Antimicrobial Activity and Antibiofilm Potential of Coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Determination of MIC and MBC Values
2.4. Inactivation of S. Typhimurium by CoQ0 in LB
2.5. Antimicrobial Effect of CoQ0 on Inoculated S. Typhimurium on Raw Chicken
2.6. Determination of the Antibacterial Mechanism of CoQ0 against Planktonic S. Typhimurium Cells
2.6.1. Membrane Potential
2.6.2. Intracellular ATP
2.6.3. Release of Cellular Constituents
2.6.4. Membrane Integrity
2.6.5. Bacterial Morphology
2.7. CoQ0 Inactivation of S. Typhimurium Biofilms on Stainless Steel Surfaces
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MICs and MBCs
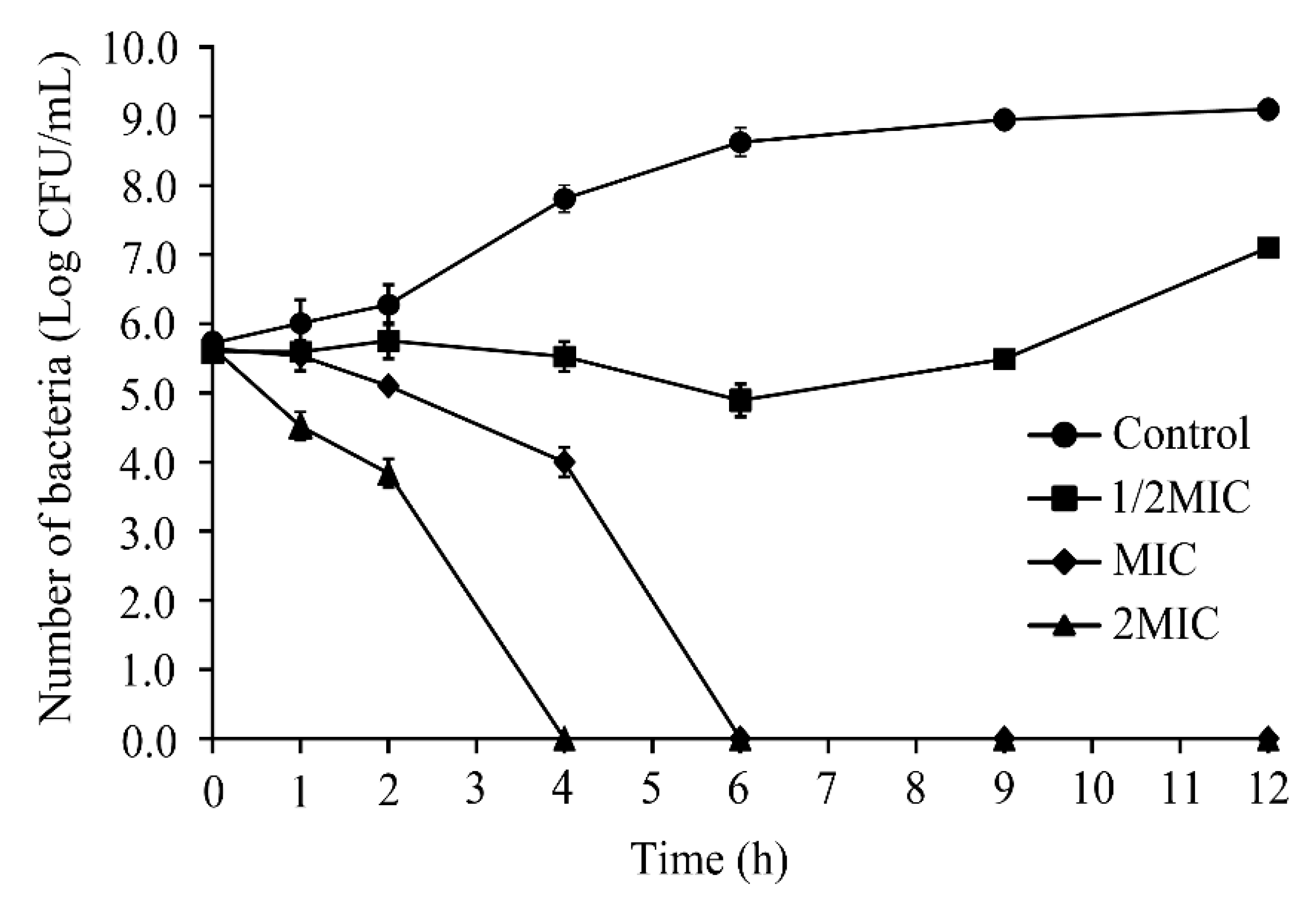
3.2. Inactivation of S. Typhimurium by CoQ0 in LB
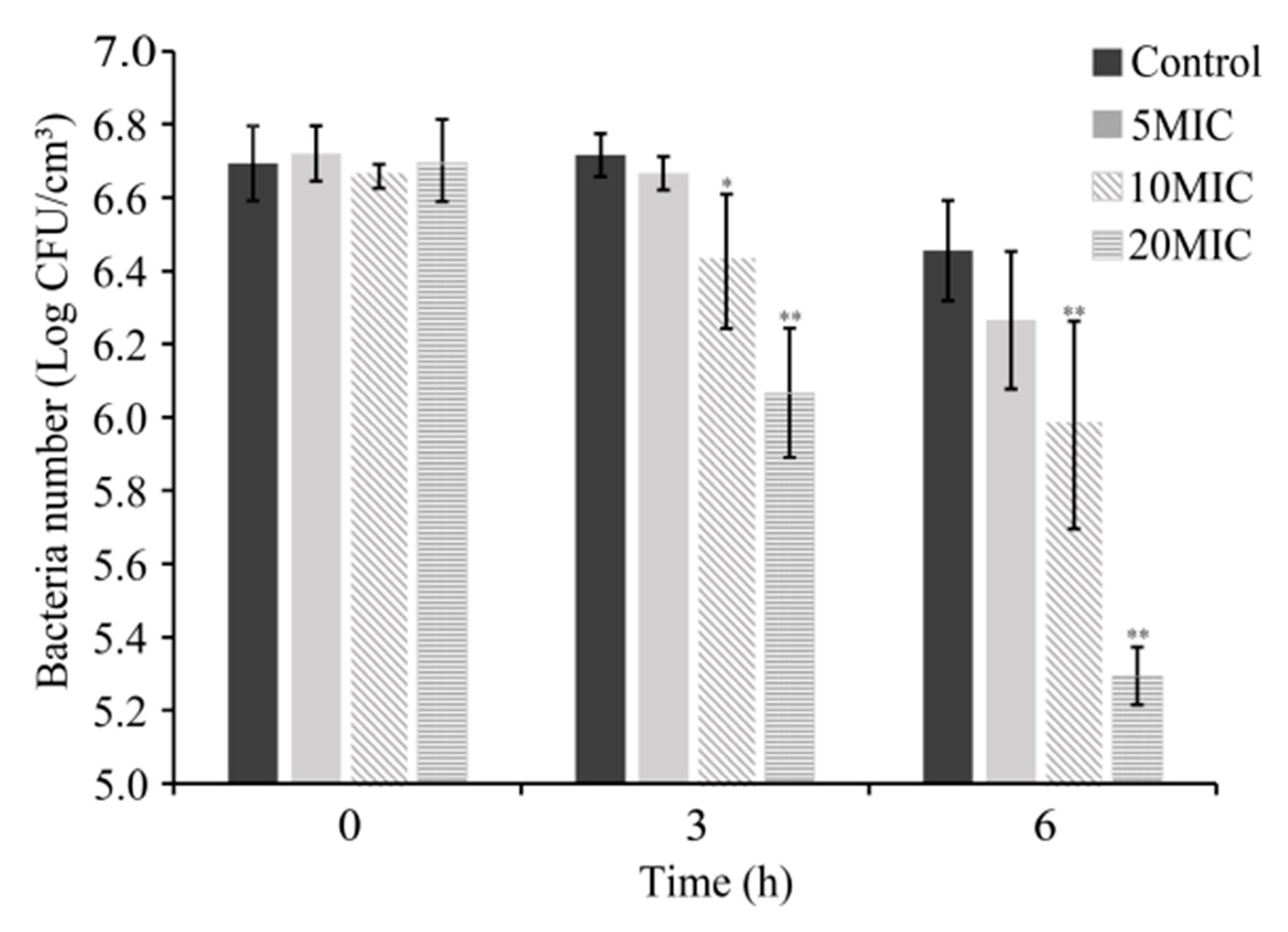
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of CoQ0 on Raw Chicken
3.4. Release of Cell Constituents
3.5. Membrane Potential
3.6. Intracellular ATP
3.7. Membrane Integrity
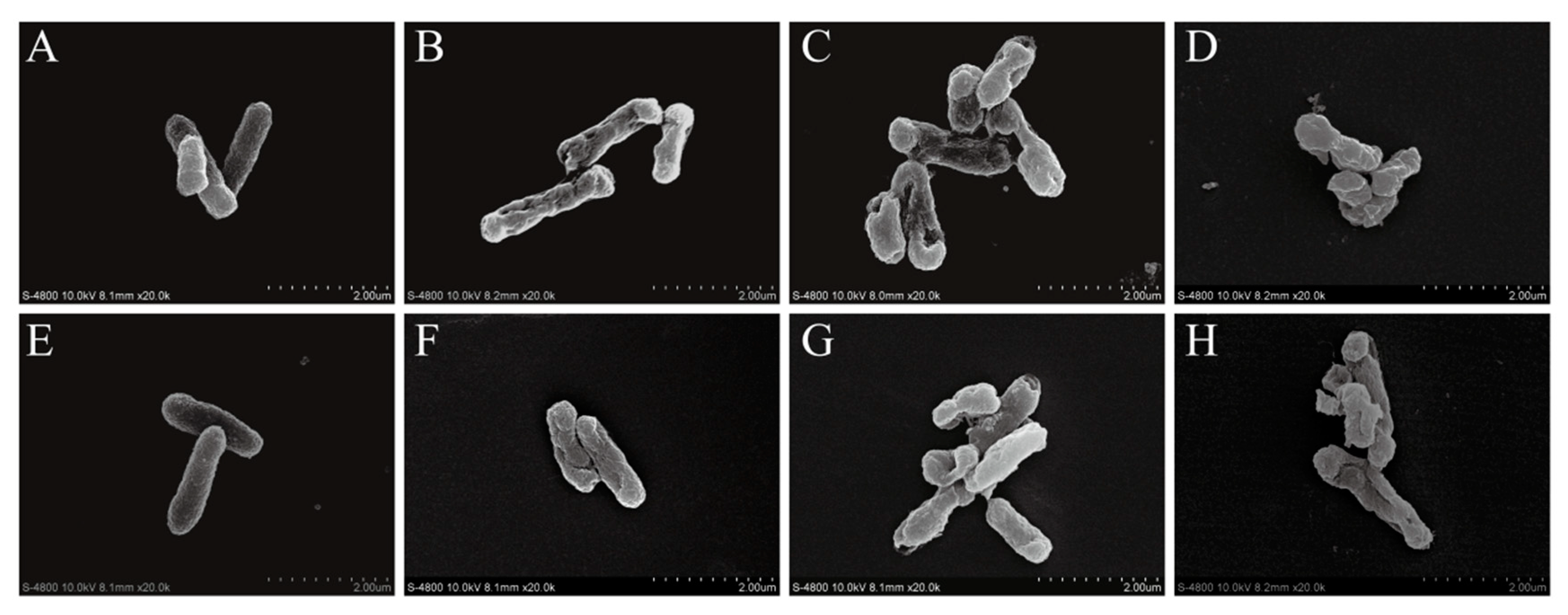
3.8. FESEM-Based Observation of Cell Morphology
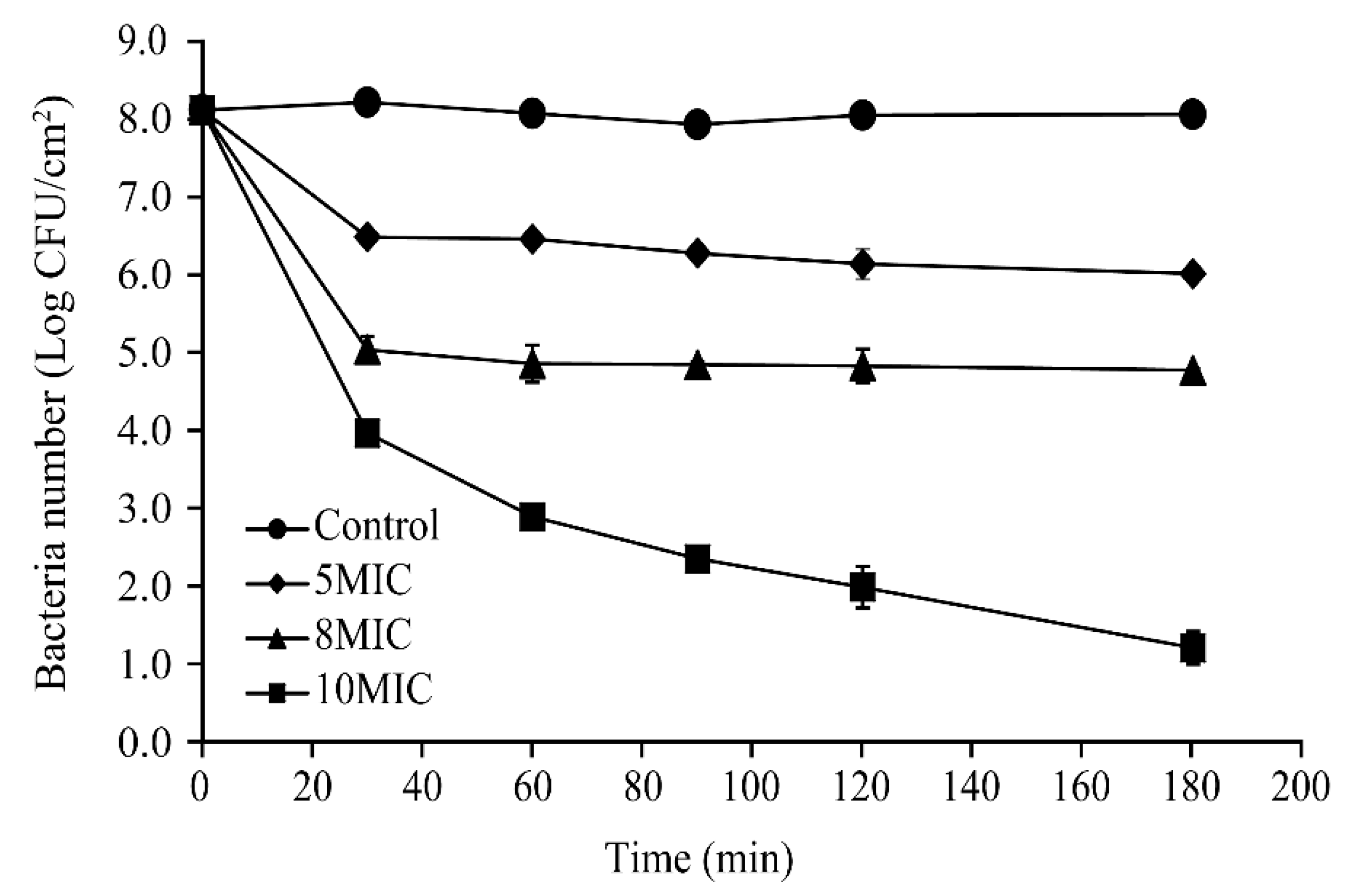
3.9. Inactivation of S. Typhimurium Biofilms on Stainless Steel Surfaces by CoQ0 Treatment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patrick, M.; Michael, M.; Hee-Jeong, Y.; Steffen, P.; Lydia, B.; Juei-Suei, C. Contribution of asparagine catabolism to Salmonella virulence. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fardsanei, F.; Dallal, M.M.S.; Douraghi, M.; Salehi, T.Z.; Mahmoodi, M.; Memariani, H. Genetic diversity and virulence genes of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serotype Enteritidis isolated from meats and eggs. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.J.; Kendall, M.M. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strategies for host adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ana, H.; Elmerdhahl, O.J. Salmonella Typhimurium metabolism affects virulence in the host—A mini-review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 71, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinu, V.S. Insight into biofilm-associated microbial life. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 10, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, L.; Procura, F.; Trejo, F.M.; Bueno, D.J.; Golowczyc, M.A. Biofilm formation by Salmonella sp. in the poultry industry: Detection, control and eradication strategies. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lars, L.; Douglas, W. Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giaouris, E.; Heir, E.; Hebraud, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Langsrud, S.; Moretro, T. Attachment and biofilm formation by foodborne bacteria in meat processing environments: Causes, implications, role of bacterial interactions and control by alternative novel methods. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarikou, C.; Kostoglou, D.; Simões, M.; Giaouris, E. Exploitation of plant extracts and phytochemicals against resistant Salmonella spp. in biofilms. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buket, E.; Demirhan, B.; Ozgacar, F.K.; Ozgacar, S.O.; Oktem, A.B. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of selected food preservatives against Salmonella spp. isolated from chicken samples. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, C.M.; Gallego, M.; Cabezas, L.; Fernandez-Salguero, J. Detection of regulated disinfection by-products in cheeses. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Nisha, S.A.; Sakthivel, R.; Pandian, S.K. Eugenol (an essential oil of clove) acts as an antibacterial agent against Salmonella typhi by disrupting the cellular membrane. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Mallikarjuna, K.; Lin, M.; Chen, S.; Chou, C.; Hseu, Y. Anti-angiogenic properties of coenzyme Q0 through downregulation of MMP-9/NF-κB and upregulation of HO-1 signaling in TNF-α-activated human endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lin, M.; Mallikarjuna, K.; Wu, J.; Liao, C.; Chang, C. Coenzyme Q0 regulates NFκB/AP-1 activation and enhances Nrf2 stabilization in attenuation of LPS-induced inflammation and redox imbalance: Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1859, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers-Edgar, J.T.; Rhonda, J.R. Coenzyme Q0 induces apoptosis and modulates the cell cycle in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells. Anti Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.; Varadharajan, T.; Hsiao-Tung, T.; Lin, K.; Chen, H.; Lin, C. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of coenzyme Q0 against melanoma cells: Inhibition of metastasis and induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis through modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Bai, F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y. The antimicrobial activity of coenzyme Q0 against planktonic and biofilm forms of Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, C.; Zhang, C. Effect of coenzyme Q0 on biofilm formation and attachment-invasion efficiency of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2018, 90, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yan, C.; Shi, C.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C. Inhibitory effect of coenzyme Q0 on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Song, K.B. Antibacterial activity of the noni fruit extract against Listeria monocytogenes and its applicability as a natural sanitizer for the washing of fresh-cut produce. Food Microbiol. 2019, 84, 103260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Min, S.C. Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and Tulane virus in processed chicken breast via atmospheric in-package cold plasma treatment. LWT 2020, 127, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Song, K.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Yue, S.; Chen, Y. Antimicrobial activity and possible mechanism of action of citral against Cronobacter sakazakii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, P.; Ali, M.A.; Gong, S.; Sun, Q.; Bi, X.; Liu, S. Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action of olive oil polyphenols extract against Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Control 2018, 94, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xia, X. Antimicrobial effect and mode of action of chlorogenic acid on Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 238, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakomi, H.L.; Mättö, J.; Virkajärvi, I.; Saarela, M. Application of a microplate scale fluorochrome staining assay for the assessment of viability of probiotic preparations. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 62, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Guo, J.; Rao, H.; Du, G.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of coenzyme Q0 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 2020, 109, 106955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.M.; Joy, W.; Huang, E. Control of Salmonella on chicken meat using a combination of a commercial bacteriophage and plant-based essential oils. Food Control 2020, 110, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Cui, H. Cold plasma treated thyme essential oil/silk fibroin nanofibers against Salmonella Typhimurium in poultry meat. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Antibacterial activity of gallic acid against Shigella flexneri and its effect on biofilm formation by repressing mdoH gene expression. Food Control 2018, 94, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Vadivel, V.; Rubini, D.; Nithyanand, P. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of linalool nanoemulsions against Salmonella Typhimurium. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.I.; Rhee, M.S. Inhibitory effect of caprylic acid and mild heat on Cronobacter spp. (Enterobacter sakazakii) in reconstituted infant formula and determination of injury by flow cytometry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, B.; Prakash, G.; Suganya, K.; Murugan, M.; Kathiresan, S. Anti-listerial activity of microalgal fatty acid methyl esters and their possible applications as chicken marinade. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, T.; Wei, C.; Lan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y. Antibacterial effect and mechanism of anthocyanin rich Chinese wild blueberry extract on various foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2018, 94, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.; Lemos, A.S.O.; Silva, T.P.; Oliveira, L.G.; Nascimento, A.L.R.; Carvalho, J.J. Mitracarpus frigidus is active against Salmonella enterica species including the biofilm form. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 141, 11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Gong, S.; Guo, L. Olive oil polyphenol extract inhibits vegetative cells of Bacillus cereus isolated from raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3894–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Antimicrobial mechanism of pulsed light for the control of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its application in carrot juice. Food Control 2019, 106, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, H. Synergistic efficacy of pulsed magnetic fields and Litseacubeba essential oil treatment against Escherichia coli O157:H7 in vegetable juices. Food Control 2019, 106, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Purohit, A.S. Anti-Salmonella activity of pyruvic and succinic acid in combination with oregano essential oil. Food Control 2020, 110, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.H.; Sang, H.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Si, H.P.; Ha, S.D. Efficacy of chlorine-based disinfectants (sodium hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide) on Salmonella Enteritidis planktonic cells, biofilms on food contact surfaces and chicken skin. Food Control 2020, 123, 107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strain | Serovar | MIC (mg/mL) | MIC (µM) | MBC (mg/mL) | MBC (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 14028 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
| AS1.1174 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
| 22 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
| 63 | Typhimurium | 0.1 | 549 | 0.1 | 549 |
| 64 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
| 80 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
| 98 | Typhimurium | 0.2 | 1098 | 0.2 | 1098 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Shi, C. Antimicrobial Activity and Antibiofilm Potential of Coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium. Foods 2021, 10, 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061211
Yang Z, Ma X, Li Y, Xu H, Han X, Wang R, Zhao P, Li Z, Shi C. Antimicrobial Activity and Antibiofilm Potential of Coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium. Foods. 2021; 10(6):1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061211
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhuokai, Xiaoyu Ma, Yan Li, Huidong Xu, Xinyi Han, Ruixia Wang, Pengyu Zhao, Ziyi Li, and Chao Shi. 2021. "Antimicrobial Activity and Antibiofilm Potential of Coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium" Foods 10, no. 6: 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061211
APA StyleYang, Z., Ma, X., Li, Y., Xu, H., Han, X., Wang, R., Zhao, P., Li, Z., & Shi, C. (2021). Antimicrobial Activity and Antibiofilm Potential of Coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium. Foods, 10(6), 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061211






