Kefir and Its Biological Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Types of Kefir
2.1. Dairy Kefir
2.2. Non-Dairy Kefir
3. Biological Activities of Kefir
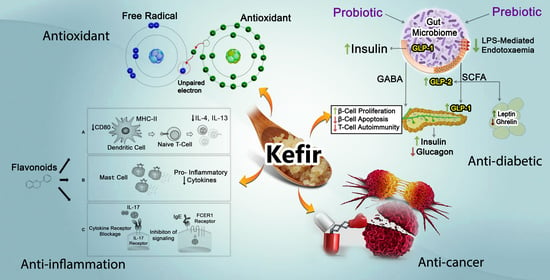
3.1. Anti-Hypertensive
3.2. Anti-Cancer
3.3. Anti-Diabetic
3.4. Anti-Microbial
3.5. Anti-Inflammation
3.6. Antioxidant
3.7. Hypocholesterolemic Effect
4. Commercial Kefir Products
5. Future Prospect and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamberi, N.R.; Abu, N.; Mohamed, N.E.; Nordin, N.; Keong, Y.S.; Beh, B.K.; Zakaria, Z.A.B.; Nik Abdul Rahman, N.M.A.; Alitheen, N.B. The Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenesis Effects of Kefir Water on Murine Breast Cancer Cells. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, NP53–NP66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Sabbatini, R.; Milanović, V.; Alkić-Subašić, M.; Boscaino, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Pasquini, M.; Trombetta, M.F.; et al. Study of kefir drinks produced by backslopping method using kefir grains from Bosnia and Herzegovina: Microbial dynamics and volatilome profile. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorda, F.A.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; Vandenberghe, L.P.d.S.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, biochemical, and functional aspects of sugary kefir fermentation—A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesenkaş, H.; Gürsoy, O.; Özbaş, H. Kefir. Fermented Foods in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 339–361. [Google Scholar]
- Talib, N.; Mohamad, N.E.; Yeap, S.K.; Hussin, Y.; Mubin Aziz, M.N.; Masarudin, M.J.; Sharifuddin, S.A.; Hui, Y.W.; Ho, C.L.; Alitheen, N.B. Isolation and characterization of Lactobacillus spp. From kefir samples in Malaysia. Molecules 2019, 24, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, M. Autogenic successions of bacteria and fungi in kefir grains from different origins when sub-cultured in goat milk. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Nan, B.; Wang, Z. Isolation of exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria and yeasts from Tibetan kefir and characterisation of the exopolysaccharides. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2016, 69, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, I.B.; Kim, H.; Song, K.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, K.H. Characterization and antibacterial activity of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens DN1 isolated from kefir. Food Control 2017, 78, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Mehwish, H.M.; Fang, H.; Padhiar, A.A.; Zeng, X.; Khurshid, M.; He, Z.; Zhao, L. Characterization and anti-tumor activity of exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiri isolated from Chinese kefir grains. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, J. Kefir: The Champagne of Fermented Beverages; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128152713. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, B.; Gürakan, G.C.; Ünlü, G. Kefir: A Multifaceted Fermented Dairy Product. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2014, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrie, B.C.T.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The microbiota and health promoting characteristics of the fermented beverage kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosa, D.D.; Dias, M.M.S.; Grześkowiak, Ł.M.; Reis, S.A.; Conceição, L.L.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G. Milk kefir: Nutritional, microbiological and health benefits. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorda, F.A.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Medeiros, A.P.; Rakshit, S.K.; Soccol, C.R. Development of kefir-based probiotic beverages with DNA protection and antioxidant activities using soybean hydrolyzed extract, colostrum and honey. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, M.J. Effects of cow’s and goat’s milk as fermentation media on the microbial ecology of sugary kefir grains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Iraporda, C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir micro-organisms: Their role in grain assembly and health properties of fermented milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leite, A.M.d.O.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, A.S.; Silva, J.T.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Microbiological, technological and therapeutic properties of kefir: A natural probiotic beverage. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Shah, N.P. Other Fermented Dairy Products: Kefir and Koumiss; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128052723. [Google Scholar]
- Rattray, F.P.; O’Connell, M.J. Fermented Milks: Kefir. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780123744029. [Google Scholar]
- Anfiteatro, D.N. Dom’s All about Kefir In-Site. Available online: http://users.sa.chariot.net.au/~dna/kefirpage.html (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Sarkar, S. Potential of kefir as a dietetic beverage—A review. Br. Food J. 2007, 109, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, J. Kefir D’Aqua and Its Probiotic Properties. Probiotic Anim. 2012, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldonado, R.R.; Pedreira, A.J.R.M.; Cristianini, L.B.; Guidi, M.F.; Capato, M.O.; Ávila, P.F.; Goldbeck, R.; Kamimura, E.S. Application of soluble fibres in the osmotic dehydration of pineapples and reuse of effluent in a beverage fermented by water kefir. LWT 2020, 132, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azi, F.; Tu, C.; Meng, L.; Zhiyu, L.; Tekliye Cherinet, M.; Ahmadullah, Z.; Dong, M. Metabolite dynamics and phytochemistry of a soy whey-based beverage bio-transformed by water kefir consortium. Food Chem. 2020, 342, 128225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, O.; Randazzo, W.; Miceli, A.; Guarcello, R.; Francesca, N.; Erten, H.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Characterization of kefir-like beverages produced from vegetable juices. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, Z.E.; Mousavi, S.M.; Razavi, S.H.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Kiani, H. Fermentation of pomegranate juice by probiotic lactic acid bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, C.M.; Peres, C.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Malcata, F.X. Review on fermented plant materials as carriers and sources of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria—With an emphasis on table olives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Corona, O.; Guarcello, R.; Francesca, N.; Germanà, M.A.; Erten, H.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Development of new non-dairy beverages from Mediterranean fruit juices fermented with water kefir microorganisms. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Açik, M.; Çakiroğlu, F.P.; Altan, M.; Baybo, T. Alternative source of probiotics for lactose intolerance and vegan individuals: Sugary kefir. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bvenura, C.; Sivakumar, D. The role of wild fruits and vegetables in delivering a balanced and healthy diet. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Melnyk, J.P.; Tsao, R.; Marcone, M.F. How natural dietary antioxidants in fruits, vegetables and legumes promote vascular health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, G.C.; Jackson, R.E.; Gadhia, R.; Román, A.N.; Reis, J. Mediterranean diet: The role of long-chain ω-3 fatty acids in fish; polyphenols in fruits, vegetables, cereals, coffee, tea, cacao and wine; probiotics and vitamins in prevention of stroke, age-related cognitive decline, and Alzheimer disease. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, C.; Banik, K.; Bordoloi, D.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Antiulcer properties of fruits and vegetables: A mechanism based perspective. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerari, C.; Magalhães, K.T.; Schwan, R.F. New cocoa pulp-based kefir beverages: Microbiological, chemical composition and sensory analysis. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laureys, D.; De Vuyst, L. Microbial species diversity, community dynamics, and metabolite kinetics of water Kefir fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, K.T.; de Pereira, G.V.M.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. Microbial communities and chemical changes during fermentation of sugary Brazilian kefir. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Rementeria, A.; Elguezabal, N.; Garaizar, J. Kefir: A symbiotic yeasts-bacteria community with alleged healthy capabilities. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2006, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, W.F.; Dias, D.R.; Oliveira, J.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; de Almeida e Silva, J.B.; Schwan, R.F. Characterization of different fruit wines made from cacao, cupuassu, gabiroba, jaboticaba and umbu. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Majid, N.L.; Omar, M.A.; Khoo, Y.Y.; Mahadir Naidu, B.; Ling Miaw Yn, J.; Rodzlan Hasani, W.S.; Mat Rifin, H.; Abd Hamid, H.A.; Robert Lourdes, T.G.; Mohd Yusoff, M.F. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control of hypertension in the Malaysian population: Findings from the National Health and Morbidity Survey 2006–2015. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, G.A.; Silva-Cutini, M.d.A.; Moraes, F.d.S.A.; Pereira, T.d.M.C.; Vasquez, E.C.; Lenz, D.; Bissoli, N.S.; Endringer, D.C.; de Lima, E.M.; Biancardi, V.C.; et al. The benefits of soluble non-bacterial fraction of kefir on blood pressure and cardiac hypertrophy in hypertensive rats are mediated by an increase in baroreflex sensitivity and decrease in angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Nutrition 2018, 51–52, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, J.; Aşçi Arslan, A.; Fedorova, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Küçükçetin, A.; Pischetsrieder, M. Peptide profiling of bovine kefir reveals 236 unique peptides released from caseins during its production by starter culture or kefir grains. J. Proteomics 2015, 117, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, D.C.; Citerne, F.; Tian, T.; Silva, V.L.M.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Frese, S.A.; Robinson, R.C.; Mills, D.A.; Barile, D. Peptidomic analysis reveals proteolytic activity of kefir microorganisms on bovine milk proteins. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patten, D.A.; Laws, A.P. Lactobacillus-produced exopolysaccharides and their potential health benefits: A review. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, A.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Ramos, M.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of peptides derived from caprine kefir. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friques, A.G.F.; Arpini, C.M.; Kalil, I.C.; Gava, A.L.; Leal, M.A.; Porto, M.L.; Nogueira, B.V.; Dias, A.T.; Andrade, T.U.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Chronic administration of the probiotic kefir improves the endothelial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klippel, B.F.; Duemke, L.B.; Leal, M.A.; Friques, A.G.F.; Dantas, E.M.; Dalvi, R.F.; Gava, A.L.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Andrade, T.U.; Meyrelles, S.S.; et al. Effects of kefir on the cardiac autonomic tones and baroreflex sensitivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aihara, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kajimoto, O.; Hirata, H.; Takahashi, R. Effect of Powdered Fermented Milk with Lactobacillus helveticus on Subjects with High-Normal Blood Pressure or Mild Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, T.L.; Trikha, S.R.J.; Thompson, H.J. Diet and cancer risk reduction: The role of diet-microbiota interactions and microbial metabolites. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 70, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Moridnia, A.; Mortazavi, D.; Salehi, M.; Bagheri, M.; Sheikhi, A. Kefir: A powerful probiotics with anticancer properties. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.R.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lin, C.W. Antitumor activity of milk kefir and soy milk kefir in tumor-bearing mice. Nutr. Cancer 2002, 44, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagira, T.; Narisawa, J.; Teruya, K.; Katakura, Y.; Shim, S.Y.; Kusumoto, K.i.; Tokumaru, S.; Tokumaru, K.; Barnes, D.W.; Shirahata, S. Suppression of UVC-induced cell damage and enhancement of DNA repair by the fermented milk, Kefir. Cytotechnology 2002, 40, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Matar, C.; Farnworth, E.; Perdigon, G. Study of cytokines involved in the prevention of a murine experimental breast cancer by kefir. Cytokine 2006, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moreno De LeBlanc, A.; Matar, C.; Farnworth, E.; Perdigón, G. Study of immune cells involved in the antitumor effect of kefir in a murine breast cancer model. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Hing, M.C.; Kubow, S. Kefir extracts suppress in vitro proliferation of estrogen-dependent human breast cancer cells but not normal mammary epithelial cells. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, S.; Maalouf, K.; Baydoun, E. The antiproliferative effect of kefir cell-free fraction on HuT-102 malignant T lymphocytes. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2009, 9 (Suppl. 3), S198–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, S.; Maalouf, K.; Nasser, H.; El-Hayek, S. The Pro-apoptotic Effect of Kefir in Malignant T-lymphocytes Involves a p53 Dependent Pathway. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, K.; Baydoun, E.; Rizk, S. Kefir induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in HTLV-l-negative malignant T-lymphocytes. Cancer Manag. Res. 2011, 3, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Gu, F.; Ruan, H.; Chen, Q.; He, J.; He, G. Induction of apoptosis of gastric cancer cells SGC7901 in vitro by a cell-free fraction of Tibetan kefir. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 30, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Gimzewski, J. Apoptotic effect of a novel kefir product, PFT, on multidrug-resistant myeloid leukemia cells via a hole-piercing mechanism. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoury, N.; El-Hayek, S.; Tarras, O.; El-Sabban, M.; El-Sibai, M.; Rizk, S. Kefir exhibits anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on colon adenocarcinoma cells with no significant effects on cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Felo, N. Selective induction of apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells by Lactobacillus kefiri (PFT), a novel kefir product. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalali, F.; Sharifi, M.; Salehi, R. Kefir induces apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in human acute erythroleukemia. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almostafa Alsha’ar, I.; Aloklah, B.; Al-Deen, R.B.; Aljamali, M.; Alkadry, R.; Albiski, F. In Vitro AnticancerPropertiesof Kefirand Kefir Products Produced by aNovel Method in Syria. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent. ISSN 2017, 6, 2319–2670. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Cheng, W.N.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Han, S.G. Effects of kefir on doxorubicin-induced multidrug resistance in human colorectal cancer cells. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 78, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Duvoor, C.; Reddy Dendi, V.S.; Kraleti, S.; Chada, A.; Ravilla, R.; Marco, A.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Montales, M.T.; Kuriakose, K.; et al. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Federación Internacional de Diabetes (IDF) International Diabetes Federation-Search. Available online: https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Tiss, M.; Souiy, Z.; Abdeljelil, N.b.; Njima, M.; Achour, L.; Hamden, K. Fermented soy milk prepared using kefir grains prevents and ameliorates obesity, type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia and Liver-Kidney toxicities in HFFD-rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayadi, M.; Jawfi, Y.A.; Belarbi, M.; Soualem-Mami, Z.; Merzouk, H.; Sari, D.C.; Sabri, F.; Ghalim, M. Evaluation of Anti-Hyperglycemic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Water Kefir as Probiotic on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2014, 4, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teruya, K.; Yamashita, M.; Tominaga, R.; Nagira, T.; Shim, S.Y.; Katakura, Y.; Tokumaru, S.; Tokumaru, K.; Barnes, D.; Shirahata, S. Fermented milk, Kefram-Kefir enhances glucose uptake into insulin-responsive muscle cells. Cytotechnology 2002, 40, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Zhu, X.; Omura, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kitamura, S. Effects of an exopolysaccharide (kefiran) on lipids, blood pressure, blood glucose, and constipation. BioFactors 2004, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.I.; Apostolidis, E.; Shetty, K. Anti-diabetes functionality of Kefir culture-Mediated fermented soymilk supplemented with Rhodiola extracts. Food Biotechnol. 2006, 20, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadisaputro, S.; Djokomoeljanto, R.R.; Judiono; Soesatyo, M.H.N.E. The effects of oral plain kefir supplementation on proinflammatory cytokine properties of the hyperglycemia Wistar rats induced by streptozotocin. Acta Med. Indones. 2012, 44, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Punaro, G.R.; Maciel, F.R.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Rogero, M.M.; Bogsan, C.S.B.; Oliveira, M.N.; Ihara, S.S.M.; Araujo, S.R.R.; Sanches, T.R.C.; Andrade, L.C.; et al. Kefir administration reduced progression of renal injury in STZ-diabetic rats by lowering oxidative stress. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2014, 37, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurliyani; Harmayani, E. Sunarti Antidiabetic Potential of Kefir Combination from Goat Milk and Soy Milk in Rats Induced with Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostadrahimi, A.; Taghizadeh, A.; Mobasseri, M.; Farrin, N.; Payahoo, L.; Beyramalipoor Gheshlaghi, Z.; Vahedjabbari, M. Effect of probiotic fermented milk (Kefir) on glycemic control and lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Iran. J. Public Health 2015, 44, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bashiti, T.A.; Zabut, B.M.; Safia, F.F.A. Effect of probiotic fermented milk (Kefir) on some blood biochemical parameters among newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic adult males in Gaza governorate. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 7, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.L.; Hendrich, S. Glycemic index, insulinemic index, and satiety index of kefir. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2012, 31, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, R.J.; Viora, S.S.; Ojeda, P.A.; Lausada, L.I. Efecto antagónico del kefir sobre endosporas y células vegetativas de bacillus cereus y clostridium perfringens. Inf. Technol. 2010, 21, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carasi, P.; Díaz, M.; Racedo, S.M.; De Antoni, G.; Urdaci, M.C.; Serradell, M.D.L.A. Safety characterization and antimicrobial properties of kefir-isolated lactobacillus kefiri. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakisu, E.J.; Abraham, A.G.; Pérez, P.F.; De Antoni, G.L. Inhibition of Bacillus cereus in milk fermented with kefir grains. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2613–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, M.; Pérez, P.F.; Abraham, A.G. Kefiran antagonizes cytopathic effects of Bacillus cereus extracellular factors. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, B.H.; Çolak, H.; Hampikyan, H.; Erkan, M.E. An in vitro study on the antibacterial effect of kefir against some food-borne pathogens flma. Vet. Med. 2007, 37, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chifiriuc, M.C.; Cioaca, A.B.; Lazar, V. In vitro assay of the antimicrobial activity of kephir against bacterial and fungal strains. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Guo, H.; Ou, Y.; Liu, G.; Fang, X.; Liao, Z.; Ke, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Cao, Y. Purification and characterization of bacteriocin F1, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans FX-6 from Tibetan kefir, a traditional fermented milk from Tibet, China. Food Control 2014, 42, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, P.A.; Carasi, P.; Bolla, M.d.l.A.; De Antoni, G.L.; Serradell, M.d.l.A. Protective effect of a mixture of kefir-isolated lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in a hamster model of Clostridium difficile infection. Anaerobe 2013, 21, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, M.C.; Clayton, E.; O’Connor, P.M.; Shanahan, F.; Kiely, B.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Antimicrobial activity of lacticin 3147 against clinical Clostridium difficile strains. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanirati, D.F.; Abatemarco, M.; Sandes, S.H.d.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, Á.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from Brazilian kefir grains for potential use as starter or probiotic cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; De Antoni, G.L. Inhibitory power of kefir: The role of organic acids. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golowczyc, M.A.; Gugliada, M.J.; Hollmann, A.; Delfederico, L.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Semorile, L.; De Antoni, G. Characterization of homofermentative lactobacilli isolated from kefir grains: Potential use as probiotic. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulmez, M.; Guven, A. Note: Behaviour of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes 4b and Yersinia enterocolitica O3 in Pasteurised and Non-pasteurised Kefir Fermented for One or Two Days. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2003, 9, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakisu, E.; Abraham, A.G.; Farinati, C.T.; Ibarra, C.; De Antoni, G.L. Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from kefir protects vero cells from cytotoxicity by type-II shiga toxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, A.M.O.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Peixoto, R.S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Mayo, B.; Delgado, S. Probiotic potential of selected lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Brazilian kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, Q.X.; Lu, R.R. Surface layer protein from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM inhibit intestinal pathogen-induced apoptosis in HT-29 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Liu, G.; Ke, C.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Dixon, W.; Song, M.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, H. Inhibitory effects of a novel antimicrobial peptide from kefir against Escherichia coli. Food Control 2016, 65, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.M.; Hickey, R.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Efficient method for the detection of microbially produced antibacterial substances from food systems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.L.; Gaudino Caputo, L.R.; Tavares Carvalho, J.C.; Evangelista, J.; Schneedorf, J.M. Antimicrobial and healing activity of kefir and kefiran extract. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; San Mauro, M.; Sanchez, A.; Torres, J.M.; Marquina, D. The antimicrobial properties of different strains of Lactobacillus spp. isolated from kefir. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 26, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, K.R.; Rodrigues, S.A.; Filho, L.X.; Lima, Á.S. Antimicrobial activity of broth fermented with kefir grains. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 152, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüksekdag, Z.N.; Beyatli, Y.; Aslim, B. Determination of some characteristics coccoid forms of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Turkish kefirs with natural probiotic. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Osato, M.S.; Han, X.; Bennett, G.; Hong, W.K. Folk yoghurt kills Helicobacter pylori. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zubillaga, M.; Weill, R.; Postaire, E.; Goldman, C.; Caro, R.; Boccio, J. Effect of probiotics and functional foods and their use in different diseases. Nutr. Res. 2001, 21, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.E.; Witthuhn, R.C.; Todorov, S.D.; Dicks, L.M.T. Characterization of bacteriocin ST8KF produced by a kefir isolate Lactobacillus plantarum ST8KF. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likotrafiti, E.; Valavani, P.; Argiriou, A.; Rhoades, J. In Vitro Evaluation of Potential Antimicrobial Synbiotics Using Lac-tobacillus Kefiri Isolated from Kefir Grains. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 45, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseini, H.F.; Rahimzadeh, G.; Fazeli, M.R.; Mehrazma, M.; Salehi, M. Evaluation of Wound Healing Activities of Kefir Products. Burns 2012, 38, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, R.J.; Viora, S.S.; Lausada, L.I. Efecto Del Bactericida Kefir Sobre Salmonella spp. Inf. Technol. 2001, 12, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Golowczyc, M.A.; Mobili, P.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; De Antoni, G.L. Protective Action of Lactobacillus Kefir Carrying S-Layer Protein against Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolla, P.A.; Abraham, A.G.; Pérez, P.F.; De Los Angeles Serradell, M. Kefir-isolated bacteria and yeasts inhibit Shigella flexneri invasion and modulate pro-inflammatory response on intestinal epithelial cells. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.A.; Ghaly, M.F.; El-Naggar, A.K. Milk kefir: Ultrastructure, antimicrobial activity and efficacy on aflatoxin b1 production by Aspergillus flavus. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, R.R.; Caro, C.A.; Martínez, O.L.; Moretti, A.F.; Giannuzzi, L.; De Antoni, G.L.; León Peláez, A. Antifungal effect of kefir fermented milk and shelf life improvement of corn arepas. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 235, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caro Vélez, C.A.; León Peláez, Á.M. Fungal growth inhibition of Aspergillus ochraceus with “panela”fermented with water kefir grains. Vitae 2014, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Topuz, E.; Derin, D.; Can, G.; Kürklü, E.; Çinar, S.; Aykan, F.; Çevikbaş, A.; Dişçi, R.; Durna, Z.; Şakar, B.; et al. Effect of oral administration of kefir on serum proinflammatory cytokines on 5-FU induced oral mucositis in patients with colorectal cancer. Invest. New Drugs 2008, 26, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirat, D.; Jelena, P. Bacterial Inhibition and Antioxidant Activity of Kefir. Biotechnology 2010, 9, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, A.S.; Kalamaki, M.S.; Pexara, A.S.; Papageorgiou, D. Investigation of Staphylococcus aureus growth and enterotoxin production during artisanal kefir fermentation. LWT 2020, 134, 109956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraporda, C.; Abatemarco Júnior, M.; Neumann, E.; Nunes, Á.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Abraham, A.G.; Garrote, G.L. Biological activity of the non-microbial fraction of kefir: Antagonism against intestinal pathogens. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamida, R.S.; Shami, A.; Ali, M.A.; Almohawes, Z.N.; Mohammed, A.E.; Bin-Meferij, M.M. Kefir: A protective dietary supplementation against viral infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Perdigón, G.; Duarte, J.; Farnworth, E.; Matar, C. Effects of the oral administration of the exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens on the gut mucosal immunity. Cytokine 2006, 36, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carasi, P.; Racedo, S.M.; Jacquot, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Serradell, M.A.; Urdaci, M.C. Impact of kefir derived lactobacillus kefiri on the mucosal immune response and gut microbiota. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosa, D.D.; Grześkowiak, L.M.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F.; Fonseca, A.C.M.; Reis, S.A.; Dias, M.M.; Siqueira, N.P.; Silva, L.L.; Neves, C.A.; Oliveira, L.L.; et al. Kefir reduces insulin resistance and inflammatory cytokine expression in an animal model of metabolic syndrome. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Hung, K.F.; Yen, C.C.; Laio, C.H.; Wang, J.L.; Lan, Y.W.; Chong, K.Y.; Fan, H.C.; Chen, C.M. Kefir peptides alleviate particulate matter <4 μm (PM4.0)-induced pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway using luciferase transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, H.L.; Fan, H.C.; Tung, Y.T.; Kuo, C.W.; Tu, M.Y.; Chen, C.M. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic effects of kefir peptides on salt-induced renal vascular damage and dysfunction in aged stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.K.; Park, E.J.; Ko, S.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Kim, S. Therapeutic effects of kefir grain Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles in mice with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8662–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santanna, A.F.; Filete, P.F.; Lima, E.M.; Porto, M.L.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Vasquez, E.C.; Endringer, D.C.; Lenz, D.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Chronic administration of the soluble, nonbacterial fraction of kefir attenuates lipid deposition in LDLr−/− mice. Nutrition 2017, 35, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Kwon, O.K.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, I.Y.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, H.K. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects of kefir in a mouse asthma model. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.A.; Choi, H.I.; Hong, S.W.; Kang, S.; Jegal, H.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.S. Extracellular vesicles derived from kefir grain Lactobacillus ameliorate intestinal inflammation via regulation of proinflammatory pathway and tight junction integrity. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.S.M.; Amin, N.E.D.; Abdel Fattah, S.M.; Abd El-Rahman, O. Ameliorative effect of kefir against γ-irradiation induced liver injury in male rats: Impact on oxidative stress and inflammation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35161–35173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, M.C.; Lan, Y.W.; Li, H.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.C.; Tu, M.Y.; Chen, C.M. Kefir peptides alleviate high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis by attenuating macrophage accumulation and oxidative stress in ApoE knockout mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Yan, X.; Weng, W.; Yang, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Pan, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Wei, Q.; et al. Micro integral membrane protein (MIMP), a newly discovered anti-inflammatory protein of lactobacillus plantarum, enhances the gut barrier and modulates microbiota and inflammatory cytokines. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz-Ersan, L.; Ozcan, T.; Akpinar-Bayizit, A.; Sahin, S. Comparison of antioxidant capacity of cow and ewe milk kefirs. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3788–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Nan, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Chemical and physical characteristics and antioxidant activities of the exopolysaccharide produced by Tibetan kefir grains during milk fermentation. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 43, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokbar, N.; Khodaiyan, F.; Moosavi-Nasab, M. Optimization of processing conditions to improve antioxidant activities of apple juice and whey based novel beverage fermented by kefir grains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3422–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bensmira, M.; Jiang, B. Total phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of a novel peanut based kefir. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaçalı, R.; Özdemİr, N.; Çon, A.H. Aromatic and functional aspects of kefir produced using soya milk and Bifidobacterium species. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Abdulmalek, S.; Pan, D. Reversal of age-associated oxidative stress in mice by PFT, a novel kefir product. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Gonçalves, C.; Maia, F.R.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Biological performance of a promising Kefiran-biopolymer with potential in regenerative medicine applications: A comparative study with hyaluronic acid. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCue, P.P.; Shetty, K. Phenolic antioxidant mobilization during yogurt production from soymilk using Kefir cultures. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayadi, M.; Al Jawfi, Y.; Belarbi, M.; Sabri, F.Z. Antioxidant Potency of Water Kefir. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2016, 2, 2444–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Nurliyani; Sadewa, A.H.; Sunarti. Kefir properties prepared with goat milk and black rice (Oryza sativa L.) Extract and its influence on the improvement of pancreatic β-cells in diabetic rats. Emirates J. Food Agric. 2015, 27, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.R.; Chen, M.J.; Lin, C.W. Antimutagenic and antioxidant properties of milk-kefir and soymilk-kefir. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satir, G.; Guzel-Seydim, Z.B. Influence of Kefir fermentation on the bioactive substances ofdifferent breed goat milks. LWT 2015, 63, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohian, F.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Koohiyan, M.; Shanei, A. The Radioprotective Effect of Ascorbic Acid and Kefir against Genotoxicity Induced by Exposure in Mice Blood Lymphocytes. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 73, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, D.; Nuraida, L.; Dewanti-Hariyadi, R.; Hunaefi, D. In Vitro Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Indonesian Kefir Grains as Probiotics with Cholesterol-Lowering Effect. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-R.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Chen, H.-L.; Yueh, P.-Y.; Lin, C.-W. Hypocholesterolaemic effects of milk-kefir and soyamilk-kefir in cholesterol-fed hamsters. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Pan, C.; Huang, Y. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Tibetan Kefir Grains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, N.; Xi, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum MA2 isolated from Tibet kefir on lipid metabolism and intestinal microflora of rats fed on high-cholesterol diet. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Sui, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum strains as potential probiotic cultures with cholesterol-lowering activity. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2746–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Sui, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp27 isolated from Tibetan kefir grains: A potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guneser, O.; Hosoglu, M.I.; Guneser, B.A.; Yuceer, Y.K. Engineering of Milk-Based Beverages: Current Status, Developments, and Consumer Trends; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 2015, ISBN 9780128155042. [Google Scholar]
- Borgie, M. 5 Succes-Driving Beverage Industry Trends of 2017. Available online: https://www.repsly.com/blog/consumer-goods/beverage-industry-trends-of-2017 (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Argan, B.E.; Güneşer, O.; Toklucu, A.K.; Yüceer, Y.K. Türk Tarım—Gıda Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi Peyniraltı Suyu Tozu İlave Edilmiş Meyveli İçecek Üretimi ve Bazı. Türk Tarım-Gıda Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 2015, 3, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, B. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of kefir grains and their fermented dairy products: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1272152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, K.T.; Pereira, M.A.; Nicolau, A.; Dragone, G.; Domingues, L.; Teixeira, J.A.; de Almeida Silva, J.B.; Schwan, R.F. Production of fermented cheese whey-based beverage using kefir grains as starter culture: Evaluation of morphological and microbial variations. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8843–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimitrellou, D.; Kandylis, P.; Mallouchos, A.; Komaitis, M.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kourkoutas, Y. Effect of freeze-dried kefir culture on proteolysis in feta-type and whey-cheeses. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrellou, D.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kanellaki, M. Thermally-dried immobilized kefir on casein as starter culture in dried whey cheese production. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourkoutas, Y.; Kandylis, P.; Panas, P.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Nigam, P.; Koutinas, A.A. Evaluation of freeze-dried kefir coculture as starter in feta-type cheese production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6124–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katechaki, E.; Panas, P.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Koliopoulos, D.; Koutinas, A.A. Thermally-dried free and immobilized kefir cells as starter culture in hard-type cheese production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3618–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzourani, I.; Plessas, S.; Saxami, G.; Alexopoulos, A.; Galanis, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Study of kefir grains application in sourdough bread regarding rope spoilage caused by Bacillus spp. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessas, S.; Alexopoulos, A.; Bekatorou, A.; Mantzourani, I.; Koutinas, A.A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Examination of freshness degradation of sourdough bread made with kefir through monitoring the aroma volatile composition during storage. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessas, S.; Pherson, L.; Bekatorou, A.; Nigam, P.; Koutinas, A.A. Bread making using kefir grains as baker’s yeast. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessas, S.; Trantallidi, M.; Bekatorou, A.; Kanellaki, M.; Nigam, P.; Koutinas, A.A. Immobilization of kefir and Lactobacillus casei on brewery spent grains for use in sourdough wheat bread making. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bio-based active food packaging materials: Sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based packaging materials. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motedayen, A.A.; Khodaiyan, F.; Salehi, E.A. Development and characterisation of composite films made of kefiran and starch. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Oromiehie, A.; Yarmand, M.S. Development and characterisation of a new biodegradable edible film made from kefiran, an exopolysaccharide obtained from kefir grains. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, M.E.; Peltzer, M.A.; Delgado, J.F.; Salvay, A.G. Water kefir grains as an innovative source of materials: Study of plasticiser content on film properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermaria, J.A.; Pinotti, A.; Garcia, M.A.; Abraham, A.G. Films based on kefiran, an exopolysaccharide obtained from kefir grain: Development and characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensmira, M.; Jiang, B. Effect of some operating variables on the microstructure and physical properties of a novel Kefir formulation. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Kefiran improves rheological properties of glucono-δ-lactone induced skim milk gels. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, M.F.; Piermaria, J.A.; Abraham, A.G. Selection of EPS-producing Lactobacillus strains isolated from kefir grains and rheological characterization of the fermented milks. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermaría, J.; Bengoechea, C.; Abraham, A.G.; Guerrero, A. Shear and extensional properties of kefiran. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajšek, K.; Goršek, A.; Kolar, M. Cultivating conditions effects on kefiran production by the mixed culture of lactic acid bacteria imbedded within kefir grains. Food Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, V.R.A.; Teixeira, C.G.; Lima, T.S.; De Almeida Prata, E.R.B.; Vidigal, M.C.T.R.; Martins, E.; Perrone, Í.T.; de Carvalho, A.F. Health beliefs towards kefir correlate with emotion and attitude: A study using an emoji scale in Brazil. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Xu, M.; Guo, H.; He, L.; Gao, X.; DiMarco-Crook, C.; Xiao, H.; Cao, Y. Optimization of culture conditions for the production of antimicrobial substances by probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. Tolerans FX-6. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Dixon, W.; Song, M.; Xiao, H.; Cao, Y. Membrane disruption and DNA binding of Staphylococcus aureus cell induced by a novel antimicrobial peptide produced by Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans FX-6. Food Control 2016, 59, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Peng, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Cao, Y. Biopreservative effect of the natural antimicrobial substance from Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans FX-6 on fresh pork during chilled storage. Food Control 2015, 56, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandón, L.M.; Islan, G.A.; Castro, G.R.; Noseda, M.D.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Kefiran-alginate gel microspheres for oral delivery of ciprofloxacin. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinler, J.K.; Ross, C.L.; Savidge, T.C. Probiotics as adjunctive therapy for preventing Clostridium difficile infection—What are we waiting for? Anaerobe 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, M.C.; Golowczyc, M.A.; De Antoni, G.L.; Pérez, P.F.; Humen, M.; de los Angeles Serradell, M. Administration of Kefir-Fermented Milk Protects Mice against Giardia Intestinalis Infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62 Pt 12, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teruya, K.; Myojin-Maekawa, Y.; Shimamoto, F.; Watanabe, H.; Nakamichi, N.; Tokumaru, K.; Tokumaru, S.; Shirahata, S. Protective Effects of the Fermented Milk Kefir on X-Ray Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Damage in B6C3F1 Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.K.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.H. Role of probiotics in human gut microbiome-associated diseases. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellikci-Koyu, E.; Sarer-Yurekli, B.P.; Akyon, Y.; Aydin-kose, F.; Karagozlu, C.; Ozgen, A.G.; Brikmann, A.; Nitsche, A.; Ergunay, K.; Yilmaz, E.; et al. Effects of Regular Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiemsma, L.T.; Nakamura, R.E.; Nguyen, J.G.; Michels, K.B. Does Consumption of Fermented Foods Modify the Human Gut Microbiota? J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; de Moura e Dias, M.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Kefir and Intestinal Microbiota Modulation: Implications in Human Health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Dardis, C.; Gagliarini, N.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Exopolysaccharides From Lactobacillus paracasei Isolated From Kefir as Potential Bioactive Compounds for Microbiota Modulation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazda, I.; Krūmiņa, A.; Zeltiņa, I.; Krūmiņa, N.; ķibilds, J.; Siksna, I.; Vīksna, L.; Derovs, A. Microbial Community of Kefir and its Impact on the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B. Nat. Exact. Appl. Sci. 2020, 74, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, M.; De Grandi, R.; Miniello, V.L.; Mattina, R.; Drago, L. Ability of Lactobacillus kefiri LKF01 (DSM32079) to colonize the intestinal environment and modify the gut microbiota composition of healthy individuals. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, E.; Sharma, R.; Smith, K.B.; Mar, K.D.; Barve, R.; Lukasik, M.; Pirwani, A.F.; Malette-Guyon, E.; Lamba, S.; Thomas, B.J.; et al. Probiotic consumption during puberty mitigates LPS-induced immune responses and protects against stress-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in adulthood in a sex-specific manner. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, E.L.; Pinto, A.M.; Baima, C.L.B.; da Silva, H.R.; da Silva Sena, I.; Sanchez-Ortiz, B.L.; de Lima Teixeira, A.V.T.; Pereira, A.C.M.; da Silva Barbosa, R.; Carvalho, H.O.; et al. Evaluation of the in vitro release of isoflavones from soybean germ associated with kefir culture in the gastrointestinal tract and anxiolytic and antidepressant actions in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Jomaa, S.A.; El-wahed, A.A.; El-seedi, H.R. The many faces of kefir fermented dairy products: Quality characteristics, flavour chemistry, nutritional value, health benefits, and safety. Nutrients 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Kefir | Biological Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Milk kefir and soy milk kefir | Anti-inflammatory effect on murine sarcoma (in vivo) | Liu et al., 2002 [52] |
| Kefram–Kefir aqueous extract | Anti-oxidant and apoptosis effect on human melanoma cell line HMV-1/SK-MEL (in vitro) | Nagira et al., 2002 [53] |
| Kefir and kefir cell-free fraction (KF) | Anti-inflammatory effect on murine breast cancer (in vivo) | de Moreno de LeBlanc et al., 2006; De Moreno De LeBlanc et al., 2007 [54,55] |
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Anti-proliferative effect on human mammary cancer cell line MCF-7 (in vitro) | C. Chen et al., 2007 [56] |
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Anti-proliferative and apoptosis effect on human T-cell leukemia cell line HuT-102 (HTLV-1 negative/HTLV-1 positive) (in vitro) | Rizk et al., 2009; 2013 [57,58] |
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Anti-proliferative and apoptosis effect on HTLV-1-negative malignant T-lymphocytes (in vitro) | Maalouf et al., 2011 [59] |
| Cell-free fraction of Tibetan kefir | Anti-proliferative effect on human gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 (in vitro) | Gao et al., 2013 [60] |
| Lentilactobacillus kefiri | Apoptosis of human myeloid leukemia cell line HL60/AR (in vitro) | Ghoneum & Gimzewski, 2014 [61] |
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Anti-proliferative and apoptosis effect on colorectal cancer cell line Caco-2/HT-29 (in vitro) | Khoury et al., 2014 [62] |
| Lentilactobacillus kefiri | Apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell line (AGS) | Ghoneum & Felo, 2015 [63] |
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Anti-proliferative and apoptosis effect on human acute erythroleukemia cell line KG-1 (in vitro) | Jalali et al., 2016 [64] |
| Kefir, Exopolysaccharides(EPS), Alkaline Kefir (AK), Alkaline EPS (AEPS) | Apoptosis in human sarcoma cells (in vitro) | Almostafa Alsha’ar et al., 2017 [65] |
| Exopolysaccharide from Lentilactobacillus kefiri MSR101 | Anti-proliferative and apoptosis effect on human colon cancer cell line HT-29 (in vitro) | Riaz Rajoka et al., 2019 [10] |
| Milk kefir | ||
| Cell-free fraction of kefir | Adjuvant anti-cancer effects on multidrug-resistant human colorectal cancer cells (HT-29) | Kim et al., 2021 [66] |
| Microbial Species | Reference |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | |
| Bacillus cereus | Anselmo et al., 2010; Carasi et al., 2014; Kakisu et al., 2007; Medrano et al., 2008; Ulusoy et al., 2007 [80,81,82,83,84] |
| Bacillus subtilis | Chifiriuc et al., 2011 [85] |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | Miao et al., 2014 [86] |
| Clostridium difficile | Bolla et al., 2013; Rea et al., 2007 [87,88] |
| Clostridium perfringens | Anselmo et al., 2010 [80] |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Chifiriuc et al., 2011; Zanirati et al., 2015 [85,89] |
| Escherichia coli | Chifiriuc et al., 2011; Ebner et al., 2015; Garrote et al., 2000; Golowczyc et al., 2008; Gulmez & Guven, 2003; E. Kakisu et al., 2013; A. M. O. Leite et al., 2015; Meng et al., 2017; Miao et al., 2014; Miao, Liu, et al., 2016; Morgan et al., 2000; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Santos et al., 2003; Silva et al., 2009; Suriasih, 2011; Ulusoy et al., 2007; Yüksekdag et al., 2004; Zanirati et al., 2015 [43,84,85,86,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101] |
| Helicobacter pylori | Oh et al., 2002; Zubillaga et al., 2001 [102,103] |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Garrote et al., 2000; Yüksekdag et al., 2004 [90,101] |
| Listeria innocua | Morgan et al., 2000; Powell et al., 2007 [97,104] |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Gulmez & Guven, 2003; Jeong et al., 2017; A. M. O. Leite et al., 2015; Likotrafiti et al., 2015; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Santos et al., 2003; Ulusoy et al., 2007; Zanirati et al., 2015 [9,84,89,92,94,98,99,105] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Carasi et al., 2014; Huseini et al., 2012; Rahimzadeh et al., 2011; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Yüksekdag et al., 2004; Zanirati et al., 2015 [81,89,98,101,106] |
| Salmonella enterica | Golowczyc et al., 2008; A. M. O. Leite et al., 2015; Miao et al., 2014 [86,91,94] |
| Salmonella Enteriditis | Czamanski et al., 2004; R. J. Anselmo et al., 2001; Carasi et al., 2014; Chifiriuc et al., 2011; M. A. Golowczyc et al., 2007; Jeong et al., 2017; Santos et al., 2003; Ulusoy et al., 2007 [9,81,84,85,99,107,108] |
| Salmonella Gallinarum | Golowczyc et al., 2008 [91] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Marina A. Golowczyc et al., 2008; Meng et al., 2017; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Santos et al., 2003; Silva et al., 2009; Suriasih, 2011; Zanirati et al., 2015 [89,91,95,98,99,100] |
| Shigella dysenteriae | Miao et al., 2014 [86] |
| Shigella flexneri | P. A. Bolla et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2003 [99,109] |
| Shigella sonnei | Golowczyc et al., 2008; Silva et al., 2009 [91,100] |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Carasi et al., 2014; A. M. O. Leite et al., 2015; Miao, Zhou, et al., 2016; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Silva et al., 2009; Ulusoy et al., 2007; Yüksekdag et al., 2004; Zanirati et al., 2015 [81,84,89,94,96,98,100,101] |
| Staphylococcus salivarius | Rodrigues et al., 2005 [98] |
| Streptococcus faecalis | Ismaiel et al., 2011 [110] |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Rodrigues et al., 2005 [98] |
| Fungi | |
| Aspergillus flavus | Gamba et al., 2016; Miao et al., 2014 [86,111] |
| Aspergillus niger | Miao et al., 2014 [86] |
| Aspergillus ochraceus | Caro Vélez & León Peláez, 2014 [112] |
| Candida albicans | Rodrigues et al., 2005; Silva et al., 2009 [98,100] |
| Fusarium graminearum | Ismaiel et al., 2011 [110] |
| Penicillium glaucum | Miao et al., 2014 [86] |
| Rhizopus nigricans | Miao et al., 2014 [86] |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Topuz et al., 2008 [113] |
| Yersinia enterocolitica | Gulmez & Guven, 2003; Santos et al., 2003 [92,99] |
| Companies | Product | General Information |
|---|---|---|
| Bionova | Milk kefir (Natural, vanilla, blueberry, barley, ginger and strawberry) | Natural source of calcium, gluten-free and produced from high-quality milk. |
| Kefir water (Natural, wellness, red fruits, relax, antioxidant and energy) | Natural source of calcium and gluten-free. | |
| Probioflora kefir | Food supplement contains freeze-dried granules of Kefir and selected live lactic ferments. | |
| Actiplus kefir | Natural source of calcium and gluten-free packed with billions of live and active lactic ferments. | |
| milk | Kefir Plus (Tropical fruits, blueberry, royal jelly) | Lactose-free fermented cow’s milk with live lactic ferments specific to kefir, a natural source of calcium and vitamin. |
| Kefir to Drink (Natural white, orange ginger and cardamom, multi-fruits, mango turmeric, pomegranate and raspberry, | Lactose-free fermented cow’s milk with live lactic ferments specific to kefir, a natural source of calcium and vitamin. | |
| Kefir to Drink Bio (Natural white) | Lactose-free fermented cow’s milk produced from organic farming with live lactic ferments specific to kefir, a natural source of calcium and vitamin. | |
| Creamy Kefir (White, strawberry and wild strawberries, blackberry, plum and cereals, pomegranate and chia, oats and nuts) | Lactose-free fermented cow’s milk kefir with milk cream, with live lactic ferments specific to kefir, a natural source of calcium and vitamin. | |
| Kefir Mix White (With wholemeal cornflakes and red fruits, with pumpkin, sunflower and cranberry seeds, with crunchy hazelnut, with berries). | Lactose-free fermented cow’s milk kefir with milk cream mixtures, with live lactic ferments specific to kefir, a natural source of calcium and vitamin. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Osman, M.A.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061210
Azizi NF, Kumar MR, Yeap SK, Abdullah JO, Khalid M, Omar AR, Osman MA, Mortadza SAS, Alitheen NB. Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods. 2021; 10(6):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061210
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Nor Farahin, Muganti Rajah Kumar, Swee Keong Yeap, Janna Ong Abdullah, Melati Khalid, Abdul Rahman Omar, Mohd. Azuraidi Osman, Sharifah Alawieyah Syed Mortadza, and Noorjahan Banu Alitheen. 2021. "Kefir and Its Biological Activities" Foods 10, no. 6: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061210
APA StyleAzizi, N. F., Kumar, M. R., Yeap, S. K., Abdullah, J. O., Khalid, M., Omar, A. R., Osman, M. A., Mortadza, S. A. S., & Alitheen, N. B. (2021). Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods, 10(6), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061210