Real-Time PCR Method for the Rapid Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Staphylococcus Species Based on Novel Molecular Target Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Evaluation of Staphylococci Genomes
2.2. Mining of Molecular Target Genes
2.3. Design of Specific Primers
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Real-Time PCR Condition
2.6. Specificity of the Primer Pairs
2.7. Application in Artificially Contaminated Food Samples
2.8. Application in Isolated Staphylococcus Strains
2.9. Detection of Staphylococcus Species in Food Samples
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Staphylococci Whole-Genome Sequences
3.2. Pan-Genome Analysis
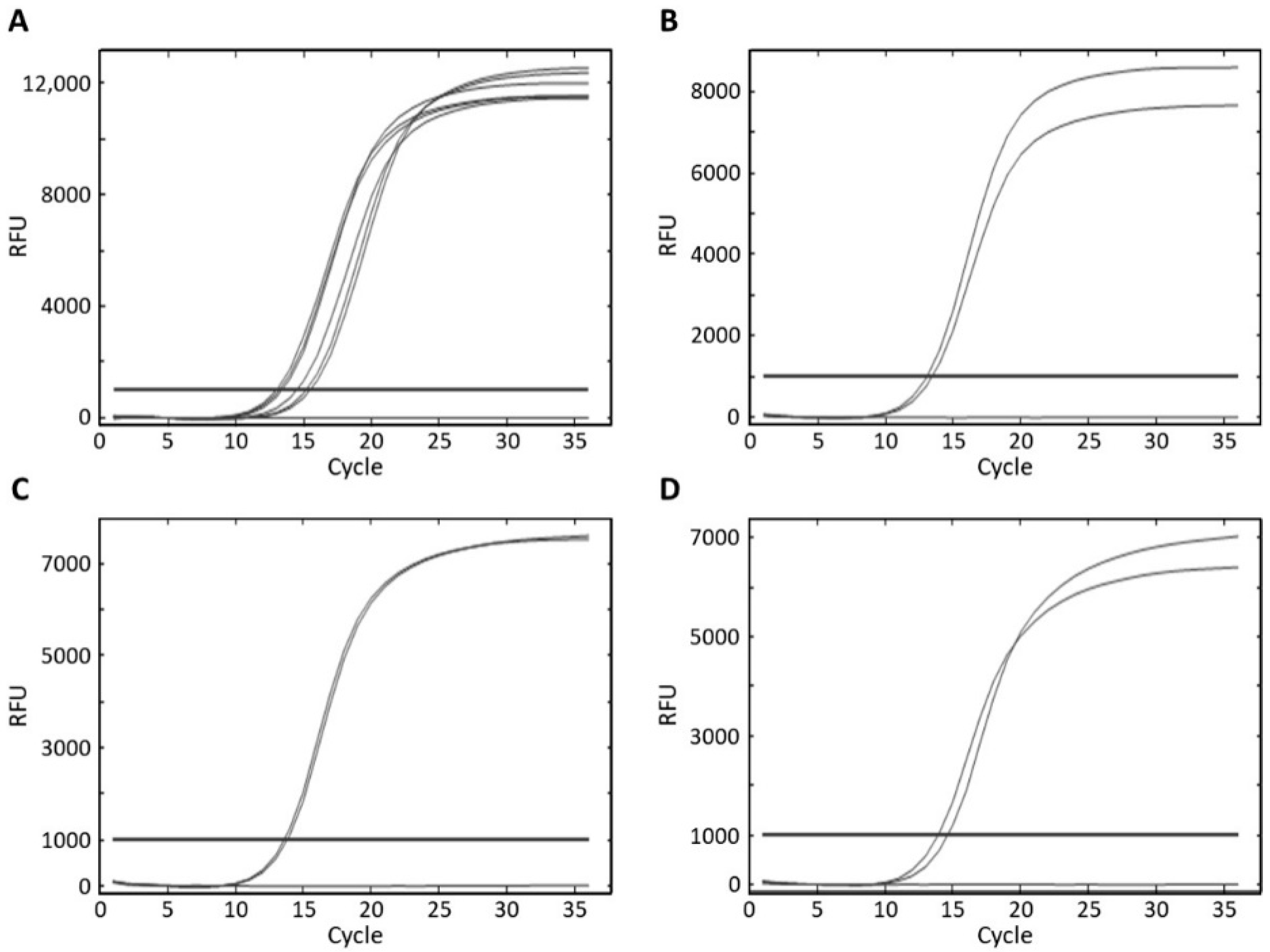
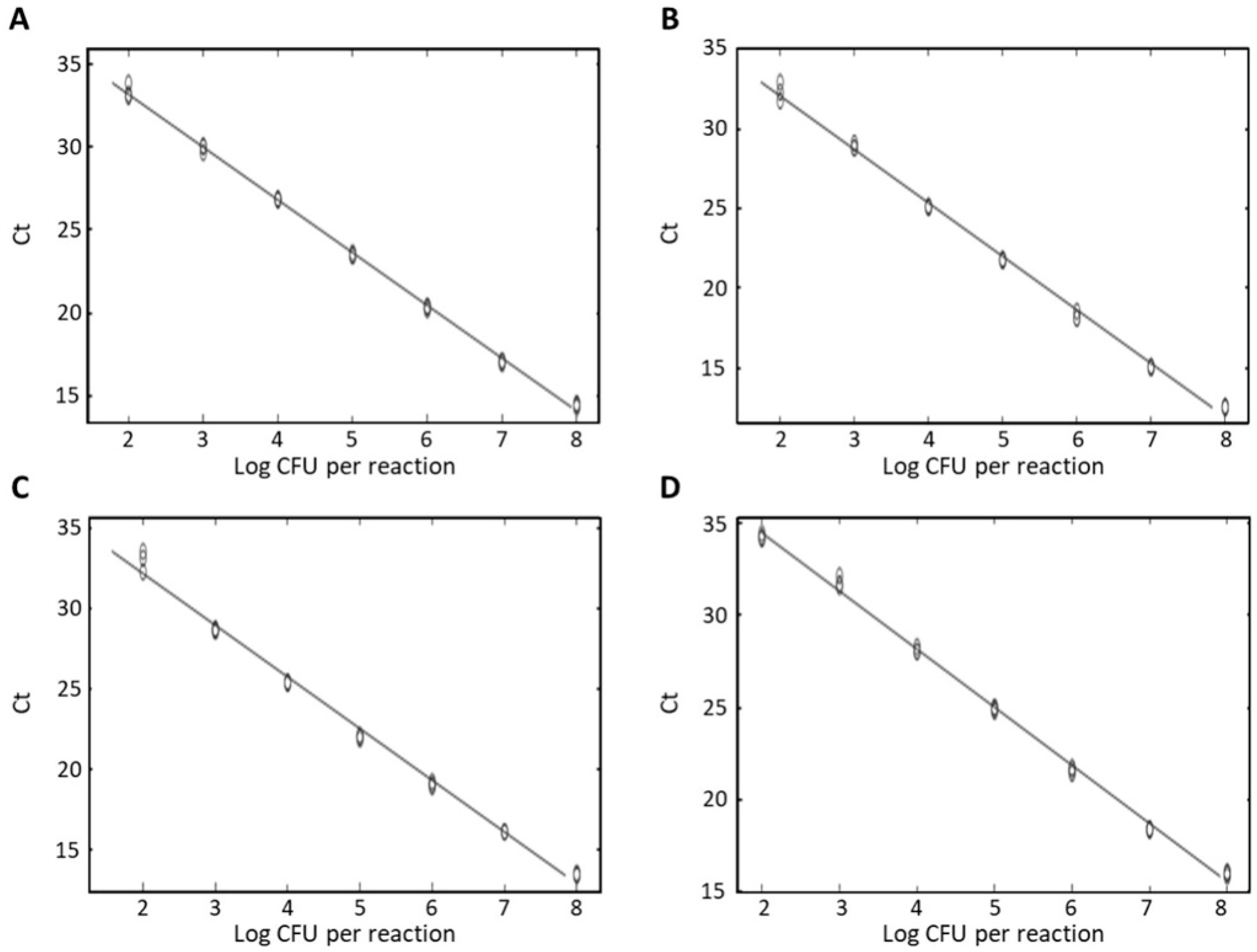
3.3. Specificity and Sensitivity of Real-Time PCR
3.4. Detection of Staphylococcus Species in Artificially Contaminated Food Samples
3.5. Real-Time PCR Detection of Isolates
3.6. Detection of Contamination by the Four Staphylococcus Species in Food Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, B.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, F.; Xiang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Novel species-specific targets for real-time PCR detection of four common pathogenic Staphylococcus spp. Food Control 2022, 131, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.Á.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, D.R.; Jiang, J.H.; Hassan, K.A.; Elbourne, L.D.H.; Tuck, K.L.; Paulsen, I.T.; Peleg, A.Y. Insights on virulence from the complete genome of Staphylococcus capitis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, S.; Aiba, Y.; Tan, X.E.; Li, F.Y.; Boonsiri, T.; Thitiananpakorn, K.; Cui, B.; Sato’O, Y.; Kiga, K.; Sasahara, T.; et al. Complete genome sequencing of three human clinical isolates of Staphylococcus caprae reveals virulence factors similar to those of S. epidermidis and S. capitis. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahle, C.M.; Stødkilde, K.; Afshar, M.; Poehlein, A.; Ogilvie, L.A.; Söderquist, B.; Hüpeden, J.; Brüggemann, H. Staphylococcus saccharolyticus: An overlooked human skin colonizer. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Nan, H.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Tan, K. Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Food Using a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification-Based Assay. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Z. Simultaneous enumeration of Cronobacter sakazakii and Staphylococcus aureus in powdered infant foods through duplex TaqMan real-time PCR. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, J.; Wei, C.; Lin, C.W.; Ding, T. Current perspectives on viable but non-culturable state in foodborne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćirković, I.; Hauschild, T.; Ježek, P.; Dimitrijević, V.; Vuković, D.; Stepanović, S. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Staphylococcus vitulinus by the BD Phoenix automated microbiology system. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hong, J.; Lim, J.A.; Heu, S.; Roh, E. Improved multiplex PCR primers for rapid identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, C.G.; Choo, D.W.; Kim, H.Y. Rapid identification of Staphylococcus species isolated from food samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koop, G.; De Visscher, A.; Collar, C.A.; Bacon, D.A.C.; Maga, E.A.; Murray, J.D.; Supré, K.; De Vliegher, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; Rowe, J.D.; et al. Short communication: Identification of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species from goat milk with the API Staph identification test and with transfer RNA-intergenic spacer PCR combined with capillary electrophoresis. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, M.S.; Carvajal, H.D.; Calle-Echeverri, D.A.; Chinchilla-Cárdenas, D. Molecular Detection and Characterization of the mecA and nuc Genes From Staphylococcus Species (S. aureus, S. pseudintermedius, and S. schleiferi) Isolated From Dogs Suffering Superficial Pyoderma and Their Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaluś-Jordanow, O.; Chrobak, D.; Pyrgiel, M.; Lutyńska, A.; Kaba, J.; Czopowicz, M.; Witkowski, L.; Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Binek, M.; Frymus, T. PFGE and AFLP genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus subsp. anaerobius isolated from goats with Morel’s disease. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandal, P.K.; Biswas, A.K.; Choi, K.; Pal, U.K. Methods for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens: An overview. Am. J. Food Technol. 2011, 6, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Daliri, E.B.M.; Chelliah, R.; Park, B.J.; Lim, J.S.; Baek, M.A.; Nam, Y.S.; Seo, K.H.; Jin, Y.G.; Oh, D.H. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR for simultaneous detection of Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus in food samples. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.-M.; Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.-B.; Baek, J.; Ko, S.; Kim, D.; Yoon, H.; Kim, H.-Y. Rapid Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction for Salmonella Serotyping Based on Novel Unique Gene Markers by Pangenome Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.B.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.Y. Real-time PCR assay for detecting Lactobacillus plantarum group using species/subspecies-specific genes identified by comparative genomics. LWT 2021, 138, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, H.Y. Differentiation of lacticaseibacillus zeae using pan-genome analysis and real-time pcr method targeting a unique gene. Foods 2021, 10, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.Y. Real-time PCR method for qualitative and quantitative detection of Lactobacillus sakei group species targeting novel markers based on bioinformatics analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 355, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Gordillo, R.; Andrade, M.J.; Córdoba, J.J.; Rodríguez, M. Development of an efficient real-time PCR assay to quantify enterotoxin-producing staphylococci in meat products. Food Control 2016, 60, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Basustaoglu, A.C. Double triplex real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus hominis, and Staphylococcus haemolyticus and determination of their methicillin resistance directly from positive blood cult. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.; Iihara, H.; Noda, M.; Song, S.X.; Nhung, P.H.; Ohkusu, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Ezaki, T. dnaJ gene sequence-based assay for species identification and phylogenetic grouping in the genus Staphylococcus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Propidium monoazide combined with real-time PCR for selective detection of viable Staphylococcus aureus in milk powder and meat products. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okolie, C.E.; Wooldridge, K.G.; Turner, D.P.J.; Cockayne, A.; James, R. Development of a heptaplex PCR assay for identification of Staphylococcus aureus and CoNS with simultaneous detection of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Cai, S.; Wu, Q.; Pang, R.; Yang, S.; Xiang, X.; Wang, C.; Zha, F.; Ding, Y.; et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Salmonella in foods based on new molecular targets. LWT 2021, 142, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, A.M.; Esen, O.C.; Quince, C.; Vineis, J.H.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Delmont, T.O. Anvi’o: An advanced analysis and visualization platformfor ’omics data. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, L.; Glover, R.H.; Humphris, S.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Toth, I.K. Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: Soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Dutta, C. BPGA-an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, P.N.; Savka, M.A.; Gan, H.M. In-silico taxonomic classification of 373 genomes reveals species misidentification and new genospecies within the genus Pseudomonas. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyts, S.; Wittouck, S.; De Boeck, I.; Allonsius, C.N.; Pasolli, E.; Segata, N.; Lebeer, S. Large-Scale Phylogenomics of the Lactobacillus casei Group Highlights Taxonomic Inconsistencies and Reveals Novel Clade-Associated Features. mSystems 2017, 2, e00061-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irlinger, F. Safety assessment of dairy microorganisms: Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeders, S.; Huber, I.; Grohmann, L.; Berben, G.; Taverniers, I.; Mazzara, M.; Roosens, N.; Morisset, D. Guidelines for validation of qualitative real-time PCR methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mustapha, A. Multiplex real-time PCR assays for detection of eight Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in food samples by melting curve analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, S.; Bordoloi, P.; Vijaya, D.; Amarnath, S.K.; Sheela Devi, C.; Indumathi, V.A.; Prashanth, K. Simple and economical method for identification and speciation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase negative Staphylococci and its validation by molecular methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 149, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Frigo, F.; Bartolomeoli, I.; Maifreni, M. Safety-related properties of staphylococci isolated from food and food environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebremedhin, B.; Layer, F.; König, W.; König, B. Genetic classification and distinguishing of Staphylococcus species based on different partial gap, 16S rRNA, hsp60, rpoB, sodA, and tuf gene sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Zeng, H.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Multiplex PCR for the Identification of Pathogenic Listeria in Flammulina velutipes Plant Based on Novel Specific Targets Revealed by Pan-Genome Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhou, B.; Xiang, X.; Wang, C.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pang, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Mining of novel target genes through pan-genome analysis for multiplex PCR differentiation of the major Listeria monocytogenes serotypes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Song, L.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Identification and Discrimination of Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum Based on a One-Step Multiplex PCR Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, B.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Yu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M. Multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the simultaneous detection of three foodborne pathogens in seafood. Foods 2020, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilic, A.; Muldrew, K.L.; Tang, Y.W.; Basustaoglu, A.C. Triplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci and determination of methicillin resistance directly from positive blood culture bottles. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 66, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Classification | Species | Strain Number |
|---|---|---|
| Target Staphylococcus | Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC 29213 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | KCTC 1928 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | NCCP 14560 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC 25923 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC 29737 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus | ATCC 6538 | |
| Staphylococcus capitis | NCCP 14663 | |
| Staphylococcus capitis subsp. capitis | KACC 13242 | |
| Staphylococcus caprae | KCTC 3583 | |
| Staphylococcus caprae | NCCP 15629 | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | NCCP 14723 | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | KACC 13234 | |
| Non-target Staphylococcus | Staphylococcus auricularis | KACC 13252 |
| Staphylococcus carnosus subsp. utilis | KACC 13190 | |
| Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii | KACC 13237 | |
| Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. urealyticus | KCTC 3574 | |
| Staphylococcus delphini | KACC 13258 | |
| Staphylococcus equorum subsp. equorum | KACC 13255 | |
| Staphylococcus fleurettii | KACC 13199 | |
| Staphylococcus gallinarum | KACC 13253 | |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | NCCP 14691 | |
| Staphylococcus hominis | NCCP 10748 | |
| Staphylococcus hominis | KACC 13409 | |
| Staphylococcus kloosii | KACC 13256 | |
| Staphylococcus lentus | KCCM 41469 | |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | NCCP 15630 | |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | KACC 11270 | |
| Staphylococcus pasteuri | KCTC 13167 | |
| Staphylococcus pettenkoferi | DSM 19554 | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | NCCP 14670 | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | KCTC 3345 | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | KACC 15799 | |
| Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans | KCCM 41634 | |
| Staphylococcus sciuri subsp. rodentium | KACC 13217 | |
| Staphylococcus sciuri subsp. sciuri | KCCM 41468 | |
| Staphylococcus warneri | KCTC 3340 | |
| Staphylococcus warneri | KACC 10785 | |
| Staphylococcus xylosus | NCCP 10937 | |
| Staphylococcus xylosus | KACC 13239 | |
| Non-Staphylococcus | Bacillus cereus | KCTC 3624 |
| Bacillus cereus | KCTC 1661 | |
| Bacillus cereus | KCCM 1173 | |
| Bacillus cereus | KCCM 1174 | |
| Bacillus cereus | KCCM 40133 | |
| Bacillus cereus | ATCC 11778 | |
| Bacillus cereus | ATCC 10876 | |
| Bacillus cereus | ATCC 14579 | |
| Bacillus circulans | KCTC 3347 | |
| Bacillus licheniformis | KCTC 1026 | |
| Bacillus megaterium | KCTC 3007 | |
| Bacillus subtilis | KCTC 3725 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | ATCC 14810 | |
| Enterococcus avium | KACC 10788 | |
| Enterococcus casseliflavus | KCTC 3552 | |
| Enterococcus cecorum | KACC 13884 | |
| Enterococcus durans | KCTC 13289 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | KCTC 5290 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | KACC 11859 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | KCTC 3206 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | KACC 15681 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | KACC 11954 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | KCTC 13225 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | KACC 14552 | |
| Enterococcus gallinarum | NCCP 11518 | |
| Enterococcus gilvus | KACC 13847 | |
| Enterococcus hirae | KACC 16328 | |
| Enterococcus hirae | KACC 10782 | |
| Enterococcus hirae | KACC 10779 | |
| Enterococcus malodoratus | KACC 13883 | |
| Enterococcus mundtii | KCTC 3630 | |
| Enterococcus raffinosus | KACC 13782 | |
| Enterococcus saccharolyticus | KACC 10783 | |
| Enterococcus thailandicus | KCTC 13134 | |
| Escherichia coli | KCTC 1682 | |
| Escherichia coli | ATCC 25922 | |
| Escherichia coli | ATCC 23763 | |
| Escherichia coli | ATCC 35150 | |
| Escherichia coli | ATCC 43890 | |
| Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli | NCCP 14039 | |
| Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli | NCCP 11076 | |
| Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli | NCCP 15663 | |
| Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli | NCCP 13715 | |
| Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli | NCCP 15732 | |
| Listeria ivanovii | ATCC 19119 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | ATCC 19115 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | KCTC 3569 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | KCTC 2566 | |
| Proteus vulgaris | KCTC 2579 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | KCTC 1636 | |
| Pseudomonas chlororaphis | KCCM 41854 | |
| Pseudomonas oryzihabitans | KCCM 42984 | |
| Salmonella bongori | ATCC 43975 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae | ATCC 13314 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae | ATCC 43973 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica | ATCC 19585 | |
| Salmonella Choleraesuis | ATCC 13312 | |
| Salmonella Gallinarum | ATCC 9120 | |
| Salmonella Paratyphi B | ATCC 10719 | |
| Salmonella Paratyphi C | ATCC 13428 | |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | ATCC 14028 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. houtenae | ATCC 43974 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. indica | ATCC 43976 | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. salamae | ATCC 15793 | |
| Shigella dysenteriae | ATCC 13313 | |
| Shigella sonnei | KCTC 2518 | |
| Vibrio cholerae | NCCP 13589 | |
| Vibrio cholerae | ATCC 14033 | |
| Vibrio cholerae | ATCC 14035 | |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ATCC 17802 | |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | KCCM 41664 | |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ATCC 27969 | |
| Vibrio vulnificus | ATCC 33814 |
| Species | Primer | Sequence | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | Aureus_F | CAA GCA CAA GGC AGT GGT AT | 145 |
| Aureus_R | GTG GCG TTG CAA TCT CCT TA | ||
| S. capitis | Capitis_F | CGC AAG GTG GTC AAC TTG AT | 150 |
| Capitis_R | GCG CAT CGT GAA GTA ATT CC | ||
| S. caprae | Caprae_F | TCG TCG CAA CGA AGT TCA TC | 146 |
| Caprae_R | CCT GGC GCA TAT GTA TGC TT | ||
| S. epidermidis | Epidermidis_F | TGG CAC GGC TGG TAT TAG AG | 121 |
| Epidermidis_R | GAC AGG ATG CGC GAT ACT TG |
| Sample Type | No. of Isolates | No. of Positive Results by Real-Time PCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Aureus | S. Capitis | S. Caprae | S. Epidermidis | ||
| chicken (n = 4) | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| beef (n = 3) | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pork (n = 5) | 38 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| fish (n = 3) | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| salted fish (n = 5) | 22 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 18 |
| raw milk (n = 2) | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| Total (n = 22) | 103 | 36 | 4 | 0 | 63 |
| Sample Type | No. of Samples | No. of Positive Results by Real-Time PCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Aureus | S. Capitis | S. Caprae | S. Epidermidis | ||
| beef | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pork | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| lettuce | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| cucumber | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| raw milk | 34 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 9 |
| fermented fish | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 50 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.; Yang, S.-M.; Won, J.-E.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, H.-Y. Real-Time PCR Method for the Rapid Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Staphylococcus Species Based on Novel Molecular Target Genes. Foods 2021, 10, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112839
Kim E, Yang S-M, Won J-E, Kim D-Y, Kim D-S, Kim H-Y. Real-Time PCR Method for the Rapid Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Staphylococcus Species Based on Novel Molecular Target Genes. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112839
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eiseul, Seung-Min Yang, Ji-Eun Won, Da-Young Kim, Da-Som Kim, and Hae-Yeong Kim. 2021. "Real-Time PCR Method for the Rapid Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Staphylococcus Species Based on Novel Molecular Target Genes" Foods 10, no. 11: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112839
APA StyleKim, E., Yang, S.-M., Won, J.-E., Kim, D.-Y., Kim, D.-S., & Kim, H.-Y. (2021). Real-Time PCR Method for the Rapid Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Staphylococcus Species Based on Novel Molecular Target Genes. Foods, 10(11), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112839







