Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents
Abstract
:1. Use and Sourcing of Rare Earths Elements
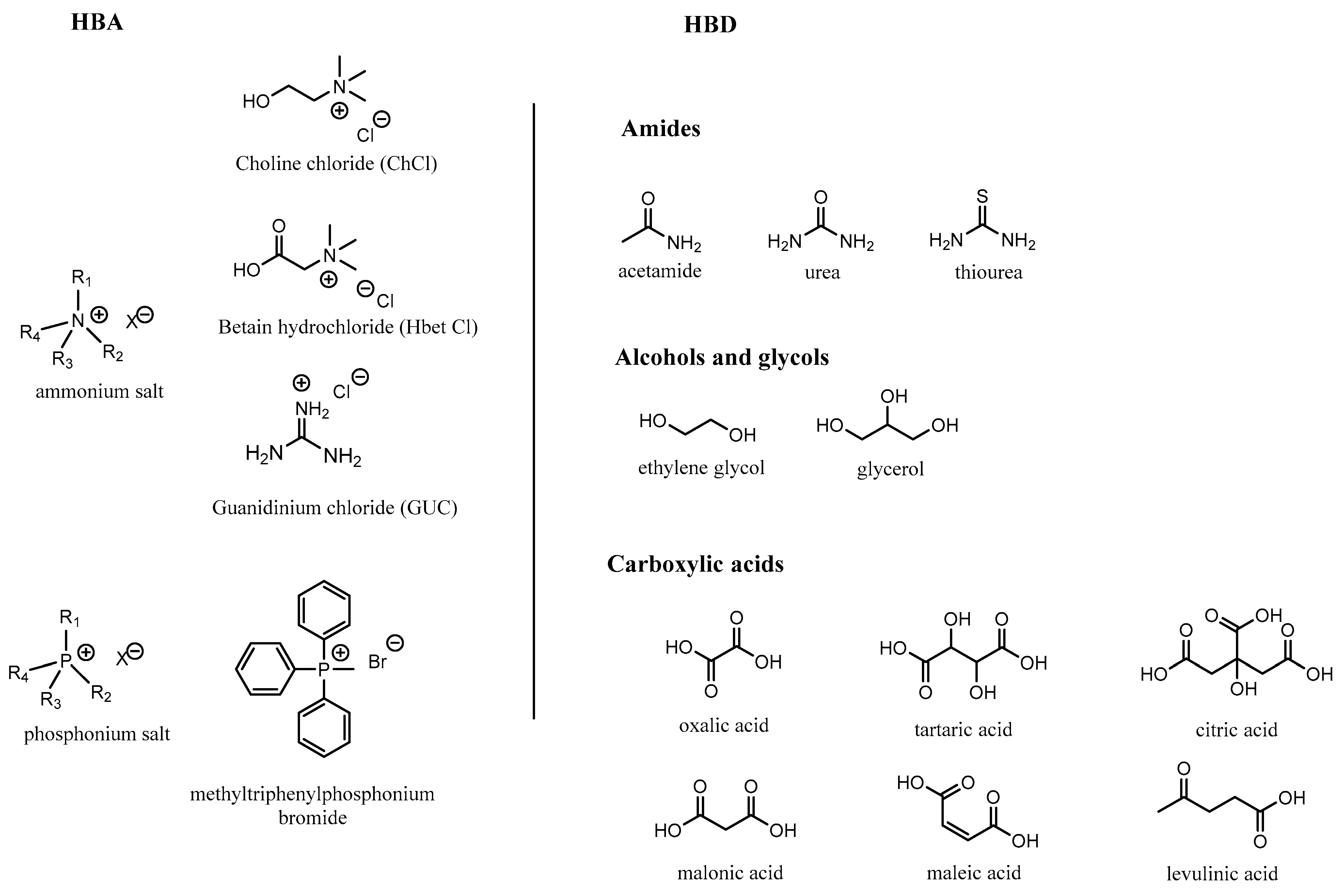
2. Description and Properties of Ionic Solvents
- -
- Cat+ is usually a quaternary ammonium or phosphonium salt;
- -
- X is the anionic moiety (generally a halide anion);
- -
- Y is a metal chloride for type I, a metal chloride hydrate for type II and a hydrogen bond donor for type III.
3. Use of ILs and DESs for the Recovery of REEs
3.1. Leaching Processes
| Ionic Solvent | Extracted/Feed | Matrix | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl:U + MA (1:1:0.5) | HREEs leaching against Ca, Mg and Fe | Carbonate salts | Entezari-Zarandi et al. [81] |
| EG:Maleic (4:1) | LREEs leaching against HREEs | REO | Chen et al. [82] |
| ChCl:U | LREEs leaching | REO | Söldner et al. [83] |
| [Hbet] [NTf2] | REE leaching | REO | Nockemann et al. [76] |
| [Hbet] [NTf2] | REE leaching against Fe | Bauxite residue | Davris et al. [77] |
| [Hbet] [NTf2] | REE leaching against Fe | NdFeB magnet | Dupont et al. [78] |
| [Hbet] [NTf2] | Nd leaching against Fe | NdFeB magnet | Orefice et al. [79] |
| [Py] [Cl] | Complete dissolution | NdFeB magnet | Orefice et al. [80] |
| ChCl:LAC (1:2) | Complete dissolution | NdFeB magnet | Riaño et al. [84] |
| GUC:LAC (1:2) | Nd leaching against Fe | NdFeB magnet | Liu et al. [85] |
| ChCl:LevA (1:3) | YOX phosphor (Y2O3:Eu3+) | Fluorescent lamps | Pateli et al. [87] |
| [Hbet] [NTf2] | YOX phosphor (Y2O3:Eu3+) | Fluorescent lamps | Dupont et al. [88] |
| [C1Him] [HSO4] | YOX phosphor (Y2O3:Eu3+) | Fluorescent lamps | Schaeffer et al. [89] |
| [C1C4im] [Cl]; ChCl:U (1:2) | Complete dissolution | Coal by-products | Rozelle et al. [91] |
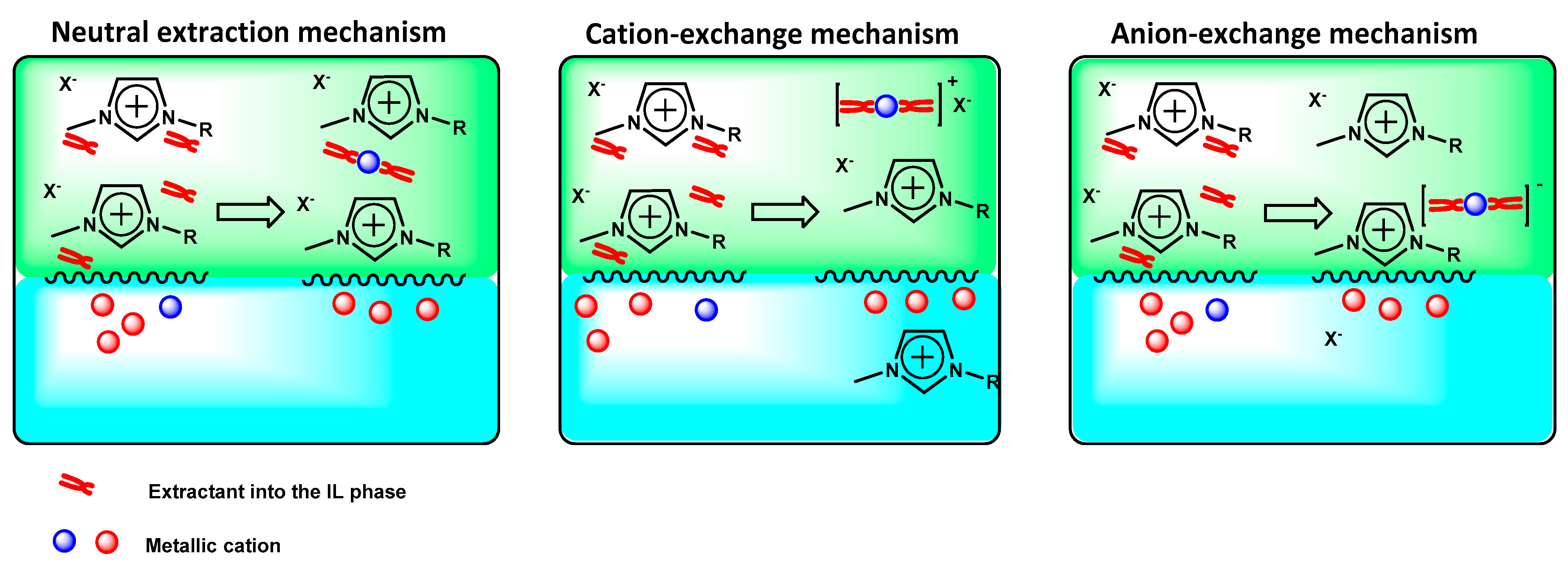
3.2. Solvent Extraction Processes
- -
- Neutral extraction mechanism: A neutral complex is formed and extracted in the IL phase. This mechanism is similar to those encountered in conventional solvents; however, the detailed mechanisms are often different. In this extraction mode, the IL acts as a polar non-aqueous solvent [104];
- -
- Cation exchange: This extraction mode is specific to IL systems. The IL acts as a liquid ion exchanger with cationic complexes extracted from the aqueous phase into the IL phase. Consequently, an IL cation has to be transferred to the aqueous phase while, in exchange, a metallic cation is transferred to the IL phase to respect electroneutrality [105];
- -
- Anion exchange: This extraction mode is also specific to IL systems. An anionic extractant forms over-neutralized anionic complexes that can be transferred to the IL phase, in exchange for the transfer of an IL anion to the aqueous phase [106]. Anion exchange is less common than cation exchange.
3.3. IL-Based Extraction Systems for REE Recovery
3.3.1. Ionic Exchangers
| Extractants | Ionic Solvent | Extracted (Feed) | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
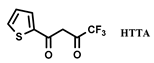 | [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Eu(III) chelate | Okamura et al. [114] |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Nd(III) chelate | Gujar et al. [115] | |
| [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 2–10 | Eu(III) chelate | Okamura et al. [116] | |
| [C1C4im] [NfO] | Nd; Eu (NaClO4−) | Jensen et al. [117] | |
| [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 2, 4 | Ce (NO3−) | Hidayah et al. [118] | |
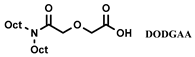 | [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4, 8, 12 | REEs (SO42−) | Yang et al. [119] |
| [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4, 8, 12 | Y, Eu (NO3−) | Kubota et al. [120] | |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Y, La, Ce, Eu, Tb (SO42−; (NO3−) | Yang et al. [121] | |
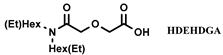 | [N8888] [DS] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [124] |
| [N1888] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [125] | |
 | [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4–10 | Ln (NO3−) | Sun et al. [126] |
| [N8888] [DS] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [124] | |
| [N1888] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [125] | |
 | [N8888] [DS] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [124] |
| [N1888] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Rout et al. [125] |
3.3.2. Neutral Extractants
| Extractants | Ionic Solvent | Extracted (Feed) | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
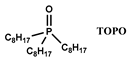 | [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4, 8 | Y, Eu, Dy, Nd (NO3−) | Yang et al. [128] |
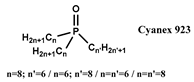 | [C1C4im] [NTf2], [N1444] [NTf2], [N1888] [NTf2], [P66614] [NTf2] | Nd (NO3−) | Rout et al. [129] |
| [N1888] [NO3], [P66614] [NO3] | La, Ce, Pr (Cl−) | Regadío et al. [130] | |
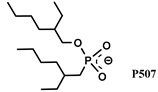
| [P66614] [SCN], [P66614] [NO3] | Nd, Dy (Cl−) | Riaño et al. [131] | |
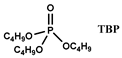 | [N1888] [NO3] | Pr, Nd, Dy (NO3−) | Kikuchi et al. [132] |
| [P2225] [NTf2] | Pr, Nd, Dy (NTf2) | Matsumiya et al. [133] | |
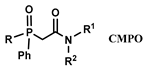 | [C1C4im] [NTf2] | REEs (Cl−) | Turanov et al. [134] |
| [C1C6im] [NTf2] | Ce, Eu, Lu (Cl−) | Atanassova et al. [135] | |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | REEs (NO3−) | Nakashima et al. [136] | |
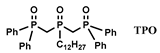 | [C2CnPip] [NTf2] n = 4, 8 | La, Nd, Eu, Dy, Yb (NO3−) | Turgis et al. [137] |
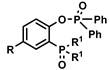 | [C1C4im] [NTf2] | REEs (NO3−) | Turanov et al. [138] |
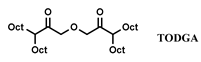 | [C1C6im] [NTf2] | Ce, Eu, Lu (Cl−) | Atanassova et al. [135] |
| [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 2, 4, 6 | La, Eu, Lu (NO3−) | Shimojo et al. [140] | |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Sypula et al. [141] | |
| [N1114] [NTf2], [C1C4Pyro] [NTf2] | Sm, Eu, Yb (Cl−) | Pan et al. [142] | |
| [P2225] [NTf2] | Pr, Nd, Dy (NTf2) | Murakami et al. [143] | |
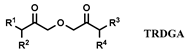 | [C1C8im] [NTf2] | Nd, Eu (NO3−) | Ansari et al. [144] |
| [C1C8im] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Rama et al. [145] | |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | La, Nd, Sm, Gd, Yb (NO3−) | Chen et al. [146] | |
 | [C2C8Pip] [NTf2] | La, Eu, Yb (NO3−) | Whebie et al. [147] |
3.3.3. Combination of Extractant and Synergistic Systems
| Extractants | Ionic Solvent | Extracted (Feed) | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
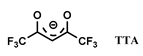
| HTTA-TOPO | [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Ln (HTTA) | Okamura et al. [151] |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Sc, Y, La, Nd, Eu, Dy (NO3−) | Zhao et al. [152] | |
| [P2225] [NTf2] | Pr, Nd, Dy (NTf2) | Matsumiya et al. [153] | |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | La, Eu, Lu (Cl−) | Okamura et al. [154] | |
| HBA-TOPO | [C1C4im] [NTf2] | Eu (Cl−) | Okamura et al. [154] |
| [C1C4im] [NTf2] | La, Nd, Eu, Dy, Lu (Cl−) | Hatakeyama et al. [155] | |
| HTTA-CMPO | [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4–10 | Eu (Cl−) | Atanassova et al. [156] |
| HBA-CMPO | [C1Cnim] [NTf2] n = 4, 10 [C1C4pyrro] [NTf2] | Eu (Cl−) | Atanassova et al. [157] |
| TBP-TODGA | [C1C8im] [NTf2] | Eu (NO3−) | Rama et al. [145] |
| CMPO-TODGA | [C1C6im] [NTf2] | Ce, Eu, Lu (Cl−) | Atanassova et al. [135] |
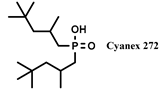
| TBP-Cyanex 272 | [C1C6im] [PF6] | Gd, Sm (NO3−) | Asadollahzadeh et al. [158] |
| TBP-HDEHP | [C1C6im] [PF6] | Gd, Sm (NO3−) | Asadollahzadeh et al. [158] |
3.3.4. Task-Specific Ionic Liquids (TSILs)
- TSILs with functionalized anion (Table 5)
| TSIL Anion | TSIL Cation | Extracted (Feed) | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
 | [C1C6im]+, [C1C6pyrro]+ [N4444]+ | Nd (NO3−) | Rout et al. [165] |
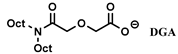
| [N4444]+, [N1888]+, [N66614]+ | REEs (DTPA-glycolic acid) | Sun et al. [166] | |
| [N1888]+ | REEs (DTPA-glycolic acid) | Sun et al. [167] | |
| [N2222]+, [N4444]+, [N6666]+, [N8888]+, [N1888]+ | REEs (DTPA-glycolic acid) | Sun et al. [168] | |
| [N2222] | Nd, Eu, Dy, Er (Cl−) | Sun et al. [169] | |
| Cyphos® IL 104 | Y (Cl−,NO3−) | Devi et al. [170] | |
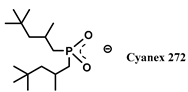 | [P66614]+ | La, Nd, Gd, Lu (Cl−) | Kumari et al. [171] |
| Ce, La (NO3−) | Makowka et al. [172] | ||
| Y, La, Nd, Eu, Dy, Ho, Yb ([C1C2im] [Cl]) | Rout et al. [173] | ||
 | [N1888]+ | Y, La, Gd, Tb, Tm, Yb, Lu (SO42−) | Shen et al. [174] |
| [N1888]+ | Gd (NO3−) | Dutta et al. [175] | |
 | [C1Cnim]+ n = 1–17, [C1C1C4im]+, [C1C4pyrro]+ | Nd (NTf2−) | Mehdi et al. [176] |
| [Ch]+ | Nd (NO3−) | Onghena et al. [177] | |
 | [N1888]+ | Nd (NO3−) | Rout et al. [178] |
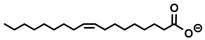 | [P8888]+ | La, Nd, Sm, Dy, Er, Yb (Cl−) | Parmentier et al. [179] |
 | [N1888]+ | REEs (Cl−) | Wang et al. [180] |
| [N1888]+ | Y, La, Eu, Ho (NO3−) | Yang et al. [181] | |
| [N1888]+ | REEs (Cl−) | Wang et al. [182] | |
| [N1888]+ | Y (Cl−) | Chen et al. [183] | |
 | [P66614]+ | Nd (Cl−) | Panigrahi et al. [184] |
- TSILs with a functionalized cation (Table 6)
| TSIL Cation | TSIL Anion | Extracted (Feed) | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
 [1-alkyl-3-(1-carboxylpropyl)im] | [PF6]− | Y (NO3−) | Wang et al. [186] |
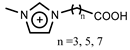 [C1(CH2)nCOOHim] | [NTf2]− | Sm, Nd | Chen et al. [187] |
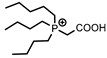 [P444C1COOH] | [Cl]− | Sc (Cl−) | Depuydt et al. [188] |
 [Hbet] | [NTf2]− | Nd (Cl−) | Fagnant et al. [189] |
| [NTf2]− | Nd (NTf2−) | Vander Hoogerstraete et al. [190] | |
| [NTf2]− | Nd (NTf2−) | Vander Hoogerstraete et al. [191] | |
| [NTf2]− | Sc (Cl−, NO3−) | Onghena et al. [192] | |
| [NTf2]− | Sc (SO42−) | Onghena et al. [193] | |
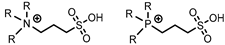 sulfonic acid | [NTf2]− | Dy, Nd, Sc (Cl−) | Dupont et al. [194] |
 alkylsulfuric acid | [NTf2]− | Y, Dy, Nd, La (Cl−, SO42−) | Dupont et al. [195] |
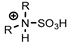 N-alkylated sulfamic acid | [NTf2]− | La, Nd, Dy (Cl−, NO3−) | Dupont et al. [196] |
 CMPO CMPO | [PF6]− | Eu (NO3−) | Odinets et al. [198] |
| [NTf2]− | Eu (NO3−) | Mohapatra et al. [199] | |
| [NTf2]− | La, Eu, Tb, Ho, Er, Lu (NO3−) | Turanov et al. [200] | |
 PFILs PFILs | [PF6]−, [NTf2]− | Nd (NO3−) | Wang et al. [201] |
 DGA DGA | [NTf2]− | Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm (NO3−) | Sengupta et al. [202] |
 DGA DGA | [NTf2]−, [BETI]− | La, Eu, Lu (NO3−) | Yun et al. [203] |
4. Outlook—Open Questions and Needed Research
4.1. Future of Leaching
4.2. Future of Liquid–Liquid Extraction
4.3. Electrochemical Behaviour
4.4. Mechanism and Predictive Models
4.5. Industrial Applications and Prospects
4.6. Environmental Impact
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Connelly, N.G.; Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R.M.; Hutton, A.T. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry—IUPAC Recommendations 2005. R. Soc. Chem. 2005, 27, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Longman Scientific & Technica: Harlow, Essex, UK, 1993; ISBN 9780582067011. [Google Scholar]
- Balaram, V. Rare Earth Elements: A Review of Applications, Occurrence, Exploration, Analysis, Recycling, and Environmental Impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Wall, F. Rare Earth Elements: Minerals, Mines, Magnets (and More). Elements 2012, 8, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, T.; Nansai, K.; Nakajima, K. Review of Critical Metal Dynamics to 2050 for 48 Elements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Richards, B.; Jose, G.; Teddy-Fernandez, T.; Joshi, P.; Jiang, X.; Lousteau, J. Rare-Earth Ion Doped TeO2 and GeO2 Glasses as Laser Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1426–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A. Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres. Fibers 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Perspective and Prospects for Rare Earth Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trench, A.; Sykes, J.P. Rare Earth Permanent Magnets and Their Place in the Future Economy. Engineering 2020, 6, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; Lucas, P.; Le Mercier, T.; Rollat, A.; Davenport, W. Chapter 10—Rare Earths in Rechargeable Batteries. In Rare Earths; Lucas, J., Lucas, P., Le Mercier, T., Rollat, A., Davenport, W.B.T.-R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 167–180. ISBN 978-0-444-62735-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, J.; Yin, D.; Luo, M.; Yan, C.; Du, Y. Rare Earth Incorporated Electrode Materials for Advanced Energy Storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 390, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating Rare Earth Element Availability: A Case with Revolutionary Demand from Clean Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Rare Earths and the Balance Problem. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanazawa, Y.; Kamitani, M. Rare Earth Minerals and Resources in the World. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408–412, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Kim, K.-H.; Uchimiya, M.; Kwon, E.E.; Jeon, B.-H.; Deep, A.; Yun, S.-T. Global Demand for Rare Earth Resources and Strategies for Green Mining. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Bakar, A.F.A.; Ashraf, M.A. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in the Ecosystem: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22764–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennebel, T.; Boon, N.; Maes, S.; Lenz, M. Biotechnologies for Critical Raw Material Recovery from Primary and Secondary Sources: R&D Priorities and Future Perspectives. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of Rare Earths: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaustad, G.; Williams, E.; Leader, A. Rare Earth Metals from Secondary Sources: Review of Potential Supply from Waste and Byproducts. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Ounoughene, G.; Malfliet, A.; Vind, J.; Panias, D.; Vassiliadou, V.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. A Study of the Occurrence of Selected Rare-Earth Elements in Neutralized–Leached Bauxite Residue and Comparison with Untreated Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Akhmadiyeva, N.; Abdulvaliyev, R.; Abhilash; Meshram, P. Overview On Extraction and Separation of Rare Earth Elements from Red Mud: Focus on Scandium. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards Zero-Waste Valorisation of Rare-Earth-Containing Industrial Process Residues: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cánovas, C.R.; Pérez-López, R.; Macías, F.; Chapron, S.; Nieto, J.M.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Exploration of Fertilizer Industry Wastes as Potential Source of Critical Raw Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, C.R.; Chapron, S.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Leaching of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) and Impurities from Phosphogypsum: A Preliminary Insight for Further Recovery of Critical Raw Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, R.; Macías, F.; Cánovas, C.R.; Pérez-López, R.; Ayora, C.; Nieto, J.M.; Olías, M. Mine Waters as a Secondary Source of Rare Earth Elements Worldwide: The Case of the Iberian Pyrite Belt. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 224, 106742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Kimura, R.; Arai, S. Rare Earth Elements and Other Trace Elements in Wastewater Treatment Sludges. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1998, 44, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer-Lavallée, A.; Neculita, C.M.; Coudert, L. Removal and Potential Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Mine Water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 89, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rezaee, M.; Bhagavatula, A.; Li, Y.; Groppo, J.; Honaker, R. A Review of the Occurrence and Promising Recovery Methods of Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal By-Products. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2015, 35, 295–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, A.; Rybak, A. Characteristics of Some Selected Methods of Rare Earth Elements Recovery from Coal Fly Ashes. Metals 2021, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunsu, C.; Petranikova, M.; Gergorić, M.; Ekberg, C.; Retegan, T. Reclaiming Rare Earth Elements from End-of-Life Products: A Review of the Perspectives for Urban Mining Using Hydrometallurgical Unit Operations. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fontana, D.; Akcil, A.; Deveci, H.; Batinic, B.; Leal, J.P.; Gasche, T.A.; Ali Kucuker, M.; Kuchta, K.; et al. Recent Advances on Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Critical and Precious Elements from End of Life Electronic Wastes—A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 212–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rademaker, J.H.; Kleijn, R.; Yang, Y. Recycling as a Strategy against Rare Earth Element Criticality: A Systemic Evaluation of the Potential Yield of NdFeB Magnet Recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10129–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, H.M.D.; Darcy, J.W.; Apelian, D.; Emmert, M.H. Value Analysis of Neodymium Content in Shredder Feed: Toward Enabling the Feasibility of Rare Earth Magnet Recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6553–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Perspectives for the Recovery of Rare Earths from End-of-Life Fluorescent Lamps. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Q.; Li, J.; Zeng, X. Rare Earth Elements Recovery from Waste Fluorescent Lamps: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 749–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.K.; Krishnamurthy, N. Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths. Int. Mater. Rev. 1992, 37, 197–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Adhikari, N. An Overview on Common Organic Solvents and Their Toxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2019, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Reichert, W.M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Wilkes, J.S.; Sun, L.; Thrasher, J.S.; Kirichenko, K.; Singh, S.; Katritzky, A.R.; Rogers, R.D. Combustible Ionic Liquids by Design: Is Laboratory Safety Another Ionic Liquid Myth? Chem. Commun. 2006, 24, 2554–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Gilea, M.A.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The Distillation and Volatility of Ionic Liquids. Nature 2006, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Tariq, M.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Magee, J.W.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Volatility of Aprotic Ionic Liquids—A Review. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez de María, P. Chapter 6—Ionic Liquids, Switchable Solvents, and Eutectic Mixtures. In The Application of Green Solvents in Separation Processes; Pena-Pereira, F., Tobiszewski, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 139–154. ISBN 978-0-12-805297-6. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic Liquids Synthesis and Applications: An Overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Gurman, S.J.; Hillman, A.R.; Hartley, J.; Holyoak, F.; Ryder, K.S. Ionometallurgy: Designer Redox Properties for Metal Processing. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10031–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc, N.; Legeai, S.; Balva, M.; Hazotte, C.; Comel, J.; Lapicque, F.; Billy, E.; Meux, E. Recovery of Metals from Secondary Raw Materials by Coupled Electroleaching and Electrodeposition in Aqueous or Ionic Liquid Media. Metals 2018, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Chemical Industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-Based Ionic Liquids with Metal-Containing Anions and Cations. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids: “Designer” Solvents for Green Chemistry. In Methods and Reagents for Green Chemistry: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 103–130. ISBN 9780471754008. [Google Scholar]
- Micheau, C.; Arrachart, G.; Turgis, R.; Lejeune, M.; Draye, M.; Michel, S.; Legeai, S.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Ionic Liquids as Extraction Media in a Two-Step Eco-Friendly Process for Selective Tantalum Recovery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, J.; Husson, P.; Padua, A.A.H.; Majer, V. Density and Viscosity of Several Pure and Water-Saturated Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonhôte, P.; Dias, A.-P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Grätzel, M. Hydrophobic, Highly Conductive Ambient-Temperature Molten Salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. How Do We Drive Deep Eutectic Systems towards an Industrial Reality? Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 11, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florindo, C.; Lima, F.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Overcoming 21st Century Challenges. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Overview of Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvents on Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Water-Immiscible Extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwamena, A.K. Recent Advances in Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extraction. Separations 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makos, P.; Slupek, E.; Gebicki, J. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents in Microextraction Techniques—A Review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-Based Eutectic Mixtures: Hydrophobic Low Viscosity Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phenolic Hydrogen Bond Donors in the Formation of Non-Ionic Deep Eutectic Solvents: The Quest for Type V DES. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10253–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; McKenzie, K.J.; Obi, S.U. Solubility of Metal Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Bai, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W.; Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Mu, T. Poly-Quasi-Eutectic Solvents (PQESs): Versatile Solvents for Dissolving Metal Oxides. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 5571–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Thompson, D.; Alabdullah, S.S.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. The Effect of PH and Hydrogen Bond Donor on the Dissolution of Metal Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-K.; Lee, E.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, J.-J. Application of Ionic Liquids for Metal Dissolution and Extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söldner, A.; Zach, J.; König, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extraction Media for Metal Salts and Oxides Exemplarily Shown for Phosphates from Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Thijs, B.; Pittois, S.; Thoen, J.; Glorieux, C.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Kirchner, B.; Binnemans, K. Task-Specific Ionic Liquid for Solubilizing Metal Oxides. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 20978–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I. Selective Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud), Using a Functionalized Hydrophobic Ionic Liquid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Binnemans, K. Recycling of Rare Earths from NdFeB Magnets Using a Combined Leaching/Extraction System Based on the Acidity and Thermomorphism of the Ionic Liquid [Hbet][Tf2N]. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orefice, M.; Van den Bulck, A.; Blanpain, B.; Binnemans, K. Selective Roasting of Nd–Fe‒B Permanent Magnets as a Pretreatment Step for Intensified Leaching with an Ionic Liquid. J. Sustain. Metall. 2020, 6, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orefice, M.; Binnemans, K. Solvometallurgical Process for the Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Nd–Fe–B Magnets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 117800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari-Zarandi, A.; Larachi, F. Selective Dissolution of Rare-Earth Element Carbonates in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, J.; Lan, X.; Zhao, X.; Mou, H.; Mu, T. A Strategy for the Dissolution and Separation of Rare Earth Oxides by Novel Bronsted Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4748–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söldner, A.; König, B. Optical Analysis and Separation of Trivalent Lanthanides in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, S.; Petranikova, M.; Onghena, B.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Banerjee, D.; Foreman, M.R.S.; Ekberg, C.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals from Deep-Eutectic Solvents: A New Alternative for the Recycling of Used NdFeB Magnets. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32100–32113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lei, L.; Xiao, C. Efficient Recovery of End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnets by Selective Leaching with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10370–10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardana, A.; Sánchez Cupido, L.; Hidalgo Betanzos, J.; Nieto Maestre, F.J. Extraction of Rare Earth Elements with Deep Eutectic Solvents. European Patent EP 17382134, 19 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pateli, I.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Binnemans, K.; Rodriguez Rodriguez, N. Recovery of Yttrium and Europium from Spent Fluorescent Lamps Using Pure Levulinic Acid and the Deep Eutectic Solvent Levulinic Acid-Choline Chloride. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 28879–28890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Binnemans, K. Rare-Earth Recycling Using a Functionalized Ionic Liquid for the Selective Dissolution and Revalorization of Y2O3:Eu3+ from Lamp Phosphor Waste. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, N.; Feng, X.; Grimes, S.; Cheeseman, C. Recovery of an Yttrium Europium Oxide Phosphor from Waste Fluorescent Tubes Using a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid, 1-Methylimidazolium Hydrogen Sulfate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Franklin, M.S. Ionic Liquids for Coal Dissolution, Extraction and Liquefaction. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozelle, P.L.; Khadilkar, A.B.; Pulati, N.; Soundarrajan, N.; Klima, M.S.; Mosser, M.M.; Miller, C.E.; Pisupati, S.V. A Study on Removal of Rare Earth Elements from U.S. Coal Byproducts by Ion Exchange. Metall. Mater. Trans. E 2016, 3, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ju, Y.H.; Barnes, C.E. Solvent Extraction of Strontium Nitrate by a Crown Ether Using Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1999, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, N. Chelate Extraction of Metals into Ionic Liquids. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2011, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, S.Q.; Ma, P.S. Use of Ionic Liquids as ‘green’ Solvents for Extractions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toita, M.; Morita, K.; Hirayama, N. Mutual Separation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Using Cyclohexane/Water/Ionic-Liquid Triphasic Extraction System with 2,2′-Bipyridine and Tri-n-Octylphosphine Oxide. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the Aqueous Miscibility of Ionic Liquids: Aqueous Biphasic Systems of Water-Miscible Ionic Liquids and Water-Structuring Salts for Recycle, Metathesis, and Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, R.; Sen, K. Aqueous Biphasic Extraction of Metal Ions: An Alternative Technology for Metal Regeneration. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanyire, T.; Sanchez-Segado, S.; Jha, A. Separation and Recovery of Critical Metal Ions Using Ionic Liquids. Adv. Manuf. 2016, 4, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukhbaatar, T.; Dourdain, S.; Turgis, R.; Rey, J.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Ionic Liquids as Diluents in Solvent Extraction: First Evidence of Supramolecular Aggregation of a Couple of Extractant Molecules. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15960–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billard, I.; Ouadi, A.; Gaillard, C. Is a Universal Model to Describe Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Cations by Use of Ionic Liquids in Reach? Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 6203–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietz, M.L. Ionic Liquids as Extraction Solvents: Where Do We Stand? Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 2047–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocalia, V.A.; Holbrey, J.D.; Gutowski, K.E.; Bridges, N.J.; Rogers, R.D. Separations of Metal Ions Using Ionic Liquids: The Challenges of Multiple Mechanisms. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2006, 11, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, C.H.C.; Macías-Ruvalcaba, N.A.; Aguilar-Martínez, M.; Kobrak, M.N. Metal Extraction to Ionic Liquids: The Relationship between Structure, Mechanism and Application. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2015, 34, 591–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocalia, V.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Spear, S.K.; Stepinski, D.C.; Rogers, R.D. Identical Extraction Behavior and Coordination of Trivalent or Hexavalent F-Element Cations Using Ionic Liquid and Molecular Solvents. Dalt. Trans. 2005, 11, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ji, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Li, D. A Novel Ammonium Ionic Liquid Based Extraction Strategy for Separating Scandium from Yttrium and Lanthanides. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Neuefeind, J.; Beitz, J.V.; Skanthakumar, S.; Soderholm, L. Mechanisms of Metal Ion Transfer into Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: The Role of Anion Exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15466–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, S.L.; Dietz, M.L. Ionic Liquid Anion Effects in the Extraction of Metal Ions by Macrocyclic Polyethers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 123, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Depuydt, D.; Binnemans, K. Overview of the Effect of Salts on Biphasic Ionic Liquid/Water Solvent Extraction Systems: Anion Exchange, Mutual Solubility, and Thermomorphic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6747–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, M.L.; Dzielawa, J.A.; Laszak, I.; Young, B.A.; Jensen, M.P. Influence of Solvent Structural Variations on the Mechanism of Facilitated Ion Transfer into Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, D.C.; Boltoeva, M.; Billard, I.; Georg, S.; Mazan, V.; Ouadi, A.; Ternova, D.; Hennig, C. Insights into the Mechanism of Extraction of Uranium (VI) from Nitric Acid Solution into an Ionic Liquid by Using Tri-n-Butyl Phosphate. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2015, 16, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, H.; Hirayama, N. Recent Progress in Ionic Liquid Extraction for the Separation of Rare Earth Elements. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Adidharma, H.; Radosz, M.; Wan, P.; Xu, X.; Russell, C.K.; Tian, H.; Fan, M.; Yu, J. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements with Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4469–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Guo, Q.J.; Lee, M.S. Recent Advances in Metal Extraction Improvement: Mixture Systems Consisting of Ionic Liquid and Molecular Extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Sakae, H.; Kidani, K.; Hirayama, N.; Aoyagi, N.; Saito, T.; Shimojo, K.; Naganawa, H.; Imura, H. Laser-Induced Fluorescence and Infrared Spectroscopic Studies on the Specific Solvation of Tris(1-(2-Thienyl)-4,4,4-Trifluoro-1,3-Butanedionato)Europium(III) in an Ionic Liquid. Polyhedron 2012, 31, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, R.B.; Verma, P.K.; Ansari, S.A.; Mohapatra, P.K. Complexation of 2-Thenoyltrifluoroacetone (HTTA) with Trivalent f-Cations in an Ionic Liquid: Solvent Extraction and Spectroscopy Studies. New. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13675–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Aoyagi, N.; Shimojo, K.; Naganawa, H.; Imura, H. Role of Tf2N—Anions in the Ionic Liquid–Water Distribution of Europium(Iii) Chelates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7610–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, M.P.; Borkowski, M.; Laszak, I.; Beitz, J.V.; Rickert, P.G.; Dietz, M.L. Anion Effects in the Extraction of Lanthanide 2-Thenoyltrifluoroacetone Complexes into an Ionic Liquid. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, N.N.; Nurihan, M.F.S.; Abidin, S.Z. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Cerium Using Synergist Extractant. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 12, 3302–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Baba, Y.; Kubota, F.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Extraction and Separation of Rare Earth Metal Ions with DODGAA in Ionic Liquids. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2012, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, F.; Shimobori, Y.; Baba, Y.; Koyanagi, Y.; Shimojo, K.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Application of Ionic Liquids to Extraction Separation of Rare Earth Metals with an Effective Diglycol Amic Acid Extractant. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2011, 44, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Kubota, F.; Baba, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Selective Extraction and Recovery of Rare Earth Metals from Phosphor Powders in Waste Fluorescent Lamps Using an Ionic Liquid System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, M.T.; Parker, T.G.; Mastren, T.; Mocko, V.; Brugh, M.; Birnbaum, E.R.; Fassbender, M.E. Extraction Chromatography of 225Ac and Lanthanides on N,N-Dioctyldiglycolamic Acid /1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Solvent Impregnated Resin. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Grimes, S.M.; Cheeseman, C.R. Use of Extraction Chromatography in the Recycling of Critical Metals from Thin Film Leach Solutions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 457, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.; Souza, E.R.; Binnemans, K. Solvent Extraction of Europium(III) to a Fluorine-Free Ionic Liquid Phase with a Diglycolamic Acid Extractant. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 11899–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rout, A.; Ramanathan, N. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Europium(III) in an Alkyl Ammonium Based Ionic Liquid Containing Diglycolamic Acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bell, J.R.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Extraction Separation of Rare-Earth Ions via Competitive Ligand Complexations between Aqueous and Ionic-Liquid Phases. Dalt. Trans. 2011, 40, 8019–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchu, N.K.; Li, Z.; Verbelen, B.; Binnemans, K. Structural Effects of Neutral Organophosphorus Extractants on Solvent Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements from Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Nitrate Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kubota, F.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. A Comparative Study of Ionic Liquids and a Conventional Organic Solvent on the Extraction of Rare-Earth Ions with TOPO. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2013, 20, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rout, A.; Binnemans, K. Influence of the Ionic Liquid Cation on the Solvent Extraction of Trivalent Rare-Earth Ions by Mixtures of Cyanex 923 and Ionic Liquids. Dalt. Trans. 2015, 44, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regadío, M.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Banerjee, D.; Binnemans, K. Split-Anion Solvent Extraction of Light Rare Earths from Concentrated Chloride Aqueous Solutions to Nitrate Organic Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34754–34763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaño, S.; Sobekova Foltova, S.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Neodymium and Dysprosium by Solvent Extraction Using Ionic Liquids Combined with Neutral Extractants: Batch and Mixer-Settler Experiments. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Matsumiya, M.; Kawakami, S. Extraction of Rare Earth Ions from Nd-Fe-B Magnet Wastes with TBP in Tricaprylmethylammonium Nitrate. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2014, 21, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumiya, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kawakami, S. Extraction of Rare Earth Ions by Tri-n-Butylphosphate/Phosphonium Ionic Liquids and the Feasibility of Recovery by Direct Electrodeposition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turanov, A.N.; Karandashev, V.K.; Yarkevich, A.N. Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements from Hydrochloric Acid by Carbamoyl Methyl Phosphine Oxides in the Presence of Ionic Liquids. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 63, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, M. Investigation of Synergism and Selectivity Using Mixture of Two Neutral Extractants in IL Media for Lanthanoids Extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 169, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Kubota, F.; Maruyama, T.; Goto, M. Ionic Liquids as a Novel Solvent for Lanthanide Extraction. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 1097–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgis, R.; Arrachart, G.; Dubois, V.; Dourdain, S.; Virieux, D.; Michel, S.; Legeai, S.; Lejeune, M.; Draye, M.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Performances and Mechanistic Investigations of a Triphosphine Trioxide/Ionic Liquid System for Rare Earth Extraction. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turanov, A.N.; Karandashev, V.K.; Baulin, V.E.; Baulin, D.V.; Khvostikov, V.A. Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements(III) from Nitric Acid Solutions with Diethyl 2-[(Diphenylphosphoryl)Methoxy]-5-Ethylphenylphosphonate. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 64, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.K. Diglycolamide-Based Solvent Systems in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids for Actinide Ion Extraction: A Review. Chem. Prod. Process. Model. 2015, 10, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, K.; Kurahashi, K.; Naganawa, H. Extraction Behavior of Lanthanides Using a Diglycolamide Derivative TODGA in Ionic Liquids. Dalt. Trans. 2008, 5083–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sypula, M.; Ouadi, A.; Gaillard, C.; Billard, I. Kinetics of Metal Extraction in Ionic Liquids: Eu3+/HNO3//TODGA/[C1C4im][Tf2N] as a Case Study. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10736–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Hussey, C.L. Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Investigation of Ln3 + (Ln = Sm, Eu, and Yb) Solvation in Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide-Based Ionic Liquids and Coordination by N,N,N′,N′-Tetraoctyl-3-Oxa-Pentane Diamide (TODGA) and Chloride. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Matsumiya, M.; Yamada, T.; Tsunashima, K. Extraction of Pr(III), Nd(III), and Dy(III) from HTFSA Aqueous Solution by TODGA/Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2016, 34, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Gujar, R.B.; Mohapatra, P.K. Complexation of Tetraalkyl Diglycolamides with Trivalent F-Cations in a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: Extraction and Spectroscopic Investigations. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 7584–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, R.; Rout, A.; Venkatesan, K.A.; Antony, M.P.; Vasudeva Rao, P.R. Loading Behavior of Eu(III) at High Aqueous Concentrations in Diglycolamide/Ionic Liquid Systems. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 308, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, C.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, C.; Zhang, M.; Hou, H.; Gao, Y.; Tian, G. Extraction Behavior of Several Lanthanides from Nitric Acid with DMDODGA in [C4mim][NTf2] Ionic Liquid. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 327, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbie, M.; Arrachart, G.; Ghannam, L.; Karamé, I.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. An Ionic Liquid-Based Extraction System Using Diglycolamide Functionalized Macrocyclic Platforms for the Extraction and Recovery of Lanthanides. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 16505–16515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usma, C.L.; Dourdain, S.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Rare Earths Elements by Use of Ionic Liquids. In Proceedings of the Hydroprocess, Santiago, Chile, 19–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Usma, C.L.; Dourdain, S.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Rare Earths Elements from Nitrate Media in DMDOHEMA/Ionic Liquid System: Performance and Mechanism Studies. Unpublished work.
- Atanassova, M.; Kurteva, V.; Lubenov, L.; Billard, I. Comparing Extraction, Synergism and Separation of Lanthanoids Using Acidic and Neutral Compounds in Chloroform and One Ionic Liquid: Is the Latter Always “Better”? RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38820–38829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, H.; Mizuno, M.; Hirayama, N.; Shimojo, K.; Naganawa, H.; Imura, H. Synergistic Enhancement of the Extraction and Separation Efficiencies of Lanthanoid(III) Ions by the Formation of Charged Adducts in an Ionic Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Baba, Y.; Kubota, F.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Synergistic Extraction of Rare-Earth Metals and Separation of Scandium Using 2-Thenoyltrifluoroacetone and Tri-n-Octylphosphine Oxide in an Ionic Liquid System. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2014, 47, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumiya, M.; Nomizu, D.; Tsuchida, Y.; Sasaki, Y. Separation of Rare Earth Elements by Synergistic Solvent Extraction with Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids Using a β-Diketone Extractant and a Neutral Ligand. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Takagi, H.; Isomura, T.; Morita, K.; Nagatani, H.; Imura, H. Highly Selective Synergism for the Extraction of Lanthanoid(III) Ions with Beta-Diketones and Trioctylphosphine Oxide in an Ionic Liquid. Anal. Sci. 2014, 30, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Nagatani, H.; Okamura, H.; Imura, H. Synergistic Extraction Equilibrium of Lanthanide(III) Ions with Benzoylacetone and a Neutral Ligand in an Ionic Liquid. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2018, 25, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atanassova, M.; Kurteva, V. Synergism in the Solvent Extraction of Europium(III) with Thenoyltrifluoroacetone and CMPO in Methylimidazolium Ionic Liquids. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, M.; Kurteva, V. Peculiar Synergistic Extraction Behavior of Eu(III) in Ionic Liquids: Benzoylacetone and CMPO Fusion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 183, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahzadeh, M.; Torkaman, R.; Torab-Mostaedi, M.; Hemmati, A.; Ghaemi, A. High Performance Separation of Gadolinium from Samarium with the Imidazolium Ionic Liquid through Selective Complexation of Organophosphorus Extractants. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappe, C.; Pomelli, C.S. Point-Functionalization of Ionic Liquids: An Overview of Synthesis and Applications. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 6120–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Extraction and Separation of Neodymium and Dysprosium from Used NdFeB Magnets: An Application of Ionic Liquids in Solvent Extraction towards the Recycling of Magnets. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiguel, S.; Depuydt, D.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Thomas, J.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Selective Alkaline Stripping of Metal Ions after Solvent Extraction by Base-Stable 1,2,3-Triazolium Ionic Liquids. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 5269–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, D.; den Bossche, A.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Metal Extraction with a Short-Chain Imidazolium Nitrate Ionic Liquid. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5271–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, R.; Forte, F.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Yttrium and Europium Separation by Solvent Extraction with Undiluted Thiocyanate Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4876–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.D.; Foersterling, F.H.; Dietz, M.L. Solvent Structural Effects on the Solubility of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl)Phosphoric Acid (HDEHP) in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.; Kotlarska, J.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Neodymium(III) by Dialkylphosphate Ionic Liquids from Acidic Medium: The Importance of the Ionic Liquid Cation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 16533–16541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Solvent Extraction of Rare-Earth Ions Based on Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Talanta 2012, 90, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Mechanistic Investigation of Solvent Extraction Based on Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Selective Separation of Rare-Earth Ions. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 8270–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Do-Thanh, C.-L.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. The Optimization of an Ionic Liquid-Based TALSPEAK-like Process for Rare Earth Ions Separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Waters, K.E. Synergistic Effect between Bifunctional Ionic Liquids and a Molecular Extractant for Lanthanide Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Sukla, L.B. Studies on Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Yttrium and Separation from Other Rare Earth Elements Using Bifunctional Ionic Liquids. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2019, 40, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Pandey, B.D. Solvent Extraction and Separation of Trivalent Lanthanides Using Cyphos IL 104, a Novel Phosphonium Ionic Liquid as Extractant. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2016, 34, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowka, A.; Pospiech, B. Studies on Extraction and Permeation of Lanthanum(III) and Cerium(III) Using Cyphos IL 104 as Extractant and Ion Carrier. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.; Wellens, S.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Rare Earths and Nickel by Solvent Extraction with Two Mutually Immiscible Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5753–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Su, W.; Deng, Y. Extraction of Mid-Heavy Rare Earth Metal Ions from Sulphuric Acid Media by Ionic Liquid [A336][P507]. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Ruhela, R.; Yadav, M.; Singh, A.K.; Sahu, K.K.; Padmanabhan, N.P.H.; Chakravartty, J.K. Liquid-Liquid Extraction Studies of Gadolinium with N-Methyl-N,N,N-Trioctyl Ammonium-Bis-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phosphonate—Task Specific Ionic Liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 175, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, H.; Binnemans, K.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Nockemann, P. Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids with Strongly Coordinating Anions. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onghena, B.; Jacobs, J.; Van Meervelt, L.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Neodymium(Iii) by Choline Hexafluoroacetylacetonate in the Ionic Liquid Choline Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide. Dalt. Trans. 2014, 43, 11566–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rout, A.; Binnemans, K. Solvent Extraction of Neodymium(III) by Functionalized Ionic Liquid Trioctylmethylammonium Dioctyl Diglycolamate in Fluorine-Free Ionic Liquid Diluent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6500–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, D.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Metz, S.J.; Binnemans, K.; Kroon, M.C. Selective Extraction of Metals from Chloride Solutions with the Tetraoctylphosphonium Oleate Ionic Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5149–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Application of Bifunctional Ionic Liquid Extractants [A336][CA-12] and [A336][CA-100] to the Lanthanum Extraction and Separation from Rare Earths in the Chloride Medium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 7534–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Wang, W.; Cui, H.-M.; Chen, J. Extraction Mechanism of Rare Earths with Bifuncional Ionic Liquids (Bif-ILs) [A336][CA-12]/[A336][CA-100] in Nitrate Medium. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 39, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, X. The Development of Sustainable Yttrium Separation Process from Rare Earth Enrichments Using Bifunctional Ionic Liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Sun, X. Extraction Behavior of Bifunctional Ionic Liquid [N1888][SOPAA] and TBP for Rare Earth Elements. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, M.; Grabda, M.; Kozak, D.; Dorai, A.; Shibata, E.; Kawamura, J.; Nakamura, T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Neodymium Ions from Aqueous Solutions of NdCl3 by Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X. A Synergistic Extraction Strategy by [N1888][SOPAA] and Cyphos IL 104 for Heavy Rare Earth Elements Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, A.; Yang, H.; Cui, H.; Chen, J. Solvent Extraction of Yttrium by Task-Specific Ionic Liquids Bearing Carboxylic Group. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, J. PH-Controlled Selective Separation of Neodymium (III) and Samarium (III) from Transition Metals with Carboxyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, D.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Solvent Extraction of Scandium(III) by an Aqueous Biphasic System with a Nonfluorinated Functionalized Ionic Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 8988–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnant, D.P.; Goff, G.S.; Scott, B.L.; Runde, W.; Brennecke, J.F. Switchable Phase Behavior of [HBet][Tf2N]–H2O upon Neodymium Loading: Implications for Lanthanide Separations. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Metal Ions with a Functionalized Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Rare Earths with the Betaine—Betainium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Ionic Liquid System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21353–21377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of Scandium(III) from Aqueous Solutions by Solvent Extraction with the Functionalized Ionic Liquid Betainium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onghena, B.; Borra, C.R.; Van Gerven, T.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of Scandium from Sulfation-Roasted Leachates of Bauxite Residue by Solvent Extraction with the Ionic Liquid Betainium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Raiguel, S.; Binnemans, K. Sulfonic Acid Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Dissolution of Metal Oxides and Solvent Extraction of Metal Ions. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9006–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Renders, E.; Binnemans, K. Alkylsulfuric Acid Ionic Liquids: A Promising Class of Strongly Acidic Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4640–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Renders, E.; Raiguel, S.; Binnemans, K. New Metal Extractants and Super-Acidic Ionic Liquids Derived from Sulfamic Acid. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7032–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Waheed, K.; Rahat, S.B.; Mehmood, T.; Lee, M.S. An Overview of Molecular Extractants in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids and Task Specific Ionic Liquids for the Partitioning of Actinides/Lanthanides. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 325, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinets, I.L.; Sharova, E.V.; Artyshin, O.I.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Nelyubina, Y.V.; Myasoedova, G.V.; Molochnikova, N.P.; Zakharchenro, E.A. Novel Class of Functionalized Ionic Liquids with Grafted CMPO-Moieties for Actinides and Rare-Earth Elements Recovery. Dalt. Trans. 2010, 39, 4170–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.K.; Kandwal, P.; Iqbal, M.; Huskens, J.; Murali, M.S.; Verboom, W. A Novel CMPO-Functionalized Task Specific Ionic Liquid: Synthesis, Extraction and Spectroscopic Investigations of Actinide and Lanthanide Complexes. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 4343–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turanov, A.N.; Karandashev, V.K.; Artyushin, O.I.; Sharova, E. V Extraction of U(VI), Th(IV), and Lanthanides(III) from Nitric Acid Solutions with CMPO-Functionalized Ionic Liquid in Molecular Diluents. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2015, 33, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Feng, D.; Kang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H. Enhancing Extraction Ability by Rational Design of Phosphoryl Functionalized Ionic Liquids and Mechanistic Investigation on Neodymium (III) Extraction. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Kadam, R.M.; Manna, D.; Ghanty, T.K.; Iqbal, M.; Huskens, J.; Verboom, W. Diglycolamide-Functionalized Task Specific Ionic Liquids for Nuclear Waste Remediation: Extraction, Luminescence, Theoretical and EPR Investigations. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46613–46623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, W.; Youwen, Z.; Fuyou, F.; Huimin, L.; Peizhuo, H.; Yinglin, S. Synthesis of Task-Specific Ionic Liquids with Grafted Diglycolamide Moiety. Complexation and Stripping of Lanthanides. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 299, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Solvometallurgy: An Emerging Branch of Extractive Metallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khazalpour, S.; Yarie, M.; Kianpour, E.; Amani, A.; Asadabadi, S.; Seyf, J.Y.; Rezaeivala, M.; Azizian, S.; Zolfigol, M.A. Applications of Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids in Chemical Processes. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 1775–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Passos, H.; Billard, I.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Recovery of Metals from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Using Unconventional Solvents Based on Ionic Liquids. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 859–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Wang, J. A Green Separation Strategy for Neodymium (III) from Cobalt (II) and Nickel (II) Using an Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase System. Talanta 2018, 182, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.J.R.; Quintao, J.C.; Ferreira, G.M.D.; Da Silva, L.H.M.; Hespanhol, M.C. Lanthanum and Cerium Separation Using an Aqueous Two-Phase System with Ionic Liquid. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4239–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Parmentier, D.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Tuinier, R.; Kroon, M.C. Removal of Alkali and Transition Metal Ions from Water with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11987–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, N.; Liu, L.; Yin, C.; Zhu, G.; Huang, Q.; Dong, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Environmentally Benign Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Palladium(II) Extraction from Hydrochloric Acid Solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Lv, C.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Recovery of Gold from Hydrochloric Medium by Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Quaternary Ammonium Salts. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 188, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, K.; Fan, J. Highly Efficient Extraction/Separation of Cr (VI) by a New Family of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; An, Y.; Row, K.H. Emerging Applications of (Micro) Extraction Phase from Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Opportunities and Trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Su, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhi, H.; Sun, X. A Cleaner Strategy for Comprehensive Recovery of Waste SmCo Magnets Based on Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.; McCourt, É.N.; Connolly, F.; Nockemann, P.; Swadźba-Kwaśny, M.; Holbrey, J.D. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Incorporating Trioctylphosphine Oxide: Advanced Liquid Extractants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 17323–17332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, N.; Conceição, J.H.F.; Martins, M.A.R.; Neves, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, G.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Non-Ionic Hydrophobic Eutectics—Versatile Solvents for Tailored Metal Separation and Valorisation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Romero, J. Solvent Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements with Ionic Liquids: Toward a Selective and Sustainable Extraction of These Valuable Elements. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. Electrochemical Oxidation as Alternative for Dissolution of Metal Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8360–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Endres, F.; Macfarlane, D. (Eds.) Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783527682706. [Google Scholar]
- Bourbos, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Karantonis, A.; Paspaliaris, I.; Panias, D. Electrodeposition of rare earth metals from ionic liquids. In Rare Earths Industry; De Lima, I., Filho, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Legeai, S.; Diliberto, S.; Stein, N.; Boulanger, C.; Estager, J.; Papaiconomou, N.; Draye, M. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid for Lanthanum Electrodeposition. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurachi, A.; Matsumiya, M.; Tsunashima, K.; Kodama, S. Electrochemical Behavior and Electrodeposition of Dysprosium in Ionic Liquids Based on Phosphonium Cations. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.-H.; Hussey, C.L. An Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Study of Nd(III) and Pr(III) Coordination in the 1-Butyl-1-Methylpyrrolidinium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Ionic Liquid Containing Chloride Ion. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 5750–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengio, D.; Dumas, T.; Arpigny, S.; Husar, R.; Mendes, E.; Solari, P.L.; Schlegel, M.L.; Schlegel, D.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Moisy, P. Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Study of Eu(III) and Eu(II) Coordination in the 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Ionic Liquid. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14385–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, P. Non-Haloaluminate Ionic Liquids for Low-Temperature Electrodeposition of Rare-Earth Metals—A Review. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, H.; Hallett, J.P.; Villar-Garcia, I.J.; Hunt, P.A.; Welton, T. Mixtures of Ionic Liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7780–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutowski, K.E. Industrial Uses and Applications of Ionic Liquids. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nockemann, P.; Brolly, D.; Bradley, E.; McCourt, E. Enhanced Separation of Rare Earth Metals 2019. International Patent WO2019239150A1, 19 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nockemann, P.; Brolly, D.; Bradley, E.; McCourt, E. Countercurrent Rare Earth Separation Process 2019. International Patent WO2019239151A1, 19 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nomngongo, P.N.; Biata, N.R.; Sihlahla, M.; Mpupa, A.; Mketo, N. Recent Advances in the Application of Greener Solvents for Extraction, Recovery and Dissolution of Precious Metals and Rare Earth Elements from Different Matrices. In Nanotechnology-Based Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids; Inamuddin, M., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 299–309. ISBN 978-3-030-44995-7. [Google Scholar]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic Liquids Toxicity-Benefits and Threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental Fate and Toxicity of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, R.F.; Afonso, C.A. Impact of Ionic Liquids in Environment and Humans: An Overview. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viboud, S.; Papaiconomou, N.; Cortesi, A.; Chatel, G.; Draye, M.; Fontvieille, D. Correlating the Structure and Composition of Ionic Liquids with Their Toxicity on Vibrio Fischeri: A Systematic Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; de la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents vs Ionic Liquids: Similarities and Differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Jesus, F.; Pereira, J.L.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Unraveling the Ecotoxicity of Deep Eutectic Solvents Using the Mixture Toxicity Theory. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrachart, G.; Couturier, J.; Dourdain, S.; Levard, C.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents. Processes 2021, 9, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071202
Arrachart G, Couturier J, Dourdain S, Levard C, Pellet-Rostaing S. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents. Processes. 2021; 9(7):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071202
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrachart, Guilhem, Julien Couturier, Sandrine Dourdain, Clément Levard, and Stéphane Pellet-Rostaing. 2021. "Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents" Processes 9, no. 7: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071202
APA StyleArrachart, G., Couturier, J., Dourdain, S., Levard, C., & Pellet-Rostaing, S. (2021). Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents. Processes, 9(7), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071202







