Valle Agricola Chickpeas: Nutritional Profile and Metabolomics Traits of a Typical Landrace Legume from Southern Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Material and Sampling
2.3. Ash, Moisture Content and Macronutrient Content
2.4. Amino Acid Composition
2.5. Determination of Trypsin and Chymotrypsin Inhibitory Activities
2.6. Digestibility of Proteins In Vitro
2.7. Determination of Minerals Content
2.8. Chemical Composition Insight by Means of UHPLC-TOF-MS and TOF-MS2 Analyses
2.8.1. Sample Preparation
2.8.2. UHPLC Parameters
2.8.3. TOF-MS and TOF-MS2 Parameters
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
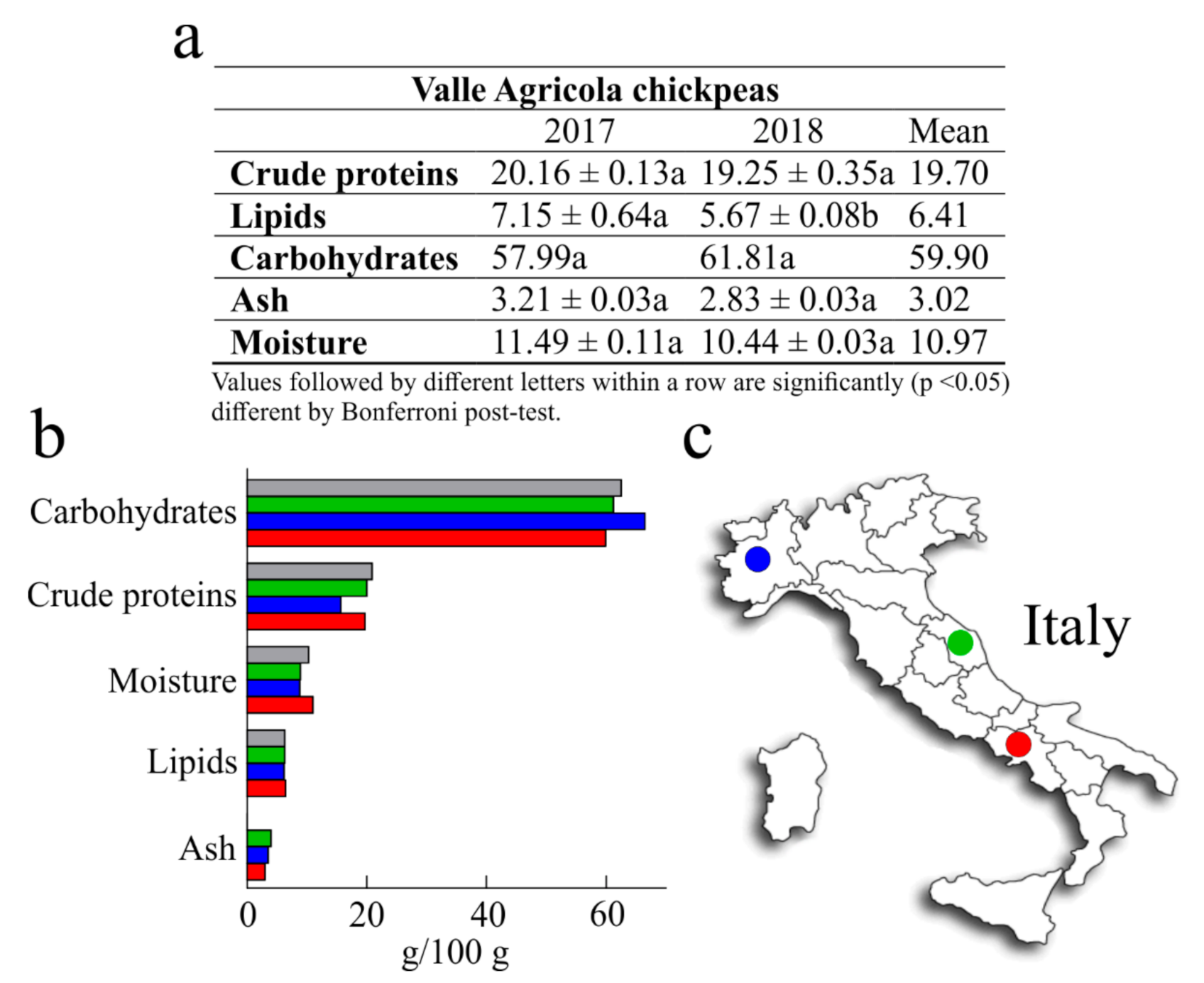
3.1. Nutritional Values
3.2. Amino Acid Content
3.3. Anti-Proteinase Inhibitor Activity
3.4. Digestibility of Soluble Raw Chickpeas Proteins Extract In Vitro
3.5. Mineral Content
3.6. UHPLC-HRMS Profiling of Cf-W Extract
3.7. UHPLC-HRMS Profiling of Cf-O Extract
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saulle, R.; La Torre, G. The Mediterranean Diet, recognized by UNESCO as a cultural heritage of humanity. Ital. J. Public Health 2010, 7, 414–415. [Google Scholar]
- Keys, A.; Menotti, A.; Karvonen, M.J.; Aravanis, C.; Blackburn, H.; Buzina, R.; Djordjevic, B.S.; Dontas, A.S.; Fidanza, F.; Keys, M.H.; et al. The diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, P.; Montinari, M.R. The Mediterranean Diet and Cardioprotection: Historical Overview and Current Research. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2019, 12, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health status: An updated meta-analysis and a proposal for a literature-based adherence score. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontou, N.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Panagiotakos, D.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Linos, A. The mediterranean diet in cancer prevention: A review. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquiaga, I.; Echeverria, G.; Dussaillant, C.; Rigotti, A. Origin, components and mechanisms of action of the Mediterranean diet. Rev. Med. Chile 2017, 145, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchenak, M.; Lamri-Senhadji, M. Nutritional quality of legumes, and their role in cardiometabolic risk prevention: A review. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudryj, A.N.; Yu, N.; Aukema, H.M. Nutritional and health benefits of pulses. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennetau-Pelissero, C. Plant Proteins from Legumes. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 223–265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D. Legume Consumption and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8450618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lam, H.-M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Varshney, R.K.; Colmer, T.D.; Cowling, W.; Bramley, H.; Mori, T.A.; Hodgson, J.M.; et al. Neglecting legumes has compromised human health and sustainable food production. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knights, E.J.; Hobson, K.B. Chickpea Overview. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho Villa, T.C.; Maxted, N.; Scholten, M.; Ford-Lloyd, B. Defining and identifying crop landraces. Plant Genet. Resour. 2005, 3, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.; Mezzacapo, M.C.; Ragucci, S.; Iannuzzi, F.; Zarrelli, A.; Di Maro, A. Valle Agricola lentil, an unknown lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) seed from Southern Italy as a novel antioxidant and prebiotic source. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburino, R.; Guida, V.; Pacifico, S.; Rocco, M.; Zarelli, A.; Parente, A.; Di Maro, A. Nutritional values and radical scavenging capacities of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Seeds in valle agricola district, Italy. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Fiorentino, M.; Guida, V.; Di Maro, A. Nutritional values and metabolic profile with and without boiled treatment of ‘Gallo Matese’ beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), a landrace from Southern Italy. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2017, 16, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regione_Campania Prodotti tipici Regione Campania. Gazz. Uff. 2019, 60 (Suppl. 9), 10–16.
- Wood, J.A.; Grusak, M.A. Nutritional Value of Chickpea. In Chickpea Breeding and Management; Yadav, S.S., Chen, W., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; pp. 101–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, T.C.; Murray, R.; Zelman, K.M. The Nutritional Value and Health Benefits of Chickpeas and Hummus. Nutrients 2016, 8, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Ragucci, S.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.; Iannuzzi, F.; Zarrelli, A.; Piccolella, S.; Di Maro, A. Pioppino mushroom in southern Italy: An undervalued source of nutrients and bioactive compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5388–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Di Maro, A.; Dosi, R.; Ferrara, L.; Rocco, M.; Sepe, J.; Ferrari, G.; Parente, A. Free amino acid profile in Malus domestica cv Annurca apples from the Campania region and other Italian vegetables. AJCS 2011, 5, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; He, X.; Ma, H. Subunit, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of protein isolates from Chinese kabuli and desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, N.; Ruocco, M.R.; Ragucci, S.; Aliotta, F.; Nasso, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Di Maro, A. Quinoa as source of type 1 ribosome inactivating proteins: A novel knowledge for a revision of its consumption. Food Chem. 2020, 128337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarpazhooh, E.; Boye, J.I. Composition of Processed Dry Beans and Pulses. In Dry Beans and Pulses Production, Processing and Nutrition; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 101–128. [Google Scholar]
- CREA. Centro di Ricerca per Gli Alimenti e la Nutrizione. Available online: http://nut.entecra.it/ (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Rizzello, C.G.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Curiel, J.A.; Pinto, D.; Marzani, B.; Coda, R.; Gobbetti, M. Italian legumes: Effect of sourdough fermentation on lunasin-like polypeptides. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaccardelli, M.; Sonnante, G.; Lupo, F.; Piergiovanni, A.R.; Laghetti, G.; Sparvoli, F.; Lioi, L. Characterization of Italian chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm by multidisciplinary approach. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2013, 60, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, C. Variation and relationships among some nutritional traits in Sicilian genotypes of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Food Qual. 2006, 29, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Todd, C.D.; Trovato, M.; Forlani, G.; Funck, D. Physiological implications of arginine metabolism in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortés-Giraldo, I.; Megías, C.; Alaiz, M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J. Purification of free arginine from chickpea (Cicer arietinum) seeds. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, C.F.; Mueller, D.D.; Faubion, J.M.; Paulsen, G.M. Identification of l-Tryptophan as an Endogenous Inhibitor of Embryo Germination in White Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1988, 88, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comai, S.; Bertazzo, A.; Bailoni, L.; Zancato, M.; Costa, C.V.L.; Allegri, G. Protein and non-protein (free and protein-bound) tryptophan in legume seeds. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Dhewa, T. Plant food anti-nutritional factors and their reduction strategies: An overview. FPPN 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shridhar, K.S. Chemistry and Implications of Antinutritional Factors in Dry Beans and Pulses. In Dry Beans and Pulses Production, Processing and Nutrition; Muhammad, S., Mark, A.U., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Ames, IA, USA, 2012; pp. 359–377. [Google Scholar]
- Aviles-Gaxiola, S.; Chuck-Hernandez, C.; Serna Saldivar, S.O. Inactivation Methods of Trypsin Inhibitor in Legumes: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nkhata, S.G.; Ayua, E.; Kamau, E.H.; Shingiro, J.B. Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals and legumes through activation of endogenous enzymes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2446–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Türkdoğan, M.K.; Kilicel, F.; Kara, K.; Tuncer, I.; Uygan, I. Heavy metals in soil, vegetables and fruits in the endemic upper gastrointestinal cancer region of Turkey. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regione_Campania Regional Agro-Meteorological Center. Available online: http://agricoltura.regione.campania.it/meteo/agrometeo.htm (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Guo, J.; Kang, Z.; Babar, M.A. Comparative Physiological and Metabolic Analysis Reveals a Complex Mechanism Involved in Drought Tolerance in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Induced by PGPR and PGRs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueckert, R.A.; Thavarajah, D.; Thavarajah, P.; Pritchard, J. Phytic acid and mineral micronutrients in field-grown chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars from western Canada. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 233, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, H.; Bett, K.; Tar’an, B.; Vandenberg, A.; Thavarajah, D.; Warkentin, T. Mineral Micronutrient Content of Cultivars of Field Pea, Chickpea, Common Bean, and Lentil Grown in Saskatchewan, Canada. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, E.M.; Blank, L.M.; Heyland, J.; Baumbach, J.I.; Schmid, A.; Hayen, H. Glycerophospholipid profiling by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry using exact mass measurements and multi-stage mass spectrometric fragmentation experiments in parallel. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y. Fragmentation patterns of five types of phospholipids by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, D.L.; Toan, T.Q.; Dang, L.P.; Imbs, A.B.; Long, P.Q.; Thang, T.D.; Matthaeus, B.; Bach, L.G.; Bui, L.M. Lipid isolation process and study on some molecular species of polar lipid isolated from seed of Madhuca ellitica. Processes 2019, 7, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Clemente, A.; Vioque, J.; Bautista, J.; Millán, F. Polar lipids of defatted chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour and protein isolates. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obendorf, R.L.; Horbowicz, M.; Lahuta, L.B. CHAPTER 11 Characterization of Sugars, Cyclitols and Galactosyl Cyclitols in Seeds by GC. In Dietary Sugars: Chemistry, Analysis, Function and Effects; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 167–185. [Google Scholar]
- Peterbauer, T.; Richter, A. Biochemistry and physiology of raffinose family oligosaccharides and galactosyl cyclitols in seeds. Seed Sci. Res. 2001, 11, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gangola, M.P.; Jaiswal, S.; Kannan, U.; Gaur, P.M.; Båga, M.; Chibbar, R.N. Galactinol synthase enzyme activity influences raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFO) accumulation in developing chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds. Phytochemistry 2016, 125, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunraj, R.; Skori, L.; Kumar, A.; Hickerson, N.M.N.; Shoma, N.M.V.; Samuel, M.A. Spatial regulation of alpha-galactosidase activity and its influence on raffinose family oligosaccharides during seed maturation and germination in Cicer arietinum. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1709707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, D.; He, J.; Dai, Z.; Asad, R.; Ou, S.; Zeng, X. Effects of ciceritol from chickpeas on human colonic microflora and the production of short chain fatty acids by in vitro fermentation. LWT 2017, 79, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekky, R.H.; Contreras, M.d.M.; El-Gindi, M.R.; Abdel-Monem, A.R.; Abdel-Sattar, E.; Segura-Carretero, A. Profiling of phenolic and other compounds from Egyptian cultivars of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and antioxidant activity: A comparative study. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17751–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, G. Isoflavone content and composition in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) sprouts germinated under different conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megías, C.; Cortés-Giraldo, I.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J.; Girón-Calle, J. Isoflavones in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) protein concentrates. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Camargo, A.C.; Favero, B.T.; Morzelle, M.C.; Franchin, M.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; de la Rosa, L.A.; Geraldi, M.V.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R.; Shahidi, F.; Schwember, A.R. Is Chickpea a Potential Substitute for Soybean? Phenolic Bioactives and Potential Health Benefits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.R.; Wang, J.; Qi, H.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Pang, L.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Duan, M.J.; Chen, H.; Cao, X.; et al. Assessment of the estrogenic activities of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) sprout isoflavone extract in ovariectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hur, H.; Rafii, F. Biotransformation of the isoflavonoids biochanin A, formononetin, and glycitein by Eubacterium limosum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 192, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolleson, W.H.; Doerge, D.R.; Churchwell, M.I.; Marques, M.M.; Roberts, D.W. Metabolism of biochanin A and formononetin by human liver microsomes in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4783–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Iqbal, S.; Ahmad, S.; Imran, M.; Niaz, A.; Bhanger, M.I. Nutritional and compositional study of Desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars grown in Punjab, Pakistan. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, A.; Barros, L.; Fernandes, Â.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C. Valorization of traditional foods: Nutritional and bioactive properties of Cicer arietinum L. and Lathyrus sativus L. pulses. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachwa-Rosiak, D.; Nebesny, E.; Budryn, G. Chickpeas—Composition, nutritional value, health benefits, application to bread and snacks: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.I.; Mota, J.; Monteiro, S.A.; Ferreira, R.M. Legume seeds and colorectal cancer revisited: Protease inhibitors reduce MMP-9 activity and colon cancer cell migration. Food Chem. 2016, 197 Pt A, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Valle Agricola Chickpeas | CREA Chickpeas | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | 2017 | 2018 | Mean | |
| Essential amino acids | ||||
| His | 0.67 ± 0.05 a | 0.55 ± 0.06 a | 0.61 | 0.53 |
| Ile | 0.76 ± 0.02 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 a | 0.71 | 0.89 |
| Leu | 1.42 ± 0.01 a | 1.20 ± 0.10 a | 1.31 | 1.61 |
| Lys | 1.50 ± 0.02 a | 1.35 ± 0.17 a | 1.42 | 1.43 |
| Met | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| Phe | 1.33 ± 0.01 a | 1.14 ± 0.03 a | 1.23 | 1.27 |
| Thr | 0.92 ± 0.01 a | 0.82 ± 0.02 a | 0.87 | 0.79 |
| Trp | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.22 |
| Val | 0.80 ± 0.01 a | 0.68 ± 0.03 a | 0.74 | 0.97 |
| Non-essential amino acids | ||||
| Ala | 0.97 ± 0.00 a | 0.79 ± 0.04 a | 0.88 | 0.86 |
| Arg | 2.21 ± 0.03 a | 1.58 ± 0.07 b * | 1.89 | 1.92 |
| Asx | 2.02 ± 0.08 a | 1.65 ± 0.05 a | 1.83 | 2.40 |
| Cys § | 0.33 ± 0.01 a | 0.35 ± 0.03 a | 0.34 | 0.25 |
| Glx | 3.76 ± 0.17 a | 3.00 ± 0.07 b ** | 3.38 | 3.41 |
| Gly | 0.83 ± 0.03 a | 0.68 ± 0.03 a | 0.76 | 0.81 |
| Pro | 0.81 ± 0.07 a | 0.57 ± 0.08 a | 0.69 | 0.83 |
| Ser | 1.35 ± 0.07 a | 1.12 ± 0.01 a | 1.23 | 1.06 |
| Tyr | 0.62 ± 0.04 a | 0.53 ± 0.02 a | 0.58 | 0.66 |
| Total | 20.55 | 16.87 | 18.71 | 20.14 |
| Element | 2017 | 2018 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 2.29 ± 0.115 | 2.52 ±0.126 | 2.40 |
| Ca | 174.6 ± 8.733 * | 226.4 ± 11.32 * | 200 |
| Mn | 0.231 ± 0.011 * | 0.668 ± 0.033 * | 0.45 |
| Fe | 2.025 ± 0.101 * | 6.625 ± 0.331 * | 4.30 |
| Zn | 2.437 ± 0.122 * | 5.937 ± 0.297 * | 4.20 |
| Mg | 141.2 ± 7.058 * | 187.7 ± 9.384 * | 164 |
| Cu | 0.79 ± 0.039 | 0.87 ± 0.043 | 0.83 |
| K | 645 ± 32.25 * | 852 ± 42.6* | 748 |
| Peak n. | RT (min) | Tentative Identification | Formula | (M-H)− calc. (m/z) | (M-H)− Found (m/z) | RDB | Error (ppm) | MS/MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerophoshpolipids | ||||||||
| 1 | 0.603 | GPE(18:2/16:0) | C39H74NO8P | 714.5079 | 714.5077 | 4 | −0.3 | 714.5079; 452.2753; 434.2707; 279.2330; 255.2330, 196.0363; 140.0125 |
| 2 | 0.604 | GPE(18:2/18:2) | C41H74NO8P | 738.5079 | 738.5062 | 6 | −2.3 | 738.5079; 476.2783; 458.2659; 279.2330; 196.0363; 140.0113 |
| 3 | 0.608 | GPE(18:2/18:2-diOH) | C41H74NO10P | 770.4978 | 770.4961 | 6 | −2.2 | 770.4978; 752.4895; 293.2122; 281.2500; 279.2330; 196.0401; 140.0133 |
| 4 | 0.609 | GPC(18:2/16:0) | C43H82NO10P | 802.5604 (M + FA)− | 802.5585 | 4 | −2.3 | 802.5604; 742.5443; 480.3130; 293.2130; 279.2330; 255.2341; 168.0451 |
| 5 | 0.611 | GPC(18:2/18:2) | C45H82NO10P | 826.5604 (M + FA)− | 826.5579 | 6 | −3.0 | 826.5604; 766.5409; 504.3070; 486.2995; 279.2330; 168.0436 |
| Carbohydrates | ||||||||
| 6 | 2.237 | Dihexose (e.g., sucrose) | C12H22O11 | 341.1089 | 341.1076 | 2 | −3.9 | 341.1089; 179.0557; 161.0456; 149.0455; 143.0352; 131.0347; 119.0352; 113.0245; 101.0247; 89.0248 |
| 7 | 2.630 | Galactopinitol (or methylgalactinol) 1 | C13H24O11 | 355.1246 | 355.1229 | 2 | −4.8 | 355.1244; 193.0708; 179.0566; 175.0608; 161.0448; 149.0445; 143.0337; 131.0342; 125.0240; 119.0347; 113.0242; 101.0242; 89.0245 |
| 8 | 2.781 | Galactopinitol (or methylgalactinol) 2 | C13H24O11 | 355.1246 | 355.1252 | 2 | 1.7 | 355.1250; 193.0719; 161.0458; 157.0509; 141.0197; 125.0255; 119.0355; 113.0254; 101.0253; 99.0099; 89.0250 |
| 9 | 3.549 | Dihexosylglycerol | C15H28O13 | 415.1457 | 415.1441 | 2 | −3.9 | 415.1457; 305.0889; 287.0756; 263.0768; 253.0934; 235.0826; 221.0663; 185.0456; 179.0561; 161.0457; 149.0468; 143.0350; 131.0349; 125.0244; 119.0350; 113.0246; 101.0245; 89.0247 |
| 10 | 3.740 | Trihexose (e.g., raffinose) | C18H32O16 | 503.1618 | 503.1614 | 3 | −0.7 | 503.1627; 341.1077; 323.0983; 281.0877; 251.0769; 221.0669; 179.0563; 161.0453; 149.0452; 143.0350; 131.0347; 119.0351; 113.0245; 101.0244; 89.0248 |
| 11 | 3.991 | Galactinol | C12H22O11 | 341.1089 | 341.1073 | 2 | −0.1 | 341.1087; 179.0566; 161.0455; 149.0450; 143.0357; 131.0349; 125.0242; 119.0347; 113.0243; 107.0335; 101.0243; 89.0243 |
| 12 | 4.122 | Ciceritol | C19H34O16 | 517.1774 | 517.1773 | 3 | −0.2 | 517.1774; 337.1128; 281.0869; 263.0760; 221.0661; 193.0713; 179.0561; 161.0454; 149.0455; 143.0349; 131.0349; 125.0241; 119.0350; 113.0245; 101.0246; 89.0249 |
| 13 | 4.967 | Tetrasaccharide (e.g., stachyose) | C24H42O21 | 665.2150 | 665.2146 | 4 | 0.6 | 665.2152; 503.1611; 485.1504; 443.1403; 425.1305; 383.1194; 341.1086; 281.0872; 251.0763; 221.0665; 203.0562; 179.0562; 161.0441; 143.0344; 119.0348; 113.0249; 101.0247; 89.0248. |
| 14 | 5.141 | Fagopyritol B2 | C18H32O16 | 503.1618 | 503.1609 | 3 | −1.7 | 503.1613; 341.1095; 323.0972; 281.0898; 263.0760; 221.0651; 179.0560; 161.0455; 149.0441; 143.0352; 131.0351; 125.0246; 119.0349; 113.0245; 101.0245; 89.0247. |
| 15 | 5.254 | Galactosyl-ciceritol | C25H44O21 | 679.2302 | 679.2298 | 4 | −0.6 | 679.2309; 661.2172; 499.1667; 443.1388; 383.1191; 341.1076; 281.0866; 251.0764; 221.0668; 179.0565; 161.0456; 143.0353; 131.0354; 125.0249; 119.0351; 113.0248; 101.0249; 89.0251. |
| Hydroxybenzoic acids and isoflavones | ||||||||
| 16 | 0.508 | O-Methylgenistein 1 | C16H12O5 | 283.0612 | 283.0608 | 11 | −1.4 | 283.0612; 268.0385; 267.0312; 239.0323; 211.0374; 195.0423; 167.0466; 132.0168 |
| 17 | 0.533 | O-Methyldaidzein | C16H12O4 | 267.0663 | 267.0664 | 11 | 0.4 | 267.0663; 252.0419; 251.0334; 224.0452; 223.0379; 195.0418; 167.0460; 145.0040; 132.0170; 91.0132 |
| 18 | 0.534 | O-Methylgenistein 2 | C16H12O5 | 283.0612 | 283.0611 | 11 | −0.3 | 283.0612; 268.0381; 267.0311; 239.0331; 211.0373; 195.0412; 167.0469; 132.0164 |
| 19 | 2.315 | Hydroxybenzoic acid hexosylpentoside | C18H24O12 | 431.1195 | 431.1204 | 7 | 2.1 | 431.1195; 299.0780; 137.0244; 93.0347; 89.0245 |
| 20 | 5.209 | Dihydroxybenzoic acid hexoside | C13H16O9 | 315.0722 | 315.0721 | 6 | −0.2 | 315.0721; 153.0185; 152.0111; 109.0291; 108.0212 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landi, N.; Piccolella, S.; Ragucci, S.; Faramarzi, S.; Clemente, A.; Papa, S.; Pacifico, S.; Di Maro, A. Valle Agricola Chickpeas: Nutritional Profile and Metabolomics Traits of a Typical Landrace Legume from Southern Italy. Foods 2021, 10, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030583
Landi N, Piccolella S, Ragucci S, Faramarzi S, Clemente A, Papa S, Pacifico S, Di Maro A. Valle Agricola Chickpeas: Nutritional Profile and Metabolomics Traits of a Typical Landrace Legume from Southern Italy. Foods. 2021; 10(3):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030583
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandi, Nicola, Simona Piccolella, Sara Ragucci, Shadab Faramarzi, Angela Clemente, Stefania Papa, Severina Pacifico, and Antimo Di Maro. 2021. "Valle Agricola Chickpeas: Nutritional Profile and Metabolomics Traits of a Typical Landrace Legume from Southern Italy" Foods 10, no. 3: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030583
APA StyleLandi, N., Piccolella, S., Ragucci, S., Faramarzi, S., Clemente, A., Papa, S., Pacifico, S., & Di Maro, A. (2021). Valle Agricola Chickpeas: Nutritional Profile and Metabolomics Traits of a Typical Landrace Legume from Southern Italy. Foods, 10(3), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030583












