Assessing the Impact of Various Decontamination Instruments on Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ti and Zr Discs
2.2. Sample Numbers
2.3. Instrumentation Protocols
2.4. Profilometric Analysis and SEM Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
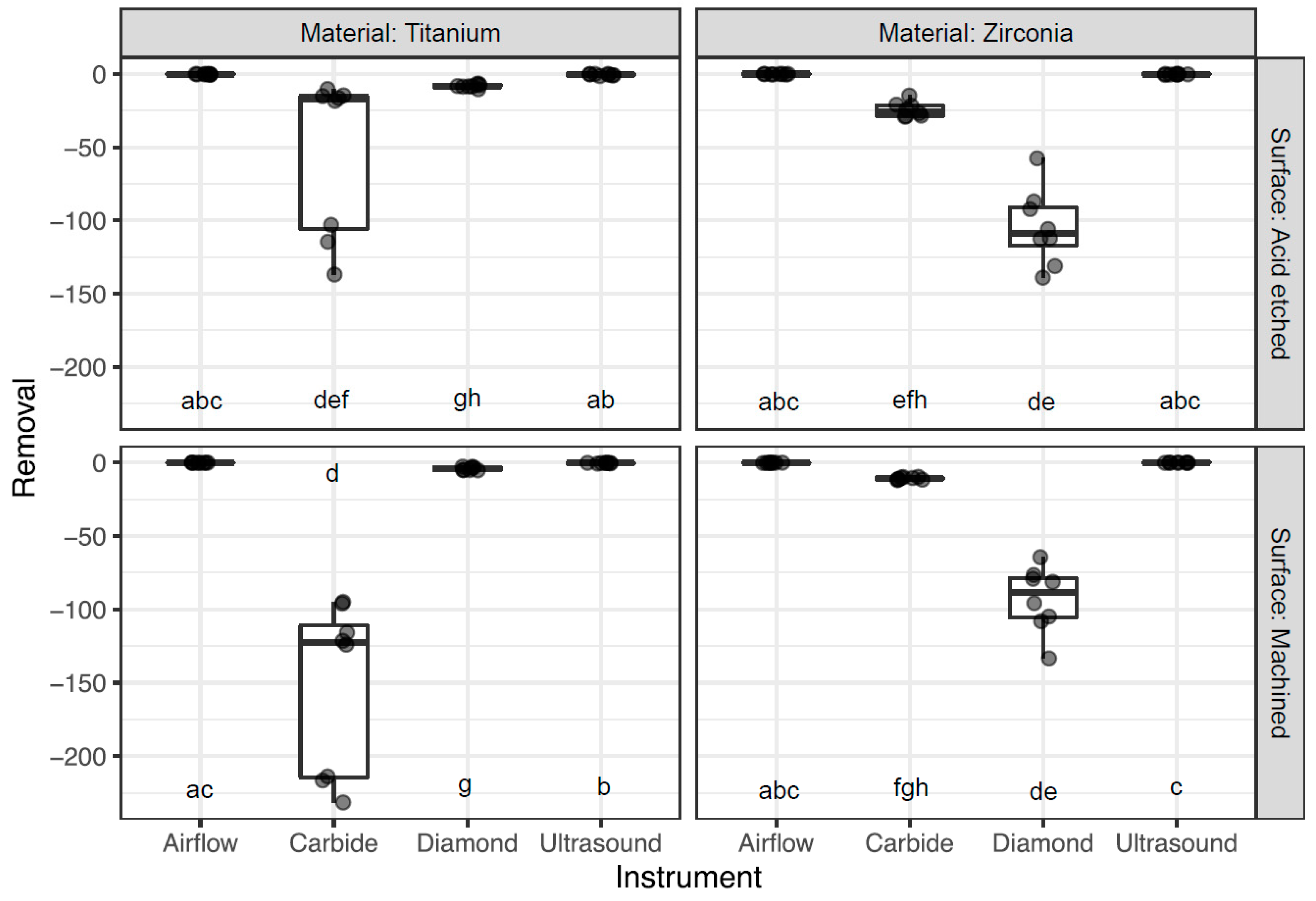
3.1. Surface Abrasion
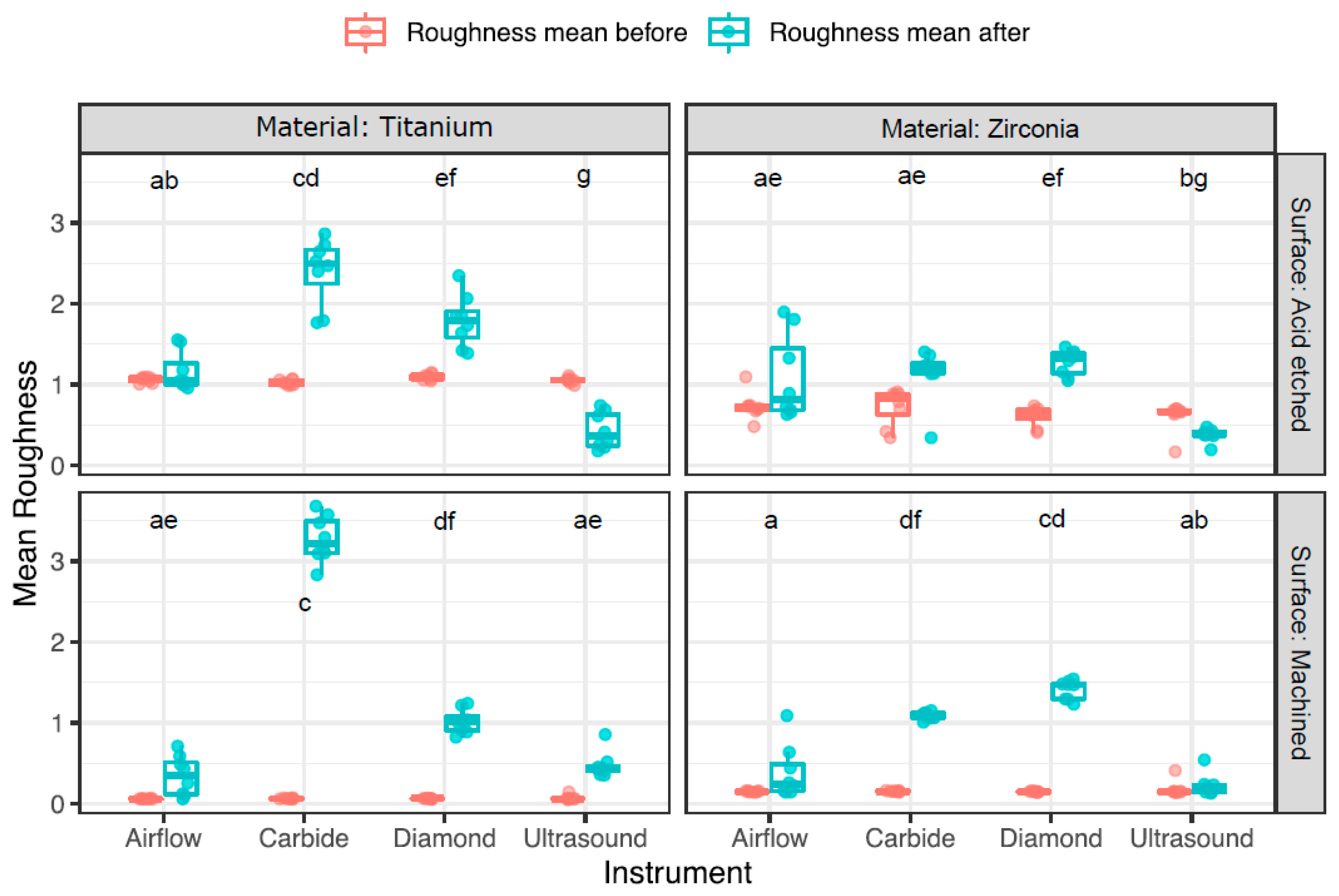
3.2. Change in Surface Roughness
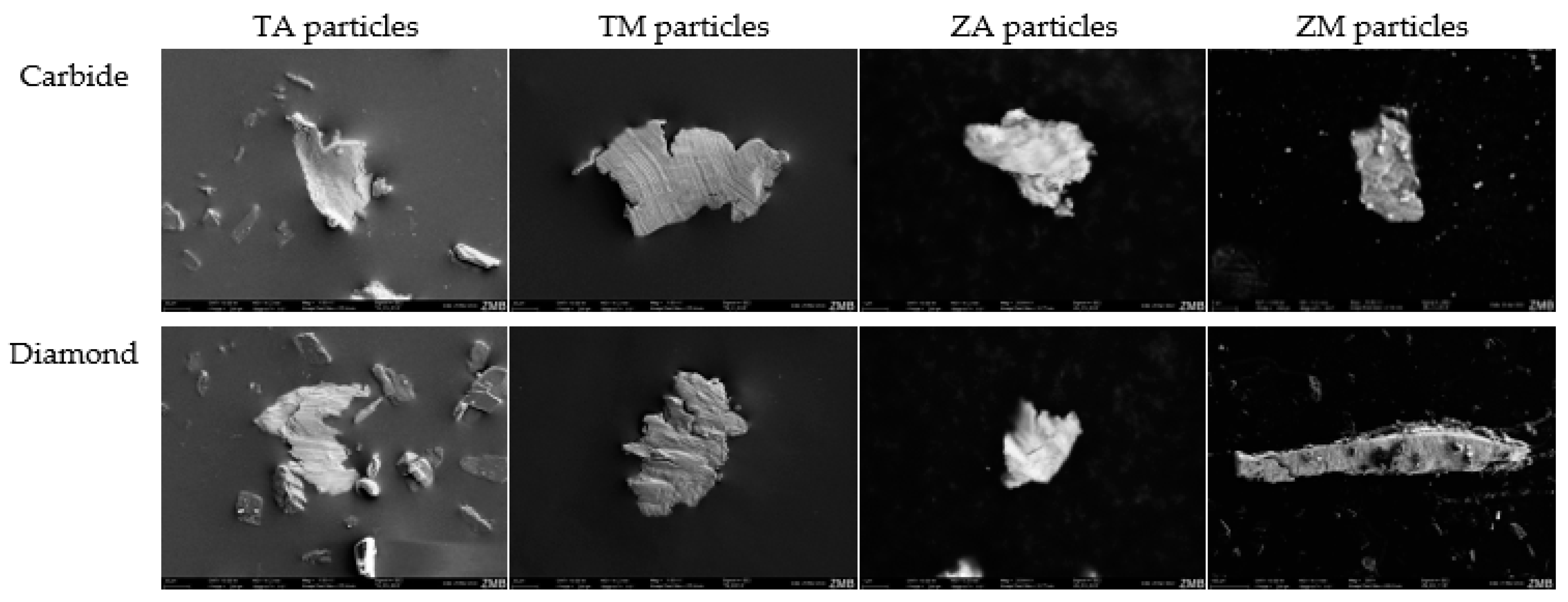
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Particle Analysis
3.4. SEM Analysis of Disc Surface
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Chappuis, V.; Buser, D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: Current knowledge and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakic, M.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Monje, A.; Radovanovic, S.; Wang, H.-L.; Cochran, D.; Sculean, A.; Canullo, L. How frequent does peri-implantitis occur? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Wisitrasameewon, W.; Humagain, M.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Peri-implantitis update: Risk indicators, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; John, G.; Schmucker, A.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface decontamination: A 7-year follow-up observation. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, O.; Sahrmann, P.; Ramos, J.; Caramelo, F.; Matos, S.; Baptista, I.P. Implantoplasty Improves Clinical Parameters over a 2-Year Follow-Up: A Case Series. Medicina 2022, 58, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravidà, A.; Siqueira, R.; Saleh, I.; Saleh, M.H.A.; Giannobile, A.; Wang, H.L. Lack of Clinical Benefit of Implantoplasty to Improve Implant Survival Rate. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Parasrampuria, N.; Pal, D. Efficacy of implantoplasty in management of peri?implantitis: A systematic review. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2023, 23, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzola, F.; Ionescu, A.C.; Ottobelli, M.; Cavalli, N.; Brambilla, E.; Corbella, S.; Francetti, L. Biofilm formation on dental implant surface treated by implantoplasty: An in situ study. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawse-Smith, A.; Ma, S.; Wu, H.; Yeah, A.; Jansen, L.; Vuuren, V.; Jansen Van Vuuren, W. Changes in Surface Characteristics of Moderately Roughened Grade Iv Titanium Disc Following a Standardised Implantoplasty Technique: An in-Vitro Study. J. Periodontol. 2015, 25, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Eger, M.; Sterer, N.; Liron, T.; Kohavi, D.; Gabet, Y. Scaling of titanium implants entrains inflammation-induced osteolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Pettersson, J.; Johansson, A.; Molin Thorén, M. Titanium release in peri-implantitis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatebø, R.S.; Høl, P.J.; Leknes, K.N.; Kosler, J.; Lie, S.A.; Gjerdet, N.R. Mapping of titanium particles in peri-implant oral mucosa by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry and high-resolution optical darkfield microscopy. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heringa, M.B.; Peters, R.J.B.; Bleys, R.L.A.W.; van der Lee, M.K.; Tromp, P.C.; van Kesteren, P.C.E.; van Eijkeren, J.C.H.; Undas, A.K.; Oomen, A.G.; Bouwmeester, H. Detection of titanium particles in human liver and spleen and possible health implications. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljateeli, M.; Fu, J.H.; Wang, H.L. Managing Peri-Implant Bone Loss: Current Understanding. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14 (Suppl. 1), 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicilia, A.; Cuesta, S.; Coma, G.; Arregui, I.; Guisasola, C.; Ruiz, E.; Maestro, A. Titanium allergy in dental implant patients: A clinical study on 1500 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, X.; Wan, P.; Zhu, B.; Chen, W. The anatase phase of nanotopography titania plays an important role on osteoblast cell morphology and proliferation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen, M.; Bollen, C.M.; Papaioannou, W.; Van Elderer, J.; van Steenberghe, D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: Short-term observations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1996, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fürst, M.M.; Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P.; Persson, G.R. Bacterial colonization immediately after installation on oral titanium implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2007, 18, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. The Pairwise Multiple Comparison of Mean Ranks Package (PMCMR). R Package. 2014. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=PMCMR (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Pohlert, T. PMCMRplus: Calculate Pairwise Multiple Comparisons of Mean Rank Sums Extended. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=PMCMRplus (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Montero, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, A.; Pardal-Peláez, B.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Nicolás-Silvente, A.I.; Monsalve-Guil, L. Effect of rough surface platforms on the mucosal attachment and the marginal bone loss of implants: A dog study. Materials 2020, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. 4), 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, C.M.L.; Papaioanno, W.; Van Eldere, J.; Schepers, E.; Quirynen, M.; Van Steenberghe, D. The influence of abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and peri-implant mucositis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, 7, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.; Claffey, N. How do implant surface characteristics influence periimplant disease? J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38 (Suppl. 11), 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, D.; Cionca, N. A Comprehensive Review of Peri-implantitis Risk Factors. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2020, 7, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhein, J.; Haller, C.; Reichl, F.X.; Milz, S.; Hickel, R.; Kollmuss, M.; Högg, C. Intranuclear cell uptake and toxicity of titanium dioxide and zirconia particles as well as bacterial adhesion on dental titanium- and zirconia-implants. Dent. Mater. 2022, 38, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayachawan, P.; McDonald, A.; Young, A.; Knowles, J.C. Flexural strength, fatigue life, and stress-induced phase transformation study of Y-TZP dental ceramic. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88B, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, F.F. Transformation toughening. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzavi, M.; Zhang, F.; Meille, S.; Douillard, T.; Adrien, J.; Noumbissi, S.; Nowzari, H.; Chevalier, J. Influence of artificial aging on mechanical properties of commercially and non-commercially available zirconia dental implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 101, 103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Reichl, F.X.; Milz, S.; Michalke, B.; Wu, X.; Sprecher, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Gahlert, M.; Röhling, S.; Kniha, H.; et al. Titanium and zirconium release from titanium- and zirconia implants in mini pig maxillae and their toxicity in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, G.A.; Black, R.; Kum, J.; Berbel, L.; Sadr, A.; Karoussis, I.; Simopoulou, M.; Daubert, D. Effect of implant cleaning on titanium particle dissolution and cytocompatibility. J. Periodontol. 2021, 92, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Font, O.; González-Barnadas, A.; Mir-Mari, J.; Figueiredo, R.; Gay-Escoda, C.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E. Fracture resistance after implantoplasty in three implant-abutment connection designs. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, O.P.; Baptista, I.P.; Caramelo, F.J. Disease recurrence after surgical treatment of peri-implantitis —Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oral Maxillofac. Med. 2021, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrel, S.K.; Wilson, T.G.; Pandya, M.; Diekwisch, T.G.H. Titanium particles generated during ultrasonic scaling of implants. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-López del Amo, F.; Rudek, I.; Wagner, V.; Martins, M.; O’Valle, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Giannobile, W.; Wang, H.-L.; Castilho, R. Titanium Activates the DNA Damage Response Pathway in Oral Epithelial Cells: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. The unfavorable role of titanium particles released from dental implants. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Kelk, P.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Bylund, D.; Molin Thorén, M.; Johansson, A. Titanium ions form particles that activate and execute interleukin-1β release from lipopolysaccharide-primed macrophages. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 52, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, A.; Hashim, D.; Cionca, N. What is the impact of titanium particles and biocorrosion on implant survival and complications? A critical review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, M.; Hiram-Bab, S.; Liron, T.; Sterer, N.; Carmi, Y.; Kohavi, D.; Gabet, Y. Mechanism and Prevention of Titanium Particle-Induced Inflammation and Osteolysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Pierre, C.A.; Chan, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Ayers, D.C.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Periprosthetic osteolysis: Characterizing the innate immune response to titanium wear-particles. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warashina, H.; Sakano, S.; Kitamura, S.; Yamauchi, K.I.; Yamaguchi, J.; Ishiguro, N.; Hasegawa, Y. Biological reaction to alumina, zirconia, titanium and polyethylene particles implanted onto murine calvaria. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3655–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 64 Ti Discs, 64 Zr Discs (128 Discs) (per Group n = 8) | Ti Discs | Zr Discs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid-Etched Surface (TA) | Machined Surface (TM) | Acid-Etched Surface (ZA) | Machined Surface (ZM) | |
| Carbide burs | Diameter = 15 mm Thickness = 0.7 mm | Diameter = 5 mm Thickness = 0.7 mm | Diameter = 15 mm Thickness = 1.4 mm | |
| Diamond burs | ||||
| Ultrasonic scaler | ||||
| Airflow with glycine powder | ||||
| Disc | Instrument | Mean ± Sd (µm) | Median ± IQR (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA | Airflow | −0.2 ± 0.2 | −0.1 ± 0.2 |
| TA | Carbide | −53.6 ± 54.3 | −17.4 ± 90.9 |
| TA | Diamond | −8.2 ± 1.2 | −8.4 ± 1.2 |
| TA | Ultrasound | −0.5 ± 0.5 | −0.3 ± 0.8 |
| TM | Airflow | −0.1 ± 0.1 | 0 ± 0.1 |
| TM | Carbide | −151.8 ± 58.3 | −122.7 ± 103.7 |
| TM | Diamond | −4.1 ± 1.1 | −4.4 ± 1.9 |
| TM | Ultrasound | −0.3 ± 0.2 | −0.2 ± 0.02 |
| ZA | Airflow | −0.1 ± 0.2 | 0 ± 0.3 |
| ZA | Carbide | −24.4 ± 5.04 | −25.6 ± 7.1 |
| ZA | Diamond | −104.7 ± 25.9 | −108.9 ± 26.2 |
| ZA | Ultrasound | −0.2 ± 0.2 | −0.2 ± 0.4 |
| ZM | Airflow | −0.1 ± 0.1 | −0.1 ± 0.2 |
| ZM | Carbide | −10.8 ± 0.8 | −10.9 ± 1.3 |
| ZM | Diamond | −92.9 ± 22.1 | −88.5 ± 27.2 |
| ZM | Ultrasound | −0.03 ± 0.1 | 0 ± 0.03 |
| Disc | Instrument | Mean ± Sd (µm) | Median ± IQR (µm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Diff. | Before | After | Diff. | ||
| TA | Airflow | 1.1 ± 0.03 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | −0.03 ± 0.2 |
| TA | Carbide | 1 ± 0.03 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| TA | Diamond | 1.1 ± 0.04 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.4 |
| TA | Ultrasound | 1.1 ± 0.04 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | −0.6 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.02 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | −0.7 ± 0.4 |
| TM | Airflow | 0.1 ± 0.004 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.004 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.4 |
| TM | Carbide | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 0.4 |
| TM | Diamond | 0.1 ± 0.004 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.003 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.2 |
| TM | Ultrasound | 0.1 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| ZA | Airflow | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 0.2 ± 0.7 |
| ZA | Carbide | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| ZA | Diamond | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| ZA | Ultrasound | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | −0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.04 | −0.3 ± 0.1 |
| ZM | Airflow | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.3 |
| ZM | Carbide | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.05 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| ZM | Diamond | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| ZM | Ultrasound | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.04 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.03 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vierling, L.; Liu, C.C.; Wiedemeier, D.; Gubler, A.; Schmidlin, P.R. Assessing the Impact of Various Decontamination Instruments on Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12050136
Vierling L, Liu CC, Wiedemeier D, Gubler A, Schmidlin PR. Assessing the Impact of Various Decontamination Instruments on Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study. Dentistry Journal. 2024; 12(5):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12050136
Chicago/Turabian StyleVierling, Louisa, Chun Ching Liu, Daniel Wiedemeier, Andrea Gubler, and Patrick R. Schmidlin. 2024. "Assessing the Impact of Various Decontamination Instruments on Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study" Dentistry Journal 12, no. 5: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12050136
APA StyleVierling, L., Liu, C. C., Wiedemeier, D., Gubler, A., & Schmidlin, P. R. (2024). Assessing the Impact of Various Decontamination Instruments on Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study. Dentistry Journal, 12(5), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12050136








