Experimental Whisky Fermentations: Influence of Wort Pretreatments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wort Collection
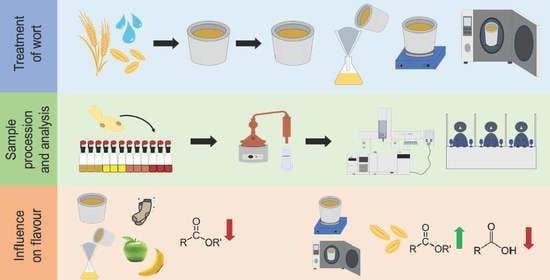
2.2. Wort Pretreatment
2.3. Fermentation Setup
2.4. Monitoring of the Fermentation Performance with the Ankom RG Gas Production System
2.5. Measuring Particle Count, Yeast Count, and Yeast Viability
2.6. Photomicroscopy
2.7. Production of Low Wines by Distillation
2.8. Sensory Analysis with Quantitative Descriptive Analysis
2.9. Congener Measurements by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Pretreatments on Wort Quality
3.2. Effect of Filtration on Wort Quality
3.3. Effect of Boiling and Autoclaving on Wort Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scottish Government, The Scotch Whisky Regulations. 2009. Available online: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2009/2890/pdfs/uksi_20092890_en.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Guild, I.B.; Street, H.; Simmonds, P.G.W.; Lloyd, W.J.W. The Sections. J. Inst. Brew. 1985, 91, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, S.; Priest, F.G. Evolution of the Lactic Acid Bacterial Community during Malt Whisky Fermentation: A Polyphasic Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, S.J.; Speers, R.A.; Willoughby, N.; Lumsden, W.B.; Maskell, D.L. Pre-Fermentation of Malt Whisky Wort Using Lactobacillus plantarum and Its Influence on New-Make Spirit Character. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.P.; Arendt, E.K. The Use and Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Malting and Brewing with Their Relationships to Antifungal Activity, Mycotoxins and Gushing: A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2004, 110, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriesekoop, F.; Krahl, M.; Hucker, B.; Menz, G. 125th Anniversary Review: Bacteria in Brewing: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. J. Inst. Brew. 2012, 118, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, E.A.; Priest, F.G. Some Effects of Lactobacillus Contamination in Scotch Whisky Fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1988, 94, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.L.; Pettersson, B.; Priest, F.G. Characterization of Lactobacilli from Scotch Malt Whisky Distilleries and Description of Lactobacillus ferintoshensis sp. nov., a New Species Isolated from Malt Whisky Fermentations. Microbiology 2001, 147, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J. Scotch Whisky: Raw Material Selection and Processing. In Whisky Technology, Production and Marketing; Russell, I., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 49–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathgate, G.N. A Review of Malting and Malt Processing for Whisky Distillation. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriesekoop, F.; Rathband, A.; MacKinlay, J.; Bryce, J.H. The Evolution of Dextrins during the Mashing and Fermentation of All-Malt Whisky Production. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.W.; Bringhurst, T.A.; Broadhead, A.L.; Brosnan, J.M.; Pearson, S.Y. The Survival of Limit Dextrinase during Fermentation in the Production of Scotch Whisky. J. Inst. Brew. 2001, 107, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, G.B.; Berry, D.R. Malted Barley Enzyme Activity under Optimum and Process Conditions from the Scotch Malt Whisky Industry. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1996, 19, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.; Van Wegen, B.; Ma, Y.; Eglinton, J. The Impact of the Thermostability of α-Amylase, β-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase on Potential Wort Fermentability. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2004, 61, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.C. The Development of Specialised Yeast Strains for Use in Scotch Malt Whisky Fermentations. In Advances in Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G.; Hill, A.E.; Russell, I. 125th Anniversary Review: Developments in Brewing and Distilling Yeast Strains. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.; Brosnan, J.; Bringhurst, T.; Jack, F. Selecting New Distilling Yeasts for Improved Fermentation and for Sustainability. In Distilled Spirits—Future Challenges, New Solutions; Goodall, I., Fotheringham, R., Murray, D.R.A., Walker, G.M., Eds.; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2011; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Hill, A. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae in the Production of Whisk(e)Y. Beverages 2016, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyraleou, M.; Herb, D.; Reilly, G.O.; Conway, N.; Bryan, T.; Kilcawley, K.N. The Impact of Terroir on the Flavour of Single Malt Whisk(e)y New Make Spirit. Foods 2021, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master of Malt. Glen Elgin 18 Year Old 1998 (Special Release 2017). Available online: https://www.masterofmalt.com/whiskies/glen-elgin/glen-elgin-18-year-old-1998-special-release-2017-whisky/ (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Broom, D. Is Yeast Whisky’s New Frontier of Flavour? 2019. Available online: https://scotchwhisky.com/magazine/features/22834/is-yeast-whisky-s-new-frontier-of-flavour/ (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Ramsay, C.M.; Berry, D.R. Development of a Small Scale Mashing and Fermentation System for Studies on Malt Whisky Production. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1983, 18, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, T.C.S. Some Aspects of the Impact of Brewing Science on Scotch Malt Whisky Production. J. Inst. Brew. 1976, 82, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Brewing Convention (EBC). 4.6.1—Hot Water Extract of Malt: Constant Temperature Mash Analytica EBC. BrewUp; Brewers of Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa, T.; Stewart, G.G. Monitoring and Controlling of Whisky Fermentation. In Distilled Spirits—Tradition and Innovation; Bryce, J.H., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2004; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, C.M.; Berry, D.R. The Effect of Inoculum Level on the Formation of Higher Alcohols, Fatty Acids and Esters in the Malt Whisky Fermentation. Food Microbiol. 1984, 1, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanikawa, A.; Hosoi, K.; Kato, T. Conversion of Unsaturated Fatty Acids to Precursors of γ-Lactones by Lactic Acid Bacteria during the Production of Malt Whisky. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2000, 58, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensor, M.; Bryce, J.H.; Hill, A. An Investigation into the Use of Different Yeast Strains and Lactobacillus on New Make Spirit. In Distilled Spirits—Future Challenges, New Solutions; Goodall, I., Fotheringham, R., Murray, D.R.A., Walker, G.M., Eds.; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2015; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, H.B.d.A.; Pearson, S.Y.; Walker, J.W.; Walker, G.M.; Brosnan, J. Application of Nocel Yeast Strains to the Scotch Whisky Fermentation Process. In Distilled Spirits, Production, Technology and Innovation; Bryce, J.H., Piggott, J.R., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2008; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Berbert de Amorim Neto, H.; Yohannan, B.K.; Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J.M.; Pearson, S.Y.; Walker, J.W.; Walker, G.M. Evaluation of a Brazilian Fuel Alcohol Yeast Strain for Scotch Whisky Fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storr, A.; Walker, J.W. Assessment of Pinnacle MG+ Yeast for the Scotch Whisky Industry. In Distilled Spirits: Local Roots; Global Reach: Delivering Distilling Expertise to the World; Jack, F., Dabrowska, D., Davies, S., Garden, M., Maskell, D., Murray, D., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2018; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, M. Effects of Wort Gravity and Nitrogen Level on Fermentation Performance of Brewer’s Yeast and the Formation of Flavor Volatiles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.W. Designing for Cleanliness in the Distillery. In Whisky; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanjuola, D.B.; Tymon, A.; Springham, D.G. Some Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Laboratory-Scale Yeast Fermentations. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1992, 14, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N. Contamination: Bacteria and Wild Yeasts in a Whisky Fermentation. In Whisky; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HM Revenue & Customse Notice 226: Beer Duty. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/excise-notice-226-beer-duty/excise-notice-226-beer-duty--2 (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Black, K.; Daute, M.; Tziboula-Clarke, A.; White, P.J.; Iannetta, P.P.M.; Walker, G. Utilization of Low Nitrogen Barley for Production of Distilling Quality Malt. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021, 79, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food, 2nd ed.; Heldman, D.R., Ed.; Food Science Text Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.; Sidel, J.; Oliver, S.; Woolsey, A.; Singleton, R.C. Sensory Evaluation by Quantitative Descriptive Analysis. Food Technol. 1974, 8, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daute, M.; Jack, F.; Baxter, I.; Harrison, B.; Grigor, J.; Walker, G. Comparison of Three Approaches to Assess the Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Spirit. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štěrba, K.; Čejka, P.; Olšovská, J. Influence of Beer and Wort Sample Freezing on the Result of Analysis. Kvas. Prum. 2020, 66, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, P.; Schmidt, J.J. Interactions of Cooling Velocity, Temperature, and Warming Velocity on the Survival of Frozen and Thawed Yeast. Cryobiology 1968, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, R.S.; Hargiss, C.O. Studies on the Death of Bacteria at Low Temperatures. J. Bacteriol. 1946, 52, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandil, S.; El Soda, M. Influence of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Intracellular Enzymatic Activity and Autolytic Properties of Some Lactic Acid Bacterial Strains. Adv. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bravo-Ferrada, B.M.; Brizuela, N.; Gerbino, E.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A.; Semorile, L.; Tymczyszyn, E.E. Effect of Protective Agents and Previous Acclimation on Ethanol Resistance of Frozen and Freeze-Dried Lactobacillus plantarum Strains. Cryobiology 2015, 71, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giulio, B.; Orlando, P.; Barba, G.; Coppola, R.; De Rosa, M.; Sada, A.; De Prisco, P.P.; Nazzaro, F. Use of Alginate and Cryo-Protective Sugars to Improve the Viability of Lactic Acid Bacteria after Freezing and Freeze-Drying. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 21, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; Welch, L.C.; Robinson, M.R.; Sturgeon, C.M.; Crow, M.M.; Segarra, V.A. Cryopreservation and the Freeze–Thaw Stress Response in Yeast. Genes 2020, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, F.; Marechal, P.A.; Gervais, P. Cell Size and Water Permeability as Determining Factors for Cell Viability after Freezing at Different Cooling Rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanikawa, A.; Hosoi, K.; Takise, I.; Kato, T. Detection of γ-Lactones in Malt Whisky. J. Inst. Brew. 2000, 106, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanikawa, A. Flavors in Malt Whisky: A Review. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2020, 78, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühbeck, F.; Back, W.; Krottenthaler, M. Influence of Lauter Turbidity on Wort Composition, Fermentation Performance and Beer Quality -in Large-Scale Trials. J. Inst. Brew. 2006, 112, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacWilliam, I.C. Wort Compostion—A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 1968, 74, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G.J.; McKechnie, M.T. Filtration and Stabilization of Beers. In Fermented Beverage Production; Lea, A.G.H., Piggott, J.R., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 365–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, C.W. Wort Composition and Beer Quality. In Brewing Yeast Fermentation Performance; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Krottenthaler, M.; Back, W.; Weisser, H. Study on the Membrane Filtration of Mash with Particular Respect to the Quality of Wort and Beer. J. Inst. Brew. 2005, 111, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddie, H.A.B. Ester Formation in Brewery Fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1990, 96, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, S.M.G.; Delvaux, F.R.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Van Dijck, P.; Thevelein, J.M.; Delvaux, F.R. Parameters Affecting Ethyl Ester Production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deak, T. Environmental Factors Influencing Yeasts. In Biodiversity and Ecophysiology of Yeasts; Rosa, C.A., Peter, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willaert, R.G.; Baron, G.V. Wort Boiling Today-Boiling Systems with Low Thermal Stress in Combination with Volatile Stripping. Cerevisia 2001, 26, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, J.; Lin, L.; Guo-Qin, L.; Bing, L.; Yu-Kui, Z.; Liao-Ning, L. Structural Changes of Malt Proteins during Boiling. Molecules 2009, 14, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Control | Filtered | Boiled | Autoclaved | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG (°) | 1000.7 ± 0.8 c | 1015.3 ± 0.8 a | 1005.3 ± 0.6 b | 1005.4 ± 0.2 b |
| pH | 3.90 ± 0.00 b | 3.75 ± 0.04 c | 4.54 ± 0.00 a | 4.56 ± 0.01 a |
| ABV (%) | 9.2 ± 0.1 a | 7.2 ± 0 c | 8.4 ± 0 b | 8.5 ± 0 b |
| End of lag phase (h) | 7.6 ± 0.1 b | 8.03 ± 0.15 a | 7.63 ± 0.05 b | 7.63 ± 0.15 b |
| Vmax (h) | 13 ± 0.08 b | 14.94 ± 1.1 a | 13.44 ± 0.17 b | 13.64 ± 0.19 a,b |
| Start of stationary phase (h) | 19.69 ± 0.04 c | 22.33 ± 0.25 a | 19.11 ± 0.29 c | 21.33 ± 0.36 b |
| Cumulative CO2 production (mL/100 mL) | 3332.82 ± 56.52 a | 2563.09 ± 27.65 c | 3095.57 ± 36.94 b | 3225.02 ± 153.01 a,b |
| Total count (Count/mL) | 1.00 × 108 ± 2.06 × 106 a | 8.72 × 107 ± 9.48 × 106 a | 2.62 × 107 ± 1.22 × 107 c | 4.81 × 107 ± 4.45 × 106 b |
| Yeast count (Count/mL) | 4.33 × 107 ± 2.66 × 105 a | 2.55 × 107 ± 1.71 × 106 b,c | 1.93 × 107 ± 1.02 × 107 c | 3.88 × 107 ± 2.40 × 106 a,b |
| Alive yeast (%) | 51.6 ± 4.4 b | 55.4 ± 0.6 a,b | 63 ± 3.4.0 a | 60.2 ± 2.0 a |
| Dead yeast (%) | 40.6 ± 4.2 a | 34.4 ± 0.5 a | 24.8 ± 3.2 b | 26.9 ± 1.0 b |
| Inactive yeast (%) | 3.8 ± 0.1 b | 3.7 ± 0.4 b | 8.7 ± 0.3 a | 8.5 ± 0.1 a |
| Wort Stage | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh Industry | as close to industry as possible no influence on microorganisms or enzymes | cannot be stored not stable difficult to obtain |
| Fresh Lab-Scale | easy to obtain right batch size producible on the same day | small batches microflora other than industry wort |
| Frozen | possible long-time storage provides the possibility of using the same wort for several fermentations | reduction of microorganism needs freezer space |
| Filtered | reduction of congener precursor difficult to reduce microorganisms by filtering loss of alcohol | |
| Boiled | easy sterile | agglomeration of enzymes sterile loss of alcohol |
| Autoclaved | only applicable in the lab sterile | agglomeration of enzymes sterile loss of alcohol |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daute, M.; Jack, F.; Harrison, B.; Walker, G. Experimental Whisky Fermentations: Influence of Wort Pretreatments. Foods 2021, 10, 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112755
Daute M, Jack F, Harrison B, Walker G. Experimental Whisky Fermentations: Influence of Wort Pretreatments. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112755
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaute, Martina, Frances Jack, Barry Harrison, and Graeme Walker. 2021. "Experimental Whisky Fermentations: Influence of Wort Pretreatments" Foods 10, no. 11: 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112755
APA StyleDaute, M., Jack, F., Harrison, B., & Walker, G. (2021). Experimental Whisky Fermentations: Influence of Wort Pretreatments. Foods, 10(11), 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112755