Abstract
On the basis of binary perfectly inelastic collision theory, the time evolutions of kinetic energy and surface area for a particle agglomerate system, due to Brownian motion, are investigated by using the Taylor series expansion technology. The asymptotic behaviors over a long time period show a significantly negative power function of time. The thermodynamic constraints of this system are then obtained according to the principle of maximum entropy, which establishes a relationship of inequality between the first three particle moments and some physical parameters (i.e., surface tension and temperature). In the thermodynamic equilibrium state, this function provides a new approach for estimating the effect of molecular structure on surface tension of liquid polymers.
1. Introduction
Particle agglomeration is a common phenomenon in both nature and industrial applications, such as particle synthesis and soot formation processes. It plays a significant role in these aerosol processes by profoundly affecting the size distribution of a particle system [1], which strongly determines the physical properties of aerosol particles, such as light scattering, toxicity, deposition rate and diffusion. Nowadays with the escalation of fine particle pollution, the agglomeration processes are also widely used in the field of contamination control to improve removal efficiency, especially for the particles whose diameters are less than 2.5 μm [2,3]. The main principle is that through physical or chemical action, particles can coagulate with each other to form particles with larger particle size and then be removed efficiently. An appropriate approach for investigating the time evolution of particle size distribution (PSD) due to agglomeration is typically called the population balance equation (PBE) or the classic Smoluchowski equation (SE), which can be expressed as the following form [4]:
where n(υ, t) is the number density function of the particles with volume from υ to υ + dυ at time t; β(υ, υ1) is the collision frequency function between particles with volume υ and υ1.
Due to the strong non-linear integro-differential structure, the PBE is difficult to solve analytically. By trading off between accuracy and computational cost, three main numerical methods are proposed and developed, including the method of moments (MOM) [5,6], sectional method (SM) [7] and Monte Carlo method (MCM) [8]. It can’t be ignored that the analytical solutions show great merit in computational cost and direct physical insights into agglomeration mechanisms. Thus, some researchers focus on the asymptotic or analytical solutions of the moments of PSD by converting the original PBE to a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Due to the complexity of its kernel function and the universality of Brownian motion, the study on the solution of the PBE for Brownian agglomeration is considered to be important but one of the most difficulties. Mainly using the log-normal method of moments (LG-MOM) [6] or the Taylor series expansion method of moments (TEMOM) [9], the asymptotic behavior of moments, due to Brownian coagulation (for spherical particles) and agglomeration (for agglomerates) over the entire particle size regimes [10,11,12,13], the analytical solution for Brownian coagulation in the free-molecule and the continuum regime [14], and so on, are obtained. These articles reveal that the geometric standard deviation will reach a constant for a long period of time, namely, the self-preserving size distribution theory [15].
Particle coalescence upon collisions subject to conservation of mass and momentum is called ballistic aggregation, but it is well known that the kinetic energy of this system decreases with time [16]. However, the loss of particle kinetic energy after collisions is rarely taken into account in the framework of PBE. Nowadays, with an assumption of a perfectly inelastic collision process, the rate of change for kinetic energy is correlated with that of particle number density, and the relationship of inequality between particle moments and some physical parameters (i.e., surface tension and temperature) for Brownian coagulation have been firstly proposed by Xie and Yu based on the principle of maximum entropy [17,18]. In this paper, we will extend their efforts to Brownian agglomeration, and the asymptotic behaviors of kinetic energy, surface area and entropy over a long period of time are obtained.
2. Theory and Model
2.1. Brownian Agglomeration
Particle agglomeration due to thermal motion is called Brownian agglomeration. Unlike spherical particles, agglomerates are not rigid structures and can be described as fractal morphology statistically. They are clusters of primary particles, which are ideally considered to be spherical with point contacts and uniform size. Considering the case of monodisperse primary particles, which form power law agglomerates, the Brownian agglomeration kernels β are represented as [1]:
Here, the subscripts FM and CR stand for agglomeration in the free molecular and continuum regimes, respectively; the constants and B2 = 2kBT/3μ, with kB the Boltzmann’s constant; T is the temperature; μ is the gas viscosity; ρp is the particle density; ap0 is the radius of a primary particle; υ is the particle volume; Df is called the fractal dimension, which can be related to the arrangement of the primary particles within an agglomerate. It should be noted that Df < 2 is not applicable for Equation (2) in physics [1], thus the following discussions are limited to a range of 2 ≤ Df ≤ 3.
2.2. Taylor Series Expansion Method of Moments
With the definition of k-th order moment Mk,
Equation (1) can be converted into a system of original differential equations by multiplying both sides with νk and then integrating over all particle sizes:
The main objective of all MOMs is to achieve the closure of Equation (5). In the classic TEMOM, this is accomplished in two procedures [9,19]: (1) the collision kernel is directly approximated by a two-variable third-order Taylor series expansion, for example, the power function in Equation (2) can be expanded with respect to mean volume u = M1/M0; (2) and all the higher and fractional moments are approximated by the polynomial equation with respect to the first three moments:
Here the dimensionless moment MC = M0M2/M12 is the function of geometric standard deviation σ which can be noted as [6]. The moment equations based on TEMOM in the free molecule regime are obtained [11]:
where the coefficients a1, a2, a3, b1, b2, b3 are:
Now the most important moments for describing the particle dynamics, namely, the particle number density M0, total particle volume M1 and a polydispersity variable M2, can be obtained. Here, M1 remains constant due to the rigorous mass conservation requirement. The corresponding moment equations in the continuum regime are:
where the coefficients p1, p2, p3 are:
2.3. Principle of Maximum Entropy
As a characteristic function composed of internal energy U, total particle volume M1, and particle number M0, the rate of change for entropy S of a disperse system can be expressed as:
According to the thermodynamic analysis [18], the rate of change for S can be arranged and then correlated with that of M0, the particle kinetic energy ke, and the particle specific surface area s:
in which λth is the thermal wavelength and γ is the surface tension. Thus, the focal point is to determine dke/dt and ds/dt. With the assumption of simplified physical model according to the binary perfectly inelastic collision theory, the loss of particle kinetic energy after collision for two colliding particles and the whole system are [18]:
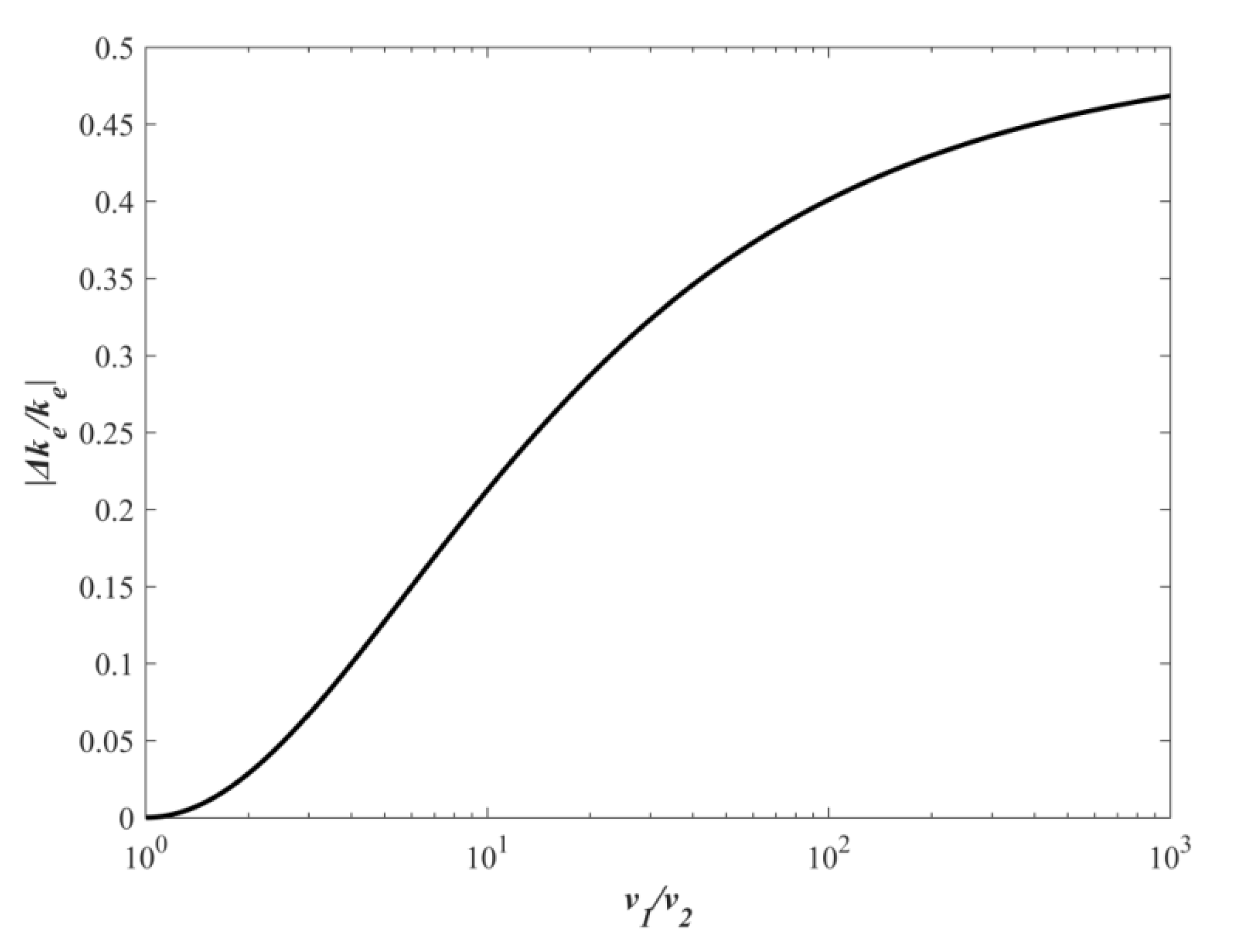
Assuming that υ1 is the larger particle, the relative loss of ke increases with a larger ratio of υ1 to υ2, which is illustrated in Figure 1. This shows that a wider range of PSD, namely, a larger MC, would lead to a more rapid reduction in ke. Substituting Equation (2) into the above equation and then using the Taylor series expansion technology, we can get the rate of change for kinetic energy in the free molecular regime:
in which x1, x2, x3 are:
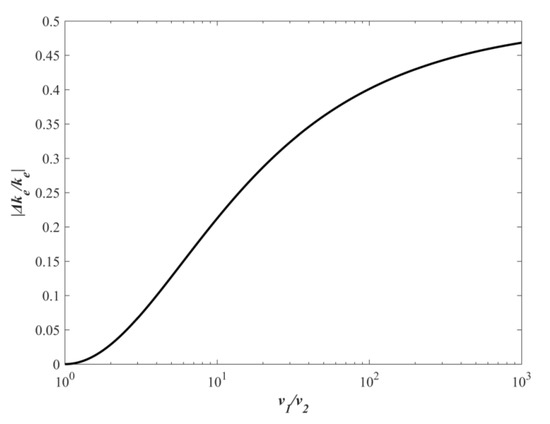
Figure 1.
The relationship between |Δke/ke| and υ1/υ2.
As the structure of agglomerate is complex, modeling of its surface area is even more difficult, given the scarcity of experimental data. It is also very difficult to numerically determine which part of primary particles are the boundary particles and which part of the surface of these boundary particles forms the agglomerate surface. For an ideal case that k primary particles agglomerate with point contacts, its surface area equals , where ap0 is the radius of primary particle [20]. Obviously, it is more suitable for chain-like structures with Df→1 but not compact aggregates with Df →3. In a statistical sense, the collision radius of agglomerates composed of k monomer is [1]:
where A is the dimensionless proportionality constant and can be assumed to be in unity to simplify calculations. In this paper, we will use this collision radius to calculate the surface area approximately:
in which the constant . Thus, for chain-like structures with Df = 2, s = equals to that of an agglomerate without necking and for compact aggregates with Df = 3, s = (36π)1/3υ2/3 equals to that of a spherical particle. Apparently, the agglomerates composed of the same number of primary particles with smaller Df would have larger specific surface area and collision radius. Now the total surface area of this system can be expressed as:
and the rate of change for s can be written as:
where the fractional moment M2/Df is approximated by using Equation (6):
and its derivative with time t can be achieved:
Combining the first and third equations in Equation (7) gives:
Then Equation (23) can be rearranged as:
Substituting the above equation into Equation (21), the rate of change for s in the free molecular regime has the following form:
Analogously, the rate of change for particle kinetic energy and surface area in the continuum regime can be calculated as:
where q1, q2, q3 are noted as:
Finally, the rate of change for S can be found:
in which C1, C2 are functions of the dimensionless moment MC and fractal dimension Df:
From the viewpoint of the second law of thermodynamics, the entropy of an isolated system will never decrease: dS/dt ≥ 0. Moreover, the total particle number M0 will decrease with time due to agglomeration: dM0/dt < 0. Thus, the thermodynamics constraints for Brownian agglomeration at a certain temperature and pressure can be obtained:
The equality would hold in the thermodynamic equilibrium state, and the critical time to reach this state can be determined. Moreover, the growth of the mean particle size M1/M0 will tend to a limit depending on the operating temperature and specific surface energy for thermal agglomeration technology.
3. Results
According to the self-preserving size distribution theory, the dimensionless particle moment MC will tend to a constant at long time periods, and the asymptotic solutions of particle moments based on the TEMOM model can be found [11]. Here, the results are listed in the Appendix A. In the free molecular regime, the asymptotic solution of kinetic energy can be solved by directly integrating Equation (15) with respect to t:
where C3 = ke(t1) − keTC2(t1)M0(t1) is the integral constant, t1 is the critical time in which the particle size distribution approaches self-preserving and the definition of g1 is shown as Equation (A7). In our previous work [21], a criterion to calculate this critical time has been given based on the asymptotic solution of M0 in the continuum regime, which can also be available in the free molecular regime. Now the effect of primary particle size ap0 on ke can be obtained, which is as the same as that on M0:
Thus, its relative dissipative rate becomes:
The asymptotic solution of surface area and the effect of primary particle size can be expressed as the following forms after substitution of Equations (A6) and (22) into Equation (19):
and its relative dissipative rate becomes:
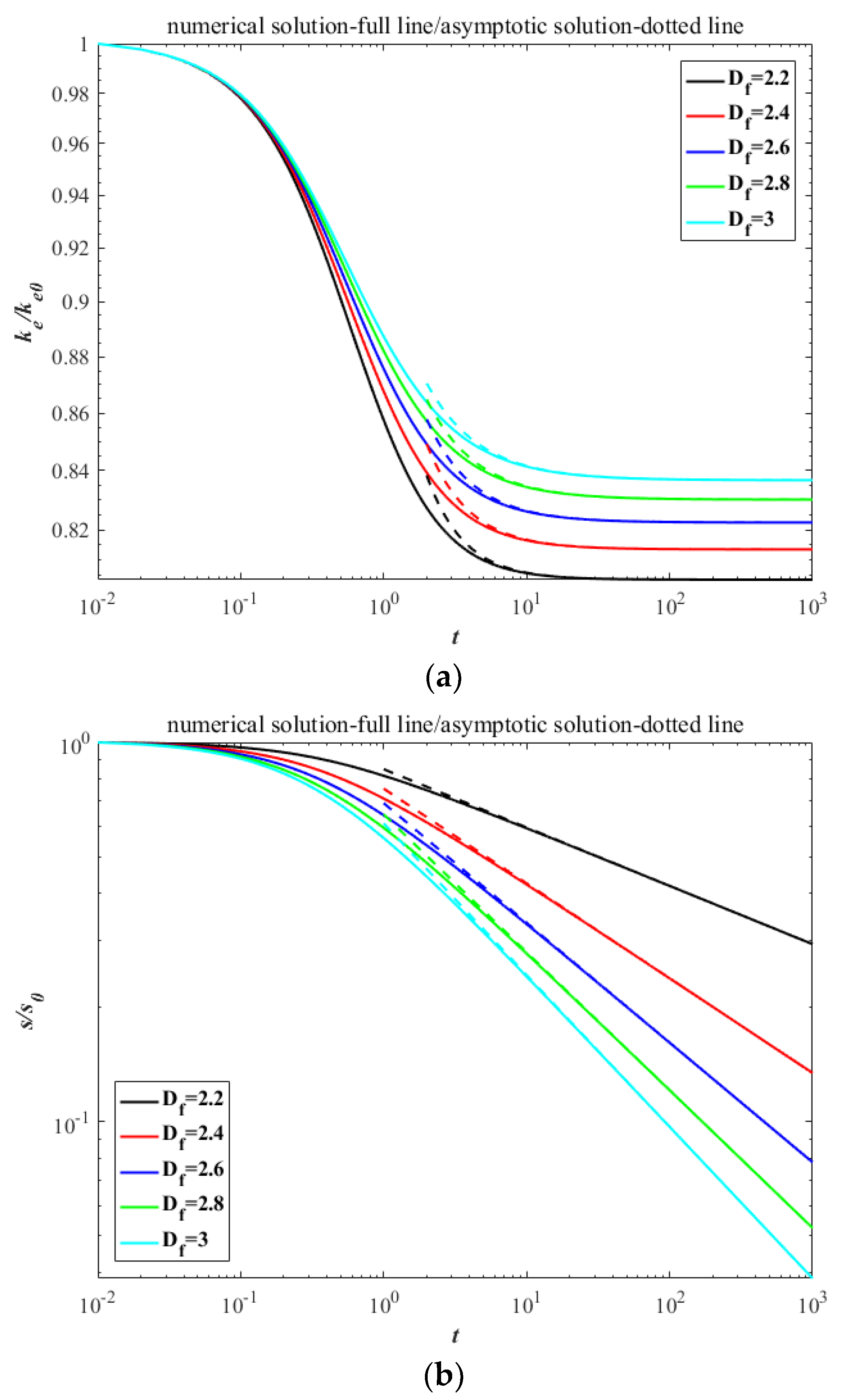
For simplification and without loss of generality, the calculation can be non-dimensionalized through the following relations: M0 * = M0 /M00, M1 * = M1/M10, M2 * = MC0M2/M20, , ke * = ke/(M00kbT), . Then the Equation (7) coupling with Equations (15) and (19) can be solved numerically by means of fourth-order Runge–Kutta method with the initial dimensionless conditions set as M00 = 1, M10 = 1, M20 = 4/3, ke0 = 1/2 (the star symbol ‘*’ is omitted thereafter). The numerical and asymptotic solutions of kinetic energy and surface area are shown in Figure 2. According to the principle of equipartition of energy, the agglomerates share the molecular thermal motion of the fluid and have the same initial kinetic energy, thus the dissipative rate of ke strongly depends on the collision rate. The evolutions of kinetic energy with time show the larger descent at lower fractal dimension because of the larger collision radius, which result in a more rapid agglomerated rate [22]. Oppositely, the contacting surface between primary particles in an agglomerate with smaller fractal dimension is less than that in an agglomerate with larger fractal dimension, thus the decay of surface area shows the reverse trend in the dual role of the higher specific surface area and more rapid agglomerated rate.
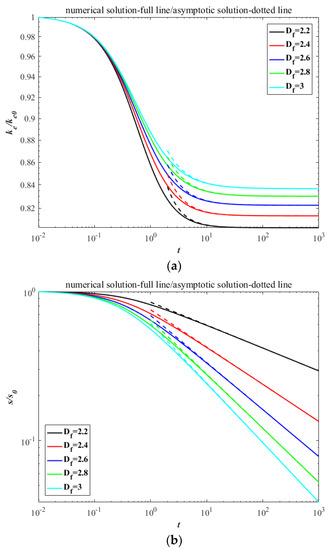
Figure 2.
The decay with time between numerical solutions and asymptotic solutions in the free molecular regime: (a) kinetic energy; (b) surface area.
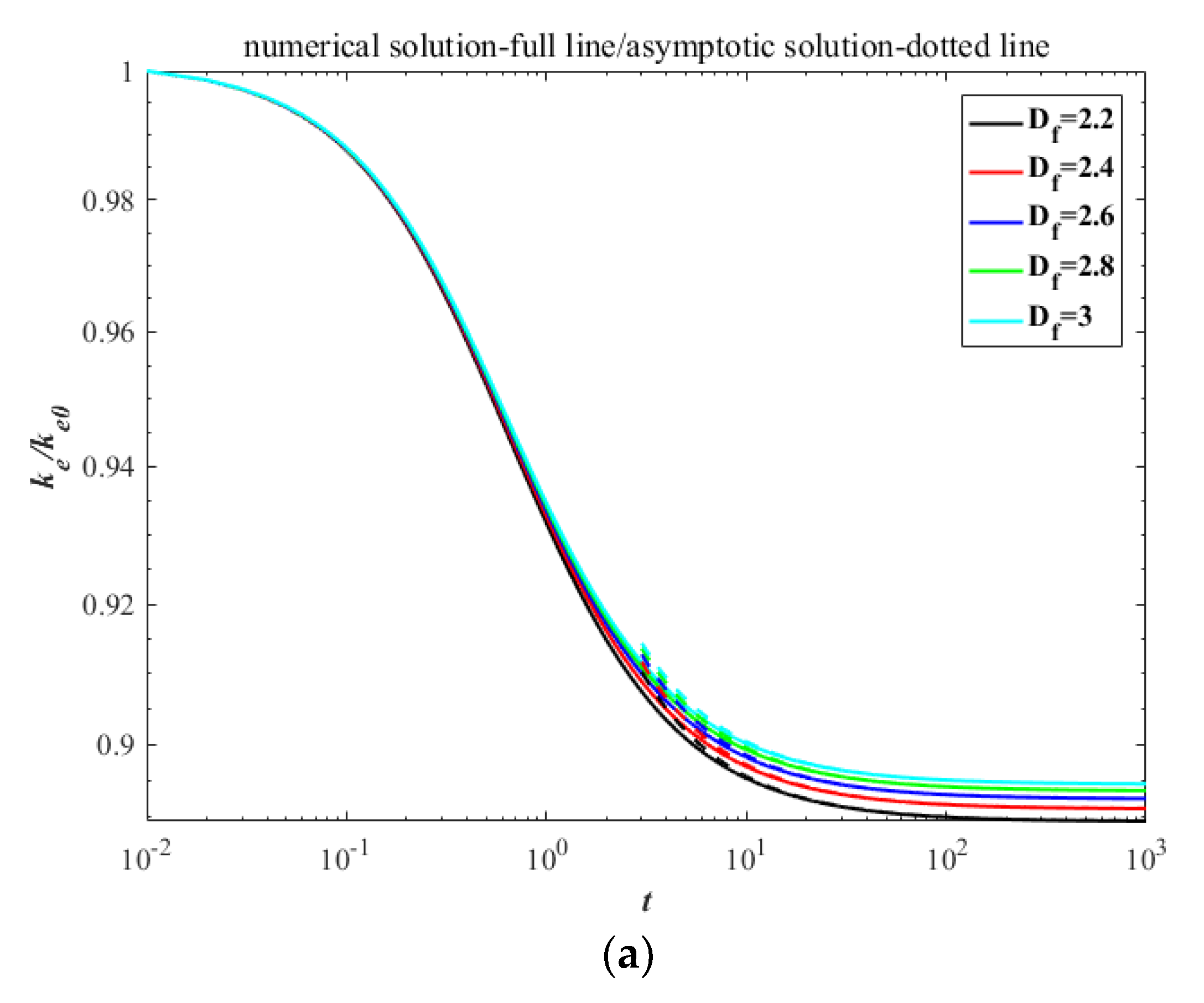
Analogously, the asymptotic solutions of kinetic energy and surface area, as well as their relative dissipative rates, in the continuum regime can be expressed as:
where g2 is a function of Df showed as Equation (A12). The results are showed in Figure 3. These allow us to simplify the rate of change for S as the asymptotic form in both the free molecular and continuum regime:
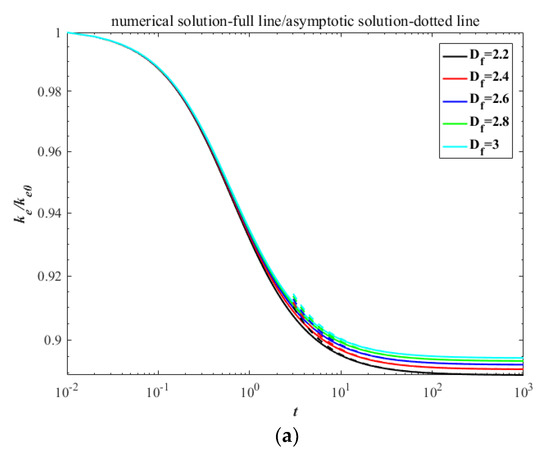
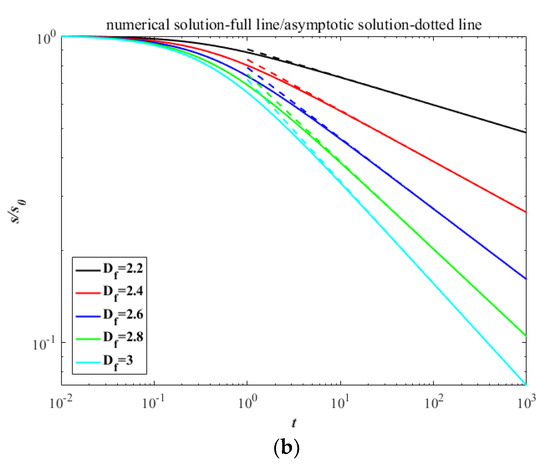
Figure 3.
The decay with time between numerical solutions and asymptotic solutions in the continuum regime: (a) kinetic energy; (b) surface area.
And the corresponding thermodynamics constraints are:
4. Discussion
The above equation establishes an inequality relationship between moments and some physical parameters, such as temperature and specific surface energy, and the equality holds if and only if the system reaches the thermodynamic equilibrium. Obviously, increasing temperature leads to decreasing particle number density and greater mean volume, which can be useful for dust collection efficiency. It also shows the effect of molecular structure on surface tension. By substituting the expression of surface area into this equation, we can get the following formula in the thermal equilibrium state:
For liquid pure substance, M0λth3 usually takes the value as Vm in the free molecular regime and M1/M0 = Vm /NA, where Vm is the molar volume and NA is the Avogadro constant. A modification coefficient γ∞, which is equal to the value of surface tension at infinite molar volume, should be introduced because the surface tension decreases almost linearly with the increase of temperature. Then a correction function of molar volume can be constructed:
where k1 is a function of the temperature and fractal dimension:
The surface tension increases as molar volume increases and tends toward the constant γ∞ at infinite molar volume, and it decreases monotonously with increasing temperature and tends to zero at the critical temperature. Unfortunately, it should be noted that some important factors, i.e., the effect of end groups, cannot be considered. It also can be written as the molecular weight-surface tension relationship with Vm = M/ρ,
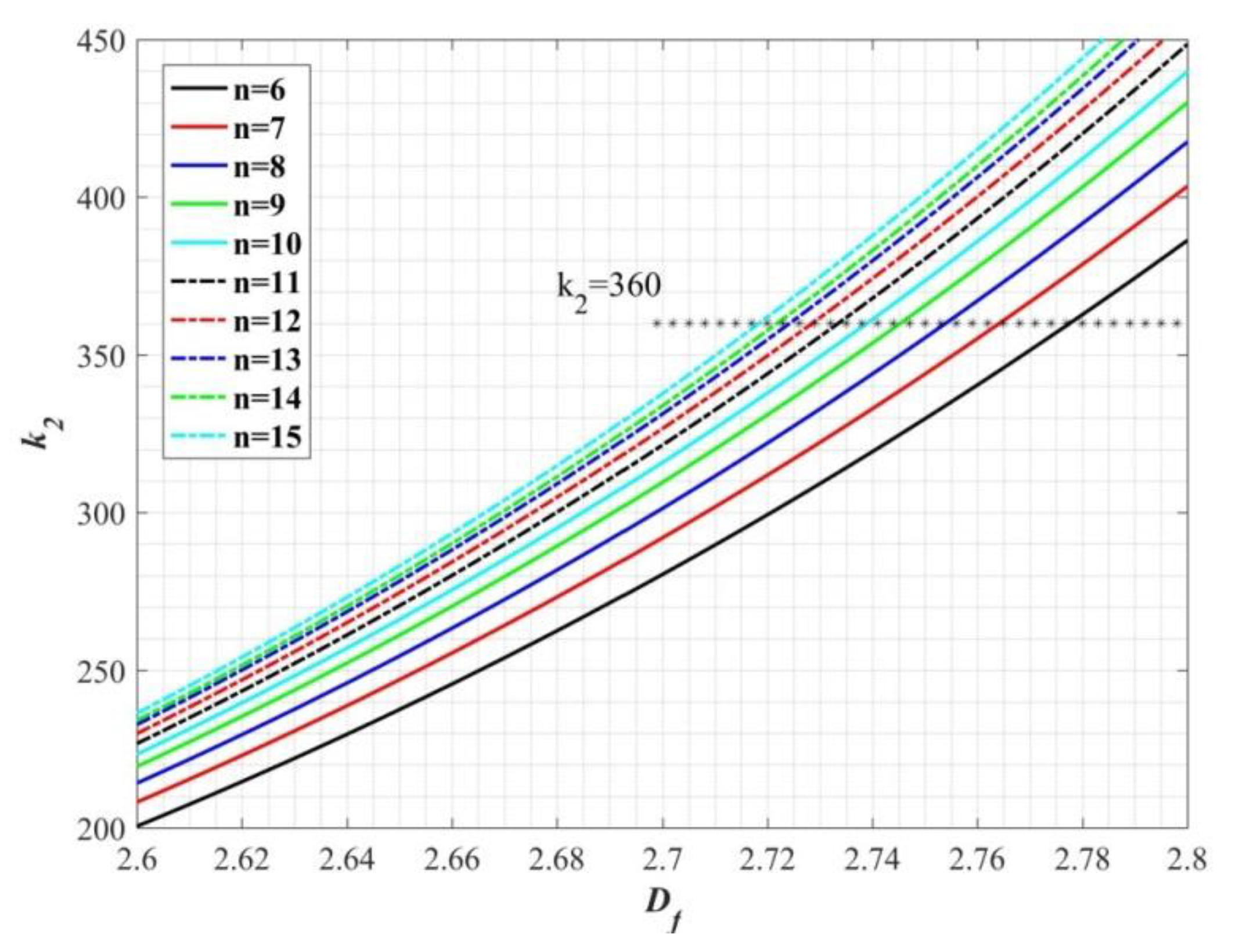
where M is the molecular weight and ρ is the density. Some research shows that the correlation with molecular weight is better than that with molar volume for alkanes and perfluoro alkanes, but the discrepancy can be ignored for the siloxanes [23]. The effect of fractal dimension on the slope k2 is illustrated in Figure 4 for n-alkanes at 0 °C, where ap0 = 0.2 nm is equal to the radius of methane and n is the number of carbons. Compared to bulks, the surface tension of molecules with long-chain structure generally increases due to the large contact areas and intermolecular forces, which leads to a small slope k2. In the range of 2.7 to 2.8, the result is mostly close to the value k2 = 360 of least-squares fitting based on experimental data [24].
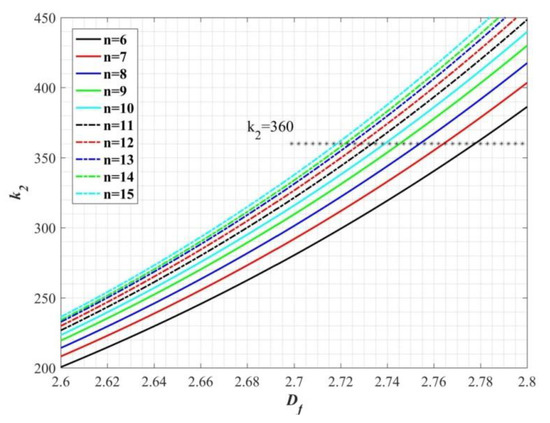
Figure 4.
The effect of fractal dimension on the slope k2 for n-alkanes.
5. Conclusions
On the basis of the theory of maximum entropy and binary perfectly inelastic collision, the thermodynamic constraints of Brownian coagulation for spherical particles are extended to agglomerates, and a relationship of inequality between particle moments and some physical parameters is established using the TEMOM. Meanwhile, the evolutions of kinetic energy and surface area with time are presented, as well as their asymptotic behaviors. While some of our present simplifying assumptions will have to be relaxed, even our present results are of potential interest for a number of applications, for example, the estimation of surface tension of liquid polymers and the enhancement of dust collection efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.H. and M.X.; methodology, Q.H. and M.X.; validation, M.X.; investigation, Q.H. and M.X.; resources, Q.H. and M.X.; data curation, Q.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.H.; writing—review and editing, Q.H.; supervision, M.X.; funding acquisition, Q.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Number 11902075.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. The Asymptotic Solutions of TEMOM Model for Brownian Agglomeration
The self-preserving size distribution theory implies that the dimensionless moment MC approaches a constant as time advances, thus we have:
Substituting the first and the third equations of Equation (7) into Equation (A1) leads to a third-order algebraic equation of MC in the free molecular regime:
In which c1, c2, c3 and c4 are functions of Df:
and for a given value of Df, the solution of MC, which is also an invariant constant, can be solved as [11]:
where d1, d2 and d3 are:
Then the asymptotic solution of M0 can be obtained:
where g1 is a function of Df:
And its relative agglomerate growth rate is:
Analogously, the asymptotic solution of MC in the continuum regime is:
And the asymptotic solution of M0 and its relative growth rate are:
where g2 is a function of Df:
References
- Friedlander, S.K. Smoke, Dust and Haze: Fundamentals of Aerosol Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Yi, Y.; Liang, C.; Yuan, Z.L.; Szczepan, R.; Yang, L.J. Experimental study on particles agglomeration by chemical and turbulent agglomeration before electrostatic precipitators. Powder Technol. 2018, 335, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.P.; Chen, L.Q.; Lin, Q. Removal of fine particles in WFGD system using the simultaneous acoustic agglomeration and supersaturated vapor condensation. Powder Technol. 2017, 315, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H. Zur allgemeinen theorie ser raschen koagulation. Kolloidchem. Beih. 1928, 27, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, R.; Bück, A. Approximate moment methods for population balance equations in particulate and bioengineering processes. Processes 2020, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratsinis, S.E. Simultaneous nucleation, condensation and coagulation in aerosol reactors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 124, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbard, F.; Tambour, Y.; Seinfeld, J.H. Sectional representations for simulating aerosol dynamics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 76, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Rosner, D.E. Monte Carlo simulation of particle aggregation and simultaneous restructuring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.Z.; Lin, J.Z.; Chan, T. A new moment method for solving the coagulation equation for particles in Brownian motion. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.L. Asymptotic behavior of TEMOM model for particle population balance equation over the entire particle size regimes. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.L. Asymptotic solution of moment approximation of the particle population balance equation for Brownian agglomeration. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Lin, J.Z.; Yu, M.Z. Asymptotic behavior of the Taylor-expansion method of moments for solving a coagulation equation for Brownian particles. Particuology 2014, 14, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.L.; Wang, L.P. Asymptotic solution of population balance equation based on TEMOM model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 94, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.L.; He, Q. Analytical solution of TEMOM model for particle population balance equation due to Brownian coagulation. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 66, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander, S.; Wang, C. The self-preserving particle size distribution for coagulation by Brownian motion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1966, 22, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trizac, E.; Krapivsky, P.L. Correlations in Ballistic Processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 218–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, M.L. On the growth rate of particle surface area for Brownian coagulation. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 113, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.L.; Yu, M.Z. Thermodynamic analysis of Brownian coagulation based on moment method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.Z.; Lin, J.Z. Taylor series expansion scheme applied for solving population balance equation. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 561–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.N.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Fissan, H.; Asbach, C.; Pui, D.Y.H. Development of a geometric surface area monitor (GSAM) for aerosol nanoparticles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 114, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Shchekin, A.K.; Xie, M.L. New analytical TEMOM solutions for a class of collision kernels in the theory of Brownian coagulation. Phys. A 2015, 428, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Friedlander, S. Enhanced power law agglomerate growth in the free molecule regime. J. Aerosol Sci. 1993, 24, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, D.G.; Gaines, G.L. The molecular weight dependence of polymer surface tension. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 31, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, D.G.; Gaines, G.L. Surface Tension of Homologous Series of Liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 42, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).