Distribution-Independent Empirical Modeling of Particle Size Distributions—Coarse-Shredding of Mixed Commercial Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Describing Particle Size Distributions
1.2. Modeling Particle Size Distributions
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Setup
2.1.1. Experimental Design
2.1.2. Setup of the Shredding Experiment
2.1.3. Sampling
2.1.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.2. Analysis of the Results
2.2.1. Isometric Log-Ratios
2.2.2. Model Reduction: MANOVA
2.2.3. Analysis of the Residuals
2.2.4. Confidence and Prediction
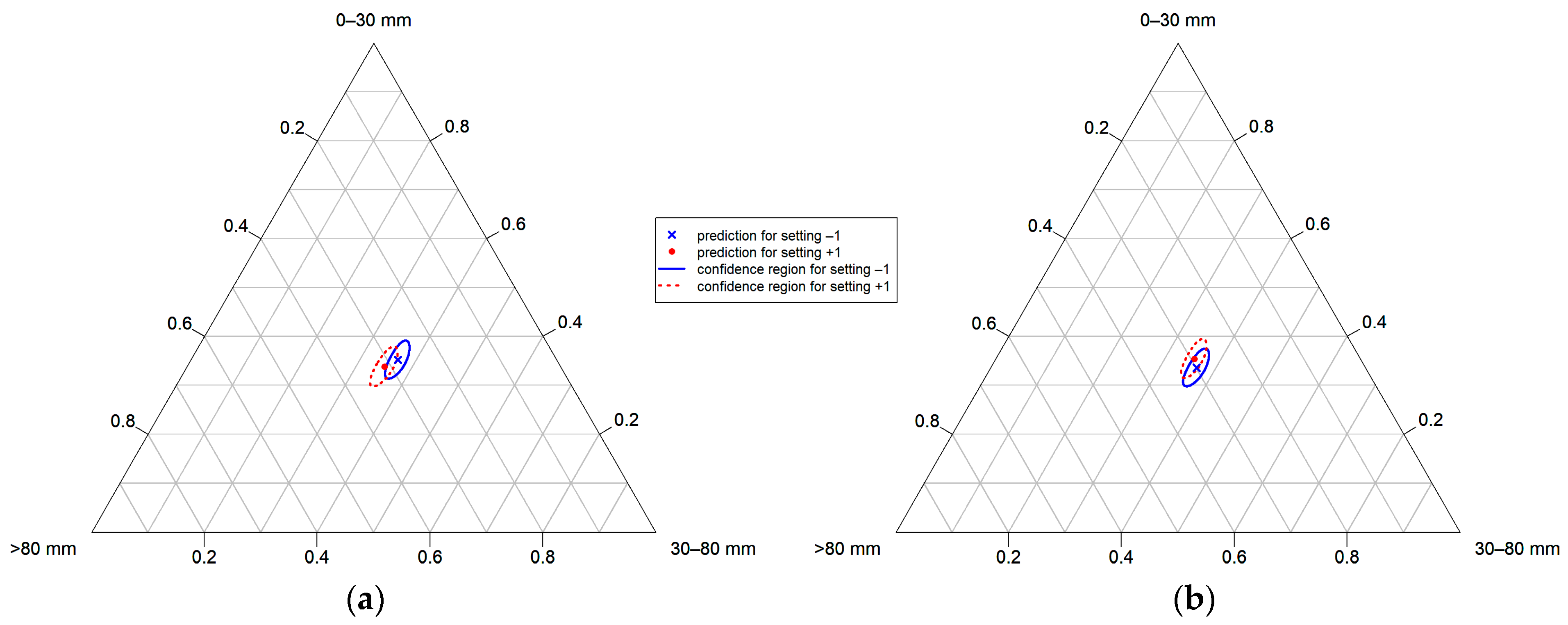
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data and Model
3.2. Discussion of the Method
3.3. Discussion of the Modeling Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| scaling factor for the th compositional part and the th ilr coordinate | |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| total surface area of all particles | |
| cutting tool geometry | |
| , | coded representation of the cutting tool geometry |
| particle size | |
| arithmetic average particle size | |
| characteristic particle size of the RRSB distribution | |
| th percentile particle size | |
| size of the ith particle | |
| maximum particle size | |
| Sauter diameter | |
| number of particle size classes | |
| DEM | discrete element method |
| DMFMS | digital material flow monitoring system |
| GGS | Gates-Gaudin-Schuhmann |
| ilr | isometric log-ratios |
| th ilr dimension | |
| factor exponent | |
| factor exponent | |
| model constant for the factor or interaction and the response | |
| factor exponent | |
| uniformity parameter of the GGS distribution | |
| MANOVA | multivariate analysis of variance |
| factor exponent | |
| uniformity parameter of the RRSB distribution | |
| number of particles | |
| empirical significance | |
| number of observations | |
| probability density function | |
| prediction residual sum of squares | |
| PSC | particle size class |
| PSD | particle size distribution |
| frequency density for particles of size | |
| number of independent variables | |
| number of dimensions of the dependent variable | |
| coefficient of determination | |
| adjusted coefficient of determination | |
| prediction coefficient of determination | |
| -dimensional real space | |
| -dimensional positive real space, including 0 | |
| RRSB | Rosin-Rammler-Sperling-Bennet |
| shaft rotation speed | |
| sample standard deviation | |
| -dimensional simplex | |
| SRF | solid recovered fuel |
| total sum of squares | |
| number of parts in group +1 | |
| TOS | Theory of Sampling |
| number of parts in group −1 | |
| total volume of all particles | |
| radial gap width | |
| width of a distribution | |
| th setting of the th independent variable | |
| matrix of settings of the independent variables | |
| compositional vector | |
| ilr-transformed compositional vector | |
| model prediction of the shares of the particle size classes | |
| th element of | |
| th observation of the th dimension of the dependent variable | |
| th observation of the th dimension of the ilr-transformed dependent variable | |
| model prediction for | |
| model prediction of the response | |
| arithmetic mean of the th ilr coordinate | |
| matrix of the dependent variable | |
| matrix of the ilr-transformed dependent variable | |
| matrix of model predictions of the dependent variable | |
| matrix of the regression coefficients | |
| matrix of least squares estimates of the regression coefficients | |
| th regression coefficient for the th dimension of the dependent variable | |
| least squares estimate of | |
| Aitchison distance | |
| Euclidian distance | |
| matrix of the model residuals | |
| matrix of the ilr-transformed residuals | |
| model residual corresponding to | |
| arithmetic average of a population | |
| standard deviation of a population |
Appendix A

| Type | F | XXF | V |
|---|---|---|---|
| number of cutting teeth (shaft) [pcs.] | 32 | 22 | 32 |
| position of cutting teeth (shaft) [-] | double helix | chevron | chevron |
| width of cutting teeth (shaft) [mm] | 70 | 70 | 42/85 * |
| height of cutting teeth (shaft) [mm] | 124 | 124 | 183 |
| width of cutting teeth (counter comb) [mm] | 64 | 54 | 81/100 * |
| height of cutting teeth (counter comb) [mm] | 142 | 136 | 202 |
| cutting circle [mm] | 1070 | 1070 | 1170 |
| length of shredding-shaft [mm] | 3000 | ||
| right side cutting gap (axial) [mm] | 3.5 | 2 | 3 |
| left side cutting gap (axial) [mm] | 39 | 2 | 3 |
| minimum cutting gap (radial) [mm] | 0 | ||
| maximum cutting gap (radial) [mm] | 33 | 35 | 30/38 * |
| comb-system [-] | no | no | yes |


| side length of the square-shaped holes (mm) | 80 | 60 | 40 | 20 | 10 |
| total hole area (m2) | 16, 61 | 17, 06 | 17, 14 | 17, 96 | 14, 55 |
References
- Sarc, R.; Lorber, K.E.; Pomberger, R. Manufacturing of Solid Recovered Fuels (SRF) for Energy Recovery Processes. In Waste Management; Thomé-Kozmiensky, K.J., Thiel, S., Eds.; TK Verlag Karl Thomé-Kozmiensky: Neuruppin, Germany, 2016; pp. 401–416. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Banks, C.J. Impact of different particle size distributions on anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xiao, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, L. Influence of particle size on pyrolysis and gasification performance of municipal solid waste in a fixed bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6517–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarc, R.; Curtis, A.; Kandlbauer, L.; Khodier, K.; Lorber, K.E.; Pomberger, R. Digitalisation and intelligent robotics in value chain of circular economy oriented waste management—A review. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarc, R.; Seidler, I.M.; Kandlbauer, L.; Lorber, K.E.; Pomberger, R. Design, quality and quality assurance of solid recovered fuels for the substitution of fossil feedstock in the cement industry—Update 2019. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leschonski, K. Windsichten [wind sifting]. In Handbuch der Mechanischen Verfahrenstechnik [Handbook of Mechanical Process Engineering]; Schubert, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 584–612. ISBN 3-527-30577-7. [Google Scholar]
- Khodier, K.; Viczek, S.A.; Curtis, A.; Aldrian, A.; O’Leary, P.; Lehner, M.; Sarc, R. Sampling and analysis of coarsely shredded mixed commercial waste. Part I: Procedure, particle size and sorting analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möllnitz, S.; Khodier, K.; Pomberger, R.; Sarc, R. Grain size dependent distribution of different plastic types in coarse shredded mixed commercial and municipal waste. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, A.; Coskun, E.; Bosling, M.; Kaufeld, S.; Pretz, T. Improvement of the recycling of plastics in lightweight packaging treatment plants by a process control concept. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundupalli, S.P.; Hait, S.; Thakur, A. A review on automated sorting of source-separated municipal solid waste for recycling. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, A.; Küppers, B.; Möllnitz, S.; Khodier, K.; Sarc, R. Digital material flow monitoring in waste processing—The relevance of material and throughput fluctuations. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möllnitz, S.; Küppers, B.; Curtis, A.; Khodier, K.; Sarc, R. Influence of pre-screening on down-stream processing for the production of plastic enriched fractions for recycling from mixed commercial and municipal waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Bockreis, A. Mechanical-Biological Waste Treatment and Utilization of Solid Recovered Fuels—State of the Art. In Waste Management; Thomé-Kozmiensky, K.J., Thiel, S., Eds.; TK Verlag Karl Thomé-Kozmiensky: Neuruppin, Germany, 2015; pp. 321–338. [Google Scholar]
- Polke, R.; Schäfer, M.; Scholz, N. Charakterisierung disperser Systeme [Characterization of disperse systems]. In Handbuch der Mechanischen Verfahrenstechnik [Handbook of Mechanical Process Engineering]; Schubert, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 7–129. ISBN 3-527-30577-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, L. All of Statistics: A Concise Course in Statistical Inference; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-387-21736-9. [Google Scholar]
- Micula, G.; Micula, S. Handbook of Splines; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; ISBN 978-94-010-6244-2. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.W. Multivariate Density Estimation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 9780471547709. [Google Scholar]
- Heumann, C.; Michael Schomaker, S. Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis: With Exercises, Solutions and Applications in R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3319461601. [Google Scholar]
- German Institute for Standardization. DIN 66143:1974-03, Darstellung von Korn-(Teilchen-)Größenverteilungen; Potenznetz [Graphical Representation of Particle Size Distributions; Power-Function Grid]; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- German Institute for Standardization. DIN 66145:1976-04, Darstellung von Korn-(Teilchen-)Größenverteilungen; RRSB-Netz [Graphical Representation of Particle Size Distributions; RRSB-Grid]; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Sinnott, M.D.; Cleary, P.W. Simulation of particle flows and breakage in crushers using DEM: Part 2—Impact crushers. Miner. Eng. 2015, 74, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, H.C. Application of DEM model to breakage and liberation behaviour of recycled aggregates from impact-breakage of concrete waste. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Esfandiary, A.H.; Yu, A.B. Discrete particle simulation of particle flow and separation on a vibrating screen: Effect of aperture shape. Powder Technol. 2017, 314, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodier, K.; Feyerer, C.; Möllnitz, S.; Curtis, A.; Sarc, R. Efficient derivation of significant results from mechanical processing experiments with mixed solid waste: Coarse-shredding of commercial waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-13-187715-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, D.J.; Taylor, C.C. Multivariate Analysis of Variance and Repeated Measures; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; ISBN 978-94-010-7913-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J.; Tolosana-Delgado, R. Modeling and Analysis of Compositional Data; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2015; ISBN 9781118443064. [Google Scholar]
- Pomberger, R.; Sarc, R.; Lorber, K.E. Dynamic visualisation of municipal waste management performance in the EU using Ternary Diagram method. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodier, K.; Lehner, M.; Sarc, R. Multilinear modeling of particle size distributions. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Compositional Data Analysis (CoDaWork2019): Terrassa, 3–8 June 2019; Ortego, M.I., Ed.; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya-BarcelonaTECH: Barcelona, Spain, 2019; pp. 82–85. ISBN 978-84-947240-1-5. [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1982, 44, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egozcue, J.J. Isometric Logratio Tranformations for Compositional Data Analysis. Math. Geol. 2003, 35, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, D.R.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Johnson, T.J.; Jung, H. Analyzing Wildland Fire Smoke Emissions Data Using Compositional Data Techniques. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edjabou, M.E.; Martín-Fernández, J.A.; Scheutz, C.; Astrup, T.F. Statistical analysis of solid waste composition data: Arithmetic mean, standard deviation and correlation coefficients. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.M.; Hastie, T.J. Statistical Models. In Statistical Models in S; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 13–44. ISBN 978-0-534-16765-3. [Google Scholar]
- Siebertz, K.; van Bebber, D.; Hochkirchen, T. Statistische Versuchsplanung [Design of Experiments]; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-05492-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stat-Ease Inc. Optimality Criteria. Available online: https://www.statease.com/docs/v11/contents/advanced-topics/optimality-criteria/ (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Dean, A.; Voss, D.; Draguljić, D. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-52250-0. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Standards Foundation. DS 3077 Representative Sampling—Horizontal Standard; Danish Standards Foundation: Charlottenlund, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Esbensen, K.H.; Wagner, C. Theory of sampling (TOS) versus measurement uncertainty (MU)—A call for integration. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 57, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Boogaart, K.G.; Tolosana-Delgado, R. Analyzing Compositional Data with R; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-3-642-36809-7. [Google Scholar]
- Khodier, K.; Lehner, M.; Sarc, R. Empirical modeling of compositions in chemical engineering. In Proceedings of the 16th Minisymposium Verfahrenstechnik and 7th Partikelforum (TU Wien, Sept. 21/22, 2020); Jordan, C., Ed.; TU Wien: Vienna, Austria, 2020; pp. 118–121. ISBN 978-3-903337-01-5. [Google Scholar]
- Greenacre, M. Compositional Data Analysis in Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-138-31643-0. [Google Scholar]
- van den Boogart, K.G.; Tolosana-Delgado, R. Package ‘Compositions’ (Version 2.0-1). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/compositions/compositions.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Stahel, W.A. Package Regr for an Augmented Regression Analysis. Available online: https://rdrr.io/rforge/regr/f/inst/doc/regr-description.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Olson, C.L. On choosing a test statistic in multivariate analysis of variance. Psychol. Bull. 1976, 83, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareto, A. Predictive R-Squared According to Tom Hopper. Available online: https://rpubs.com/RatherBit/102428 (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Braun, W.J.; MacQueen, S. Package ‘MPV’ (Version 1.56). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MPV/MPV.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Wang, C.-C. A MATLAB package for multivariate normality test. J. Stat. Comput. 2014, 85, 166–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardia, K.V. Measures of multivariate skewness and kurtosis with applications. Biometrika 1970, 57, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, S.; Goksuluk, D.; Zararsiz, G. Package ‘MVN’ (Version 5.8). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MVN/MVN.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Biemann, T. Logik und Kritik des Hypothesentests [Logic and criticism of the hypothesis test]. In Methodik der Empirischen Forschung [Methodology of Empirical Research]; Albers, S., Klapper, D., Konradt, U., Walter, A., Wolf, J., Eds.; Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-8349-0469-0. [Google Scholar]
- Feyerer, C. Interaktion des Belastungskollektives und der Werkzeuggeometrie Eines Langsamlaufenden Einwellenzerkleinerers [Interaction of the Load Collective and Tool Geometry of a Low-Speed Single-Shaft Shredder]. Master’s Thesis, Montanuniversitaet Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]




| Cutting Tool Geometry | ||
|---|---|---|
| F | 1 | 0 |
| XXF | −1 | −1 |
| V | 0 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khodier, K.; Sarc, R. Distribution-Independent Empirical Modeling of Particle Size Distributions—Coarse-Shredding of Mixed Commercial Waste. Processes 2021, 9, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030414
Khodier K, Sarc R. Distribution-Independent Empirical Modeling of Particle Size Distributions—Coarse-Shredding of Mixed Commercial Waste. Processes. 2021; 9(3):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030414
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhodier, Karim, and Renato Sarc. 2021. "Distribution-Independent Empirical Modeling of Particle Size Distributions—Coarse-Shredding of Mixed Commercial Waste" Processes 9, no. 3: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030414
APA StyleKhodier, K., & Sarc, R. (2021). Distribution-Independent Empirical Modeling of Particle Size Distributions—Coarse-Shredding of Mixed Commercial Waste. Processes, 9(3), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030414







