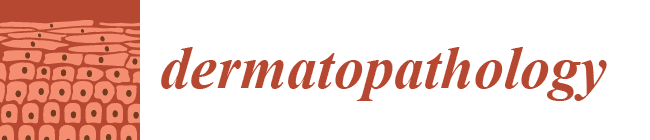Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Is HPV-42-Associated and BRAFV600E Negative: Perspectives for Diagnostic Practice
Abstract
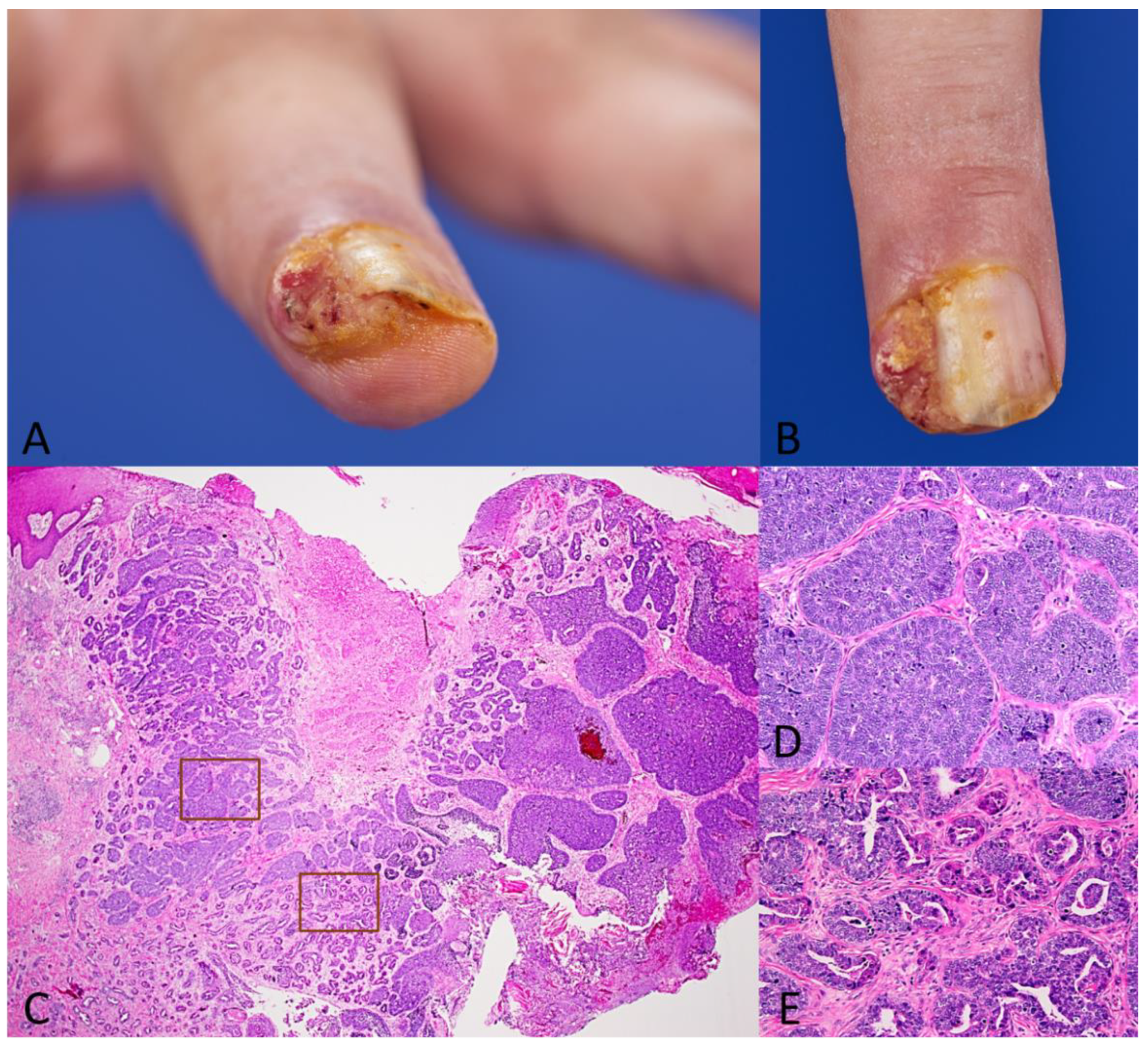
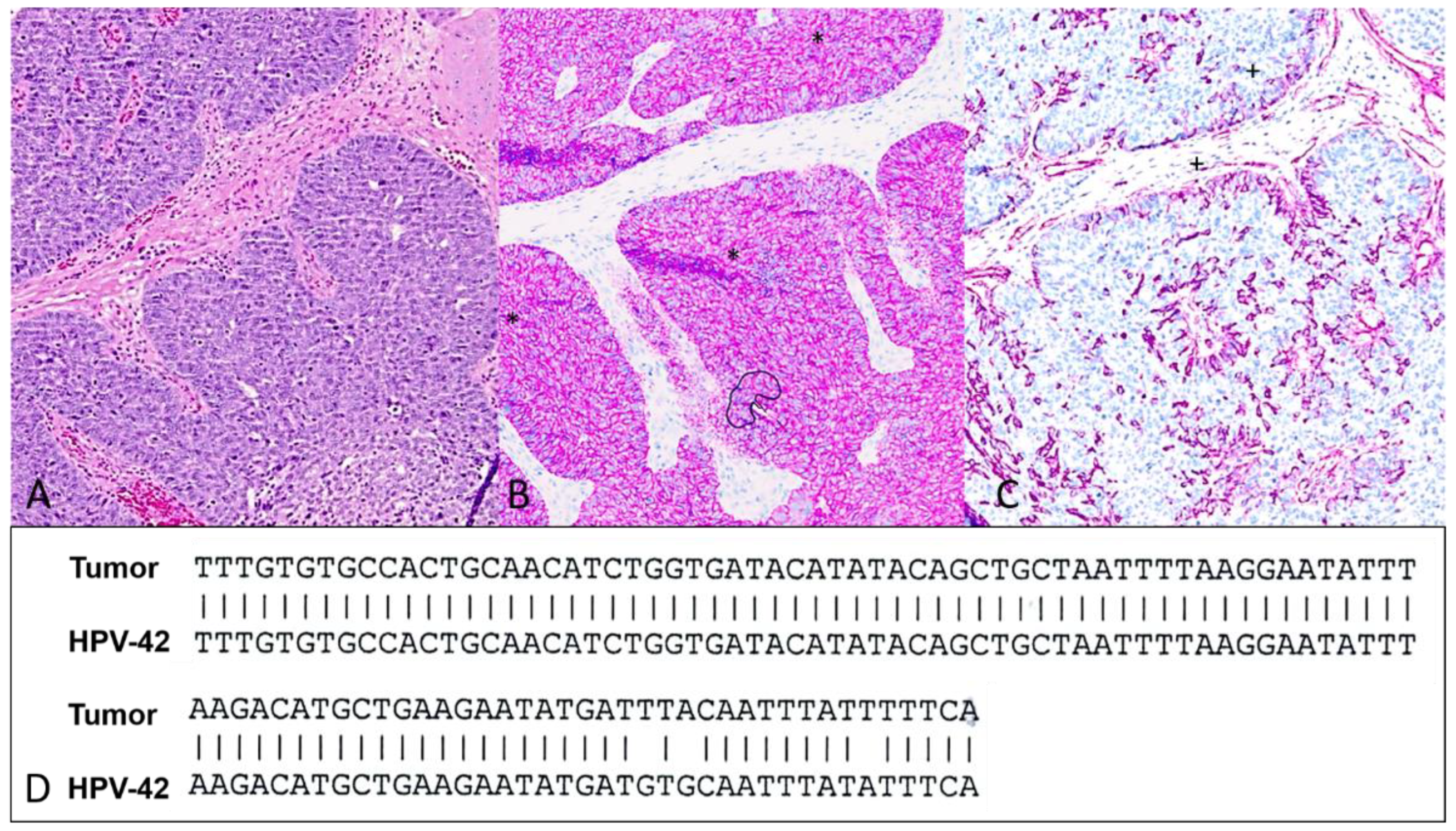
1. Case Presentation
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kao, G.F.; Helwig, E.B.; Graham, J.H. Aggressive digital papillary adenoma and adenocarcinoma. A clinicopathological study of 57 patients, with histochemical, immunopathological, and ultrastructural observations. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1987, 14, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchak, R.; Wang, W.L.; Prieto, V.G.; Ivan, D.; Lazar, A.J.; Brenn, T.; Calonje, E. Cutaneous digital papillary adenocarcinoma: A clinicopathologic study of 31 cases of a rare neoplasm with new observations. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Khullar, G.; Divyashree, R.; Sharma, S. Unusual presentation of digital papillary adenocarcinoma in a sporotrichoid pattern. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2024, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorva, A.D.; Mohil, R.; Srinivasan, M.S. Aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma presenting as a paronychia of the finger. J. Hand Surg. Br. 2005, 30, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Villén, G.; Alvarez Alegret, R.; Canales, V.; Herrera, A. Aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma of the hand: An unsuspected malignant tumour of the sweat glands. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2012, 46, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.; Leonard, N.; Theopold, C. Aggressive Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Mimicking a Giant Cell Tumour—A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C.; Saade, R.; Nagarajan, P.; Aung, P.P.; Milton, D.R.; Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Hudgens, C.; Ledesma, D.; Nelson, K.; Ivan, D.; et al. Nectin-4 expression in a subset of cutaneous adnexal carcinomas: A potential target for therapy with enfortumab vedotin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2024, 51, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.L.; Rosenberg, J.E. Targeting nectin-4 by antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of urothelial carcinoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, L.; Mentzel, T.; Paredes, B.; Griewank, K.; Itzlinger-Monshi, B.; Rütten, A. Digital papillary adenocarcinoma: Four case reports with brief literature review. Der. Hautarzt. 2019, 70, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, C.; Brenn, T.; Moy, A.P.; Harloe, G.; Ariyan, C.; Athanasian, E.; Busam, K.J. Association of HPV42 with digital papillary adenocarcinoma and the use of in situ hybridization for its distinction from acral hidradenoma and diagnosis at non-acral sites. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervarrec, T.; Imbeaud, S.; Veyer, D.; Pere, H.; Puech, J.; Pekár-Lukacs, A.; Markiewicz, D.; Coutts, M.; Tallet, A.; Collin, C.; et al. Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma in Nonacral Skin: Clinicopathologic and Genetic Characterization of 5 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcaro, M.; Castañon, A.; Ndlela, B.; Checchi, M.; Soldan, K.; Lopez-Bernal, J.; Elliss-Brookes, L.; Sasieni, P. The effects of the national HPV vaccination programme in England, UK, on cervical cancer and grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia incidence: A register-based observational study. Lancet 2021, 398, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olczak, P.; Matsui, K.; Wong, M.; Alvarez, J.; Lambert, P.; Christensen, N.D.; Hu, J.; Huber, B.; Kirnbauer, R.; Wang, J.W. RG2-VLP: A vaccine designed to broadly protect against anogenital and skin human papillomaviruses causing human cancer. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e00566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, C.M.; Pukhalskaya, T.; Smoller, B.R.; Zengin, H.B.; Heneidi, S.; Vail, E.; Makhoul, E.; Balzer, B. Two distinct pathogenic pathways of digital papillary adenocarcinoma—BRAF mutation or low-risk HPV infection. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2023, 50, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, W.H.; Sherrod, T.T.; Lupton, G.P. Aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma: (Aggressive digital papillary adenoma and adenocarcinoma revisited). Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Nagarajan, P.; Aung, P.P. Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma: The Detection of Low-Risk Human Papillomaviruses and the BRAF p.V600E Mutation in a Subset of Cases. Dermatopathology 2024, 11, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.S.; Nanda, V.S.; Grekin, S.; Rabinovitz, H.S. Apocrine adenocarcinoma: Case report and review of the literature. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1990, 16, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemeyer, K.; Gill, P.; Schneider, M.; Kind, P.; Brenn, T. Clinicopathologic characterization of hidradenoma on acral sites: A diagnostic pitfall with digital papillary adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadari, E.; Mehregan, A.; Lee, K. Malignant transformation of eccrine tumors. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1987, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolyer, R.A.; Karim, R.Z.; Thompson, J.F.; Stretch, J.R.; McCarthy, S.W.; Murali, R. Digital papillary adenocarcinoma: A tumour that should be considered in the differential diagnosis of neoplasms involving the digits. Pathology 2013, 45, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, J.-Y.; Tsai, J.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Lan, J.; Hong, J.-B.; Yuan, C.-T. BRAF and KRAS mutations in tubular apocrine adenoma and papillary eccrine adenoma of the skin. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 73, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.J.; Johnson, E.; Camilleri, M.; Wieland, C.; Lehman, J.S.; Agrawal, S.; Comfere, N.; Fadra, N.; Knudson, R.A.; Greipp, P. Ancillary immunohistochemical and molecular testing in the classification of cutaneous sweat gland/duct neoplasms: A validation study with emphasis on histomorphologic correlation and pathological diagnosis. Hum. Pathol. 2024, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Asgari, M. Is aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma really aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma? Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2014, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervarrec, T.; Busam, K.J. Acral BRAF-mutated tubular adenoma should be distinguished from HPV42-related digital papillary adenocarcinoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2023, 50, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the European Society of Dermatopathology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dege, T.; Rütten, A.; Goebeler, M.; Kneitz, H. Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Is HPV-42-Associated and BRAFV600E Negative: Perspectives for Diagnostic Practice. Dermatopathology 2024, 11, 348-353. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11040037
Dege T, Rütten A, Goebeler M, Kneitz H. Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Is HPV-42-Associated and BRAFV600E Negative: Perspectives for Diagnostic Practice. Dermatopathology. 2024; 11(4):348-353. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11040037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDege, Tassilo, Arno Rütten, Matthias Goebeler, and Hermann Kneitz. 2024. "Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Is HPV-42-Associated and BRAFV600E Negative: Perspectives for Diagnostic Practice" Dermatopathology 11, no. 4: 348-353. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11040037
APA StyleDege, T., Rütten, A., Goebeler, M., & Kneitz, H. (2024). Digital Papillary Adenocarcinoma Is HPV-42-Associated and BRAFV600E Negative: Perspectives for Diagnostic Practice. Dermatopathology, 11(4), 348-353. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11040037