Investigating the Factors Affecting the Ionic Conduction in Nanoconfined NaBH4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Infiltration of NaBH4 in MCM-41
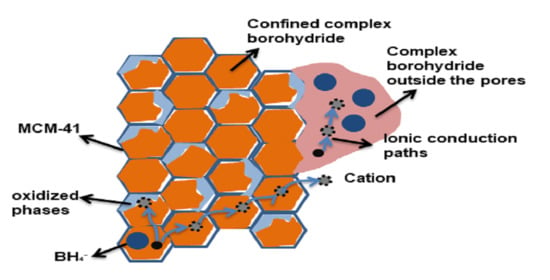
2.2. Ionic Conductivity of Nanoconfined NaBH4
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. Synthesis of the Nanoconfined Complex Borohydrides
3.1.2. Synthesis of the Mixture of NaBH4 and Na2B12H12 Was via Solid–Gas Reaction
3.2. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachman, J.C.; Muy, S.; Grimaud, A.; Chang, H.-H.; Pour, N.; Lux, S.F.; Paschos, O.; Maglia, F.; Lupart, S.; Lamp, P.; et al. Inorganic solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: Mechanisms and properties governing ion conduction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Qi, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L. Solid-State Sodium Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, G.-Y.; Imanaka, N.; Tamura, S. Ionic Conducting Lanthanide Oxides. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 2405–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, K.; Hong, Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Interfaces between Cathode and Electrolyte in Solid State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Perspectives. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, Y.; Hori, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, M.; Mitsui, A.; Yonemura, M.; Iba, H.; Kanno, R. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, A.; Hayashi, A.; Tatsumisago, M. Sulfide Solid Electrolyte with Favorable Mechanical Property for All-Solid-State Lithium Battery. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-J.; Yoon, K.; Park, I.; Kang, K. Progress in the Development of Sodium-Ion Solid Electrolytes. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Liang, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Whiteley, J.; Dong, H.; Hu, P.; Lee, S.; Yao, Y. Tailored Organic Electrode Material Compatible with Sulfide Electrolyte for Stable All-Solid-State Sodium Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2630–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ciucci, F. Metal Borohydrides as Electrolytes for Solid-State Li, Na, Mg, and Ca Batteries: A First-Principles Study. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9308–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.; Nale, A.; Sveinbjörnsson, D.; Eggenhuisen, T.M.; Verkuijlen, M.H.; Suwarno; Vegge, T.; Kentgens, A.P.M.; de Jongh, P.E. Nanoconfined LiBH4 as a Fast Lithium Ion Conductor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Kuromoto, S.; Sato, T.; Oguchi, H.; Takamura, H.; Orimo, S.-I. Sodium ionic conduction in complex hydrides with [BH4]− and [NH2]− anions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 203904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, M.; Takamura, H.; Maekawa, H.; Li, H.-W.; Orimo, S.-I. Stabilization of lithium superionic conduction phase and enhancement of conductivity of LiBH4 by LiCl addition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 084103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, V.; Brighi, M.; Dematteis, E.M.; Murgia, F.; Nervi, C.; Černý, R.; Baricco, M. Phase Stability and Fast Ion Conductivity in the Hexagonal LiBH4–LiBr–LiCl Solid Solution. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5133–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verkuijlen, M.H.W.; Ngene, P.; de Kort, D.W.; Barré, C.; Nale, A.; van Eck, E.R.H.; van Bentum, P.J.M.; de Jongh, P.E.; Kentgens, A.P.M. Nanoconfined LiBH4 and Enhanced Mobility of Li+ and BH4− Studied by Solid-State NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22169–22178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambregts, S.F.H.; van Eck, E.R.H.; Suwarno; Ngene, P.; de Jongh, P.E.; Kentgens, A.P.M. Phase Behavior and Ion Dynamics of Nanoconfined LiBH4 in Silica. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 25559–25569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, T.; Ling, S.; Rui, K.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, X. Borohydride-Scaffolded Li/Na/Mg Fast Ionic Conductors for Promising Solid-State Electrolytes. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Ngene, P.; Norby, P.; Vegge, T.; de Jongh, P.E.; Blanchard, D. All-Solid-State Lithium–Sulfur Battery Based on a Nanoconfined LiBH4 Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A2029–A2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, S.; Okuda, K.; Machida, N.; Naito, M.; Sigematsu, T. All-solid-state lithium battery with sulfur/carbon composites as positive electrode materials. Solid State Ion. 2014, 256, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lou, X.W. Metal Oxide Hollow Nanostructures for Lithium-ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, B.P.; Do-Thanh, C.-L.; Jafta, C.J.; Tao, R.; Lyu, H.; Borisevich, A.Y.; Yang, S.-Z.; Sun, X.-G.; Dai, S. Simultaneously Boosting the Ionic Conductivity and Mechanical Strength of Polymer Gel Electrolyte Membranes by Confining Ionic Liquids into Hollow Silica Nanocavities. Batter. Supercaps 2019, 2, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Tian, L.; Xiao, J.; Cui, R.; Liu, Z. Significantly enhancing the lithium-ion conductivity of solid-state electrolytes via a strategy for fabricating hollow metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14629–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łodziana, Z.; Błoński, P. Structure of nanoconfined LiBH4 from first principles 11B NMR chemical shifts calculations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9842–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remhof, A.; Mauron, P.; Züttel, A.; Embs, J.P.; Łodziana, Z.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Ngene, P.; de Jongh, P. Hydrogen Dynamics in Nanoconfined Lithiumborohydride. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rawal, A.; Quadir, M.Z.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. Nanoconfined lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) and hydrogen reversibility. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 14144–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettl, R.; de Kort, L.; Gombotz, M.; Wilkening, H.M.R.; de Jongh, P.E.; Ngene, P. Combined Effects of Anion Substitution and Nanoconfinement on the Ionic Conductivity of Li-Based Complex Hydrides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihai, G.D.; Meynen, V.; Mertens, M.; Bilba, N.; Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. ZnO nanoparticles supported on mesoporous MCM-41 and SBA-15: A comparative physicochemical and photocatalytic study. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5786–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosalawit-Utke, R.; Suarez, K.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.M.; Bösenberg, U.; Jensen, T.R.; Cerenius, Y.; Bonatto Minella, C.; Pistidda, C.; Barkhordarian, G.; Schulze, M.; et al. Ca(BH4)2−MgF2 Reversible Hydrogen Storage: Reaction Mechanisms and Kinetic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 3762–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmesser, H.; Kosslick, H.; Storek, W.; Fricke, R. Interior surface hydroxyl groups in ordered mesoporous silicates. Solid State Ion. 1997, 101–103, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.; Shuping, X.; Shiyang, G. FT-IR and Raman spectroscopic study of hydrated borates. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 1995, 51, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElBatal, H.A.; Abdelghany, A.M.; ElBatal, F.H.; EzzElDin, F.M. Gamma rays interactions with WO3− doped lead borate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, L.; Burkholder, T.R. Infrared spectra of molecular B(OH)3 and HOBO in solid argon. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 7203–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.L.; Nik Abdul Khalil, N.N.A.; Islam, A.; Rashid, U.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Sinar Mashuri, S.I.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Preparation of Na2O supported CNTs nanocatalyst for efficient biodiesel production from waste-oil. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngene, P.; Lambregts, S.F.H.; Blanchard, D.; Vegge, T.; Sharma, M.; Hagemann, H.; de Jongh, P.E. The influence of silica surface groups on the Li-ion conductivity of LiBH4/SiO2 nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22456–22466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, J.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Liu, H. Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of NaBH4 Destabilized by CaH2 and Ca(BH4)2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9283–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garroni, S.; Milanese, C.; Pottmaier, D.; Mulas, G.; Nolis, P.; Girella, A.; Caputo, R.; Olid, D.; Teixdor, F.; Baricco, M.; et al. Experimental Evidence of Na2[B12H12] and Na Formation in the Desorption Pathway of the 2NaBH4 + MgH2 System. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16664–16671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łodziana, Z.; Błoński, P.; Yan, Y.; Rentsch, D.; Remhof, A. NMR Chemical Shifts of 11B in Metal Borohydrides from First-Principle Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, A.D.; Holmgren, J.S.; Jonas, J. Solid state 29Si and 11B NMR studies of sol-gel derived borosilicates. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 101, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Bowman, R.C.; Reiter, J.W.; Rijssenbeek; Soloveichik, G.L.; Zhao, J.-C.; Kabbour, H.; Ahn, C.C. NMR Confirmation for Formation of [B12H12]2− Complexes during Hydrogen Desorption from Metal Borohydrides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 3164–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngene, P.; Adelhelm, P.; Beale, A.M.; de Jong, K.P.; de Jongh, P.E. LiBH4/SBA-15 Nanocomposites Prepared by Melt Infiltration under Hydrogen Pressure: Synthesis and Hydrogen Sorption Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6163–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Rawal, A.; Cazorla, C.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. Facile Self-Forming Superionic Conductors Based on Complex Borohydride Surface Oxidation. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 1900113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigadlo, N.D.; Zhang, M.; Salje, E.K.H. An infrared spectroscopic study of Li2B4O7. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2001, 13, 6551–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikin, Y.; Brighi, M.; Schouwink, P.; Černý, R. Superionic conduction of sodium and lithium in anion-mixed hydroborates Na3BH4B12H12 and (Li0.7Na0.3)3BH4B12H12. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngene, P.; van den Berg, R.; Verkuijlen, M.H.W.; de Jong, K.P.; de Jongh, P.E. Reversibility of the hydrogen desorption from NaBH4 by confinement in nanoporous carbon. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4108–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caputo, R.; Garroni, S.; Olid, D.; Teixidor, F.; Surinach, S.; Baro, M.D. Can Na2[B12H12] be a decomposition product of NaBH4? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 15093–15100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udovic, T.J.; Matsuo, M.; Unemoto, A.; Verdal, N.; Stavila, V.; Skripov, A.V.; Rush, J.J.; Takamura, H.; Orimo, S.-i. Sodium superionic conduction in Na2B12H12. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3750–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Kaup, K.; Zhou, L.; Roy, P.-N.; Nazar, L.F. Targeting Superionic Conductivity by Turning on Anion Rotation at Room Temperature in Fast Ion Conductors. Matter 2020, 2, 1667–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Roy, P.-N.; Li, H.; Avdeev, M.; Nazar, L.F. Coupled Cation–Anion Dynamics Enhances Cation Mobility in Room-Temperature Superionic Solid-State Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19360–19372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, K.E.; Varley, J.B.; Shea, P.; Adelstein, N.; Mehta, P.; Heo, T.W.; Udovic, T.J.; Stavila, V.; Wood, B.C. Structural, Chemical, and Dynamical Frustration: Origins of Superionic Conductivity in closo-Borate Solid Electrolytes. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9142–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, L.; Narisano, E.; Riva, R.; Baxter, E.W. Lithium borohydride. In Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiot, D.; Fayon, F.; Capron, M.; King, I.; Le Calvé, S.; Alonso, B.; Durand, J.-O.; Bujoli, B.; Gan, Z.; Hoatson, G. Modelling one- and two-dimensional solid-state NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2002, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Rawal, A.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. Investigating the Factors Affecting the Ionic Conduction in Nanoconfined NaBH4. Inorganics 2021, 9, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9010002
Luo X, Rawal A, Aguey-Zinsou K-F. Investigating the Factors Affecting the Ionic Conduction in Nanoconfined NaBH4. Inorganics. 2021; 9(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xiaoxuan, Aditya Rawal, and Kondo-Francois Aguey-Zinsou. 2021. "Investigating the Factors Affecting the Ionic Conduction in Nanoconfined NaBH4" Inorganics 9, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9010002
APA StyleLuo, X., Rawal, A., & Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. (2021). Investigating the Factors Affecting the Ionic Conduction in Nanoconfined NaBH4. Inorganics, 9(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9010002