Meshless Error Recovery Parametric Investigation in Incompressible Elastic Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Incompressible Elastic Formulation
3. Moving Least Squares Meshless Interpolation for Displacement Recovery
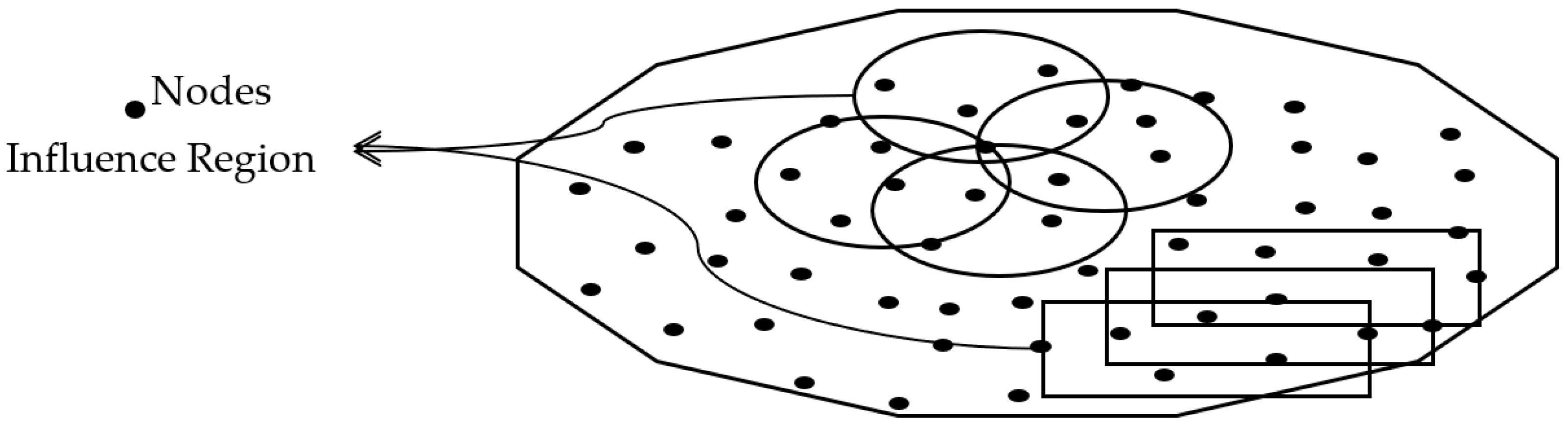
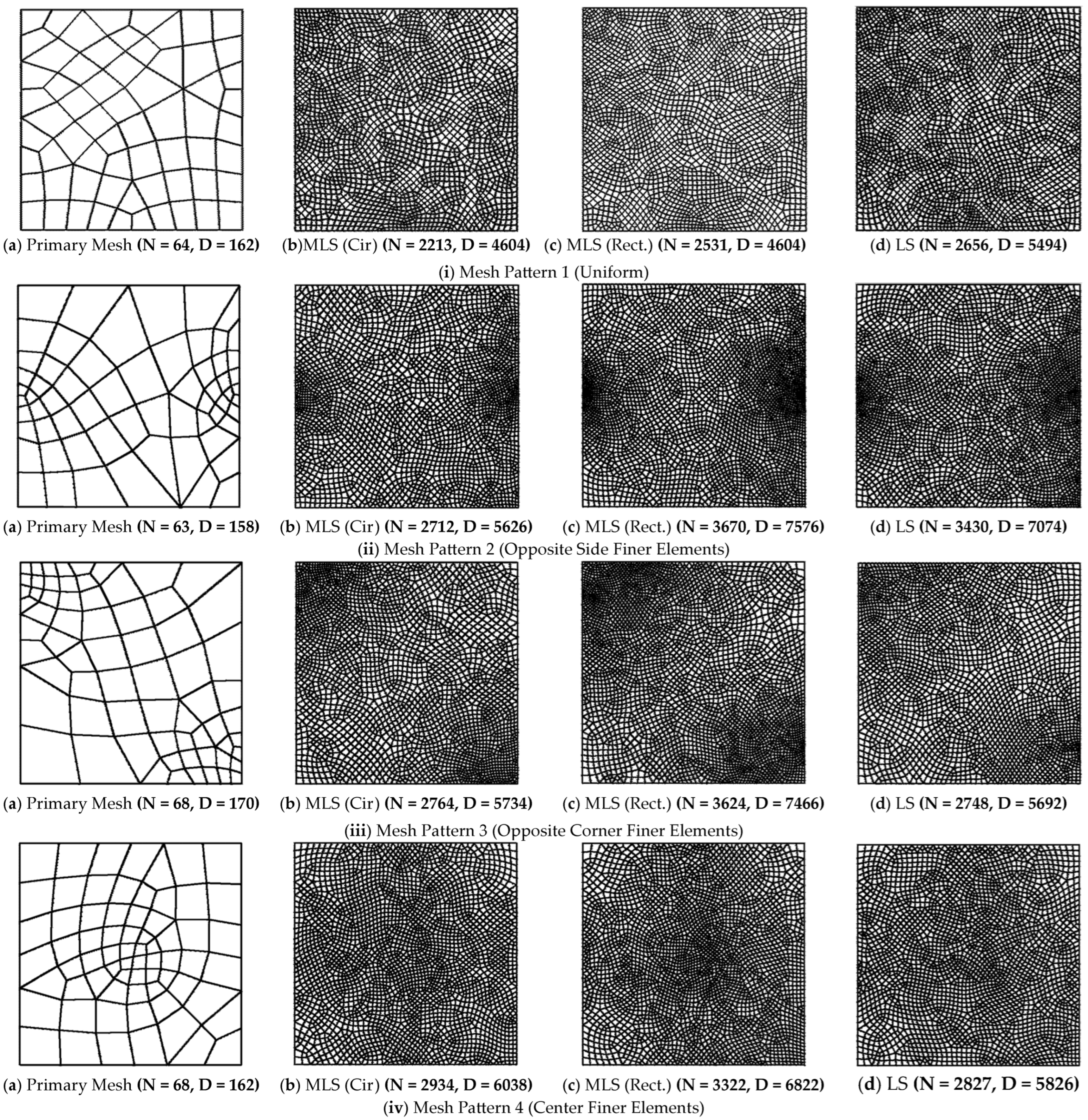
3.1. Influence Region Shapes in Moving Least Squares (MLS) Interpolation
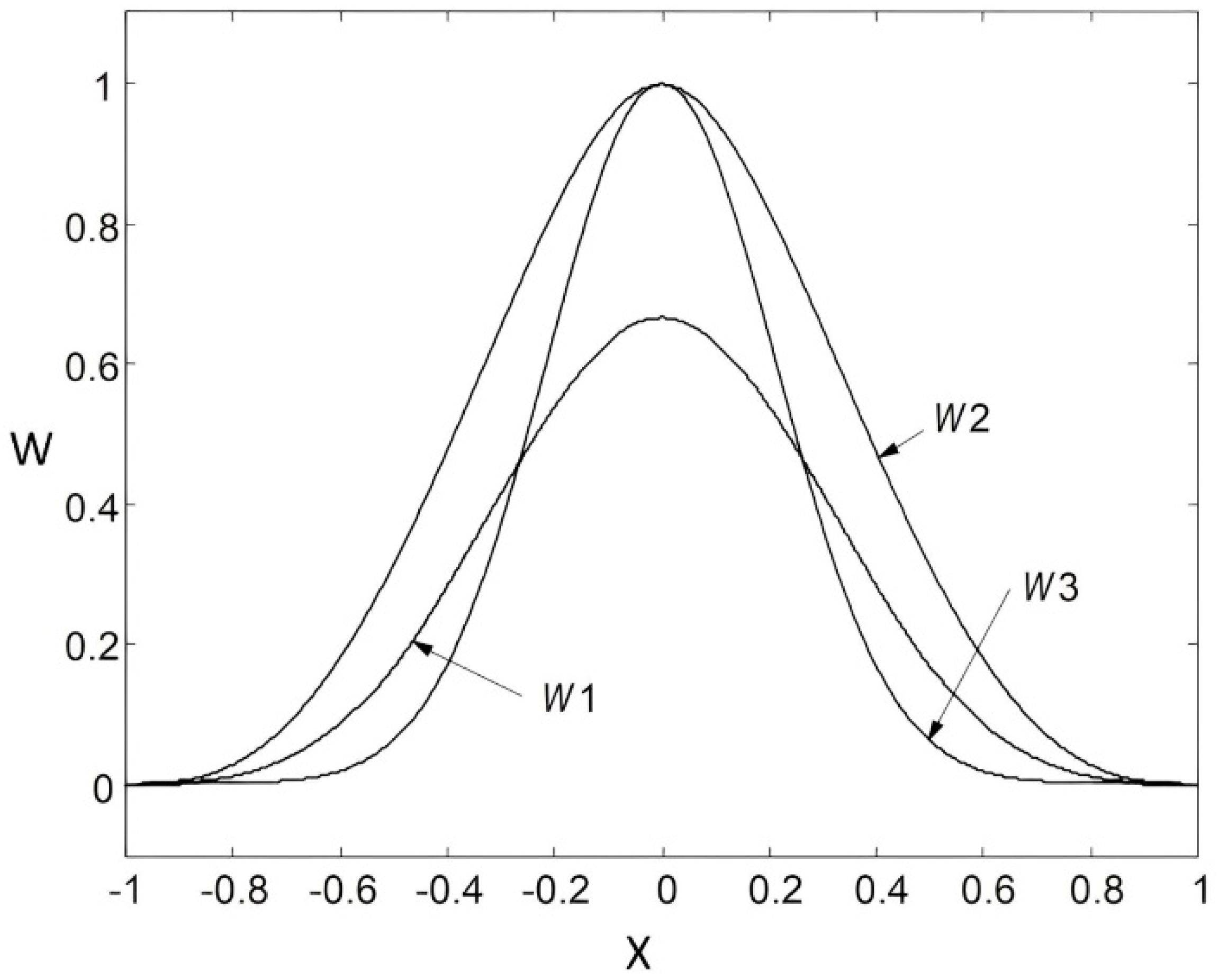
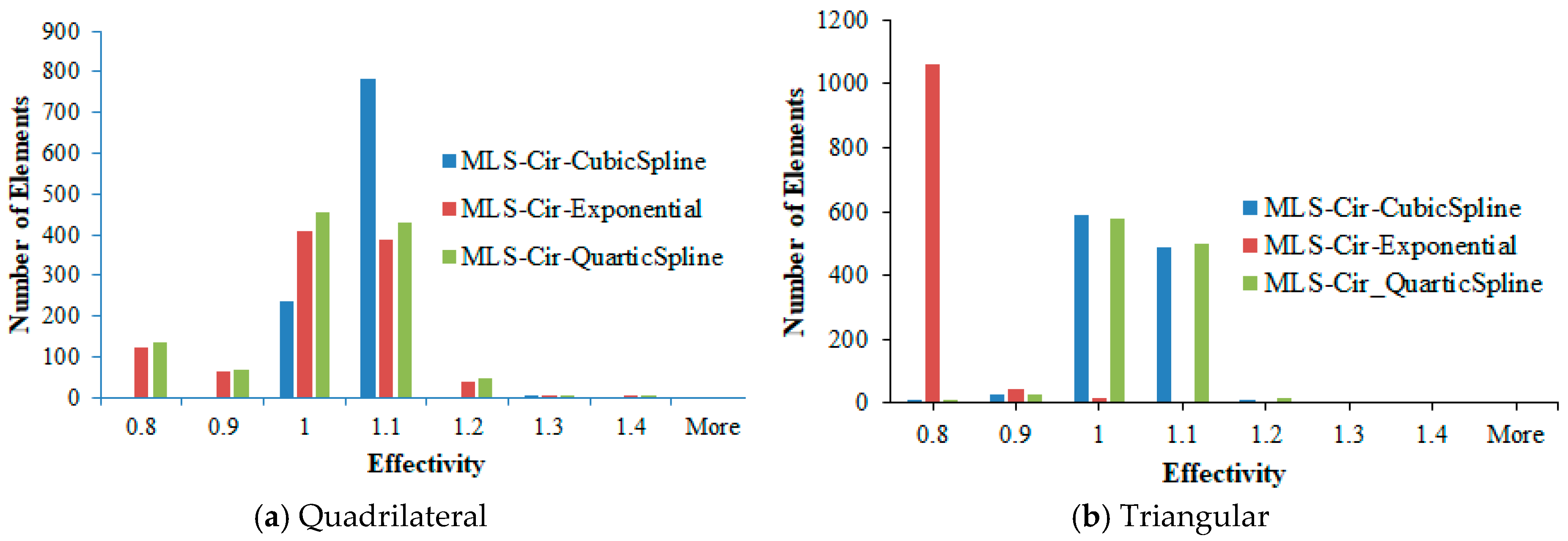
3.2. Weight Functions in Meshless MLS Interpolation
- Cubic Spline Functions (W1):
- Quartic Spline Functions (W2):
- Exponential Functions (W3):
4. Least Squares Interpolation for Displacement Recovery
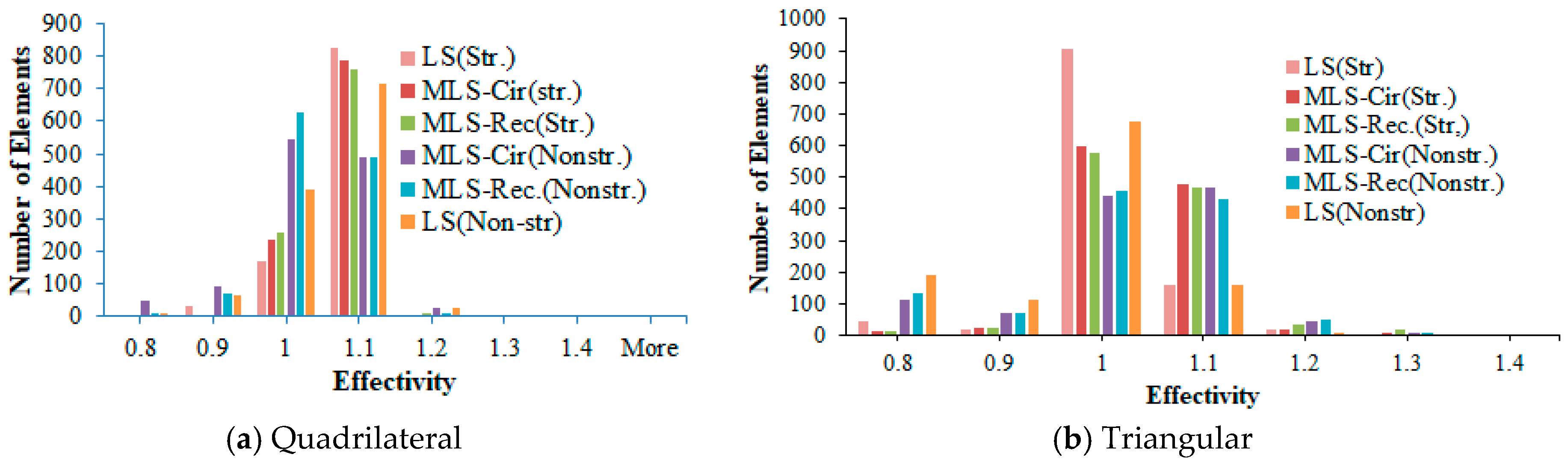
5. Finite Element Analysis Accuracy and Effectivity
6. Parametric Investigation of Meshless Error Recovery Procedures
6.1. Finite Element Method-Based Analysis of Incompressible Elastic Plate
- Problem Domain = Ω [0 × 0] × [1 × 1], u = v = 0 on Γ
- Exact solution for Displacements
- Exact solution for Strains
- Body Forces
Recovery Parameters: Interpolation Procedure Type, Mesh Pattern, Patch/Influence Region Configuration, Weight Functions and Error Norms
6.2. Finite Element Method-Based Analysis of Incompressible Elastic Cylinder Problem
Recovery Parameters: Interpolation Procedure Type, Mesh Pattern, Patch/Influence Region Configuration, Weight Functions and Error Norms
7. Discussion
Recommendations for Future Study
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ω | Problem domain |
| Tractions on Γt boundary | |
| Displacements on Γu boundary | |
| u | Displacements field |
| σ | Stress field |
| p | Pressure |
| e*u (e*σ) | Errors in computed values of u or σ |
| m | Approximating polynomial order |
| n | Unit normal vector |
| n | Number of nodes in a patch or influence region |
| E | Elastic modulus |
| ν | Poisson’s ratio |
| Tx | Uniaxial traction applied at infinity |
| θ | Effectivity |
| η | Accuracy |
| Ωi | Volume of element i |
| us | Nodal parameter vector of displacement |
| x (xi, yi) | Nodes coordinates |
| w(x−xi) | Node’s weight function |
| α | Shape parameter constant (exponential weight function) |
| P(x) | Polynomial basis function |
| a | Unknown coefficient |
References
- Dow, J.O. A Uniform Approach to the Finite Element Method and Error Analysis Procedures; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, S.; Wu, C.J.; Li, Z.; Shang, Y.; Li, C. Some advances in high-performance finite element methods. Eng. Comput. 2019, 36, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.R. Smoothed Finite Element Methods (S-FEM): An Overview and Recent Developments. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2018, 25, 397–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.E.; Gaticay, L.F.; Lamichhanez, B.; Oyarzúa, R.; Ruiz-Baier, R. Mixed Kirchhof stress-displacement—Pressure formulations for incompressible hyper elasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 374, 113562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffi, D.; Stenberg, R. A remark on finite element schemes for nearly incompressible elasticity. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 74, 2047–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulff, P.; Buntin, L.M.; Kalscheuer, T. Efficient goal-oriented mesh refinement in 3-D finite-element modelling adapted for controlled source electromagnetic surveys. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 227, 1624–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemer, R.; Larcher, A.; Coupez, T.; Hachem, E. Stabilized finite element method for incompressible solid dynamics using an updated Lagrangian formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 384, 113923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, O.; Dal, H.; Holzapfel, G.A. On the quasi-incompressible finite element analysis of anisotropic hyperelastic materials. Comput. Mech. 2019, 63, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Gao, X. Review of collocation methods and applications in solving science and engineering problems. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 140, 41–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-K.; Mihai, L.A.; Hale, J.S.; Kerfriden, P.; Bordas, S.P.A. Strain smoothing for compressible and nearly-incompressible finite elasticity. Comput. Struct. 2017, 182, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Powell, C.E.; Silvester, D.J. Robust a-posteriori error estimator for mixed approximation of nearly incompressible elasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2019, 119, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravesh, S.; Afshar, M.H.; Faraji, S. RPIM and RPIM-MLS-based MDLSM method for the solution to elasticity problems. Sci. Iran. Trans. A Civ. Eng. 2016, 23, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Xue, S. A Hermite interpolation element-free Galerkin method for elasticity problems. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2022, 17, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, N.; Perotto, S.; Cangiani, A. An Anisotropic Recovery-Based Error Estimator for Adaptive Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 90, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, A.; Chiaia, P.; Filippi, M.; Cinefra, M. Unified three-dimensional finite elements for large strain analysis of compressible and nearly incompressible solids. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuska, I.; Rheinboldt, W.C. A posteriori Error Estimator in Finite Element Method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1978, 12, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.; Johnson, C. An Adaptive Finite Element Method for Linear Elliptic Problems. Math. Comput. 1988, 50, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. Simple error estimator and adaptive procedure for practical engineering analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1987, 24, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramble, J.H.; Schatz, A.H. Higher Order Local Accuracy by Averaging in Finite Element Method. Math. Comput. 1977, 31, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, E.; Campbell, J.S. Local and Global Smoothing of Discontinuous Finite Element Functions using a Least Square Methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1974, 8, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. The Super convergent Patch Recovery and a-posteriori Error Estimates, Part I, The Error Recovery Technique. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 33, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. The Super convergent Patch Recovery and a-posteriori Error Estimates. Part II: Error Estimates and Adaptivity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 33, 1365–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, E.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. A Simple Error Estimator in The Finite Element Method. Commun. Appl. Numer. Methods 1987, 3, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, D. Analysis of Moving Least Squares Approximation Revisited. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 282, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parret-Fréaud, A.; Rey, V.; Gosselet, P.; Rey, C. Improved recovery of admissible stress in domain decomposition methods—Application to heterogeneous structures and new error bounds for FETI-DP. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2016, 111, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Gantner, G.; Innerberger, M.; Praetorius, D. Goal-oriented adaptive finite element methods with optimal computational complexity. Numer. Math. 2023, 153, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.T.; da Silva, J. Anisotropic Mesh Refinement Considering a Recovery-Based Error Estimator and Metric Tensors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5613–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.F.; Atluri, S.N.; Zuo, C.W. The Optimal Radius of the Support of Radial Weights Used in Moving Least Squares Approximation. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2006, 12, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kahla, N.B.; AlQadhi, S.; Ahmed, M. Mesh-Free MLS-Based Error-Recovery Technique for Finite Element Incompressible Elastic Computations. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, J.; Šarler, B. Weight Function Shape Parameter Optimization in Meshless Methods for Non-uniform Grids. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2007, 19, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.G.; Liu, G.R. On the Optimal Shape Parameters of Radial Basis Functions used for 2-D Meshless Methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2002, 191, 2611–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanber, B.; Bozkurt, O.Y.; Erklig, A. Investigation of RPIM Shape Parameter Effects on the Solution Accuracy of 2D Elastoplastic Problems. Int. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Sci. Mech. 2013, 14, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Ko, S.; Lee, J. Error analysis for finite element operator learning methods for solving parametric second-order elliptic PDEs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.17868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Singh, D.; Qadhi, S.A.; Thanh, N.V. Moving least squares interpolation-based a-posteriori error technique in finite element elastic analysis. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 129, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban, A.; Tufo, H.; Sture, S.; Regueiro, R. Matrix-free higher-order finite element method for parallel simulation of compressible and nearly-incompressible linear elasticity on unstructured meshes. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 129, 1283–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Natarajan, S.; Hale, J.S.; Taylor, Z.A.; Yee, J.J.; Bordas, S. Bubble-enriched smoothed finite element methods for nearly-incompressible solids. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 127, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Lui, Y.C.; Huang, G.C. Error estimates and convergence rate for various incompressible elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1989, 28, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onate, E.; Perazzo, F.; Miquel, J. A finite point method for elasticity problems. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 2151–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.R.; Liu, M.B. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics—A Meshfree Particle Method; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.: Singapore, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. Techniques for Mesh Independent Displacement Recovery in Elastic Finite Element Solutions. Trans. Famena 2021, 45, 260308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Wiberg, N.E. A Posteriori Error Estimate by Element Patch Post-processing, Adaptive Analysis in Energy and L2 Norms. Comput. Struct. 1994, 53, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, L.M.; Dolovich, A.T. Finite Element Calculations for incompressible Materials using a Modified LU Decomposition. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2006, 30, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
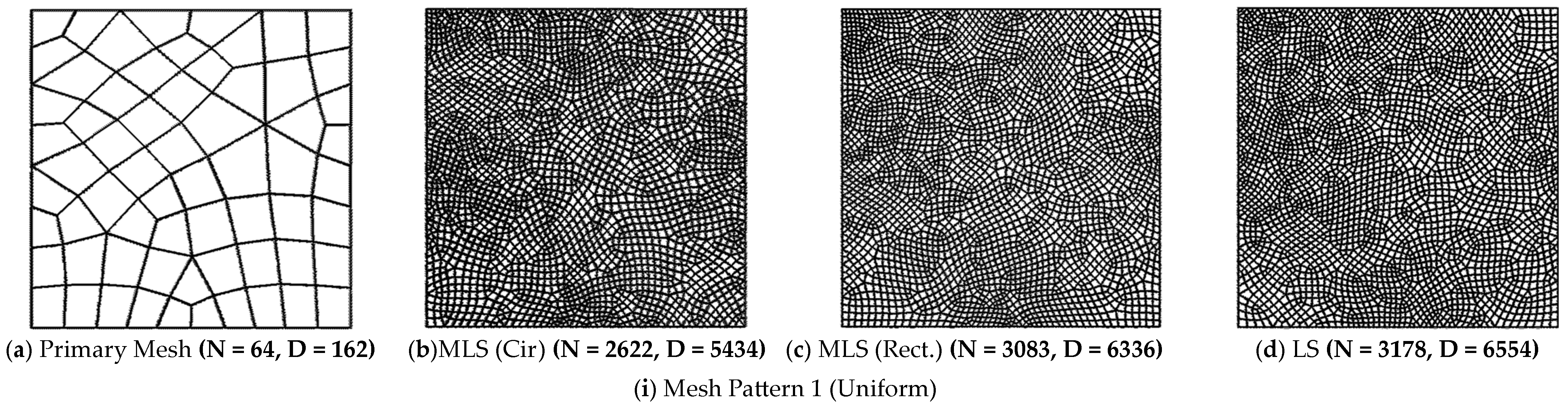
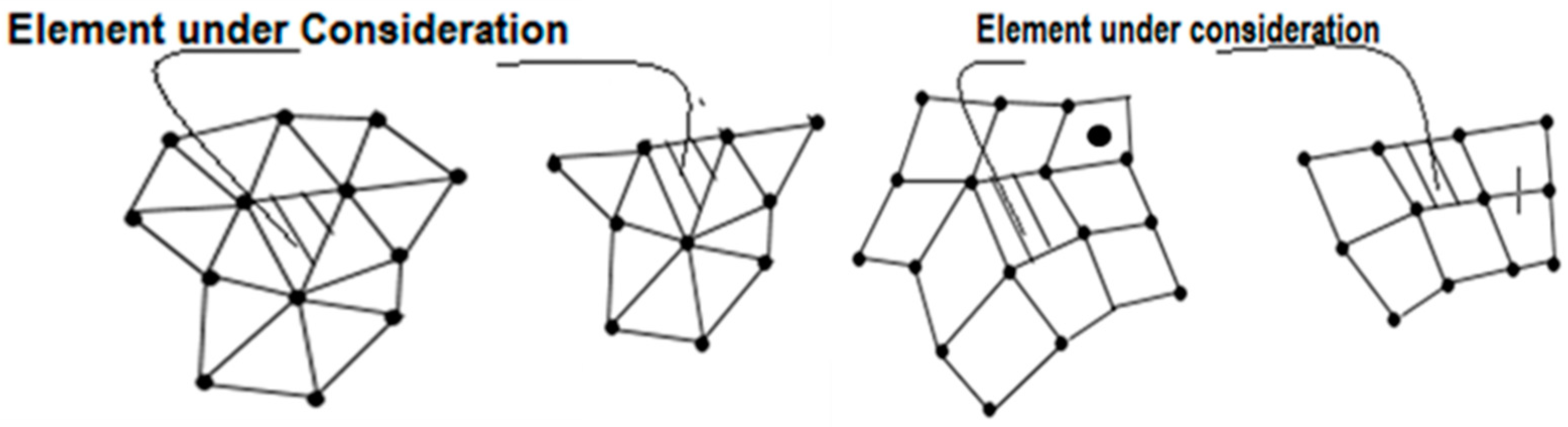


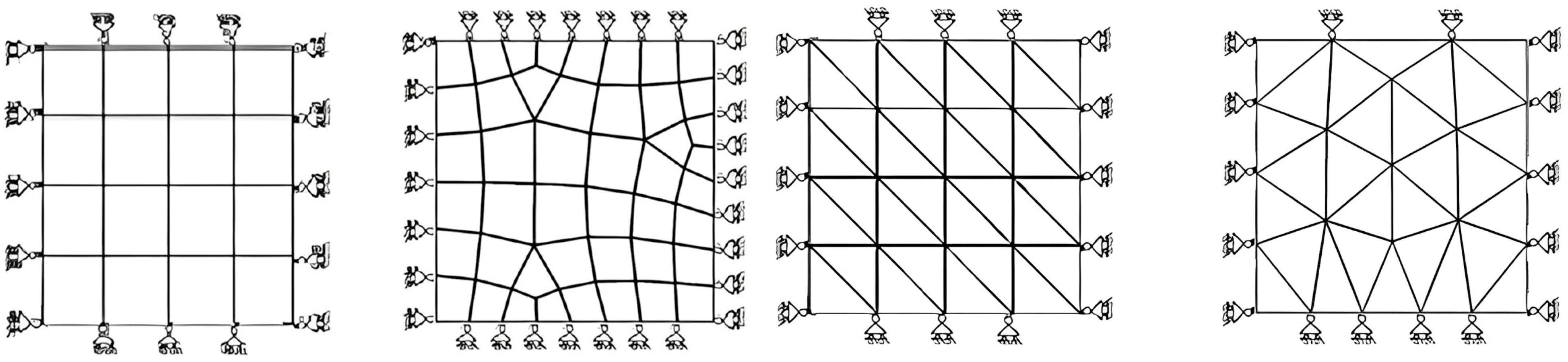

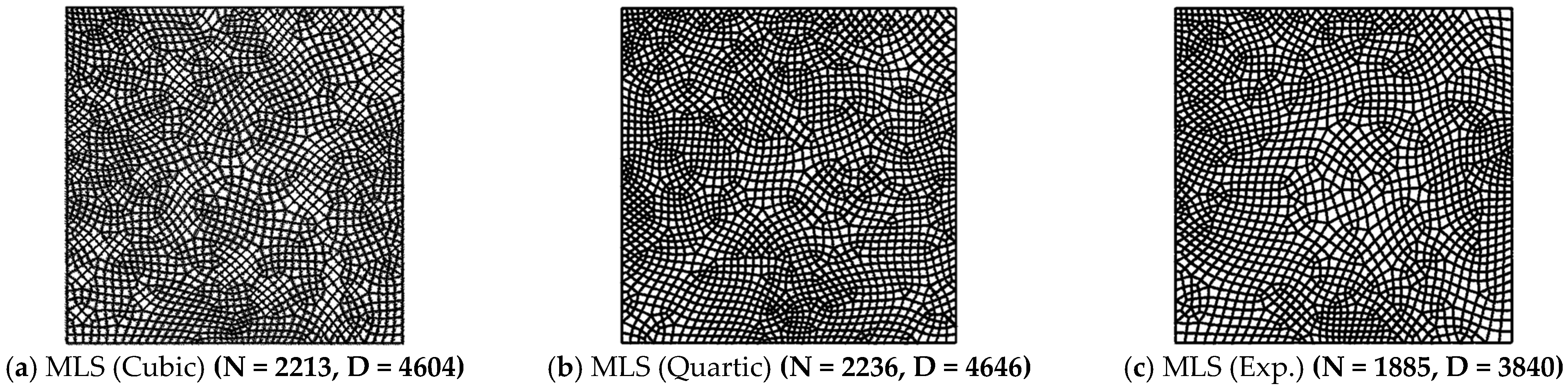
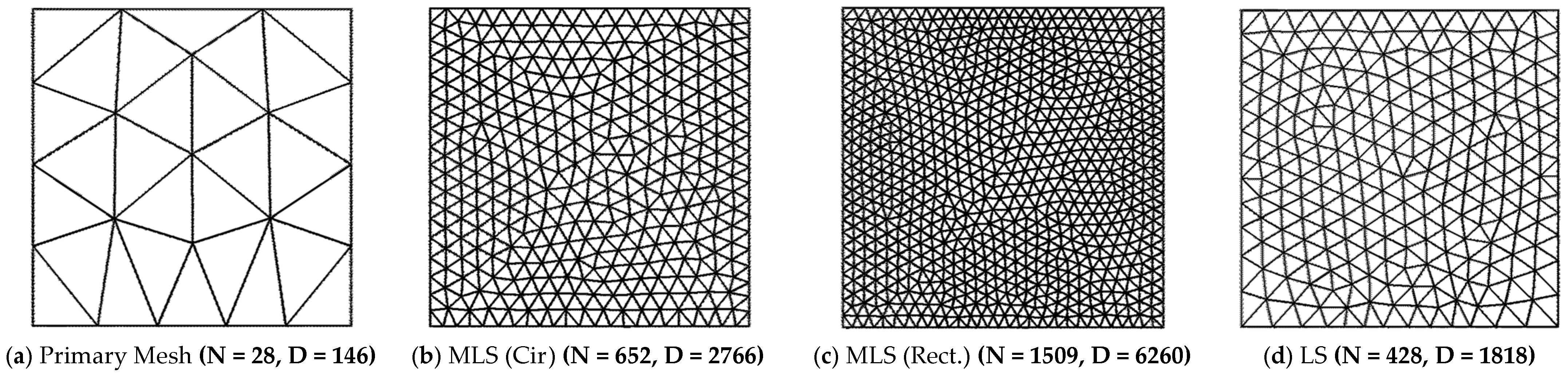


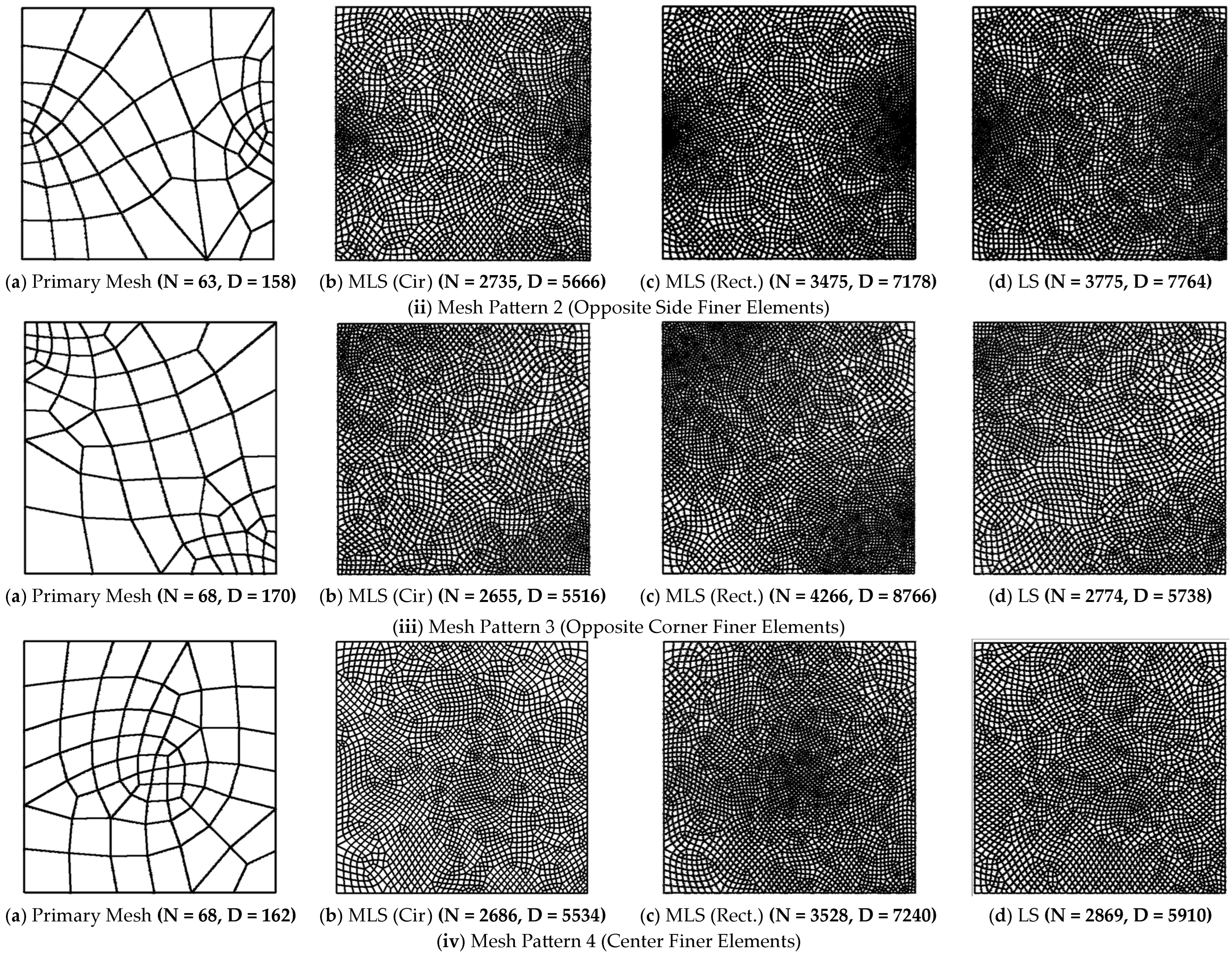
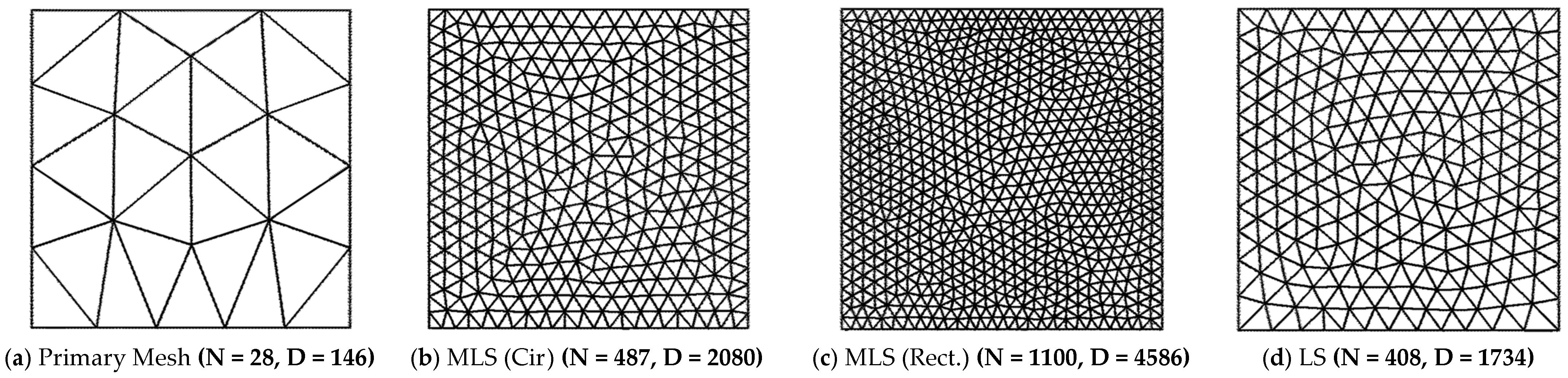
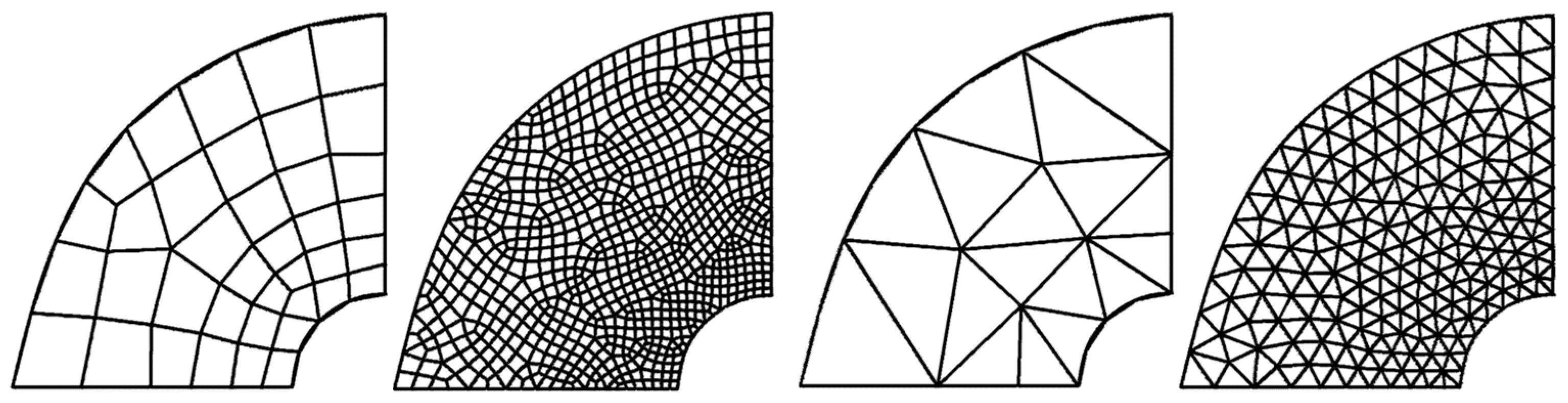
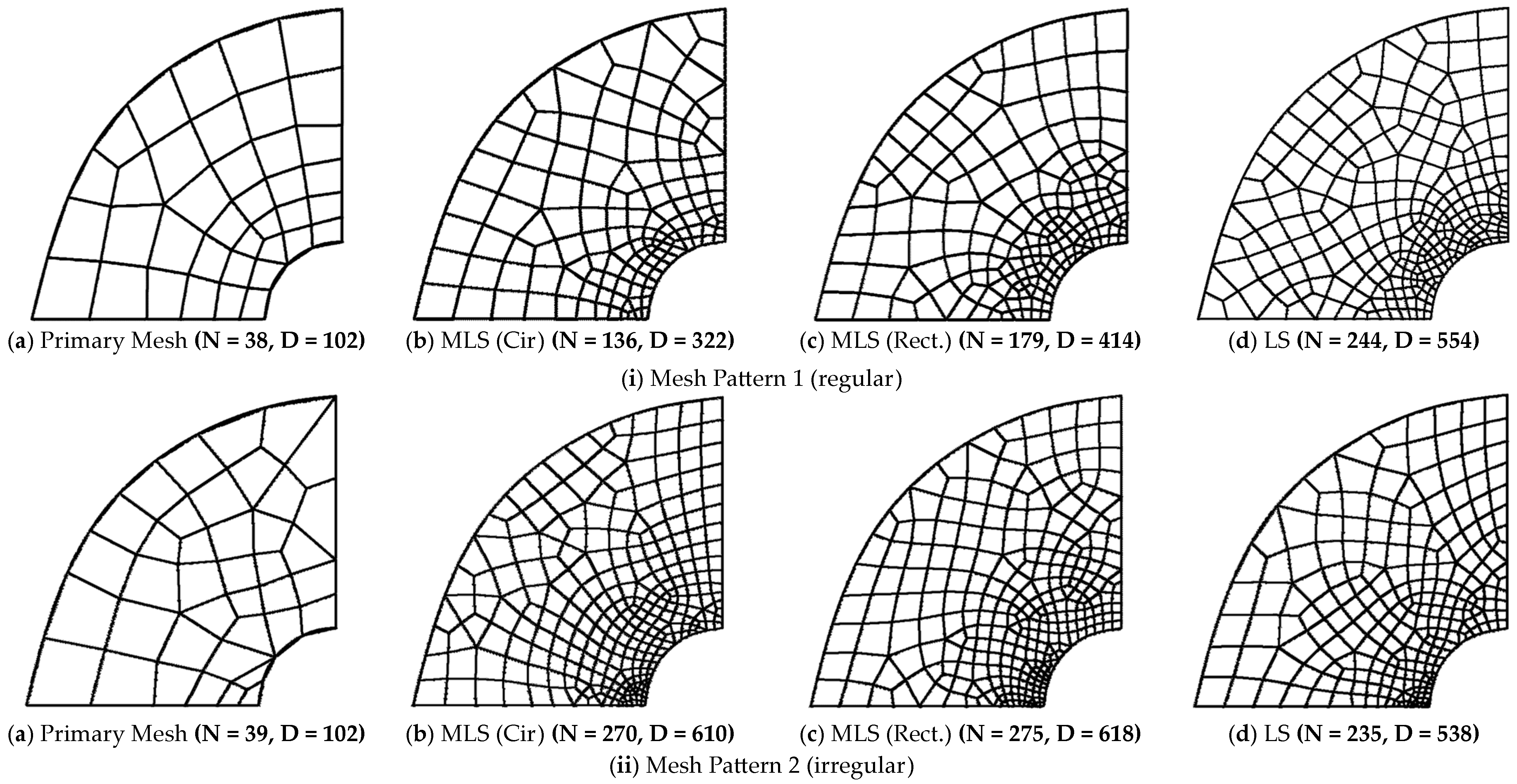
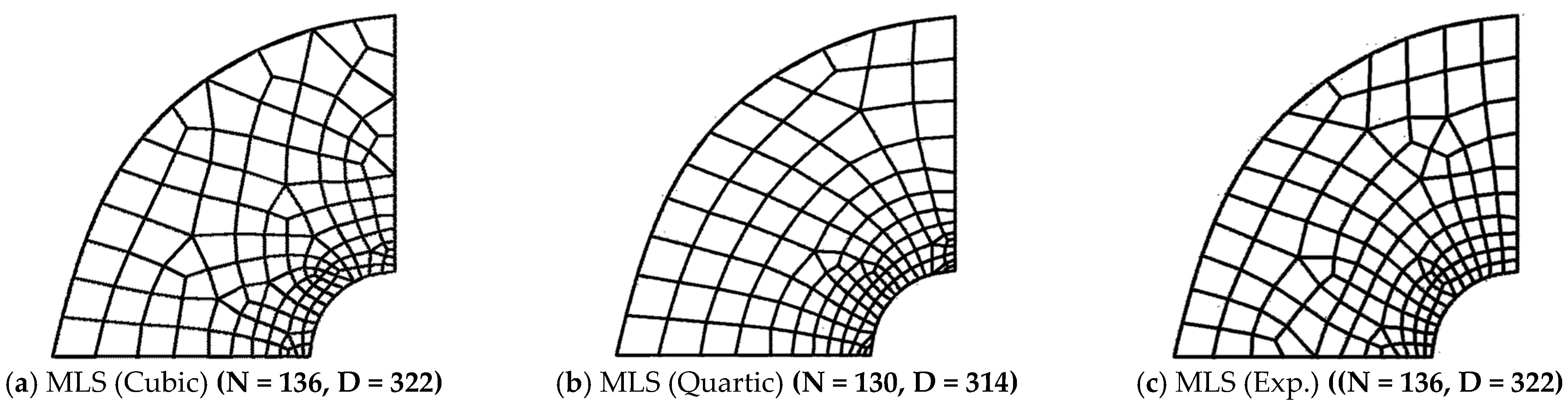
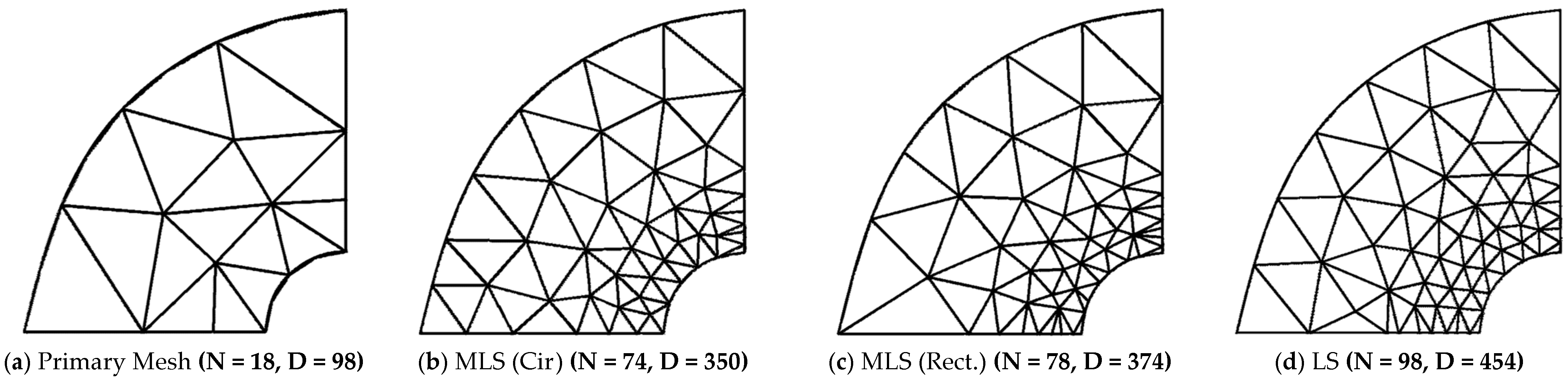
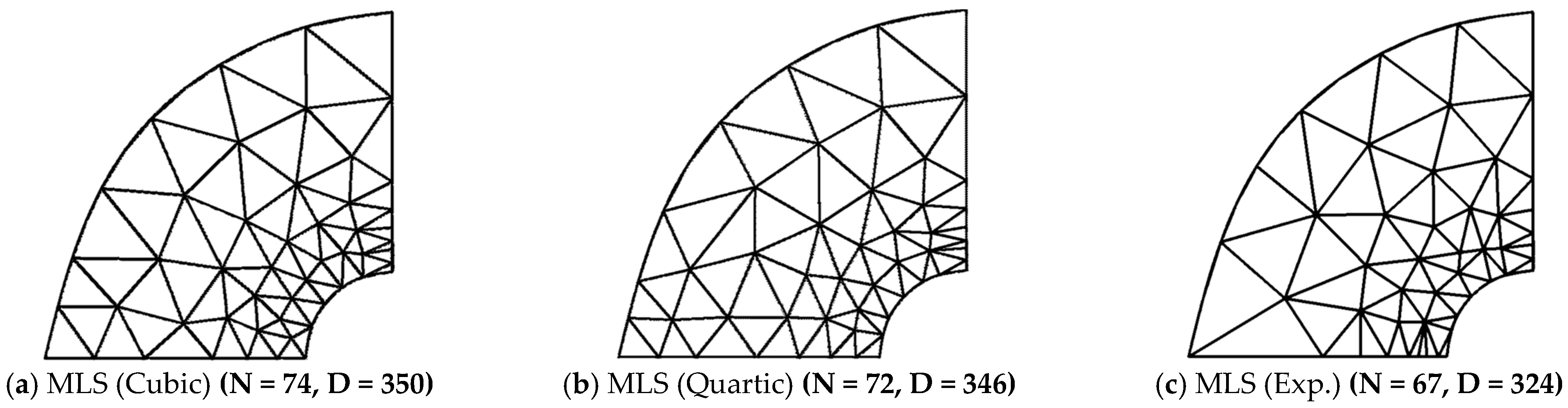
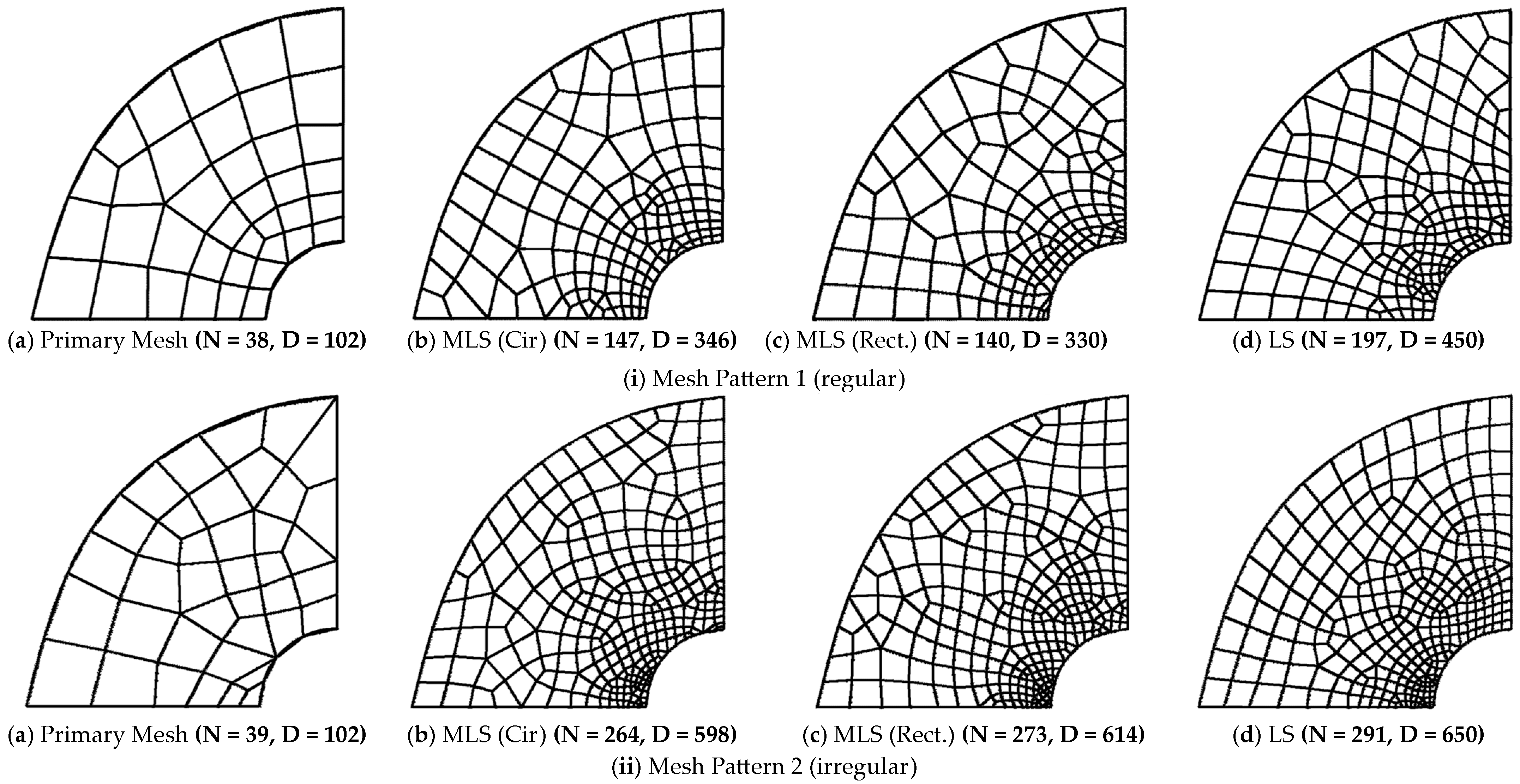
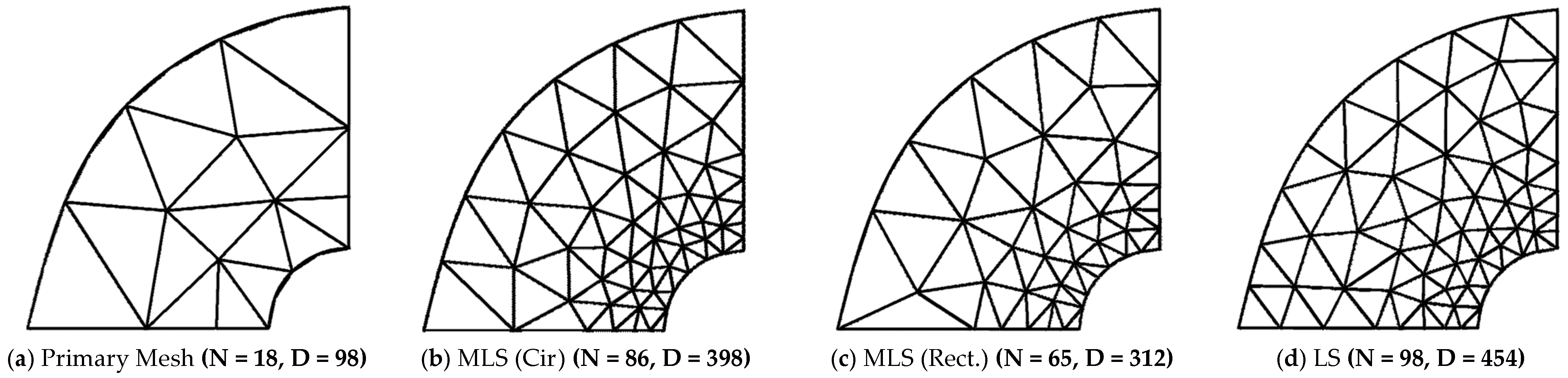
| (a) Structured Mesh | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh Size (1/h) | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [dmax= 3.0, m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region | Rectangular Influence Region | Circular Influence Region | Circular Influence Region | Element-Based Patch | ||||||||
| Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |||
| 1/4 | 29.444 | 22.733 | 0.8210 | 40.169 | 1.1796 | 17.907 | 0.8263 | 17.708 | 0.5927 | 19.800 | 0.9173 | |
| 1/8 | 15.256 | 4.635 | 0.9034 | 12.753 | 1.0836 | 3.512 | 0.9332 | 5.439 | 0.8273 | 7.036 | 0.9917 | |
| 1/16 | 7.693 | 0.934 | 0.9703 | 2.555 | 0.9857 | 0.729 | 0.9806 | 1.472 | 0.9424 | 2.131 | 1.0019 | |
| 1/32 | 3.855 | 0.197 | 0.9917 | 0.483 | 0.9910 | 0.159 | 0.9946 | 0.387 | 0.9835 | 0.589 | 1.0013 | |
| Conv. Rate | 0.9777 | 2.2847 | 2.1261 | 2.2681 | 1.8389 | 1.6900 | ||||||
| (b) Unstructured Mesh | ||||||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, dmax = 3.0, m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region | Rectangular Influence Region | Circular Influence Region | Circular Influence Region | Element-Based Patch | ||||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 16 | 50 | 29.449 | 15.853 | 0.8187 | 33.670 | 0.9813 | 18.101 | 0.8353 | 18.204 | 0.4925 | 19.795 | 0.9173 |
| 64 a | 162 | 17.999 | 8.837 | 0.8727 | 8. 999 | 0.9311 | 9.512 | 0.9442 | 10.543 | 0.7511 | 11.469 | 0.9695 |
| 63 b | 158 | 26.627 | 24.793 | 1.0273 | 16.475 | 1.0272 | - | - | - | - | 17.991 | 0.9252 |
| 68 c | 170 | 23.107 | 27.896 | 1.4885 | 16.659 | 1.0007 | - | - | - | - | 13.314 | 0.9942 |
| 68 d | 162 | 22.445 | 14.165 | 0.7617 | 19.181 | 0.8410 | - | - | - | - | 15.884 | 0.8571 |
| 282 | 630 | 8.463 | 2.264 | 0.9525 | 2.312 | 0.9677 | 3.729 | 0.9701 | 5.273 | 0.8926 | 3.063 | 0.9907 |
| 1212 | 2566 | 3.673 | 0.726 | 0.9825 | 0.544 | 0.9883 | 0.859 | 0.9812 | 0.995 | 0.9137 | 0.723 | 1.0025 |
| (a) Structured Mesh | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh Size (1/h) | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 5] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||||
| Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |||
| 1/4 | 40.201 | 23.896 | 1.0136 | 30.462 | 1.0768 | 25.733 | 1.0351 | 33.437 | 0.6657 | 19.073 | 0.9328 | |
| 1/12 | 14.110 | 2.280 | 0.9879 | 3.038 | 0.9994 | 2.429 | 0.9902 | 11.556 | 0.7101 | 2.258 | 0.9663 | |
| 1/24 | 7.025 | 0.568 | 0.9929 | 0.652 | 0.9952 | 0.584 | 0.9938 | 788.54 | 112.236 | 0.683 | 0.9720 | |
| Conv. Rate | 0.9736 | 2.0869 | 2.1452 | 2.1128 | 1.7639 | 1.8578 | ||||||
| (b) Unstructured Mesh | ||||||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 5] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 28 | 146 | 35.233 | 29.014 | 0.4241 | 33.854 | 0.6655 | 26.644 | 0.9821 | 35.354 | 0.7358 | 28.856 | 0.5690 |
| 291 | 1264 | 7.085 | 2.085 | 0.9455 | 2.583 | 0.9418 | 5.617 | 0.9876 | 13.556 | 0.8001 | 3.264 | 0.8541 |
| 1149 | 4792 | 2.805 | 0.628 | 0.9529 | 0.719 | 0.9380 | 0.846 | 0.9912 | - | - | 1.110 | 0.8838 |
| (a) Structured Mesh | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh Size (1/h) | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, dmax = 3.0, m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region | Rectangular Influence Region | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |||
| 1/4 | 32.216 | 29.485 | 0.8335 | 49.214 | 1.2418 | 26.653 | 0.9312 | |
| 1/8 | 16.525 | 5.725 | 0.8887 | 16.448 | 1.1467 | 9.668 | 0.9950 | |
| 1/16 | 8.315 | 1.135 | 0.9667 | 3.183 | 0.9869 | 2.918 | 1.0026 | |
| 1/32 | 4.164 | 0.242 | 0.9909 | 0.592 | 0.9900 | 0.805 | 1.0015 | |
| Conv. Rate | 0.9838 | 2.3092 | 2.1258 | 1.6829 | ||||
| (b) Unstructured Mesh | ||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, dmax = 3.0, m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region | Rectangular Influence Region | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 16 | 50 | 32.219 | 20.592 | 0.7850 | 41.020 | 1.0132 | 26.647 | 0.9312 |
| 64 a | 162 | 21.671 | 10.796 | 0.8864 | 11.327 | 0.9471 | 15.365 | 0.9966 |
| 63 b | 158 | 32.080 | 29.993 | 1.0440 | 20.331 | 0.9071 | 23.042 | 0.9318 |
| 68 c | 170 | 26.699 | 37.512 | 1.6384 | 20.977 | 1.0402 | 17.933 | 1.0151 |
| 68 d | 162 | 25.639 | 16.879 | 0.7708 | 22.867 | 0.8531 | 20.828 | 0.8736 |
| 282 | 630 | 10.147 | 2.792 | 0.9593 | 2.861 | 0.9747 | 4.136 | 0.9996 |
| 1212 | 2566 | 4.159 | 0.892 | 0.9800 | 0.672 | 0.9862 | 0.956 | 1.0011 |
| (a) Structured Mesh | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh Size (1/h) | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 5.0] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |||
| ¼ | 46.782 | 29.667 | 1.0381 | 36.656 | 1.1024 | 23.437 | 0.9420 | |
| 1/16 | 16.128 | 2.817 | 0.9904 | 3.833 | 1.0058 | 2.642 | 0.9647 | |
| 1/24 | 8.056 | 0.693 | 0.9930 | 0.814 | 0.9963 | 0.795 | 0.9707 | |
| Conv. Rate | 0.9818 | 2.0964 | 2.1244 | 1.8885 | ||||
| (b) Unstructured Mesh | ||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 7.5] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 5.0] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 28 | 146 | 39.720 | 23.854 | 0.6655 | 28.604 | 0.7096 | 33.072 | 0.6024 |
| 291 | 1264 | 7.721 | 2.685 | 0.9671 | 3.303 | 0.9680 | 3.444 | 0.8639 |
| 1149 | 4792 | 3.109 | 0.715 | 0.9611 | 0.790 | 0.9466 | 1.172 | 0.8913 |
| (a) Linear Quadrilateral Element | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 2] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Element-based Patch | ||||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 38 a | 102 | 1.015 | 0.464 | 0.9258 | 0.612 | 0.9317 | 0.507 | 0.9296 | 0.566 | 0.7535 | 0.724 | 1.0015 |
| 39 b | 102 | 1.338 | 0.784 | 1.0390 | 0.937 | 0.9533 | - | - | - | - | 1.160 | 1.0767 |
| 176 | 402 | 0.505 | 0.209 | 0.9325 | 0.216 | 0.9434 | 0.209 | 0.9419 | 0.220 | 0.8546 | 0.220 | 0.9704 |
| 766 | 1632 | 0.291 | 0.147 | 0.8915 | 0.174 | 0.8576 | 0.160 | 0.8386 | 0.191 | 0.8240 | 0.177 | 0.8850 |
| (b) Quadratic Triangular Element | ||||||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||||||
| Cubic Spline | Quartic Spline | Exponential | ||||||||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 2] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.25] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 18 | 98 | 0.840 | 0.740 | 1.1419 | 1.019 | 1.4419 | 0.601 | 1.0257 | 0.646 | 1.0661 | 1.059 | 1.5397 |
| 80 | 370 | 0.304 | 0.182 | 0.8379 | 0.210 | 0.9965 | 0.181 | 0.8587 | 0.243 | 0.8560 | 0.241 | 1.0241 |
| 357 | 1528 | 0.180 | 0.147 | 0.5910 | 0.155 | 0.4989 | 0.147 | 0.6133 | 0.171 | 0.4658 | 0.151 | 0.5532 |
| (a) Linear Quadrilateral Element | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, m = 6] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.0] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 2.0] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 38 a | 102 | 68.368 | 33.126 | 0.9541 | 41.137 | 0.9401 | 54.199 | 1.0568 |
| 39 b | 102 | 88.855 | 54.112 | 1.0487 | 62.241 | 0.9719 | 70.458 | 1.0539 |
| 64 | 162 | 35.872 | 14.354 | 0.9372 | 15.434 | 0.9417 | 19.845 | 1.0126 |
| 1212 | 2566 | 20.326 | 10.750 | 0.8786 | 10.798 | 0.9862 | 11.774 | 0.8710 |
| (b) Quadratic Triangular Element | ||||||||
| Irregular Mesh Detail | Exact Error (×10−2) | MLS-Based Recovered Error [Cubic Spline, m = 9] | LS-Based Recovered Error | |||||
| Circular Influence Region [dmax = 3.15] | Rectangular Influence Region [dmax = 1.65] | Element-Based Patch | ||||||
| Element Numbers | Degree of Freedom | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | Error (×10−2) | θ | |
| 18 | 98 | 58.818 | 35.570 | 0.9931 | 50.773 | 1.1076 | 66.952 | 1.4173 |
| 80 | 370 | 21.981 | 13.278 | 0.8906 | 14.602 | 0.9348 | 16.109 | 0.9732 |
| 357 | 1528 | 12.909 | 10.654 | 0.5926 | 10.752 | 0.6139 | 10.426 | 0.6694 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Althaqafi, E.; Singh, D.; Ahmed, M. Meshless Error Recovery Parametric Investigation in Incompressible Elastic Finite Element Analysis. Math. Comput. Appl. 2024, 29, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050087
Althaqafi E, Singh D, Ahmed M. Meshless Error Recovery Parametric Investigation in Incompressible Elastic Finite Element Analysis. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2024; 29(5):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlthaqafi, Essam, Devinder Singh, and Mohd Ahmed. 2024. "Meshless Error Recovery Parametric Investigation in Incompressible Elastic Finite Element Analysis" Mathematical and Computational Applications 29, no. 5: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050087
APA StyleAlthaqafi, E., Singh, D., & Ahmed, M. (2024). Meshless Error Recovery Parametric Investigation in Incompressible Elastic Finite Element Analysis. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 29(5), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca29050087






