Texturization of a Blend of Pea and Destarched Oat Protein Using High-Moisture Extrusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Destarched OPC
2.3. Proximate Composition of the Raw Materials
2.4. Characterisation of Oat Proteins
2.5. Rheological Properties
2.6. High-Moisture Extrusion Cooking
2.7. Characteristics of the Extrudates
2.7.1. Textural Properties
2.7.2. Protein–Protein Interactions of Extrudates
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of the Raw Materials
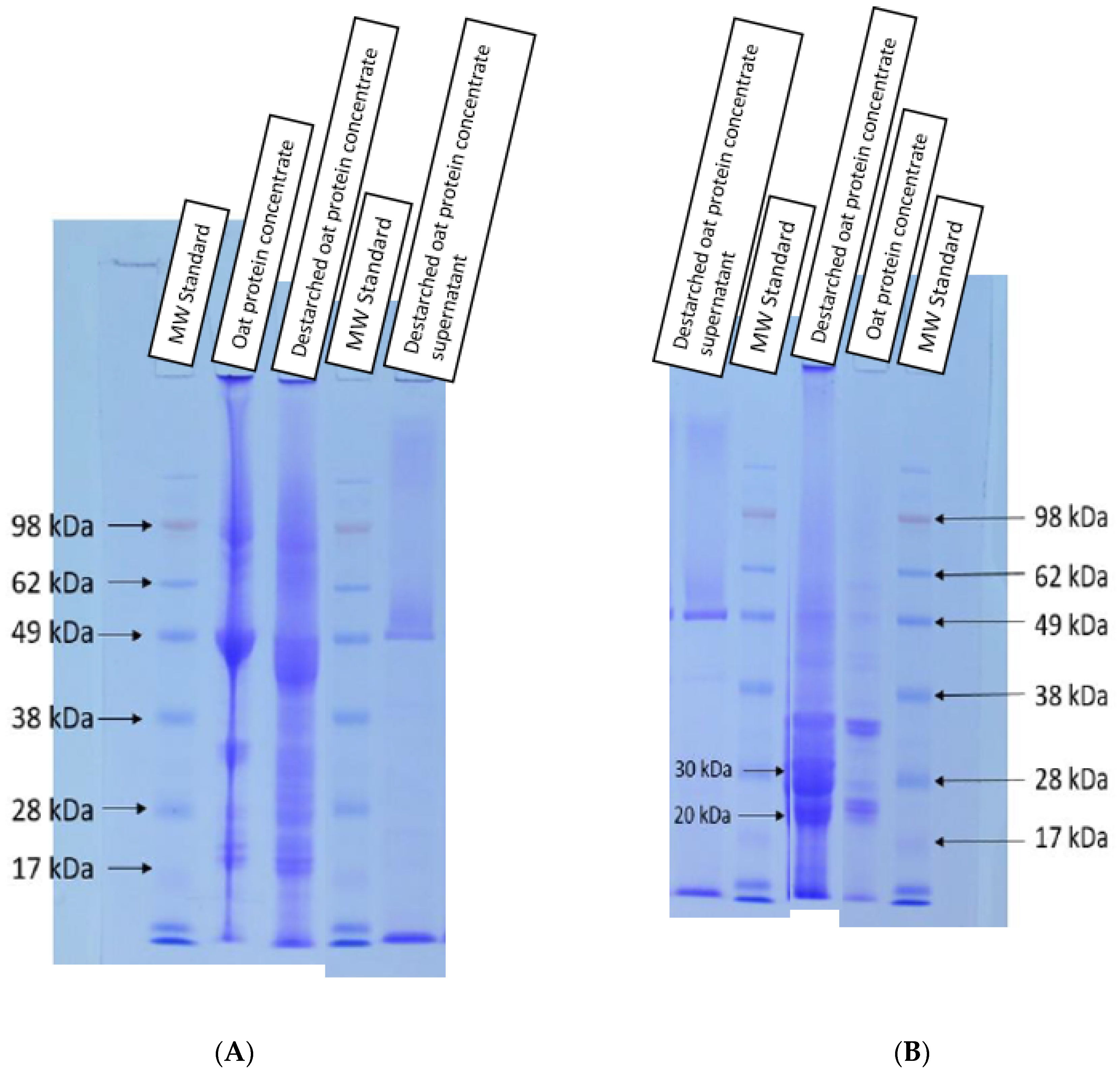
3.2. Effect of Destarching on Oat Proteins
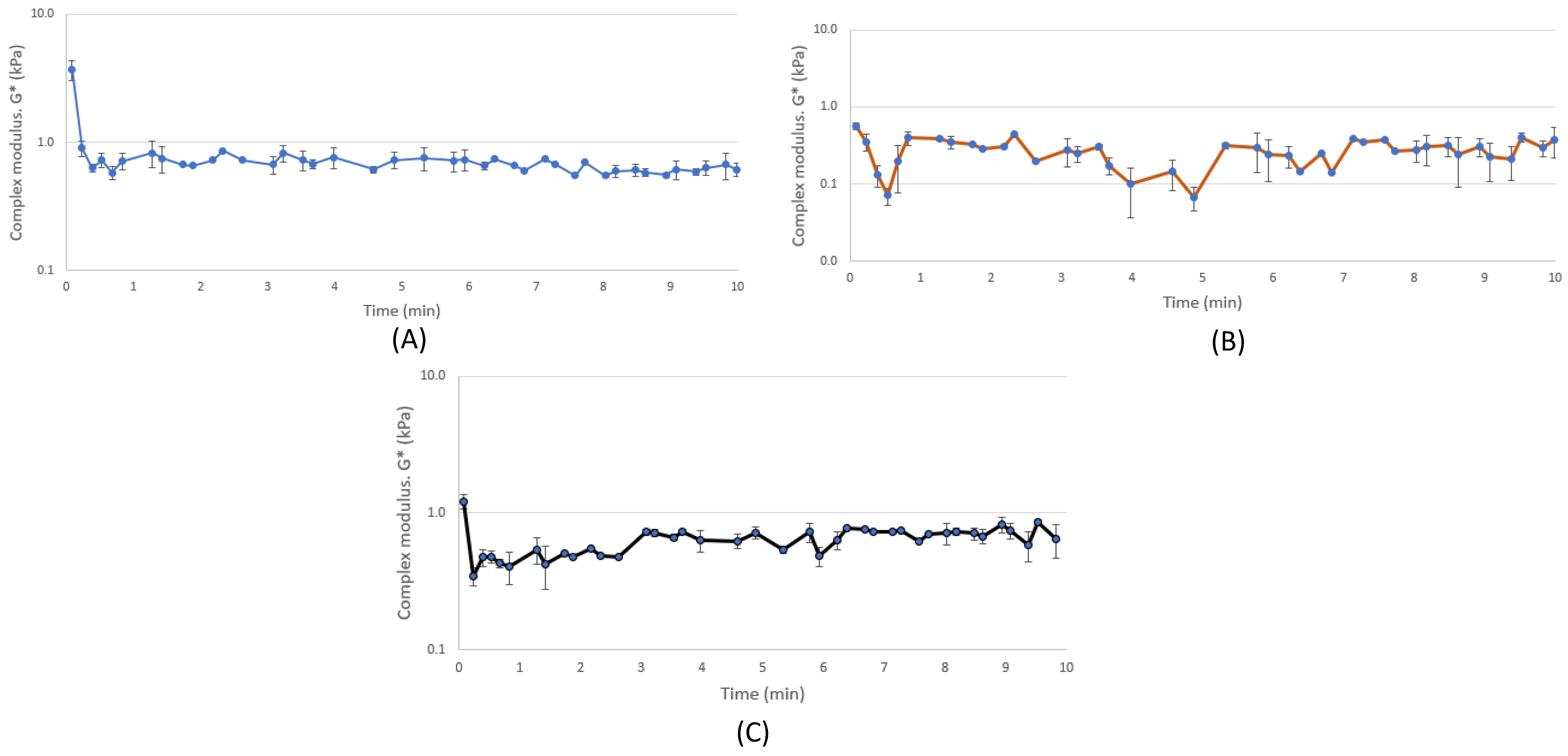
3.3. Rheological Properties
3.4. Structure Properties of the Extrudates
Effect of Extrusion Process on the Protein–Protein Interactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saget, S.; Costa, M.; Santos, C.S.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Gibbons, J.; Styles, D.; Williams, M. Substitution of Beef with Pea Protein Reduces the Environmental Footprint of Meat Balls Whilst Supporting Health and Climate Stabilisation Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 2021, 126447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Health Effects of Dietary Risks in 195 Countries, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Dekkers, B.; van der Goot, A.J. Plant-Based Meat Analogues. In Sustainable Meat Production and Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 103–126. ISBN 978-0-12-814874-7. [Google Scholar]
- Polanowska, K.; Grygier, A.; Kuligowski, M.; Rudzińska, M.; Nowak, J. Effect of Tempe Fermentation by Three Different Strains of Rhizopus Oligosporus on Nutritional Characteristics of Faba Beans. LWT 2020, 122, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.-Z.; Rombouts, F.M.; Nout, M.J.R. A Chinese Fermented Soybean Food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, Y.; Buffière, C.; Cohade, B.; Vauris, M.; Liebermann, K.; Hafnaoui, N.; Lopez, M.; Souchon, I.; Dupont, D.; Rémond, D. True Ileal Amino Acid Digestibility and Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Scores (DIAASs) of Plant-Based Protein Foods. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohrer, B.M. An Investigation of the Formulation and Nutritional Composition of Modern Meat Analogue Products. Food Sci. Human Well. 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Hong, G.-P. Effects of Microbial Transglutaminase and Alginate on the Water-Binding, Textural and Oil Absorption Properties of Soy Patties. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, G.; Bae, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, Y.; Choi, M.-J. Evaluation of the Physicochemical and Structural Properties and the Sensory Characteristics of Meat Analogues Prepared with Various Non-Animal Based Liquid Additives. Foods 2020, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.L.; Wei, Y.M.; Zhang, B. Chemical Cross-Linking and Molecular Aggregation of Soybean Protein during Extrusion Cooking at Low and High Moisture Content. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.L.; Emin, M.A.; Schuchmann, H.P. Process Conditions Influencing Wheat Gluten Polymerization during High Moisture Extrusion of Meat Analog Products. J. Food Eng. 2017, 198, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R.; Toelstede, S.; Wild, F.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. High Moisture Extrusion Cooking of Pea Protein Isolates: Raw Material Characteristics, Extruder Responses, and Texture Properties. J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huff, H.E.; Hsieh, F. Extrusion Process Parameters, Sensory Characteristics, and Structural Properties of a High Moisture Soy Protein Meat Analog. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleda, A.; Talvistu, K.; Tamm, M.; Viirma, M.; Rosend, J.; Tanilas, K.; Kriisa, M.; Part, N.; Tammik, M.-L. Impact of Fermentation and Phytase Treatment of Pea-Oat Protein Blend on Physicochemical, Sensory, and Nutritional Properties of Extruded Meat Analogs. Foods 2020, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, D.; Kaleda, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Vaikma, H.; Tamm, M.; Tammik, M.-L.; Squeo, G.; Summo, C. Physicochemical and Sensorial Evaluation of Meat Analogues Produced from Dry-Fractionated Pea and Oat Proteins. Foods 2020, 9, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, W.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Mu, D.; Zheng, Z. Formation of Macromolecules in Wheat Gluten/Starch Mixtures during Twin-Screw Extrusion: Effect of Different Additives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5131–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V.B. Thermoplastic extrusion—The mechanism of the formation of extrudate structure and properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1993, 70, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hsieh, F.-H. Protein–Protein Interactions during High-Moisture Extrusion for Fibrous Meat Analogues and Comparison of Protein Solubility Methods Using Different Solvent Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, M.A.; Quevedo, M.; Wilhelm, M.; Karbstein, H.P. Analysis of the Reaction Behavior of Highly Concentrated Plant Proteins in Extrusion-like Conditions. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Rodriguez-Alonso, E.; Bianeis, M.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Assessing Functional Properties of Rapeseed Protein Concentrate versus Isolate for Food Applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, F.K.G.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Bodnár, I.; Erni, P.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Small and Large Oscillatory Shear Properties of Concentrated Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, M.E.J.; Dekkers, B.L.; van der Padt, A.; van der Goot, A.J. Aqueous Fractionation Processes of Soy Protein for Fibrous Structure Formation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyyssölä, A.; Nisov, A.; Lille, M.; Nikinmaa, M.; Rosa-Sibakov, N.; Ellilä, S.; Valkonen, M.; Nordlund, E. Enzymatic Reduction of Galactooligosaccharide Content of Faba Bean and Yellow Pea Ingredients and Food Products. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.L.; Werner, R.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. High Moisture Extrusion of Wheat Gluten: Relationship between Process Parameters, Protein Polymerization, and Final Product Characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2019, 259, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walburg, G.; Larkins, B.A. Oat Seed Globulin: Subunit Characterization and Demonstration of Its Synthesis as a Precursor. Plant Physiol. 1983, 72, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikola, M.; Jones, B.L. Characterization of Oat Endoproteinases that Hydrolyze Oat Globulins. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mession, J.-L.; Sok, N.; Assifaoui, A.; Saurel, R. Thermal Denaturation of Pea Globulins (Pisum Sativum L.)—Molecular Interactions Leading to Heat-Induced Protein Aggregation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.Y.; Harwalkar, V.R. Chemical Characterization and Functionality Assessment of Oat Protein Fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.L.; Schöffel, F.; Rädle, M.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. High Moisture Extrusion of Wheat Gluten: Modeling of the Polymerization Behavior in the Screw Section of the Extrusion Process. J. Food Eng. 2019, 246, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, M.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Denaturation Behavior and Kinetics of Single- and Multi-Component Protein Systems at Extrusion-Like Conditions. Polymers 2020, 12, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, M.; Kulozik, U.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Kinetics of Denaturation and Aggregation of Highly Concentrated β-Lactoglobulin under Defined Thermomechanical Treatment. J. Food Eng. 2020, 274, 109825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, B.L.; Emin, M.A.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. The Phase Properties of Soy Protein and Wheat Gluten in a Blend for Fibrous Structure Formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Kang, L.N. Effect of Protein Contents on the Quality Properties of Texturized Peanut Protein Products. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2007, 8, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowska, K.J.; Zhu, S.; Dekkers, B.L.; de Ruijter, N.C.A.; Gieteling, J.; van der Goot, A.J. Shear-Induced Structuring as a Tool to Make Anisotropic Materials Using Soy Protein Concentrate. J. Food Eng. 2016, 188, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouton, P.E.; Ford, A.L.; Harris, P.V.; Ratcliff, D. Objective subjective assessment of meat tenderness. J. Texture Stud. 1975, 6, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.B.; Phillips, R.D.; Rao, V.N.M. Effects of feed moisture and barrel temperature on the rheological properties of extruded cowpea meal. J. Food Process Eng. 1986, 8, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, C.E.; Lyon, B.G. The Relationship of Objective Shear Values and Sensory Tests to Changes in Tenderness of Broiler Breast Meat. Poultry Sci. 1990, 69, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Fletcher, D.L.; Smith, D.P. Physical and Functional Properties of Intact and Ground Pale Broiler Breast Meat. Poultry Sci. 2005, 84, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saio, K. Texture characterization of vegetable protein products marketed in Japan. J Texture Stud. 1978, 9, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, D.F. Effects of Extrusion upon Soy Concentrate Solubility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R.; Toelstede, S.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Effect of High Moisture Extrusion Cooking on Protein-Protein Interactions of Pea (Pisum Sativum L.) Protein Isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arêas, J.A.G. Extrusion of Food Proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 32, 365–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudêncio-Ferreira, S.H.; Arêas, J.G. Protein-Protein Interactions in the Extrusion of Soya at Various Temperatures and Moisture Contents. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenburn, S.M.; Healy, M.; Sinclair, W. The Formation, Isolation and Importance of Isopeptides in Heated Proteins. In Protein Crosslinking: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; Volume 86, pp. 239–262. ISBN 978-1-4757-9115-0. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, L.D.; Stanley, D.W. A Possible Mechanism for Thermal Texturization of Soybean Protein. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 1976, 9, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrel, R.F.; Carpenter, K.J. Nutritional significance of crosslink formation during food processing. In Protein Crosslinking: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; Volume 86, pp. 225–238. ISBN 978-1-4757-9115-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig, M.; Löbner, J.; Schneider, A.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Henle, T. Release of Protein-Bound N-epsilon -(gamma -Glutamyl)-Lysine during Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Czech J. Food Sci. 2009, 27, S153–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuko, K.; Yasumoto, S. Aspartyl and Glutamyl-Lysine Crosslinks Formation and Their Nutritional Availability. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1990, 36, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Finot, P.-A. The Absorption and Metabolism of Modified Amino Acids in Processed Foods. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheftel, J.C. Nutritional Effects of Extrusion-Cooking. Food Chem. 1986, 20, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.S.; Pryzbyszewski, J.; Hsieh, F.-H. Soy Protein Isolate Extruded with High Moisture Retains High Nutritional Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palanisamy, M.; Franke, K.; Berger, R.G.; Heinz, V.; Töpfl, S. High Moisture Extrusion of Lupin Protein: Influence of Extrusion Parameters on Extruder Responses and Product Properties: High Moisture Extrusion of Lupin Protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Estrada, P.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Nieuwkoop, M.; Dekkers, B.L.; Janssen, A.E.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Protein Oxidation and In Vitro Gastric Digestion of Processed Soy-Based Matrices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9591–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Sample | Protein Powders (%) | Water (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat gluten | 55 | 45 |
| Destarched oat protein concentrate | 55 | 45 |
| Pea protein isolate | 55 | 45 |
| Destarched oat protein concentrate + pea protein isolate | 30 + 25 | 45 |
| Sample | Protein (wt%) | Fat (wt%) | Ash (wt%) | Moisture (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oat protein concentrate | 25.6 ± 0.0 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 7.32 ± 0.0 |
| Pea protein isolate | 77.5 ± 0.0 | 8.9 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.0 | 6.9 ± 0.1 |
| Destarched oat protein concentrate | 33.1 ± 0.4 | 6.79 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.0 | 11.6 ± 0.0 |
| Pea protein isolate + destarched oat protein concentrate blend | 60.0 ± 0.3 | 7.61 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 7.6 ± 0.1 |
| EM 1 * | 30 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 63.7 |
| EM 2 (control) * | 38.8 | 4.5 | 2.3 | 54.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Immonen, M.; Chandrakusuma, A.; Sibakov, J.; Poikelispää, M.; Sontag-Strohm, T. Texturization of a Blend of Pea and Destarched Oat Protein Using High-Moisture Extrusion. Foods 2021, 10, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071517
Immonen M, Chandrakusuma A, Sibakov J, Poikelispää M, Sontag-Strohm T. Texturization of a Blend of Pea and Destarched Oat Protein Using High-Moisture Extrusion. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071517
Chicago/Turabian StyleImmonen, Mika, Angga Chandrakusuma, Juhani Sibakov, Minna Poikelispää, and Tuula Sontag-Strohm. 2021. "Texturization of a Blend of Pea and Destarched Oat Protein Using High-Moisture Extrusion" Foods 10, no. 7: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071517
APA StyleImmonen, M., Chandrakusuma, A., Sibakov, J., Poikelispää, M., & Sontag-Strohm, T. (2021). Texturization of a Blend of Pea and Destarched Oat Protein Using High-Moisture Extrusion. Foods, 10(7), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071517







