Evaluation of Sand Filtration and Activated Carbon Adsorption for the Post-Treatment of a Secondary Biologically-Treated Fungicide-Containing Wastewater from Fruit-Packing Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
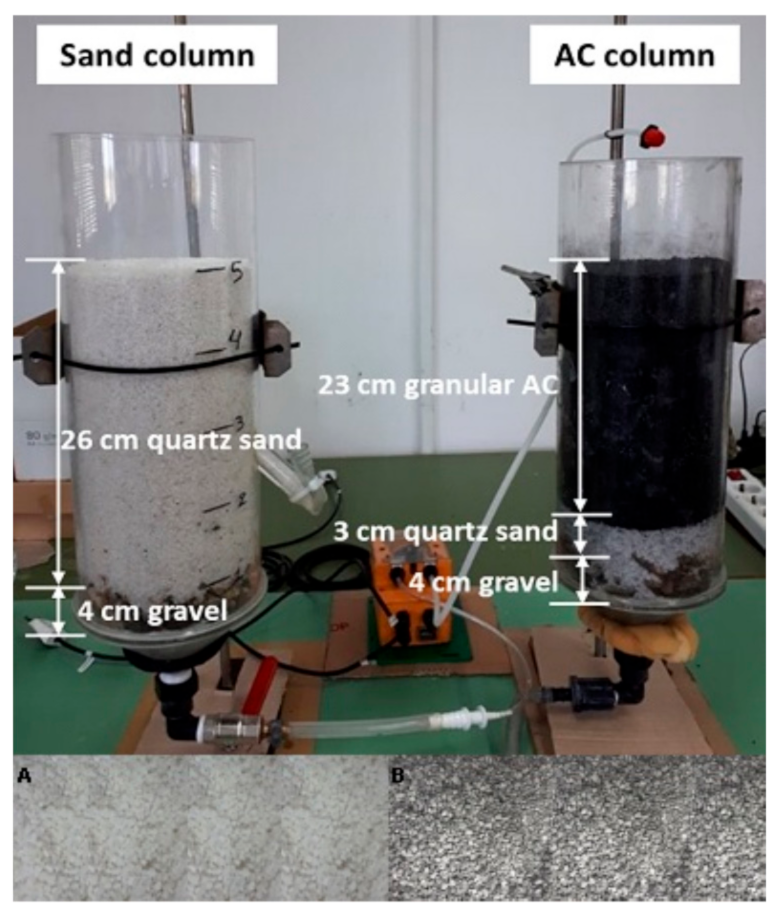
2.1. Description of the Sand Filter-Activated Carbon Column System
2.2. Sorbent Materials and Operating Conditions
2.3. Analytical Methods and Phytotoxicity Test
2.4. Wastewater Characteristics
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Tertiary Treatment System’s Ability to Remove Macronutrients from the Biologically Treated Fungicide-Containing Effluent
3.2. Evaluation of the Tertiary Treatment System’s Ability to Remove Imazalil and Fludioxonil from the Biologically Treated Fungicide-Containing Effluent
3.3. Detoxification of the Biologically Treated Fungicide-Containing Effluent in the Sand Filtration-Activated Carbon Adsorption System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langenbach, K.; Kuschk, P.; Horn, H.; Kästner, M. Slow sand filtration of secondary clarifier effluent for wastewater reuse. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5896–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Detoxification of pesticide waste via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgarejo, J.; Prats, D.; Molina, A.; Trapote, A. A case study of urban wastewater reclamation in Spain: Comparison of water quality produced by using alternative processes and related costs. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2016, 6, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matamoros, V.; Salvadó, V. Evaluation of a coagulation/flocculation-lamellar clarifier and filtration-UV-chlorination reactor for removing emerging contaminants at full-scale wastewater treatment plants in Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzate, S.; Pfister, S.; Oberschelp, C.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. Environmental impacts of an advanced oxidation process as tertiary treatment in a wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamoda, M.F.; Al-Ghusain, I.; AL-Mutairi, N.Z. Sand filtration of wastewater for tertiary treatment and water reuse. Desalination 2004, 164, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader Yettefti, I.; Aboussabiq, F.; Etahiri, S.; Mountadar, M.; Assobhei, O. Performance evaluation of sand filter for tertiary treatment of secondary effluent of wastewater: Effect of hydraulic loading. Phys. Chem. News 2013, 68, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, R.; Husain, T.; Al-Zahrani, A.M.; Sheikh, A.K.; Farooq, S. Secondary effluent treatment by slow sand filters: Performance and risk analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 143, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.; Loganathan, P.; Listowski, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Khourshed, C.; Vigneswaran, S. Simultaneous removal of natural organic matter and micro-organic pollutants from reverse osmosis concentrate using granular activated carbon. Water Res. 2019, 155, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zusman, O.B.; Kummel, M.L.; De la Rosa, J.M.; Mishael, Y.G. Dissolved organic matter adsorption from surface waters by granular composites versus granular activated carbon columns: An applicable approach. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillossou, R.; Le Roux, J.; Mailler, R.; Vulliet, E.; Morlay, C.; Nauleau, F.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V. Organic micropollutants in a large wastewater treatment plant: What are the benefits of an advanced treatment by activated carbon adsorption in comparison to conventional treatment? Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, M.; Zwickenpflug, B.; Hollender, J.; Ternes, T.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Removal of micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plants by powder-activated carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benstoem, F.; Nahrstedt, A.; Boehler, M.; Knopp, G.; Montag, D.; Siegrist, H.; Pinnekamp, J. Performance of granular activated carbon to remove micropollutants from municipal wastewater—A meta-analysis of pilot- and large-scale studies. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ma, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, K.; Wang, X.C.; Lin, Y. Removal of trace organic pollutants (pharmaceuticals and pesticides) and reduction of biological effects from secondary effluent by typical granular activated carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kårelid, V.; Larsson, G.; Björlenius, B. Pilot-scale removal of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater: Comparison of granular and powdered activated carbon treatment at three wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi-Shahraki, R.; Benally, C.; El-Din, M.G.; Park, J. High efficiency removal of heavy metals using tire-derived activated carbon vs commercial activated carbon: Insights into the adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Buleté, A.; Vulliet, E.; Deshayes, S.; Zedek, S.; Mirande-Bret, C.; Eudes, V.; Bressy, A.; et al. Removal of a wide range of emerging pollutants from wastewater treatment plant discharges by micro-grain activated carbon in fluidized bed as tertiary treatment at large pilot scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Yin, X. Adsorption of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surfactant solutions by activated carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Bal Krishna, K.C.; Sarukkalige, R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal by sorption: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, B.N.; Seo, P.W.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorption of diclofenac sodium from water using oxidized activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.R.D.C.; Féris, L.A. Use of functionalized adsorbents for tetracycline removal in wastewater: Adsorption mechanism and comparison with activated carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2020, 55, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Exposito Saintemarie, A.; Rocchi, S.; Fourmentin, M.; Jeanvoine, A.; Millon, L.; Morin-Crini, N. Simultaneous removal of five triazole fungicides from synthetic solutions on activated carbons and cyclodextrin-based adsorbents. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Rocchi, S.; Jeanvoine, A.; Garcia, C.; Millon, L.; Crini, G. Analysis of triazole fungicides in aqueous solutions and their removal on modified activated carbons. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 43, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.; Bhadra, B.N.; Seo, P.W.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorption of benzotriazole and benzimidazole from water over a Co-based metal azolate framework MAF-5(Co). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosek, K.; Luczkiewicz, A.; Fudala-Książek, S.; Jankowska, K.; Szopińska, M.; Svahn, O.; Tränckner, J.; Kaiser, A.; Langas, V.; Björklund, E. Implementation of advanced micropollutants removal technologies in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs)—Examples and challenges based on selected EU countries. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.; Ligorio, A.; Nigro, F.; Ippolito, A. Activity of salts incorporated in wax in controlling postharvest diseases of citrus fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 65, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aquino, S.; Palma, A.; Angioni, A.; Schirra, M. Residue levels and efficacy of fludioxonil and thiabendazole in controlling postharvest green mold decay in citrus fruit when applied in combination with sodium bicarbonate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.E.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Pulido-Melián, E.; Araña, J.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.; Díaz, Ó.G.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M. TiO2-based (Fe3O4, SiO2, reduced graphene oxide) magnetically recoverable photocatalysts for imazalil degradation in a synthetic wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27724–27736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libutti, A.; Gatta, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Vergine, P.; Pollice, A.; Beneduce, L.; Disciglio, G.; Tarantino, E. Agro-industrial wastewater reuse for irrigation of a vegetable crop succession under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 196, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 May 2020 on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse (Text with EEA Relevance).Official Journal of the European Union L 177/32. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2020/741/oj (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mavriou, Z.; Alexandropoulou, I.; Melidis, P.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Ntougias, S. Biotreatment and bacterial succession in an upflow immobilized cell bioreactor fed with fludioxonil wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 3774–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso Varela, A.; Vázquez Contreras, F.P.; de los Santos Villalobos, S.; Alvarez Valencia, L.H.; Ulloa Mercado, R.G.; Serrano Palacios, D. Removal of endosulfan in a sequencing batch reactor: Addition of granular activated carbon as improvement strategy. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-pajooh, E.; Turcios, A.E.; Cuff, G.; Weichgrebe, D.; Rosenwinkel, K.-H.; Vedenyapina, M.D.; Sharifullina, L.R. Removal of inert COD and trace metals from stabilized landfill leachate by granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, R.W.; Dussert, B.W.; Kovacic, S.L. Improved granular activated carbon for the stabilization of wastewater pH. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Fuel Chem. 1996, 41, 456–458. [Google Scholar]
- García-Jaramillo, M.; Cox, L.; Knicker, H.E.; Cornejo, J.; Spokas, K.A.; Hermosín, M. Characterization and selection of biochar for an efficient retention of tricyclazole in a flooded alluvial paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, F.M.; Undabeytia, T.; Jaworski, M.; Morillo, E.; Sánchez, R.M.T. Organo-montmorillonites as adsorbent materials for thiophanate-methyl removal: Adsorption-desorption studies and technological applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Lopes, T.S.; Heßler, R.; Bohner, C.; Junior, G.B.A.; de Sena, R.F. Pesticides removal from industrial wastewater by a membrane bioreactor and post-treatment with either activated carbon, reverse osmosis or ozonation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lyu, T.; Vargas, C.A.R.; Arias, C.A.; Carvalho, P.N.; Brix, H. New insights into the effects of support matrix on the removal of organic micro-pollutants and the microbial community in constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martín-González, M.A.; González-Díaz, O.; Susial, P.; Araña, J.; Herrera-Melián, J.A.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M.; Pérez-Peña, J. Reuse of Phoenix canariensis palm frond mulch as biosorbent and as precursor of activated carbons for the adsorption of imazalil in aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Cabaroglu, T.; Yilmaz, H. The influence of fining agents on the removal of some pesticides from white wine of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Emir. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3990–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.J.; Oliva, J.; Barba, A.; Cámara, M.A. Effects of clarification and filtration processes on the removal of fungicide residues in red wines (Var. Monastrell). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6156–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, E.; Pittmann, T.; Wasielewski, S.; Kugele, A.; Minke, R. Detoxification of pesticide-containing wastewater with FeIII, activated carbon and Fenton reagent and its control using three standardized bacterial inhibition tests. Water 2017, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grgić, M.; Maletić, S.; Beljin, J.; Isakovski, M.K.; Rončević, S.; Tubić, A.; Agbaba, J. Lindane and hexachlorobenzene sequestration and detoxification in contaminated sediment amended with carbon-rich sorbents. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, D.E.; Pulido Melián, E.; Fernández Rodríguez, C.; Ortega Méndez, J.A.; Pérez-Báez, S.O.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M. Degradation and detoxification of banana postharvest treatment water using advanced oxidation techniques. Green Sustain. Chem. 2011, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Parameter | Quartz Sand | Parameter | Granular AC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain shape | Sub-angular | Bulk density | 500 ± 25 kg/m3 |
| Aqueous solution pH | 5–8 | Effective size | 1.2–2.2 mm |
| Relative density | 2–3 g/cm3 | Ash content | <5% |
| Melting point | >1610 °C | Iodine number | 1050 mg/g min |
| Effective size | 2–3.5 mm | Surface area | 1050 m2/g |
| Color | White | Dechlorination half-value length | <5 cm |
| Content | 96% SiO2 | Hardness | 98% |
| Respirable quartz | <1% | Activation method | Steam |
| Solubility in water | Negligible | Humidity | 5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azis, K.; Mavriou, Z.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Ntougias, S.; Melidis, P. Evaluation of Sand Filtration and Activated Carbon Adsorption for the Post-Treatment of a Secondary Biologically-Treated Fungicide-Containing Wastewater from Fruit-Packing Industries. Processes 2021, 9, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071223
Azis K, Mavriou Z, Karpouzas DG, Ntougias S, Melidis P. Evaluation of Sand Filtration and Activated Carbon Adsorption for the Post-Treatment of a Secondary Biologically-Treated Fungicide-Containing Wastewater from Fruit-Packing Industries. Processes. 2021; 9(7):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071223
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzis, Konstantinos, Zografina Mavriou, Dimitrios G. Karpouzas, Spyridon Ntougias, and Paraschos Melidis. 2021. "Evaluation of Sand Filtration and Activated Carbon Adsorption for the Post-Treatment of a Secondary Biologically-Treated Fungicide-Containing Wastewater from Fruit-Packing Industries" Processes 9, no. 7: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071223
APA StyleAzis, K., Mavriou, Z., Karpouzas, D. G., Ntougias, S., & Melidis, P. (2021). Evaluation of Sand Filtration and Activated Carbon Adsorption for the Post-Treatment of a Secondary Biologically-Treated Fungicide-Containing Wastewater from Fruit-Packing Industries. Processes, 9(7), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071223








