Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Collection and Experimental Design
2.3. Reference HPLC Analysis
2.4. NIR Apparatus and Method
2.5. NIR Data Processing
Construction and Validation of NIR Models for Histamine Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Histamine Quantitative Analysis by HPLC
3.2. Performances of the NIR Calibration Methods for the Prediction of Histamine
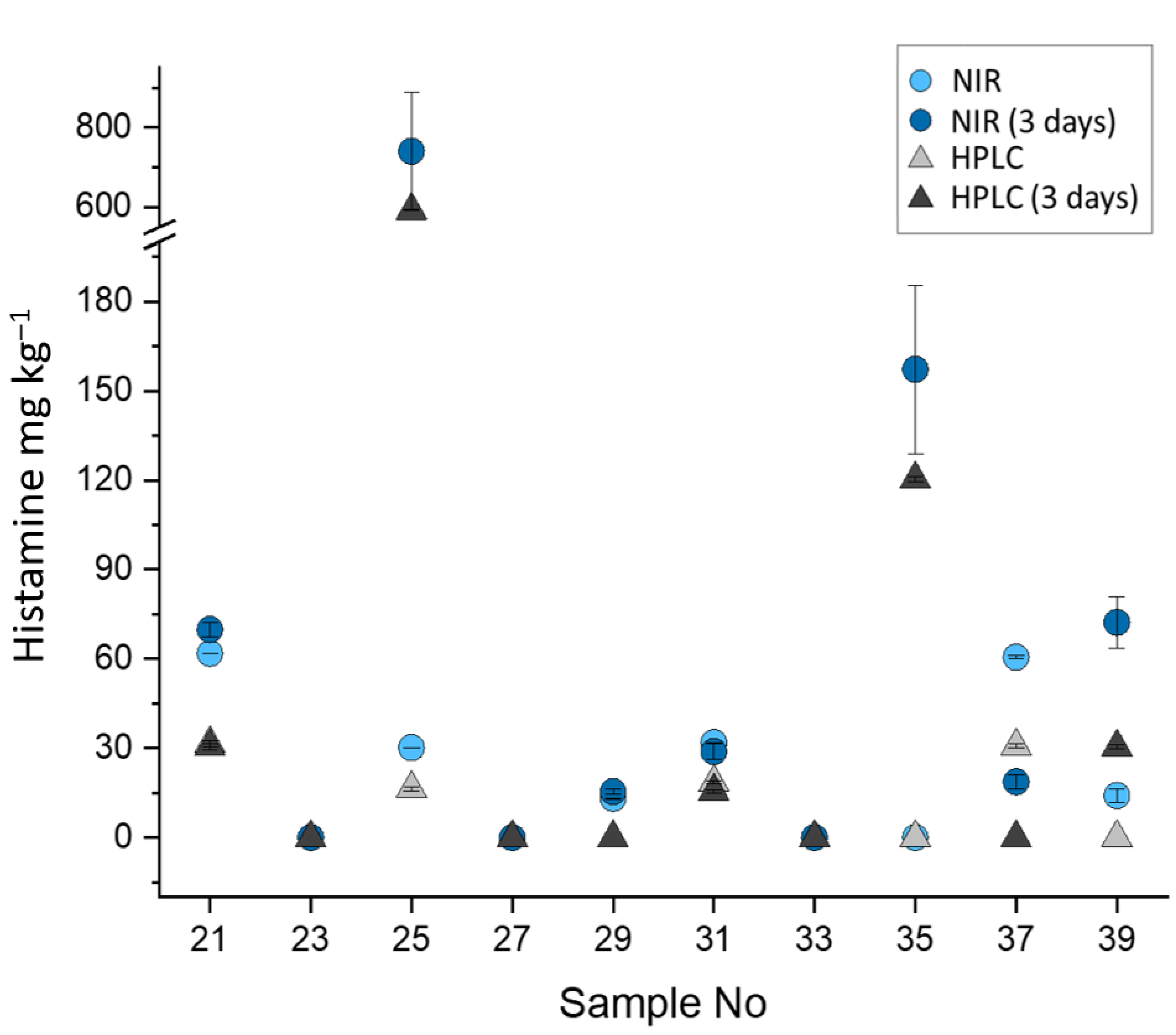
3.3. Comparison Between NIR and HPLC Analyses of Validation Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) Global Tuna Catches by Stock. Available online: www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/tuna-catches/en (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Herpandi, N.H.; Rosma, A.; Nadiah, W.W. The Tuna Fishing Industry: A New Outlook on Fish Protein Hydrolysates. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bian, Z.; Lin, T.; Tao, L.; Wu, Q.; Chu, M. Global occurrence, bioaccumulation factors and toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls in tuna: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Wang, L. The microbial safety of fish and fish products: Recent advances in understanding its significance, contamination sources, and control strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 738–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Paparella, A. An Overview of Histamine and Other Biogenic Amines in Fish and Fish Products. Foods 2020, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 338, 1–26. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32005R2073 (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance; US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition: College Park, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 1–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of Biogenic Amines on Food Quality and Safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards. Scientific Opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durak-Dados, A.; Michalski, M.; Osek, J. Histamine and other biogenic amines in food. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission—RASFF Portal. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/portal/ (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Vitali, L.; Valese, A.C.; Azevedo, M.S.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Piovezan, M.; Vistuba, J.P.; Micke, G.A. Development of a fast and selective separation method to determine histamine in tuna fish samples using capillary zone electrophoresis. Talanta 2013, 106, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzanavaras, P.D.; Deda, O.; Karakosta, T.D.; Themelis, D.G. Selective fluorimetric method for the determination of histamine in seafood samples based on the concept of zone fluidics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 778, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungerford, J.; Wu, W.-H. Comparison study of three rapid test kits for histamine in fish: BiooScientific MaxSignal enzymatic assay, Neogen Veratox ELISA, and the Neogen Reveal Histamine Screening test. Food Control 2012, 25, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounnoun, A.; Louajri, A.; Cacciola, F.; El Cadi, H.; Bougtaib, H.; Alahlah, N.; El Baaboua, A.; El Maadoudi, M. Development and Validation of a TLC-Densitometry Method for Histamine Monitoring in Fish and Fishery Products. Molecules 2020, 25, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmouzi, S.; Khaksar, R.; Ghasemlou, M. Development and validation of an HPLC-FLD method for rapid determination of histamine in skipjack tuna fish (Katsuwonus pelamis). Food Chem. 2011, 126, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, A. A review: Current analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, T.; Sivaraman, B.; Alamelu, V.; Priyatharshini, A.; Arisekar, U.; Sundhar, S. Rapid Methods for Histamine Detection in Fishery Products. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 14th ed.; Williams, S., Ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-1-910348-09-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stroka, J.; Bouten, K.; Mischke, C.; Breidbach, A.; Ulberth, F. Equivalence Testing of Histamine Methods—Final Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2014; ISBN 9789279378003. [Google Scholar]
- Spink, J.; Ortega, D.L.; Chen, C.; Wu, F. Food fraud prevention shifts the food risk focus to vulnerability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Jimenez-Colmenero, F. Biogenic Amines in Seafood Products. In Handbook of seafood and seafood products analysis; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldra, F., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 4633–4635. ISBN 978-1-4200-4633-5. [Google Scholar]
- López-Maestresalas, A.; Insausti, K.; Jarén, C.; Pérez-Roncal, C.; Urrutia, O.; Beriain, M.J.; Arazuri, S. Detection of minced lamb and beef fraud using NIR spectroscopy. Food Control 2019, 98, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.V.D.S.; Fernandes, D.D.D.S.; de Araújo, M.C.U.; Diniz, P.H.G.D.; Maciel, M.I.S. Simultaneous determination of goat milk adulteration with cow milk and their fat and protein contents using NIR spectroscopy and PLS algorithms. LWT 2020, 127, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrà, M.O.; Fasolato, L.; Serva, L.; Ghidini, S.; Novelli, E.; Zanardi, E. Use of near infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics for fast detection of irradiated dry fermented sausages. Food Control 2020, 110, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbin, D.F.; ElMasry, G.; Sun, D.-W.; Allen, P.; Morsy, N. Non-destructive assessment of microbial contamination in porcine meat using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, G.; Vázquez, M. Fraud detection in hen housing system declared on the eggs’ label: An accuracy method based on UV-VIS-NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, C.; Barbosa, F.; Barbosa, R.M. Predicting the botanical and geographical origin of honey with multivariate data analysis and machine learning techniques: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolato, L.; Balzan, S.; Riovanto, R.; Berzaghi, P.; Mirisola, M.; Ferlito, J.C.; Serva, L.; Benozzo, F.; Passera, R.; Tepedino, V.; et al. Comparison of Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy to Authenticate Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Swordfish (Xiphias gladius L.). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2012, 21, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannia, M.; Serva, L.; Balzan, S.; Segato, S.; Novelli, E.; Fasolato, L. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy for frozen-thawed characterization of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4437–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, S.; Casiraghi, E.; Alamprese, C. Handheld NIR device: A non-targeted approach to assess authenticity of fish fillets and patties. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Xu, W.; You, J.; Xiong, S. Classification of freshwater fish species by linear discriminant analysis based on near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2017, 25, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotte, A.D.; Ottavian, M.; Concollato, A.; Serva, L.; Martelli, R.; Parisi, G. Authentication of raw and cooked freeze-dried rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by means of near infrared spectroscopy and data fusion. Food Res. Int. 2014, 60, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidini, S.; Varrà, M.O.; Dall’Asta, C.; Badiani, A.; Ianieri, A.; Zanardi, E. Rapid authentication of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) according to production method, farming system, and geographical origin by near infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrà, M.O.; Ghidini, S.; Ianieri, A.; Zanardi, E. Near infrared spectral fingerprinting: A tool against origin-related fraud in the sector of processed anchovies. Food Control 2021, 123, 107778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cai, R.; Wang, S.; Tang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W. Non-destructive geographical traceability of sea cucumber ( Apostichopus japonicus) using near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometric methods. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Zeng, X.-A.; Pu, H.-B. Non-destructive and rapid determination of TVB-N content for freshness evaluation of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) by hyperspectral imaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 21, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsdottir, M.G.; Arason, S.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Sveinsdottir, K. The application of near infrared spectroscopy to study lipid characteristics and deterioration of frozen lean fish muscles. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkestad, A.; Wold, J.P.; Rørvik, K.-A.; Tschudi, J.; Haugholt, K.H.; Kolstad, K.; Mørkøre, T. Rapid and non-invasive measurements of fat and pigment concentrations in live and slaughtered Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2008, 280, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochanagone, S.; Rittiron, R. Preliminary Study on the Determination of ppm-Level Concentration of Histamine in Tuna Fish Using a Dry Extract System for Infrared Coupled with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19164–19171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, J.K.; Maher, W.A.; Purss, M.B. Near infra-red spectroscopy quantitative modelling of bivalve protein, lipid and glycogen composition using single-species versus multi-species calibration and validation sets. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 193, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, D.-H.; Wang, X.-C.; Liu, L.-P.; Fan, Y.-X.; Cao, J.-X. Prediction of chemical composition and geographical origin traceability of Chinese export tilapia fillets products by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. LWT 2015, 60, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascant, M.M.; Breil, C.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Chemat, F.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Determination of fatty acids and lipid classes in salmon oil by near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cavinato, A.; Mayes, D.; Kangas, L.; Bledsoe, G.; Rasco, B. Nondestructive Determination of Moisture and Sodium Chloride in Cured Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) (Teijin) Using Short-wavelength Near-infrared Spectroscopy (SW-NIR). J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, A.A.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Mintah, B.K.; Annavaram, V.; Zareef, M.; Hassan, M.; Arslan, M.; Chen, Q. Rapid and Nondestructive Quantification of Trimethylamine by FT-NIR Coupled with Chemometric Techniques. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shan, J.; Han, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Optimization of Fish Quality by Evaluation of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) and Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) by Near-Infrared (NIR) Hyperspectral Imaging. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 1845–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-J.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.-W. Rapid and non-destructive determination of drip loss and pH distribution in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo Salar) fillets using visible and near-infrared (Vis–NIR) hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiya, T.; Sivertsen, A.H.; Heia, K. VIS/NIR spectroscopy for non-destructive freshness assessment of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sun, D.-W. Colour measurements by computer vision for food quality control—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Mousavi, M.; Al-Holy, M.; Cavinato, A.G.; Rasco, B.A. Rapid Near Infrared Spectroscopic Method for the Detection of Spoilage in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fillet. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.; Jeong, Y. Freshness Evaluation in Chub Mackerel (Scomber japonicus) Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Determination of the Cadaverine Content. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janči, T.; Mikac, L.; Ivanda, M.; Radovčić, N.M.; Medić, H.; Vidaček, S. Optimization of parameters for histamine detection in fish muscle extracts by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using silver colloid SERS substrates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 48, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Determination of histamine in canned tuna by molecularly imprinted polymers-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, N.; Wu, F. Tuneable surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy hyphenated to chemically derivatized thin-layer chromatography plates for screening histamine in fish. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflos, G.; Dervin, C.; Malle, P.; Bouquelet, S. Relevance of Matrix Effect in Determination of Biogenic Amines in Plaice (Pleuronectes platessa) and Whiting (Merlangus merlangus). J. AOAC Int. 1999, 82, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiesa, L.; Panseri, S.; Pavlovic, R.; Arioli, F. Biogenic amines evaluation in wild Bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) originating from various FAO areas. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2018, 13, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearn, T. Assessing Calibrations: SEP, RPD, RER and R2. NIR News 2002, 13, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P. Near-infrared technology-getting the best out of light. In A Short Course in the Practical Implementation of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for the User; PDK Projects, Inc.: Nanaimo, BC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission regulation (EC) No 1441/2007 of 5 December 2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, 322. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32007R1441&from=EN (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- D.’Amico, P.; Nucera, D.; Guardone, L.; Mariotti, M.; Nuvoloni, R.; Armani, A. Seafood products notifications in the EU Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) database: Data analysis during the period 2011–2015. Food Control 2018, 93, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF). Annual Report 2018; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 978-92-76-02637-2. [Google Scholar]
- Magro, S.L.; Summa, S.; Iammarino, M.; D’Antini, P.; Marchesani, G.; Chiaravalle, A.; Muscarella, M. A 5-Years (2015–2019) Control Activity of an EU Laboratory: Contamination of Histamine in Fish Products and Exposure Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenk, J.S.; Westerhaus, M.O. Calibration the ISI way. In Near Infrared Spectroscopy: The Future Waves, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Near Infrared Spectroscopy, Montréal, QC, Canada, 6–11 August 1995; Davies, M.C., Williams, P., Eds.; Nir Publications: Chichester, UK, 1996; pp. 198–202. ISBN 978-1-906715-20-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rinnan, Å.; Berg, F.V.D.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dračková, M.; Navrátilová, P.; Hadra, L.; Vorlová, L.; Hudcová, L. Determination Residues of Penicillin G and Cloxacillin in Raw Cow Milk Using Fourier Transform Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Acta Vet. Brno 2009, 78, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersson, H.; Åberg, L. Near infrared spectroscopy for determination of mycotoxins in cereals. Food Control 2003, 14, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Mishra, H. A rapid FT-NIR method for estimation of aflatoxin B1 in red chili powder. Food Control 2009, 20, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Castillo, M.; Peinado, A.; Beneyto, R. Determination of low analyte concentrations by near-infrared spectroscopy: Effect of spectral pretreatments and estimation of multivariate detection limits. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 581, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambo, M.K.D.; Macêdo, L.P.R.; Da Silva, M.M. Predição por Calibração Multivariada dos Parâmetros de Qualidade de Biomassas de Café. Ciência e Natura 2015, 37, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenk, J.S.; Workman, J.J.; Westerhous, M.O. Application of NIR spectroscopy to agricultural products. In Handbook of Near-Infrared Analysis; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 356–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Field, K.G.; Morrissey, M.T.; Price, R.J.; Wei, C.-I.; An, H. Source and Identification of Histamine-Producing Bacteria from Fresh and Temperature-Abused Albacore†. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornsdottir, K.; Bolton, G.E.; McClellan-Green, P.D.; Jaykus, L.-A.; Green, D.P. Detection of Gram-Negative Histamine-Producing Bacteria in Fish: A Comparative Study. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1987–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, T.; Marsico, A.D.; Perniola, R. NIR Analysis of Intact Grape Berries: Chemical and Physical Properties Prediction Using Multivariate Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossoba, M.M.; Karunathilaka, S.R.; Chung, J.K.; Srigley, C.T. Advancement in Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Analyses of Dietary Fatty Acids. In Fatty Acids; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 505–528. [Google Scholar]

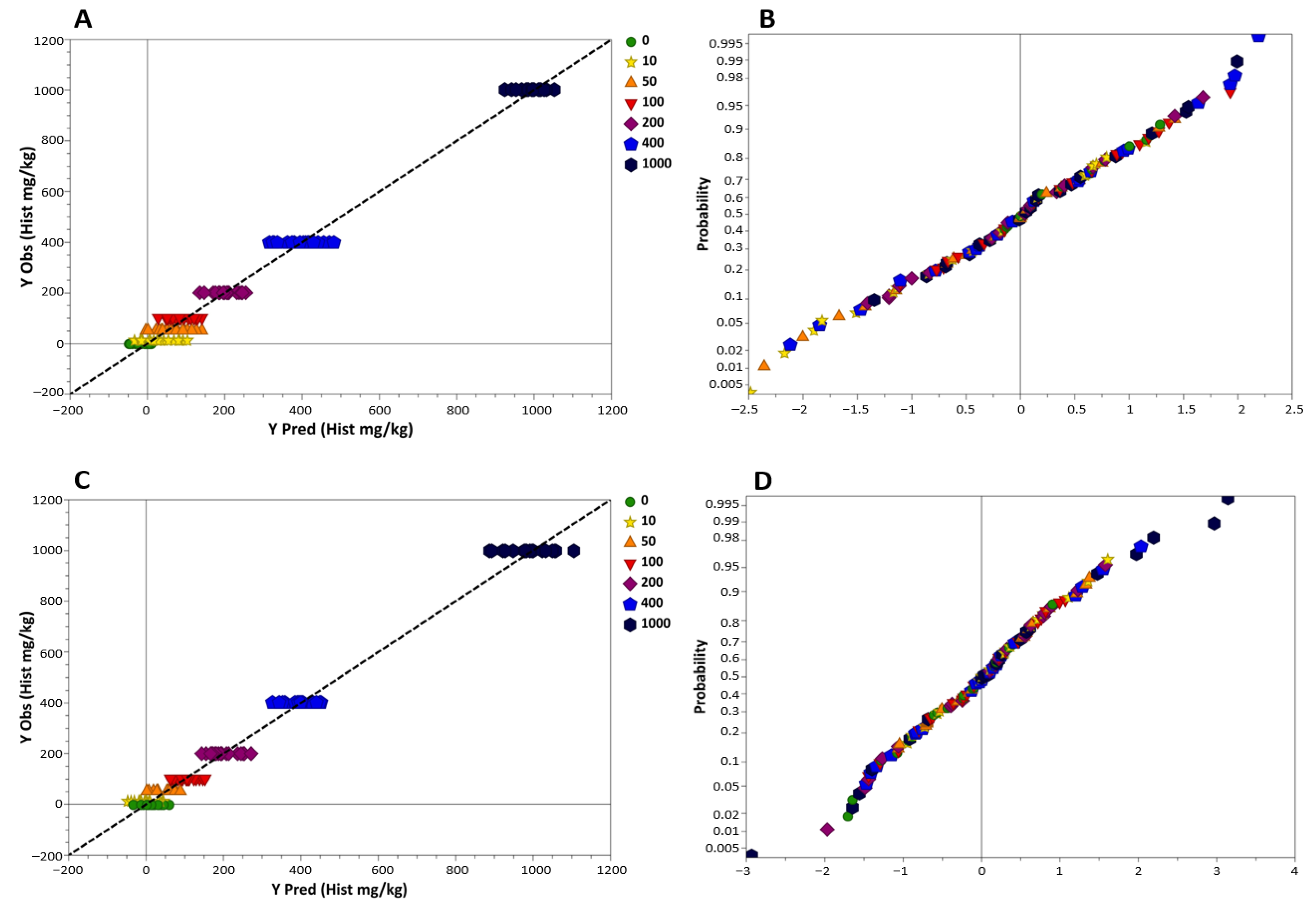
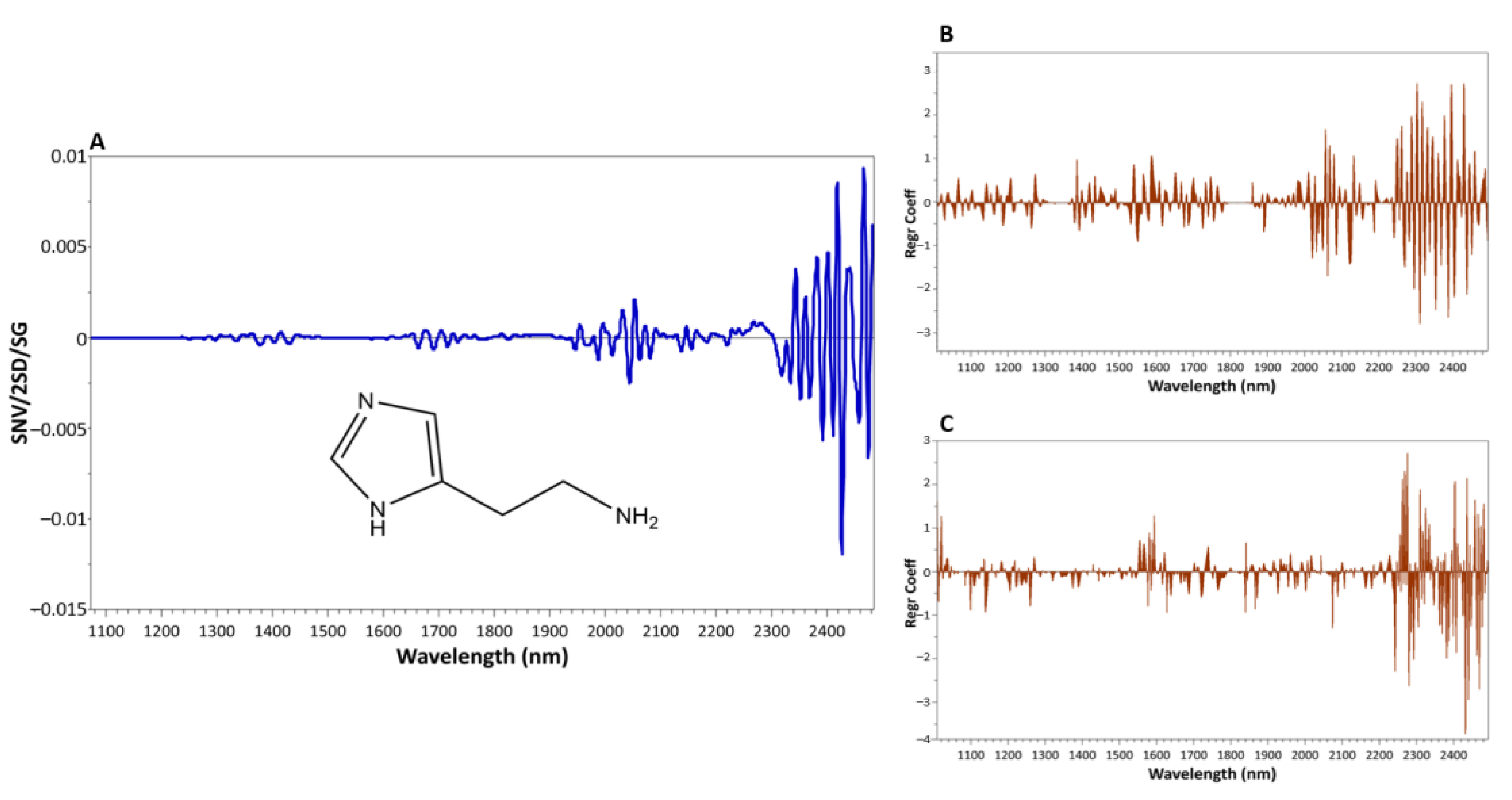
| Dataset | Raw Tuna | Processed Tuna |
|---|---|---|
| OPLSR Factors (p + o) | 1 + 4 | 1 + 5 |
| R2X | 0.698 | 0.784 |
| Q2 | 0.915 | 0.949 |
| RMSECV (mg kg−1) | 6 | 4 |
| RMSEE (mg kg−1) | 6 | 5 |
| r2 | 0.987 | 0.989 |
| Slope | 1 | 1 |
| Intercept | 1.768 × 10−5 | −2.942 × 10−7 |
| LOD (mg kg−1) | 4 | 2 |
| LOQ (mg kg−1) | 12 | 8 |
| Repeatability (RSD%) | 4.9 | 3.2 |
| Reproducibility (RSD%) | 8.1 | 4.8 |
| Accuracy (recovery%) | ||
| 10 mg kg−1 | 89.4 | 86.2 |
| 50 mg kg−1 | 104.8 | 98.2 |
| 100 mg kg−1 | 102.6 | 98.4 |
| Raw Tuna Fish | Processed Tuna Fish | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | NIR Prediction | HPLC Prediction | Absolute Error | Sample | NIR Prediction | HPLC Prediction | Absolute Error |
| 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 1 | 75.67 ± 0.01 | 60.1 ± 0.4 | 15.6 |
| 2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 2 | 102.4 ± 7.9 | 94.3 ± 1.2 | 8.1 |
| 3 | 1694 ± 300 | 1279 ± 300 | 415 | 3 | 36.2 ± 0.4 | 15.6 ± 0.2 | 20.6 |
| 4 | 18 ± 4 | <LOQ | 17.7 | 4 | 32 ± 2 | 14.3 ± 0.2 | 17.4 |
| 5 | 15.7 ± 0.9 | <LOQ | 15.7 | 5 | 15 ± 3 | <LOQ | 15.4 |
| 6 | 34.7 ± 0.4 | 16.4 ± 0.4 | 18.4 | 6 | 10 ± 4 | <LOQ | 10.0 |
| 7 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 7 | 22.1 ± 0.1 | <LOQ | 22.1 |
| 8 | 23± 2 | <LOQ | 23.2 | 8 | 26.1 ± 1.4 | <LOQ | 26.1 |
| 9 | 25 ± 2 | <LOQ | 24.8 | 9 | 52.5 ± 1.0 | 37.2 ± 0.5 | 15.3 |
| 10 | 12 ± 3 | <LOQ | 12.1 | 10 | 21.8 ± 1.9 | <LOQ | 21.8 |
| 11 | 17 ± 5 | <LOQ | 17.4 | 11 | 83.3 ± 0.6 | 72.4 ± 0.9 | 10.9 |
| 12 | 17 ± 4 | <LOQ | 16.6 | 12 | 32.2 ± 0.8 | 15.6 ± 0.2 | 16.7 |
| 13 | 32.1 ± 0.7 | 10.9 ± 0.4 | 21.2 | 13 | 24.7 ± 1.5 | <LOQ | 24.74 |
| 14 | 46.4 ± 1.5 | 18.4 ± 0.6 | 27.9 | 14 | 41.5 ± 0.4 | 25.7 ± 0.3 | 15.8 |
| 15 | 62.5 ± 1.9 | <LOQ | 62.5 | 15 | 41 ± 2 | 24.3 ± 0.3 | 16.6 |
| 16 | 36 ± 5 | <LOQ | 35.7 | 16 | 17.6 ± 1.1 | <LOQ | 17.6 |
| 17 | 30.9 ± 1.4 | <LOQ | 30.9 | 17 | 65.0 ± 1.4 | 40.3 ± 0.5 | 24.7 |
| 18 | 28 ± 4 | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 7.0 | 18 | <LOD | <LOQ | – |
| 19 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 19 | <LOD | 0.86 ± 0.01 | – |
| 20 | <LOD | <LOQ | – | 20 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 8.2 |
| 21 | 61.9 ± 0.1 | 31.5 ± 1.0 | 30.3 | 21 | <LOD | <LOQ | – |
| 22 | 33.3 ± 0.3 | <LOQ | 33.3 | 22 | 30.4 ± 0.7 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 14.8 |
| 23 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 23 | 54 ± 3 | 40.3 ± 0.5 | 14.1 |
| 24 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 24 | 50 ± 4 | 22.4 ± 0.3 | 27.8 |
| 25 | 30.18 ± 0.02 | 16.4 ± 0.8 | 13.8 | 25 | 46.1 ± 1.9 | 21.0 ± 0.3 | 25.0 |
| 26 | 25 ± 4 | 11.4 ± 1.0 | 13.9 | 26 | <LOD | <LOQ | – |
| 27 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 27 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – |
| 28 | <LOD | <LOQ | – | 28 | 12 ± 3 | <LOQ | 12.2 |
| 29 | 13.1 ± 0.2 | <LOQ | 13.1 | 29 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – |
| 30 | <LOD | <LOQ | – | 30 | 49.9 ± 0.6 | 30.3 ± 0.4 | 19.6 |
| 31 | 31.89 ± 0.08 | 18.5 ± 0.5 | 13.4 | 31 | 56.6 ± 0.1 | 40.9 ± 0.5 | 15.7 |
| 32 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 32 | 60.5 ± 0.7 | 30.5 ± 0.4 | 30.1 |
| 33 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 33 | 45.8 ± 1.5 | 25.4 ± 0.3 | 20.4 |
| 34 | <LOD | <LOQ | – | 34 | 46.8 ± 1.3 | 20.7 ± 0.3 | 26.1 |
| 35 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 35 | 30.6 ± 0.4 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 14.9 |
| 36 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 36 | 37.2 ± 0.8 | 16.3 ± 0.2 | 20.9 |
| 37 | 60.6 ± 0.5 | 30.8 ± 0.6 | 29.9 | 37 | 29.4 ± 0.5 | <LOQ | 29.4 |
| 38 | 61.2 ± 1.9 | 27.1 ± 0.5 | 34.1 | 38 | 21.5 ± 0.5 | <LOQ | 24.5 |
| 39 | 14 ± 2 | <LOQ | 14.0 | 39 | 11.7 ± 1.9 | <LOQ | 11.7 |
| 40 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – | 40 | <LOQ | <LOQ | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghidini, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Panseri, S.; Varrà, M.O.; Ianieri, A.; Pessina, D.; Zanardi, E. Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy. Foods 2021, 10, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040885
Ghidini S, Chiesa LM, Panseri S, Varrà MO, Ianieri A, Pessina D, Zanardi E. Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy. Foods. 2021; 10(4):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040885
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhidini, Sergio, Luca Maria Chiesa, Sara Panseri, Maria Olga Varrà, Adriana Ianieri, Davide Pessina, and Emanuela Zanardi. 2021. "Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy" Foods 10, no. 4: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040885
APA StyleGhidini, S., Chiesa, L. M., Panseri, S., Varrà, M. O., Ianieri, A., Pessina, D., & Zanardi, E. (2021). Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy. Foods, 10(4), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040885








