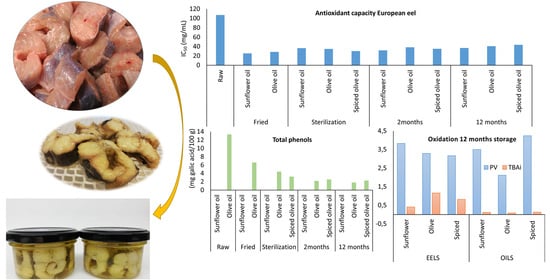
Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Activity in Canned Eels: Effect of Processing and Filling Medium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Measurement of the Acidity, Peroxide Value, and Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Index in Eels and Oils
2.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.5. Determination of Vitamin E Content
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Processing and Filling Medium on Acidity
3.2. Effect of Processing and Filling Medium on Peroxide and TBARS Values
3.3. Effect of Processing and Filling Medium on Antioxidant Capacity
3.4. Effect of Processing and Filling Medium on Vitamin E Content
3.5. Effect of Processing and Filling Medium on Total Phenolic Content
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gómez-Limia, L.; Cobas, N.; Franco, I.; Martínez-Suárez, S. Fatty acid profiles and lipid quality indices in canned European eels: Effects of processing steps, filling medium and storage. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.O.; Remya, S.; Murthy, L.N.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Asok Kumar, K. Effect of filling medium on cooking time and quality of canned yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Control 2015, 50, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Limia, L.; Franco, I.; Martínez-Suárez, S. Effects of processing step, filling medium and storage on amino acid profiles and protein quality in canned European eels. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, G.; Parisi, G. From farm to fork: Lipid oxidation in fish products. A review. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A comprehensive review on lipid oxidation in meat and meat products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleem, A.; Aziz, S.; Iqtedar, M.; Abdullah, R.; Aftab, M.; Rashid, F.; Shakoori, F.R.; Naz, S. Investigating changes and effect of peroxide values in cooking oils subject to light and heat. FUUAST J. Biol. 2015, 5, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Zhou, J.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Nutritional characterization of sea bass processing by-products. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Wang, M.; Barba, F.J.; Bermúdez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Nutritional profiling and the value of processing by-products from gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Mechanisms and factors for edible oil oxidation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2006, 5, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, E.; Mangione, A.; Marconi, O.; Perretti, G. Comparative study of oxidation in canned foods with a combination of vegetables and covering oils. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2015, 27, 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pateiro, M.; Barba, F.J.; Domínguez, R.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Gavahian, M.; Gómez, B.; Lorenzo, J.M. Essential oils as natural additives to prevent oxidation reactions in meat and meat products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Domínguez, R.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Application of essential oils as antimicrobial agents against spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. AOAC. 2005. Available online: https://www.aoac.org/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- European Commission Regulation. European Regulation EU 2016/1227 of 27 July 2016 amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis. Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOCS Official methods and recommended practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society 2009. Available online: https://www.aocs.org/attain-lab-services/methods (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Kirk, S.; Sawyer, R. Pearson’s Composition and Analysis of Foods, 9th ed.; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armesto, J.; Gómez-Limia, L.; Carballo, J.; Martínez, S. Impact of vacuum cooking and boiling and refrigerated storage on the quality of galega kale (Brassica oleracea var. acephala cv. Galega). LWT Food Sc.Tech. 2017, 79, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- El Lahamy, A.A. Mohamed changes in fish quality during canning process and storage period of canned fish products: Review article. Glob. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Regulation. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 1348/2013 of 16 December 2013 amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis 2013. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 338, 31–67. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.S.P.; Cruz, R.; Cunha, S.C.; Casal, S. Effect of cooking on olive oil quality attributes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Pinto, J.; Carrola, J.; Paiva-Martins, F. Oxidative stability of olive oil after food processing and comparison with other vegetable oils. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerretani, L.; Bendini, A.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Vittadini, E.; Chiavaro, E. Microwave heating of different commercial categories of olive oil: Part I. Effect on chemical oxidative stability indices and phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiro, R.; Oliveira, I.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Falcão, S.; Bento, A.; Pereira, J.A. Effect of microwave heating with different exposure times on physical and chemical parameters of olive oil. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, M.A.; Grati-Kamoun, N.; Attia, H. Physico-chemical change and heat stability of extra virgin olive oils flavoured by selected Tunisian aromatic plants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2613–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Pickova, J.; Ahmad, T.; Liaquat, M.; Farid, A.; Jahangir, M. Oxidation of lipids in foods. Sarhad J. Agric. 2016, 32, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Bochi, V.C.; Ribeiro, C.P.; Victório, A.d.M.; Emanuelli, T. Effect of different cooking methods on the oxidation, proximate and fatty acid composition of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) fillets. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, K.M. Lipid oxidation: Theoretical aspects. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; Wiley, A., Ed.; Interscience Publication, John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 269–299. [Google Scholar]
- Estevez, M. Oxidative damage to poultry: From farm to fork. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, S.; Monser, L.; Sadok, S. The influence of local canning process and storage on pelagic fish from Tunisia: Fatty acid profiles and quality indicators. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2008, 32, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shehawy, S.M.; Farag, Z.S. Safety assessment of some imported canned fish using chemical, microbiological and sensory methods. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, A.; Jasour, M.S. Improvement of lipid stability of refrigerated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets by pre-storage α-tocopherol acetate dipping treatment. Vet. Res. Forum 2012, 3, 269–73. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, M.; Rezaei, M.; Moieni, S.; Hosseini, H.; Eskandari, S. Effects of different filling media on the oxidation and lipid quality of canned silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Oliveira, A.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B.; Crapo, C. Salt effect on heat-induced physical and chemical changes of salmon fillet (O. gorbuscha). Food Chem. 2008, 106, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmesat, S.; Morales, A.; Velasco, J.; Dobarganes, M.C. Action and fate of natural and synthetic antioxidants during frying. Grasas Aceites 2010, 61, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Uriarte-Montoya, M.H.; Villalba-Villalba, A.G.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Ramirez-Suarez, J.C.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; García-Sánchez, G.; Carvallo-Ruíz, M.G. Changes in quality parameters of Monterey sardine (Sardinops sagax caerulea) muscle during the canning process. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, B.; Singh, V.K.; Shrestha, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Jeevaratnam, K.; Koner, B.C. Comparative evaluation of peroxidation of sesame and cottonseed oil induced by different methods of heating. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2019, 78, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, I.; Sacchi, R.; Biondi, L.; Aubourg, S.P.; Livio, P. Effect of packing media on the oxidation of canned tuna lipids. antioxidant effectiveness of extra virgin olive oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, B.; Gençcelep, H. Determination of biogenic amines in fish products. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguy, I.S.; Dana, D. Integrated approach to deep fat frying: Engineering, nutrition, health and consumer aspects. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talab, A.S. Effect of cooking methods and freezing storage on the quality characteristics of fish cutlets. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, J.; Zakipour Rahimabadi, E.; Che Man, Y.B. Lipid characteristics in cooked, chill reheated fillets of Indo-Pacificking mackerel (Scomberomorous guttatus). LWT Food Sci. Tech. 2008, 41, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneniwa, M.; Miao, S.; Yuan, C.; Iida, H.; Fukuda, Y. Lipid components and enzymatic hydrolysis of lipids in muscle of Chinese fresh-water fish. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.S.; Galano, J.M.; Durand, T.; Lee, J.C.Y. Profiling of omega-polyunsaturated fatty acids and their oxidized products in salmon after different cooking methods. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saghir, S.; Thurner, K.; Wagner, K.H.; Frisch, G.; Luf, W.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Elmadfa, I. Effects of different cooking procedures on lipid quality and cholesterol oxidation of farmed salmon fish (Salmo salar). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5290–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Mahoonak, A.S.; Nikoo, A.M.; Rahmanian, N.; Hajitabar, J.; Meshginfar, N. The effect of natural antioxidants extracted from plant and animal resources on the oxidative stability of soybean oil. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhibshi, E.A.; Ibraheim, J.A.; Hadad, A.S. Effect of heat processing and storage on characteristic and stability of some edible oils. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Agriculture, Environment and Biological Sciences, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21–22 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naz, S.; Siddiqi, R.; Sheikh, H.; Sayeed, S.A. Deterioration of olive, corn and soybean oils due to air, light, heat and deep-frying. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajtal, A.I.; Sherami, F.E.; Elbagermi, M.A. Acid, Peroxide, ester and saponification values for some vegetable oils before and after frying. AASCIT J. Mater. 2018, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.C.O.; Santos, I.M.G.; Souza, A.G. Effect of heating and cooling on rheological parameters of edible vegetable oils. J. Food Eng. 2005, 67, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponio, F.; Giarnetti, M.; Summo, C.; Paradiso, V.M.; Cosmai, L.; Gomes, T. A comparative study on oxidative and hydrolytic stability of monovarietal extra virgin olive oil in bakery products. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, J.M.; Miles, D.R.B.; Crockett, E.L. Temperature acclimation alters oxidative capacities and composition of membrane lipids without influencing activities of enzymatic antioxidants or susceptibility to lipid peroxidation in fish muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhouri, A.M.; Fekih, S.; Hanene, J.H.; Madiha, D.; Imen, B.; ElCafsi, M.; Hammami, M.; Chaouch, A. Antioxidant property of wild and farmed sea bream (Sparus aurata)cooked in different ways. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 19623–19630. [Google Scholar]
- Pazos, M.; González, M.J.; Gallardo, J.M.; Torres, J.L.; Medina, I. Preservation of the endogenous antioxidant system of fish muscle by grape polyphenols during frozen storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, W.S.; Sarojnalini, C. Effect of cooking on the polyunsaturated fatty acid and antioxidant properties of small indigenous fish species of the Eastern Himalayas. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 4, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, M.; Church, S.; Pinchen, H.; Finglas, P. Nutrient Analysis of Fish and Fish Products—Analytical Report; Institute of Food Research: Surrey, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, I.; Satué-Gracia, M.T.; German, J.B.; Frankel, E.N. Comparison of natural polyphenol antioxidants from extra virgin olive oil with synthetic antioxidants in tuna lipids during thermal oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4873–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merdzhanova, A.; Stancheva, M.; Dobreva, D.A.; Makedonski, L. Fatty acid and fat soluble vitamins composition of raw and cooked Black Sea horse mackerel. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2013, 24, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ersoy, B.; Özeren, A. The effect of cooking methods on mineral and vitamin contents of African catfish. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel-Ikpeme, C.; Henry, P.; Augustine Okiri, O. Comparative evaluation of the nutritional, phytochemical and microbiological quality of three pepper varieties. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.; Romero, N.; Robert, P.; Araya, J.; Lopez-Hernández, J.; Bozzo, C.; Navarrete, E.; Osorio, A.; Rios, A. Dietary fiber, amino acid, fatty acid and tocopherol contents of the edible seaweeds Ulva lactuca and Durvillaea antarctica. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiles, J.L.; Ramírez-Tortosa, M.C.; Gómez, J.A.; Huertas, J.R.; Mataix, J. Role of vitamin E and phenolic compounds in the antioxidant capacity, measured by ESR, of virgin olive, olive and sunflower oils after frying. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckelmann, S.W.; Riegel, D.W.; Van Zonneveld, M.J.; Ríos, L.; Peña, K.; Ugas, R.; Quinonez, L.; Mueller-Seitz, E.; Petz, M. Compositional characterization of native Peruvian chili peppers (Capsicum spp.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2530–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, B.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Schulze, N.; Ozcelik, B.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. Comprehensive analysis of polyphenols in 55 extra virgin olive oils by HPLC-ECD and their correlation with antioxidant activities. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2012, 67, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, T.H.; Serna, A.; López, L.C.; Lara, L.; Nieto, R.; Seiquer, I. Composition and antioxidant properties of spanish extra virgin olive oil regarding cultivar, harvest year and crop stage. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.D.; Shahidi, F. Effect of hydrothermal processing on changes of insoluble-bound phenolics of lentils. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nergiz, C.; Unal, K. Determination of phenolic acids in virgin olive oil. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaus, B.; Spener, F. Introduction: What we know and what we should know about virgin oils—A general introduction. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.N.; Galeano-Díaz, T.; López, Ó.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Sánchez, J.; De Miguel, C.; Gil, M.V.; Martín-Vertedor, D. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of virgin olive oil. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N. Microwave heating induces oxidative degradation of extra virgin olive oil. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A.; Terracone, C.; Gambacorta, G.; Notte, E. La Changes in quality indices, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of flavored olive oils during storage. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Steps | Eel Muscle | Oils | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | --- | 107.05 ± 9.63 a | Sunflower oil | 7.88 ± 0.17 a |
| Olive oil | 13.09 ± 1.08 b | |||
| Frying | In sunflower oil | 25.24 ± 5.39 b | Sunflower oil | 7.29 ± 0.08 a |
| In olive oil | 28.39 ± 4.94 b,d | Olive oil | 13.96 ± 1.07 b | |
| Sterilization | In sunflower oil | 36.43 ± 4.32 c,e | Sunflower oil | 7.51 ± 0.48 a |
| In olive oil | 34.71 ± 1.42 c,d | Olive oil | 12.88 ± 0.18 b | |
| In spiced olive oil | 30.28 ± 1.77 c,d | Spiced olive oil | 16.85 ± 0.62 c | |
| 2 months storage | In sunflower oil | 31.77 ± 2.83 c,d | Sunflower oil | 8.57 ± 0.48 d |
| In olive oil | 38.31 ± 3.32 c,e | Olive oil | 12.58 ± 0.44 b | |
| In spiced olive oil | 35.03 ± 6.02 c,e | Spiced olive oil | 16.11 ± 0.28 c,f | |
| 12 months storage | In sunflower oil | 36.77 ± 5.44 c,e | Sunflower oil | 10.34 ± 0.24 e |
| In olive oil | 40.67 ± 0.53 e,f | Olive oil | 15.75 ± 0.67 f | |
| In spiced olive oil | 43.54 ± 1.59 f | Spiced olive oil | 15.92 ± 0.26 f | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Limia, L.; Sanmartín, N.M.; Carballo, J.; Domínguez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Martínez, S. Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Activity in Canned Eels: Effect of Processing and Filling Medium. Foods 2021, 10, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040790
Gómez-Limia L, Sanmartín NM, Carballo J, Domínguez R, Lorenzo JM, Martínez S. Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Activity in Canned Eels: Effect of Processing and Filling Medium. Foods. 2021; 10(4):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040790
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Limia, Lucía, Nicolás Moya Sanmartín, Javier Carballo, Rubén Domínguez, José M. Lorenzo, and Sidonia Martínez. 2021. "Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Activity in Canned Eels: Effect of Processing and Filling Medium" Foods 10, no. 4: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040790
APA StyleGómez-Limia, L., Sanmartín, N. M., Carballo, J., Domínguez, R., Lorenzo, J. M., & Martínez, S. (2021). Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Activity in Canned Eels: Effect of Processing and Filling Medium. Foods, 10(4), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040790