Effect of a Baffle on Bubble Distribution in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
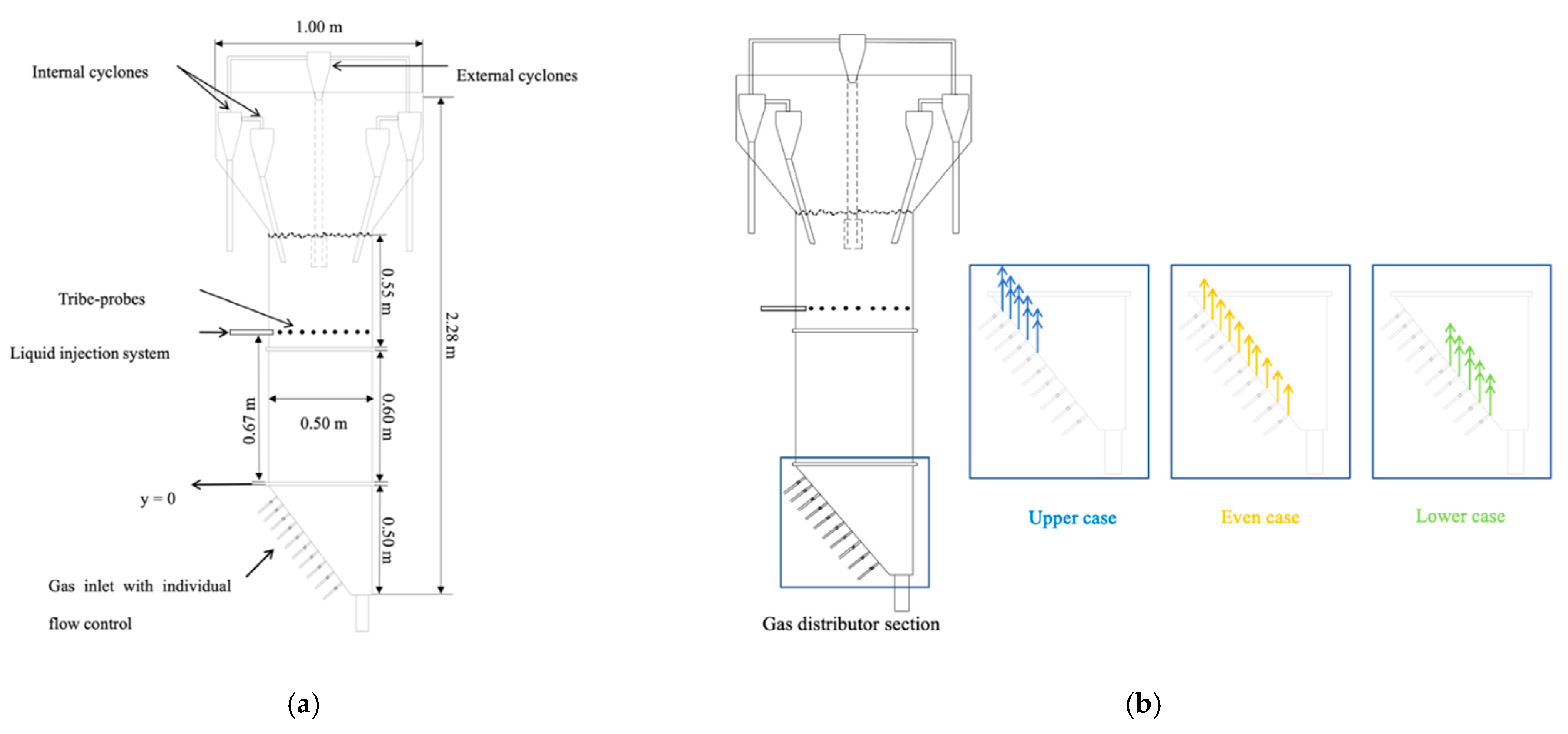
2. Configuration of the Fluidized Bed
3. Numerical Simulations
3.1. Computational Domain
3.2. Governing Equations and Numerical Methods
3.3. Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
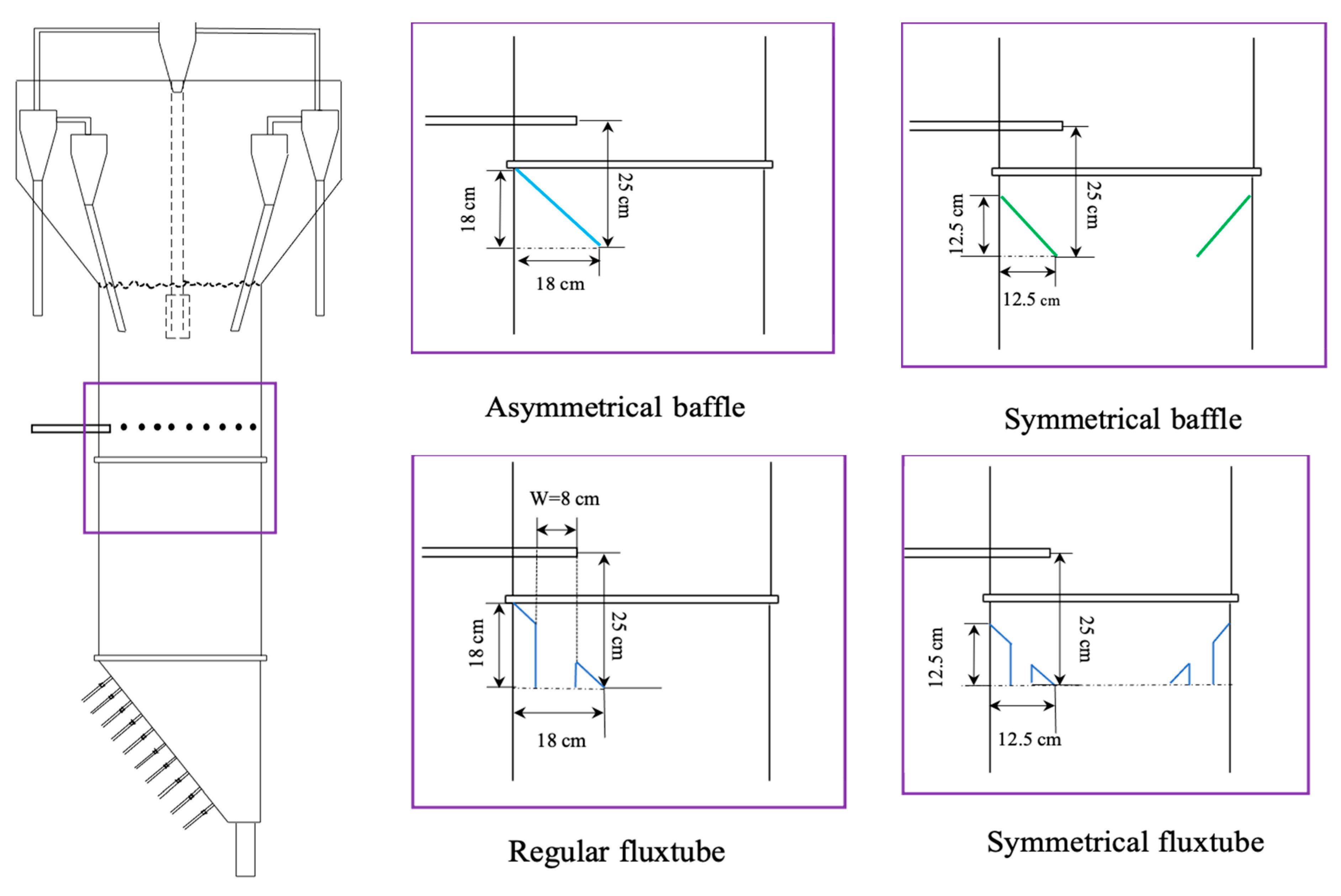
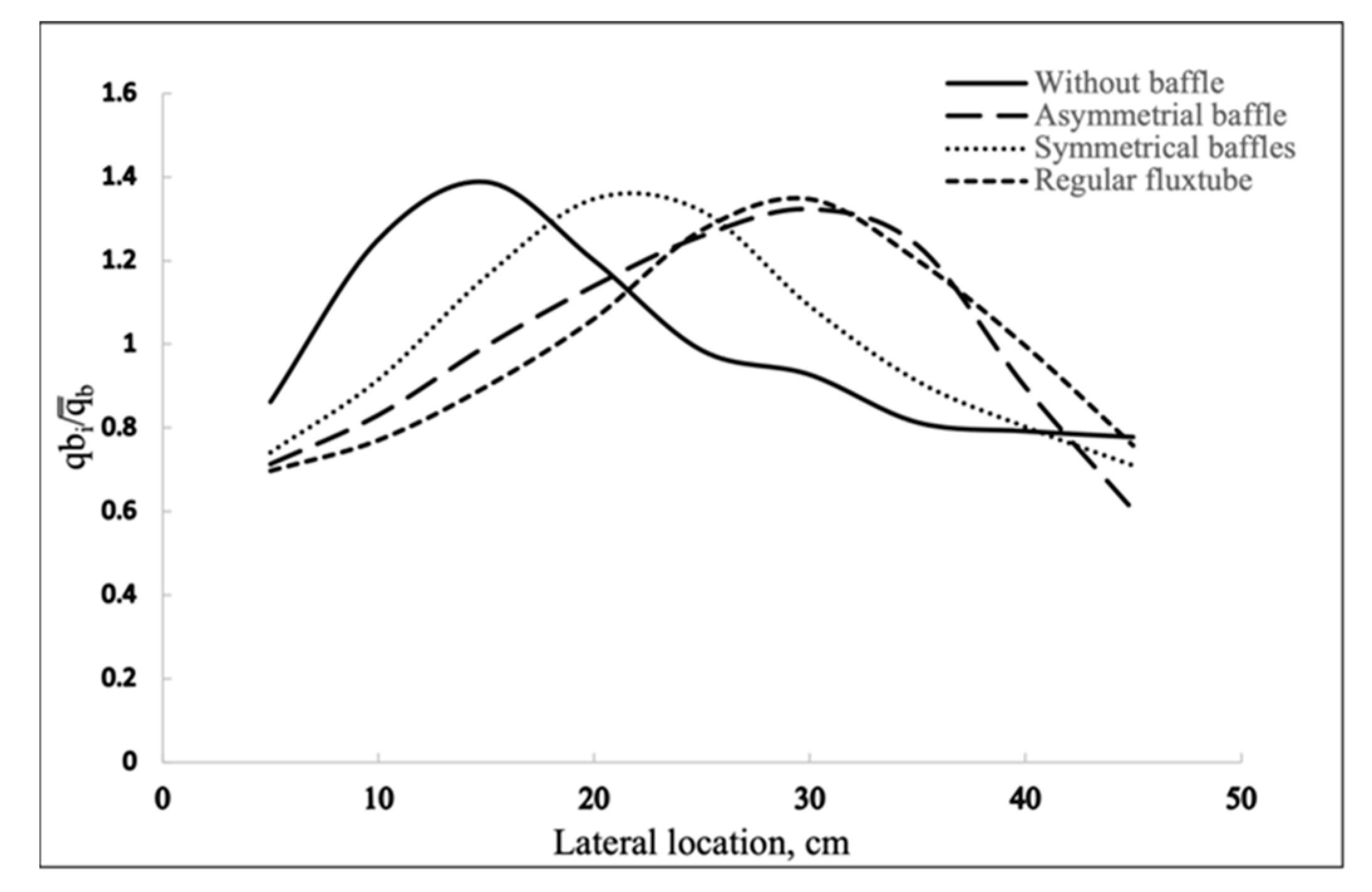
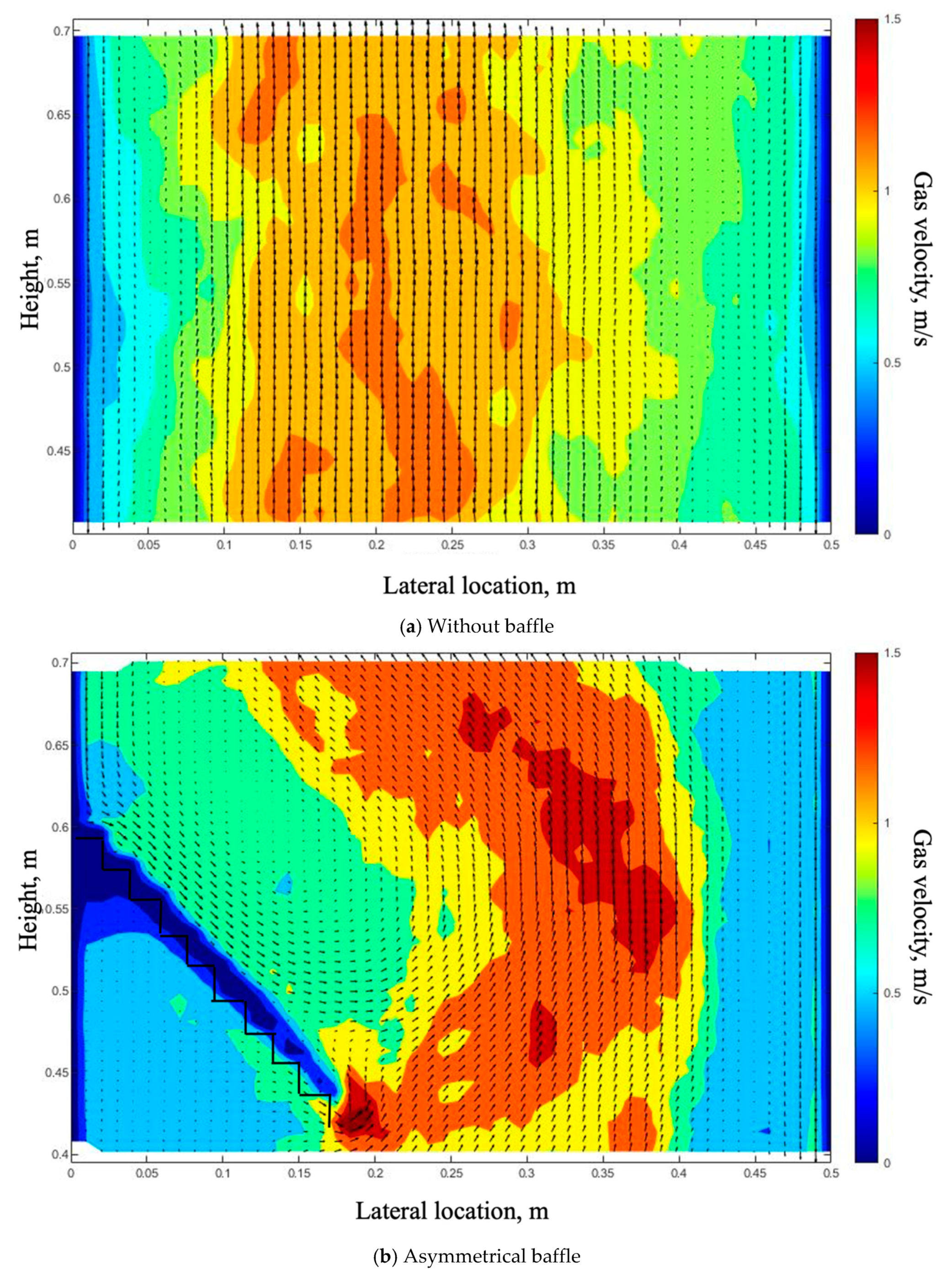
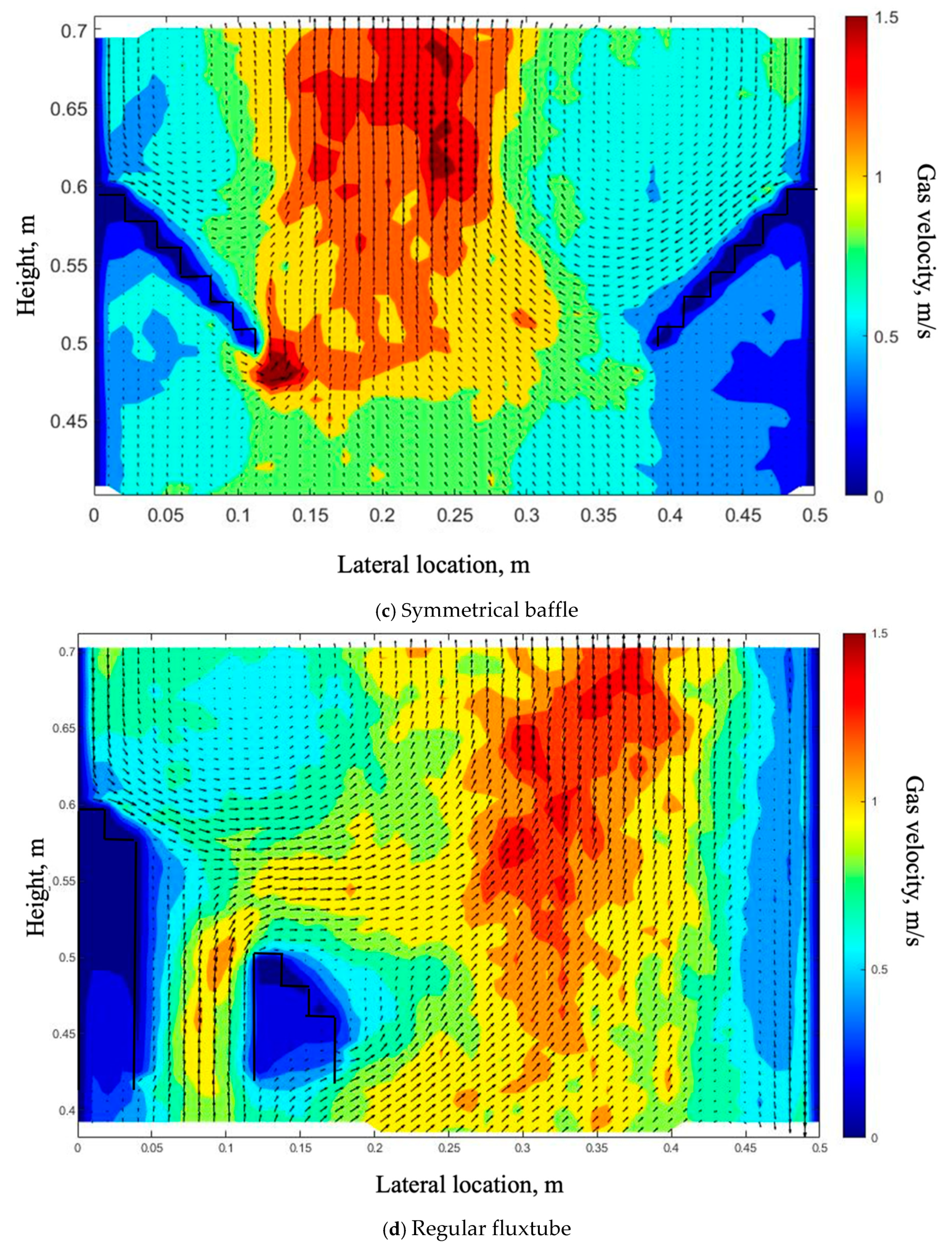
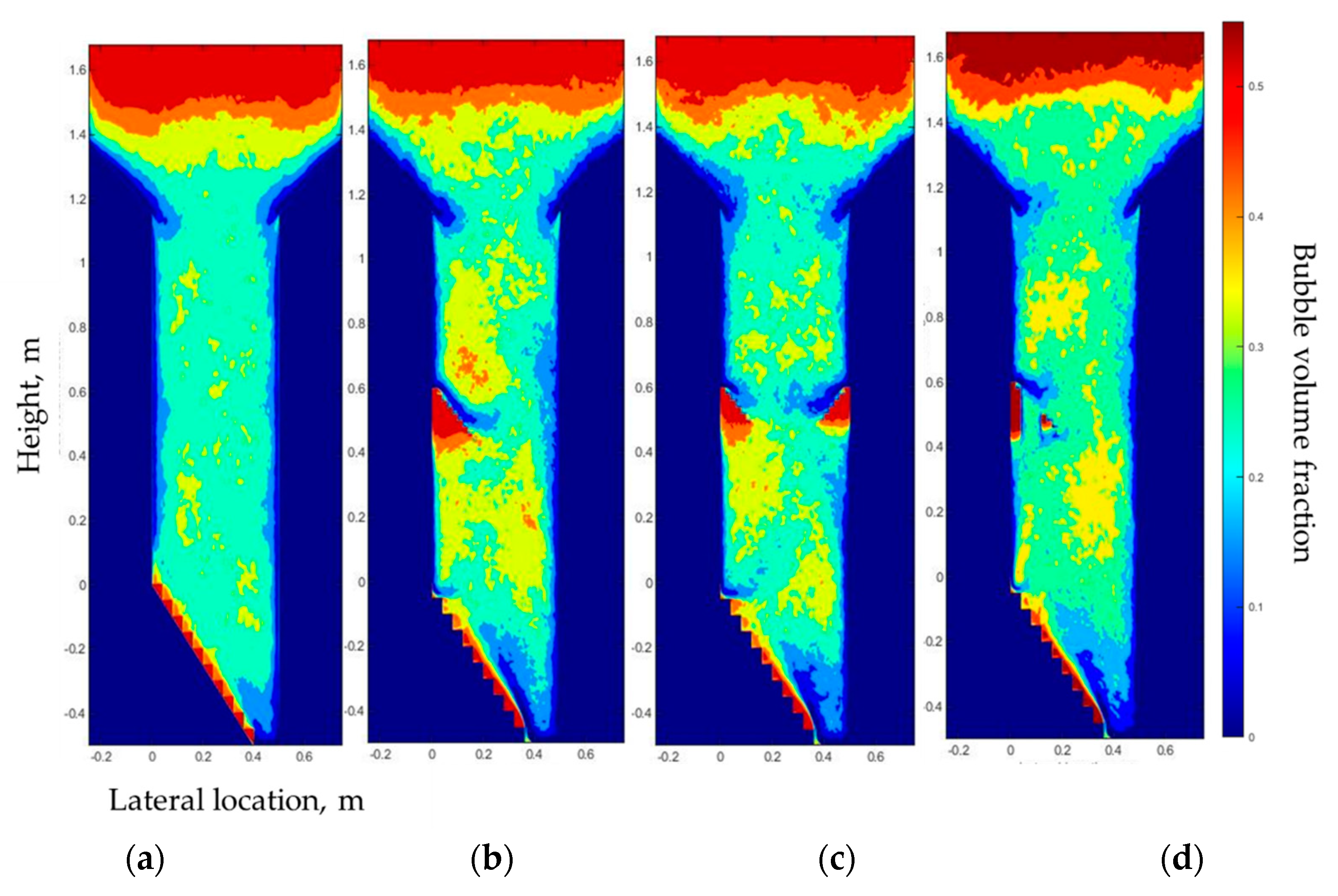
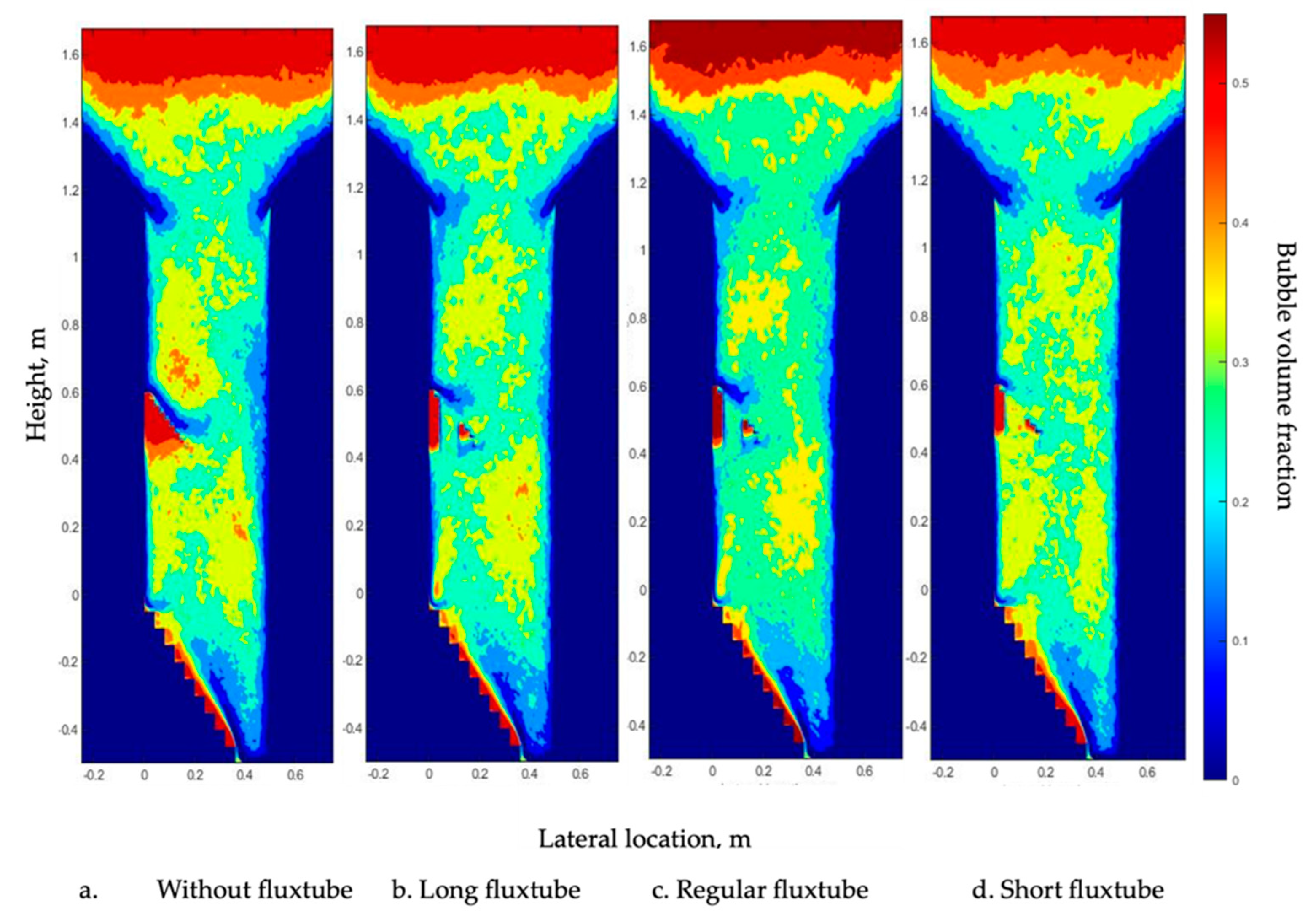
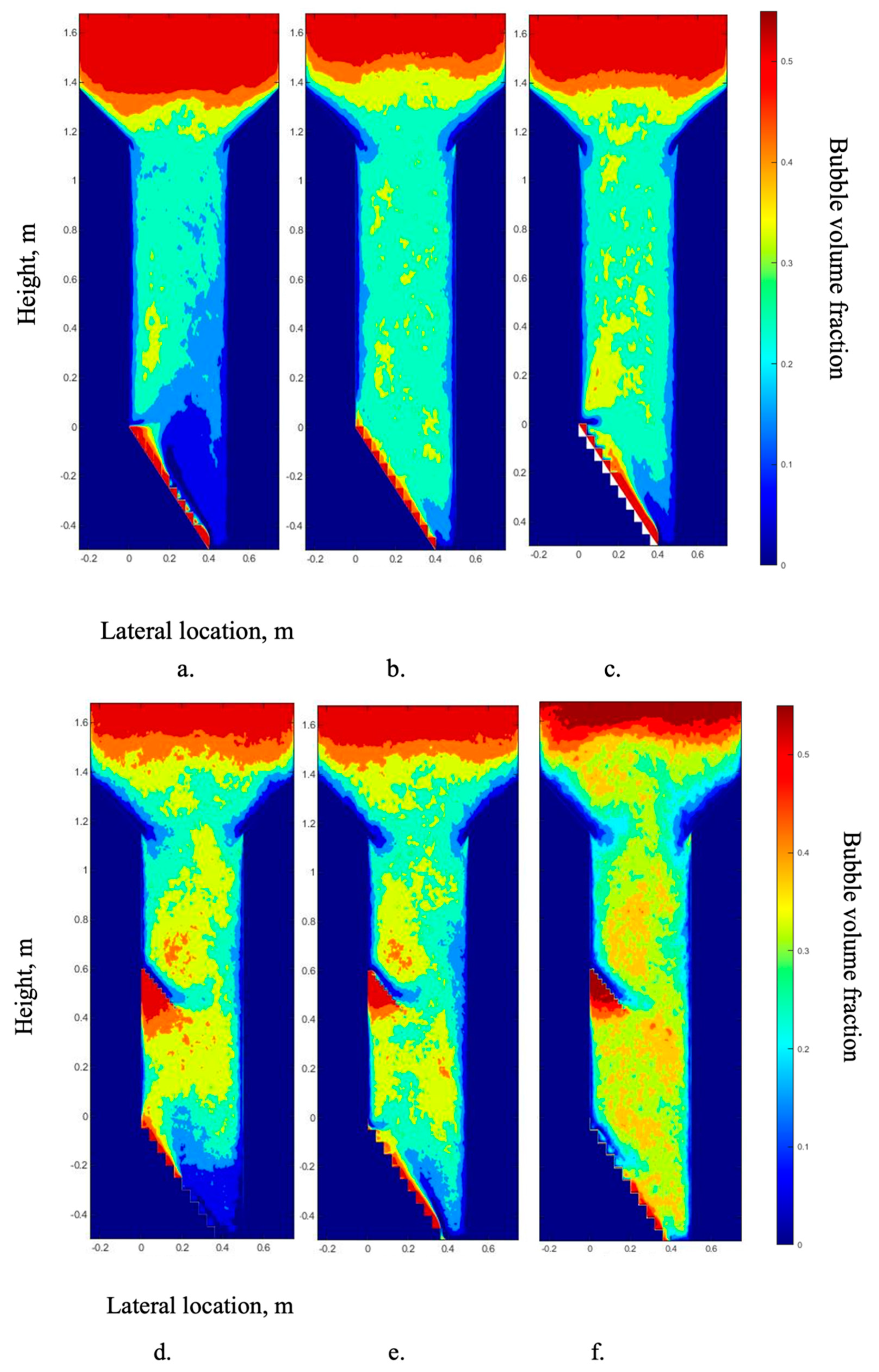
4.1. Effect of Baffles on the Gas Bubble Distribution
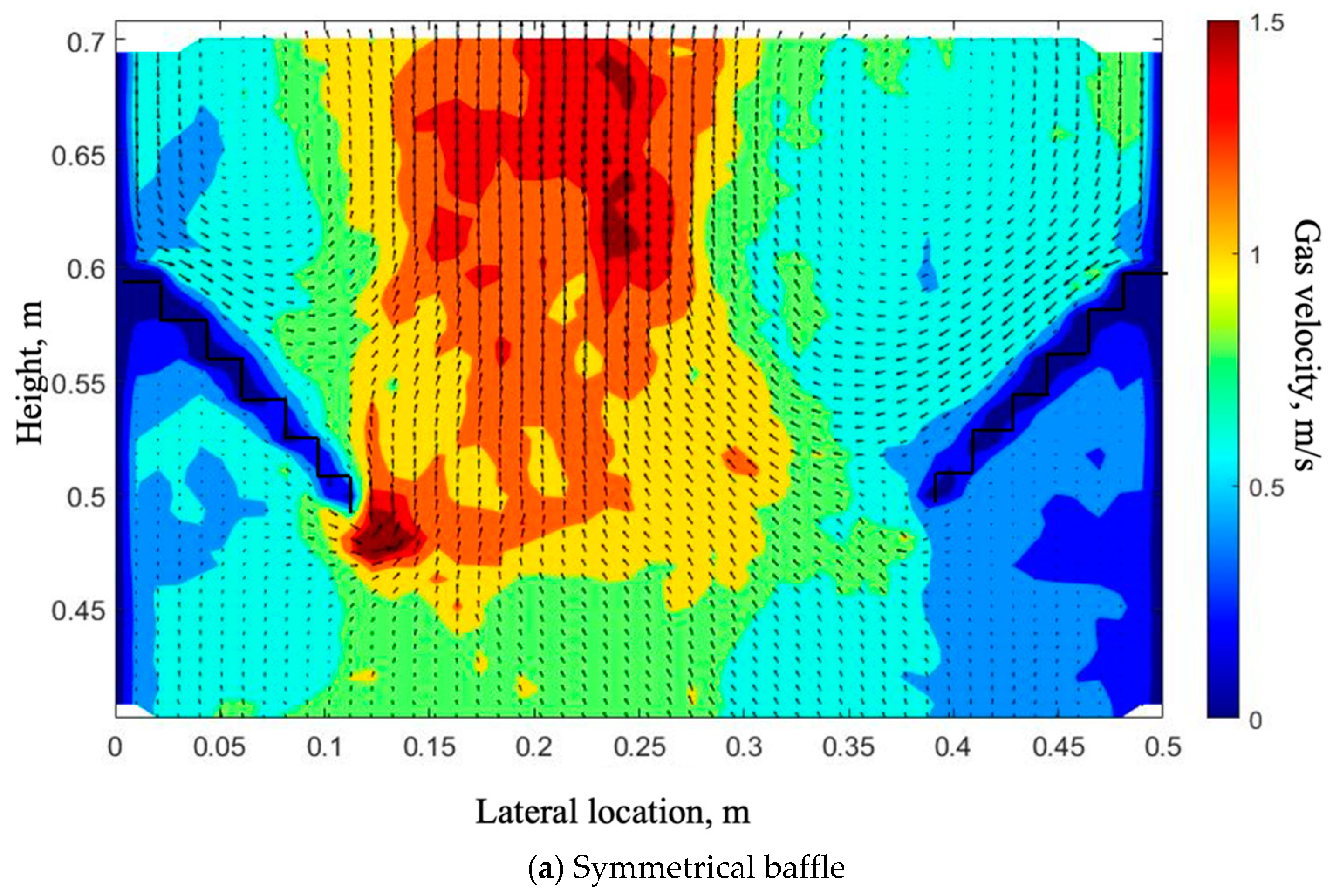
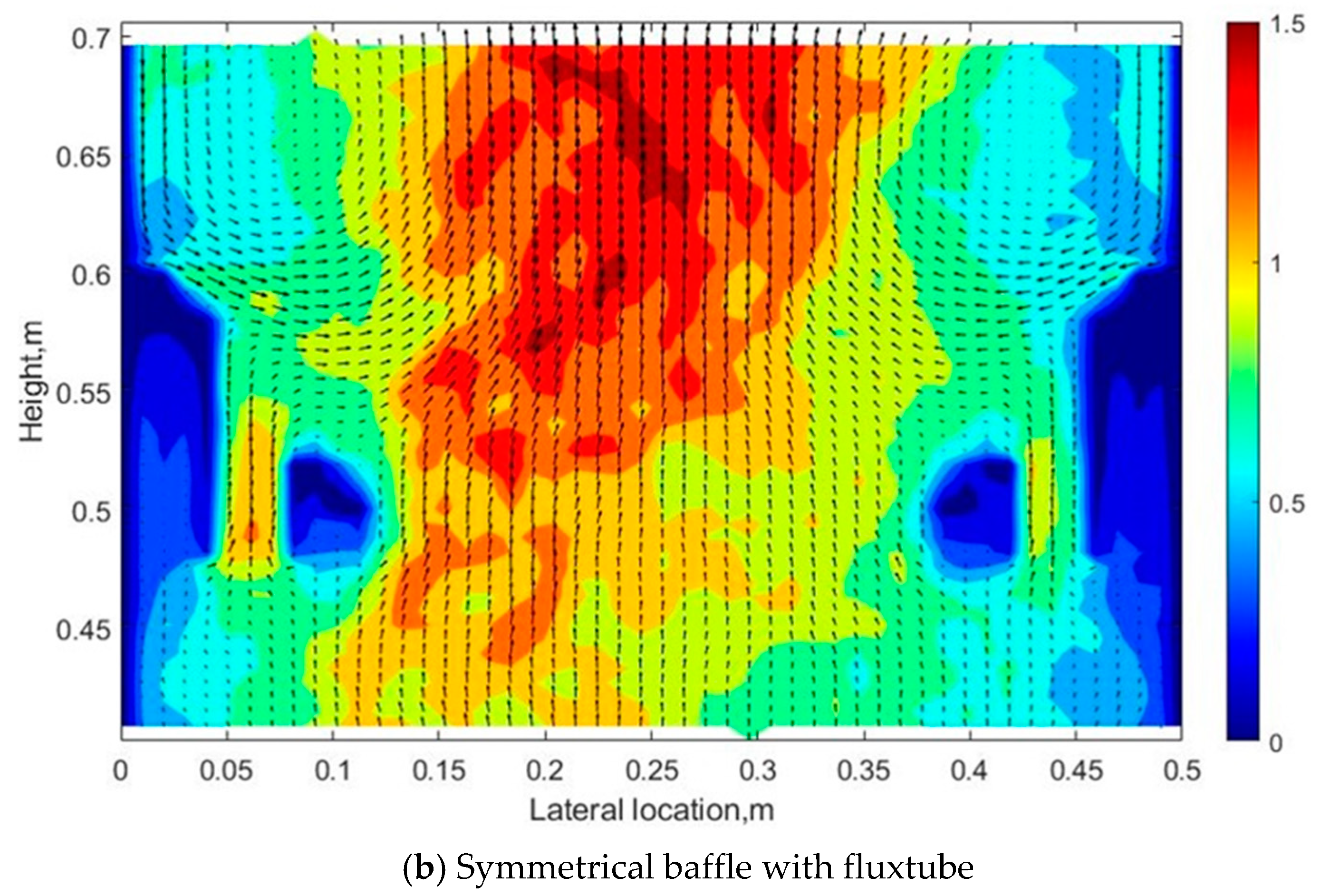
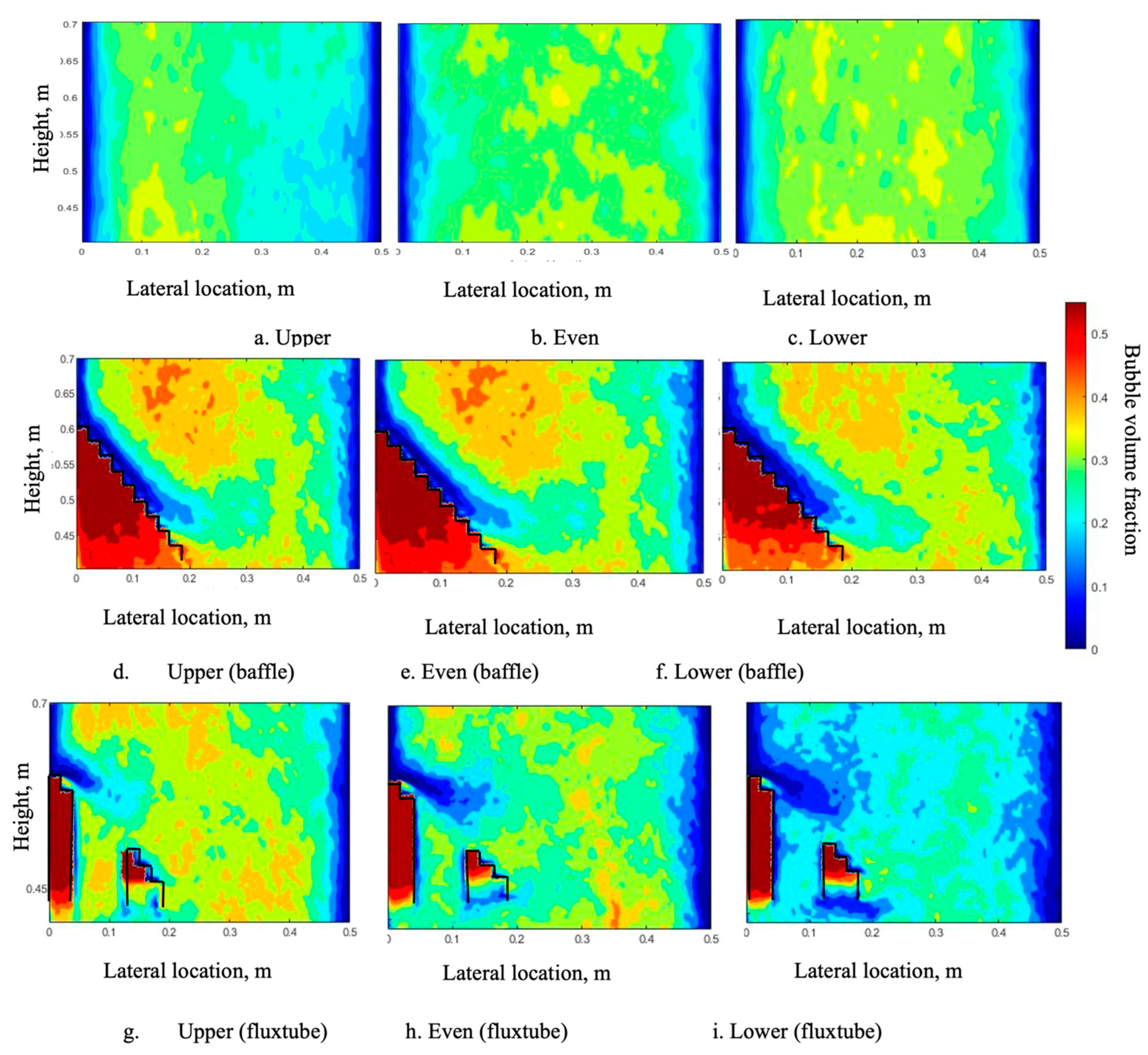
4.2. Effect of the Symmetrical Baffle
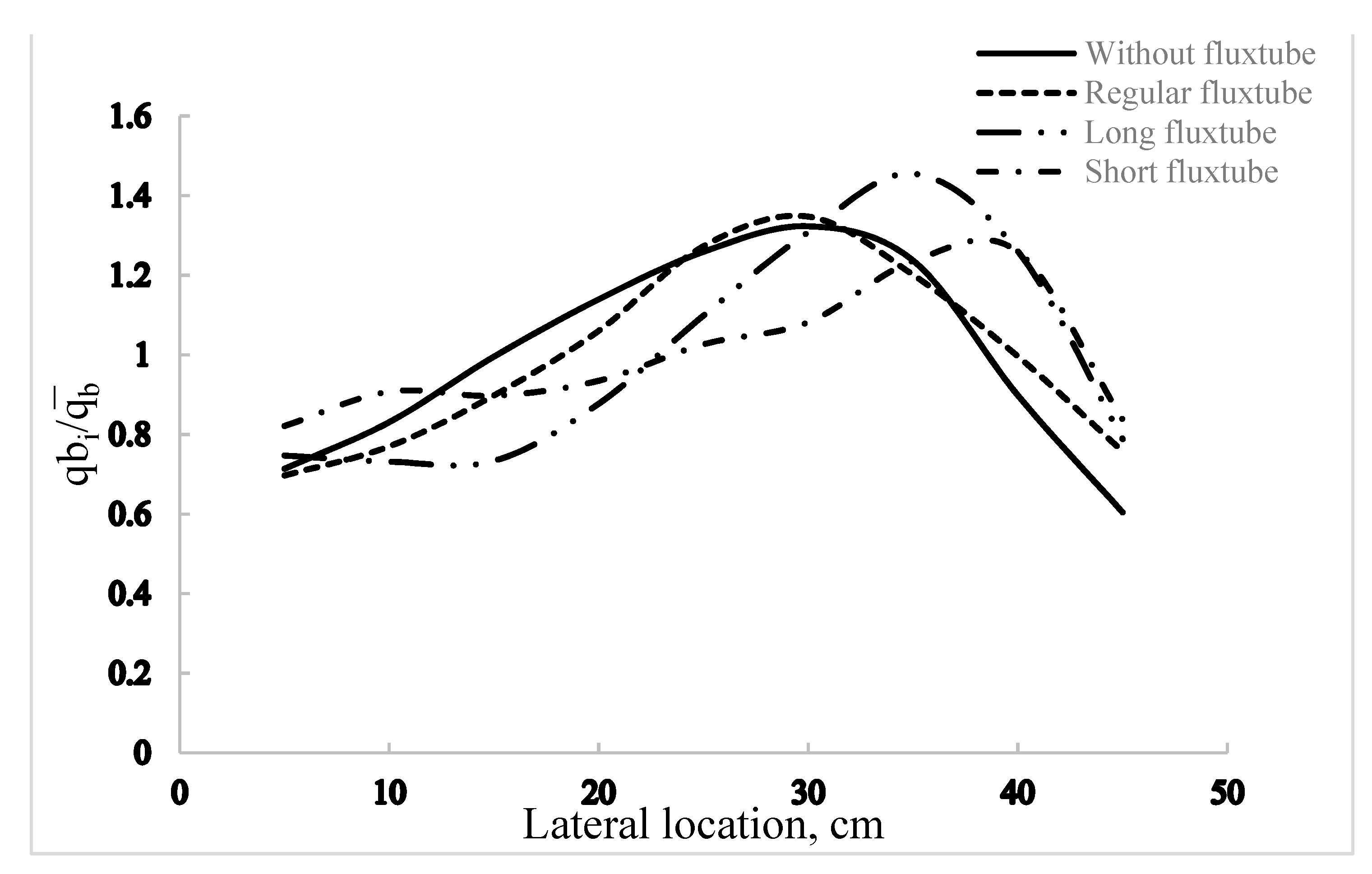
4.3. Effect of the Fluxtube Length
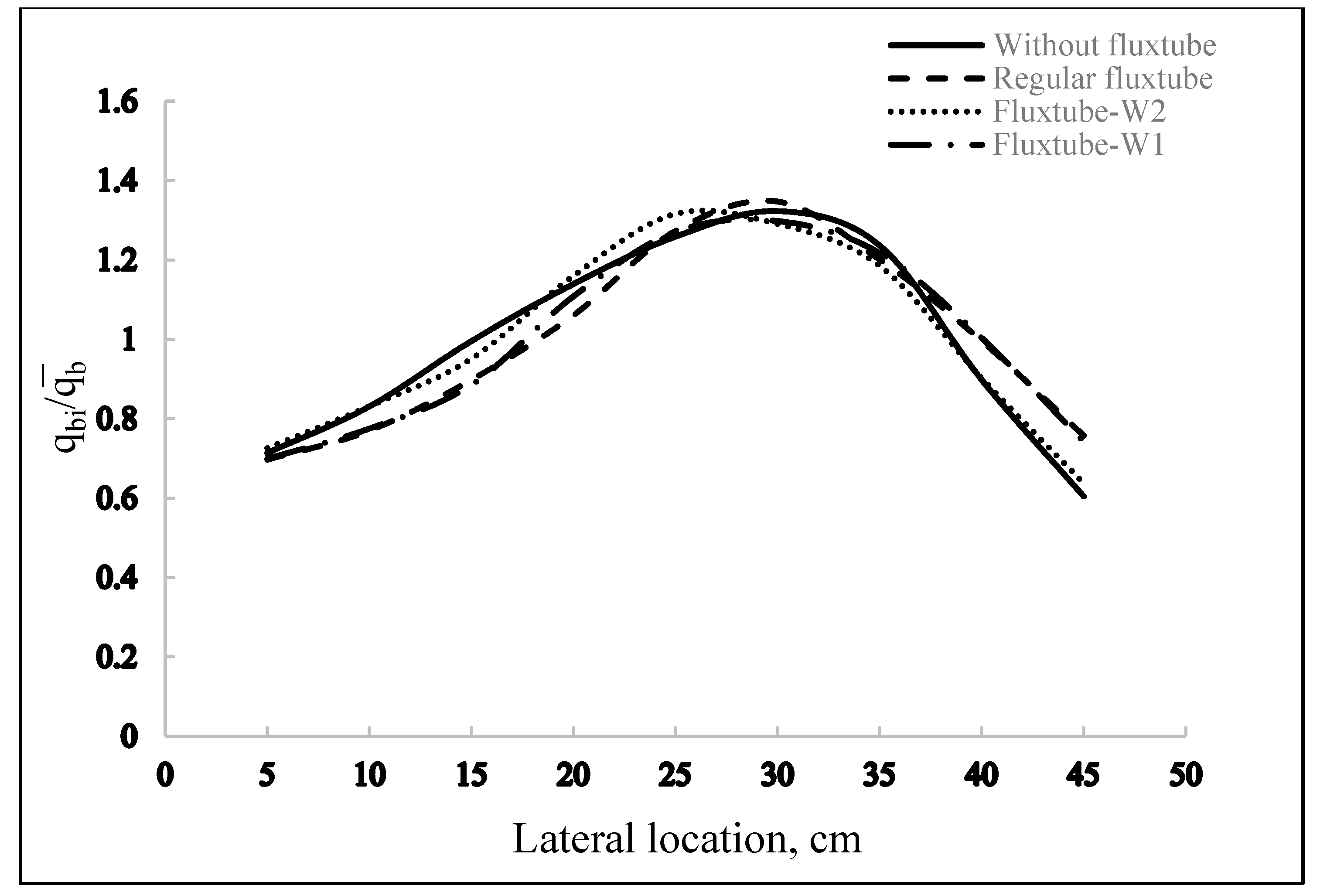
4.4. Effect of the Fluxtube Diameter
4.5. Combined Baffle and Gas Inlet Configuration
5. Conclusions
- Adding a baffle can change the gas bubble radial distribution. A symmetrical baffle works better on concentrating bubbles to the center and an asymmetrical baffle works better on moving the gas bubble peak location.
- An asymmetrical baffle with a fluxtube works better on evening the gas bubble distribution.
- There is a “gas pocket” that appeared under the baffle, and a denser region appeared above the baffle under all gas inlet configurations.
- A baffle can also increase the gas holdup throughout the bed, and this increase can be moderated by adding a fluxtube to the baffle.
- The length of the fluxtube has a stronger impact on the column hydrodynamics than its diameter. The gas bubble distribution above the baffle can be changed by modifying the length of the fluxtube.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| volume fraction of gas phase | |
| volume fraction of solid phase | |
| gas density, kg m−3 | |
| solid density, kg m−3 | |
| gas velocity, m s−1 | |
| Solid velocity, m s−1 | |
| gas volume fraction | |
| gas volume fraction | |
| Gas-solid momentum exchange coefficient | |
| P | Pressure, Pa |
| particulate phase pressure, Pa | |
| t | flow time, s |
| minimum fluidization velocity | |
| particle terminal velocity | |
| μ | shear viscosity |
| granular temperature, m2 s−2 |
References
- Yang, W. Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Geldart, D. Fluidization Engineering, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, J.G.; Lettieri, P. Fluidized-Bed Reactors: Processes and Operating Conditions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, J.R.; Bi, X.; Ellis, N. Essentials of Fluidization Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.G. Applications of Fluidization to Food Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, J.T.; Jones, E.N.; Chen, A.U.; Sutton, R.; Healy, T.M.; Suryo, R.; Lampert, L.; Miller, J. Circulating Fluidized Bed Reactor With Improved Circulation. U.S. Patent 8,435,452 B2, 14 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cochet, Y.; Briens, C.; Berruti, F.; McMillan, J.; Careaga, F.S. Impact of column geometry and internals on gas and particle flows in a fluidized bed with downward solids circulation: Effect of lateral injection profile and baffles. Powder Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Grace, J.R.; Bi, X.; Shi, M. Gas back-mixing in a two-dimensional baffled turbulent fluidized bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8484–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Grace, J.R.; Bi, X.; Lu, C.; Shi, M. Effect of louver baffles on hydrodynamics and gas mixing in a fluidized bed of FCC particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3270–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, K.; Hu, C.; Fan, J. CFD-DEM study of the effect of ring baffles on system performance of a full-loop circulating fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 196, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossbach, V.; Utzig, J.; Decker, R.K.; Noriler, D.; Soares, C.; Martignoni, W.P.; Meier, H.F. Gas-solid flow in a ring-baffled CFB riser: Numerical and experimental analysis. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.T.; Pareek, V.K.; Evans, G.M.; Utikar, R.P. Effect of baffles on performance of fluid catalytic cracking riser. Particuology 2018, 38, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermsinsuwan, B.; Samruamphianskun, T.; Piumsomboon, P. Effect of operating parameters inside circulating fluidized bed reactor riser with ring baffles using CFD simulation and experimental design analysis. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2479–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M. Recent advances in FCC technology. Powder Technol. 2006, 163, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Careaga, F.S.; Briens, C.; Berruti, F.; McMillan, J. Impact of local fluidized bed hydrodynamics on the distribution of liquid sprayed into the bed. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluswamy, G.K.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Utikar, R.P.; Tade, M.; Evans, G.; Glenny, M.E.; Roy, S.; Pareek, V.K. Hydrodynamic study of fluid catalytic cracker unit stripper. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careaga, F.S.; Briens, C.; Berruti, F.; McMillan, J.; Gray, M. Agglomerate behavior in a recirculating fluidized bed with sheds: Effect of sheds. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1758–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghbeigi, R. Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook, 3rd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Chenglin, E.; Shi, M.; Xu, C.; Gao, J.; Lu, C. Diffusion of feed spray in fluid catalytic cracker riser. AIChE J. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issangya, A.S.; Reddy Karri, S.B.; Knowlton, T.M. Effect of Baffles on Jet Streaming in Deep Fluidized Beds of Group a Particles; Particulate Solid Research, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, C. Effect of Baffle Type on Particle Segregation in a Binary Gas-Solids Fluidized Bed; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Lu, C. Systematic investigation of particle segregation in binary fluidized beds with and without multilayer horizontal baffles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5022–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q. Experimental study and numerical simulation of baffled bubbling fluidized beds with Geldart A particles in three dimensions. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo Reyes, L.A.; Reyes, L.A.P. Effect of Temperature and Successive Sprays on Liquid Distribution in Fluidized Beds. Master’s Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 28 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Zhou, Y.L.; Qi, T.Y.; Lu, Z.Y. Bitumen cracking using liquid injection. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada’s Oil & Natural Gas Producers (CAPP). Oil Sands Oil Sands; Canada’s Oil & Natural Gas Producers (CAPP): Celgary, AB, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- House, P.K.; Saberian, M.; Briens, C.L.; Berruti, F.; Chan, E. Injection of a liquid spray into a fluidized bed: Particle-liquid mixing and impact on fluid coker yields. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 5663–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, A. Factors Affecting Bed Agglomeration in Bubbling Fluidized Bed Biomass Boilers. Master’s Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 20 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, C.B. Development and Application of an Experimental Model for the Fluid Coking Process. Master’s Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 16 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, J.T.; Jones, E.N.; Chen, A.U.; Sutton, C.R.; Healy, T.M.; Suryo, R.; Lampert, L.; Miller, J. Circulating Fluid Bed Reactor with Improved Circulation. U.S. Patent 843,545,2B2, 7 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Javier Sanchez, F.C. Hydrodynamics in Recirculating Fluidized Bed Mimicking the Stripper Section of the Fluid Coker. Ph.D. Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 10 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanmiri, M. Use of a Baffle to Enhance the Distribution of a Liquid Sprayed into a Gas-Solid Fluidized Bed. Master’s Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 24 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. CPFD simulation on effects of louver baffles in a two-dimensional fluidized bed of Geldart A particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samruamphianskun, T.; Piumsomboon, P.; Chalermsinsuwan, B. Effect of ring baffle configurations in a circulating fluidized bed riser using CFD simulation and experimental design analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Tadama, T.; Murase, K.; Bando, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Toyama, S. Simulation of gas and particle behaviors in moving-fluidized bed with inclined baffle plates by two-fluid model. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1999, 32, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Lv, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q. Simulation of hydrodynamics in gas-solid bubbling fluidized bed with louver baffles in three dimensions. Powder Technol. 2016, 296, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloete, S.; Zaabout, A.; Johansen, S.T.; Annaland, M.V.S.; Gallucci, F.; Amini, S. The generality of the standard 2D TFM approach in predicting bubbling fluidized bed hydrodynamics. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q. A new drag model for TFM simulation of gas–solid bubbling fluidized beds with Geldart-B particles. Particuology 2014, 15, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huilin, L.; Wentie, L.; Feng, L.; Guangbo, Z.; Yurong, H. Yurong, Eulerian simulations of bubble behaviour in a two-dimensional gas-solid bubbling fluidized bed. Int. J. Energy Res. 2002, 26, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askaripour, H.; Dehkordi, A.M. Simulation of 3D freely bubbling gas–solid fluidized beds using various drag models: TFM approach. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 100, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Hong, K.; Gao, Y.; Gungor, A.; Zaman, M. An overview of Eulerian CFD modeling and simulation of non-spherical biomass particles. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Grace, J.; Bi, X.; Reid, K.; Wormsbecker, M. Numerical investigation of FLUID COKINGTM units, Part I: Hydrodynamics of a scaled cold flow model. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 90, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pougatch, K.; Salcudean, M.; Grecov, D. Numerical simulation of single and multiple gas jets in bubbling fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 4884–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pougatch, K.; Salcudean, M.; Grecov, D. Mixing of secondary gas injection in a bubbling fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lan, X.; Gao, J. Numerical simulation of chemical stripping process in resid fluid catalytic cracking stripper. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2014, 12, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzarti, S.; Mhiri, H.; Bournot, P. Numerical simulation of baffled circulating fluidized bed with Geldart B particles. Powder Technol. 2021, 380, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–812. [Google Scholar]
- Syamlal, M.; Rogers, W.; O’Brien, T.J. MFIX Documentation Theory Guide; Technical Note; USDOE Morgantown Energy Technology Center: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.C.; Jackson, R. Frictional–collisional constitutive relations for granular materials, with application to plane shearing. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 176, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, J. An EMMS-based multi-fluid model (EFM) for heterogeneous gas-solid riser flows: Part, I. Formulation of structure-dependent conservation equations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 75, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Gas Phase | ||
| Continuity | (1) | |
| Momentum | (2) | |
| Volume fraction | , | |
| Solid Phase | ||
| Continuity | (3) | |
| Momentum | (4) | |
| The granular temperature transport equation: | |
| (5) | |
| Where is the generation of energy by the solid stress tensor; is the diffusion of energy; is the collisional dissipation of energy; is the energy exchange between the lth solid phase and the sth solid phase; The stress tensors for gas and solid phase are: | |
| , | (6) |
| , | (7) |
| Solid shear viscosity: | |
| , | (8) |
| Collisional viscosity: | |
| , | (9) |
| Kinetic viscosity: | |
| , | (10) |
| Frictional viscosity: | |
| (11) | |
| Solid bulk viscosity: | |
| (12) | |
| Solid pressure: | |
| (13) | |
| Radial distribution function: | |
| (14) | |
| Diffusion coefficient of granular temperature (Syamlal–O’Brien): | |
| , | (15) |
| (16) | |
| Syamlal–O’Brien Drag Function | |
|---|---|
| (17) | |
| (18) | |
| , for , for , | |
| Where | |
| , | |
| , Where CD is the drag coefficient and Res is the Reynolds number | |
| Inlet of Gas Phase | |
| Superficial gas velocity | |
| Wall | |
| Gas-phase | No-slip velocity |
| Solid-phase | Partial-slip |
| Specularity coefficient:0.0001 | |
| Particle-wall restitution coefficient: 0.9 | |
| Outlet | |
| Gas-phase | Pressure-outlet |
| Solids phase | Pressure-outlet |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Briens, C. Effect of a Baffle on Bubble Distribution in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed. Processes 2021, 9, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071150
Xing X, Zhang C, Jiang B, Sun Y, Zhang L, Briens C. Effect of a Baffle on Bubble Distribution in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed. Processes. 2021; 9(7):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071150
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Xuelian, Chao Zhang, Bin Jiang, Yongli Sun, Luhong Zhang, and Cedric Briens. 2021. "Effect of a Baffle on Bubble Distribution in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed" Processes 9, no. 7: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071150
APA StyleXing, X., Zhang, C., Jiang, B., Sun, Y., Zhang, L., & Briens, C. (2021). Effect of a Baffle on Bubble Distribution in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed. Processes, 9(7), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071150






