Effect of the (Nd,Dy)-Double Doping on the Structural Properties of Ceria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
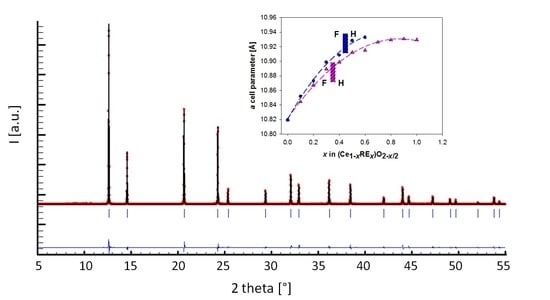
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis
4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy–Energy-Dispersive System (SEM-EDS)
4.3. Synchrotron X-Ray Powder Diffraction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Artini, C. RE-doped ceria systems and their performance as solid electrolytes: A puzzling tangle of structural issues at the average and local scale. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 13047–13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, B.C.H. Appraisal of Ce1−yGdyO2−y/2 electrolytes for IT-SOFC operation at 500 °C. Solid State Ion. 2000, 129, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presto, S.; Artini, C.; Pani, M.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Massardo, S.; Viviani, M. Ionic conductivity and local structural features in Ce1−xSmxO2−x/2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 28338–28345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coduri, M.; Scavini, M.; Pani, M.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Klein, H.; Artini, C. From nano to microcrystals: Effect of different synthetic pathways on defects architecture in heavily Gd-doped ceria. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11612–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraynis, O.; Timoshenko, J.; Huang, J.; Singh, H.; Wachtel, E.; Frenkel, A.I.; Lubomirsky, I. Modeling strain distribution at the atomic level in doped ceria films with extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7527–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, C.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Costa, G.A.; Plaisier, J.R.; Pani, M. A novel method for the evaluation of the Rare Earth (RE) coordination number in RE-doped ceria through Raman spectroscopy. Solid State Ion. 2017, 311, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Costa, G.A.; Pani, M.; Lausi, A.; Plaisier, J. Structural characterization of the CeO2/Gd2O3 mixed system by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 190, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Pani, M.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Buscaglia, M.T.; Plaisier, J.; Costa, G.A. Structural features of Sm- and Gd-doped ceria studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction and μ-Raman spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 4126–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, C.; Joseph, B.; Costa, G.A.; Pani, M. Crystallographic properties of Lu-doped ceria, Ce1−xLuxO2−x/2, at pressures up to 7 GPa. Solid State Ion. 2018, 320, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Pani, M.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Plaisier, J.R.; Costa, G.A. Lu-, Sm- and Gd-doped ceria: A comparative approach to their structural properties. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 10567–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Pani, M.; Lausi, A.; Masini, R.; Costa, G.A. High temperature structural study of Gd-doped ceria by synchrotron X-ray diffraction (673 K ≤ T ≤ 1073 K). Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 10140–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, C.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Viviani, M.; Presto, S.; Plaisier, J.R.; Costa, G.A.; Pani, M. Structural properties of Sm-doped ceria electrolytes at the fuel cell operating temperatures. Solid State Ion. 2018, 315, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Nelli, I.; Pani, M.; Costa, G.A.; Caratto, V.; Locardi, F. Thermal decomposition of Ce-Sm and Ce-Lu mixed oxalates: Influence of the Sm- and Lu-doped ceria structure. Thermochimica Acta 2017, 651, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavini, M.; Coduri, M.; Allieta, M.; Brunelli, M.; Ferrero, C. Probing complex disorder in Ce1−xGdxO2−x/2 using the pair distribution function analysis. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coduri, M.; Masala, P.; Allieta, M.; Peral, I.; Brunelli, M.; Biffi, C.A.; Scavini, M. Phase transformations in the CeO2-Sm2O3 system: A multiscale powder diffraction investigation. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuharuangrong, S. Ionic conductivity of Sm, Gd, Dy- and Er-doped ceria. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.; Wachsman, E.D.; Jones, J.L.; Nino, J.C. Crystal structure-ionic conductivity relationships in doped ceria. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, A.; Rajagopalan, R.; Hassan Tanveer, W.; Yu, W.; Cha, S.W.; Krishna Moorthy, S.B. Scalable lattice-strain in preferentially oriented acceptor-doped ceria oxide film and its impact on oxygen ion transport kinetics. Electrochem. Acta 2018, 264, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhabu, K.A.; Theertagiri, J.; Madhavan, J.; Balu, T.; Rajasekaran, T.R. Superior oxide ion conductivity of novel acceptor doped cerium oxide electrolytes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 18452–18461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, A32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Agli, G.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Pansini, M.; Accardo, G.; Yoon, S.P.; Frattini, D. Effect of the carbonate environment on morphology and sintering behaviour of variously co-doped (Ca, Sr, Er, Pr) Samarium-doped ceria in co-precipitation/hydrothermal synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17935–17944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herle, J.; Seneviratne, D.; Mc Evoy, A.J. Lanthanide co-doping of solid electrolytes: AC conductivity behaviour. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.R.; Ye, F.; Mori, T. Defect clustering and local ordering in rare earth co-doped ceria. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 9554–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbano, M.; Nadin, S.; Marrocchelli, D.; Salanne, M.; Watson, G.M. Ceria co-doping: Synergistic or average effect? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 8320–8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayąc, W.; Molenda, J. Electrical conductivity of doubly doped ceria. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, D. Effect of co-dopant addition on properties of gadolinia-doped ceria electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2000, 90, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles-Aldridge, A.V.; Baker, R.T. Ionic conductivity in multiply substituted ceria-based electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2018, 316, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Shirbhate, S.; Ojha, P.; Acharya, S. Processing and conductivity behavior of La, Sm, Fe singly and double doped ceria: As electrolytes for IT-SOFC. Solid State Ion. 2018, 320, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.; Wachsman, E.; Nino, J. Higher conductivity Sm3+ and Nd3+ co-doped ceria-based electrolyte materials. Solid State Ion. 2008, 178, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, A.; Altınçekiç, T.G.; Der, M.; Öksüzömer, M.A.F. Preparation and properties of ceramic electrolytes in the Nd and Gd Co-doped ceria systems prepared by polyol method. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 792, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.S.; Bauri, R. Rare earth co-doped nanocrystalline ceria eletrolytes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFC). ECS Trans. 2013, 57, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, A. Synthesis and characterization of Pr/Gd co-doped ceria by using the citric acid–nitrate combustion method. Solid State Ion. 2018, 326, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, A.; Sariboğa, V.; Őksüzőmer, M.A.F. Er and Gd co-doped ceria-based electrolyte materials for IT-SOFCs prepared by the cellulose-templating method. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5259–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuri, C.; Venkataramana, K.; Nurhayati, A.; Vishnuvardhan Reddy, C. Effect of La3+ and Pr3+ co-doping on structural, thermal and electrical properties of ceria ceramics as solid electrolytes for IT-SOFC applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramana, K.; Madhuri, C.; Madhusudan, C.; Suresh Reddy, Y.; Bhikshamaiah, G.; Vishnuvardhan Reddy, C. Investigation on La3+ and Dy3+ co-doped ceria ceramics with an optimized average atomic number of dopants for electrolytes in IT-SOFCs. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 6300–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlait, D.; Claparède, L.; Clavier, N.; Szencnekt, S.; Dacheux, N.; Ravaux, J.; Podor, R. Stability and structural evolution of CeIV1−xLnIIIxO2−x/2 solid solutions: A coupled μ-Raman/XRD approach. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minervini, L.; Zacate, M.O.; Grimes, R.W. Defect cluster formation in M2O3-doped CeO2. Solid State Ion. 1999, 116, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Mori, T.; Ou, D.R.; Cormack, A.N. Dopant type dependency of domain development in rare earth-doped ceria: An explanation by computer simulation of defect clusters. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H. Insight into the Mechanism of the Ionic Conductivity for Ln-Doped Ceria (Ln = La, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, and Tm) through First-Principles Calculation. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12690–12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, C.; Costa, G.A.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Masini, R. Stability fields and structural properties of intra rare earths perovskites. J. Alloy Compd. 2010, 494, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, C.; Costa, G.A.; Masini, R. Study of the formation temperature of mixed LaREO3 (RE≡Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) and NdGdO3 oxides. J. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample Name | x | RB a | χ2 b |
|---|---|---|---|
| NdDy10 | 0.09(1) | 2.27 | 1.70 |
| NdDy20 | 0.19(2) | 1.81 | 1.80 |
| NdDy30 | 0.29(7) | 2.55 | 1.73 |
| NdDy40 | 0.37(6) | 2.74 | 1.73 |
| NdDy50 | 0.47(9) | 9.73 | 1.45 |
| NdDy60 | 0.58(5) | 9.79 | 2.73 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Artini, C.; Gigli, L.; Carnasciali, M.M.; Pani, M. Effect of the (Nd,Dy)-Double Doping on the Structural Properties of Ceria. Inorganics 2019, 7, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7080094
Artini C, Gigli L, Carnasciali MM, Pani M. Effect of the (Nd,Dy)-Double Doping on the Structural Properties of Ceria. Inorganics. 2019; 7(8):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7080094
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtini, Cristina, Lara Gigli, Maria Maddalena Carnasciali, and Marcella Pani. 2019. "Effect of the (Nd,Dy)-Double Doping on the Structural Properties of Ceria" Inorganics 7, no. 8: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7080094
APA StyleArtini, C., Gigli, L., Carnasciali, M. M., & Pani, M. (2019). Effect of the (Nd,Dy)-Double Doping on the Structural Properties of Ceria. Inorganics, 7(8), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7080094