Influence of Ti Substitution on Electrochemical Performance and Evolution of LiMn1.5−x Ni0.5TixO4 (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.3) as a High Voltage Cathode Material with a Very Long Cycle Life
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
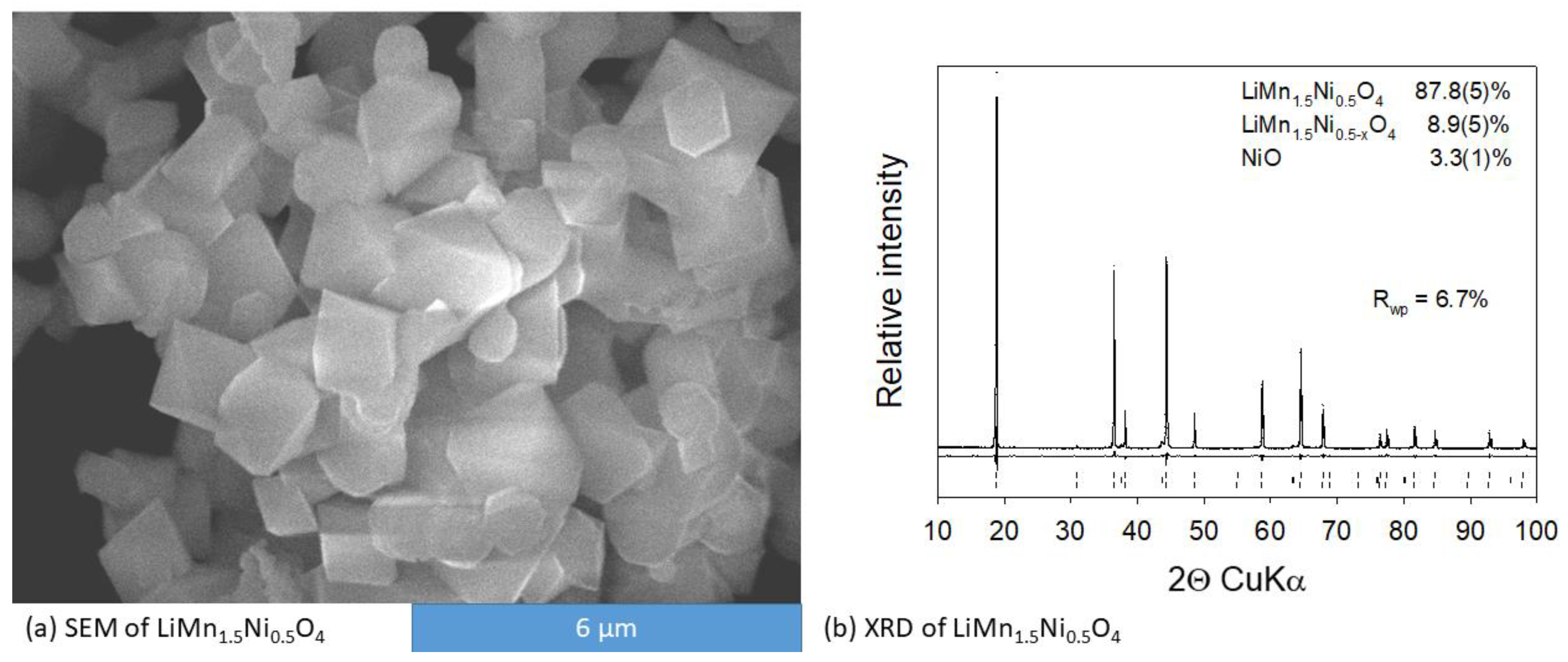
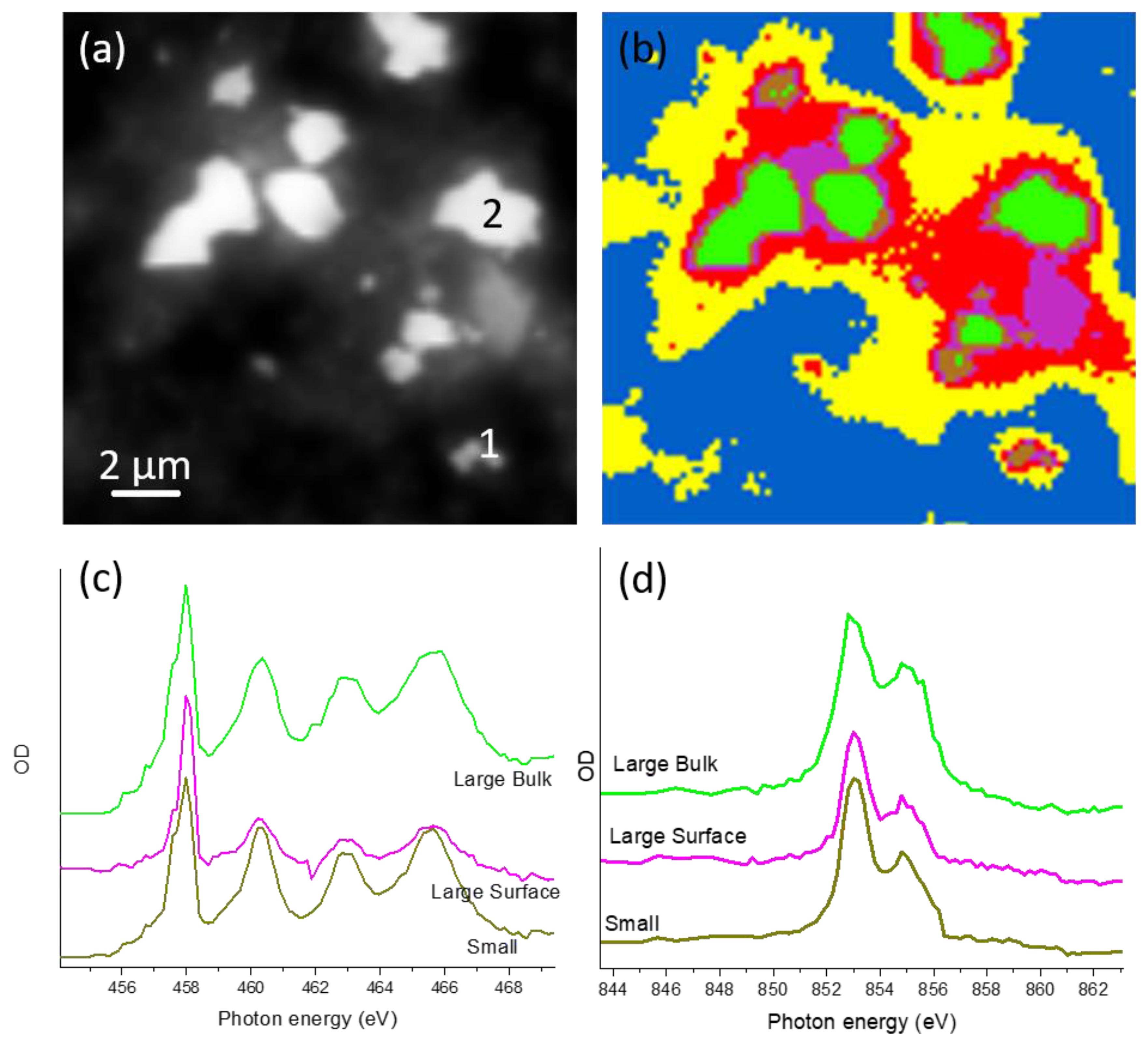
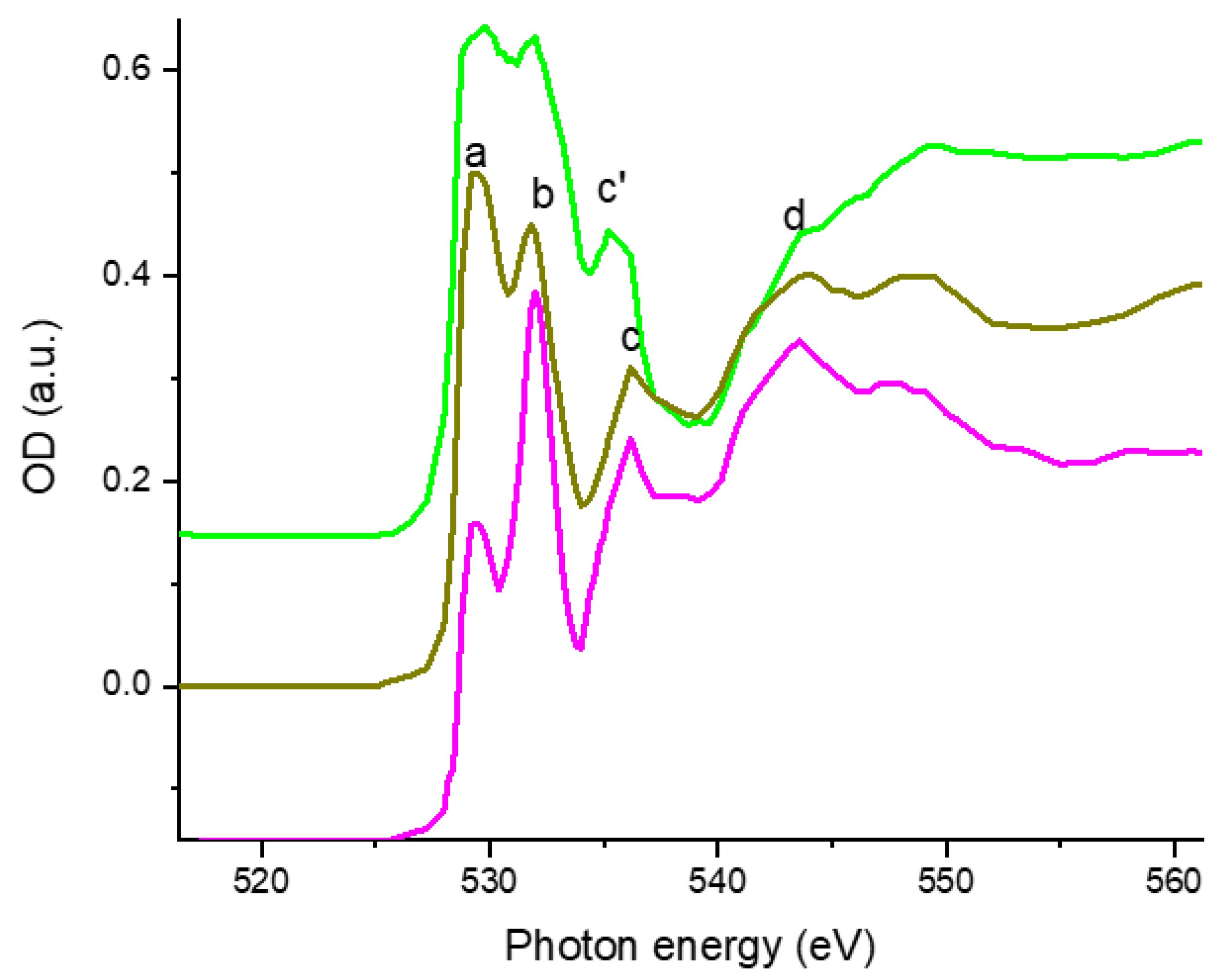
3.1. Characterization of LMNO and LMNTO Materials
The Unsubstituted LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 Cathode Material
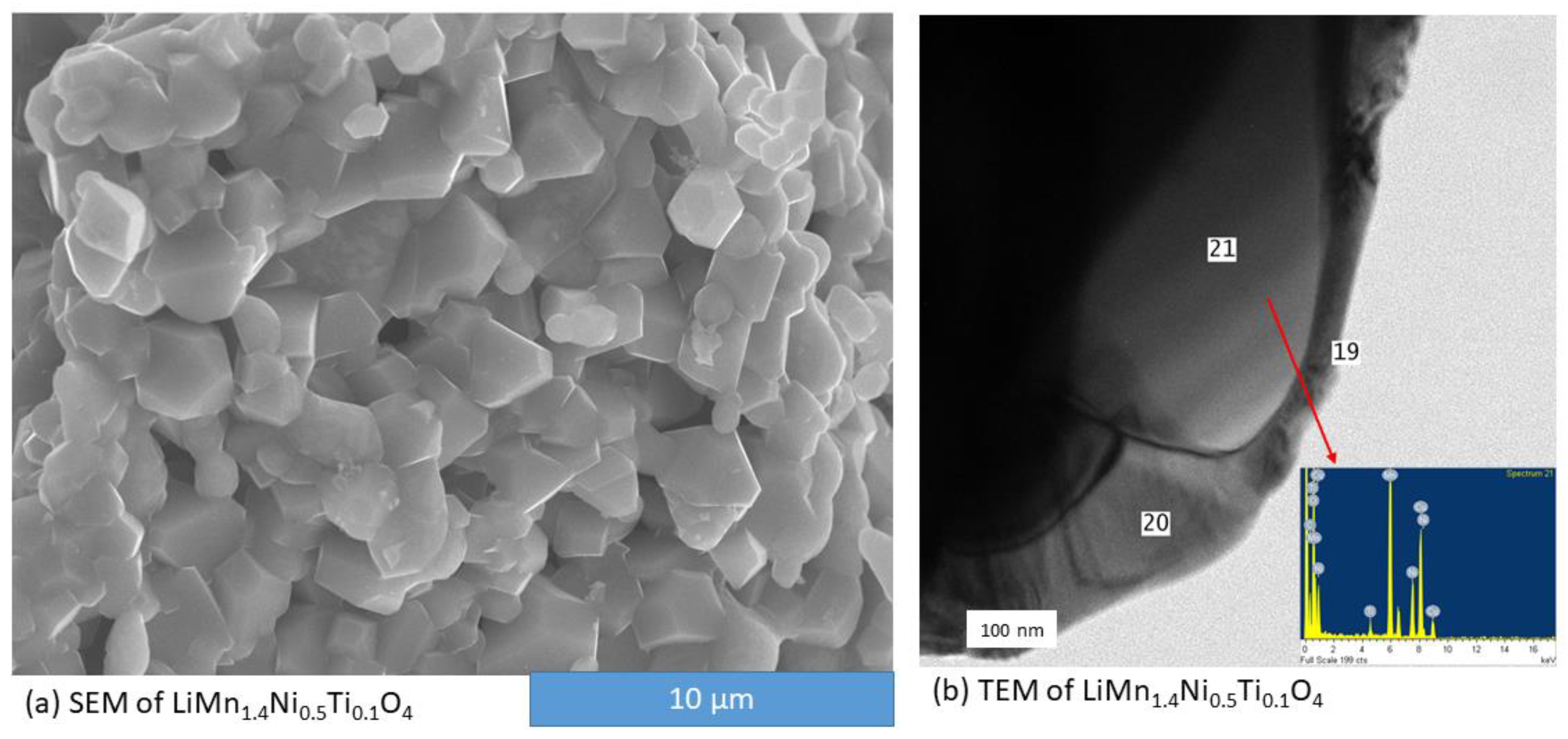
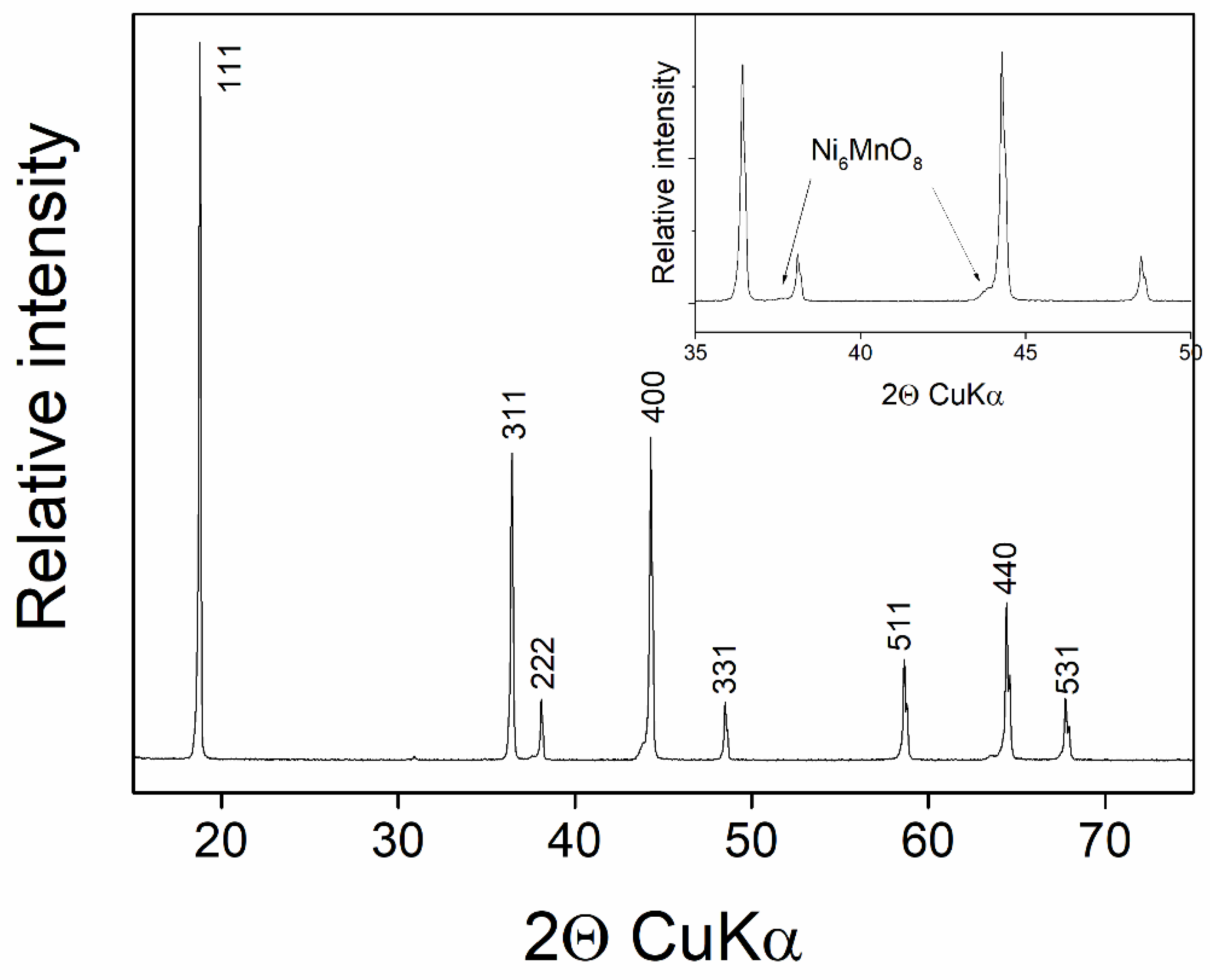
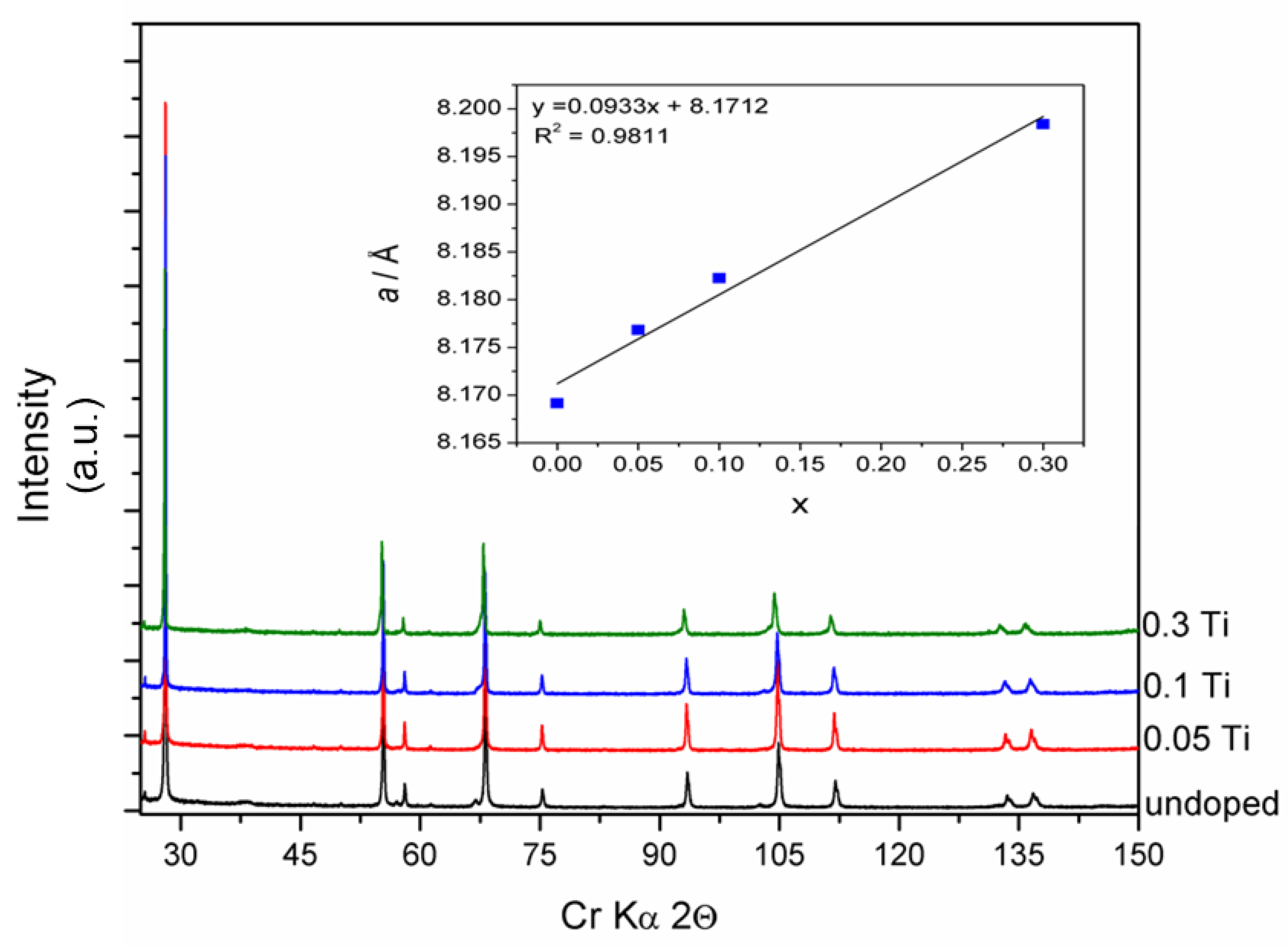
3.2. Ti Substitution of LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 Cathode Material
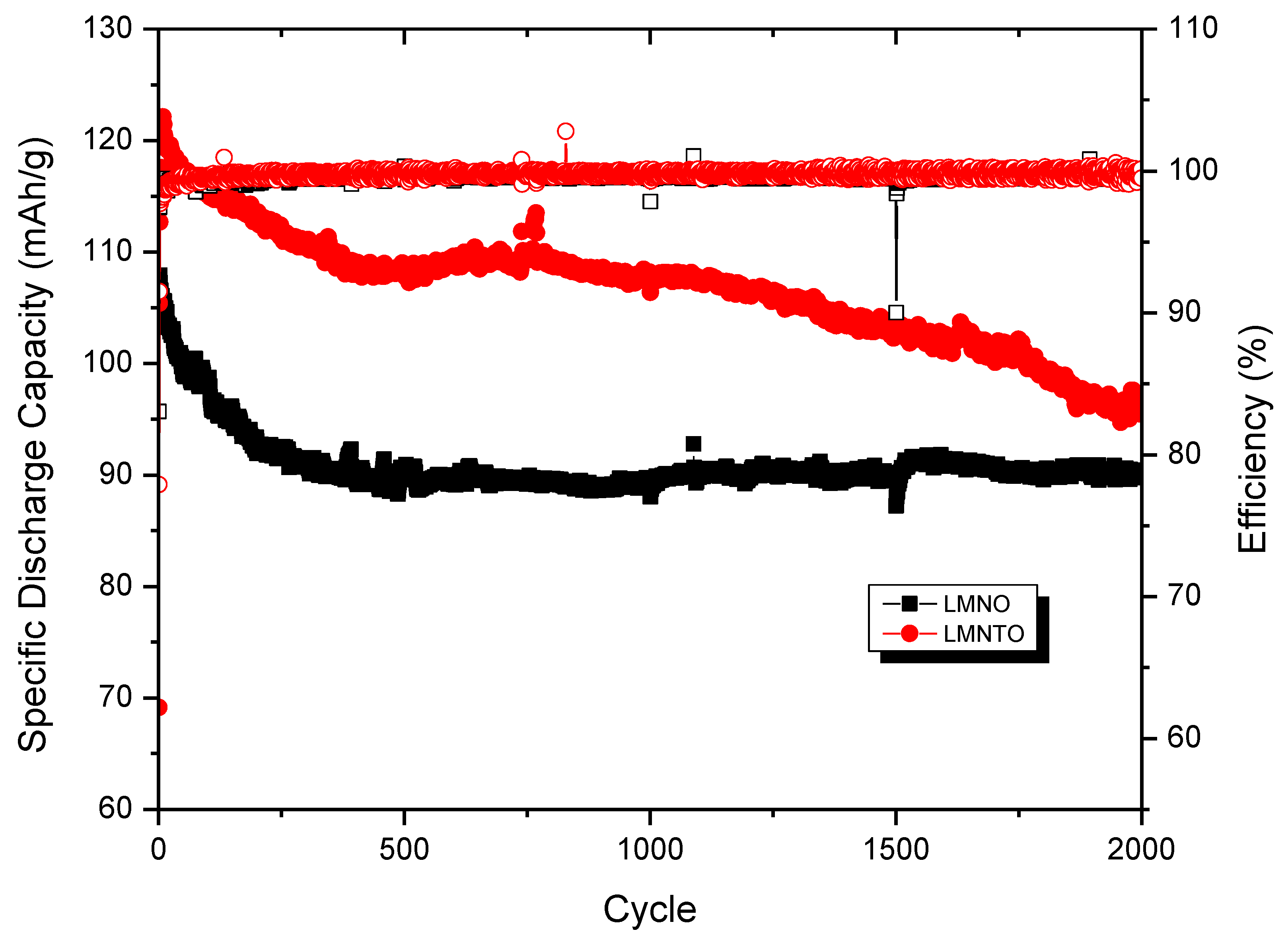
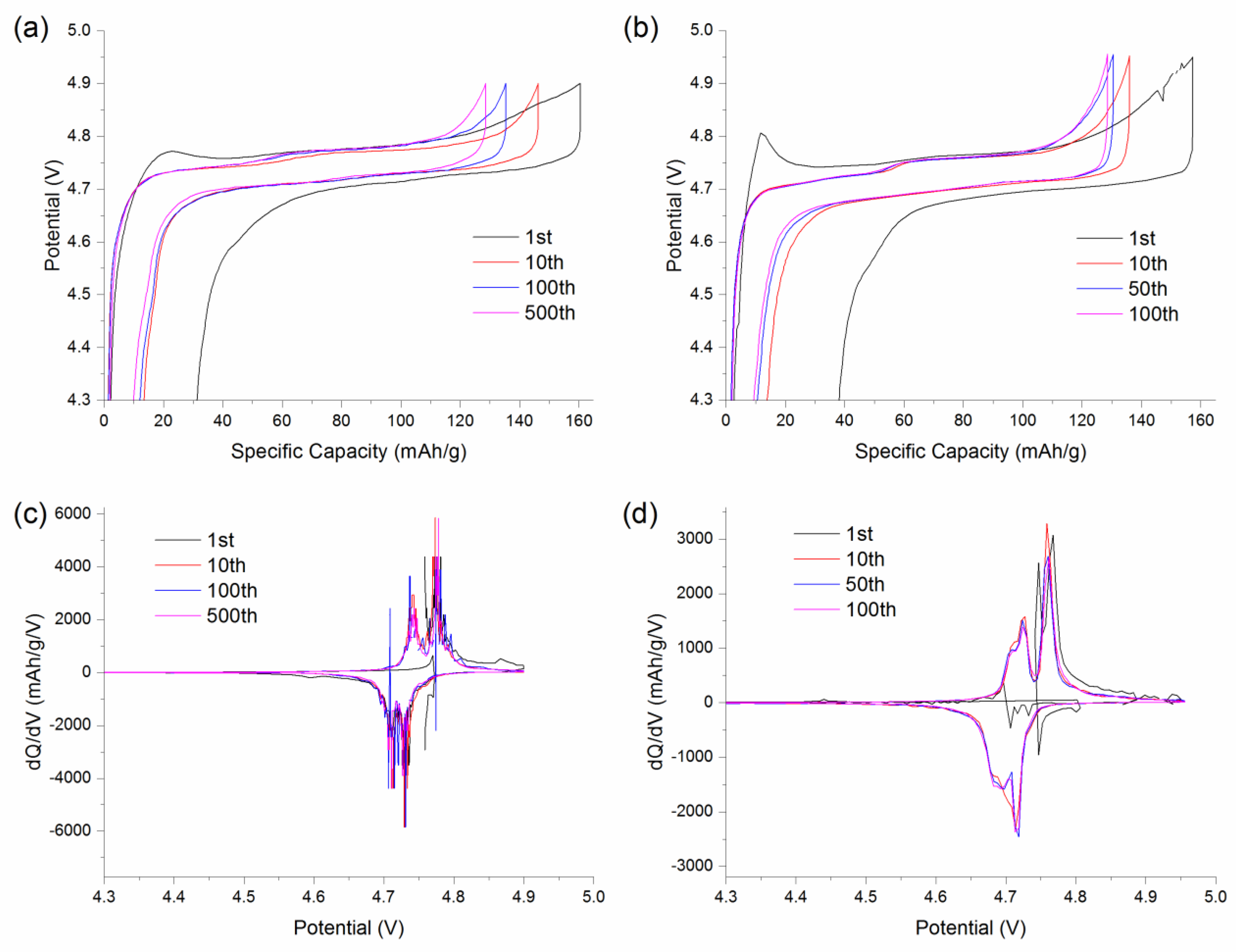
4. Battery Results
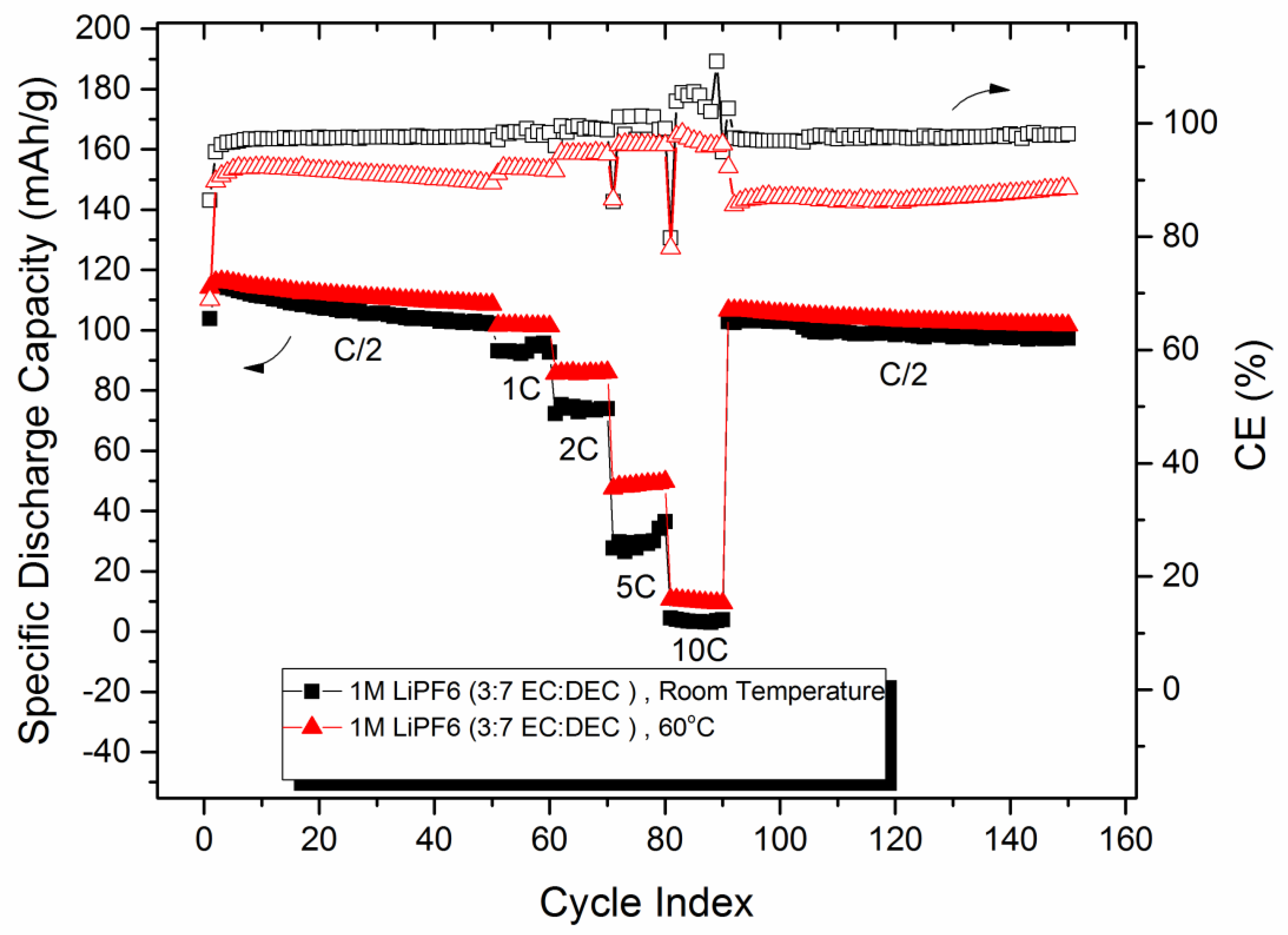
4.1. Half-Cell Testing LMNTO vs. LMNO
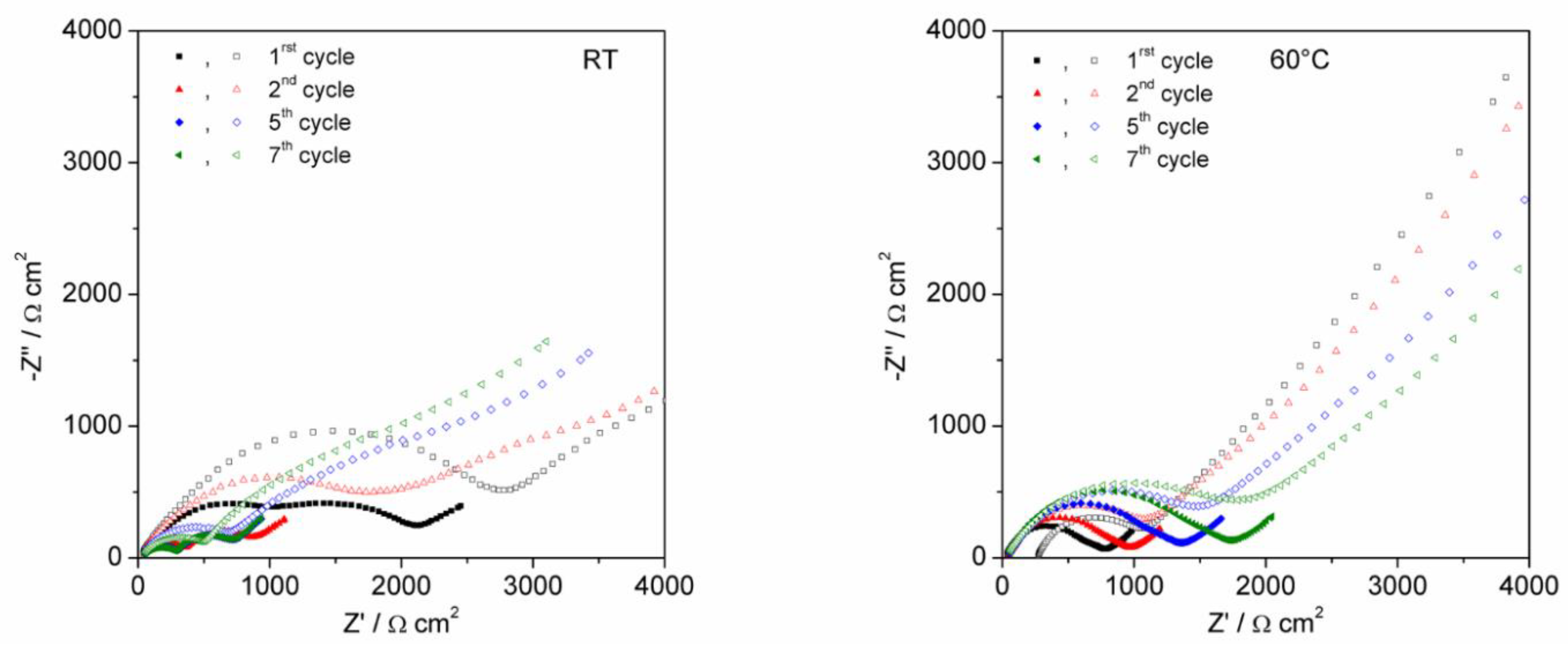
4.2. AC Impedance of Li/LiNi0.5Mn1.4Ti0.1O4 Half Cells
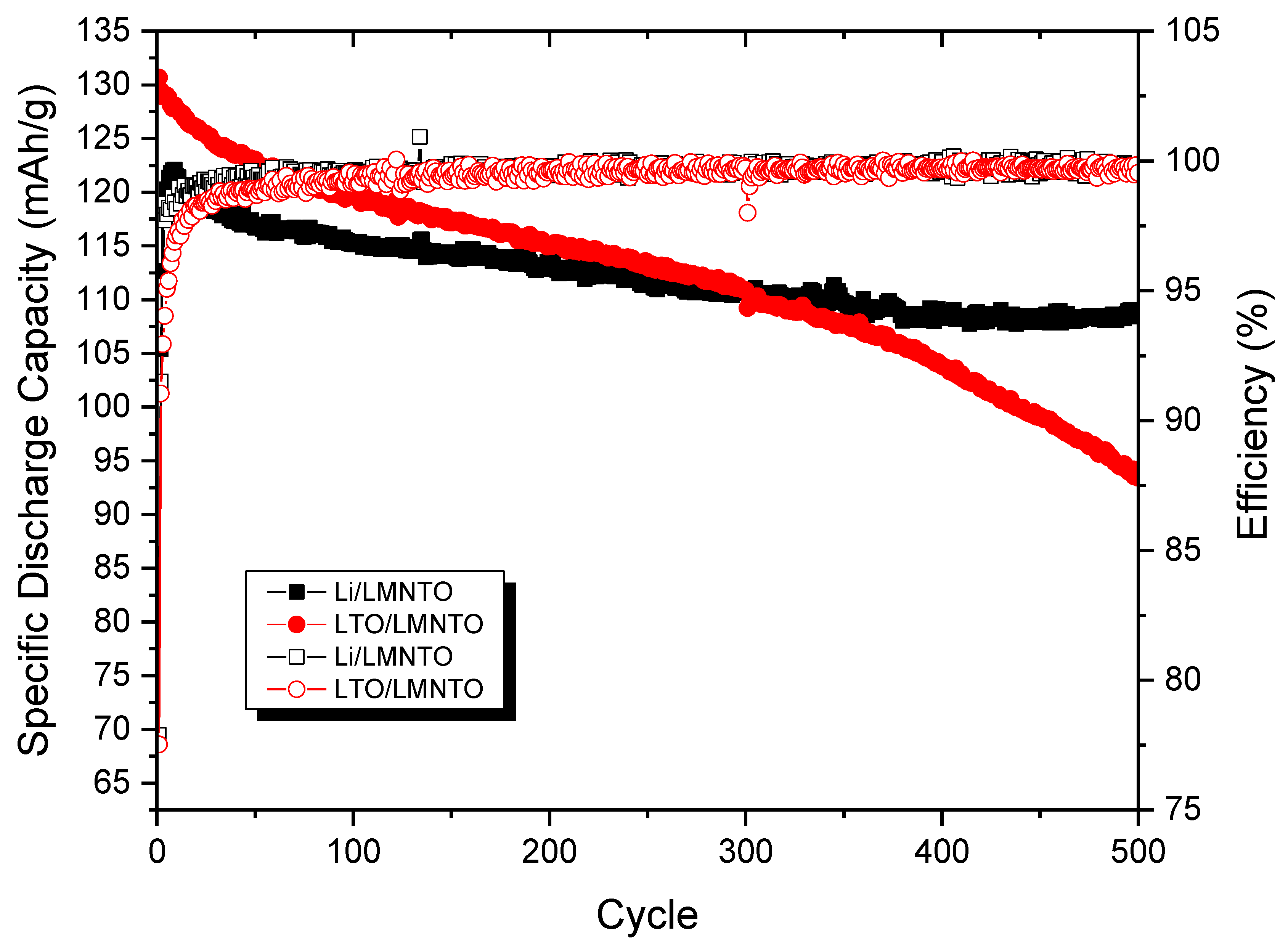
4.3. Full-Cell Testing of LMNTO Cathode with Li Metal and Li4Ti5O12 Anodes
Battery Cycling of Li4Ti5O12//LiNi0.5Mn1.4Ti0.1O4 Full Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amine, K.; Tukamoto, H.; Yasuda, H.; Fujita, Y. A new three-volt spinel Li1+xMn1.5Ni0.5O4 for secondary lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Cruz, M.; Hernán, L.; Melero, M.; Morales, J.; Castellón, E.R. Nanocrystalline materials obtained by using a simple, rapid method for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 150, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Eom, W.S.; Cho, W.I.; Jang, H. Electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode after Cr doping. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ein-Eli, Y.; Urian, R.C.; Wen, W.; Mukerjee, S. Low temperature performance of copper/nickel modified LiMn2O4 spinels. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Nam, K.W.; Kim, K.B.; Chen, G. Spectroscopic studies of the structural properties of Ni substituted spinel LiMn2O4. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduraci, M.; Amatucci, G.G. Effect of oxygen non-stoichiometry and temperature on cation ordering in LiMn2−xNixO4 (0.50 ≥ x ≥ 0.36) spinels. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, T.A.; Manthiram, A. Influence of chromium doping on the electrochemical performance of the 5 V spinel cathode LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 5568–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kim, S.B. Improvement of electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Bonakdarpour, A.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Dahn, J.R. Synthesis and Electrochemistry of LiNixMn2−xO 4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokko, K.; Mohamedi, M.; Anzue, N.; Itoh, T.; Uchida, I. In situ Raman spectroscopic studies of LiNixMn2−xO4 thin film cathode materials for lithium ion secondary batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 3688–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, W. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel compound. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idemoto, Y.; Narai, H.; Koura, N. Crystal structure and cathode performance dependence on oxygen content of LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 as a cathode material for secondary lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2003, 119, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, L.; Li, G. A low-temperature reaction route to high rate and high capacity LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamura, K.; Hoshikawa, W.; Umegaki, T. Electrochemical Characteristics of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathodes with Ti or Al Current Collectors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A339–A345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of 5 V LiNi1/2Mn3/2O4 cathode materials by low-heating solid-state reaction. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarraga, M.G.; Pascual, L.; Gadjov, H.; Kovacheva, D.; Petrov, K.; Amarilla, J.M.; Rojas, R.M.; Martin-Luengo, M.A.; Rojo, J.M. Nanosize LiNiyMn2−yO4 (0 < y ≤ 0.5) spinels synthesized by a sucrose-aided combustion method. Characterization and electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarilla, J.M.; Rojas, R.M.; Pico, F.; Pascual, L.; Petrov, K.; Kovacheva, D.; Lazarraga, M.G.; Lejona, I.; Rojo, J.M. Nanosized LiMYMn2−YO4 (M = Cr, Co and Ni) spinels synthesized by a sucrose-aided combustion method: Structural characterization and electrochemical properties. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, A.B.; Corsini, M.; Fedi, S.; Zanello, P.; Lesnikowski, Z.J. Nucleoside–metallacarborane conjugates for multipotential electrochemical coding of DNA. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Myung, S.T.; Sun, Y.K. Molten salt synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel for 5 V class cathode material of Li-ion secondary battery. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Sun, Y.-K. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of 5 V spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-H.; Goodenough, J.B.; Rabenberg, L.K. Nanocrystalline Lithium Manganese Oxide Spinel Cathode for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, A49–A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.-F.; Hu, X.-G. Preparation and characterization of sub-micro LiNi0.5−xMn1.5+xO4 for 5 V cathode materials synthesized by an ultrasonic-assisted co-precipitation method. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduraci, M.; Al-Sharab, J.F.; Amatucci, G.G. High-Power Nanostructured LiMn2−xNixO4 High-Voltage Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode Materials: Electrochemical Impact of Electronic Conductivity and Morphology. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelder, E.M.; Ooms, F.J.B.; Perego, R.; Schoonman, J. Li1+δMn2−δO4 performance measured by leaching. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduraci, M.; Amatucci, G.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanostructured 4.7 V LixMn1.5Ni0.5O4 Spinels for High-Power Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A1345–A1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niketic, S.; Couillard, M.; MacNeil, D.; Abu-Lebdeh, Y. Improving the performance of high voltage LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 cathode material by carbon coating. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wang, S.H.; Gong, Z.L.; Huang, X.K.; Yang, Y. A Strategy to Improve Cyclic Performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 in a Wide Voltage Region by Ti-Doping. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A3036–A3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, R.; Jaraba, M.; Lavela, P.; Tirado, J.L.; Biensan, P.; de Guibert, A.; Jordy, C.; Peres, J.P. Structural and Electrochemical Study of New LiNi0.5TixMn1.5−xO4 Spinel Oxides for 5 V Cathode Materials. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2376–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-Z.; Lv, Y.-Z.; Xue, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.-G.; Wang, Z.-B. Improved electrochemical performance of LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 as cathode of lithium ion battery by carbon-coating. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57041–57047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Pieczonka, N.P.W.; Sun, Y.-K.; Powell, B.R. Improved lithium-ion battery performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5−xTixO4 high voltage spinel in full-cells paired with graphite and Li4Ti5O12 negative electrodes. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höweling, A.; Glatthaar, S.; Nötzel, D.; Binder, J.R. Evidence of loss of active lithium in titanium-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawley, G. Unit-cell refinement from powder diffraction scans. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1981, 14, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H. Line profiles of neutron powder-diffraction peaks for structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr. 1967, 22, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uceda, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Gauvin, R.; Zaghib, K.; Demopoulos, G.P. Highly conductive NMP-free carbon-coated nano-lithium titanate/carbon composite electrodes via SBR-assisted electrophoretic deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, J.; Fang, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J. Unexpected phase separation in Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4 within a porous composite electrode. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4152–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hong, D.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Xie, X.; Fang, H. Electronic structure variation of the surface and bulk of a LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode as a function of state of charge: X-ray absorption spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13838–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Fang, H.; Maley, J.; Murphy, M.; Ko, J.P.; Cutler, J.; Sammynaiken, R.; Sham, T.; Liu, M.; Li, F. Electronic structure of TiO2 nanotube arrays from X-ray absorption near edge structure studies. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6804–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref | x | Synthesis Method | Electrolyte | Full Cell | Long Term Cycling | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | <0.6 | Solid-state | EC: DMC | - | 100 | 60 °C |
| [28] | 0.05–0.6 (battery test 0.05, 0.2) | Precipitation | EC:DEC | - | <5 | - |
| [29] | 0.1 (Carbon coating) | Solid-state | EC:DMC | - | <1000 | 55 °C |
| [30] | 0.3 | Solid-state | EC:EMC | Graphite/LMNO LTO/LMNO | <200 | 45 °C |
| [31] | 0.02 | Spray pyrolysis | EC:DMC | Graphite/LMNO | <200 | 25 °C |
| THIS WORK | 0.1 | Modified sol-gel | EC:DMC EC:DEC | LTO/LMNO | >2000 | 25 °C 60 °C 25 °C 60 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niketic, S.; Yim, C.-H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Abu-Lebdeh, Y. Influence of Ti Substitution on Electrochemical Performance and Evolution of LiMn1.5−x Ni0.5TixO4 (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.3) as a High Voltage Cathode Material with a Very Long Cycle Life. Inorganics 2022, 10, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10010010
Niketic S, Yim C-H, Zhou J, Wang J, Abu-Lebdeh Y. Influence of Ti Substitution on Electrochemical Performance and Evolution of LiMn1.5−x Ni0.5TixO4 (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.3) as a High Voltage Cathode Material with a Very Long Cycle Life. Inorganics. 2022; 10(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiketic, Svetlana, Chae-Ho Yim, Jigang Zhou, Jian Wang, and Yaser Abu-Lebdeh. 2022. "Influence of Ti Substitution on Electrochemical Performance and Evolution of LiMn1.5−x Ni0.5TixO4 (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.3) as a High Voltage Cathode Material with a Very Long Cycle Life" Inorganics 10, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10010010
APA StyleNiketic, S., Yim, C.-H., Zhou, J., Wang, J., & Abu-Lebdeh, Y. (2022). Influence of Ti Substitution on Electrochemical Performance and Evolution of LiMn1.5−x Ni0.5TixO4 (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.3) as a High Voltage Cathode Material with a Very Long Cycle Life. Inorganics, 10(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10010010







