Instrumental and Sensory Characteristics of Commercial Korean Rice Noodles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bending Test
2.3. Stress–Relaxation Test
2.4. Sensory Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bending Test of Cooked Rice Noodles
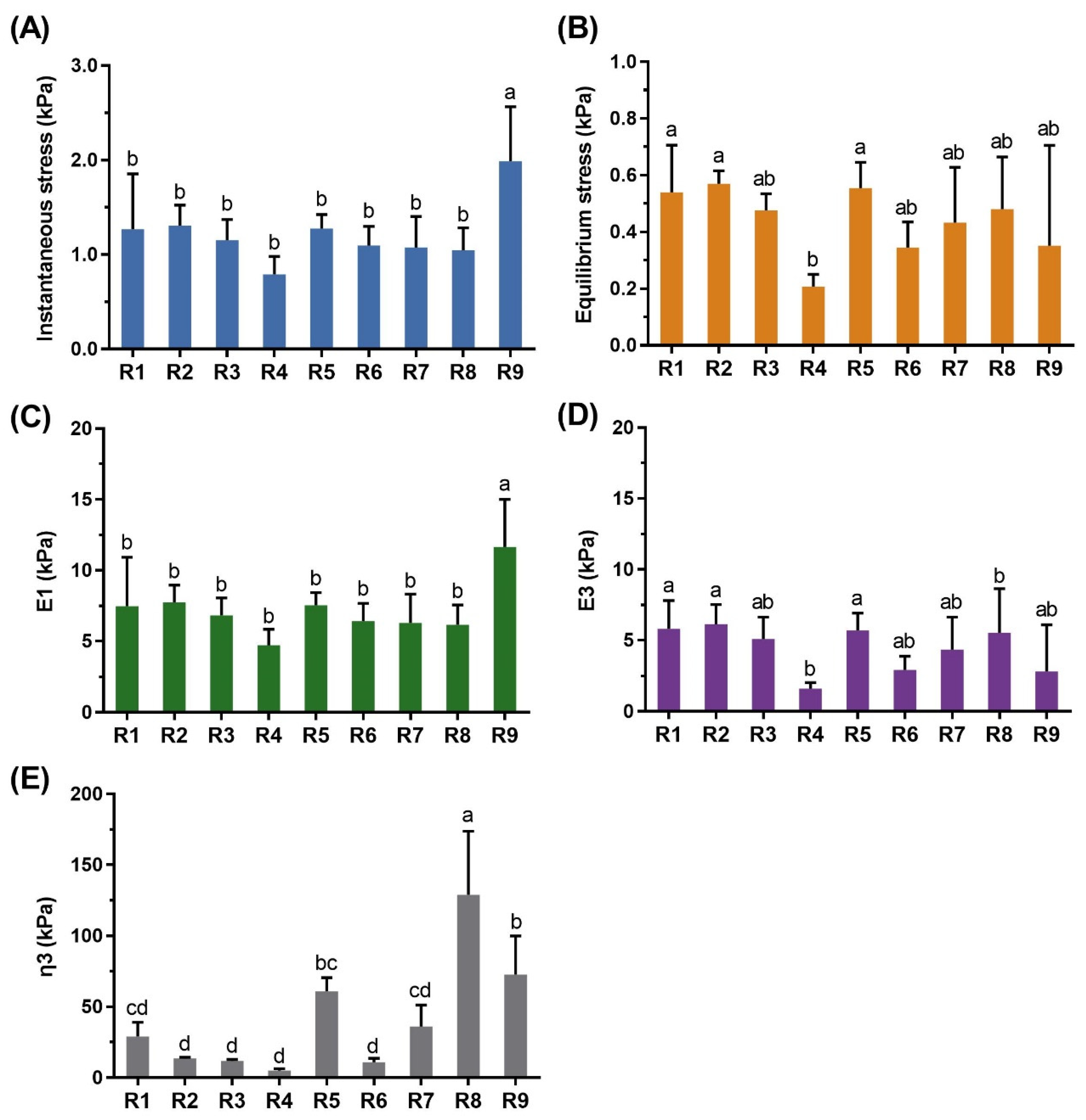
3.2. Stress–Relaxation Test of Cooked Rice Noodles
3.3. Sensory Evaluation of Cooked Rice Noodles
3.4. Correlations between the Mechanical Model Parameters and Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcoa, C.; Rosell, C.M. Effect of different protein isolates and transglutaminase on rice flour properties. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Koh, B.K. A rice noodle making procedure for evaluating rice flour noodle-making potential. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2012, 41, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, T.Y. Noodle making characteristics of goami rice composite flours. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2006, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Kim, C.S. Quality characteristics of rice noodles in Korean market. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2010, 39, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.; Ko, S.; Yoon, M.R.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S. Physicochemical characterization and in-vitro digestibility of extruded rice noodles with different amylose contents based on rheological approaches. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Sasaki, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Yoshihashi, T.; Li, L.T.; Kohyama, K. Effect of amylose content and rice type on dynamic viscoelasticity of a composite rice starch gel. Food Hydrocolloid. 2009, 23, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cham, S.; Suwannaporn, P. Effect of hydrothermal treatment of rice flour on various rice noodles quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangpring, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Ratanasumawong, S. The effect of sodium chloride on microstructure, water migration, and texture of rice noodle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, S.; Basman, A. Effects of gelatinisation level, gum and transglutaminase on the quality characteristics of rice noodle. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.E.; Hort, J.; Hollowood, T. Descriptive Analysis in Sensory Evaluation, 1st ed.; Kemp, S.E., Hort, J., Hollowood, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Delahunty, C.; Baxter, I. Descriptive sensory analysis: Past, present and future. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.S. Quality evaluation of noodles. In Asian Noodle Manufacturing: Ingredients, Technology, and Quality, 1st ed.; Hou, G.G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing and AACC International Press: Duxford, UK, 2020; pp. 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.S. Instrumental measurement of physical properties of cooked Asian wheat flour noodles. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Wang, Z.; Chuang, S.; Shoemaker, C. Viscoelastic property changes in Cheddar cheese during ripening. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffe, J.F. Rheological Methods in Food Process Engineering, 2nd ed.; Freeman Press: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1996; pp. 294–349. [Google Scholar]
- Shiau, S.Y.; Wu, T.T.; Liu, Y.L. Effect of the amount and particle size of wheat fiber on textural and rheological properties of raw, dried and cooked noodles. J. Food Qual. 2012, 35, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Opara, U.L. Texture measurement approaches in fresh and processed foods—A review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.; Prinz, J.; Agrawal, K.; Bruce, I. Food physics and oral physiology. Food Qual. Prefer. 2002, 13, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, M.; Yoon, M.-R.; Lee, S. Preparation and characterization of gluten-free sheeted doughs and noodles with zein and rice flour containing different amylose contents. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, B.K.; Lee, M.R. Effects of starch amylose content of wheat on textural properties of white salted noodles. Cereal Chem. 2003, 80, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Gill, B.; Singh, N.; Saxena, S. The impact of starch properties on noodle making properties of Indian wheat flours. Int. J. Food Prop. 2004, 7, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Sumnu, S.G. Physical Properties of Foods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 39–105. [Google Scholar]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Chillo, S.; Mentana, A.; Baiano, A. Use of the generalized Maxwell model for describing the stress relaxation behavior of solid-like foods. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.H.; Son, H.S.; Koh, B.K.; Lim, S.T. Quality of Korean wheat noodles and its relations to physicochemical properties of flour. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 31, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, N.; Seib, P.; Deyoe, C.; Ward, A. Noodles II. The surface firmness of cooked noodles from soft and hard wheat flours. Cereal Chem. 1985, 62, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Bellido, G.G.; Hatcher, D.W. Asian noodles: Revisiting Peleg’s analysis for presenting stress relaxation data in soft solid foods. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | |
|---|---|
| R1 | Rice flour (98%, Korea), vegetable oil, and refined salt |
| R2 | Rice flour (96%, Korea), potato starch, modified tapioca starch, alginic acid, and refined salt |
| R3 | Rice flour (87%, Vietnam), modified starch, white sugar, refined salt, and guar gum |
| R4 | Rice four (60%), wheat flour, wheat starch, tapioca starch, and refined salt |
| R5 | Rice flour (50%, Korea) wheat flour (34.4%), wheat starch, and refined salt |
| R6 | Rice flour (50%, Korea), wheat flour, corn starch, modified starch, dextrin, guar gum, refined salt, and alkaline reagent |
| R7 | Rice flour (43%, Korea), wheat flour, seaweed concentrated (Hizikia fusiforme, 16.3%), starch, and refined salt |
| R8 | Rice flour (30%, Korea), wheat flour (53.8%, Korea), lotus leaf powder (2%), starch, and refined salt |
| R9 | Rice flour (20%, Korea), wheat flour (78%, Korea), and refined salt (2%) |
| Diameter (mm) | Failure Stress (σ, kPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 °C | 90 °C | ||||
| 3 min | 4 min | 3 min | 4 min | ||
| R1 | 1.11 ± 0.21 | N.d *** | N.d | 0.47 ± 0.12 B,a | 0.38 ± 0.12 B,a |
| R2 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | 1.28 ± 0.21 A,*,a,** | 0.48 ± 0.05 C,b | 0.54 ± 0.18 B,b | 0.13 ± 0.01 C,c |
| R3 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | 1.03 ± 0.23 B,a | 0.76 ± 0.28 B,b | 0.38 ± 0.09 BC,c | 0.30 ± 0.04 B,c |
| R4 | 0.94 ± 0.17 | 0.70 ± 0.29 C,a | 0.43 ± 0.13 C,b | 0.23 ± 0.04 D,c | 0.14 ± 0.05 C,d |
| R5 | 0.91 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.02 D,a | 0.36 ± 0.05 D,b | 0.20 ± 0.02 D,c | 0.30 ± 0.13 B,b |
| R6 | 0.99 ± 0.28 | 0.42 ± 0.24 D,a | 0.34 ± 0.22 D,b | 0.20 ± 0.04 D,c | 0.20 ± 0.07 C,c |
| R7 | 1.10 ± 0.11 | 0.26 ± 0.08 E,a,b | 0.19 ± 0.04 E,b | 0.33 ± 0.17 C,a | 0.37 ± 0.14 B,a |
| R8 | 1.07 ± 0.13 | 0.43 ± 0.19 D,a | 0.53 ± 0.13 C,a | 0.43 ± 0.26 B,a | 0.18 ± 0.02 C,b |
| R9 | 1.12 ± 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.11 B,b | 2.48 ± 1.25 A,a | 1.15 ± 0.17 A,b | 1.20 ± 0.53 A,b |
| Sample | Modulus of Elasticity (mPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 °C | 90 °C | |||
| 3 min | 4 min | 3 min | 4 min | |
| R1 | N.d | N.d *** | 525 ± 53 A,a | 419 ± 64 A,b |
| R2 | 599 ± 32 A,*,a,** | 293 ± 28 B,C,c | 356 ± 33 C,b | 160 ± 32 D,d |
| R3 | 447 ± 11 B,a | 467 ± 77 B,a | 317 ± 27 C,b | 253 ± 24 B,c |
| R4 | 322 ± 32 C,b | 402 ± 92 B,b,a | 267 ± 45 D,c | 179 ± 10 D,d |
| R5 | 317 ± 42 C,a,b | 347 ± 97 B,C,a | 229 ± 29 D,c | 286 ± 75 B,b,c |
| R6 | 283 ± 74 D,a | 278 ± 35 C,a | 238 ± 18 D,a,b | 218 ± 37 C,b |
| R7 | 363 ± 76 C,a | 217 ± 18 D,b | 322 ± 91 C,a | 316 ± 70 B,a |
| R8 | 303 ± 71 C,b | 370 ± 40 B,C,a | 263 ± 53 D,b,c | 200 ± 19 C,c |
| R9 | 363 ± 14 C,c | 673 ± 326 A,a | 424 ± 48 B,b | 400 ± 170 A,b,c |
| Sample | Hardness | Stickiness | Overall Preference |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 5.67 ± 0.98 a,* | 3.40 ± 1.35 c | 4.33 ± 1.45 a |
| R2 | 3.60 ± 1.18 c | 4.53 ± 1.77 a,b | 4.47 ± 1.13 a |
| R3 | 3.80 ± 1.32 c | 3.27 ± 1.10 c | 3.93 ± 1.39 a,b |
| R4 | 4.73 ± 0.96 b | 4.20 ± 1.21 b | 4.80 ± 0.94 a |
| R5 | 4.40 ± 1.80 b | 4.13 ± 1.25 b | 4.00 ± 1.13 a,b |
| R6 | 3.60 ± 1.45 c | 5.20 ± 1.42 a | 4.13 ± 1.55 a,b |
| R7 | 5.47 ± 1.68 a | 4.00 ± 1.25 b | 3.53 ± 1.60 b |
| R8 | 5.00 ± 1.07 a,b | 3.67 ± 1.45 c | 3.47 ± 1.51 b |
| R9 | 3.87 ± 1.51 c | 3.67 ± 1.29 c | 4.47 ± 1.64 a |
| Diameter | FS | ME | IS | ES | E3 | η3 | SH | SS | SO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 1 | |||||||||
| FS | 0.29 | 1 | ||||||||
| ME | 0.33 | 0.60 *** | 1 | |||||||
| IS | 0.07 | 0.68 *** | 0.30 | 1 | ||||||
| ES | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 1 | |||||
| E3 | 0.08 | −0.03 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.95 *** | 1 | ||||
| η3 | 0.36 | 0.34 | −0.06 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.38 * | 1 | |||
| SH | 0.61 *** | 0.11 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 1 | ||
| SS | 0.48 * | 0.35 | 0.52 ** | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.43 * | 1 | |
| SO | 0.44 * | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.39 * | 0.44 * | 0.54 ** | 0.31 | 0.20 | 1 |
| FS | ME | IS | ES | E3 | η3 | SH | SS | SO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice content | −0.27 | 0.38 * | −0.25 | 0.43 * | 0.45 * | −0.65 ** | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, A.-H.; Oh, S.-M.; Ye, S.-J.; Kim, H.-Y.; Bae, J.-E.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, B.-Y.; Baik, M.-Y. Instrumental and Sensory Characteristics of Commercial Korean Rice Noodles. Foods 2021, 10, 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112885
Lee A-H, Oh S-M, Ye S-J, Kim H-Y, Bae J-E, Choi J-H, Kim B-Y, Baik M-Y. Instrumental and Sensory Characteristics of Commercial Korean Rice Noodles. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112885
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ah-Hyun, Seon-Min Oh, Sang-Jin Ye, Hui-Yun Kim, Ji-Eun Bae, Jong-Hyun Choi, Byung-Yong Kim, and Moo-Yeol Baik. 2021. "Instrumental and Sensory Characteristics of Commercial Korean Rice Noodles" Foods 10, no. 11: 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112885
APA StyleLee, A.-H., Oh, S.-M., Ye, S.-J., Kim, H.-Y., Bae, J.-E., Choi, J.-H., Kim, B.-Y., & Baik, M.-Y. (2021). Instrumental and Sensory Characteristics of Commercial Korean Rice Noodles. Foods, 10(11), 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112885






