Regeneration of Buccal Wall Defects after Tooth Extraction with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Injectable Form vs. Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
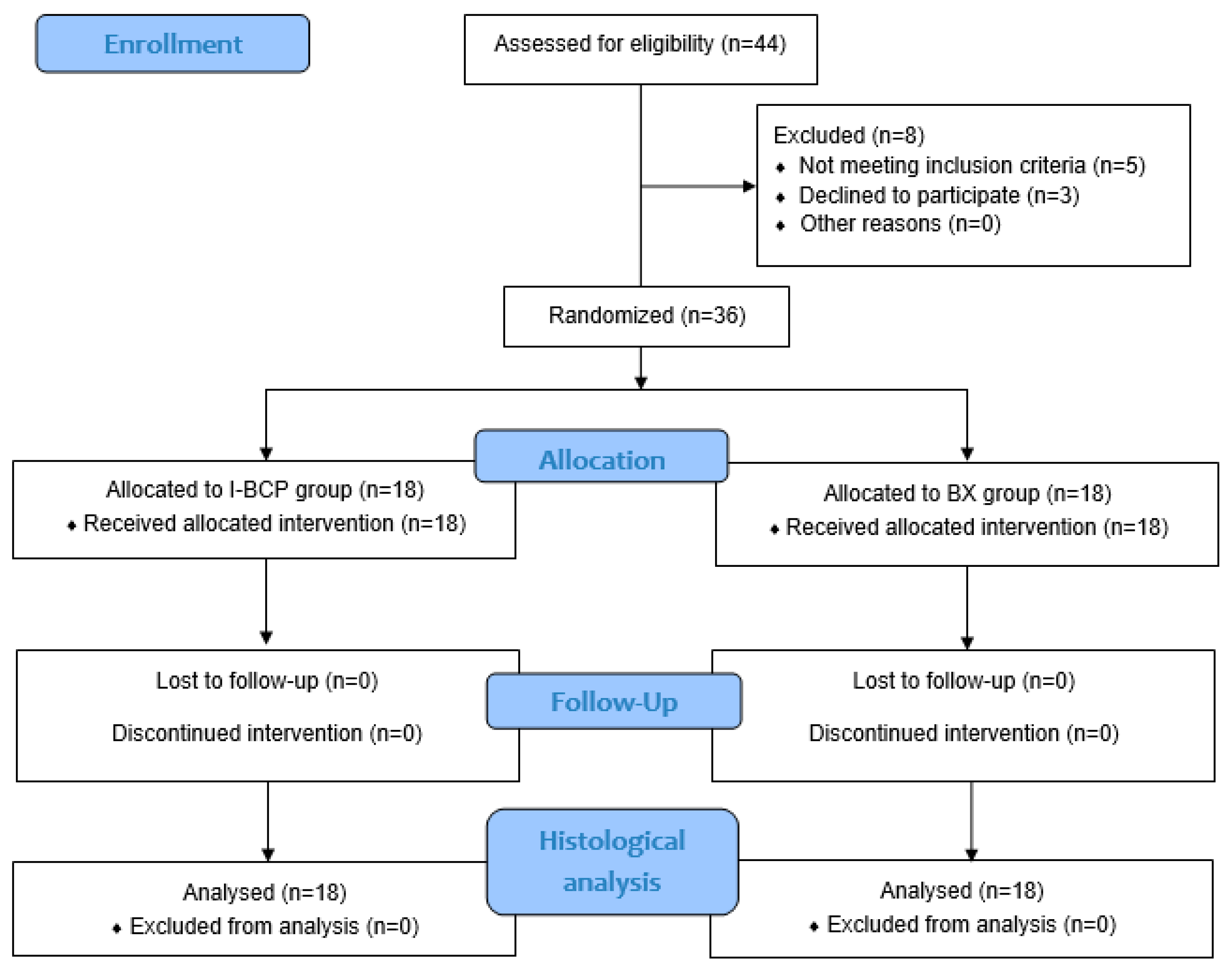
2.2. Study Design, Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Participants and Materials
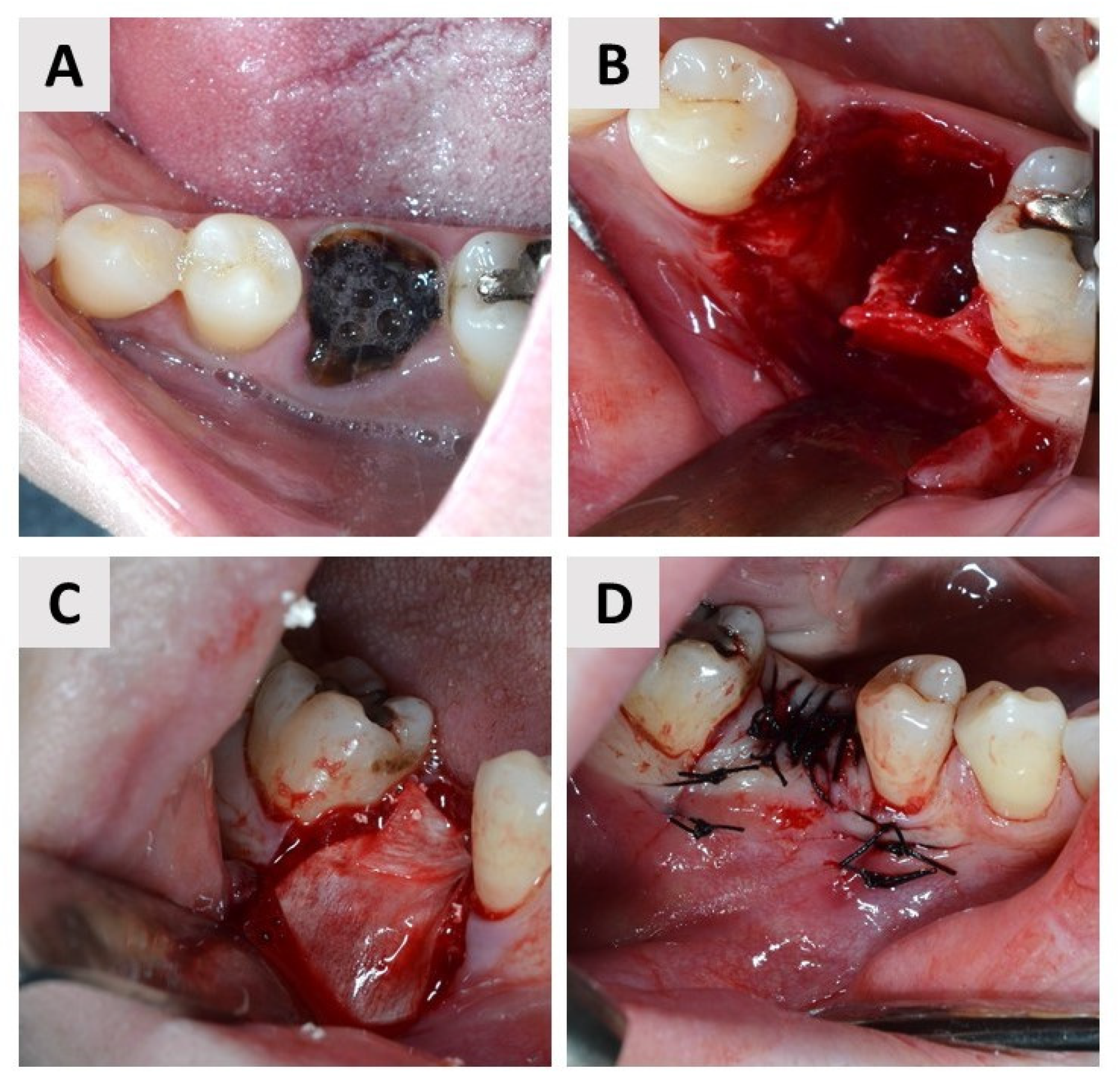
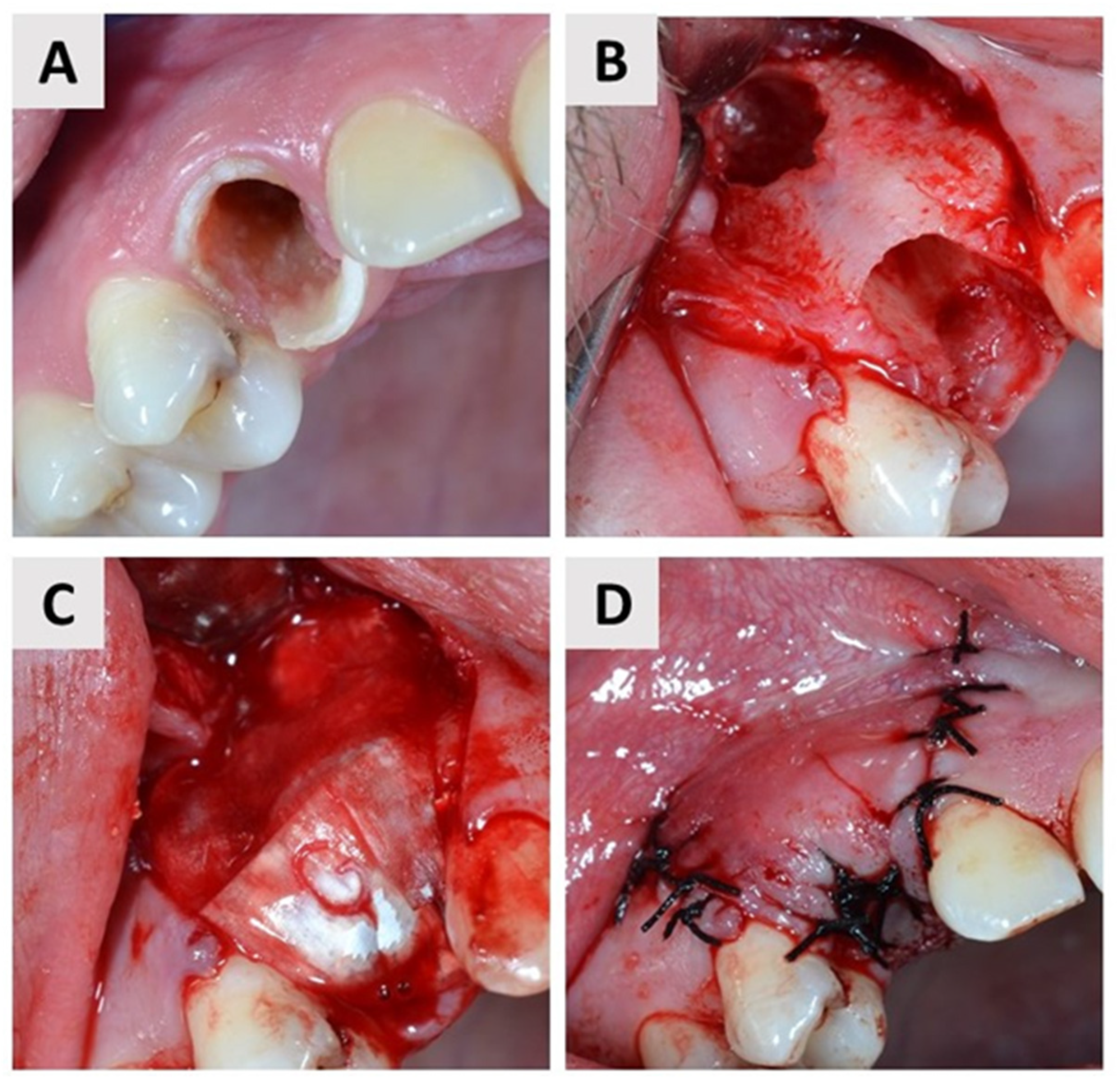
2.4. First Surgical Phase and Healing Period
2.5. Second Surgical Phase
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Histological Findings
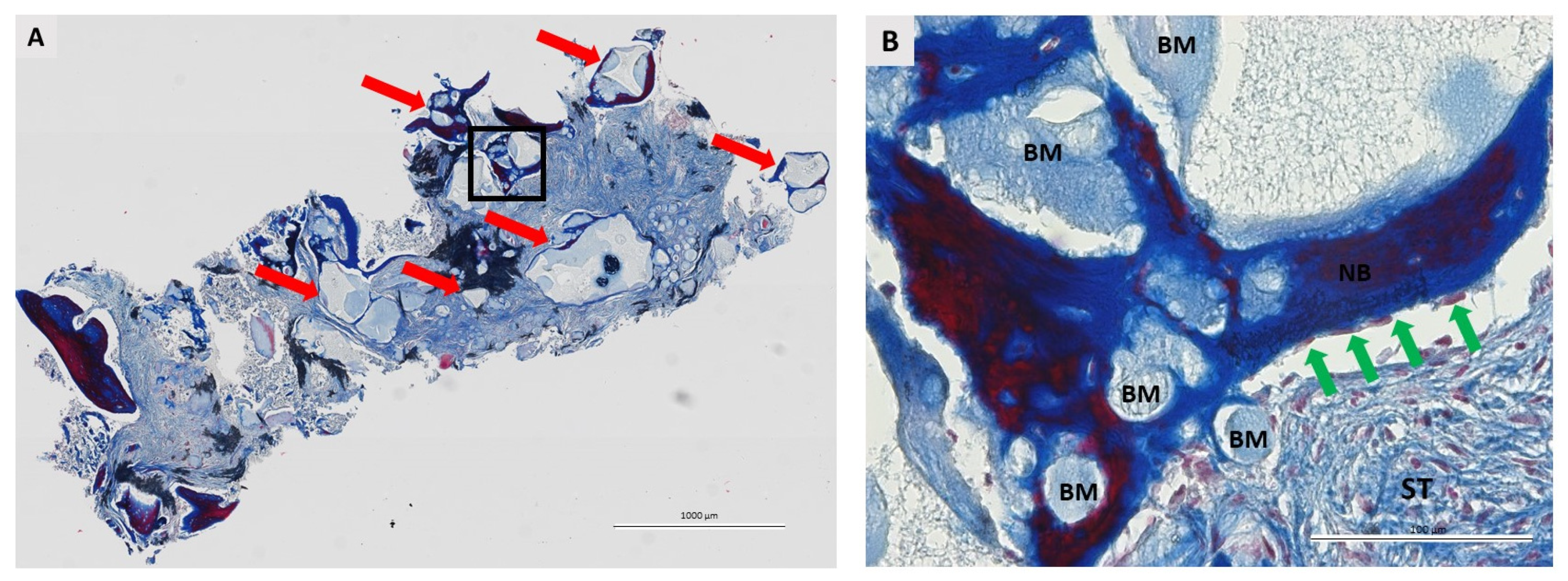
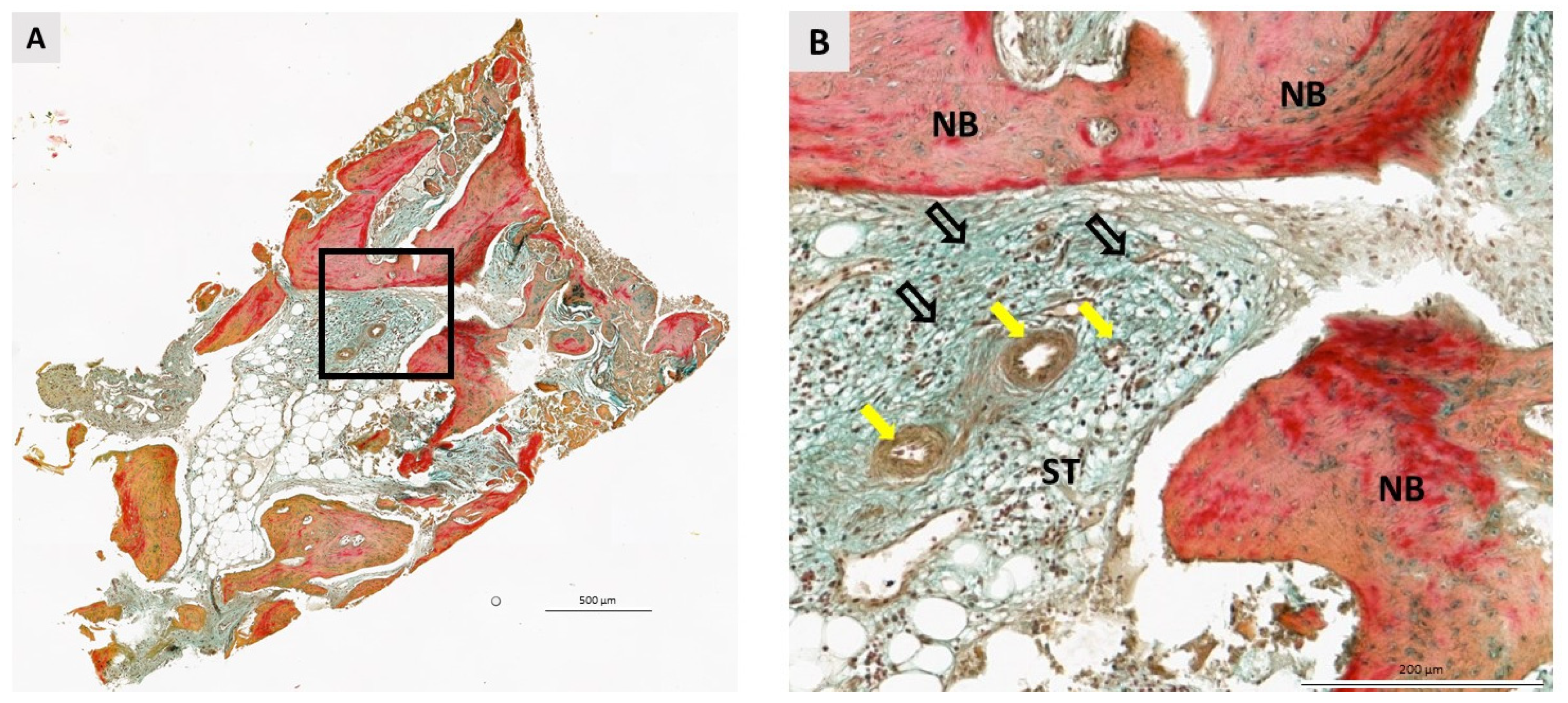
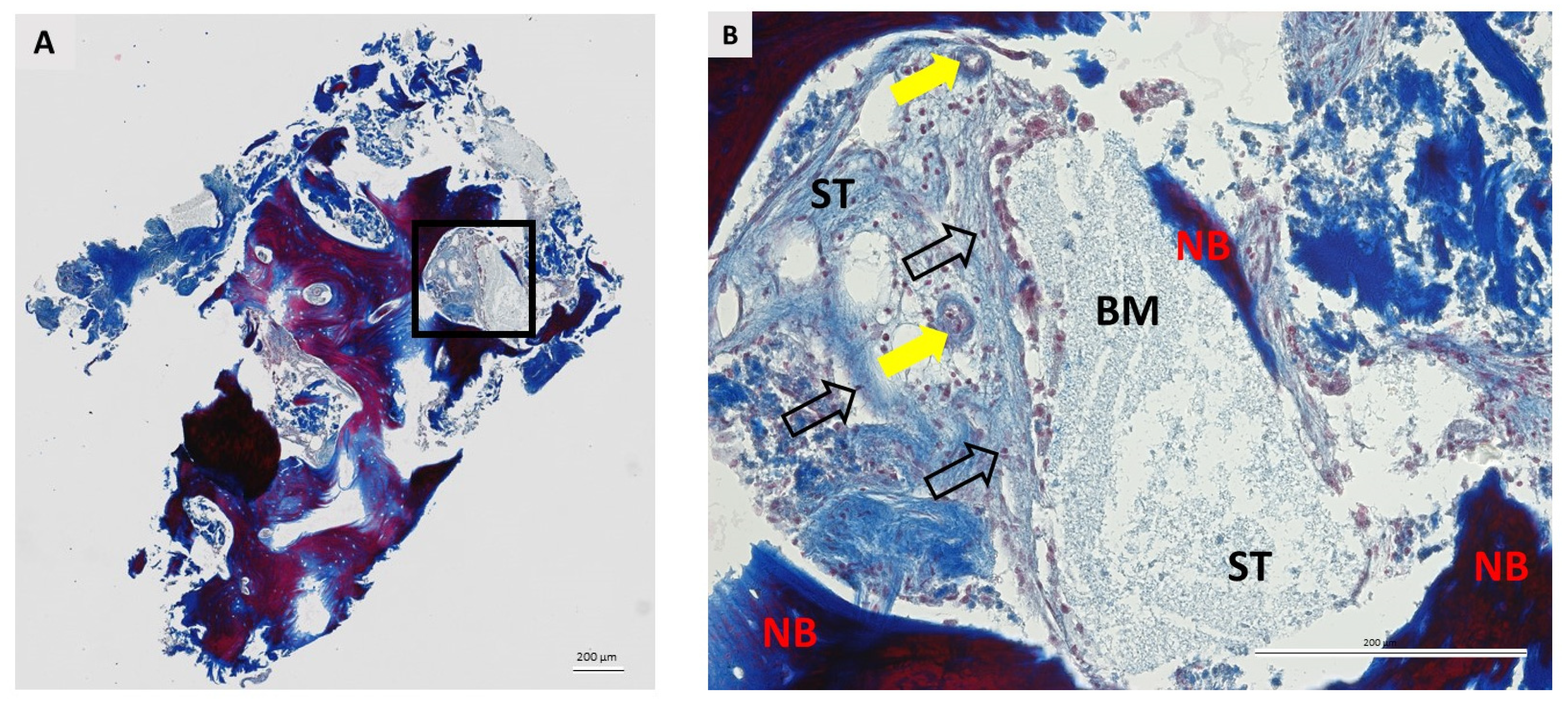
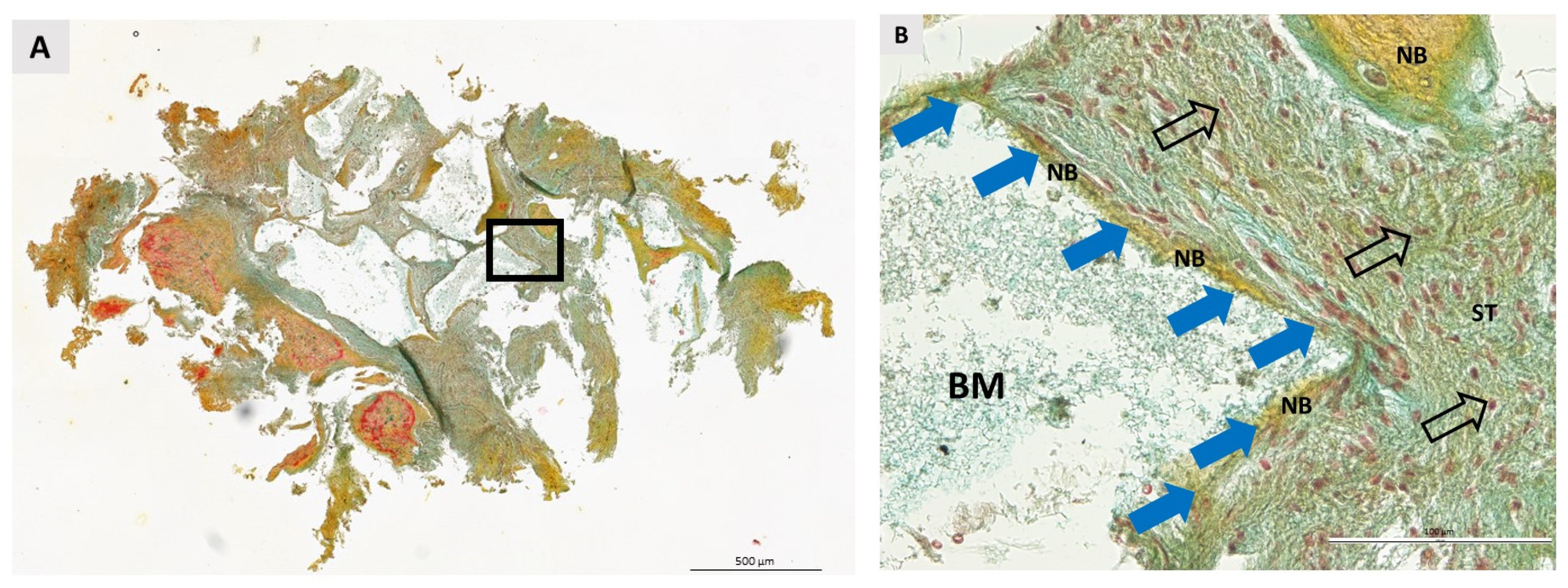
3.2. Qualitative Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanford, C.M. Application of oral implants to the general dental practice. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 136, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, F.; Costa, A.; Pereira, R.; dos Santos, P.; de Brito, R.; Rocha, E. Assessment of Satisfaction Level of Edentulous Patients Rehabilitated with Implant-Supported Prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsen, A.; Westergren, A.; Johannsen, G. Dental implants from the patients perspective: Transition from tooth loss, through amputation to implants—Negative and positive trajectories. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, J.C.; Rogers, M.J.; Coxon, F.P.; Hocking, L.J.; Helfrich, M.H. Bone remodelling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, L.; Wenzel, A.; Kostopoulos, L.; Karring, T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: A clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2003, 23, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kerns, D.G. Mechanisms of Guided Bone Regeneration: A Review. Open Dent. J. 2014, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato Pini, P.G.; Roberto, R.; Pierpaolo, C.; Carlo, T.; Robert, A. Interdental papilla management: A review and classification of the therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2004, 24, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.G.; Silva, C.O.; Misawa, M.; Sukekava, F. Alveolar socket healing: What can we learn? Periodontol. 2000 2015, 68, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassir, S.; Alhareky, M.; Wangsrimongkol, B.; Jia, Y.; Karimbux, N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Hard Tissue Outcomes of Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, N.K.; Stylianou, P.; Angelov, N.; Koidou, P.; Yukna, R.; Romanos, G.E. Limitations and options using resorbable versus nonresorbable membranes for successful guided bone regeneration. Quintessence Int. 2017, 48, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Mukherjee, N.; Cobb, R.R.; Bursac, P.; York-Ely, A. Incorporation and immunogenicity of cleaned bovine bone in a sheep model. J. Biomater. Appl. 2009, 24, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wychowanski, P.; Woliński, J.; Morawiec, T.; Kownacki, P.; Starzynska, A.; Kosieradzki, M.; Fiedor, P. Preliminary Clinical Data and the Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy of Autogenous Bone Grafts Versus Xenograft Implantations in Vertical Bone Deficiencies Before Dental Implant Installation. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, A.; Cortellini, S.; Van Dessel, J.; De Greef, A.; Jacobs, R.; Dhondt, R.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Bovine-derived xenograft in combination with autogenous bone chips versus xenograft alone for the augmentation of bony dehiscences around oral implants: A randomized, controlled, split-mouth clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano Méndez, C.A.; Lang, N.P.; Caneva, M.; Ramírez Lemus, G.; Mora Solano, G.; Botticelli, D. Comparison of allografts and xenografts used for alveolar ridge preservation. A clinical and histomorphometric RCT in humans. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Qabbani, A.; Al Kawas, S.; Razak, N.H.A.; Al Bayatti, S.W.; Enezei, H.H.; Samsudin, A.R.; Sheikh Ab Hamid, S. Three-Dimensional Radiological Assessment of Alveolar Bone Volume Preservation Using Bovine Bone Xenograft. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, e203–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, V.J.; Michalek, J.E.; Liu, Q.; Mealey, B.L. Ridge preservation following tooth extraction using bovine xenograft compared with porcine xenograft: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Mühlemann, S.; Jung, R.; Friedmann, A.; Fickl, S. Dimensional Evaluation of Different Ridge Preservation Techniques with a Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Azpur, G.; de la Fuente, A.; Chavez, E.; Valdivia, E.; Khouly, I. Horizontal ridge augmentation with guided bone regeneration using particulate xenogenic bone substitutes with or without autogenous block grafts: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Hamdan, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Grynpas, M.; Ganss, B.; Glogauer, M. Natural graft tissues and synthetic biomaterials for periodontal and alveolar bone reconstructive applications: A review. Biomater. Res. 2017, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger, R.F.; Nery, E.B.; Lynch, K.L. Histological assessment of periodontal osseous defects following implantation of hydroxyapatite and biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics: A case report. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1986, 6, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bouler, J.M.; Pilet, P.; Gauthier, O.; Verron, E. Biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics for bone reconstruction: A review of biological response. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, O.; Boix, D.; Grimandi, G.; Aguado, E.; Bouler, J.-M.; Weiss, P.; Daculsi, G. A New Injectable Calcium Phosphate Biomaterial for Immediate Bone Filling of Extraction Sockets: A Preliminary Study in Dogs. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čandrlić, M.; Kačarević, Ž.P.; Ivanišević, Z.; Tomas, M.; Včev, A.; Faj, D.; Matijević, M. Histological and radiological features of a four-phase injectable synthetic bone graft in guided bone regeneration: A case report. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, M.; Karl, M.; Čandrlić, M.; Matijević, M.; Juzbašić, M.; Peloza, O.C.; Radetić, A.T.J.; Kuiš, D.; Vidaković, B.; Ivanišević, Z.; et al. A Histologic, Histomorphometric, and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Anorganic Bovine Bone and Injectable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Humans: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čandrlić, M.; Tomas, M.; Karl, M.; Malešić, L.; Včev, A.; Perić Kačarević, Ž.; Matijević, M. Comparison of Injectable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and a Bovine Xenograft in Socket Preservation: Qualitative and Quantitative Histologic Study in Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, J.W.M.; Klijn, R.J.; Meijer, G.J.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Jansen, J.A. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation with injectable calcium phosphate cements: A pre-clinical study in sheep. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeck, M.; Lorenz, J.; Kubesch, A.; Böhm, N.; Booms, P.; Choukroun, J.; Sader, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Ghanaati, S. Porcine Dermis-Derived Collagen Membranes Induce Implantation Bed Vascularization Via Multinucleated Giant Cells: A Physiological Reaction? J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, e238–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Wang, H.-L. Medical contraindications to implant therapy: Part I: Absolute contraindications. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Wang, H.L. Medical contraindications to implant therapy: Part II: Relative contraindications. Implant Dent. 2007, 16, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research Randomizer. Available online: https://www.randomizer.org/about/ (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Sealed Envelope|Power Calculator for Continuous Outcome Equivalence Trial. Available online: https://www.sealedenvelope.com/power/continuous-equivalence/ (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Julious, S.A. Tutorial in biostatistics: Sample sizes for clinical trials with Normal data. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 1921–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, R.; Holtzclaw, D.; Rosen, P.S. A review on alveolar ridge preservation following tooth extraction. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, I.B.; Chen, S.T.; Buser, D. Ridge preservation for implant therapy. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 260–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kalsi, A.S.; Kalsi, J.S.; Bassi, S. Alveolar ridge preservation: Why, when and how. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 227, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibon, E.; Lu, L.; Goodman, S.B. Aging, inflammation, stem cells, and bone healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibon, E.; Lu, L.Y.; Nathan, K.; Goodman, S.B. Inflammation, ageing, and bone regeneration. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 10, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, P.K.; Medina, D.; Shetty, V.; Aghaloo, T.L. Dental implant failure rates and associated risk factors. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2005, 20, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tosta, M.; Cortes, A.R.G.; Corrêa, L.; Pinto, D.D.S.; Tumenas, I.; Katchburian, E. Histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of a synthetic bone substitute for maxillary sinus grafting in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibali, S.; Iezzi, G.; Sfasciotti, G.L.; Cristalli, M.P.; Vozza, I.; Mangano, C.; La Monaca, G.; Polimeni, A. Histological and histomorphometric human results of HA-Beta-TCP 30/70 compared to three different biomaterials in maxillary sinus augmentation at 6 months: A preliminary report. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 156850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benic, G.I.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 66, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.M.; Doering, H.; Schmidt, T.; Lutz, R.; Neukam, F.W.; Schlegel, K.A. Histological results after maxillary sinus augmentation with Straumann® BoneCeramic, Bio-Oss®, Puros®, and autologous bone. A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfro, R.; Fonseca, F.S.; Bortoluzzi, M.C.; Sendyk, W.R. Comparative, Histological and Histomorphometric Analysis of Three Anorganic Bovine Xenogenous Bone Substitutes: Bio-Oss, Bone-Fill and Gen-Ox Anorganic. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2014, 13, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.B.; Castro-Silva, I.I.; Da Rocha Coutinho, L.A.C.; Lenharo, A.; Granjeiro, J.M. Osteoconduction and Bioresorption of Bone Allograft versus Anorganic Bovine Bone Xenograft: A Histomorphometric Study in Humans. J. Biomim. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2013, 18, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Rodriguez, A.; Chang, D.T. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, T.; Sponer, P.; Urban, K.; Kohout, A. Histological assessment of tissue from large human bone defects repaired with β-tricalcium phosphate. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2014, 24, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappard, D.; Guillaume, B.; Mallet, R.; Pascaretti-Grizon, F.; Baslé, M.F.; Libouban, H. Sinus lift augmentation and beta-TCP: A microCT and histologic analysis on human bone biopsies. Micron 2010, 41, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, A.; Gissel, K.; Konermann, A.; Götz, W. Tissue reactions after simultaneous alveolar ridge augmentation with biphasic calcium phosphate and implant insertion—Histological and immunohistochemical evaluation in humans. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröhl, A.; Batinic, M.; Alkildani, S.; Hahn, M.; Radenkovic, M.; Najman, S.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. In Vivo Analysis of the Biocompatibility and Bone Healing Capacity of a Novel Bone Grafting Material Combined with Hyaluronic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, K.M.R.; von Rechenberg, B. Biocompatibility Issues with Modern Implants in Bone—A Review for Clinical Orthopedics. Open Orthop. J. 2008, 2, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelusic, D.; Zirk, M.L.; Fienitz, T.; Plancak, D.; Puhar, I.; Rothamel, D. Monophasic ß-TCP vs. biphasic HA/ß-TCP in two-stage sinus floor augmentation procedures—A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, e175–e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, C.; Perrotti, V.; Shibli, J.A.; Mangano, F.; Ricci, L.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Maxillary sinus grafting with biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics: Clinical and histologic evaluation in man. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Seo, Y.S.; Lee, G.J.; You, J.S.; Kim, S.G. A Comparative Study with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate to Deproteinized Bovine Bone in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Prospective Randomized and Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, W.; Wiltfang, J.; Pistner, H.; Yildirim, M.; Ploder, B.; Chapman, M.; Schiestl, N.; Hantak, E. Bone formation with a biphasic calcium phosphate combined with fibrin sealant in maxillary sinus floor elevation for delayed dental implant. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, R.; Stricker, A.; Thoma, D.; Jung, R. Sinus Floor Elevation with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate or Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral: Clinical and Histomorphometric Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, L.; Bosshardt, D.D.; Palattella, P.; Rao, W.; Serino, G.; Chiapasco, M. Maxillary sinus grafting with Bio-Oss or Straumann Bone Ceramic: Histomorphometric results from a randomized controlled multicenter clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargolzaie, N.; Rafiee, M.; Salari Sedigh, H.; Zare Mahmoudabadi, R.; Keshavarz, H.; Sedigh, H.S.; Mahmoudabadi, R.Z.; Keshavarz, H. Comparison of the effect of hemihydrate calcium sulfate granules and Cerabone on dental socket preservation: An animal experiment. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2018, 12, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Carinci, F.; Quaranta, A.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, M.; Piattelli, A. Correlation between implant stability quotient (ISQ) with clinical and histological aspects of dental implants removed for mobility. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhekar, S.; Kernen, F.; Bidra, A.S. Clinical and histologic outcomes of socket grafting after flapless tooth extraction: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-L.; Lin, G.-H.; Fu, J.-H.; Wang, H.-L. Alterations in bone quality after socket preservation with grafting materials: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| I-BCP 1 | BX 2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | 7 (39%) | 10 (55%) | 0.505 |
| Male | 11 (61%) | 8 (45%) | |
| n | 18 | 18 | |
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean | 36.0 | 36.9 | |
| SD | 10.4 | 13.4 | >0.99 |
| Min | 20 | 18 | |
| Max | 55 | 59 |
| Newly Formed Bone (NB) | Residual Biomaterial (BM) | Soft Tissue (ST) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBCP 1 | 31.5 ± 13.24% | 14.01 ± 10.81% | 54.48 ± 9.57% |
| BX 2 | 32.42 ± 16.02% | 18.88 ± 11.66% | 48.69 ± 12.09% |
| p-value * | 0.854 | 0.129 | 0.094 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čandrlić, M.; Tomas, M.; Matijević, M.; Kačarević, Ž.P.; Bićanić, M.; Udiljak, Ž.; Butorac Prpić, I.; Miškulin, I.; Čandrlić, S.; Včev, A. Regeneration of Buccal Wall Defects after Tooth Extraction with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Injectable Form vs. Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11090223
Čandrlić M, Tomas M, Matijević M, Kačarević ŽP, Bićanić M, Udiljak Ž, Butorac Prpić I, Miškulin I, Čandrlić S, Včev A. Regeneration of Buccal Wall Defects after Tooth Extraction with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Injectable Form vs. Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Dentistry Journal. 2023; 11(9):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11090223
Chicago/Turabian StyleČandrlić, Marija, Matej Tomas, Marko Matijević, Željka Perić Kačarević, Marijana Bićanić, Žarko Udiljak, Ivana Butorac Prpić, Ivan Miškulin, Slavko Čandrlić, and Aleksandar Včev. 2023. "Regeneration of Buccal Wall Defects after Tooth Extraction with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Injectable Form vs. Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial" Dentistry Journal 11, no. 9: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11090223
APA StyleČandrlić, M., Tomas, M., Matijević, M., Kačarević, Ž. P., Bićanić, M., Udiljak, Ž., Butorac Prpić, I., Miškulin, I., Čandrlić, S., & Včev, A. (2023). Regeneration of Buccal Wall Defects after Tooth Extraction with Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Injectable Form vs. Bovine Xenograft: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Dentistry Journal, 11(9), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11090223











