Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
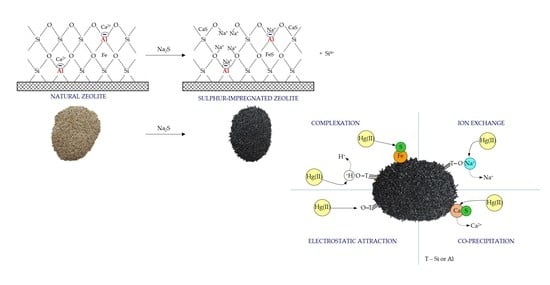
2.1. Sorbent Preparation
2.2. Sorbent Characterization
2.3. Batch Sorption Experiment
2.4. Leaching Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical and Physico-Chemical Characterization of Sorbents
3.2. Determination of Optimal Mercury Sorption Parameters
3.3. Characterization of the Mercury-Saturated Sulfur-Impregnated Zeolite
3.4. Leaching Properties of the Mercury-Saturated Sulfur-Impregnated Zeolite
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hay, R.L.; Sheppard, R.A. Occurrence of zeolites in Sedimentary Rocks: An Overview: Occurrence, properties, application. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, R.A.; Hay, R.L. Formation of zeolites in Open Hydrologic Systems: Occurrence, properties, application. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, K.; Zabukovec Logar, N.; Šiljeg, M.; Farkaš, M. Natural Zeolites in Water Treatment–How Effective is Their Use. In Water Treatment; Elshorbagy, W., Chowdhury, R.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordonez, S.; Diaz, E. Basic Zeolites: Structure, Preparation and Environmental Applications. In Handbook of Zeolites: Structure, Properties and Applications; Wong, T.W., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, G. Acidity and basicity of zeolites. A fundamental approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 254, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoliva, V.; Saviano, M.; De Luca, S. Zeolites as Acid/basic Solid Catalysts: Recent Synthetic Developments. Catalysts 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carotenuto, G. Electrical Investigation of the Mechanism of Water Adsorption/Desorption by Natural Clinoptilolite Desiccant Used in Food Preservation. Mater. Proc. 2020, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaby, S. Effect of Water Adsorption on Cation-Surface Interaction Energy in the Na-Mordenite of 5.5:1 Si/Al Ratio. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M. Structure and bonding of water molecules in zeolite hosts: Benchmarking plane-wave DFT against crystal structure dana. Z. Krist. 2015, 230, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misealidis, P. Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: A short review. Micropous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Mutter, J.; Aaseth, J. The toxicology of mercury: Current research and emerging trends. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H. Lecture on Methylmercury Poisoning in Minamata (MPM). In Mercury Pollution in Minamata; Springer Briefs in Environmental Science; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillay, K.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Coville, N.J. Improved uptake of mercury by sulphur-containing carbon nanotubes. Microchem. J. 2013, 108, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Garcia Bravo, A.; Lagerkvist, A.; Bertilsson, S.; Sjöblom, R.; Kumpiene, J. Sources and remediation techniques for mercury contaminated soil, review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Xing, Y.; Shang, L. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, D.; Cao, Y.; Sik Ok, Y.; Tack, F.M.G.; Rinklebe, J.; O’Connor, D. Remediation of mercury contaminated soil, water, and air: A review of emerging materials and innovative technologies. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105281–105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajima, T.; Sugawara, K. Adsorption behaviors of mercury from aqueous solution using sulfur-impregnated adsorbent developed from coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.S.; Ruiz, S.V.; Granados, D.L.; Santángelo, J.M. Adsorption of Mercury (II) from Liquid Solutions Modified Activated Carbons. Mater. Res. 2010, 13, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.; Da’ana, D.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Khraisheh, M. Adsorptive removal of mercury from water by adsorbents derived from daze pits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15327–15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Vidyarthi, S.R. Enhanced sorption of mercury from compact fluorescent bulbs and contaminated water streams using functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, Y.; Peng, B.; Deng, M.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z. A sulfur-resistant CuS-modified active coke for mercury removal from municipal solid waste incineration flue gas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24831–24839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Xu, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, W. Sorption of mercury (II) and atrazine by biochar, modified biochars and biochar based activated carbon in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Liu, M.-H.; Hung, C.-H. Preparation of Sulfurized Powdered Activated Carbon from Waste Tires Using an Innovative Compositive Impregnation Process. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Long, L. Preparation and characterization of Na2S-modified biochar for nickel removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9887–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelouahab-Reddam, Z.; Wahby, A.; El Mail, R.; Silvestre-Albero1, J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, R.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A. Activated Carbons Impregnated with Na2S and H2SO4: Texture, Surface Chemistry and Application to Mercury Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.H.; Jia, C.Q. Mercury Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Coke-Derived Sulfur-Impregnated Activated Carbons. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2716–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asasian, N.; Kaghazchi, T. Sulfurized activated carbons and their mercury adsorption/desorption behavior in aqueous phase. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebremedhin-Haile, T.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M. Removal of mercury ions from mixed aqueous metal solutions by natural and modified zeolitic minerals. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.-K.; Ahmad, T.; Kim, K.-Y.; Oh, K.-J.; Lee, S.-S. Mercury Adsorption Characteristics of Sulphur-Impregnated Activated Carbon Pellets for the Flue Gas Condition of a Cement-Manufacturing Process. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ahmad, N.M.; Cheema, W.A.; Zhu, S. Removal of Hg(II) in aqueous solutions through physical and chemical adsorption principles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20941–20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perego, C.; Bagatin, R.; Tagliabue, M.; Vignola, V. Zeolites and related mesoporous materials for multi-talented environmental solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Size Analysis-Sieving Analysis-Part 2: Procedure; DIN 66165-2; Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Sun, T.; Liang, D.; Yu, H. Upcycling of Electroplating Sludge to Prepare Erdite-Bearing Nanorods for the Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater Effluent. Water 2020, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voinovitch, I.; Debrad-Guedon, J.; Louvrier, J. The Analysis of Silicates; Israel Program for Scientific Translations: Jerusalem, Israel, 1966; pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bohem, H.P. Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 1994, 32, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Cation-Exchange Capacity of Soils (Ammonium Acetate): Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste. SW-846, Method 9080; US EPA, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Ievtifieieva, O.A.; Bolotov, V.V.; Kostina, T.A.; Svechnikova, O.M.; Yuschenko, T.I.; Kaminska, N.I.; Kosareva, A.E.; Slobodyanyuk, L.V.; Yashchuk, O.P. Analytical Chemistry (Qualitative Analysis) Part I; Ievtifieieva, O.A., Ed.; Publishing House the CLL Generous Farmstead Plus: Kharkiv, Ukraina, 2014; pp. 120–121. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301527607_Analytical_chemistry_Qualitative_analysis_Part_I_The_manual_for_students_of_higher_schools_O_A_Ievtifieieva_V_V_Bolotov_T_A_Kostina_O_M_Svechnikova_T_I_Yuschenko_N_I_Kaminska_A_E_Kosareva_L_V_Slobodya (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Ugrina, M.; Čeru, T.; Nuić, I.; Trgo, M. Comparative Study of Mercury(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions onto Natural and Iron-Modified Clinoptilolite Rich Zeolite. Processes 2020, 8, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German Standard Procedure for Water, Wastewater and Sediment Testing–Sludge and Sediment. Determination of Leachability; DIN 38414 S4; Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Minceva, M.; Fajagar, R.; Markovska, L.; Meshko, V. Comparative study of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ removal from water solution using natural clinoptilolitic zeolite and commercial granulated activated carbon. Equilibrium and adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2117–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleman, A.F.; Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1451–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Mozgawa, W. The influence of some heavy metals cations on the FTIR spectra of zeolites. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 555, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadiş, A.-I.; Perhaiţa, I.; Munteanu, V.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Silipas, D.T.; Mureşan, L.E. Influence of preparative conditions for obtaining ZnS:Mn nanoparticles using ultrasound-assisted precipitation. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavifar, M.; Bahramifar, N.; Younesi, H.; Li, Q. Adsorption of mercury ions from synthetic and real wastewater aqueous solution by functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube with both amino and thiolated groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qin, Y.; Liang, J. Preparation of a Stable Nanoscale Manganese Residue-Derived FeS@Starch-Derived Carbon Composite for the Adsorption of Safranine T. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, G.H.; Gao, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Z.P.; Xu, Z.S.; Li, W.D. Changes of mineralogical characteristics and osteoblast activities of raw and processed pyrites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28373–28382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C. Study on the oxidation of calcium sulfide using TGA and FTIR. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Król, M.; Barczyk, K. FT-IR studies of zeolites from different structural groups. CHEMIK 2011, 65, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Santona, L.; Cozza, C.; Giuliano, V.; Abbruzzese, C.; Nastro, V.; Melis, P. Thermal and spectroscopic studies of zeolites exchanged with metal cations. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 734, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, V.A.; Antonovich, V.P.; Nevskaja, E.M. Metal Ions Hydrolysis in Dilute Solutions; Atomizad: Moscow, Russia, 1979; pp. 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nies, D.H. The biological chemistry of the transition metal “transportome” of Cupriavidus metallidurans. Metallomics 2016, 8, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blais, J.F.; Djedidi, Z.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Mercier, G. Metals Precipitation from Effluents: Review. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2008, 12, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praus, P.; Motáková, M.; Ritz, M. Montmorillonite ion exchanged by mercury (II). Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2012, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Colonna, S.; Malferrari, D.; Medici, L.; Poppi, L. Mercury adsorption by montmorillonite and vermiculite: A combined XRD, TG-MS, and EXAFS study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumayor, M.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Lopez-Anton, M.A.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Mercury compounds characterization by thermal desorption. Talanta 2013, 114, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of Mercury by Carboxymethyl Cellulose Stabilized Iron Sulfide Nanoparticles: Reaction Mechanisms and Effects of Stabilizer and Water Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, N. Effective solidification/stabilisation of mercury-contaminated wastes using zeolites and chemically bonded phosphate ceramics. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. The Applications of Zeolite in Sustainable Binders for Soil Stabilization. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 256–259, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola-Abasi, H.; Kordtabar, B.; Kordnaeij, A. Effect of Natural Zeolite and Cement Additive on the Strength of Sand. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Sample | Content, wt % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | S | SO3 | Loss of Ignition | |
| NZ | 66.56 | 13.41 | 1.95 | 1.56 | 1.12 | 4.00 | 0.54 | 0.169 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 10.24 |
| SZ | 56.69 | 12.34 | 2.07 | 10.70 | 0.76 | 4.03 | 0.73 | 0.168 | 1.08 | 2.70 | 9.76 |
| Sample | Element Quantity, mmol/g | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | K | Ca | Mg | Al | Si | O | Fe | Ti | S | Si/Al | |
| NZ | 0.503 | 0.238 | 0.713 | 0.134 | 2.630 | 11.077 | 27.80 | 0.244 | 0.021 | 0.100 | 4.21 |
| SZ | 3.454 | 0.161 | 0.719 | 0.181 | 2.420 | 9.435 | 26.14 | 0.259 | 0.021 | 0.674 | 3.89 |
| Sample | Total Acidic Sites (meq/L) | Total Basic Sites (meq/L) | Zeta Potential (pH = 5.82) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 46.3 | 30.0 | −22.8 |
| SZ | 2.5 | 190.0 | −39.9 |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Radius (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 19.447 | 0.082 | 1.979 |
| SZ | 12.064 | 0.081 | 1.953 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 59.10 | 0.37 | 0.77 | 6.02 | 30.50 | 1.02 | 2.22 | - |
| Sp 2 | 59.36 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 6.01 | 30.00 | 0.97 | 2.09 | 0.29 |
| Sp 3 | 52.77 | 0.76 | 0.47 | 5.79 | 35.48 | 1.38 | 2.74 | 0.60 |
| Sp 4 | 55.67 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 5.89 | 32.99 | 1.34 | 2.77 | - |
| Sp 5 | 58.61 | 0.38 | 2.01 | 8.37 | 23.37 | 3.65 | 0.48 | 2.59 |
| Sp 6 | 58.14 | 0.41 | 2.11 | 8.35 | 23.44 | 3.46 | 0.53 | 3.11 |
| Sp 7 | 52.91 | 0.45 | 0.64 | 5.89 | 32.40 | 1.25 | 3.00 | 3.46 |
| Sp 8 | 45.00 | - | 0.55 | 6.05 | 33.17 | 1.76 | 4.42 | 7.50 |
| Mean | 55.20 | 0.46 | 0.99 | 6.55 | 30.17 | 1.85 | 2.28 | 2.19 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 56.59 | 16.11 | - | 6.51 | 15.80 | 1.43 | 0.33 | 0.80 | 2.43 |
| Sp 2 | 56.15 | 14.36 | 0.34 | 7.34 | 17.50 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 1.58 | 1.29 |
| Sp 3 | 56.32 | 13.21 | 0.50 | 6.62 | 18.68 | 1.02 | 0.43 | 2.12 | 1.10 |
| Sp 4 | 55.03 | 15.18 | - | 7.66 | 16.25 | 1.80 | 0.38 | 0.47 | 3.22 |
| Sp 5 | 55.97 | 15.22 | - | 8.30 | 17.86 | 1.20 | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.83 |
| Sp 6 | 57.11 | 16.45 | - | 7.77 | 16.64 | 1.13 | 0.34 | - | 0.56 |
| Sp 7 | 59.64 | 19.55 | - | 5.46 | 12.25 | 1.36 | 0.23 | 0.91 | 0.61 |
| Sp 8 | 59.78 | 18.34 | 0.30 | 5.94 | 12.50 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 1.03 | 0.44 |
| Mean | 57.07 | 16.05 | 0.14 | 6.95 | 15.94 | 1.30 | 0.32 | 0.91 | 1.31 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 50.85 | 6.67 | 1.10 | 4.43 | 24.68 | 3.32 | 1.11 | 2.49 | 5.35 |
| Sp 2 | 58.98 | 8.71 | 0.70 | 7.00 | 20.11 | 1.36 | 0.34 | 1.88 | 0.93 |
| Sp 3 | 49.02 | 8.07 | 0.50 | 8.44 | 25.67 | 2.03 | 0.70 | 2.75 | 2.83 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 34.75 | 1.60 | - | 6.75 | 16.03 | 1.07 | - | 0.34 | - | 39.46 |
| Sp 2 | 38.09 | 2.36 | - | 7.18 | 14.57 | 1.27 | 0.39 | 0.39 | - | 35.75 |
| Sp 3 | 42.84 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 4.09 | 25.85 | 0.63 | 0.37 | 0.70 | - | 24.46 |
| Sp 4 | 41.20 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 4.07 | 24.14 | 1.12 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 27.17 |
| Sp 5 | 45.83 | 0.40 | 0.83 | 4.08 | 17.43 | 1.60 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 4.53 | 24.49 |
| Sp 6 | 50.44 | 0.61 | 0.89 | 4.17 | 22.22 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.60 | 4.59 | 14.73 |
| Sp 7 | 43.81 | - | 0.28 | 4.84 | 22.75 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 2.83 | 23.20 |
| Sp 8 | 45.98 | - | 0.32 | 4.85 | 20.26 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 2.03 | 25.10 |
| Mean | 42.87 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 5.00 | 20.63 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 1.81 | 26.80 |
| Element | O | Na | Al | Si | S | Ca | Fe | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 35.69 | 1.21 | 7.95 | 15.95 | - | 0.29 | - | 38.92 |
| Sp 2 | 39.44 | 1.35 | 8.43 | 16.78 | - | 0.26 | 0.41 | 33.32 |
| Sp 3 | 9.00 | - | 0.52 | 1.53 | 11.50 | - | 1.10 | 76.34 |
| Sp 4 | 10.97 | - | 0.48 | 1.52 | 10.56 | - | 3.35 | 73.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugrina, M.; Gaberšek, M.; Daković, A.; Nuić, I. Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2021, 9, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
Ugrina M, Gaberšek M, Daković A, Nuić I. Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes. 2021; 9(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgrina, Marin, Martin Gaberšek, Aleksandra Daković, and Ivona Nuić. 2021. "Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Processes 9, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
APA StyleUgrina, M., Gaberšek, M., Daković, A., & Nuić, I. (2021). Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes, 9(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217