- Article
Defining Histological Patterns in Inherited Ichthyoses: Toward a Diagnostic Algorithm Based on 66 Confirmed Cases
- Kira Süßmuth,
- Vinzenz Oji and
- Dieter Metze
- + 8 authors
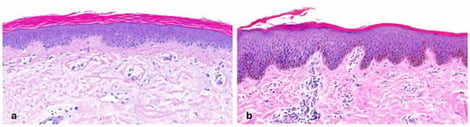
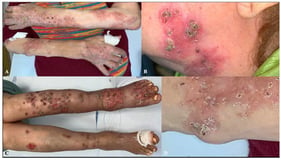
Background: Inherited ichthyoses are a heterogeneous group of disorders of cornification caused by mutations in genes encoding epidermal proteins. Clinically, patients with ichthyosis present with erythema, scaling, and occasionally blistering; some subtypes are syndromic. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for appropriate management and genetic counseling. Objectives: Diagnosis of ichthyosis typically relies on a combination of clinical features, histopathological and ultrastructural findings, immunohistochemistry, and molecular genetic testing. Dermatopathology can be particularly valuable in three diagnostic scenarios: (i) when the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis is evident, but the specific subtype remains unclear; (ii) when differential diagnoses such as inflammatory dermatoses need to be excluded; and (iii) when molecular testing is unavailable or yields variants of uncertain significance. However, definitive classification according to current nomenclature requires molecular confirmation. Methods: Despite being a routine diagnostic tool in dermatology, histopathological criteria for ichthyoses remain ill-defined and diagnostically challenging. In this retrospective study, we systematically assessed histological features in 66 patients with confirmed ichthyosis. Results: Our analysis revealed six distinct histological patterns. Based on these, we propose a pattern-based diagnostic algorithm to support the histological classification of ichthyosis subtypes. Limitations: Although some rare subtypes were underrepresented, this cohort represents the largest and most heterogeneous group of molecularly confirmed ichthyosis cases analyzed histologically to date. Conclusions: Our findings highlight the diagnostic value of skin biopsies in inherited ichthyoses. The delineation of characteristic histological patterns and the development of a diagnostic algorithm may facilitate more accurate subtype identification, particularly in settings where genetic testing is limited or inconclusive.
28 February 2026