; Starikovskii, A.Y. Self-ignition of a lean mixture of n-pentane and air over a wide range of pressures. Combust. Flame 2005, 140, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Deng, F.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. High temperature ignition delay time of DME/n-pentane mixture under fuel lean condition. Fuel 2017, 191, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Dames, E.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, H.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Propagation and extinction of premixed C5–C12 n-alkane flames. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, A.; Smallbone, A.; Zhu, D.; Law, C.K. Laminar flame speeds of C5 to C8 n-alkanes at elevated pressures: Experimental determination, fuel similarity, and stretch sensitivity. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hu, E.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Gong, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z. Experimental and kinetic study of pentene isomers and n-pentane in laminar flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousso, A.; Mao, X.; Chen, Q.; Ju, Y. Kinetic studies and mechanism development of plasma assisted pentane combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 5595–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Patrick, C.; Zhang, Z.; Rezgui, Y.; Yang, X.; Wysocki, G.; Ju, Y. Studies of low temperature oxidation of n-pentane with nitric oxide addition in a jet stirred reactor. Combust. Flame 2018, 197, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Evrendilek, F.; Buyukada, M.; Xie, W.; Sun, S. Co-pyrolytic mechanisms, kinetics, emissions and products of biomass and sewage sludge in N2, CO2 and mixed atmospheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemkin, A.N.S.Y.S. 17.0 (15151); ANSYS Reaction Design: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, K.E.; Sung, C.-J.; Raju, M.P. Skeletal mechanism generation for surrogate fuels using directed relation graph with error propagation and sensitivity analysis. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 1760–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepiot-Desjardins, P.; Pitsch, H. An efficient error-propagation-based reduction method for large chemical kinetic mechanisms. Combust. Flame 2008, 154, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Law, C.K. A directed relation graph method for mechanism reduction. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Law, C.K. On the applicability of directed relation graphs to the reduction of reaction mechanisms. Combust. Flame 2006, 146, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Law, C.K. Linear time reduction of large kinetic mechanisms with directed relation graph: N-Heptane and iso-octane. Combust. Flame 2006, 144, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, T.; Law, C.K. Experimental counterflow ignition temperatures and reaction mechanisms of 1, 3-butadiene. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, M.; Sung, C.-J. Effects of hydrogen addition on combustion characteristics of n-decane/air mixtures. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, L. A new simplified mechanism for combustion of RP-3/Jet-A kerosene. Energy Sources Part A 2020, 42, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, L. Effects of water vapor addition on NO reduction of n-decane/air flames. Energy Sources Part A 2020, 42, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
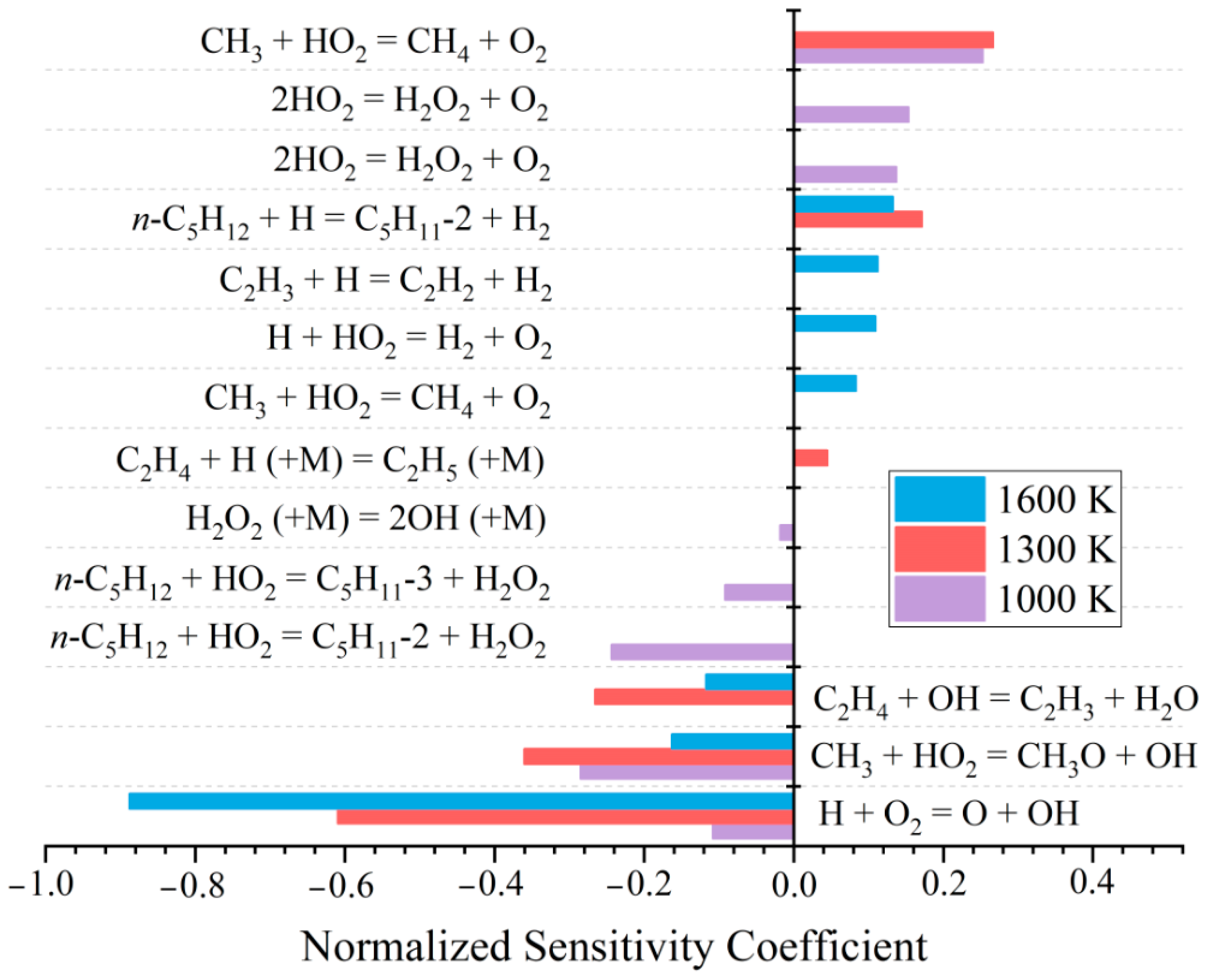
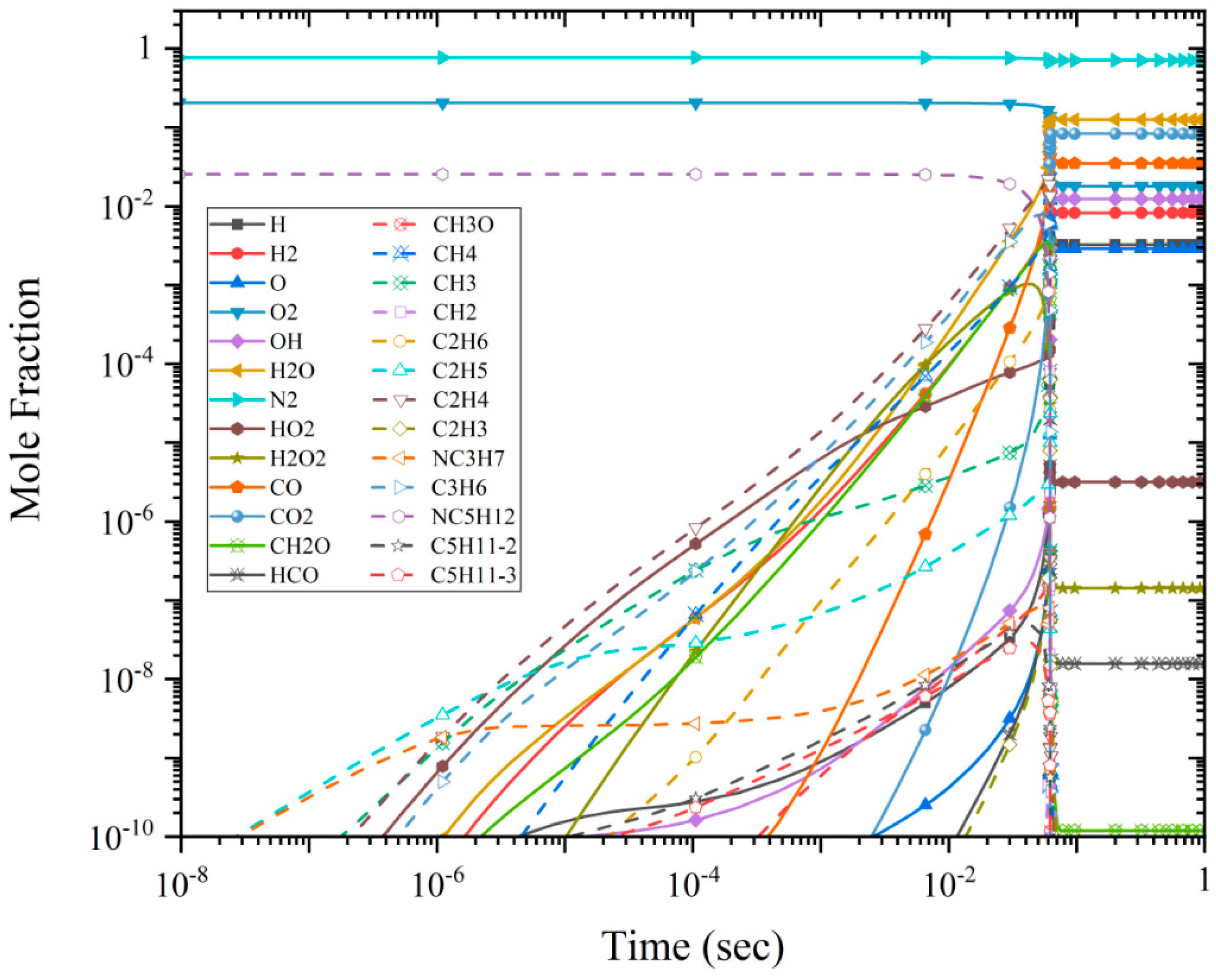
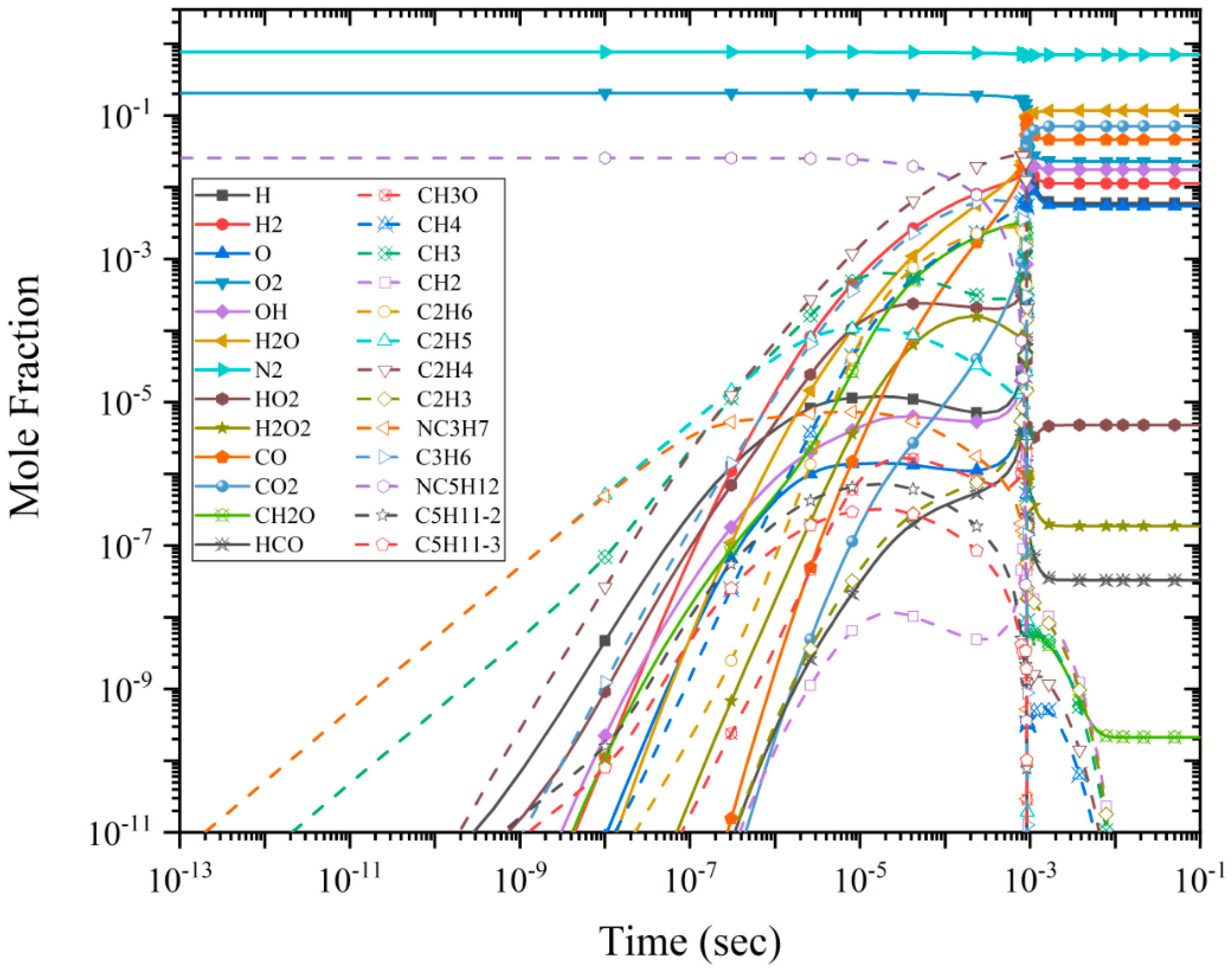

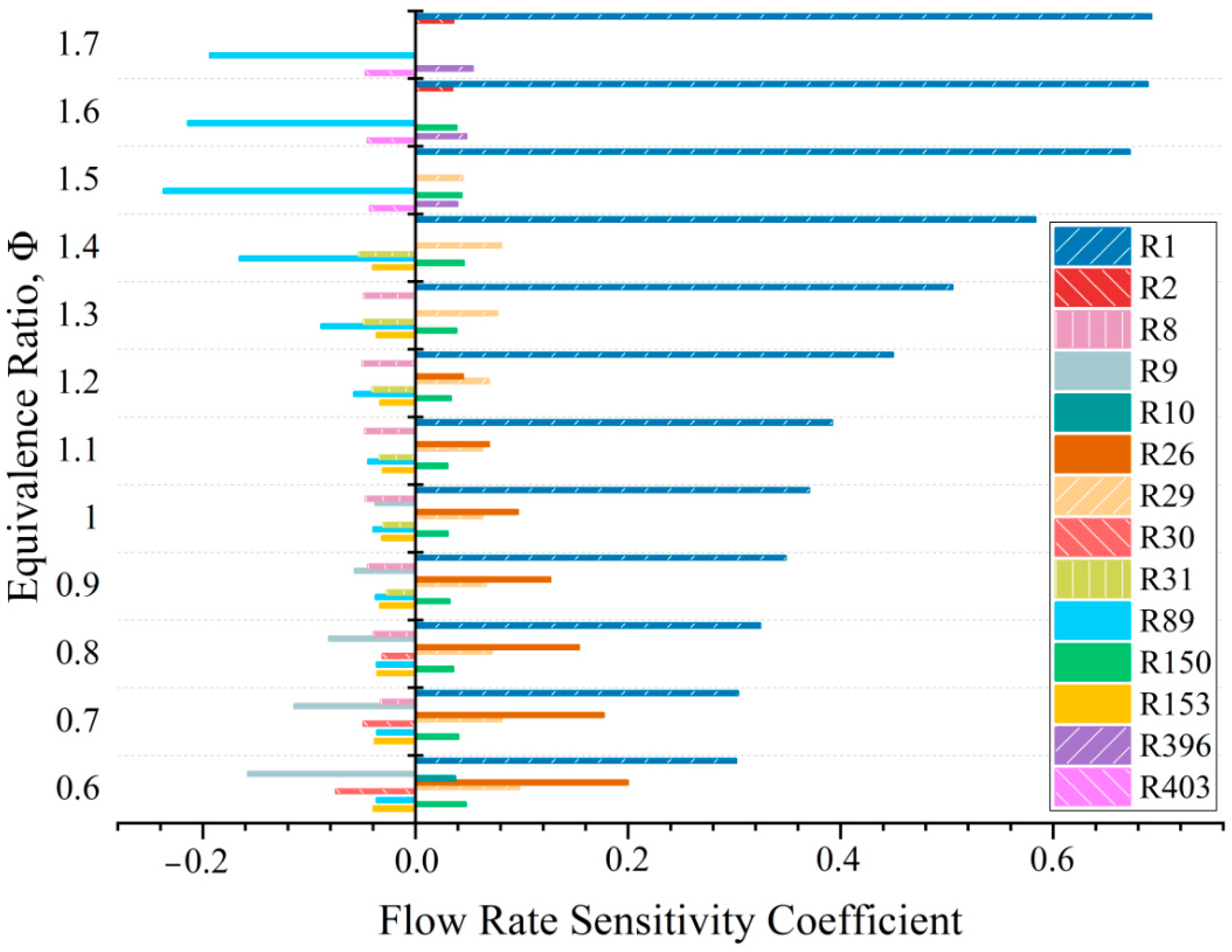


| Number | Reaction | Number | Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | H + O2 = O + OH | R30 | HCO + O2 = CO + HO2 |
| R2 | O + H2 = H + OH | R31 | HCO + H = CO + H2 |
| R8 | H + OH + M = H2O + M | R89 | CH3 + H (+M) = CH4 (+M) |
| R9 | H + O2 (+M) = HO2 (+M) | R150 | C2H4 + H (+M) = C2H5 (+M) |
| R10 | HO2 + H = 2OH | R153 | 2CH3 = H + C2H5 |
| R26 | CO + OH = CO2 + H | R396 | n-C5H12 = n-C3H7 + C2H5 |
| R29 | HCO + M = H + CO + M | R403 | n-C5H12 + H = C5H11-3 + H2 |
| Reactions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBUE | 2HO2 = H2O2 + O2 (−1) | 1 × 1014 | 0.0 | 11,040.9 |
| 2HO2 = H2O2 + O2 (−2) | 1.90 × 1011 | 0.0 | −1408.9 | |
| SEEE | 2HO2 = H2O2 + O2 (−1) | 1 × 1013 | 0.0 | 11,040.9 |
| 2HO2 = H2O2 + O2 (−2) | 1.90 × 1010 | 0.0 | −1408.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Z.; Wang, J.; Qi, J.; Xiong, C.; Hou, L.; Luo, J. A Simplified and Optimized Chemical Mechanism for Combustion of n-Pentane at Atmospheric Pressure. Processes 2020, 8, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080884
Meng Z, Wang J, Qi J, Xiong C, Hou L, Luo J. A Simplified and Optimized Chemical Mechanism for Combustion of n-Pentane at Atmospheric Pressure. Processes. 2020; 8(8):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080884
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Zhiqun, Jinggang Wang, Jiawen Qi, Chuchao Xiong, Liquan Hou, and Jinghui Luo. 2020. "A Simplified and Optimized Chemical Mechanism for Combustion of n-Pentane at Atmospheric Pressure" Processes 8, no. 8: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080884
APA StyleMeng, Z., Wang, J., Qi, J., Xiong, C., Hou, L., & Luo, J. (2020). A Simplified and Optimized Chemical Mechanism for Combustion of n-Pentane at Atmospheric Pressure. Processes, 8(8), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080884





